In-Doped ZnO Hexagonal Stepped Nanorods and Nanodisks as Potential Scaffold for Highly-Sensitive Phenyl Hydrazine Chemical Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Growth of In-Doped ZnO Nanostructures
2.2. Characterization Techniques
2.3. Fabrication of Phenyl Hydrazine Electrochemical Sensor Based on IZO Nanomaterials
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of IZO Nanostructures
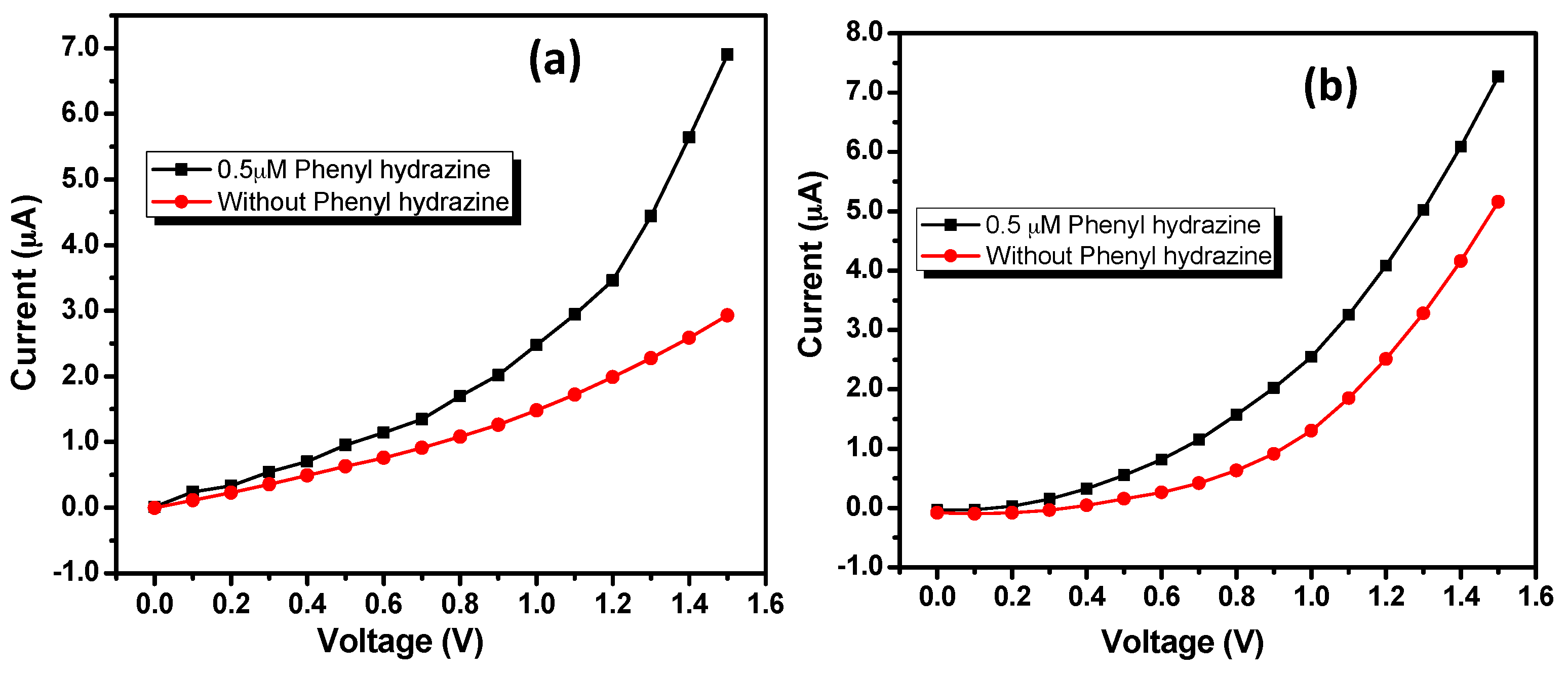
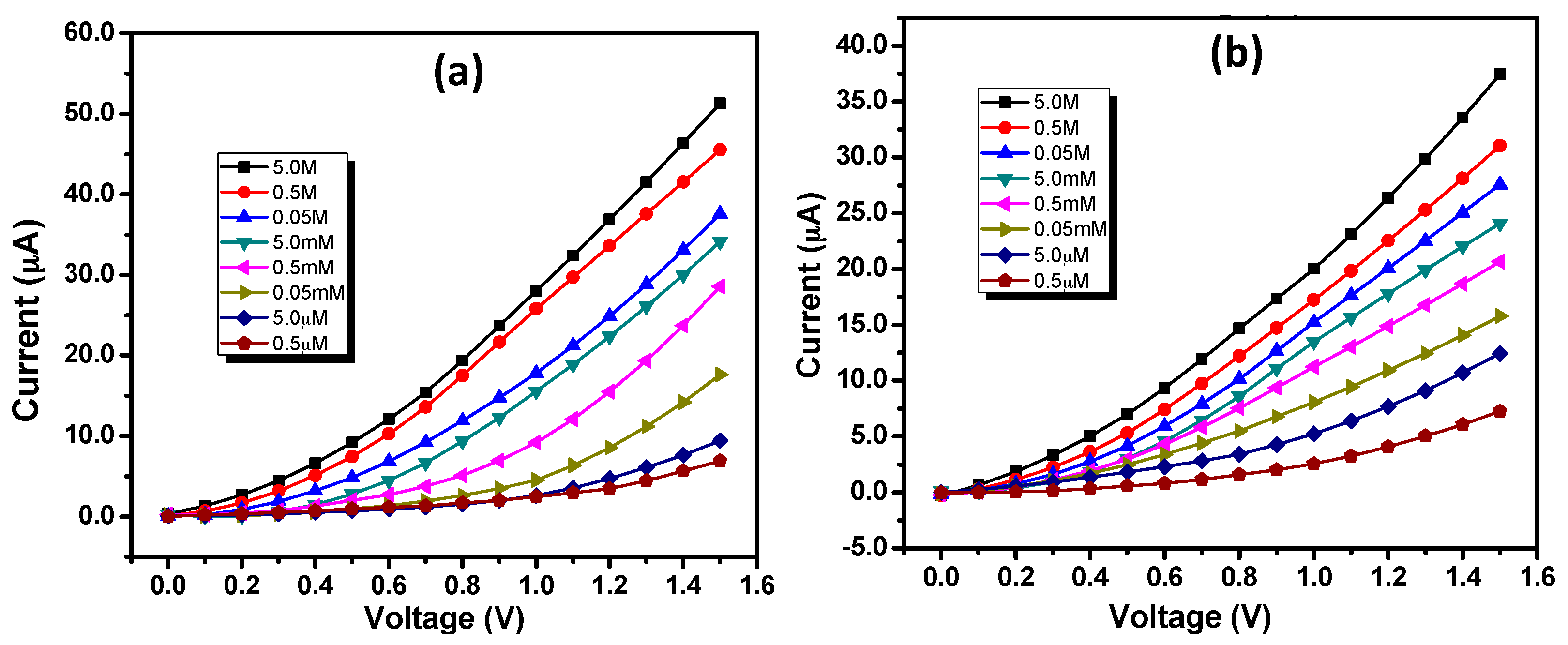
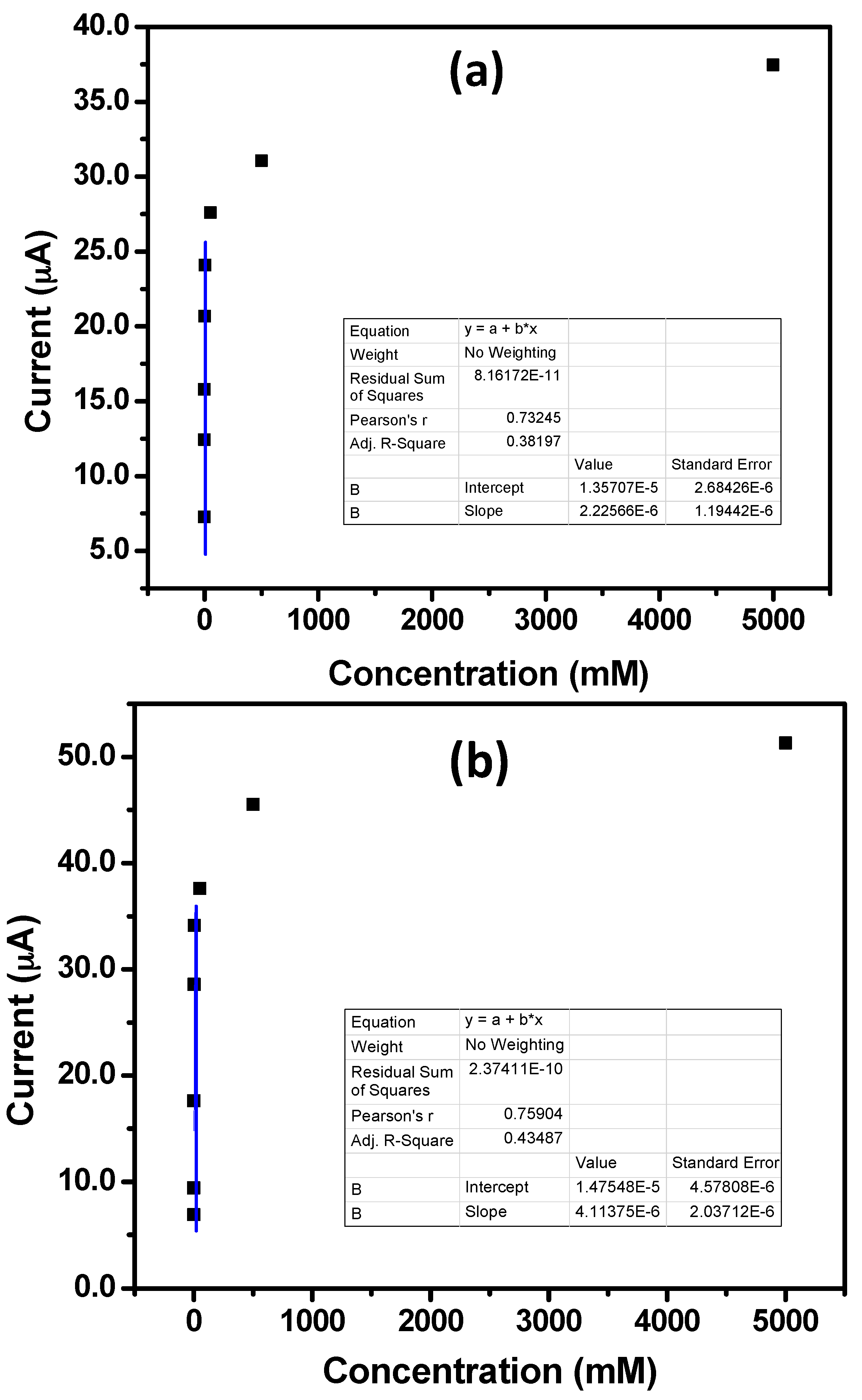
3.2. Electrochemical Sensing Applications of IZO Nanostructures
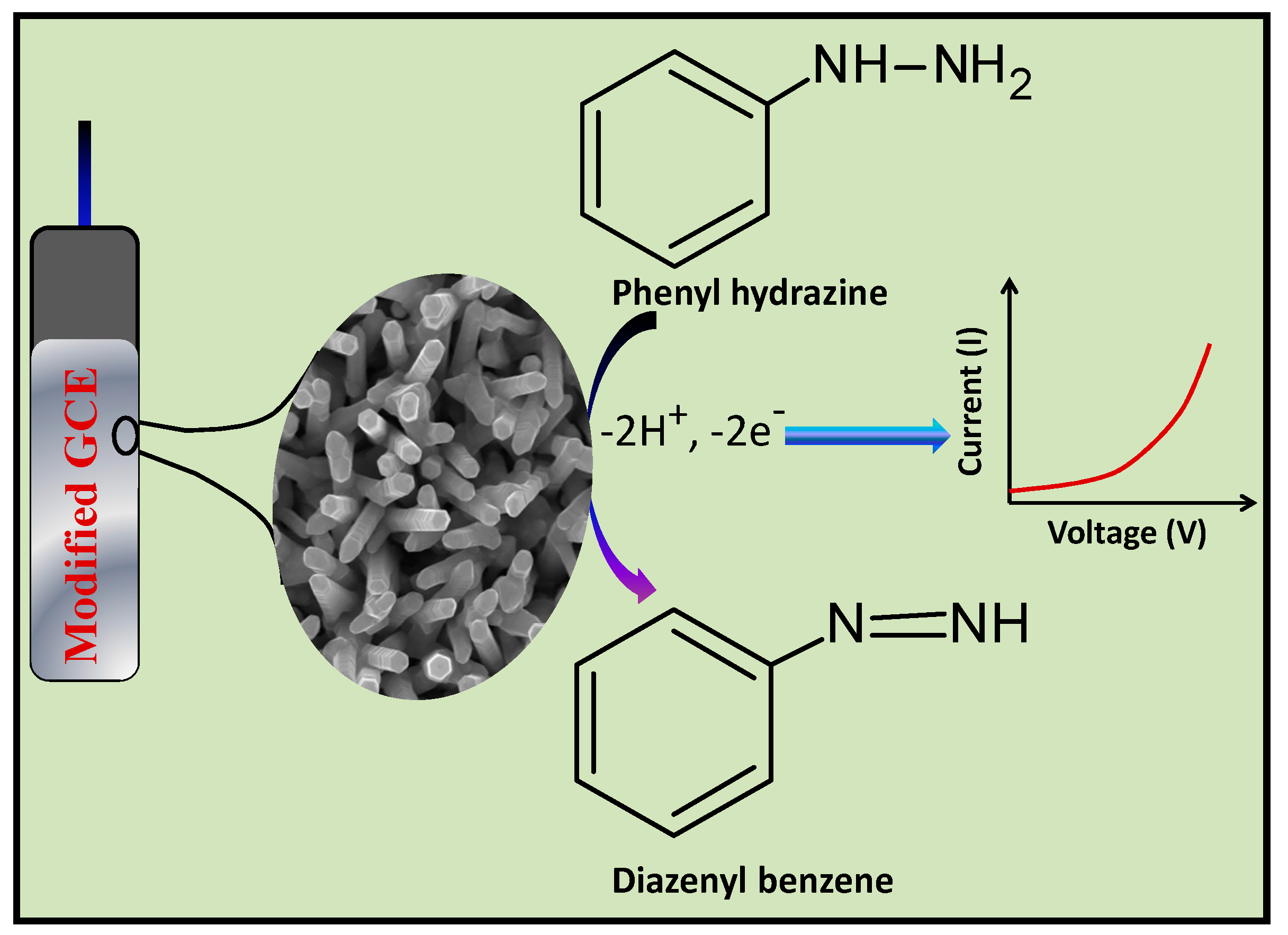
3.3. Proposed Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ibrahim, A.A.; Dar, G.N.; Zaidi, S.A.; Umar, A.; Abaker, M.; Bouzid, H.; Baskoutas, S. Growth and properties of Ag-doped ZnO nanoflowers for highly sensitive phenyl hydrazine chemical sensor application. Talanta 2012, 93, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholamian, F.; Sheikh-Mohseni, M.A.; Naeimi, H. Simultaneous determination of phenylhydrazine and hydrazine by a nanostructured electrochemical sensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 2344–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Murmu, P.P.; Leveneur, J.; Markwitz, A.; Futter, J. Controlling preferred orientation and electrical conductivity of zinc oxide thin films by post growth annealing treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 367, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murmu, P.P.; Kennedy, J.; Williams, G.V.M.; Ruck, B.J.; Granville, S.; Chong, S.V. Observation of magnetism, low resistivity, and magnetoresistance in the near-surface region of Gd implanted ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaviyarasu, K.; Geetha, N.; Kanimozhi, K.; Magdalane, C.M.; Sivaranjani, S.; Ayeshamariam, A.; Kennedy, J.; Maaza, M. In vitro cytotoxicity effect and antibacterial performance of human lung epithelial cells A549 activity of Zinc oxide doped TiO2 nanocrystals: Investigation of bio-medical application by chemical method. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 74, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathyaseelan, B.; Manikandan, E.; Sivakumar, K.; Kennedy, J.; Maaza, M. Enhanced visible photoluminescent and structural properties of ZnO/KIT-6 nanoporous materials for white light emitting diode (w-LED) application. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 651, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Fang, F.; Futter, J.; Leveneur, J.; Murmu, P.P.; Panin, G.N.; Kang, T.W.; Manikandan, E. Synthesis and enhanced field emission of zinc oxide incorporated carbon nanotubes. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 71, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaviyarasu, K.; Magdalane, C.M.; Kanimozhi, K.; Kennedy, J.; Siddhardha, B.; Reddy, E.S.; Rotte, N.K.; Sharma, C.S.; Thema, F.T.; Letsholathebe, D.; et al. Elucidation of photocatalysis, photoluminescence and antibacterial studies of ZnO thin films by spin coating method. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 173, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, J.; Murmu, P.P.; Leveneur, J.; Williams, V.M.; Moody, R.L.; Maity, T.; Chong, S.V. Enhanced power factor and increased conductivity of aluminum doped zinc oxide thin films for thermoelectric applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 1384–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, V.H.T.; Lee, B.K. Effective photocatalytic degradation of paracetamol using La-doped ZnO photocatalyst under visible light irradiation. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 96, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, U.; Khan, A.; Raza, W.; Khan, A.; Bahnemann, D.; Muneer, M. Highly efficient Y and V co-doped ZnO photocatalyst with enhanced dye sensitized visible light photocatalytic activity. Catal. Today 2017, 284, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.-L.; Wang, Q.; Xue, X.-Y. One-Step Synthesis of Pt–ZnO Nanoflowers and Their Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2016, 8, 1275–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Khan, W.; Mishra, P.; Islam, S.S.; Naqvi, A.H. Enhancement in alcohol vapor sensitivity of Cr doped ZnO gas sensor. Mater. Res. Bull. 2017, 93, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar Ganesh, R.; Durgadevi, E.; Navaneethan, M.; Patil, V.L.; Ponnusamy, S.; Muthamizhchelvan, C.; Kawasaki, S.; Patil, P.S.; Hayakawa, Y. Low temperature ammonia gas sensor based on Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticle decorated microspheres. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 721, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Fang, J. Ga doped ZnO photonic crystals with enhanced photocatalytic activity and its reaction mechanism. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 195, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movlarooy, T. Transition metals doped and encapsulated ZnO nanotubes: Good materials for the spintronic applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 441, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.A.; Tiwari, P.; Al-Assiri, M.S.; Al-Salami, A.E.; Umar, A.; Kumar, R.; Kim, S.H.; Ansari, Z.A.; Baskoutas, S. A Highly-Sensitive Picric Acid Chemical Sensor Based on ZnO Nanopeanuts. Materials 2017, 10, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.A.; Umar, A.; Kumar, R.; Kim, S.H.; Bumajdad, A.; Baskoutas, S. Sm2O3-doped ZnO beech fern hierarchical structures for nitroaniline chemical sensor. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 16505–16511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngai, K.S.; Tan, W.T.; Zainal, Z.; Zawawi, R.M.; Juan, J.C. Electrochemical Sensor Based on Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube/ZnO Photocatalyst Nanocomposite Modified Electrode for the Determination of Paracetamol. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2016, 8, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Jen, S.U.; Chiang, H.P.; Chen, S.C.; Lin, M.H.; Chen, J.Y.; Wang, X. Investigation of optoelectronic performance in In, Ga co-doped ZnO thin films with various In and Ga levels. Thin Solid Films 2016, 641, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W. Dependence of Electronic and Optical Properties of Zinc Oxide on Hydrostatic Pressure. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2016, 8, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthiban, R.; Balamurugan, D.; Jeyaprakash, B.G. Spray deposited ZnO and Ga doped ZnO based DSSC with bromophenol blue dye as sensitizer: Efficiency analysis through DFT approach. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 31, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.M.; Oh, M.; Na, Y.B.; Cheong, W.S.; Kim, H. Sputter deposition of Sn-doped ZnO/Ag/Sn-doped ZnO transparent contact layer for GaN LED applications. Mater. Lett. 2016, 180, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Jeong, H.; Lee, D. Sol-gel derived Hf- and Mg-doped high-performance ZnO thin film transistors. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 720, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Khan, M.Y.; Lee, S.-K.; Park, Y.-K.; Hahn, Y.-B. Parametric Study of Nozzle-Jet Printing for Directly Drawn ZnO Field-Effect Transistors. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2016, 8, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liau, L.C.K.; Huang, J.S. Energy-level variations of Cu-doped ZnO fabricated through sol-gel processing. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 702, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, M.S.; Villanueva, P.G.; Jardiel, T.; Calatayud, D.G.; Peiteado, M.; Caballero, A.C. Ga-doped ZnO self-assembled nanostructures obtained by microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis: Effect on morphology and optical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 722, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebatti, A.; Pflitsch, C.; Atakan, B. Unusual application of aluminium-doped ZnO thin film developed by metalorganic chemical vapour deposition for surface temperature sensor. Thin Solid Films 2017, 636, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinatha, N.; Raghu, P.; Mahesh, H.M.; Angadi, B. Spin-coated Al-doped ZnO thin films for optical applications: Structural, micro-structural, optical and luminescence studies. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 722, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, M.; Li, J.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Wei, Z.; Chu, X.; Fang, X.; Jin, F. Sol-combustion synthesis of Al-doped ZnO transparent conductive film at low temperature. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 330, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhati, V.S.; Ranwa, S.; Fanetti, M.; Valant, M.; Kumar, M. Efficient hydrogen sensor based on Ni-doped ZnO nanostructures by RF sputtering. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewale, P.S.; Lee, S.H.; Yu, Y.S. Pulse repetition rate dependent structural, surface morphological and optoelectronic properties of Ga-doped ZnO thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 725, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.; Kwon, S.J.; Cho, E.S. Nd: YVO4 Laser Direct Patterning of Aluminum-Doped Zinc Oxide Films Sputtered Under Different Process Conditions. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2016, 8, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaidashev, E.M.; Lorenz, M.; Von Wenckstern, H.; Rahm, A.; Semmelhack, H.C.; Han, K.H.; Benndorf, G.; Bundesmann, C.; Hochmuth, H.; Grundmann, M. High electron mobility of epitaxial ZnO thin films on c-plane sapphire grown by multistep pulsed-laser deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 3901–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chava, R.K.; Kang, M. Improving the photovoltaic conversion efficiency of ZnO based dye sensitized solar cells by indium doping. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 692, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Kim, Y.J.; Han, H.H.; Lim, D.; Jung, W.S.; Choi, M.S.; Nam, H.-J.; Son, S.-K.; Sergeevich, A.S.; Park, J.-H.; et al. Synthesis of P-Type ZnO Thin Films with Arsenic Doping and Post Annealing. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2016, 8, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Chai, L.; Wang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Deng, P.; Chen, Y. Evaluating the doping effect of Fe, Ti and Sn on gas sensing property of ZnO. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 147, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.C.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, H.-N. Characteristics of Amorphous Indium-Zinc-Oxide Thin-Film Transistors Fabricated with a Self-Aligned Coplanar Structure and an NH3 Plasma Contact Doping Process. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2016, 8, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liau, C.K.; Huang, J.-S. Effect of indium- and gallium-doped ZnO fabricated through sol-gel processing on energy level variations. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 97, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Saha, M.; De, S.K. Tunable surface plasmon resonance and enhanced electrical conductivity of In doped ZnO colloidal nanocrystals. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 7039–7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badadhe, S.S.; Mulla, I.S. H2S gas sensitive indium-doped ZnO thin films: Preparation and characterization. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 143, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhahri, R.; Hjiri, M.; El Mir, L.; Alamri, H.; Bonavita, A.; Iannazzo, D.; Leonardi, S.G.; Neri, G. CO sensing characteristics of In-doped ZnO semiconductor nanoparticles. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2017, 2, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tian, Z.; Han, D.; Gu, F. Highly Sensitive and Selective Ethanol Sensor Fabricated with In-Doped 3DOM ZnO. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5466–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Wei, Z.; Li, Y.; Qu, J.; Zu, B.; Dou, X. Highly sensitive and rapid chemiresistive sensor towards trace nitro-explosive vapors based on oxygen vacancy-rich and defective crystallized In-doped ZnO. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 244, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.; Akhtar, M.S.; Al-Hajry, A.; Al-Assiri, M.S.; Dar, G.N.; Saif Islam, M. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of harmful dye and phenyl hydrazine chemical sensing using ZnO nanourchins. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kumar, G.; Umar, A. ZnO nano-mushrooms for photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange. Mater. Lett. 2013, 97, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hadeethi, Y.; Umar, A.; Al-Heniti, S.H.; Kumar, R.; Kim, S.H.; Zhang, X.; Raffah, B.M. 2D Sn-doped ZnO ultrathin nanosheet networks for enhanced acetone gas sensing application. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 2418–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, X.; Tian, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; He, W.; Hou, P.; Deng, X.; Xu, X. Synthesis of Ce-doped In2O3 nanostructure for gas sensor applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 428, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, K.; Kaur, J.; Singh, R.C.; Thangaraj, R. Preparation and characterization of Ag-doped In2O3 nanoparticles gas sensor. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2017, 682, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D.-A.; Xing, L.-L.; Xue, X.-Y. High Capacity and Cyclability of SnO2–In2O3/Graphene Nanocomposites as the Anode of Lithium-Ion Battery. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2016, 8, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Murmu, P.P.; Manikandan, E.; Lee, S.Y. Investigation of structural and photoluminescence properties of gas and metal ions doped zinc oxide single crystals. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 616, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannam, R.; Kumar, E.S.; Priyadarshini, D.M.; Bellarmine, F.; DasGupta, N.; Ramachandra Rao, M.S. Enhanced photoluminescence and heterojunction characteristics of pulsed laser deposited ZnO nanostructures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 418, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhai, C.; Liu, J. Growth mechanism and photoluminescence property of hydrothermal oriented ZnO nanostructures evolving from nanorods to nanoplates. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 718, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Shang, F.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, F.; Liu, C.; Gong, W.; Lv, J.; Zhang, M.; He, G.; Sun, Z. Temperature-Dependent Photoluminescence of ZnO Nanorods Grown by a Copper-Assisted Hydrothermal Method. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2015, 7, 1800–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.Y.; Ma, C.Y.; Yuan, F.; Wang, N.; Qin, F.W.; Hu, B.C.; Zhang, Q.Y. Structural, morphological, photoluminescence and photocatalytic properties of Gd-doped ZnO films. Thin Solid Films 2017, 636, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Carder, D.A.; Markwitz, A.; Reeves, R.J. Properties of nitrogen implanted and electron beam annealed bulk ZnO. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 103518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.S.; Huang, N.M.; Nagaraja, H.S. Influence of Sn doping on photoluminescence and photoelectrochemical properties of ZnO nanorod arrays. Electron. Mater. Lett. 2014, 10, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishad, K.K.; Joseph, J.; Tiwari, N.; Kurchania, R.; Pandey, R.K. Investigation on Size Dependent Elemental Binding Energies and Structural Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles and Their Correlation with Observed Photo-Luminescence Behavior. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2015, 7, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.; Akhtar, M.S.; Dar, G.N.; Baskoutas, S. Low-temperature synthesis of α-Fe2O3 hexagonal nanoparticles for environmental remediation and smart sensor applications. Talanta 2013, 116, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Liu, Y.-R.; Lin, S.-S.; Hsu, L.-J.; Tsai, S.-L. Role of Annealing Temperature on the Formation of Aligned Zinc Oxide Nanorod Arrays for Efficient Photocatalysts and Photodetectors. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2016, 8, 2197–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, G.; Algarni, H.; Kim, S.H. Effect of annealing temperature on the properties and photocatalytic efficiencies of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 648, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Xiang, G.; Gu, G.; Zhang, X. Enhancement of ferromagnetism of ZnO:Co nanocrystals by post-annealing treatment: The role of oxygen interstitials and zinc vacancies. Mater. Lett. 2014, 122, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Harraz, F.A.; Ismail, A.A.; Al-Sayari, S.A.; Algarni, H.; Al-Sehemi, A.G. Synthesis of amorphous ZnO-SiO2 nanocomposite with enhanced chemical sensing properties. Thin Solid Films 2016, 605, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Gruner, G.; Al-Ghamdi, M.S.; Daous, M.A.; Khan, S.B.; Asiri, A.M. Fabrication of highly sensitive phenyl hydrazine chemical sensor based on as-grown ZnO-Fe2O3 microwires. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 520–534. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Khan, S.B.; Jamal, A.; Faisal, M.; Asiri, A.M. Fabrication of phenyl-hydrazine chemical sensor based on Al-doped ZnO Nanoparticles. Sens. Transducers 2011, 134, 32–44. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.B.; Faisal, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Abdel-Latif, I.A.; Ismail, A.A.; Akhtar, K.; Al-Hajry, A.; Asiri, A.M.; Alamry, K.A. Highly sensitive and stable phenyl hydrazine chemical sensors based on CuO flower shapes and hollow spheres. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.W.; Umar, A.; Dar, G.N.; Kim, S.H.; Badran, R.I. Synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles for phenyl hydrazine sensor applications. Sens. Lett. 2014, 12, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Heniti, S.H.; Umar, A.; Zaki, H.M.; Dar, G.N.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Kim, S.H. Synthesis and Characterizations of Ferrite Nanomaterials for Phenyl Hydrazine Chemical Sensor Applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 3765–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameen, S.; Shaheer Akhtar, M.; Seo, H.K.; Shin, H.S. TiO2 nanotube arrays via electrochemical anodic oxidation: Prospective electrode for sensing phenyl hydrazine. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzali, D.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Khalilzadeh, M.A. Sensitive and selective determination of phenylhydrazine in the presence of hydrazine at a ferrocene-modified carbon nanotube paste electrode. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2011, 9, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Lin, H.; Ma, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, J.; Qu, F. A Facile Method for the Synthesis of Porous ZnO Hollow Microspheres and Their Gas Sensing Properties for Acetone. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2015, 7, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.; Ahmad, R.; Lee, G.H.; Suh, E.-K.; Hahn, Y.-B. Effect of Annealing Atmosphere on the Optical and Electrical Properties of Al-Doped ZnO Films and ZnO Nanorods Grown by Solution Process. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2016, 8, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.A.; Hwang, S.W.; Dar, G.N.; Kim, S.H.; Abaker, M.; Ansari, S.G. Synthesis and Characterization of Gd-Doped ZnO Nanopencils for Acetone Sensing Application. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2015, 7, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
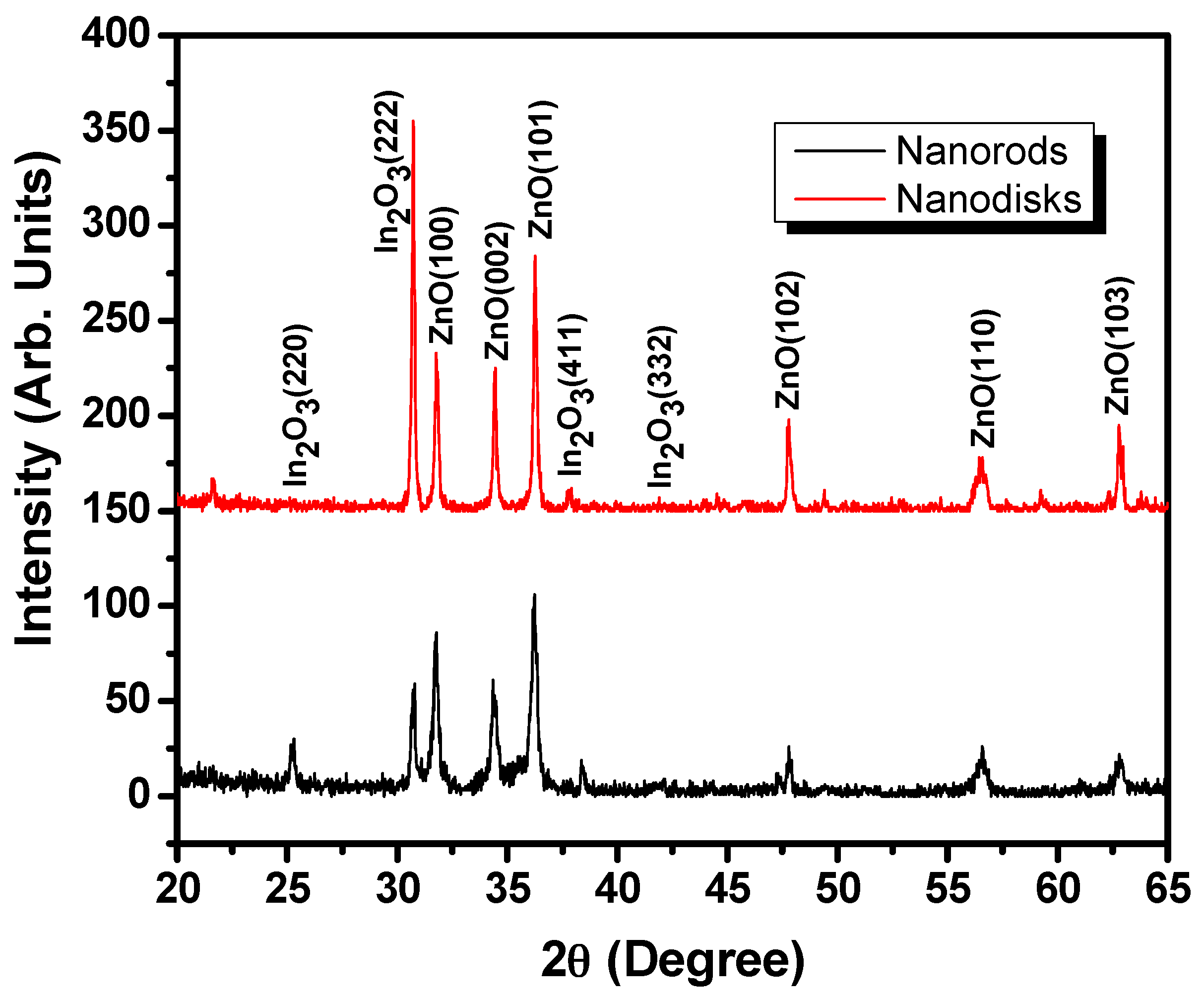

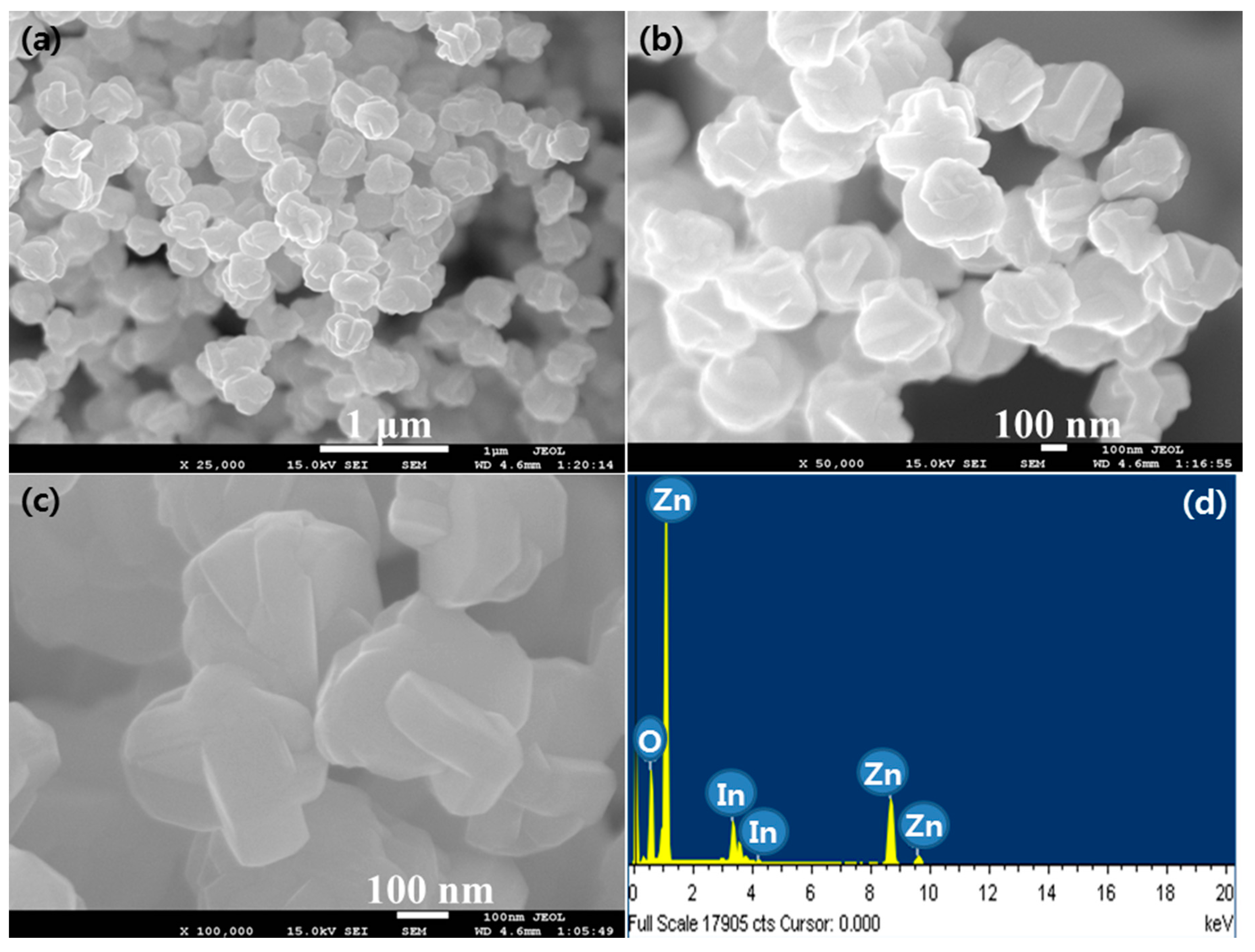
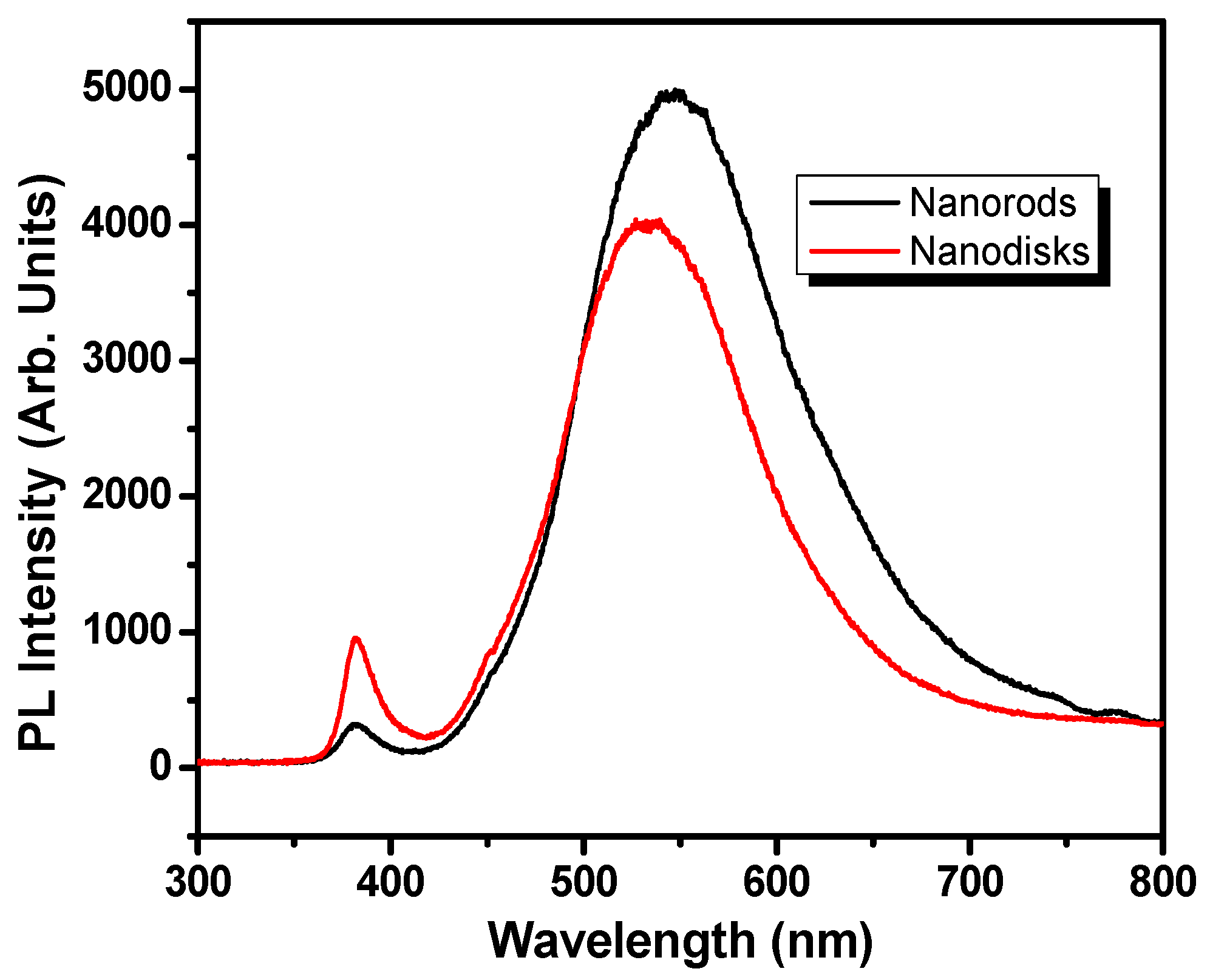
| S.N. | (hkl) | IZO Nanorods | IZO Nanodisks | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2θ (°) | FWHM (β) | Crystallite Size (nm) | 2θ (°) | FWHM (β) | Crystallite Size (nm) | ||
| 1. | (100) | 31.79 | 0.29564 | 27.65 | 31.77 | 0.19751 | 41.39 |
| 2. | (002) | 34.35 | 0.35795 | 22.99 | 34.45 | 0.1810 | 45.48 |
| 3. | (101) | 36.23 | 0.34833 | 23.75 | 36.27 | 0.20768 | 39.84 |
| Sensing Materials | Sensitivity (μA·mM−1·cm−2) | LDR (μM–mM) | Detection limit (μM) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO nanourchin | 42.1 | 98.0–3.126 | 78.6 | [45] |
| ZnO–SiO2 nanocomposite | 10.80 | 390.0–50.0 | 1.42 | [63] |
| ZnO-Fe2O3 microwires | 8.33 | 10−3–10.0 | 6.7 × 10−4 | [64] |
| Al- doped ZnO Nanoparticles | 1.143 | 10.0–50.0 | 1.215 ± 0.02 | [65] |
| CuO hollow spheres | 0.578 | 5 × 103–10.0 | 2.4 × 103 | [66] |
| CuO flowers | 7.145 | |||
| Fe2O3 nanoparticles | 57.88 | 97.0–1.56 | 97 | [67] |
| Cd0.5Mg0.5Fe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles | 7.01 | 3 × 103–100 | 3 × 103 | [68] |
| TiO2 nanotubes | 40.9 | 0.25–0.10 | 0.22 | [69] |
| Ferrocene-modified carbon nanotube | 25.3 | 0.85–0.7 | 0.6 | [70] |
| IZO nanorods | 70.43 | 0.5–5.0 | 0.5 | This study |
| IZO nanodisks | 130.18 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Umar, A.; Kim, S.H.; Kumar, R.; Al-Assiri, M.S.; Al-Salami, A.E.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Baskoutas, S. In-Doped ZnO Hexagonal Stepped Nanorods and Nanodisks as Potential Scaffold for Highly-Sensitive Phenyl Hydrazine Chemical Sensors. Materials 2017, 10, 1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111337
Umar A, Kim SH, Kumar R, Al-Assiri MS, Al-Salami AE, Ibrahim AA, Baskoutas S. In-Doped ZnO Hexagonal Stepped Nanorods and Nanodisks as Potential Scaffold for Highly-Sensitive Phenyl Hydrazine Chemical Sensors. Materials. 2017; 10(11):1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111337
Chicago/Turabian StyleUmar, Ahmad, Sang Hoon Kim, Rajesh Kumar, Mohammad S. Al-Assiri, A. E. Al-Salami, Ahmed A. Ibrahim, and Sotirios Baskoutas. 2017. "In-Doped ZnO Hexagonal Stepped Nanorods and Nanodisks as Potential Scaffold for Highly-Sensitive Phenyl Hydrazine Chemical Sensors" Materials 10, no. 11: 1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111337
APA StyleUmar, A., Kim, S. H., Kumar, R., Al-Assiri, M. S., Al-Salami, A. E., Ibrahim, A. A., & Baskoutas, S. (2017). In-Doped ZnO Hexagonal Stepped Nanorods and Nanodisks as Potential Scaffold for Highly-Sensitive Phenyl Hydrazine Chemical Sensors. Materials, 10(11), 1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111337







