Mapping Hydrogen Research Frontiers: A Multi-Query Bibliometric Analysis of Electrochemical and Biotechnological Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Data Collection Strategy
2.2. Data Processing and Keyword Normalization
2.3. Justification of Keyword Coupling
3. Results and Discussion
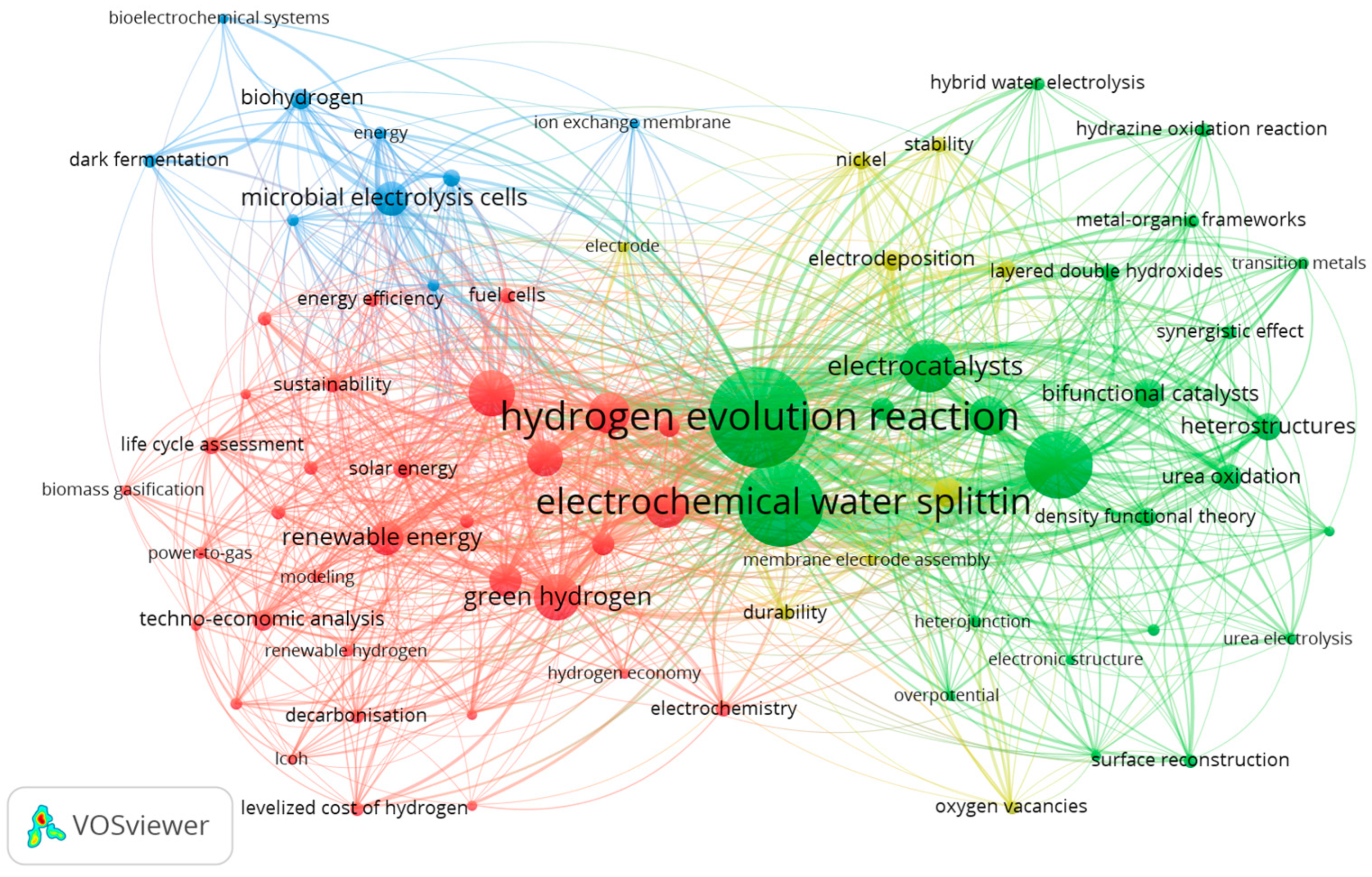
3.1. Keyword Co-Occurrence Analysis
3.1.1. Red Cluster: Hydrogen Technologies and Electrolyzer Typologies
3.1.2. Green Cluster: Electrochemical Reactions and Catalyst Development
3.1.3. Yellow Cluster: Material Stability and Electrode Engineering
3.1.4. Blue Cluster: Bioelectrochemical Systems and Sustainable Hydrogen Production
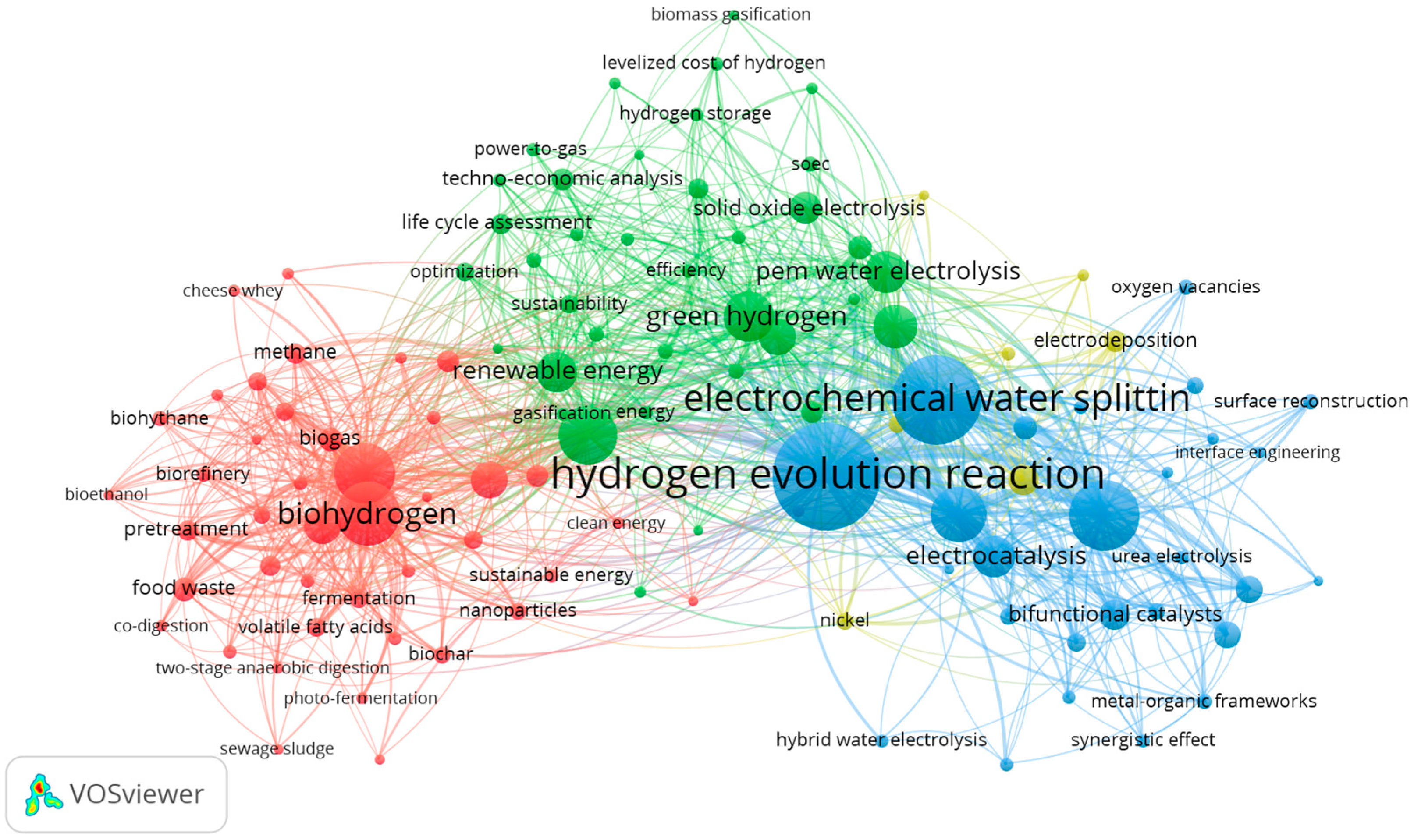
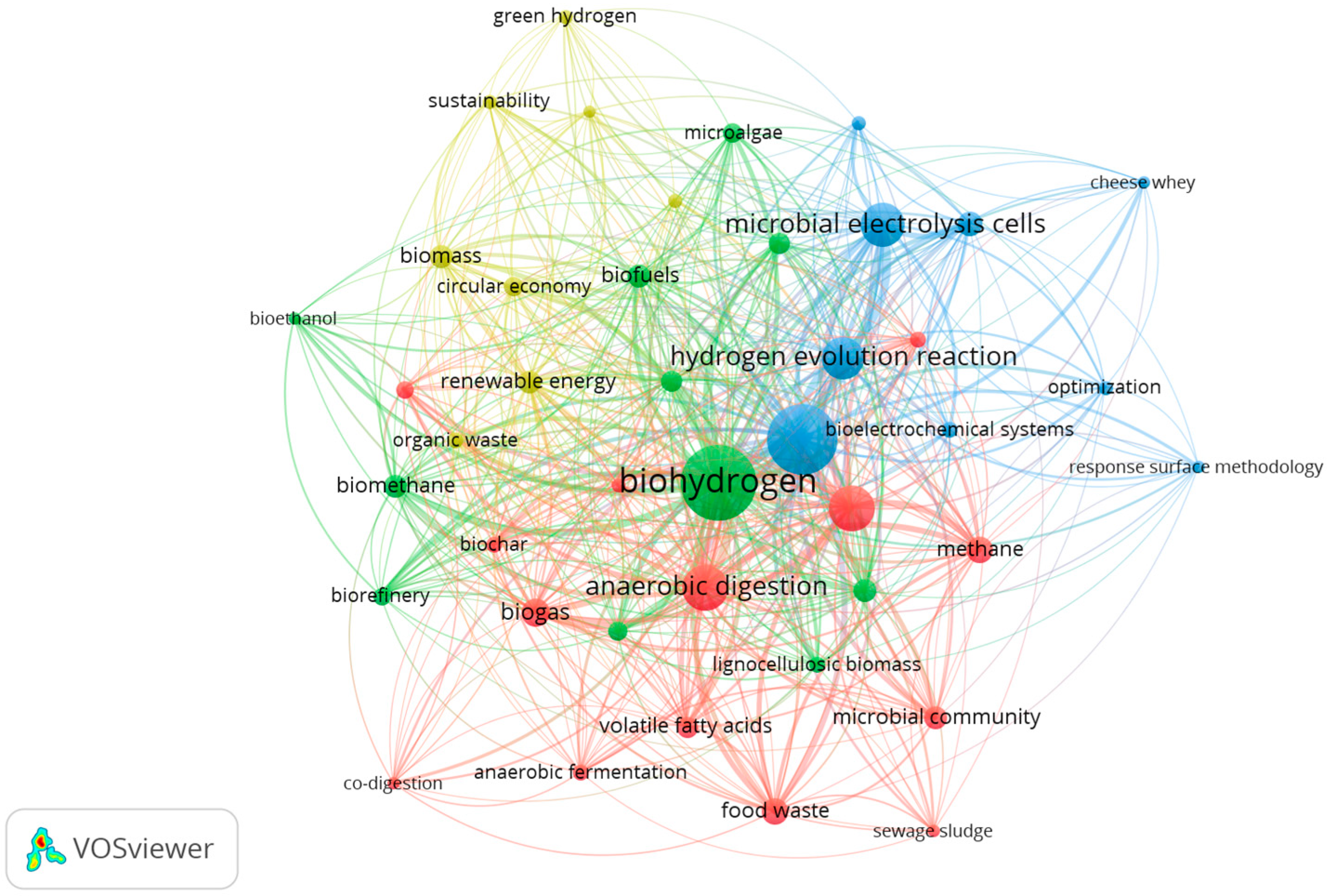
3.2. Refining the Bibliometric Strategy: Integrating Biotechnological Descriptors
3.3. The Role of MECs Within the Broader Biohydrogen Landscape
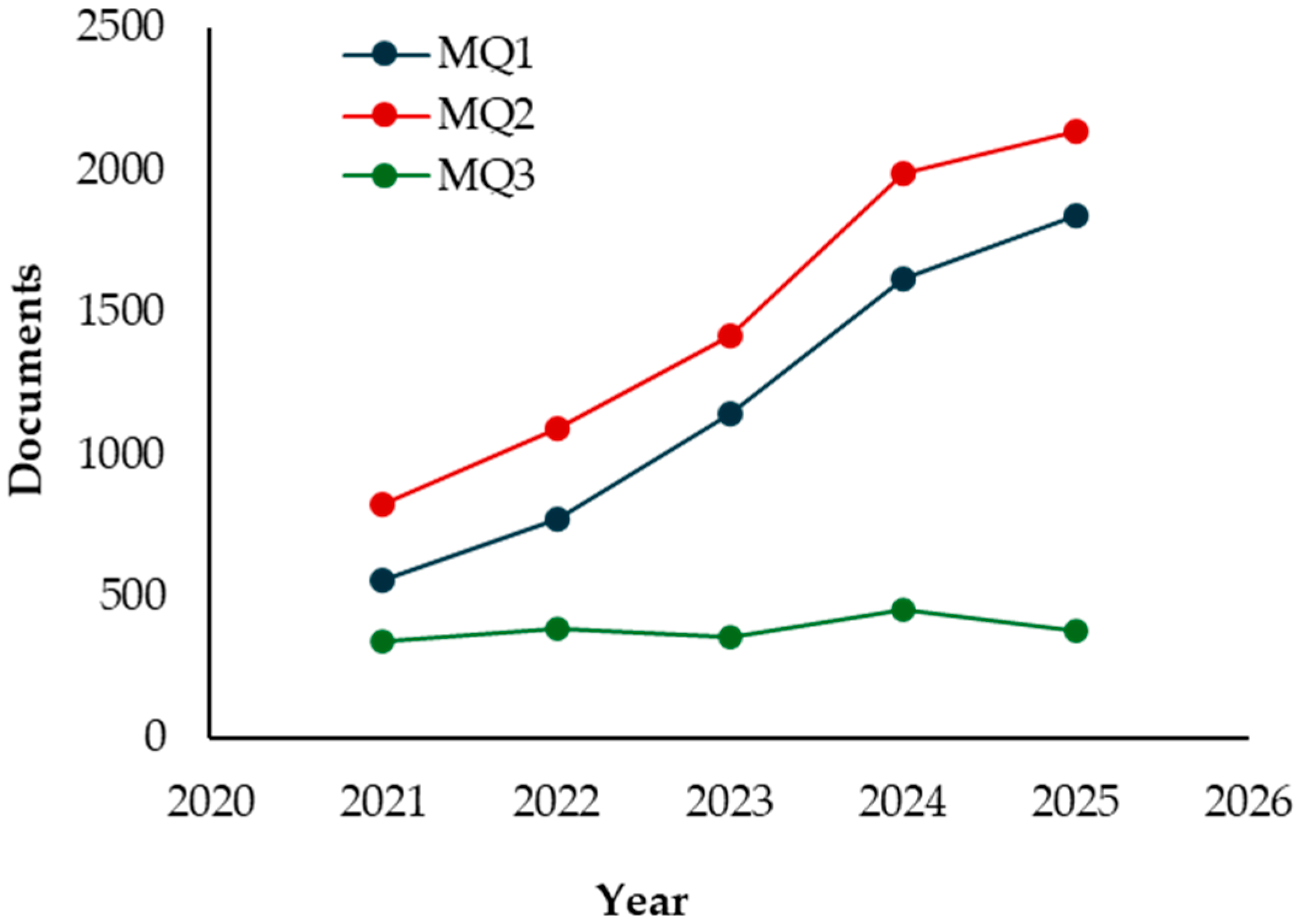
3.4. Publication Trends and Subject Area Distribution
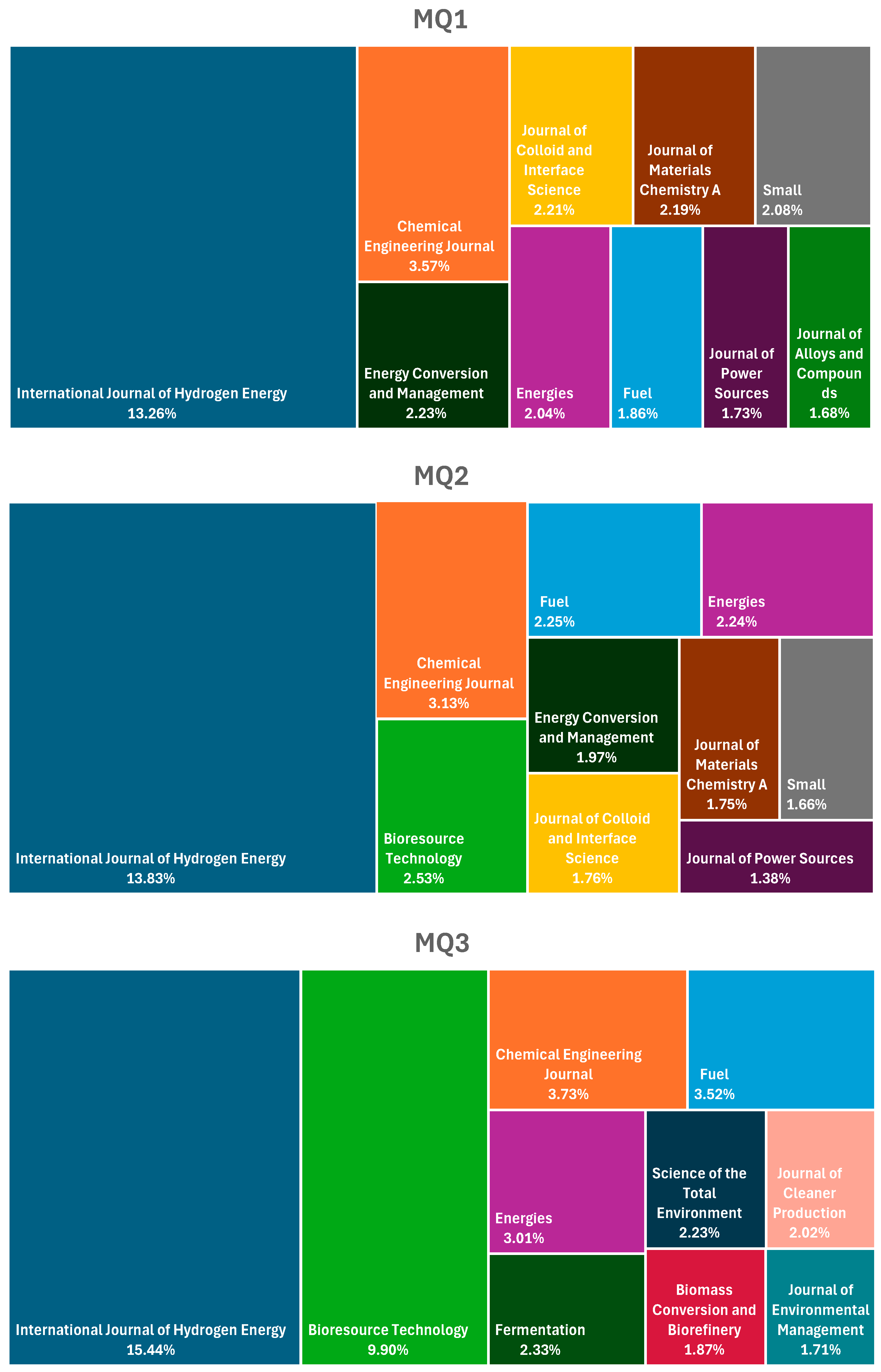
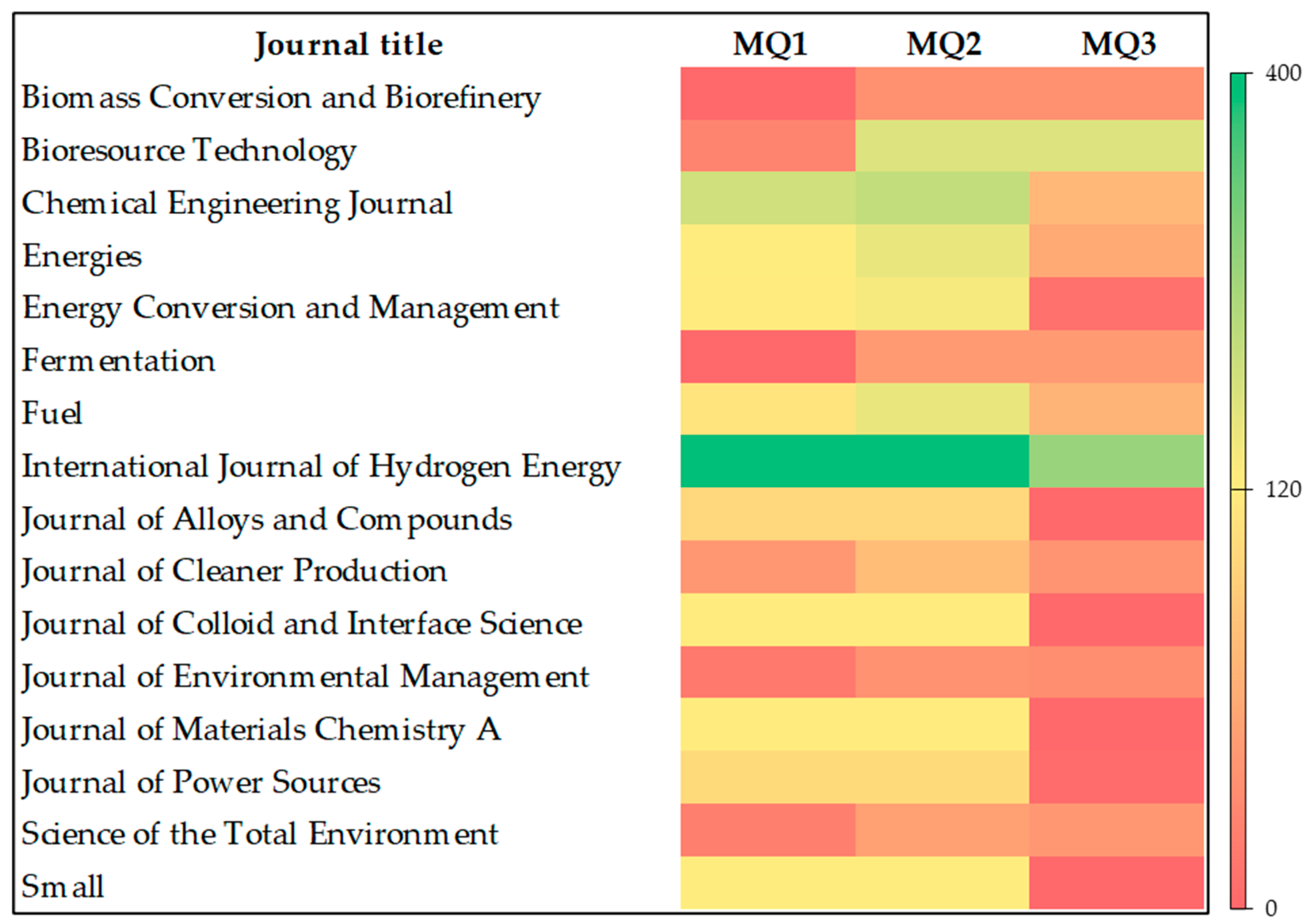
3.5. Journal Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PEM | Proton Exchange Membrane |
| MEC | Microbial Electrolysis Cell |
| HER | Hydrogen Evolution Reaction |
| OER | Oxygen Evolution Reaction |
| TRL | Technology Readiness Level |
| SMR | Steam Methane Reforming |
| ECC | Electrochemical Capacitor |
| PBR | Photobioreactor |
| MFC | Microbial Fuel Cell |
| GHG | Greenhouse Gas |
| KWD | Keyword |
References
- Angelico, R.; Giametta, F.; Bianchi, B.; Catalano, P. Green Hydrogen for Energy Transition: A Critical Perspective. Energies 2025, 18, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain Bhuiyan, M.M.; Siddique, Z. Hydrogen as an Alternative Fuel: A Comprehensive Review of Challenges and Opportunities in Production, Storage, and Transportation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 102, 1026–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, B.; Elzamar, A.A.; AlFazzani, S.; Ezzat, S.M. Green Hydrogen as a Source of Renewable Energy: A Step towards Sustainability, an Overview. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 27, 29213–29233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvinhosseini, P.; Mordue, G. The Viability of Green Hydrogen for Electric Power Generation: Evaluating Current Practicability and Future Demand. Energies 2025, 18, 5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganji, M.; Gheibi, M.; Aldaghi, A.; Dhoska, K.; Vito, S.; Atari, S.; Moezzi, R. Comprehensive Study on Hydrogen Production for Sustainable Transportation Planning: Strategic, Techno-Economic, and Environmental Impacts. Hydrogen 2025, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Antonini, G.; Hayibo, K.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Khan, S.; Tian, W.; Boutilier, M.S.H.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Bassi, A.; et al. Comparative Techno-Environmental Analysis of Grey, Blue, Green/Yellow and Pale-Blue Hydrogen Production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 116, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abawalo, M.; Pikoń, K.; Landrat, M. Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of Hydrogen Production via Biogas Reforming and Agricultural Residue Gasification. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, Z.; Gholami, F.; Šimek, J.; Svobodová, K.; Vakili, M. Hydrogen Production for a Decarbonized Future: A Review of Production Technologies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2025, 153, 240–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segovia-Hernández, J.G.; Hernández, S.; Cossío-Vargas, E.; Juarez-García, M.; Sánchez-Ramírez, E. Green Hydrogen Production for Sustainable Development: A Critical Examination of Barriers and Strategic Opportunities. RSC Sustain. 2024, 3, 134–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tüysüz, H. Alkaline Water Electrolysis for Green Hydrogen Production. Acc. Chem. Res. 2024, 57, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, E.A.; Maestre, V.M.; Ortiz, A.; Ortiz, I. Steam Electrolysis for Green Hydrogen Generation. State of the Art and Research Perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 202, 114725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Luo, F.; Yang, Z. Strategies for the Enhancements in Catalytic Performance and Stability of Anodic Electrocatalyst in PEM Water Splitting. Energy Rev. 2024, 3, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Gu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Shao, Z. Recent Advances in Innovative Systems for Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Production. Energy Environ. Sci. 2025, 18, 6456–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, C. Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzer: Electrode Design, Lab-Scaled Testing System and Performance Evaluation. EnergyChem 2022, 4, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, N.; Bayhan, S.; Fesli, U.; Sanfilippo, A. A Comprehensive Review of the State-of-the-Art of Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2025, 8, 44–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Que, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Huang, J.; Zhu, X.; Liao, Q. Low-Dimensional Metal and Metal Compound Catalysts for Water Electrolysis: A Review. J. Power Sources 2025, 652, 237658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Aepuru, R.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, S.J. Advances in Catalysts for Hydrogen Production: A Comprehensive Review of Materials and Mechanisms. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, P.; Ala, A.; Nazari, P.; Jalili, B.; Ganji, D.D. A Comprehensive Review of Microbial Fuel Cells Considering Materials, Methods, Structures, and Microorganisms. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.; Nayak, J.K.; Ress, N.V.; Steinberger-Wilckens, R.; Ghosh, U.K. Bio-Hydrogen Production through Microbial Electrolysis Cell: Structural Components and Influencing Factors. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Sodric, O.; Baeza, J.A.; Guisasola, A. Enhancing Bioelectrochemical Hydrogen Production from Industrial Wastewater Using Ni-Foam Cathodes in a Microbial Electrolysis Cell Pilot Plant. Water Res. 2024, 256, 121616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Hussain Mehdi, S.E.; Pandit, S.; Eun-Oh, S.; Natarajan, V. Factors Affecting Hydrogen Production in Microbial Electrolysis Cell (MEC): A Review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 61, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Wang, C.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; You, N.; Tang, H.; Yu, H.; Tang, L.; Han, J. Comparative Review on Microbial Electrochemical Technologies for Resource Recovery from Wastewater towards Circular Economy and Carbon Neutrality. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 376, 128906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, J.; SundarRajan, P.S.; Grace Pavithra, K.; Priyadharsini, P.; Shyam, S.; Goutham, R.; Hoang Le, Q.; Pugazhendhi, A. New Insights into Microbial Electrolysis Cells (MEC) and Microbial Fuel Cells (MFC) for Simultaneous Wastewater Treatment and Green Fuel (Hydrogen) Generation. Fuel 2024, 355, 129530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, P.; Ghosh, A.; Sunantha, G.; Sivagami, K.; Mohanakrishna, G.; Aishwarya, S.; Shah, S.; Sethumadhavan, A.; Ranjan, P.; Prajapat, R. A Comprehensive Review of Microbial Electrolysis Cells: Integrated for Wastewater Treatment and Hydrogen Generation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 190, 458–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dange, P.; Pandit, S.; Jadhav, D.; Shanmugam, P.; Gupta, P.K.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, M.; Yang, Y.H.; Bhatia, S.K. Recent Developments in Microbial Electrolysis Cell-Based Biohydrogen Production Utilizing Wastewater as a Feedstock. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadier, A.; Kalil, M.S.; Chandrasekhar, K.; Mohanakrishna, G.; Saratale, G.D.; Saratale, R.G.; Kumar, G.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Sivagurunathan, P. Surpassing the Current Limitations of High Purity H2 Production in Microbial Electrolysis Cell (MECs): Strategies for Inhibiting Growth of Methanogens. Bioelectrochemistry 2018, 119, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, M.S.; Mevada, C.; Shah, J.; Rasheed, M.A.; Mäntysalo, M. Zero-Discharge, Self-Sustained 3D-Printed Microbial Electrolysis Cell for Biohydrogen Production: A Review. Chem. Commun. 2025, 61, 5410–5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Yang, E.; Kim, B.; Obaid, M.; Jang, J.K.; Chae, K.J. Recent Application of Nanomaterials to Overcome Technological Challenges of Microbial Electrolysis Cells. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsad, S.R.; Arsad, A.Z.; Ker, P.J.; Hannan, M.A.; Tang, S.G.H.; Goh, S.M.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Recent Advancement in Water Electrolysis for Hydrogen Production: A Comprehensive Bibliometric Analysis and Technology Updates. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 60, 780–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsad, A.Z.; Hannan, M.A.; Al-Shetwi, A.Q.; Hossain, M.J.; Begum, R.A.; Ker, P.J.; Salehi, F.; Muttaqi, K.M. Hydrogen Electrolyser for Sustainable Energy Production: A Bibliometric Analysis and Future Directions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 4960–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Aburto, C.; Poma-García, J.; Montaño-Pisfil, J.; Morcillo-Valdivia, P.; Oyanguren-Ramirez, F.; Santos-Mejia, C.; Rodriguez-Flores, R.; Virú-Vasquez, P.; Pilco-Nuñez, A. Bibliometric Analysis of Global Publications on Management, Trends, Energy, and the Innovation Impact of Green Hydrogen Production. Sustainability 2024, 16, 11048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roucham, B.; Lefilef, A.; Zaghdoud, O.; Mohammed, K.S. The Evolution of Green Hydrogen in Renewable Energy Research: Insights from a Bibliometric Perspective. Energy Rep. 2025, 13, 576–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Arias, P.; Antón-Sancho, Á.; Lampropoulos, G.; Vergara, D. On Green Hydrogen Generation Technologies: A Bibliometric Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mais, L.; Rodriguez, J.; Melis, N.; Vacca, A.; Mascia, M. Computational Modelling as a Design Tool for Bioelectrochemical Systems. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2024, 44, 101460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmas, S.; Vacca, A.; Mais, L. Bibliometric Analysis on the Papers Dedicated to Microplastics in Wastewater Treatments. Catalysts 2021, 11, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perianes-Rodriguez, A.; Waltman, L.; van Eck, N.J. Constructing Bibliometric Networks: A Comparison between Full and Fractional Counting. J. Informetr. 2016, 10, 1178–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, Y.F. A Comparative Science-Based Viability Assessment Among Current and Emerging Hydrogen Production Technologies. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Dou, Z. Review of Electric Hydrogen Production Technology Combined with Technology Maturity Analysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 98, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolo, I.; Costa, V.A.F.; Brito, F.P. Hydrogen-Based Energy Systems: Current Technology Development Status, Opportunities and Challenges. Energies 2023, 17, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, M.M.; Martinez-Burgos, W.J.; de Bona Sartor, G.; Medeiros, A.B.P.; de Carvalho, J.C.; Soccol, C.R. Microbial Electrolysis Cells in Biohydrogen Production. In Biohydrogen-Advances and Processes; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 429–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, C.; Srivastava, S.; Chang, C.T. Catalytic Innovations for High-Yield Biohydrogen Production in Integrated Dark Fermentation and Microbial Electrolysis Systems. Catalysts 2025, 15, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, A.; Sun, P.; Liu, X.; Delgado, H.E.; Sun, L.; Elgowainy, A. Techno-Economic and Life Cycle Analysis of Bio-Hydrogen Production Using Bio-Based Waste Streams through the Integration of Dark Fermentation and Microbial Electrolysis. Green Chem. 2025, 27, 6213–6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaraz-Gonzalez, V.; Flores-Estrella, R.A.; Nolasco, M.; Cano, V.; González-Alvarez, V. Microbial Electrolysis Cells for Biohydrogen Generation and Wastewater Treatment—A Short Review and Current Trends. In Wastewater Management and Technologies; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, Q.H.H.; Phan, T.P.; Nguyen, P.K.T. Recent Advances in Powering Microbial Electrolysis Cells for Sustainable Hydrogen Production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 147, 150034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, G.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, G.; Su, H. CoMo/SS Cathode Catalyst for Enhanced Hydrogen Production in Microbial Electrolysis Cells. Catalysts 2025, 15, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
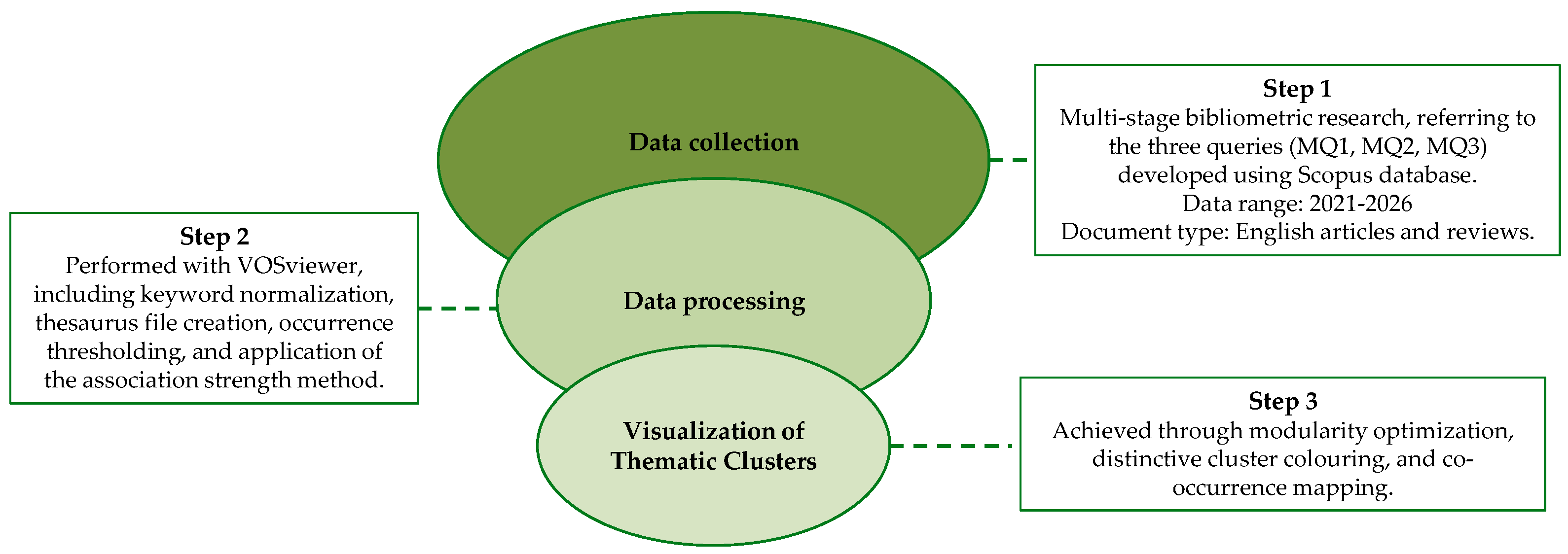
| Search Block | MQ1: Electrochemical & Bioelectrochemical Focus | MQ2: Expanded Biohydrogen Scope | MQ3: Biohydrogen-Centric Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Keywords/Query Logic | (TITLE-ABS-KEY(“hydrogen production” OR “H2 production”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(“water electrolysis” OR “electrolysis of water” OR “PEM electrolysis” OR “alkaline electrolysis” OR “solid oxide electrolysis”)) OR (TITLE-ABS-KEY(“hydrogen production” OR “H2 production”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(“microbial electrolysis” OR “microbial electrolysis cell” OR “MEC”)) | (TITLE-ABS-KEY(“hydrogen production” OR “H2 production”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(“water electrolysis” OR “electrolysis of water” OR “PEM electrolysis” OR “alkaline electrolysis” OR “solid oxide electrolysis”)) OR (TITLE-ABS-KEY(“hydrogen production” OR “H2 production” OR “biohydrogen”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(“microbial electrolysis” OR “microbial electrolysis cell” OR “MEC” OR “biotechnology”)) | (TITLE-ABS-KEY(“hydrogen production” OR “H2 production” OR “biohydrogen”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(“microbial electrolysis” OR “microbial electrolysis cell” OR “MEC” OR “biotechnology” OR “dark fermentation” OR “anaerobic digestion” OR “bioelectrochemical systems”)) |
| Purpose | Captures literature on hydrogen production via conventional electrolysis and MECs | Enhances visibility of biologically mediated hydrogen production | Isolates biohydrogen research as a standalone domain |
| Notes | Provides a dual focus on mature electrochemical systems and emerging bioelectrochemical platforms | Includes biotechnology descriptors to capture interdisciplinary MEC research indexed in life sciences | Excludes conventional electrolysis terms to focus exclusively on microbial, fermentative, and biotechnological pathways |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Mascia, M.; Melis, N.; Piro, V.M.I.; Rubanu, M.G.; Vacca, A.; Mais, L. Mapping Hydrogen Research Frontiers: A Multi-Query Bibliometric Analysis of Electrochemical and Biotechnological Pathways. Energies 2026, 19, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/en19010166
Mascia M, Melis N, Piro VMI, Rubanu MG, Vacca A, Mais L. Mapping Hydrogen Research Frontiers: A Multi-Query Bibliometric Analysis of Electrochemical and Biotechnological Pathways. Energies. 2026; 19(1):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/en19010166
Chicago/Turabian StyleMascia, Michele, Nicola Melis, Vittoria Maria Iris Piro, Maria Grazia Rubanu, Annalisa Vacca, and Laura Mais. 2026. "Mapping Hydrogen Research Frontiers: A Multi-Query Bibliometric Analysis of Electrochemical and Biotechnological Pathways" Energies 19, no. 1: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/en19010166
APA StyleMascia, M., Melis, N., Piro, V. M. I., Rubanu, M. G., Vacca, A., & Mais, L. (2026). Mapping Hydrogen Research Frontiers: A Multi-Query Bibliometric Analysis of Electrochemical and Biotechnological Pathways. Energies, 19(1), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/en19010166


_Xie.png)





