Bipolar Analog Memristors as Artificial Synapses for Neuromorphic Computing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
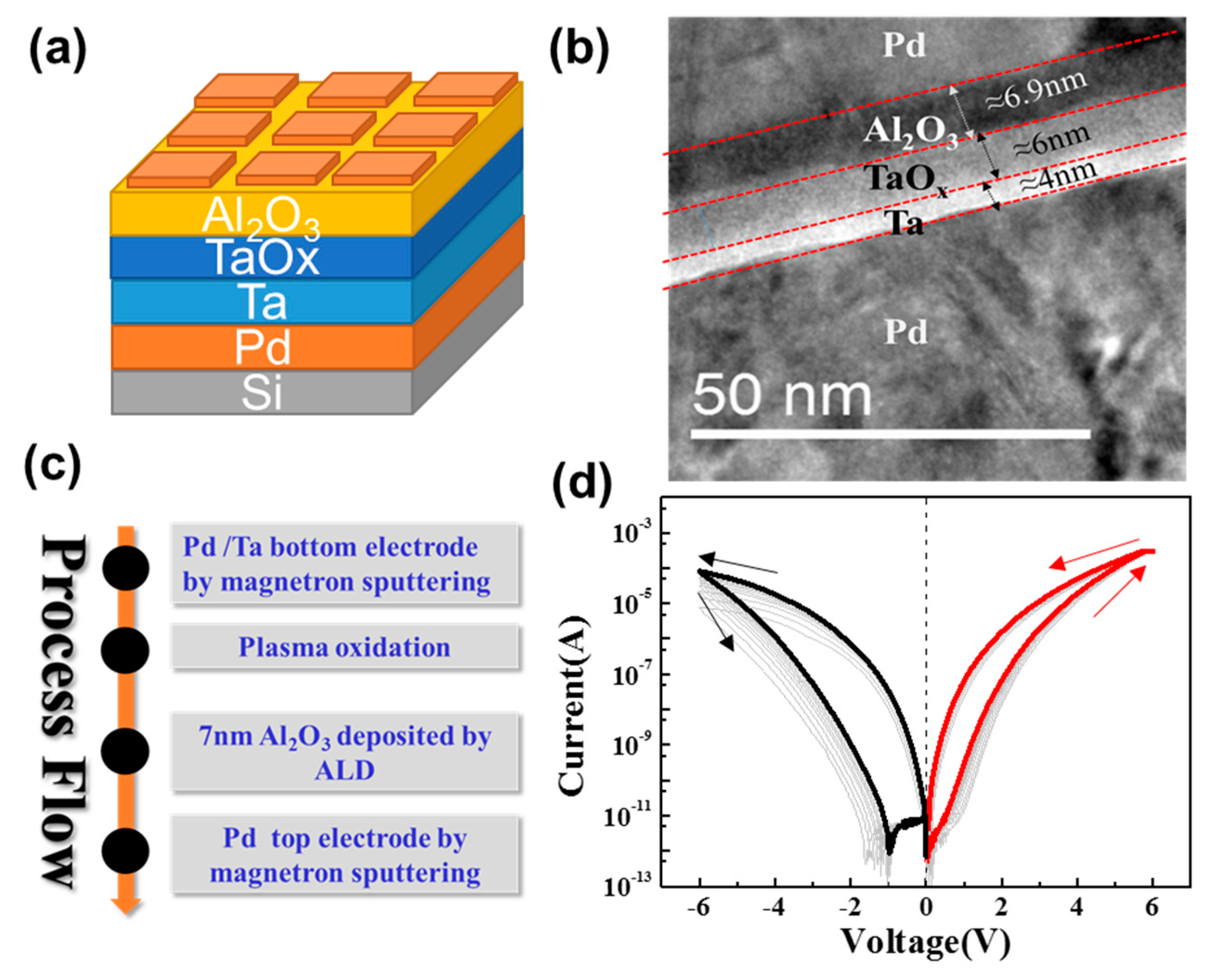
2. Materials and Methods
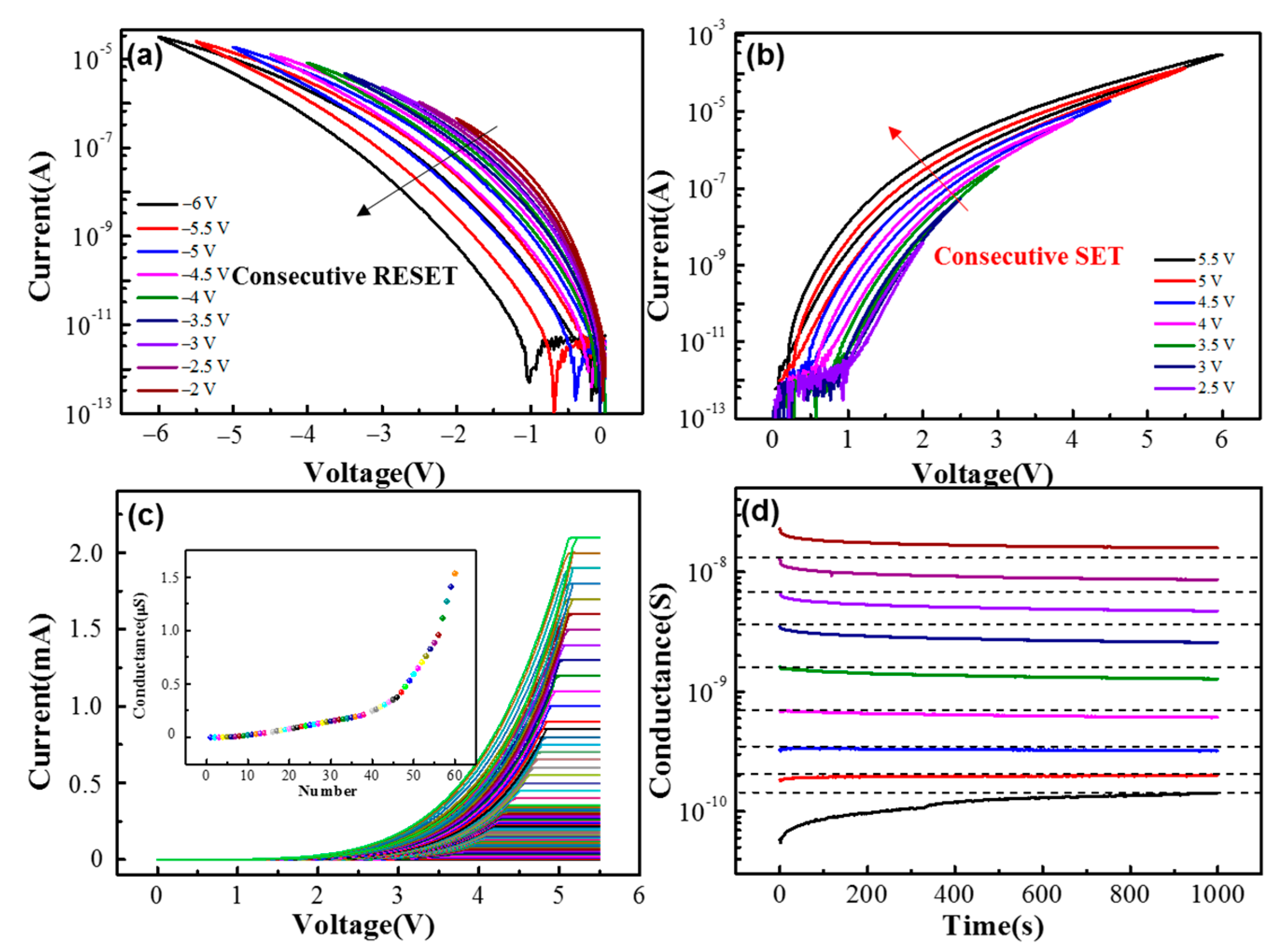
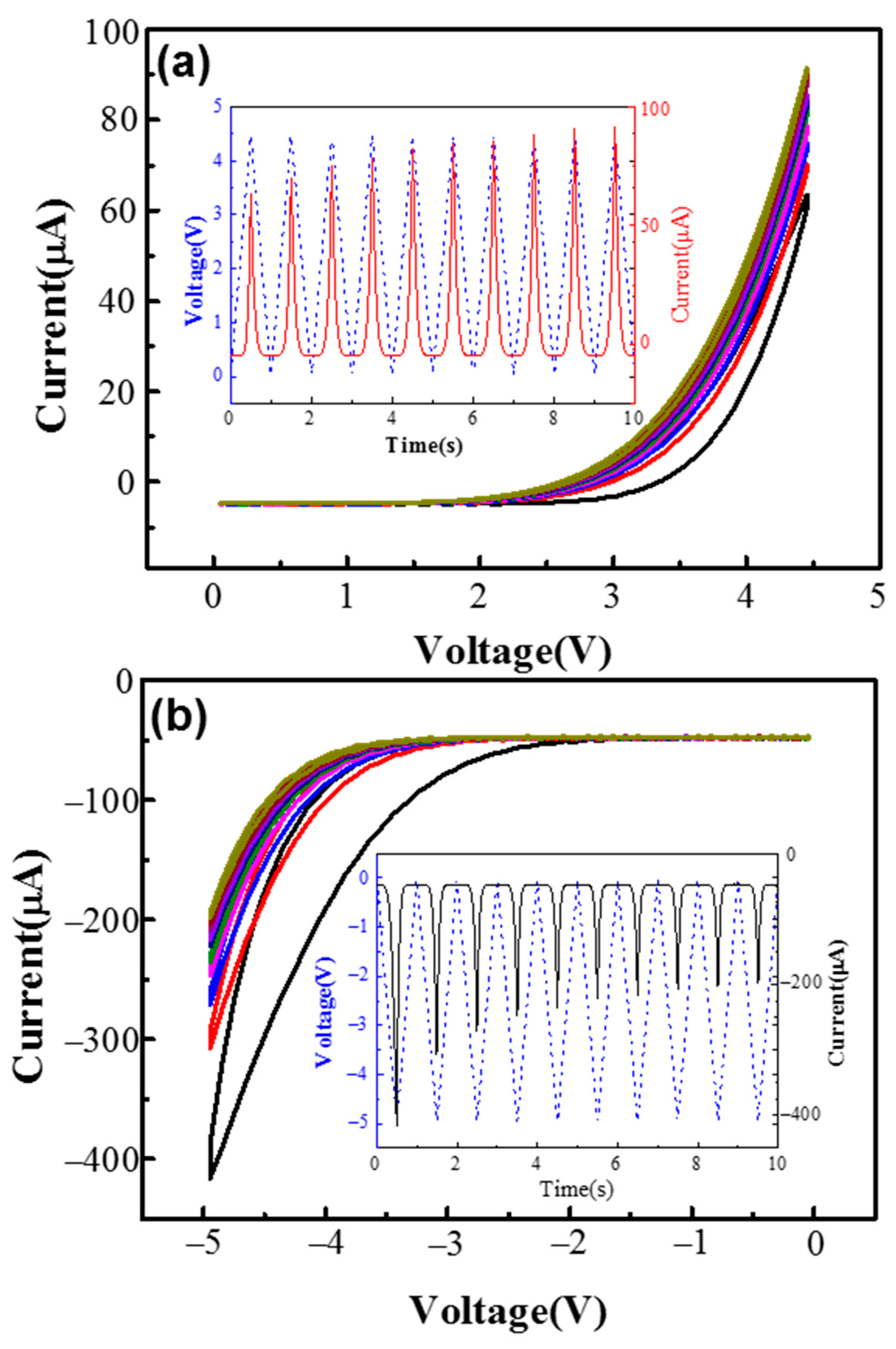
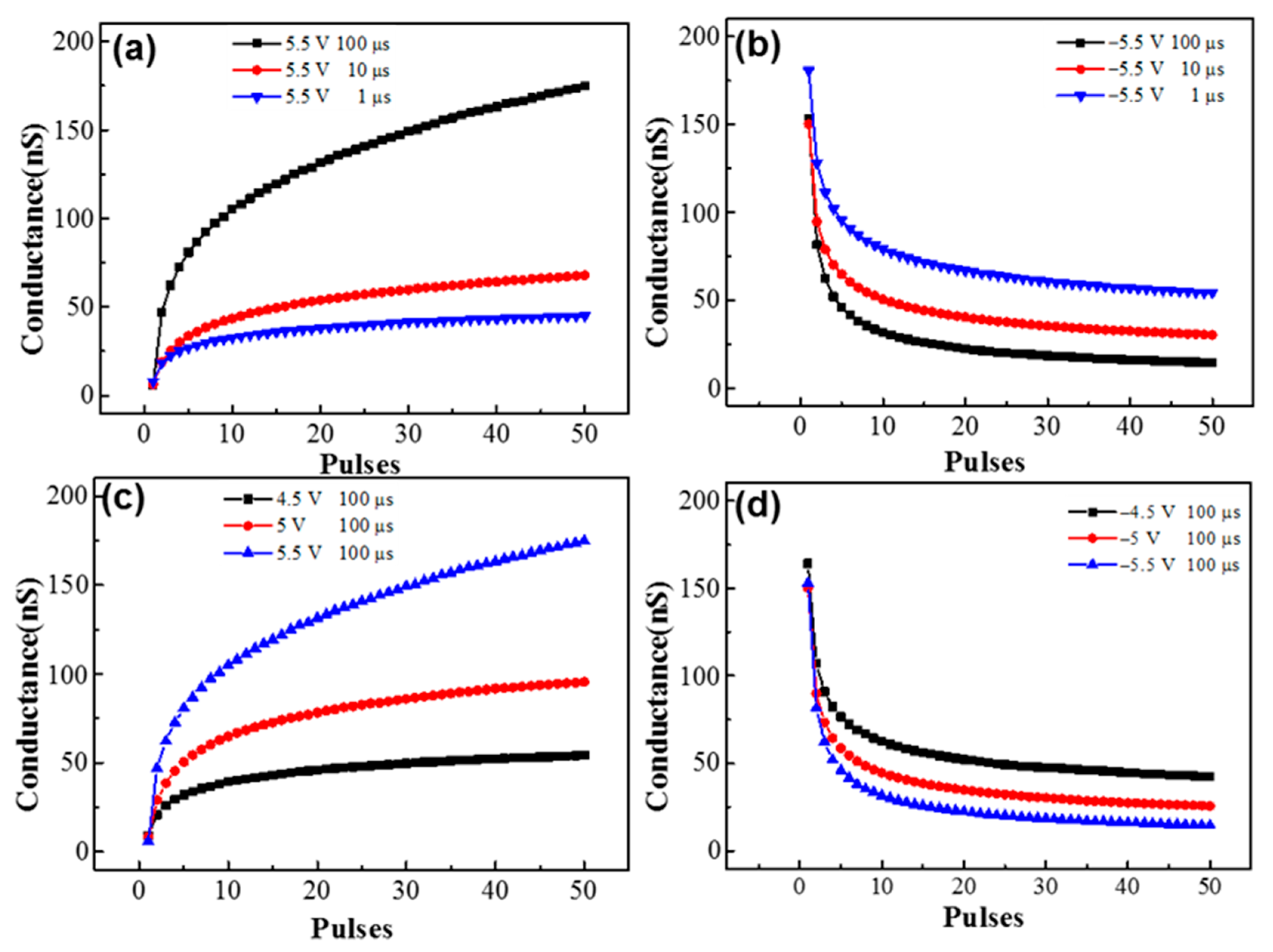
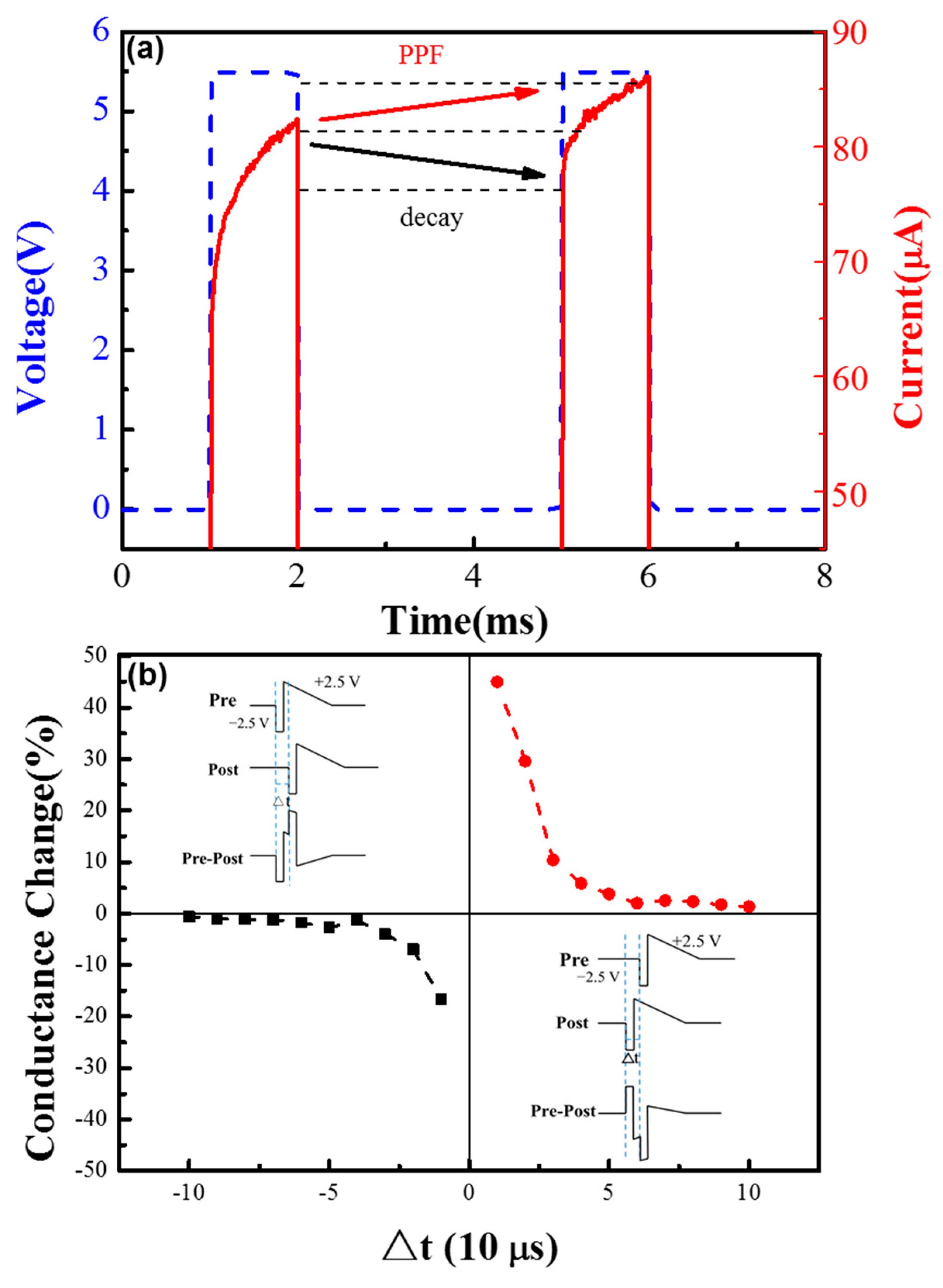
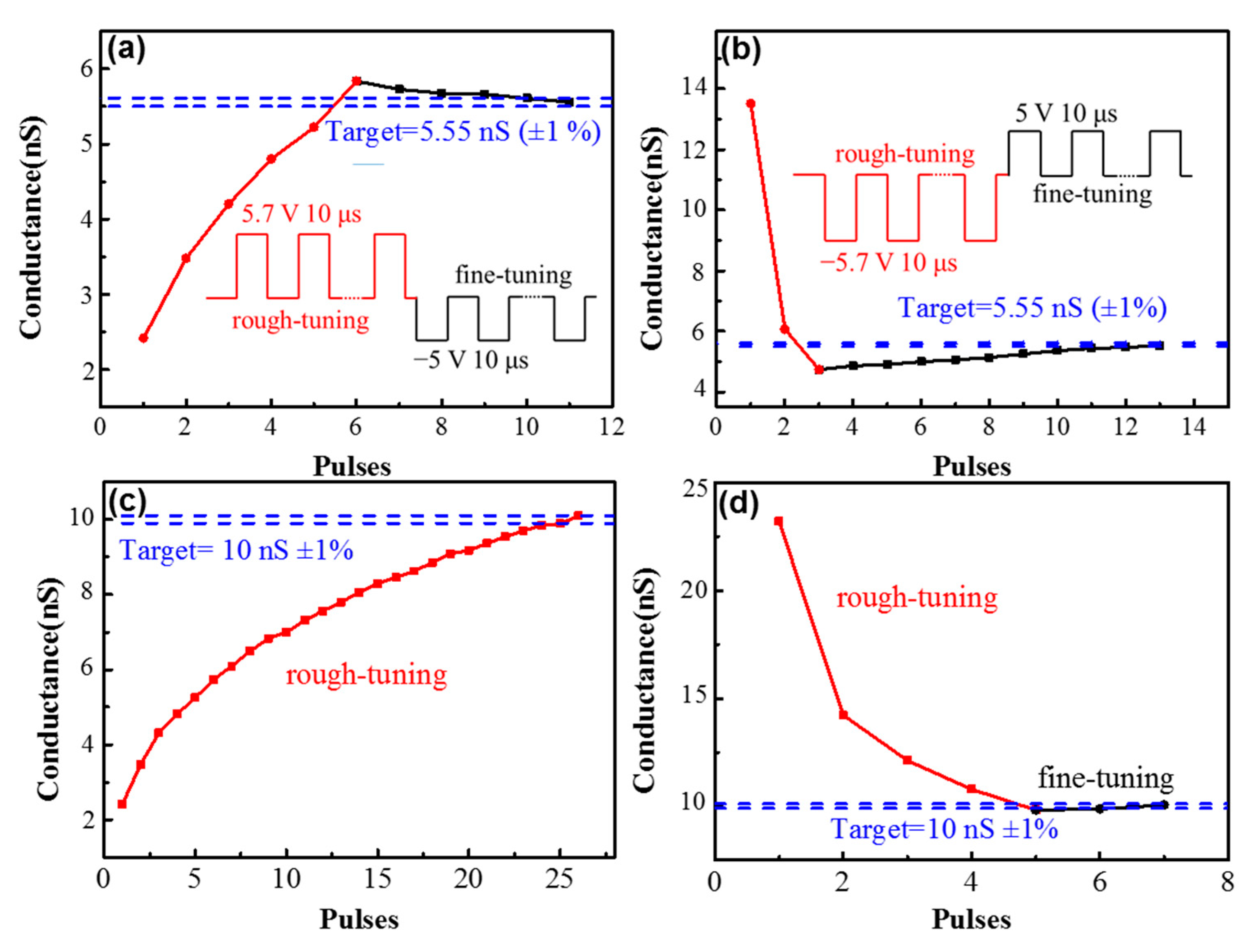
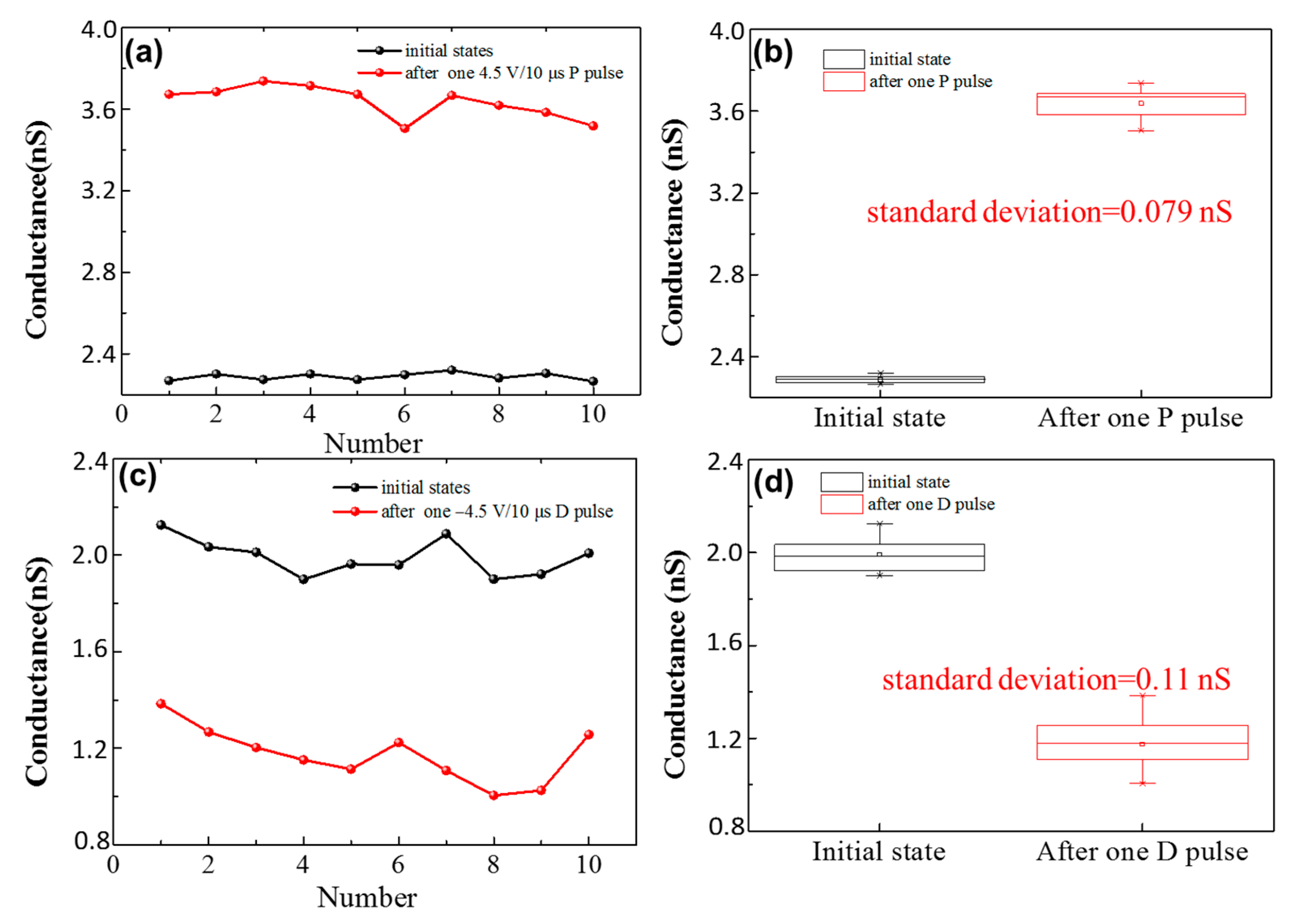
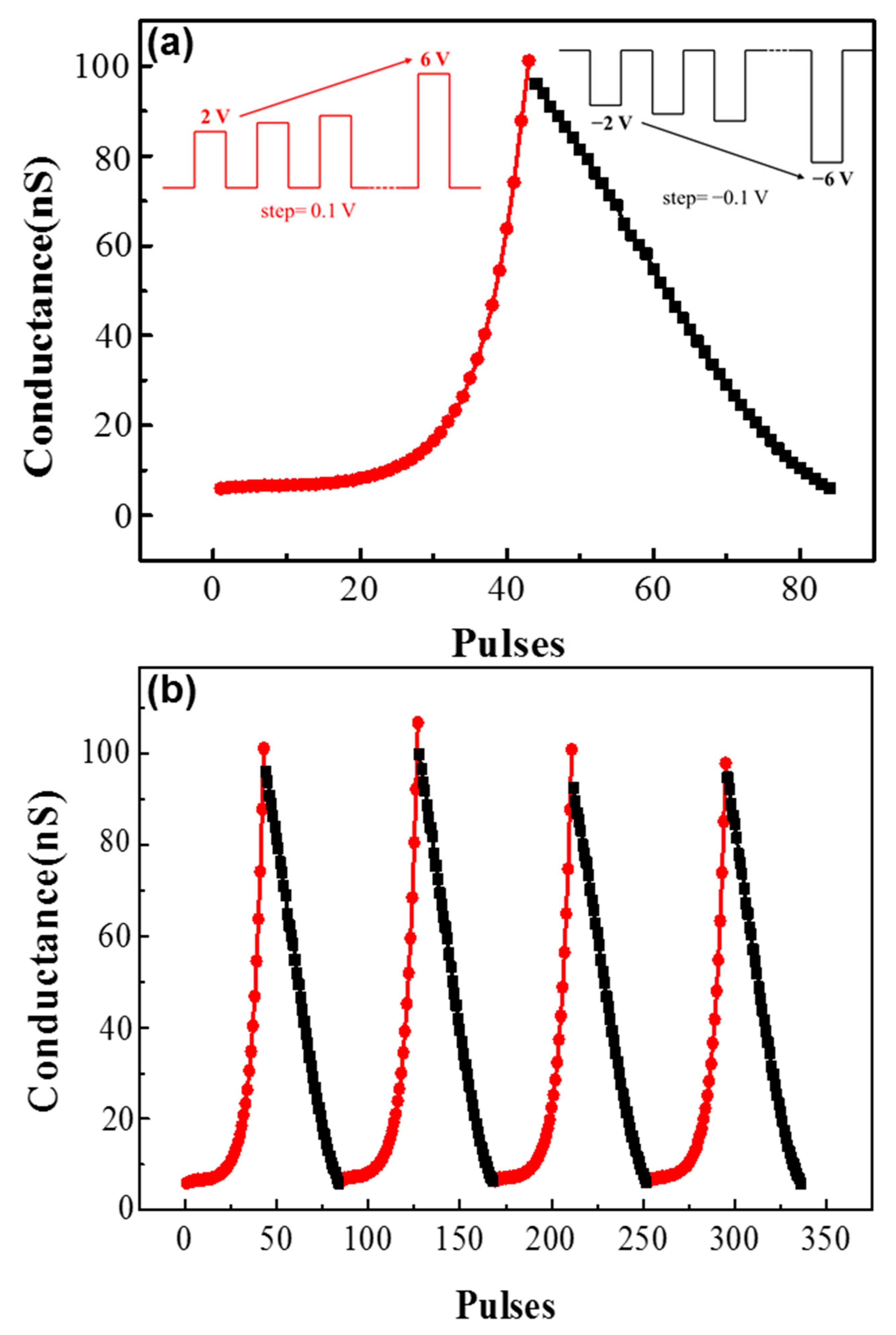
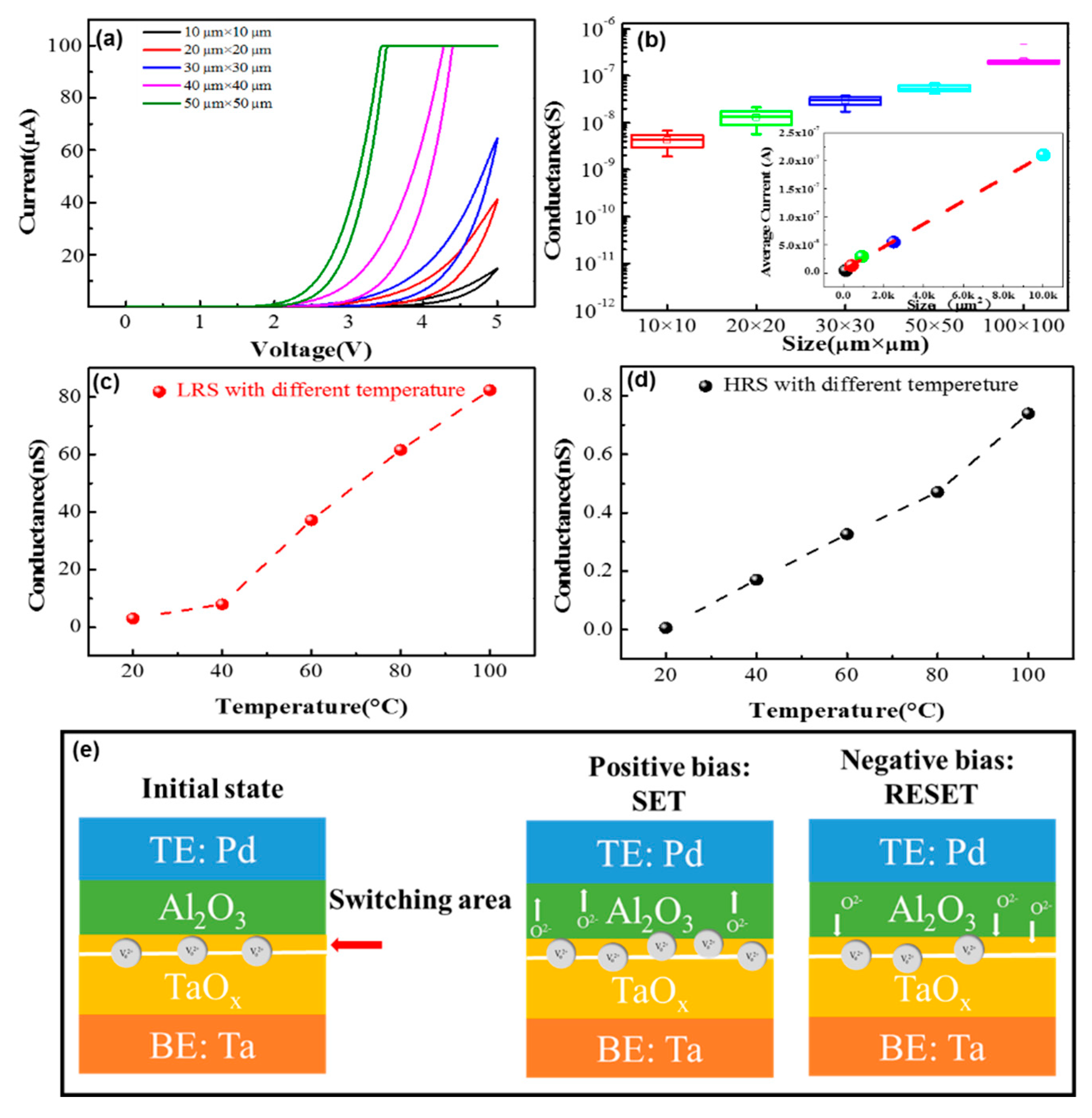
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fusi, S.; Annunziato, M.; Badoni, D.; Salamon, A.; Amit, D.J. Spike-driven synaptic plasticity: Theory, simulation, VLSI implementation. Neural Comput. 2000, 12, 2227–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laughlin, S.B.; van Steveninck, R.R.D.; Anderson, J.C. The metabolic cost of neural information. Nat. Neurosci. 1998, 1, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saremi, M. Modeling and Simulation of the Programmable Metallization Cells (PMCs) and Diamond-Based Power Devices. Ph.D. Thesis, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Strukov, D.B.; Snider, G.S.; Stewart, D.R.; Williams, R.S. The missing memristor found. Nature 2008, 453, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saremi, M. A physical-based simulation for the dynamic behavior of photodoping mechanism in chalcogenide materials used in the lateral programmable metallization cells. Solid State Ion. 2016, 290, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saremi, M. Carrier mobility extraction method in ChGs in the UV light exposure. Micro Nano Lett. 2016, 11, 762–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.H.; Chang, T.; Ebong, I.; Bhadviya, B.B.; Mazumder, P.; Lu, W. Nanoscale Memristor Device as Synapse in Neuromorphic Systems. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1297–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.M.; Liu, S.; Zhao, X.L.; Wu, F.C.; Wu, Q.T.; Wang, W.; Cao, R.R.; Fang, Y.L.; Lv, H.B.; Long, S.B. Emulating short-term and long-term plasticity of bio-synapse based on cu/a-Si/Pt memristor. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2017, 38, 1208–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.M.; Wu, Y.; Jeyasingh, R.; Kuzum, D.G.; Wong, H.S.P. An electronic synapse device based on metal oxide resistive switching memory for neuromorphic computation. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2011, 58, 2729–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.M.; Gao, B.; Fang, Z.; Yu, H.Y.; Kang, J.F.; Wong, H.S.P. A low energy oxide-based electronic synaptic device for neuromorphic visual systems with tolerance to device variation. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1774–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saremi, M.; Rajabi, S.; Barnaby, H.J.; Kozicki, M.N. The effects of process variation on the parametric model of the static impedance behavior of programmable metallization cell (PMC). MRS Proc. 2014, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, M.; Bichler, O.; Querlioz, D.; Cueto, O.; Perniola, L.; Sousa, V.; Vuillaume, D.; Gamrat, C.; DeSalvo, B. Phase change memory as synapse for ultra-dense neuromorphic systems: Application to complex visual pattern extraction. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), Washington, DC, USA, 5–7 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, Y.; Nishitani, Y.; Ueda, M. Ferroelectric artificial synapses for recognition of a multishaded image. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2014, 61, 2827–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerry, M.; Chen, P.Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Sharma, P.; Ni, K.; Yu, S.M.; Datta, S. Ferroelectric FET analog synapse for acceleration of deep neural network training. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–6 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.; Kim, T.; Kwak, M.; Song, J.; Woo, J.; Jeon, S.; Yoo, I.K.; Hwang, H. HfZrOx-based ferroelectric synapse device with 32 levels of conductance states for neuromorphic applications. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2017, 38, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, M.; Querlioz, D.; Bichler, O.; Palma, G.; Vianello, E.; Vuillaume, D.; Gamrat, C.; DeSalvo, B. Bio-inspired stochastic computing using binary CBRAM synapses. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2013, 60, 2402–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Lu, C.; Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Zhou, P. Graphene oxide quantum dots based memristors with progressive conduction tuning for artificial synaptic learning. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1803728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liang, X.; Yuan, B.; Chen, V.; Li, H.; Hui, F.; Yu, Z.; Yuan, F.; Pop, E.; Wong, H.S.P.; et al. Electronic synapses made of layered two-dimensional materials. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.M.; Gao, B.; Fang, Z.; Yu, H.Y.; Kang, J.F.; Wong, H.S.P. Stochastic learning in oxide binary synaptic device for neuromorphic computing. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garbin, D.; Vianello, E.; Bichler, O.; Rafhay, Q.; Gamrat, C.; Ghibaudo, G.; DeSalvo, B.; Perniola, L. HfO2-based OxRAM devices as synapses for convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2015, 62, 2494–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bill, J.; Legenstein, R. A compound memristive synapse model for statistical learning through STDP in spiking neural networks. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccolboni, G.; Molas, G.; Portal, J.M.; Coquand, R.; Bocquet, M.; Garbin, D.; Vianello, E.; Carabasse, C.; Delaye, V.; Pellissier, C.; et al. Investigation of the potentialities of Vertical Resistive RAM (VRRAM) for neuromorphic applications. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), Washington, DC, USA, 7–9 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.M.; Gao, B.; Fang, Z.; Yu, H.Y.; Kang, J.F.; Wong, H.S.P. A neuromorphic visual system using RRAM synaptic devices with sub-pJ energy and tolerance to variability: Experimental characterization and large-scale modeling. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–13 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Zhao, J.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.Y. Memristor with Ag-cluster-doped TiO2 films as artificial synapse for neuroinspired computing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, I.T.; Chang, C.C.; Chiu, L.W.; Chou, T.Y.; Hou, T.H. 3D Ta/TaOx/TiO2/Ti synaptic array and linearity tuning of weight update for hardware neural network applications. Nanotechnology 2016, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.; Kim, S.; Lu, W.D. Utilizing multiple state variables to improve the dynamic range of analog switching in a memristor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wu, H.Q.; Gao, B.; Deng, N.; Yu, S.M.; Qian, H. Improving analog switching in HfOx-based resistive memory with a thermal enhanced layer. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2017, 38, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Wu, J.F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, R.; Guo, X. Behavioral plasticity emulated with lithium lanthanum titanate-based memristive devices: Habituation. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2017, 3, 10–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoffrey, W.; Burr, R.M.S.; Abu, S.; Sangbum, K.; Seyoung, K.; Severin, S.; Kumar, V.; Masatoshi, I.; Pritish, N.; Alessandro, F.; et al. Neuromorphic computing using non-volatile memory. Adv. Phys. X 2017, 2, 89–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Terabe, K.; Yao, Y.; Tsuruoka, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Gimzewski, J.K.; Aono, M. Synaptic plasticity and memory functions achieved in a WO3−x-based nanoionics device by using the principle of atomic switch operation. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 384003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, R.B.; Li, J.; Zhuge, F.; Zhu, L.Q.; Liang, L.Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Gao, J.H.; Cao, H.T.; Fu, B.; Li, K. Synaptic devices based on purely electronic memristors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Lin, Y.C.; Wang, I.T.; Lin, T.P.; Hou, T.H. Characterization and modeling of nonfilamentary Ta/TaOx/TiO2/Ti analog synaptic device. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Yang, R.; Guo, X. Coexistence of analog and digital resistive switching in BiFeO3-based memristive devices. Solid State Ion. 2016, 296, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, C.; Song, B.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, Q. A Ti/AlOx/TaOx/Pt analog synapse for memristive neural network. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2018, 39, 1298–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.A. Long-term potentiation and memory. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 87–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, L.F.; Regehr, W.G. Synaptic computation. Nature 2004, 431, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.W.; Park, S.; Burr, G.W.; Hwang, H.; Jeong, Y.H. Optimization of conductance change in Pr1−xCaxMnO3-Based synaptic devices for neuromorphic systems. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2015, 36, 457–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.; Yu, S. Resistive memory-based analog synapse: The pursuit for linear and symmetric weight update. IEEE Nanotechnol. Mag. 2018, 12, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.-H.; Lim, S.; Park, B.-G.; Lee, J.-H. High-density and near-linear synaptic device based on a reconfigurable gated Schottky diode. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2017, 38, 1153–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Gong, T.; Xu, X.; Yuan, P.; Ma, H.; Dong, D.; Lv, H.; Long, S. Self-rectifying and forming-free resistive-switching device for embedded memory application. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2018, 39, 664–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Shi, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Wei, J.; Lu, J.; Zhao, X.; Wu, Z.; Cao, R.; Long, S.; et al. Bipolar Analog Memristors as Artificial Synapses for Neuromorphic Computing. Materials 2018, 11, 2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112102
Wang R, Shi T, Zhang X, Wang W, Wei J, Lu J, Zhao X, Wu Z, Cao R, Long S, et al. Bipolar Analog Memristors as Artificial Synapses for Neuromorphic Computing. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112102
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Rui, Tuo Shi, Xumeng Zhang, Wei Wang, Jinsong Wei, Jian Lu, Xiaolong Zhao, Zuheng Wu, Rongrong Cao, Shibing Long, and et al. 2018. "Bipolar Analog Memristors as Artificial Synapses for Neuromorphic Computing" Materials 11, no. 11: 2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112102
APA StyleWang, R., Shi, T., Zhang, X., Wang, W., Wei, J., Lu, J., Zhao, X., Wu, Z., Cao, R., Long, S., Liu, Q., & Liu, M. (2018). Bipolar Analog Memristors as Artificial Synapses for Neuromorphic Computing. Materials, 11(11), 2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112102




