Effects of Nano-Aluminum Nitride on the Performance of an Ultrahigh-Temperature Inorganic Phosphate Adhesive Cured at Room Temperature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
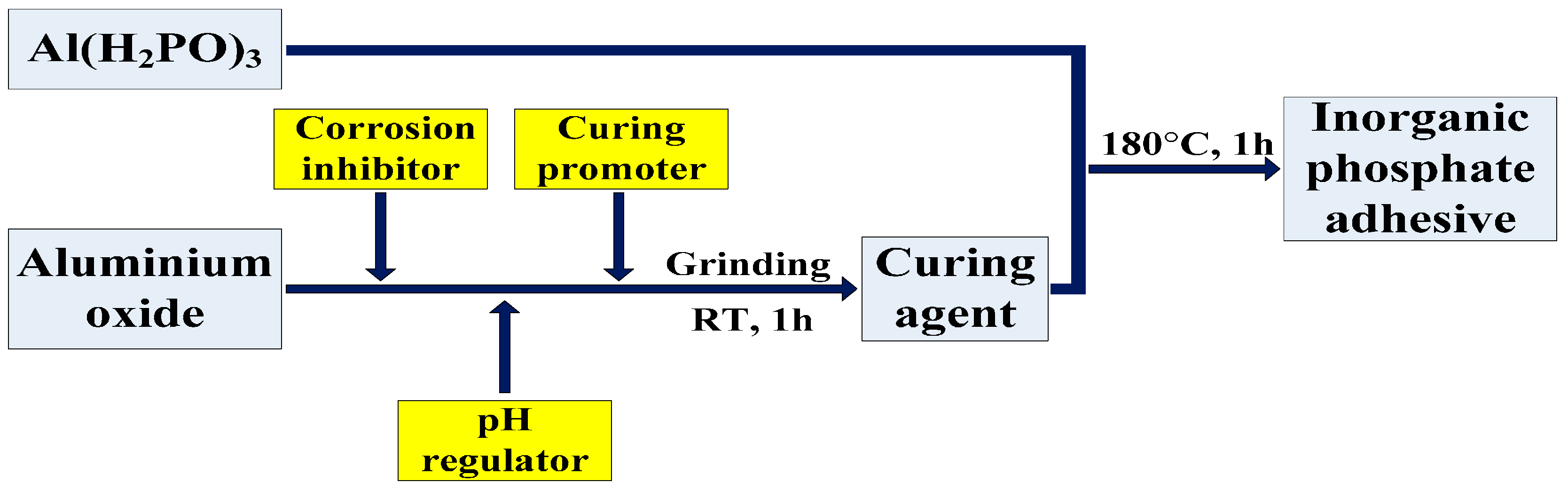
2.1. Materials and Manufacturing
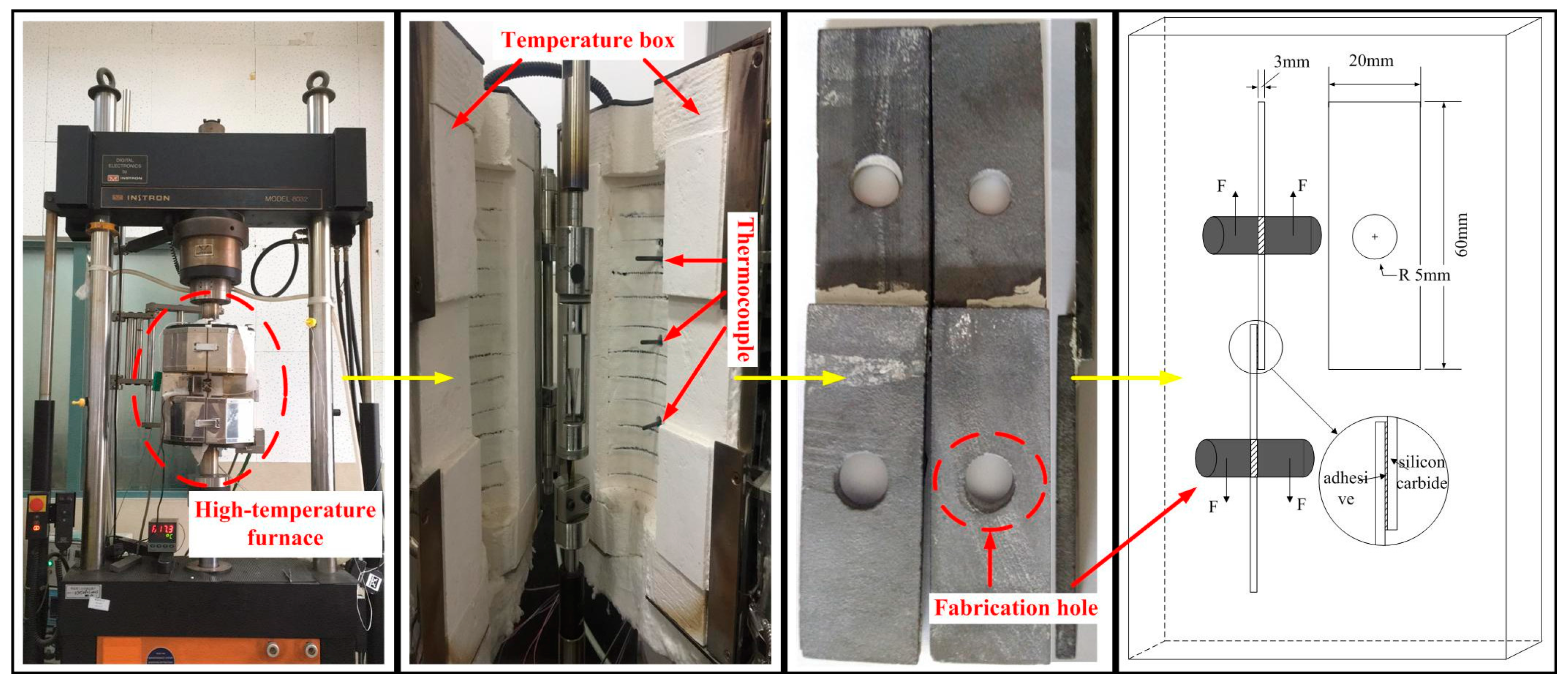
2.2. Mechanical Tests
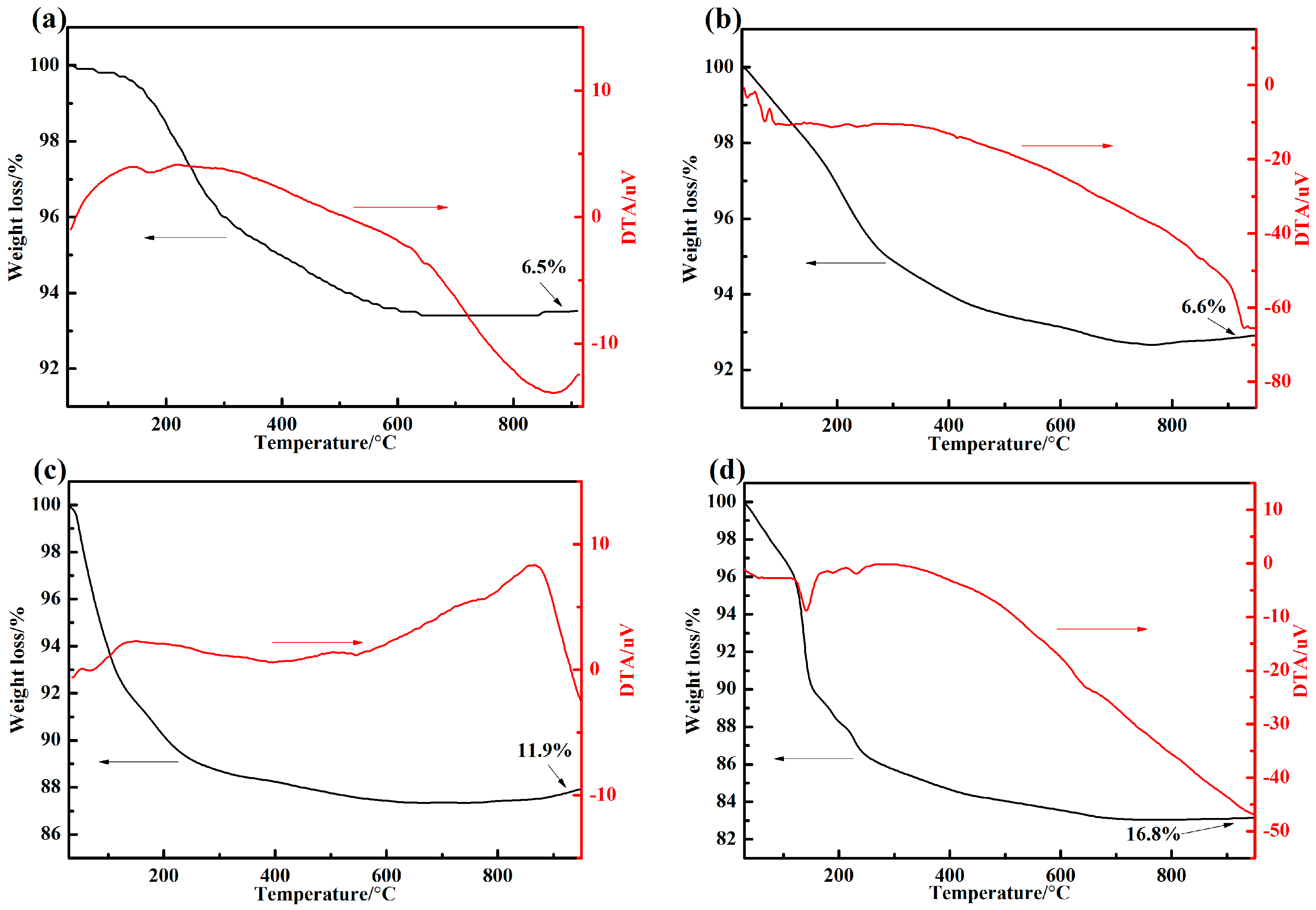
2.3. Differential Thermal Analysis Tests
2.4. X-ray Diffraction Tests
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscope Tests
3. Results and Discussion
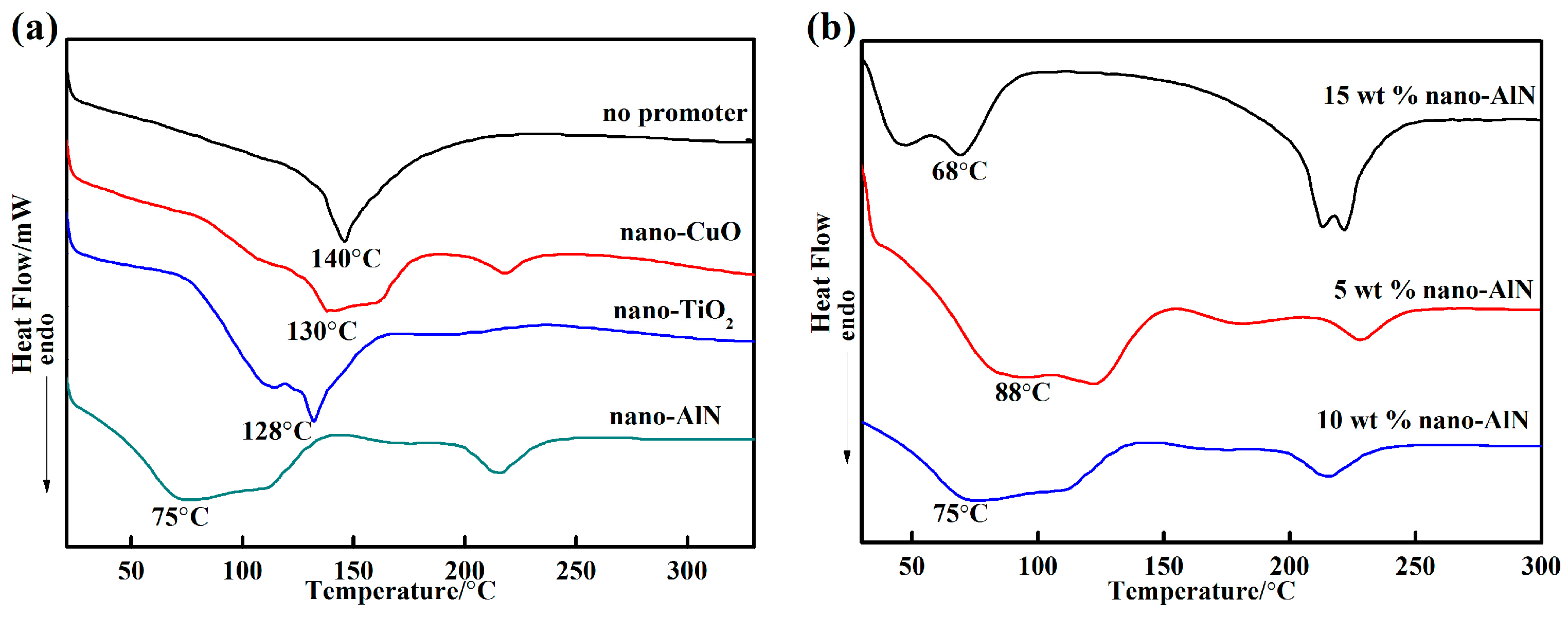
3.1. Thermal Properties
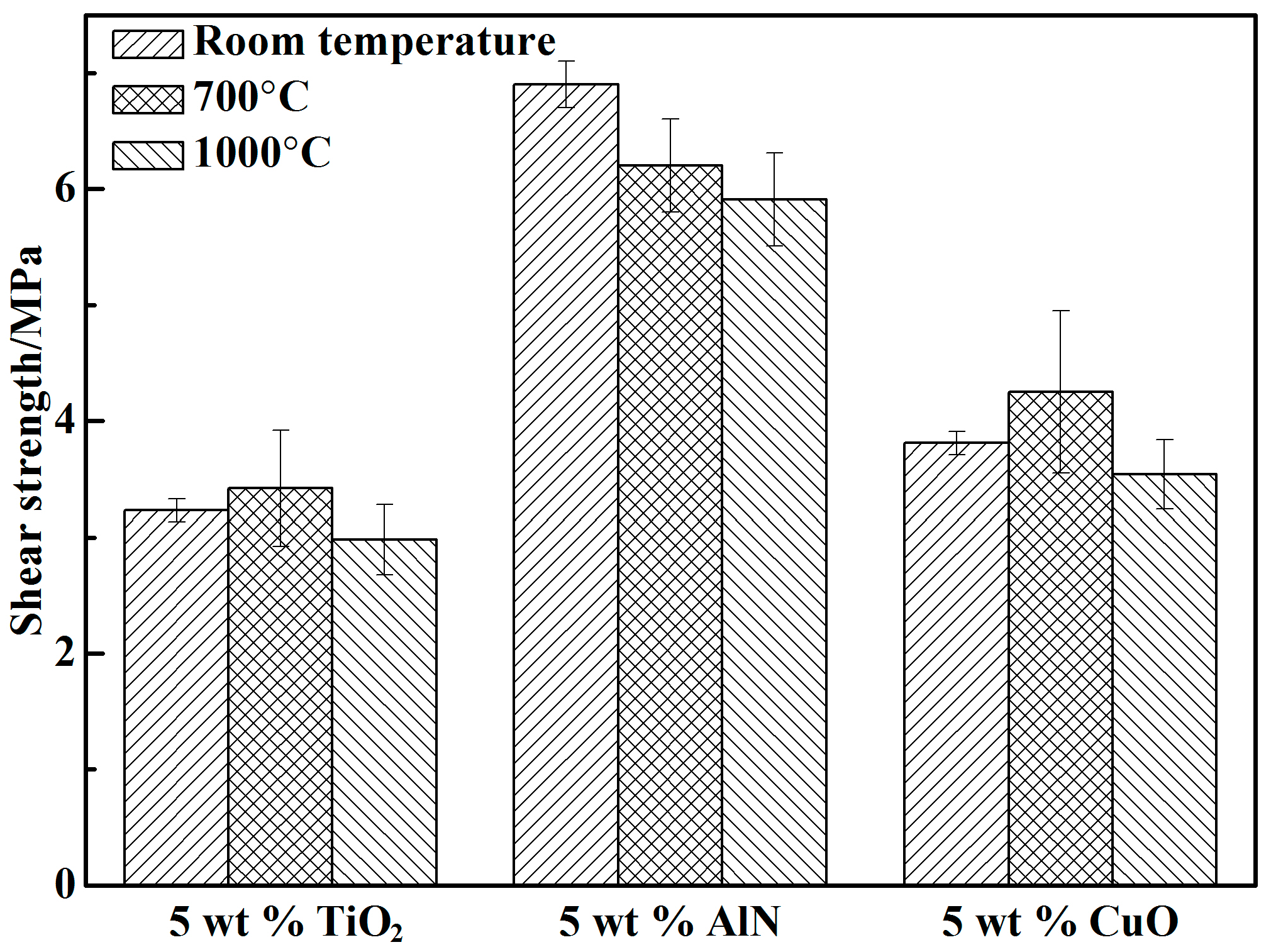
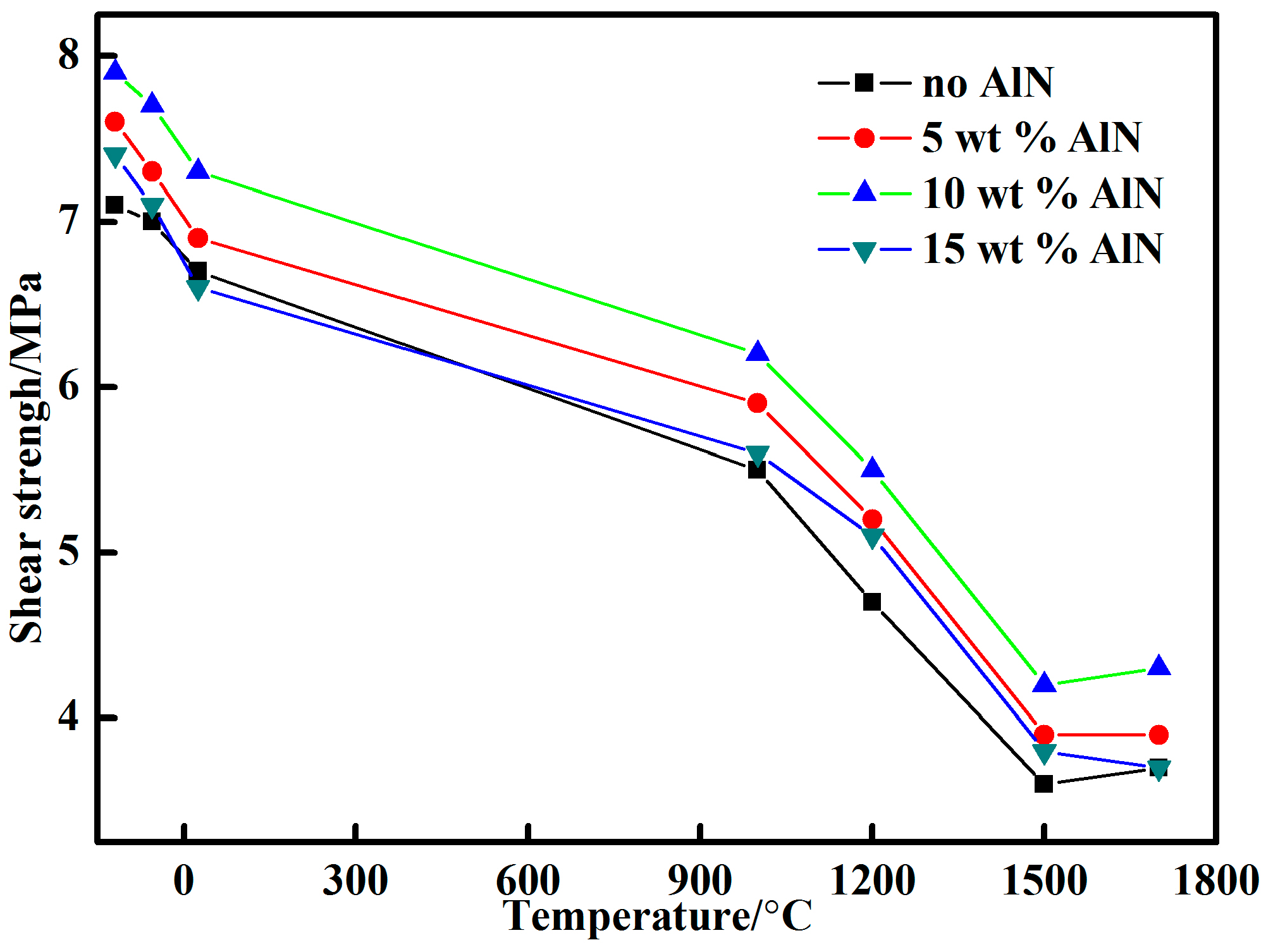
3.2. Shear Strength
3.3. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
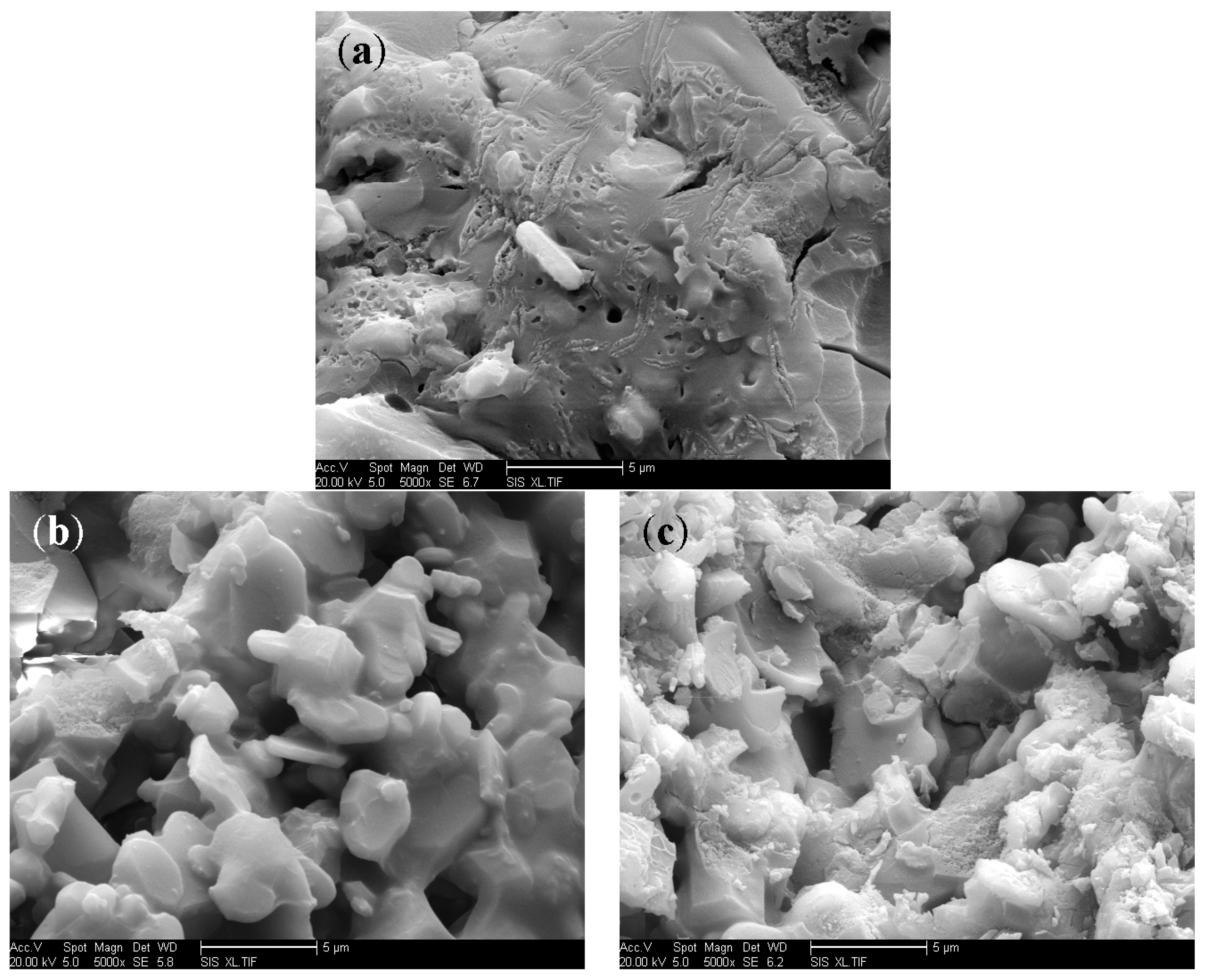
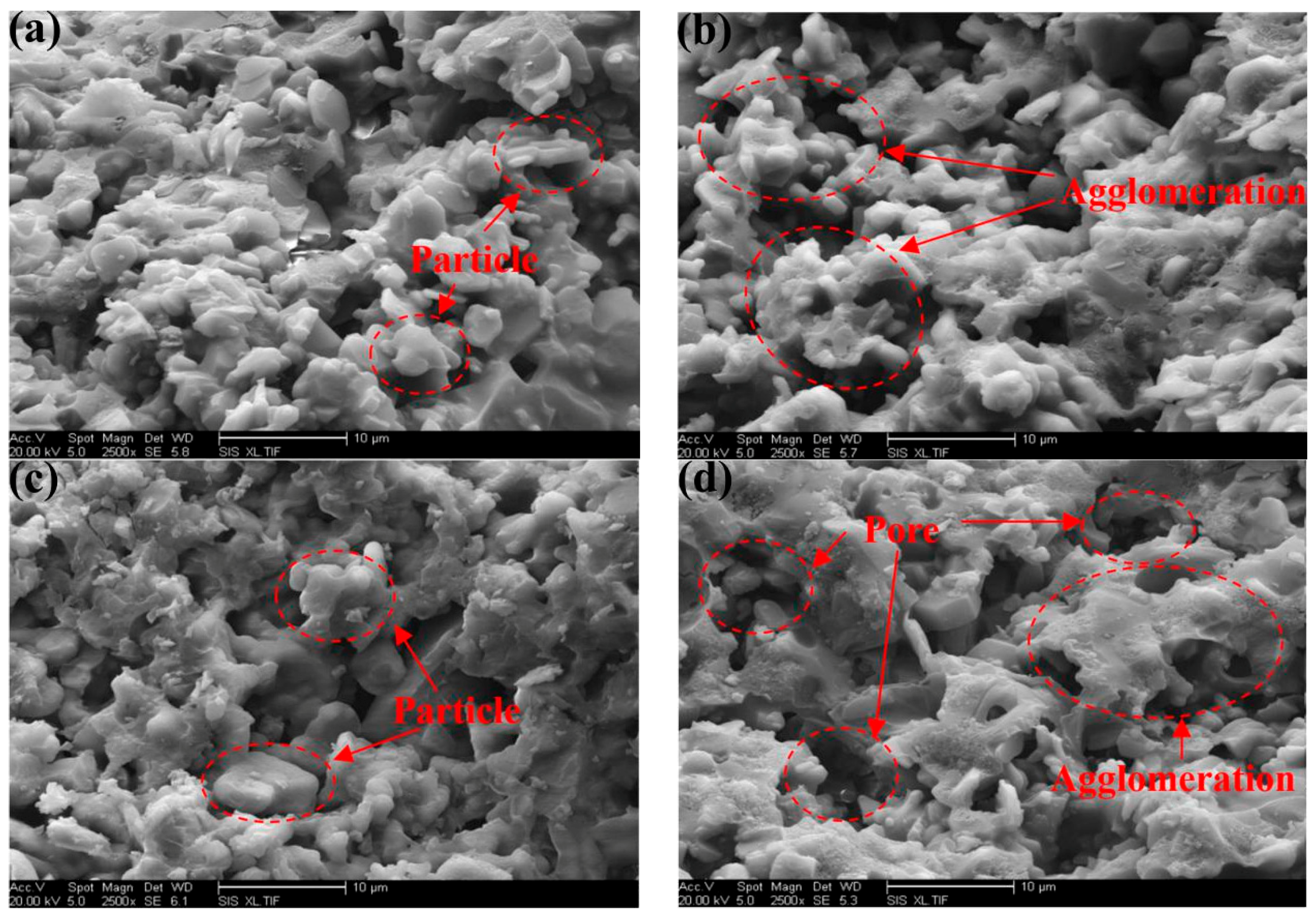
3.4. Micromorphology
4. Conclusions
- An ultrahigh-temperature inorganic phosphate adhesive cured at RT was prepared with aluminium dihydrogen phosphate as the resin and aluminium oxide (-Al2O3), etc., as the curing agent. When the content of the curing agent was more than that of resin, it had less effect on the thermal stability of the adhesive. The inorganic phosphate adhesive could be prepared with a ratio of 1:1 in consideration of heat resistance and the manufacturing process.
- The inorganic phosphate adhesive has excellent heat resistance. Addtionally, the promoters and curing agents significantly affected the curing temperature. The phase structure of the adhesive with 10 wt % nano-AlN changed from AlPO4(11-0500) to the more stable AlPO4(10-0423) at 1200 °C.
- A proper amount of nano-AlN clearly improved the shear strength of the adhesive because of the increased Al3+ content. The shear strength of the adhesive with 10 wt % nano-AlN was higher than that of the adhesives with other proportions of nano-AlN. A spot of nano-AlN did not fully promote the reaction between the resin and the curing agent. Excess nano-AlN instead decreased the shear strength due to the increase of porosity.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dadras, P.; Mehrotra, G.M. Joining of carbon-carbon composites by graphite formation. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1994, 77, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadras, P.; Mehrotra, G.M. Solid state diffusion bonding of carbon-carbon composites with borides and carbides. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1993, 76, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, X.; Xu, X.; Yun, Z.; Liu, J.; Du, H.; Guo, A. A user-friendly heat-resistant modified polymer-based adhesive for joining and repair of carbon/carbon composites. Mater. Des. 2015, 86, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, E.A.S.; da Silva, L.F.M.; Flaviani, M. Testing and simulation of mixed adhesive joints for aerospace applications. Compos. B Eng. 2015, 74, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiropoulos, C.V.; Chamos, A.N.; Tserpes, K.I.; Pantelakis, S.G. Fracture toughness and shear behavior of composite bonded joints based on a novel aerospace adhesive. Compos. B Eng. 2012, 43, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadiyala, A.K.; Sharma, M.; Bijwe, J. Exploration of thermoplastic polyimide as high temperature adhesive and understanding the interfacial chemistry using XPS, ToF-SIMS and Raman spectroscopy. Mater. Des. 2016, 109, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Guan, X.; Zhang, C.; Niu, Y. Polyglycerol-based organic-inorganic hybrid adhesive with high early strength. Mater. Des. 2017, 117, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.J.; Kim, D.P. Studies on curing chemistry of aluminum-chromium-phosphates as low temperature curable binders. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2003, 26, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, Y.D.; Wang, B. Study on heat-resistant property of adhesive/carbon-carbon composites joints. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2006, 26, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Liu, J.; Guo, A.; Ren, S.; Xu, X.; Liu, S. Fabrication of heat-resistant syntactic foams through binding hollow glass microspheres with phosphate adhesive. Mater. Des. 2016, 95, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Du, H.; Hou, F.; Guo, A.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. A new practical inorganic phosphate adhesive applied under both air and argon atmosphere. J. Alloy. Compd. 2014, 617, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.K. Effect of carbon nanotubes on the strength of adhesive lap joints of C/C and C/C-SiC ceramic fibre composites. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2011, 31, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, R.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, Q. The reinforcing mechanism of carbon fiber in composite adhesive for bonding carbon/carbon composites. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2011, 211, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.X.; Sun, R.N.; Mao, Z.P.; Wang, P.C. Effects of phosphate pretreatment and hot-humid environmental exposure on static strength of adhesive-bonded magnesium AZ31 sheets. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 3517–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, S.R.; Opila, E.J.; Halbig, M.C.; Kiser, J.D.; Singh, M.; Salem, J.A. Evaluation of ultra-high temperature ceramics for aeropropulsion use. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 22, 2757–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.X.; Sun, K.; Fan, Y.Z. Effect of high-temperature curing on the crosslink structures and dynamic mechanical properties of gum and N330-filled natural rubber vulcanizates. Polym. Test. 2001, 20, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.J.; Tu, S.H. Joining of mullite ceramics with yttrium aluminosilicate glass interlayers. Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, R.; Veronesi, P.; Han, S.; Casalegno, V.; Salvo, M.; Colombini, E.; Leonelli, C.; Ferraris, M. Microwave assisted combustion synthesis in the system Ti-Si-C for the joining of SiC: Experimental and numerical simulation results. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 33, 1707–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.Y.; Han, H.J.; Ha, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, D.P. Development of Cr-free aluminum phosphate binders and their composite applications. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, J.A.; Chung, D.D.L. Improving an alumina fiber filter membrane for hot gas filtration using an acid phosphate binder. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 5079–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, R.; Jiang, M.; Xiang, Q.; Li, J. The preparation and performance of a novel room-temperature-cured heat-resistant adhesive for ceramic bonding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 2952–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpukhin, I.A.; Vladimirov, V.S.; Moizis, S.E. A Mechanism for Phosphate Hardening and Prospects for the Use of Metal Phosphate Materials (A Review). Part I. The Nature of Hydrogen Bonding and Its Function in the Mechanism of Phosphate Hardening. Refract. Ind. Ceram. 2005, 46, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpukhin, I.A.; Vladimirov, V.S.; Moizis, S.E. A Mechanism for Phosphate Hardening and Prospects for the Use of Metal Phosphate Materials (An Overview). Part II. Adhesive Properties of Binding Phosphate Materials. Refract. Ind. Ceram. 2005, 46, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagh, A.S.; Jeong, S.Y. Chemically bonded phosphate ceramics: III, reduction mechanism and its application to iron phosphate ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2003, 86, 1850–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Du, H.; Guo, A.; Tao, X.; Dong, X.; Geng, H. A SiC whisker reinforced high-temperature resistant phosphate adhesive for bonding carbon/carbon composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 633, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Du, H.; Hou, F.; Guo, A.; Liu, S.; Dong, X. Joining of C/C composites by using B4C reinforced phosphate adhesive. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 11581–11591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Shweta Sharma, A.; Gupta, M.N. Biodiesel Preparation by Lipase-Catalyzed Transesterification of Jatropha Oil. Energy Fuels 2004, 18, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Prasad, R. Triglycerides-based diesel fuels. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2000, 4, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaobo, Y.; Yudong, H.; Jie, Z.; Hailin, C. Preparation and Properties of Phosphate Base Heat-resisting Composites. Chem. Adhes. 2005, 27, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Bao, J.; Guo, X. An investigation of hygrothermal effects on adhesive materials and double lap shear joints of CFRP composite laminates. Compos. B Eng. 2016, 91, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Formulation | Curing Promoter | Dosage (wt %) | Particle Size (μm) | Purity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | / | |||
| b | Nano-AlN | 15 | 1 | 99.5% |
| c | Nano-AlN | 10 | 1 | 99.5% |
| d | Nano-AlN | 5 | 1 | 99.5% |
| e | Nano-TiO2 | 5 | 1 | 99.5% |
| f | Nano-CuO | 5 | 1 | 99.5% |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, C.; Chen, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Qi, H.; Zhou, L. Effects of Nano-Aluminum Nitride on the Performance of an Ultrahigh-Temperature Inorganic Phosphate Adhesive Cured at Room Temperature. Materials 2017, 10, 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111266
Ma C, Chen H, Wang C, Zhang J, Qi H, Zhou L. Effects of Nano-Aluminum Nitride on the Performance of an Ultrahigh-Temperature Inorganic Phosphate Adhesive Cured at Room Temperature. Materials. 2017; 10(11):1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111266
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Chengkun, Hailong Chen, Chao Wang, Jifeng Zhang, Hui Qi, and Limin Zhou. 2017. "Effects of Nano-Aluminum Nitride on the Performance of an Ultrahigh-Temperature Inorganic Phosphate Adhesive Cured at Room Temperature" Materials 10, no. 11: 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111266
APA StyleMa, C., Chen, H., Wang, C., Zhang, J., Qi, H., & Zhou, L. (2017). Effects of Nano-Aluminum Nitride on the Performance of an Ultrahigh-Temperature Inorganic Phosphate Adhesive Cured at Room Temperature. Materials, 10(11), 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111266




