Effects of Texture and Grain Size on the Yield Strength of ZK61 Alloy Rods Processed by Cyclic Extrusion and Compression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The CEC processing is an efficient grain refinement way for the ZK61 alloy. Low temperature is more favorable for the grain refinement of ZK61 alloy than the increase of passes.
- (2)
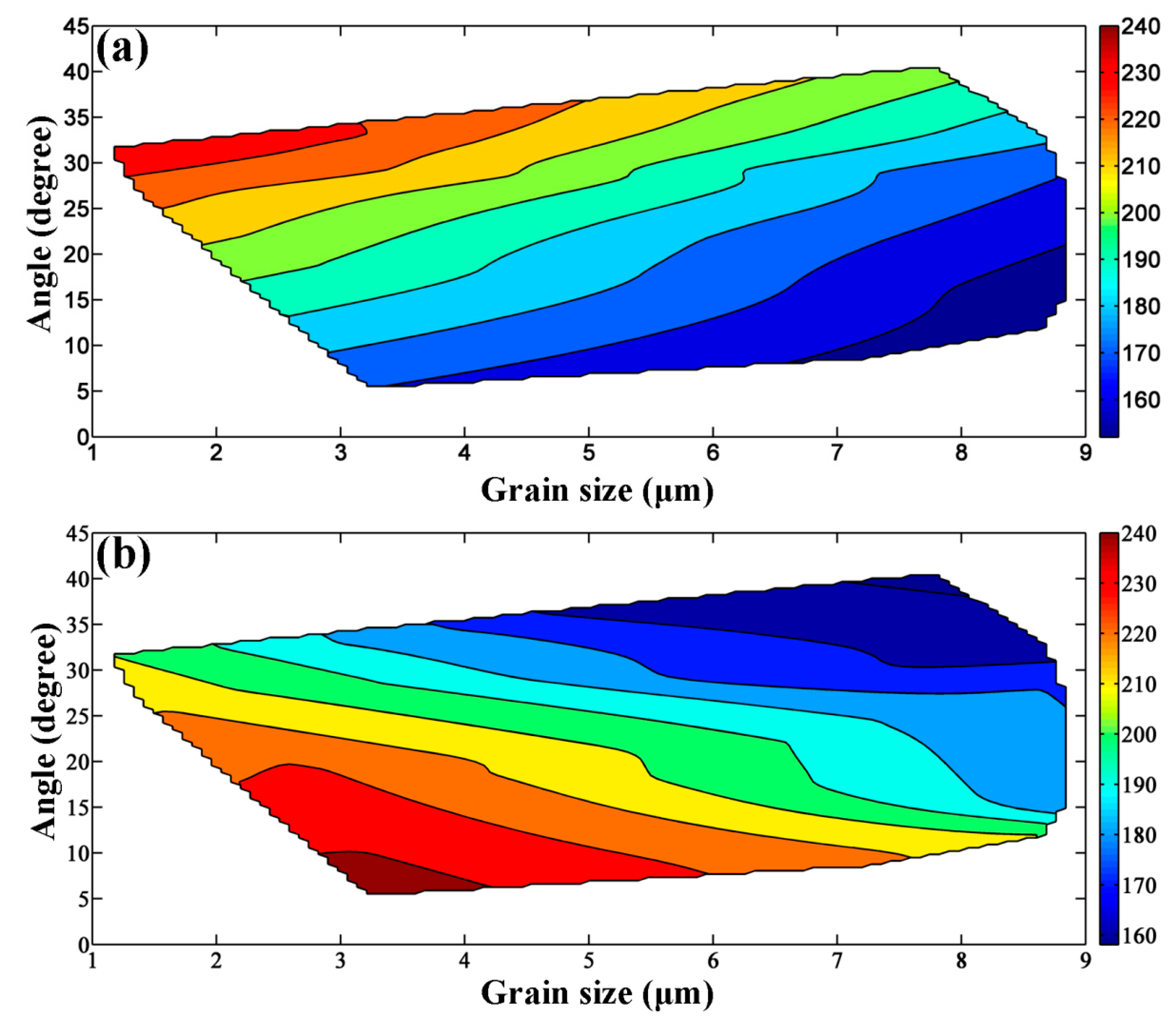
- The contour map of room-temperature tension & compression yield strength in ZK61 alloy rods as a function of grain size and the texture was constructed by means of quantifying the texture by the angle, θ, between the c-axes of the grains and the ED, which made it possible to distinguish the strengthening mechanism of texture and grain size on the tension & compression yield strength.
- (3)
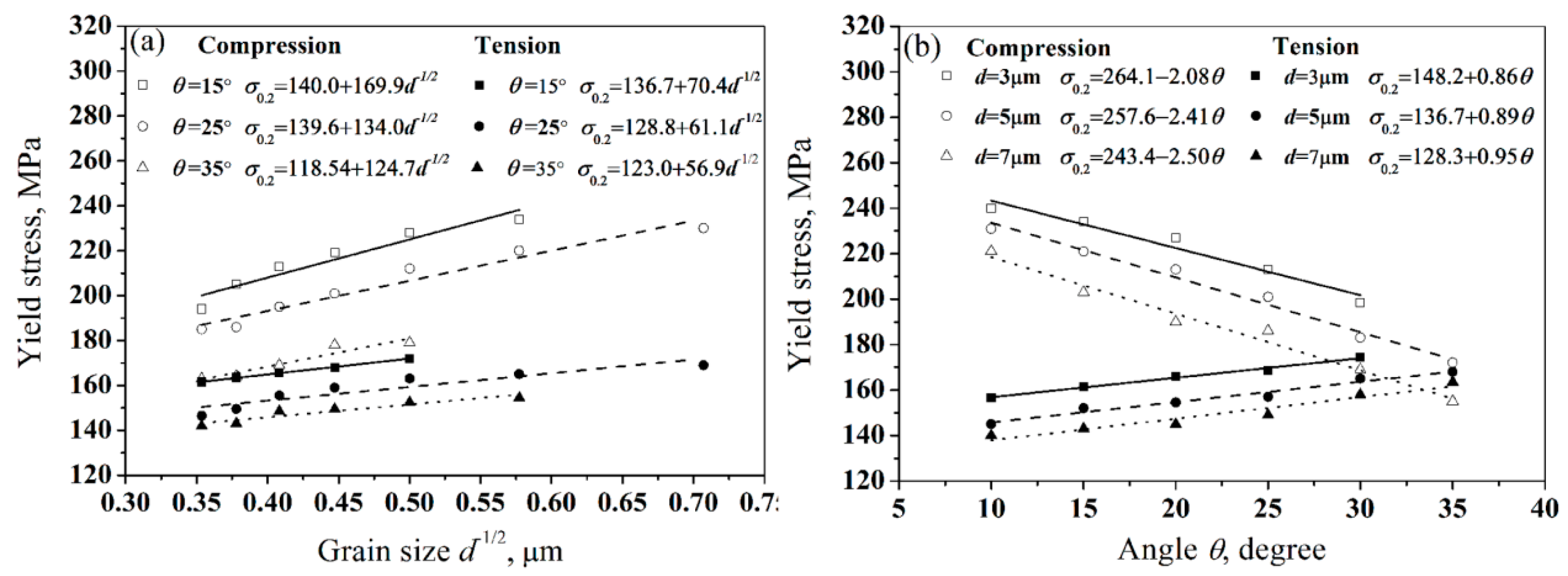
- The results shows that whether the tension yield strength or the compression yield strength of ZK61 alloy is fully consistent with the Hall-Petch relationship in certain texture, but the change trends of the tension yield strength and the compression yield strength are completely opposite with the increase of θ under the same grain size.
- (4)
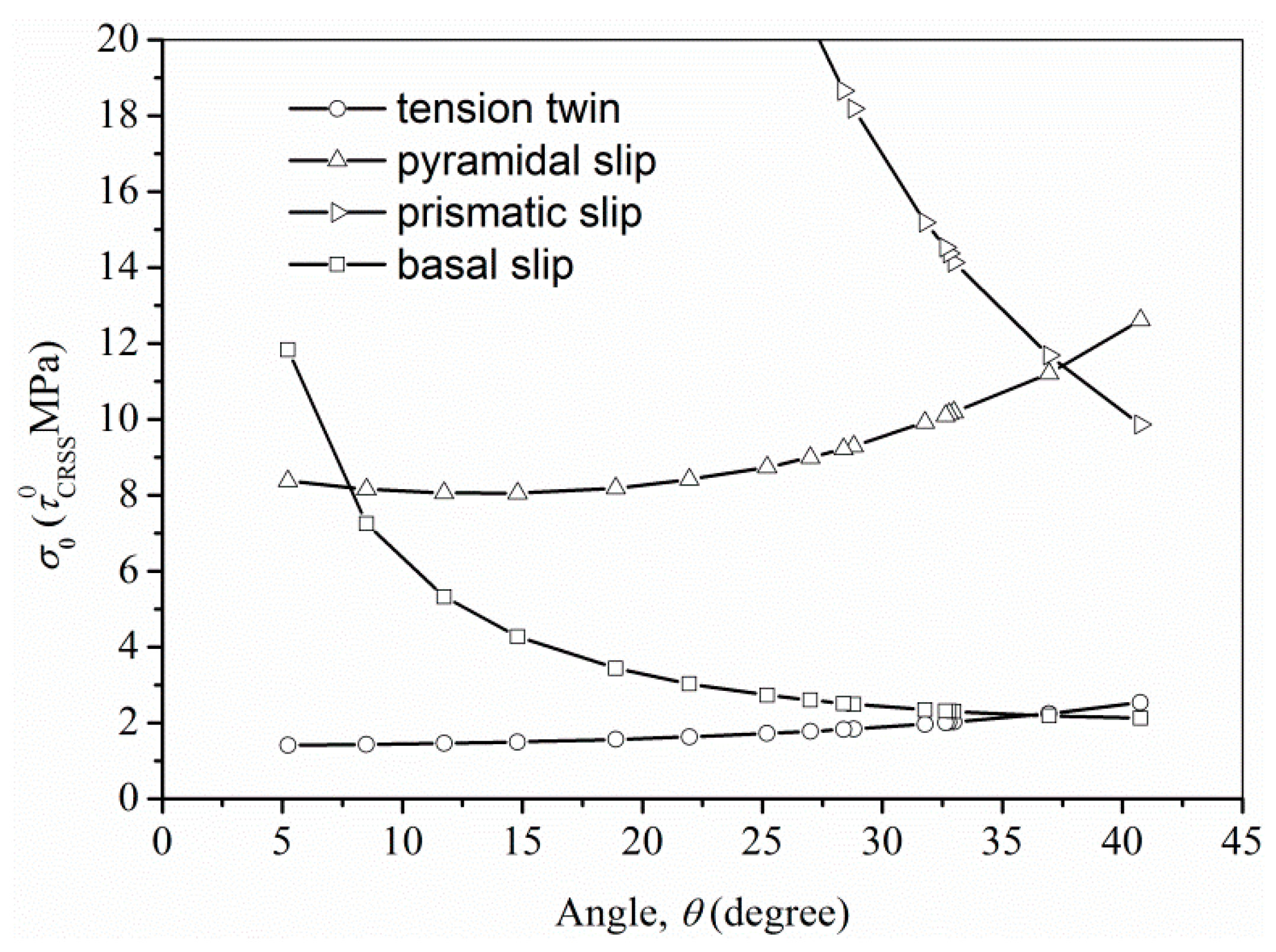
- The tension deformation of the CECed ZK61 alloy rods is determined by both the basal slip and the tension twinning at room temperature, while the compression deformation is determined only by the basal slip.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mostaed, E.; Fabrizi, A.; Dellasega, D.; Bonollo, F.; Vedani, M. Grain size and texture dependence on mechanical properties, asymmetric behavior and low temperature superplasticity of ZK60 Mg alloy. Mater. Charact. 2015, 107, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadadzadeh, A.; Wells, M.A.; Shaha, S.K.; Jahed, H.; Williams, B.W. Role of compression direction on recrystallization behavior and texture evolution during hot deformation of extruded ZK60 magnesium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 702, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostaed, E.; Hashempour, M.; Fabrizi, A.; Dellasega, D.; Bestetti, M. Microstructure, texture evolution, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of ECAP processed ZK60 magnesium alloy for biodegradable applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed Mate. 2014, 37, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.N.; Huang, J.C. Texture analysis in hexagonal materials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2003, 81, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.B.; Liu, T.M.; Zhang, Y.; Song, B.; Hou, D.; Pan, F.S. The yield asymmetry and precipitation behavior of pre-twinned ZK60 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 652, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.B.; Ren, W.J.; Wang, X.Y. Research on the tension-compression asymmetry of as-extruded ZK60 magnesium alloys at room temperature. Acta Metall. Sin. 2016, 52, 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.B.; Peng, L.M.; Wang, Q.D.; Hans, J.R.; Ding, W.J. Anisotropic plastic deformation behavior of as-extruded ZK60 magnesium alloy at room temperature. China Sci. 2009, 52, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Agnew, S.R.; Wu, P.D. Modeling twinning and detwinning behavior of Mg alloy ZK60A during monotonic and cyclic loading. Int. J. Plast. 2014, 65, 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Qiao, H.; An, K.; Guo, X.; Wu, P. Investigation of deformation dynamics in a wrought magnesium alloy. Int. J. Plast. 2014, 62, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richert, M.; Liu, Q.; Hansen, N. Microstructural evolution over a large strain range in aluminium deformed by cyclic-extrusion–compression. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 260, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Huang, H.; Yuan, G.Y.; Ding, W.J. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of quasicrystal-reinforced Mg-Zn-Gd alloy processed by cyclic extrusion and compression. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 626, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.D.; Liao, W.J.; Guo, W.; Ye, B.; Li, W.Z.; Jiang, H.Y.; Ding, W.J. Effects of cyclic extrusion and compression on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ91D magnesium composites reinforced by SiC nanoparticles. Mater. Charact. 2017, 126, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Yuan, G.Y.; Wang, Z.Z. Mechanical properties and biocorrosion resistance of Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy improved by cyclic extrusion and compression. Mater. Lett. 2012, 74, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.P.; Chen, T.; Jiang, W.Y.; Feng, Y.C.; Cao, G.J.; Zhu, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of AM60B magnesium alloy prepared by cyclic extrusion compression. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 3200–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.B.; Wang, Q.D.; Peng, L.M.; Roven, H.J. Microstructure and High Tensile Ductility of ZK60 Magnesium Alloy Processed by Cyclic Extrusion and Compression. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 476, 441–445. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.B.; Wang, Q.D.; Peng, L.M.; Peng, T. Effect of the cyclic extrusion and compression processing on microstructure and mechanical properties of As-Extruded ZK60 magnesium alloy. Mater. Trans. 2008, 49, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Wang, Q.D.; Roven, H.J.; Liu, M.P. Network-shaped fine-grained microstructure and high ductility of magnesium alloy fabricated by cyclic extrusion compression. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Tang, Z.B.; Tian, Y.; Jia, G.Z.; Niu, J.L.; Zhang, H.; Pei, J.; Yuan, G.Y.; Ding, W.J. Effects of cyclic extrusion and compression parameters on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-1.50Zn-0.25Gd alloy. Mater. Des. 2015, 869, 788–796. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.Z.; Wang, X.; Hu, L.X.; Wang, E.D. Fabrication of ZK60 magnesium alloy thin sheets with improved ductility by cold rolling and annealing treatment. Mater. Des. 2012, 40, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.C.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.N.; Chen, W.Z.; Wang, E.D. Mechanical anisotropy improvement in ultrafine-grained ZK61 magnesium alloy rods fabricated by cyclic extrusion and compression. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 600, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, A.; Barnett, M.R. Sensitivity of deformation twinning to grain size in titanium and magnesium. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 7824–7839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, J.; Poole, W.J.; Sinclair, C.W.; Gharghouri, M.A. Reducing the tension-compression yield asymmetry in a Mg–8Al–0.5Zn alloy via precipitation. Scr. Mater. 2010, 62, 301–304. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.W.; Liu, C.M.; Zhao, J.; Zeng, W.B.; Wang, Z.C. Modification of grain refinement and texture in AZ31 Mg alloy by a new plastic deformation method. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 628, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamilia, A.M.; Zarei-Hanzakia, A.; Abedia, H.R.; Minárikb, P.; Soltanic, R. The microstructure, texture, and room temperature mechanical properties of friction stir processed Mg-Y-Nd alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 690, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, D.F.; Yang, X.S.; Jiang, L.Y.; Pan, F.S. Microstructure and texture evolution of AZ31 magnesium alloy during large strain hot rolling. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Jung, J.G.; You, B.S.; Park, S.H. Microstructure and texture variation with Gd addition in extruded magnesium. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbenni, S.; Favier, V.; Berveiller, M. Impact of the grain size distribution on the yield stress of heterogeneous materials. Int. J. Plast. 2007, 23, 114–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Z.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, E.D.; Liu, Z.Y. Optimization of rolling temperature for ZK61 alloy sheets via microstructure uniformity analysis. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 575, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.D.; Lin, J.B.; Peng, L.M.; Chen, Y.J. Influence of cyclic extrusion and compression on the mechanical property of Mg alloy ZK60. Acta Metall. Sin. 2008, 44, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, E.D.; Liu, X.Y.; Hu, L.X. Texture dependence of uniform elongation for a magnesium alloy. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 858–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Choo, H. Influence of texture on Hall–Petch relationships in an Mg alloy. Acta Mater. 2014, 81, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raneet, M.R.; Keshavarz, Z.; Ma, X. A semianalytical sachs model for the flow stress of a magnesium alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 2283–2293. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, W.B.; Raneet, M.R. Effective values of critical resolved shear stress for slip in polycrystalline magnesium and other hcp metals. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromans, D. Elastic anisotropy of HCP metal crystals and polycrystals. Int. J. Res. Rev. Appl. Sci. 2011, 6, 464–483. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Godfrey, A.; Liu, W.; Liu, Q. Microtexture evolution via deformation twinning and slip during compression of magnesium alloy AZ31. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 483, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R.; Douthwaite, R.M.; Codd, I.; Petch, N.J. The plastic deformation of polycrystalline aggregates. Philos. Mag. 1962, 73, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

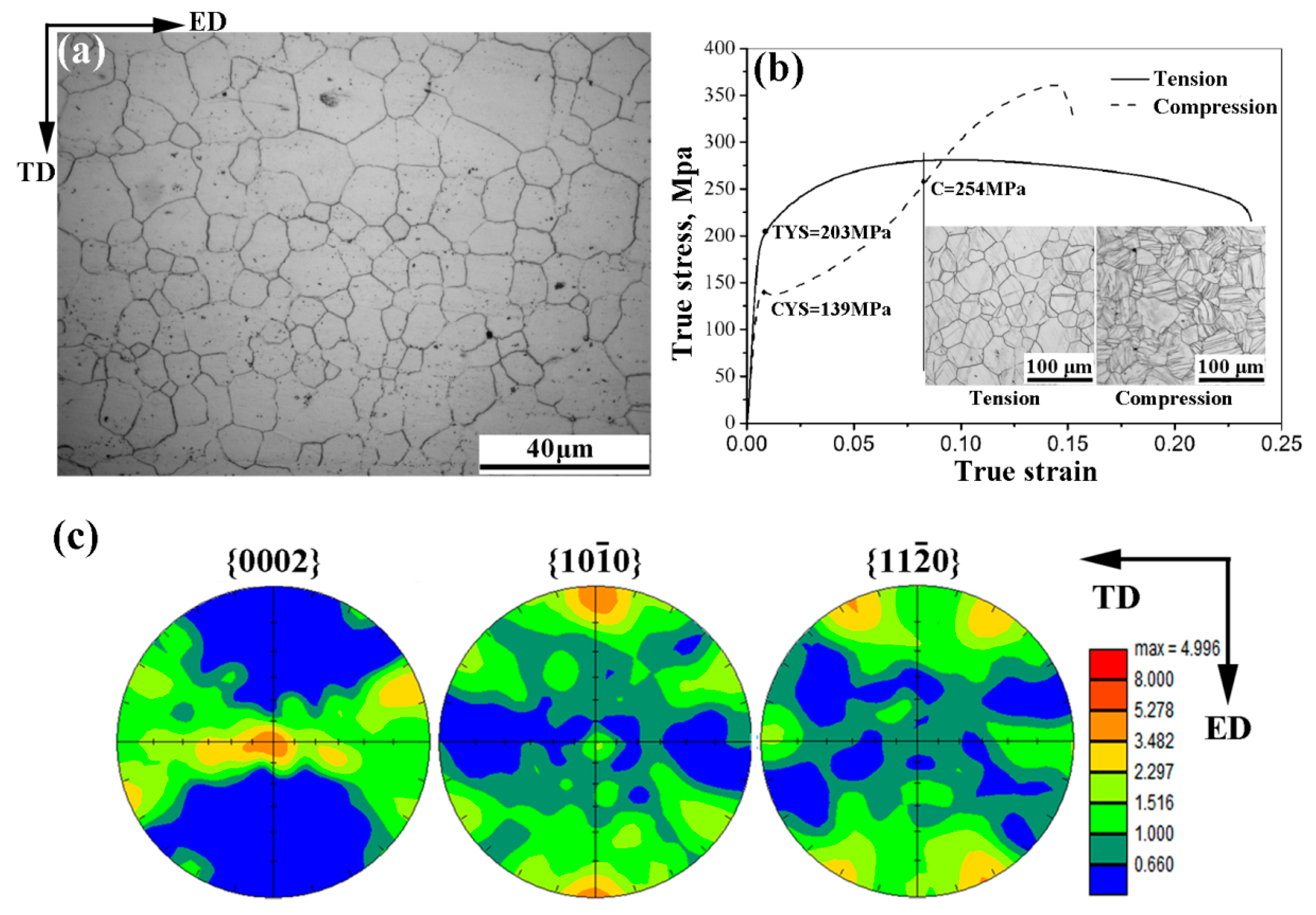

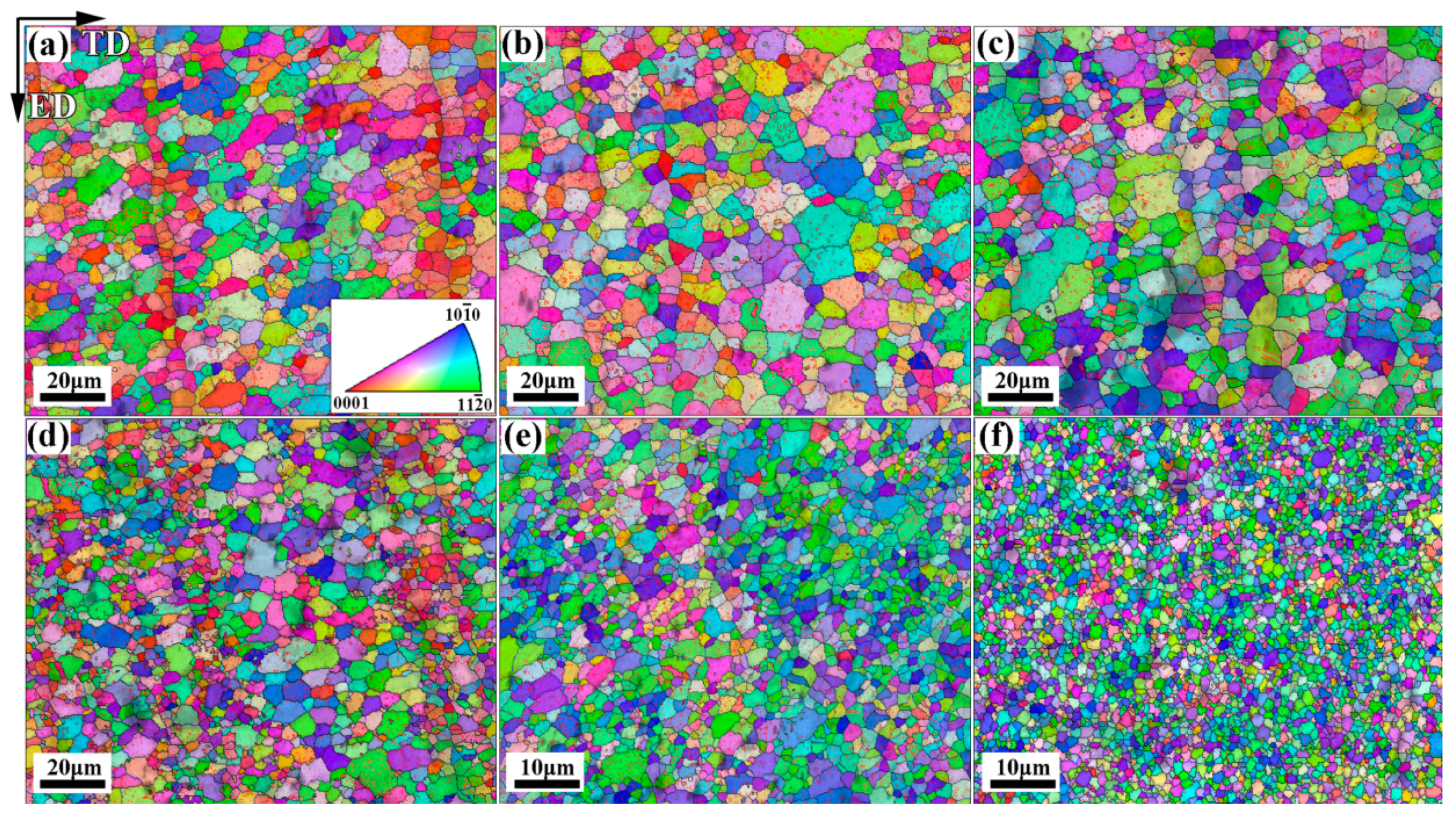
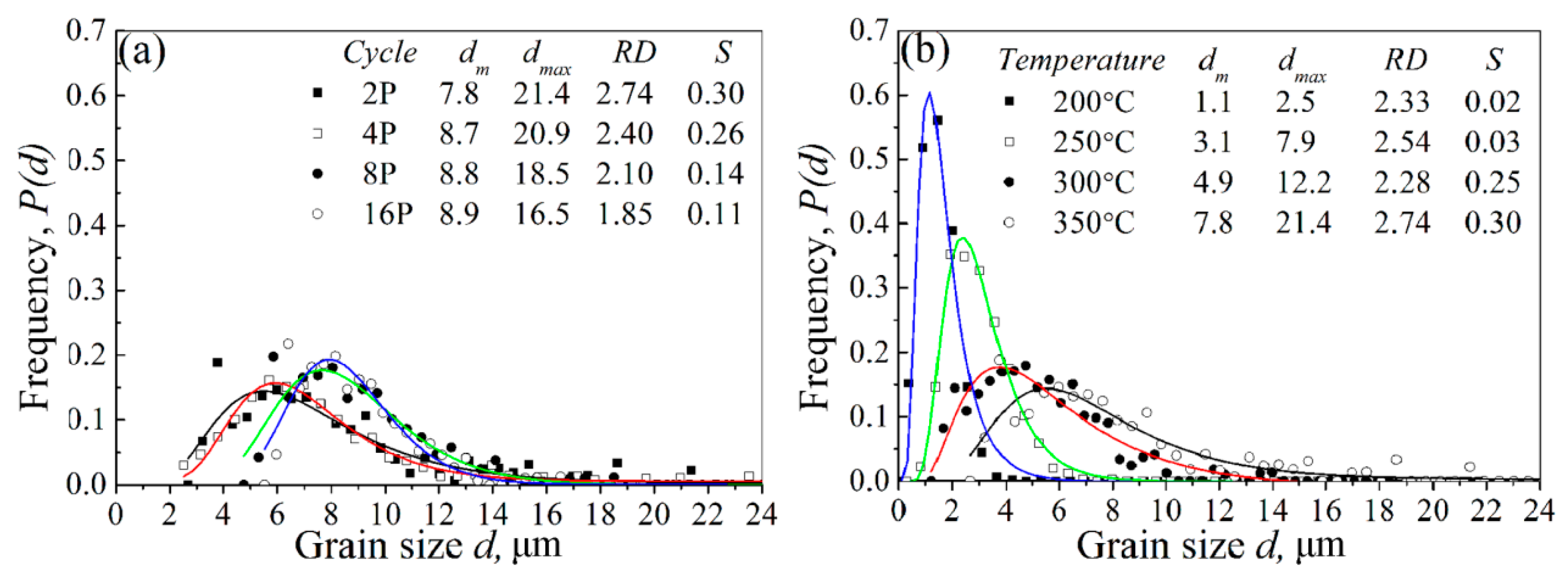


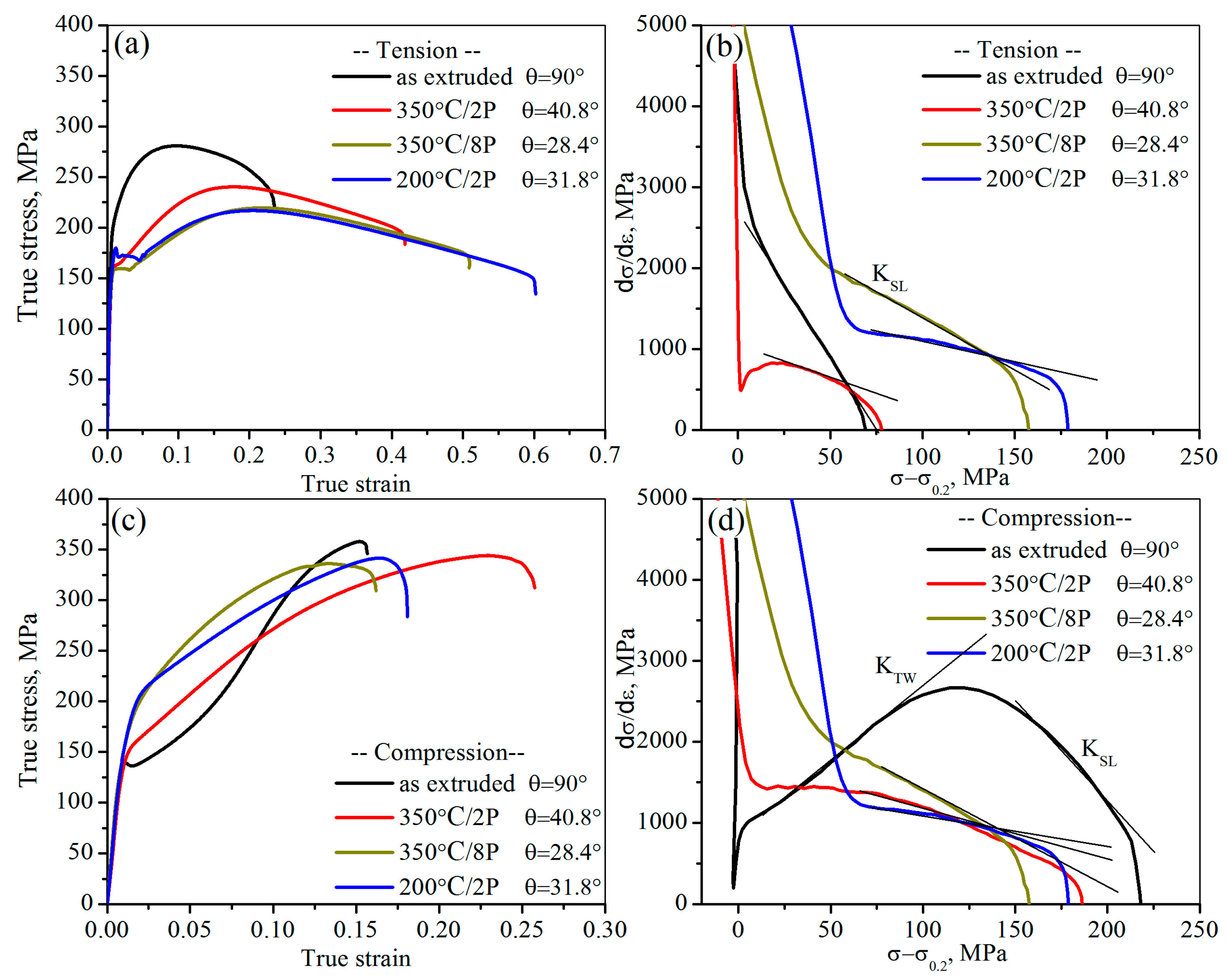
| Temperature (°C) | Extrusion Ratio | CEC Pass | Accumulated Equivalent Strain | Grain Size (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 350 | 2 | 2 | 2.77 | 7.81 |
| 4 | 5.55 | 8.73 | ||
| 8 | 11.09 | 8.84 | ||
| 16 | 22.18 | 8.85 | ||
| 300 | 2 | 2 | 2.77 | 4.89 |
| 4 | 5.55 | 6.79 | ||
| 8 | 11.09 | 7.62 | ||
| 16 | 22.18 | 8.68 | ||
| 250 | 2 | 2 | 2.77 | 3.0 |
| 4 | 5.55 | 3.87 | ||
| 8 | 11.09 | 6.51 | ||
| 16 | 22.18 | 7.29 | ||
| 200 | 2 | 2 | 2.77 | 1.1 |
| 4 | 5.55 | 1.3 | ||
| 8 | 11.09 | 2.7 | ||
| 16 | 22.18 | 3.2 |
| Temperature (°C) | Accumulated Strains | Grain Size (μm) | θ (°) | YS (MPa) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ten. | Com. | ||||
| 350 | 2.77 | 7.81 | 40.75 | 162.5 ± 2.1 | 157.8 ± 3.1 |
| 5.55 | 8.73 | 32.63 | 160.5 ± 1.9 | 164.2 ± 4.3 | |
| 11.09 | 8.84 | 28.38 | 150.9 ± 4.3 | 178.9 ± 2.8 | |
| 22.18 | 8.85 | 14.8 | 135.9 ± 3.1 | 185.1 ± 3.6 | |
| 300 | 2.77 | 4.89 | 36.94 | 165.5 ± 2.4 | 165.9 ± 2.1 |
| 5.55 | 6.79 | 32.77 | 160.0 ± 2.1 | 170.6 ± 2.8 | |
| 11.09 | 7.62 | 25.19 | 146.8 ± 4.1 | 186.6 ± 4.2 | |
| 22.18 | 8.68 | 11.74 | 135.5 ± 2.7 | 211.8 ± 5.1 | |
| 250 | 2.77 | 3.0 | 32.98 | 178.8 ± 3.3 | 189.7 ± 3.5 |
| 5.55 | 3.87 | 28.81 | 168.7 ± 2.6 | 195.5 ± 2.2 | |
| 11.09 | 6.51 | 21.96 | 147.9 ± 1.5 | 200.9 ± 4.1 | |
| 22.18 | 7.29 | 8.5 | 143.8 ± 2.1 | 222.8 ± 5.0 | |
| 200 | 2.77 | 1.1 | 31.78 | 185.7 ± 2.4 | 210.0 ± 2.6 |
| 5.55 | 1.3 | 27.0 | 180.8 ± 2.2 | 217.4 ± 3.2 | |
| 11.09 | 2.7 | 18.89 | 165.5 ± 5.1 | 231.7 ± 2.1 | |
| 22.18 | 3.2 | 5.23 | 150.6 ± 4.8 | 246.1 ± 2.7 | |
| Angle, θ (°) | Basal Slip {0001}<11-20> | Prismatic Slip {10-10}<11-20> | Pyramid Slip {10-12}<11-20> | Extension Twin {10-12}<10-11> | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ten. | Com. | ||||
| 40.75 | 0.4717 | 0.2029 | 0.3172 | 0.2763 | 0 |
| 36.94 | 0.4577 | 0.1712 | 0.3571 | 0.3121 | 0 |
| 32.98 | 0.4352 | 0.1415 | 0.3927 | 0.3464 | 0 |
| 32.77 | 0.4338 | 0.1392 | 0.3944 | 0.3481 | 0 |
| 32.63 | 0.4324 | 0.1377 | 0.3962 | 0.3498 | 0 |
| 31.78 | 0.4266 | 0.1317 | 0.4034 | 0.3565 | 0 |
| 28.81 | 0.4019 | 0.11 | 0.4305 | 0.3808 | 0 |
| 28.38 | 0.3983 | 0.1072 | 0.4339 | 0.3839 | 0 |
| 27.0 | 0.385 | 0.0977 | 0.445 | 0.3945 | 0 |
| 25.19 | 0.3665 | 0.0858 | 0.4579 | 0.407 | 0 |
| 21.96 | 0.3302 | 0.0658 | 0.4754 | 0.4292 | 0 |
| 18.89 | 0.2911 | 0.0495 | 0.4889 | 0.4477 | 0 |
| 14.8 | 0.2342 | 0.0307 | 0.4969 | 0.4681 | 0 |
| 11.74 | 0.1879 | 0.0193 | 0.4966 | 0.4803 | 0 |
| 8.5 | 0.1379 | 0.0102 | 0.4903 | 0.4898 | 0 |
| 5.23 | 0.0845 | 0.0038 | 0.4778 | 0.497 | 0 |
| Angle, θ (°) | Calculated Friction Stress, σ0 () | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basal Slip {0001}<11-20> | Prismatic Slip {10-10}<11-20> | Pyramid Slip {10-12}<11-20> | Extension Twin {10-12}<10-11> | ||
| Ten. | Com. | ||||
| 40.75 | 2.11999 | 9.85707 | 12.61034 | 2.53348 | 0 |
| 36.94 | 2.18484 | 11.68224 | 11.20134 | 2.24287 | 0 |
| 32.98 | 2.29779 | 14.13428 | 10.18589 | 2.02079 | 0 |
| 32.77 | 2.30521 | 14.36782 | 10.14199 | 2.01092 | 0 |
| 32.63 | 2.31267 | 14.52433 | 10.09591 | 2.00114 | 0 |
| 31.78 | 2.34412 | 15.18603 | 9.91572 | 1.96353 | 0 |
| 28.81 | 2.48818 | 18.18182 | 9.29152 | 1.83824 | 0 |
| 28.38 | 2.51067 | 18.65672 | 9.21871 | 1.82339 | 0 |
| 27.0 | 2.5974 | 20.47083 | 8.98876 | 1.7744 | 0 |
| 25.19 | 2.72851 | 23.31002 | 8.73553 | 1.7199 | 0 |
| 21.96 | 3.02847 | 30.39514 | 8.41397 | 1.63094 | 0 |
| 18.89 | 3.43525 | 40.40404 | 8.18163 | 1.56355 | 0 |
| 14.8 | 4.26985 | 65.14658 | 8.04991 | 1.49541 | 0 |
| 11.74 | 5.32198 | 103.62694 | 8.05477 | 1.45742 | 0 |
| 8.5 | 7.25163 | 196.07843 | 8.15827 | 1.42915 | 0 |
| 5.23 | 11.83432 | 526.31579 | 8.3717 | 1.40845 | 0 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Cao, B.; Chen, W.; Duan, J.; Cui, G. Effects of Texture and Grain Size on the Yield Strength of ZK61 Alloy Rods Processed by Cyclic Extrusion and Compression. Materials 2017, 10, 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111234
Zhang L, Zhang W, Cao B, Chen W, Duan J, Cui G. Effects of Texture and Grain Size on the Yield Strength of ZK61 Alloy Rods Processed by Cyclic Extrusion and Compression. Materials. 2017; 10(11):1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111234
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lixin, Wencong Zhang, Biao Cao, Wenzhen Chen, Junpeng Duan, and Guorong Cui. 2017. "Effects of Texture and Grain Size on the Yield Strength of ZK61 Alloy Rods Processed by Cyclic Extrusion and Compression" Materials 10, no. 11: 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111234
APA StyleZhang, L., Zhang, W., Cao, B., Chen, W., Duan, J., & Cui, G. (2017). Effects of Texture and Grain Size on the Yield Strength of ZK61 Alloy Rods Processed by Cyclic Extrusion and Compression. Materials, 10(11), 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111234




