A Rapid One-Step Process for Fabrication of Biomimetic Superhydrophobic Surfaces by Pulse Electrodeposition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Pulse Electrodeposition
2.3. Sample Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Surface Morphology
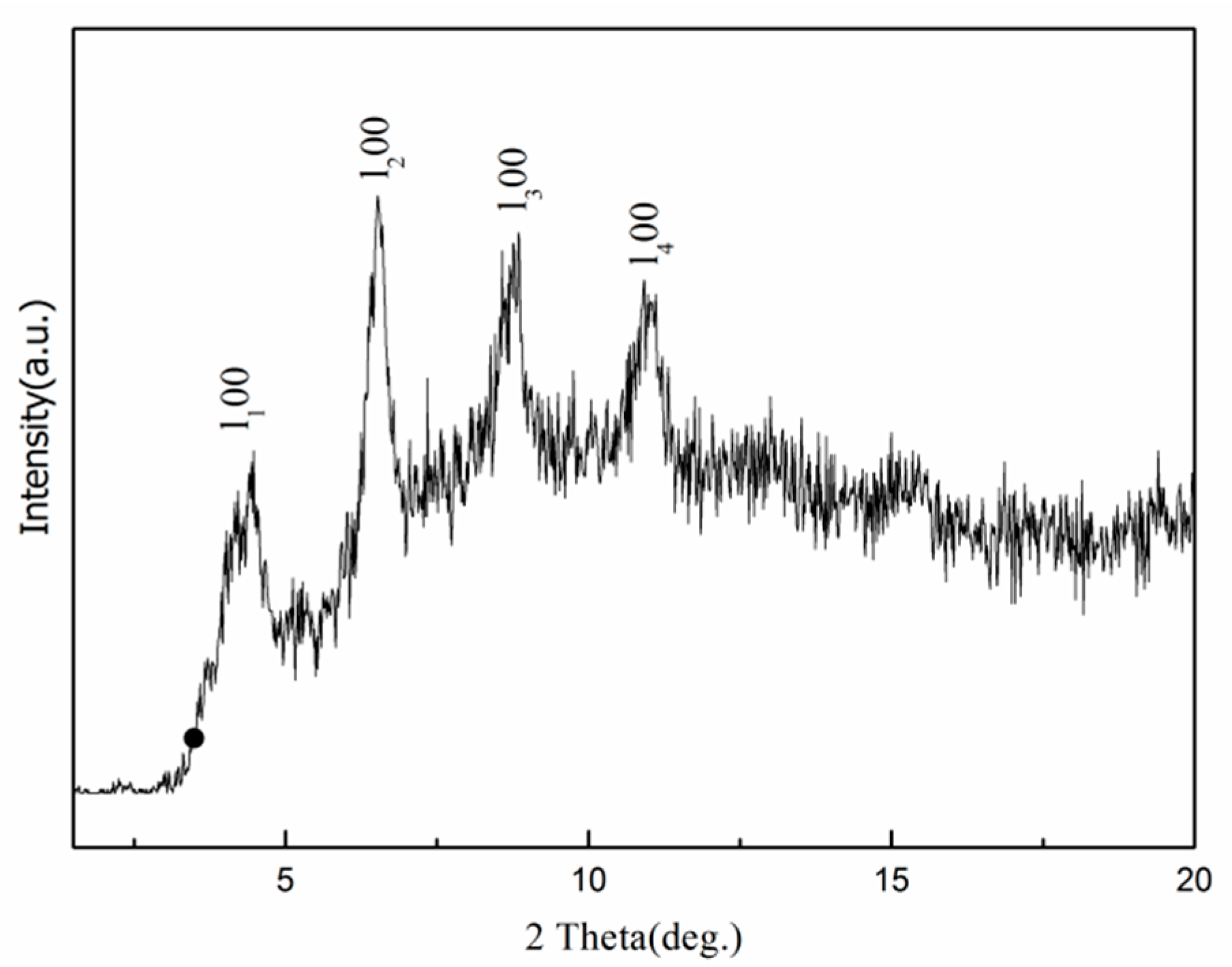
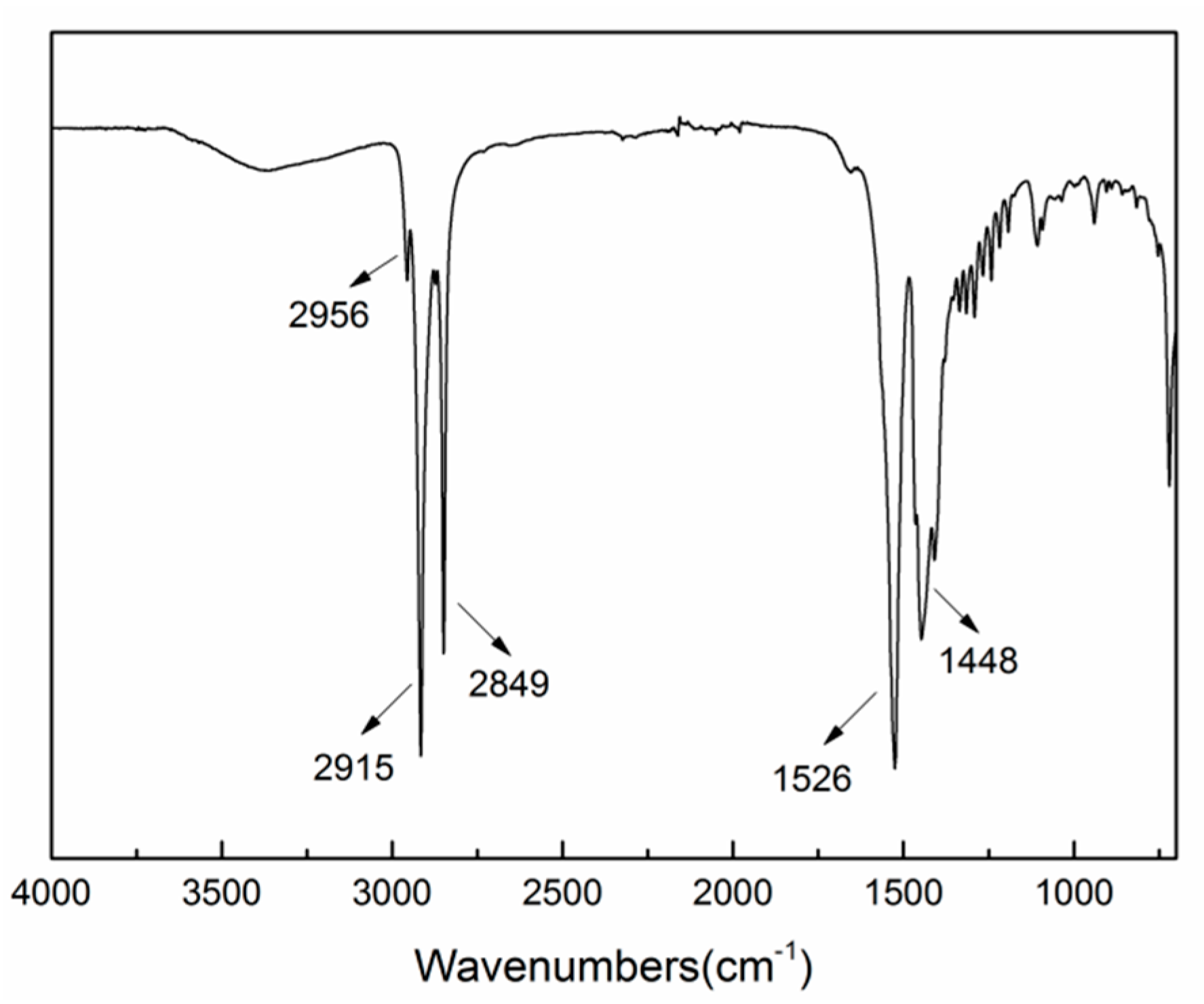
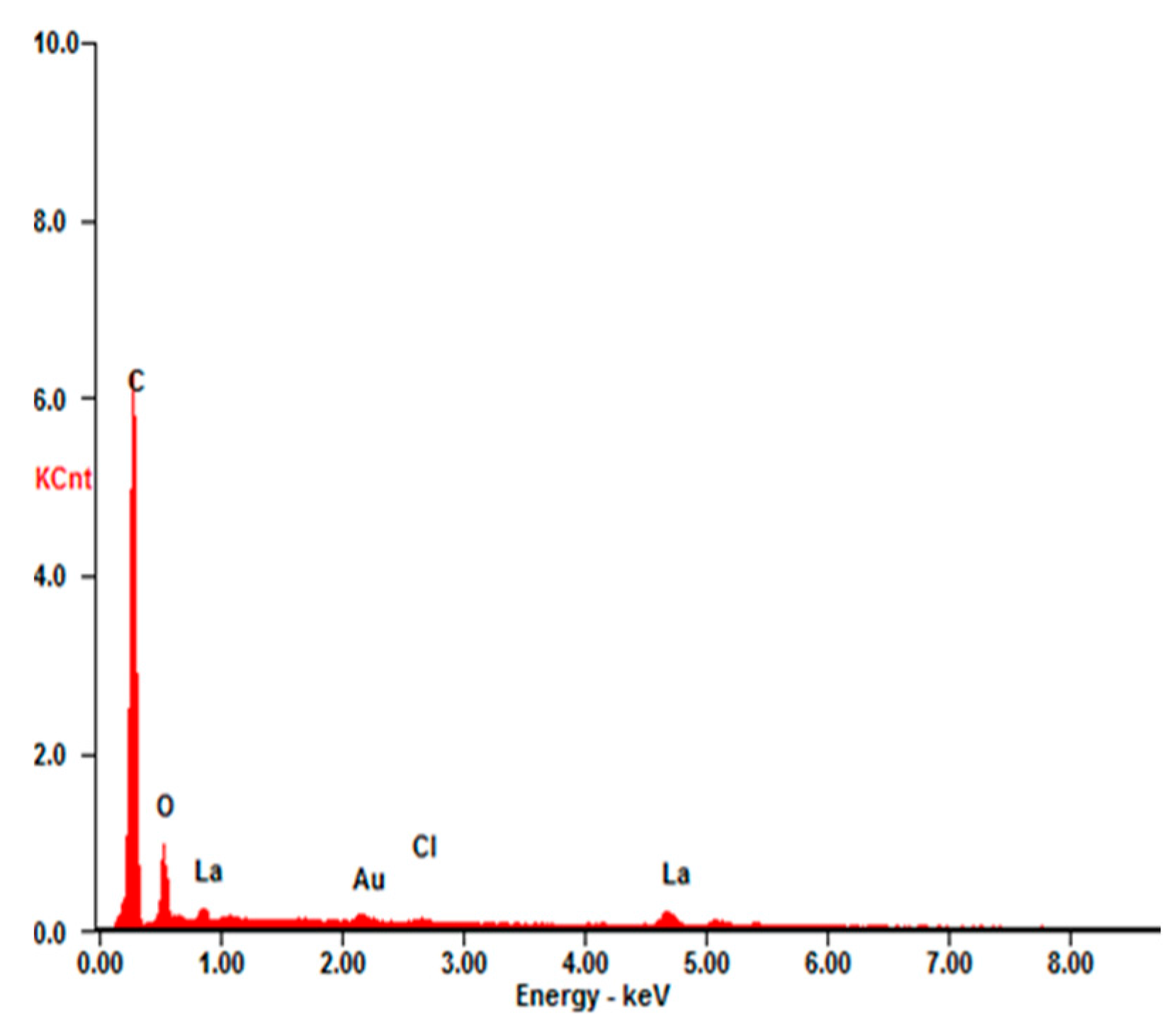
3.2. Phase and Chemical Composition
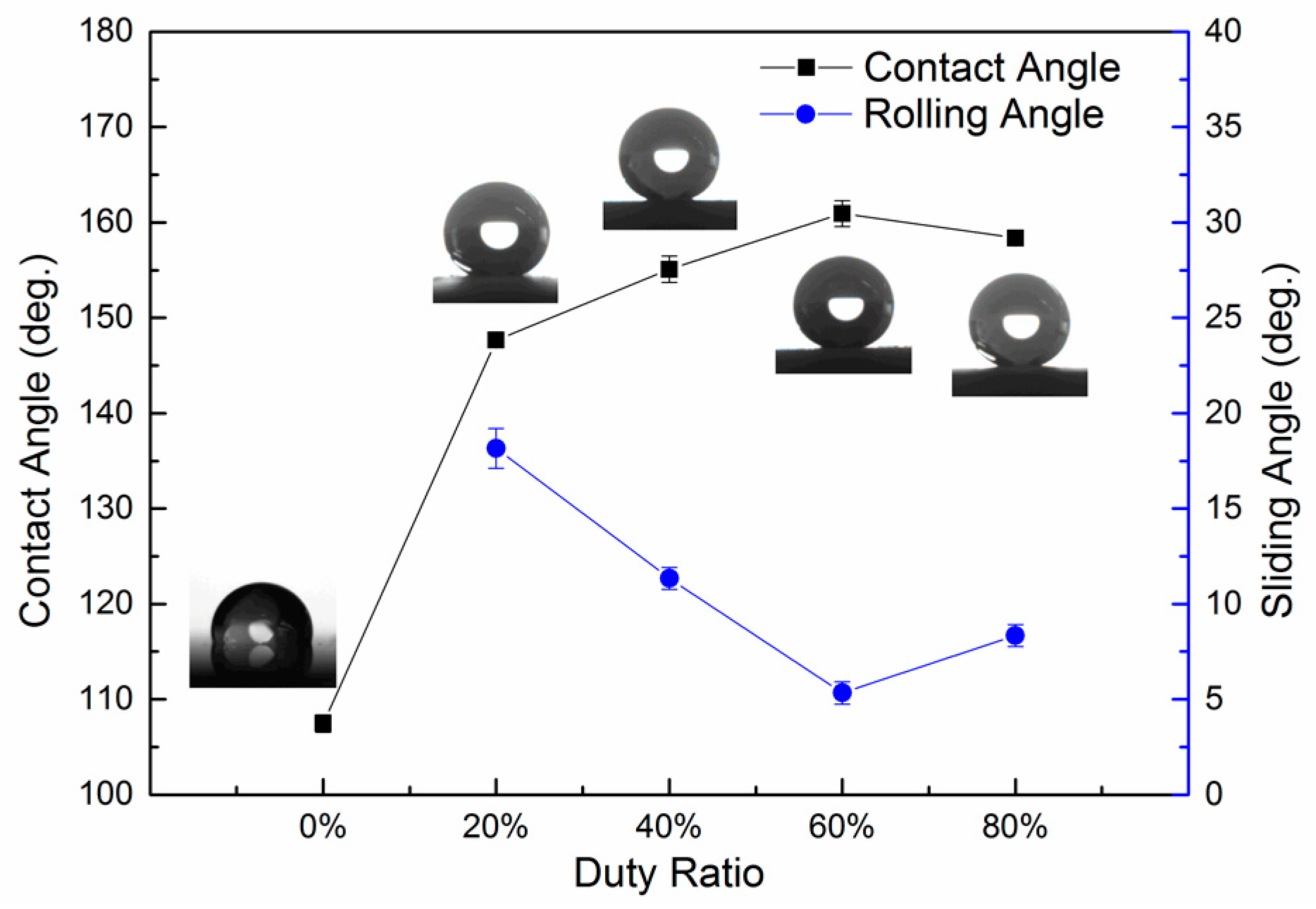
3.3. Surface Wettability
4. Discussion
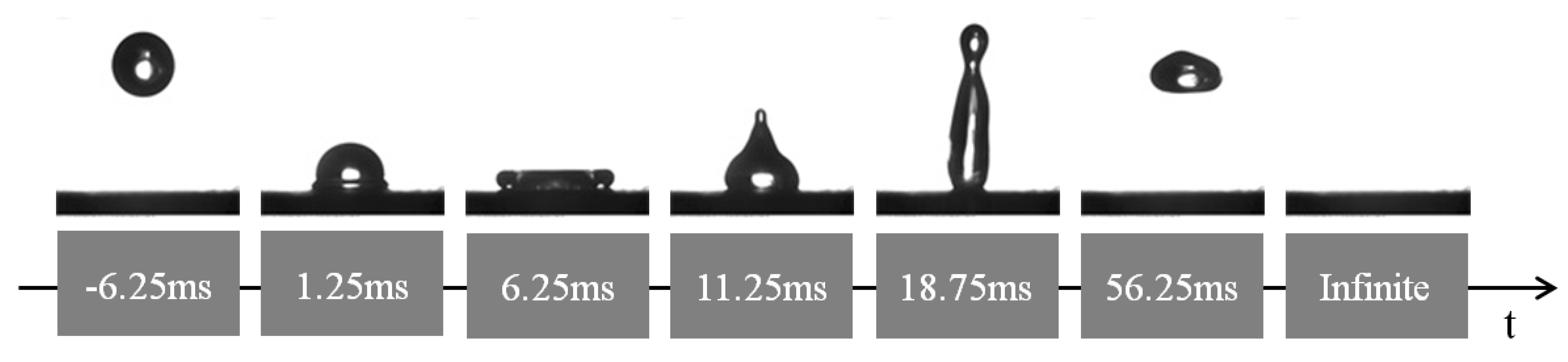
4.1. The Superhydrophobicity of the Pulse Electrodeposited Surfaces
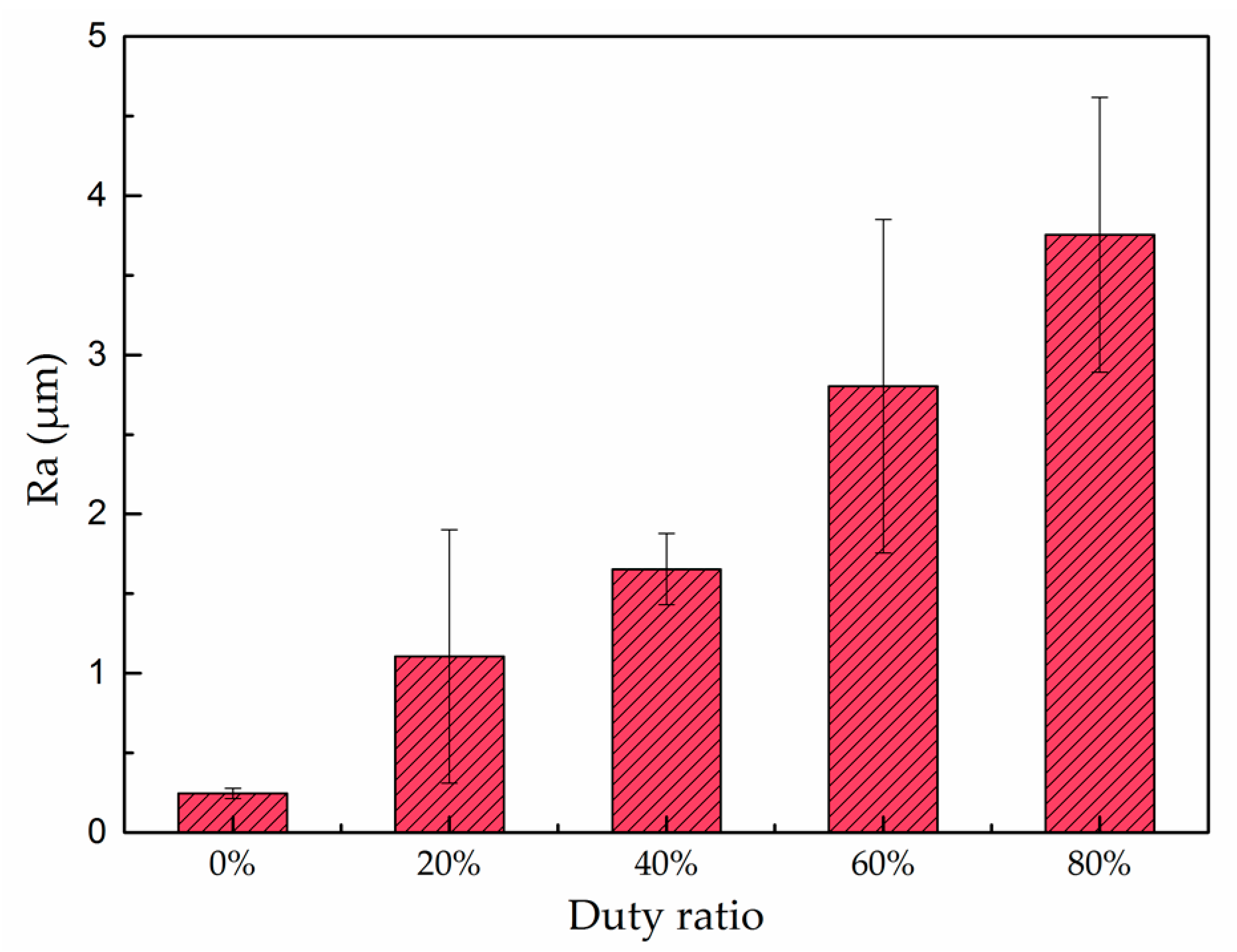
4.2. Effect of Pulse Current Duty Ratio on Surface Morphology
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, Y.Y.; Gao, N.; Barthlott, W. Mimicking natural superhydrophobic surfaces and grasping the wetting process: A review on recent progress in preparing superhydrophobic surfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 169, 80–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malshe, A.; Rajurkar, K.; Samant, A.; Hansen, H.N.; Bapat, S.; Jiang, W. Bio-inspired functional surfaces for advanced applications. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 62, 607–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liang, W.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Shi, L.; Guo, Z. Conductive and transparent superhydrophobic films on various substrates by in situ deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 203703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Lazo, M.A.; Katrantzis, I.; Dalle Vacche, S.; Karasu, F.; Leterrier, Y. A facile in situ and uv printing process for bioinspired self-cleaning surfaces. Materials 2016, 9, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Xiong, D.; Lu, Y.; Pan, S.; Wang, K.; Deng, Y.; Shi, Y. Design and fabrication of the lyophobic slippery surface and its application in anti-icing. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 11054–11059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boreyko, J.B.; Srijanto, B.R.; Nguyen, T.D.; Vega, C.; Fuentes-Cabrera, M.; Collier, C.P. Dynamic defrosting on nanostructured superhydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2013, 29, 9516–9524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulinich, S.; Farzaneh, M. Ice adhesion on super-hydrophobic surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 8153–8157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Han, Z.; Ren, L. Corrosion inhibition of biomimetic super-hydrophobic electrodeposition coatings on copper substrate. Corros. Sci. 2015, 94, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, Q.; Gao, R.; Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Liu, L. One-step method for the fabrication of superhydrophobic surface on magnesium alloy and its corrosion protection, antifouling performance. Corros. Sci. 2014, 80, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Huang, L.; Zhang, D.; Du, C.; Yu, G.; Chen, M.; Chowwanonthapunya, T. Preparation of superhydrophobic film on Ti substrate and its anticorrosion property. Materials 2017, 10, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Loughlin, T.E.; Martens, S.; Ren, S.R.; McKay, P.; Banerjee, S. Orthogonal wettability of hierarchically textured metal meshes as a means of separating water/oil emulsions. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19, 1600808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Super-hydrophobic surfaces: From natural to artificial. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 1997, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, N.; Xia, F.; Jiang, L. Petal effect: A superhydrophobic state with high adhesive force. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2008, 24, 4114–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, Y. Biomimetic fabrication and characterization of an artificial rice leaf surface with anisotropic wetting. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 2631–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, J.N.; Wu, S.Z.; Chen, Q.D.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, H.; Sun, H.B.; Jiang, L. Three-level biomimetic rice-leaf surfaces with controllable anisotropic sliding. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 2927–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Kong, X.; Wu, D. Micronanostructures of the scales on a mosquito’s legs and their role in weight support. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 76, 017301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Men, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, X. Superoleophobic textured aluminum surfaces. New J. Chem. 2011, 35, 2422–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhong, L.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Guo, X. Super-hydrophobic surface on pure magnesium substrate by wet chemical method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 3837–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleema, N.; Sarkar, D.K.; Gallant, D.; Paynter, R.W.; Chen, X. Chemical nature of superhydrophobic aluminium alloy surfaces produced via a one-step process using fluoroalkyl-silane in a base medium. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 4775–4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La, D.-D.; Nguyen, T.A.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, Y.S. A stable superhydrophobic and superoleophilic cu mesh based on copper hydroxide nanoneedle arrays. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 5705–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.-L.; Xu, W.-J.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Sun, J. Electrochemical machining of super-hydrophobic Al surfaces and effect of processing parameters on wettability. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 108, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Lu, Y.; Huang, S.; Liu, X.; Wu, L.; Xu, W. A simple immersion approach for fabricating superhydrophobic mg alloy surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 266, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, R.; Bharathidasan, T.; Basu, B.J. Superhydrophobic sol–gel nanocomposite coatings with enhanced hardness. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 10421–10426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Li, H.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y. Formation process of a strong water-repellent alumina surface by the sol–gel method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 3191–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.; Kunz, C.; Gräf, S. Bio-inspired functional surfaces based on laser-induced periodic surface structures. Materials 2016, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadeeva, E.; Truong, V.K.; Stiesch, M.; Chichkov, B.N.; Crawford, R.J.; Wang, J.; Ivanova, E.P. Bacterial retention on superhydrophobic titanium surfaces fabricated by femtosecond laser ablation. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2011, 27, 3012–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishizaki, T.; Hieda, J.; Saito, N.; Saito, N.; Takai, O. Corrosion resistance and chemical stability of super-hydrophobic film deposited on magnesium alloy az31 by microwave plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 7094–7101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grignard, B.; Vaillant, A.; de Coninck, J.; Piens, M.; Jonas, A.M.; Detrembleur, C.; Jerome, C. Electrospinning of a functional perfluorinated block copolymer as a powerful route for imparting superhydrophobicity and corrosion resistance to aluminum substrates. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2010, 27, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Sathasivam, S.; Song, J.; Crick, C.R.; Carmalt, C.J.; Parkin, I.P. Robust self-cleaning surfaces that function when exposed to either air or oil. Science 2015, 347, 1132–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.X.; Chen, Y.X.; Guo, Z.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, D.P.; Huang, X.J. Bioinspired multifunctional hetero-hierarchical micro/nanostructure tetragonal array with self-cleaning, anticorrosion, and concentrators for the sers detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10633–10642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Law, K.Y.; Sambhy, V. Fabrication, surface properties, and origin of superoleophobicity for a model textured surface. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2011, 27, 5927–5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Guo, L.; Jia, D.; Ouyang, J.; Zhou, Y. The fabrication and hydrophobic property of micro-nano patterned surface on magnesium alloy using combined sparking sculpture and etching route. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 389, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Han, Z.; Ren, L. Fabrication of biomimetic superhydrophobic surface with controlled adhesion by electrodeposition. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 248, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Hao, L.; Chen, C. A fast electrodeposition method for fabrication of lanthanum superhydrophobic surface with hierarchical micro-nanostructures. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 401, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, D.; Wang, D.; Liu, K.; Chen, L. Preparation of stable superhydrophobic film on stainless steel substrate by a combined approach using electrodeposition and fluorinated modification. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 293, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, J.; Palumbo, G.; Erb, U. Recent advances in superhydrophobic electrodeposits. Materials 2016, 9, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivasakthi, P.; Bapu, G.R.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Sreejakumari, S. Synthesis of a super-hydrophobic ni–ito nanocomposite with pine-cone and spherical shaped micro-nanoarchitectures by pulse electrodeposition and its electrocatalytic application. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 44766–44773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmanin, T.; de Givenchy, E.T.; Amigoni, S.; Guittard, F. Superhydrophobic surfaces by electrochemical processes. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1378–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darmanin, T.; Guittard, F. Superhydrophobic fiber mats by electrodeposition of fluorinated poly (3,4-ethyleneoxythiathiophene). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15627–15634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landolt, D.; Marlot, A. Microstructure and composition of pulse-plated metals and alloys. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 169, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagotto, S.O.; de Alvarenga Freire, C.M.; Ballester, M. Zn–ni alloy deposits obtained by continuous and pulsed electrodeposition processes. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 122, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, R.; Toguri, J.; El-Sherik, A.; Erb, U. Mass transfer and electrocrystallization analyses of nanocrystalline nickel production by pulse plating. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1995, 25, 384–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollia, C.; Spyrellis, N.; Amblard, J.; Froment, M.; Maurin, G. Nickel plating by pulse electrolysis: Textural and microstructural modifications due to adsorption/desorption phenomena. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1990, 20, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.A.; Suter, U.W. Surface treatment of calcite with fatty acids: Structure and properties of the organic monolayer. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 4408–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, F. Coming to an unsticky end. Nature 1994, 368, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Drelich, J. Guidelines to measurements of reproducible contact angles using a sessile-drop technique. Surf. Innov. 2013, 1, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmur, A.; Della Volpe, C.; Siboni, S.; Amirfazli, A.; Drelich, J.W. Contact angles and wettability: Towards common and accurate terminology. Surf. Innov. 2017, 5, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Mammen, L.; Butt, H.J.; Vollmer, D. Candle soot as a template for a transparent robust superamphiphobic coating. Science 2012, 335, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, J.C.; Dhiman, R.; Kwon, H.-M.; Varanasi, K.K. Reducing the contact time of a bouncing drop. Nature 2013, 503, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassie, A.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
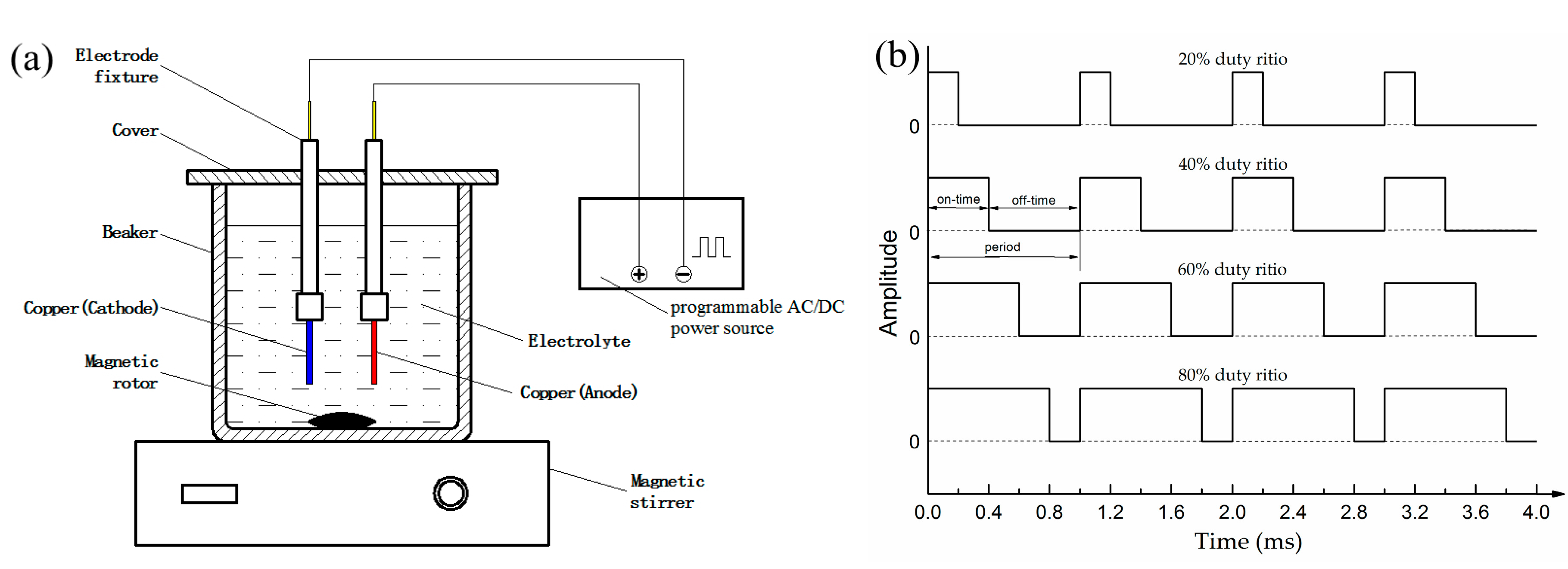

| Electrolytic Composition | Value | Electrical Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| LaCl3·6H2O (M) | 0.04 | Voltage (V) | 30 |
| CH3(CH2)12COOH (M) | 0.1 | Frequency (Hz) | 1000 |
| C2H5OH (mL) | 150 | Duty ratio | 20%, 40%, 60%, 80% |
| Element | Wt % | At % |
|---|---|---|
| C-K | 63.73 | 84.16 |
| O-K | 12.74 | 12.62 |
| Cl-K | 1.61 | 0.72 |
| La-L | 21.92 | 2.50 |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Guo, Z.; Liu, G.; Gyimah, G.K.; Li, X.; Dong, H. A Rapid One-Step Process for Fabrication of Biomimetic Superhydrophobic Surfaces by Pulse Electrodeposition. Materials 2017, 10, 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111229
Jiang S, Guo Z, Liu G, Gyimah GK, Li X, Dong H. A Rapid One-Step Process for Fabrication of Biomimetic Superhydrophobic Surfaces by Pulse Electrodeposition. Materials. 2017; 10(11):1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111229
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Shuzhen, Zhongning Guo, Guixian Liu, Glenn Kwabena Gyimah, Xiaoying Li, and Hanshan Dong. 2017. "A Rapid One-Step Process for Fabrication of Biomimetic Superhydrophobic Surfaces by Pulse Electrodeposition" Materials 10, no. 11: 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111229
APA StyleJiang, S., Guo, Z., Liu, G., Gyimah, G. K., Li, X., & Dong, H. (2017). A Rapid One-Step Process for Fabrication of Biomimetic Superhydrophobic Surfaces by Pulse Electrodeposition. Materials, 10(11), 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111229





