Harmonic Current Suppression of Dual Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Improved Proportional-Integral Resonant Controller
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- By transforming the fifth and seventh harmonic currents in the xy plane into sixth harmonic currents via coordinate transformation, only two improved PIR controllers are required to achieve harmonic suppression. This reduces the number of controllers and simplifies the control structure.
- (2)
- Digital delay compensation is achieved by correcting the angles in the coordinate transformation, while phase compensation is implemented by adjusting the transfer function of the resonant term. These improvements enhance both system stability and harmonic current suppression, especially at high speeds.
- (3)
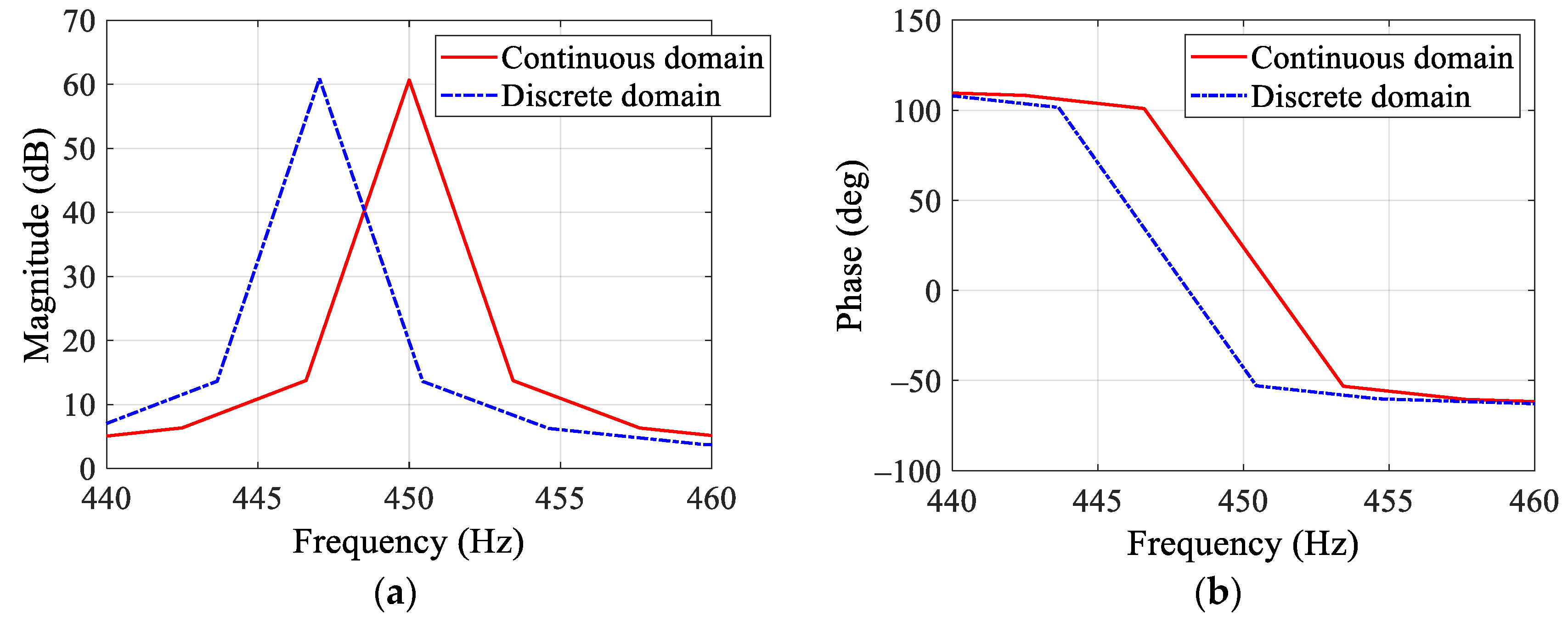
- The coefficients of the bilinear transformation formula are corrected to maintain consistent amplitude–frequency and phase–frequency characteristics between the continuous and discrete transfer functions. This eliminates deviations between the discretized and actual resonant frequencies, ensuring effective harmonic current suppression at high speeds.
2. Modeling and Harmonic Current Analysis of DTP-PMSM
2.1. Mathematical Model
2.2. Harmonic Current Analysis
2.2.1. Non-Sinusoidal Back-EMF
2.2.2. Inverter Nonlinearity
3. Improved PIR Controller
3.1. Unification of PIR Controllers
3.2. Digital Delay Compensation and Phase Compensation
3.3. Discretization Correction
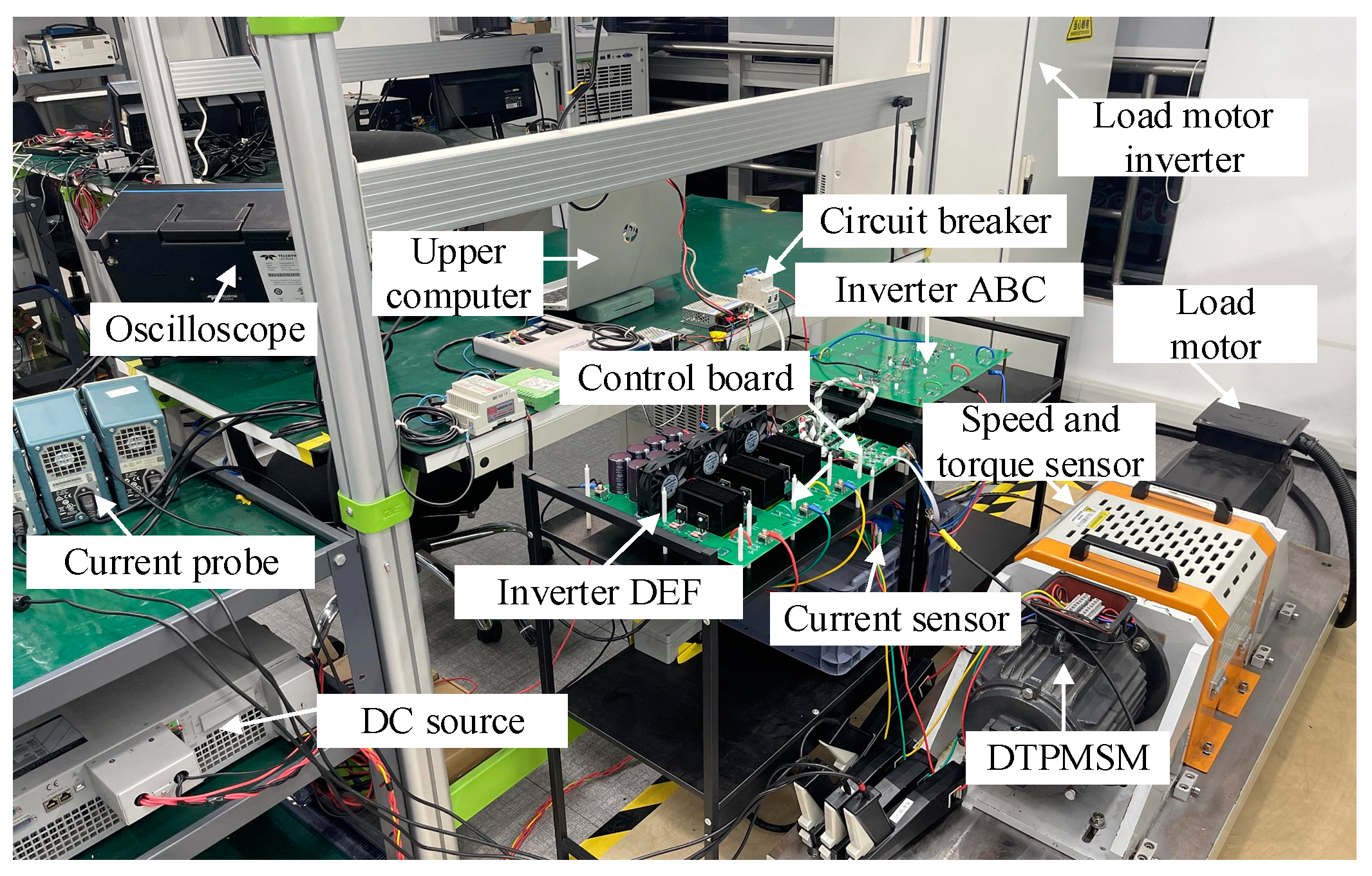
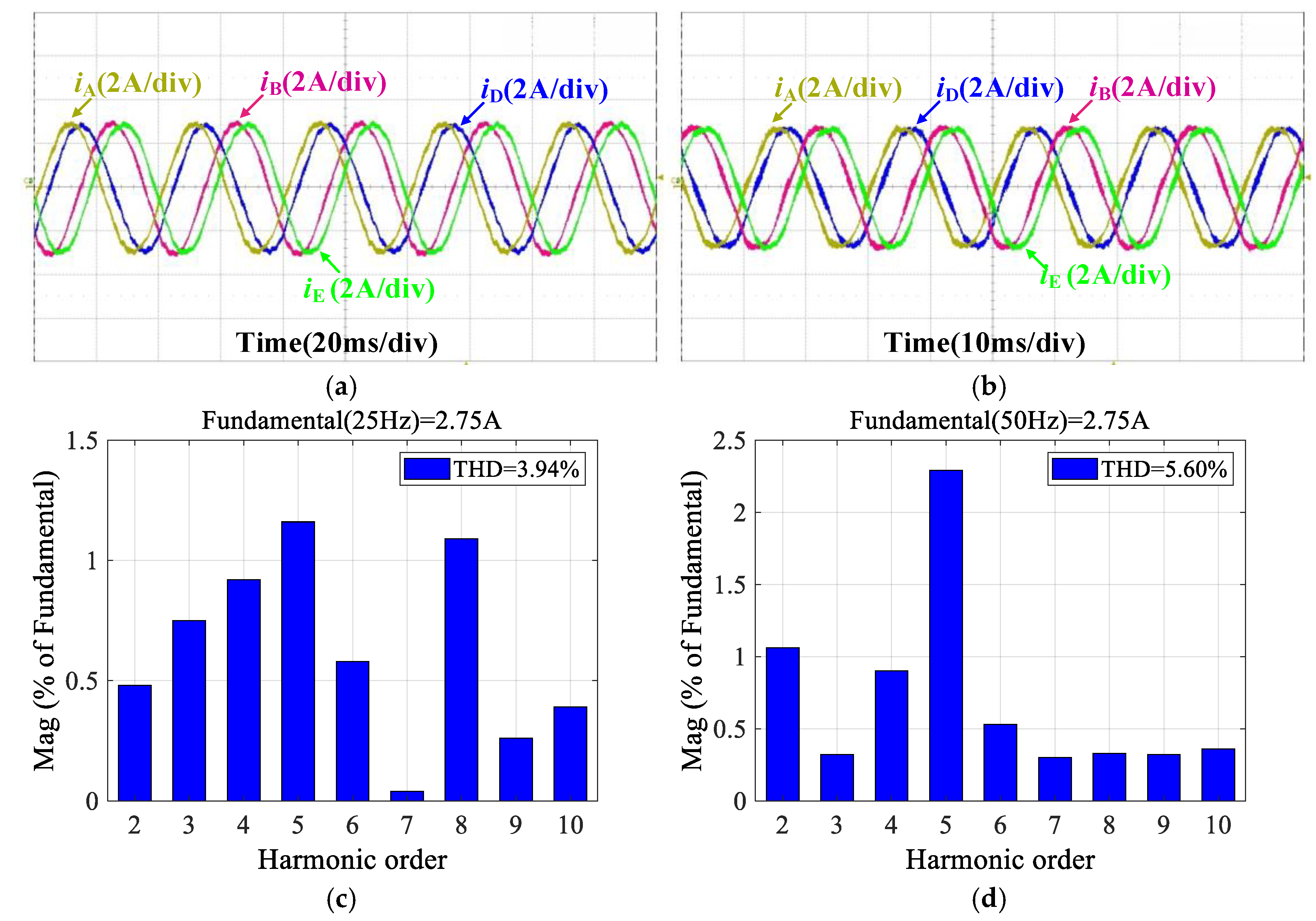
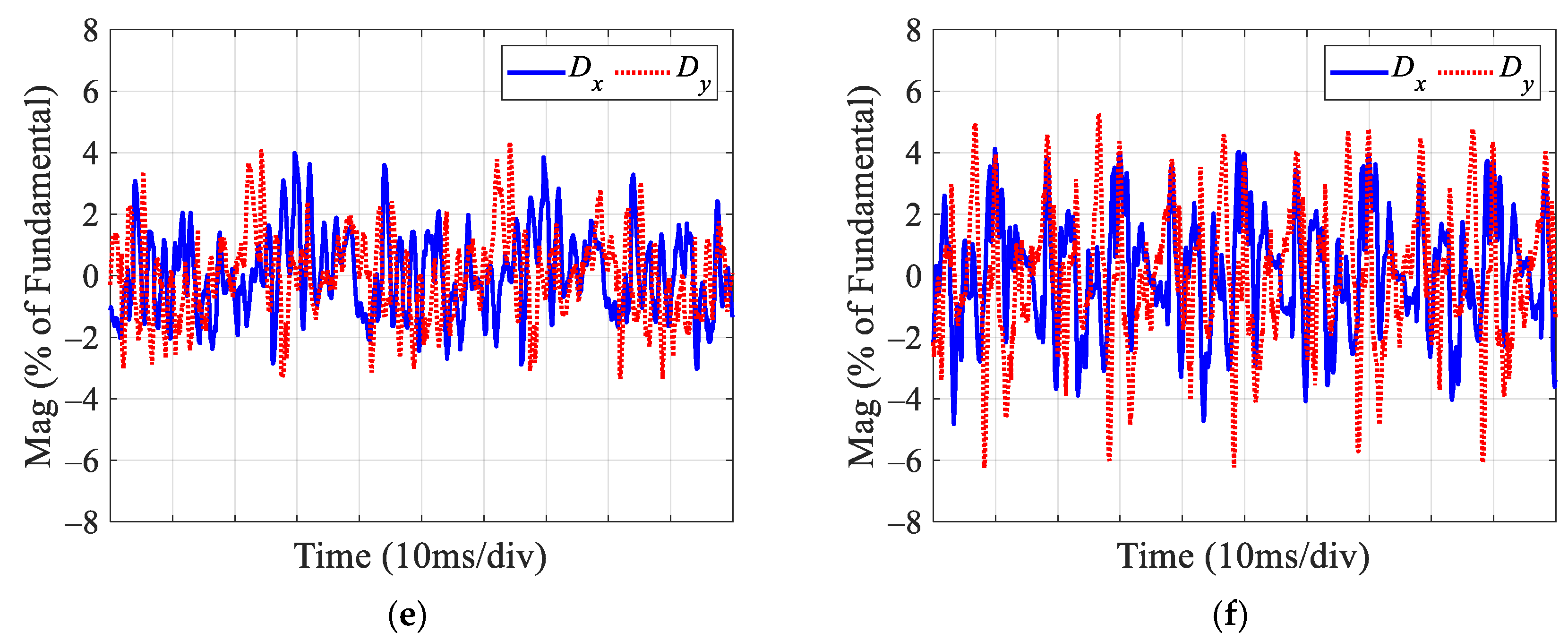
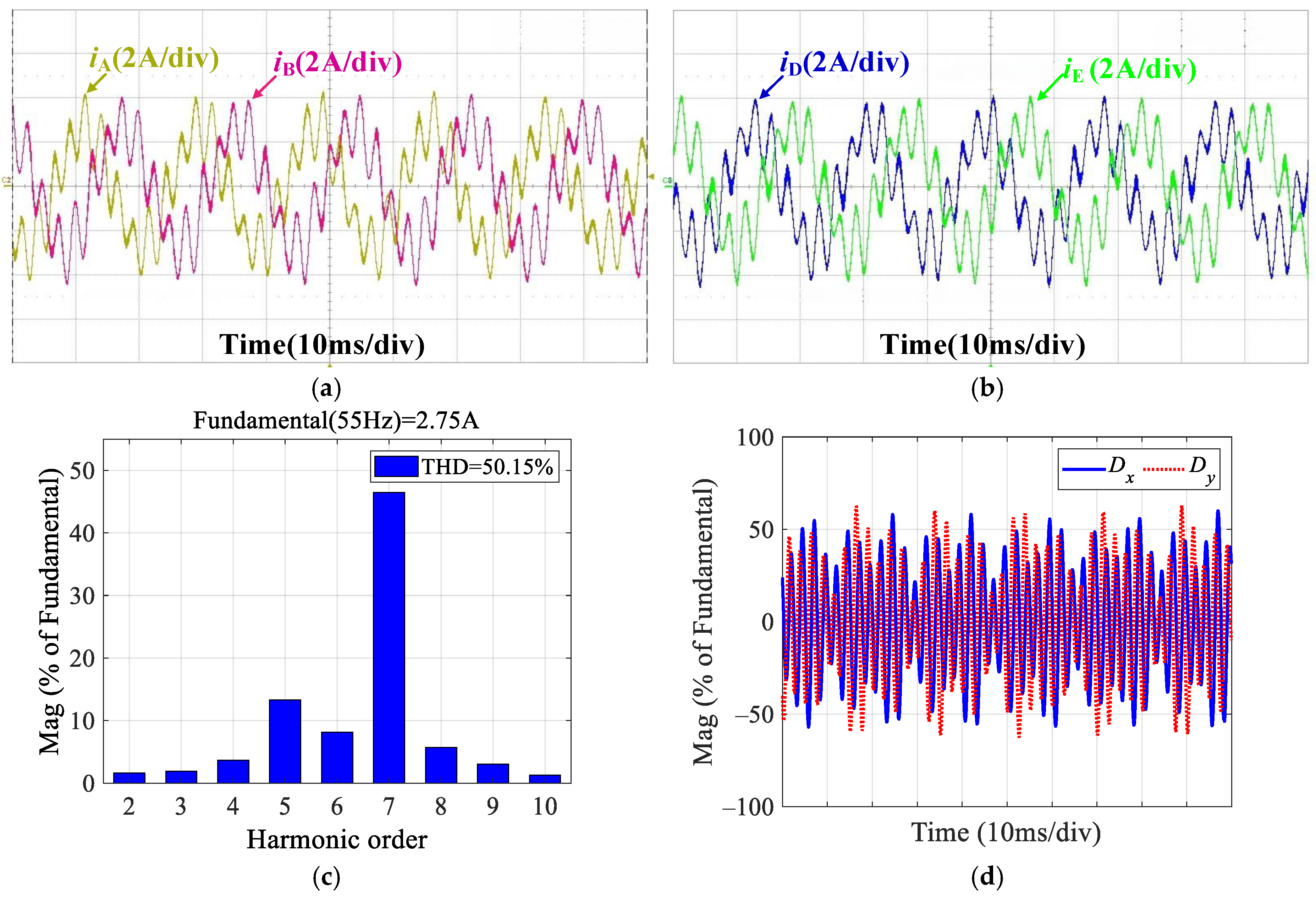
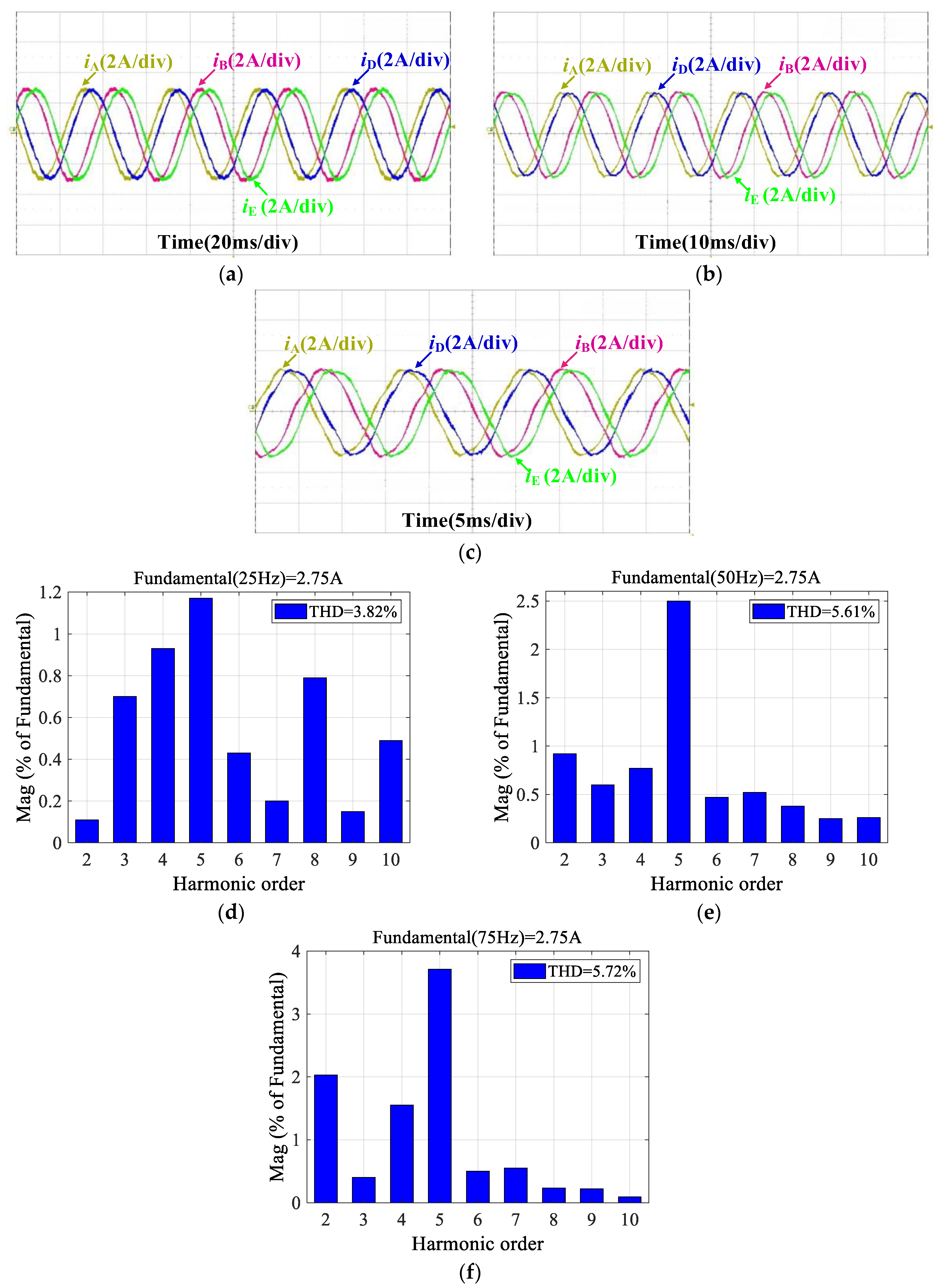
4. Experimental Verification
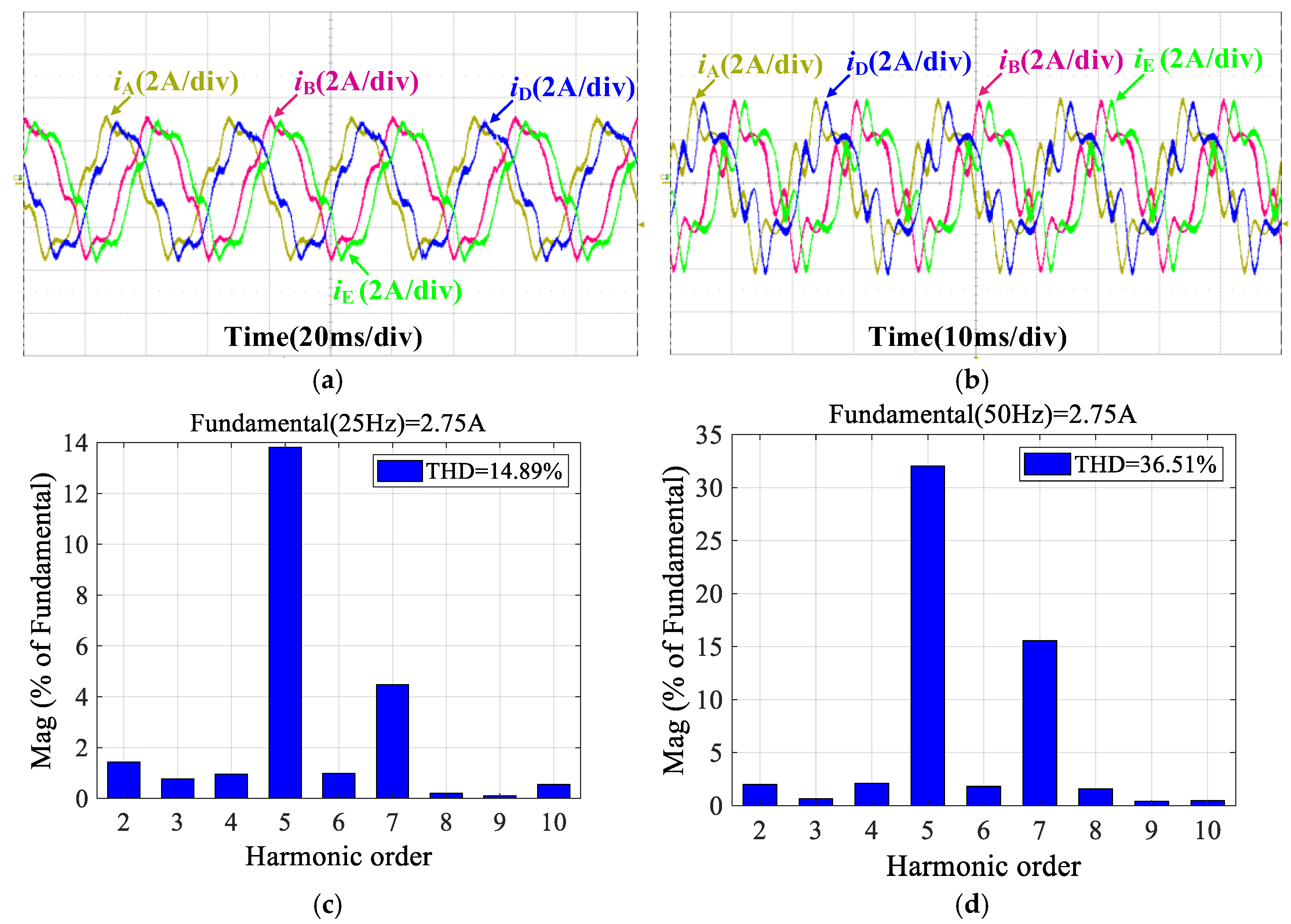
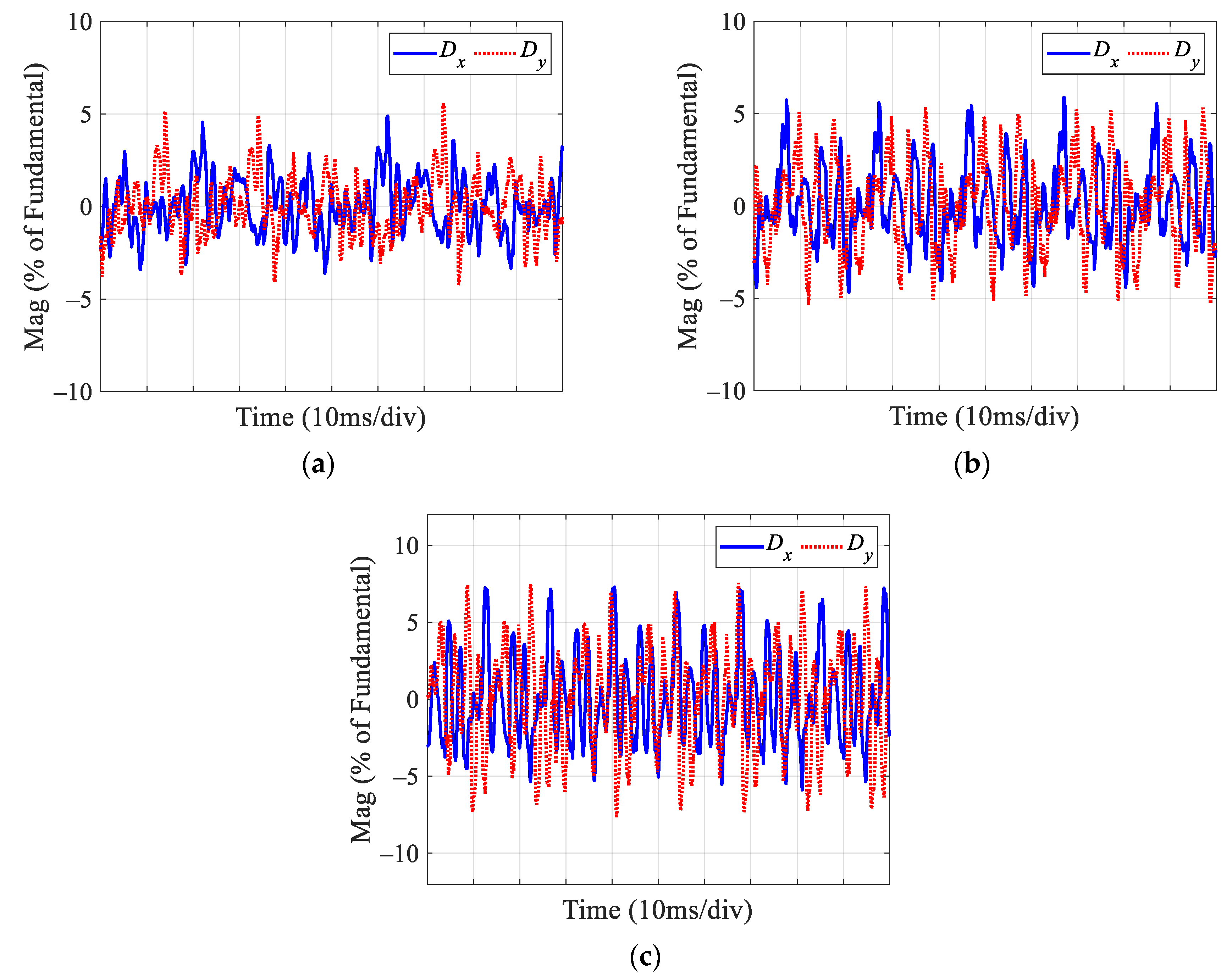
4.1. Traditional Dual PI Controllers
4.2. Traditional Dual PIR Controllers
4.3. Proposed Dual Improved PIR Controllers
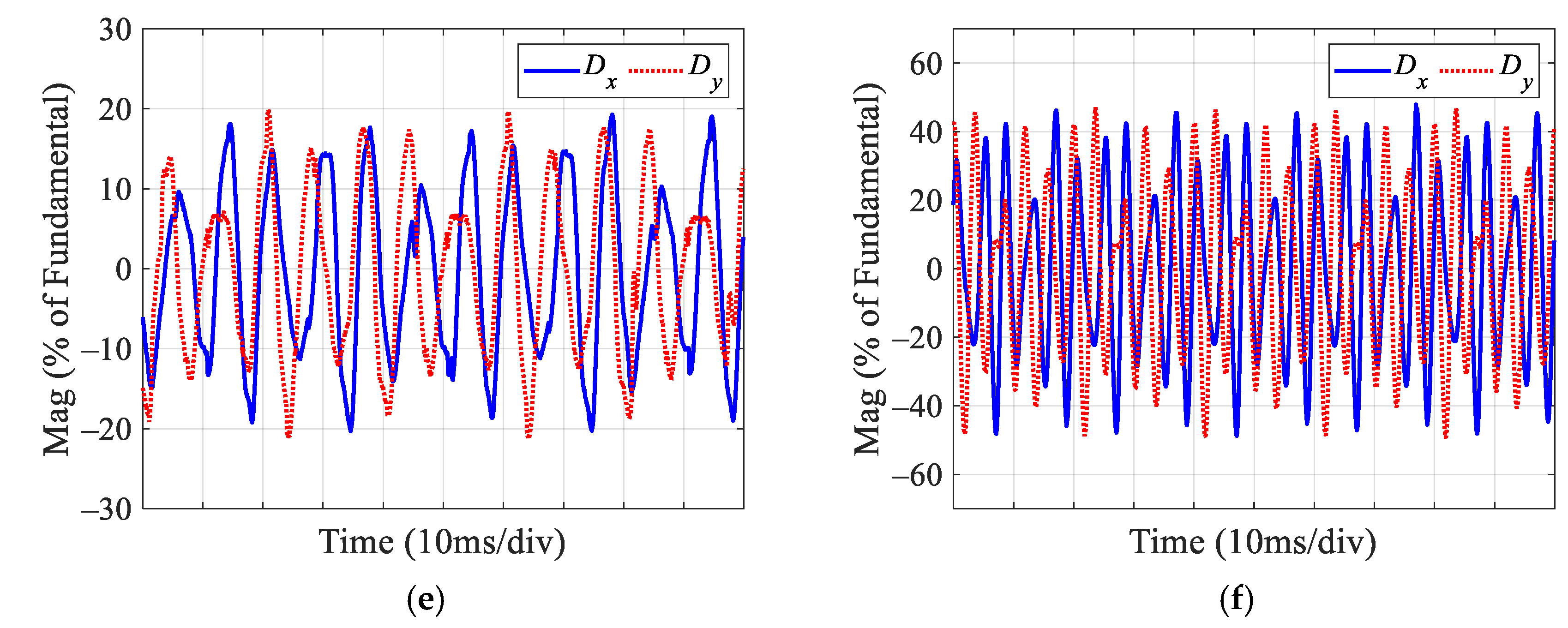
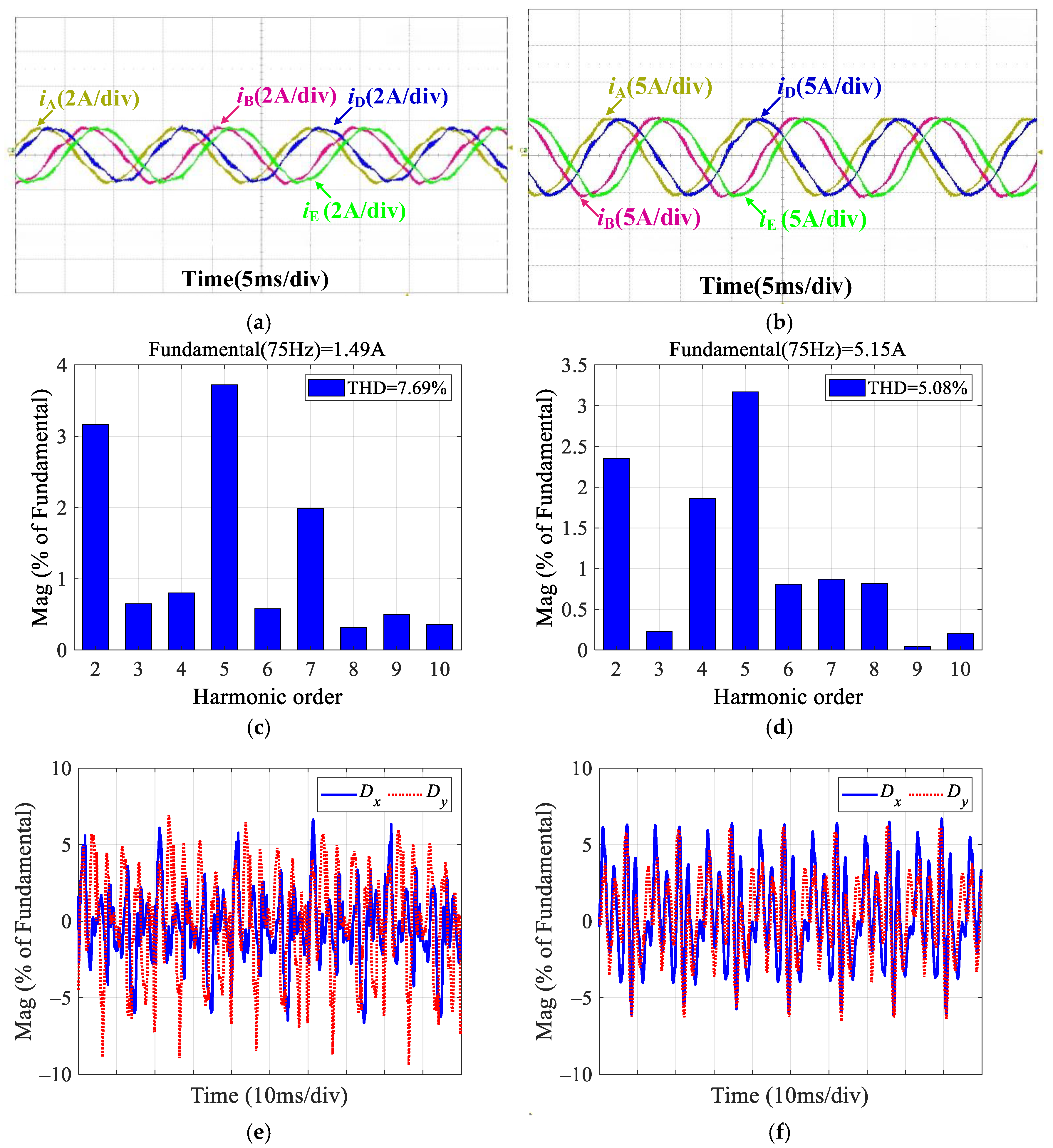
4.4. Results, Comparison, and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| θe, ωe | Electrical angle and electrical angular speed. |
| ud, uq, ux, uy | Voltages in the dq-plane and the xy-plane. |
| id, iq, ix, iy | Currents in the dq-plane and the xy-plane. |
| Ld, Lq | D-axis and q-axis inductances. |
| Lls | Leakage inductance. |
| Rs, Ψf | Stator resistance and permanent magnet flux linkage. |
| np | Pole pairs. |
| Te | Electromagnetic torque. |
| γ | Electrical angle between the current vector and q-axis. |
| ΔUd | Distortion voltage amplitude. |
| Td, Ton, Toff, Ts | Dead time, switching on-time, switching off-time, and switching period. |
| Udc | DC bus voltage. |
| Usat | Voltage drop when the switch is on. |
| Ud | Forward voltage drop of the anti-parallel diode. |
| Z5, Z7 | Impedance of the fifth and seventh harmonic plane |
| ix5, ix7, iy5, iy7 | The fifth and seventh harmonic currents of x-axis and y-axis. |
| φ5, φ7 | Phase angles of the fifth and seventh harmonic currents. |
| Kp, Ki | Proportional and integral gains of PI controller. |
| Kpr, Kr | Proportional and resonant gains of QPR controller. |
| ωc, ωn | Cutoff frequency and resonant frequency. |
| θ1 | Electrical angle with digital delay compensation. |
| Km | Correction factor. |
| ωz | Actual resonant frequency. |
| Dx, Dy | Ratio of the xy-plane current to the fundamental amplitude of the phase current. |
| iA, iB, iD, iE | Currents of phase A, B, C, and D. |
| rcu | Ratio of harmonic copper losses to fundamental copper losses. |
| Irms | Root mean square (RMS) value of the fundamental harmonic current. |
| Inrms | RMS value of the nth harmonic current. |
References
- Levi, E. Advances in converter control and innovative exploitation of additional degrees of freedom for multiphase machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Huang, W.; Xue, H. Development and analysis of dual three-phase PMSM with phase-shifted hybrid winding for aircraft electric propulsion application. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 10, 6497–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillo, L.; Empringham, L.; Wheeler, P.; Khwan-On, S.; Gerada, C.; Othman, M. Multiphase power converter drive for fault-tolerant machine development in aerospace applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulligoi, G.; Vicenzutti, A.; Menis, R. All-electric ship design: From electrical propulsion to integrated electrical and electronic power systems. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2016, 2, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frikha, M.A.; Croonen, J.; Deepak, K.; Benômar, Y.; El Baghdadi, M.; Hegazy, O. Multiphase motors and drive systems for electric vehicle powertrains: State of the art analysis and future trends. Energies 2023, 16, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Han, Y.; Lee, K.; Bhattacharya, S. A sinusoidal current control strategy based on harmonic voltage injection for harmonic loss reduction of PMSMs with non-sinusoidal back-EMF. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 7032–7043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Lai, C.; Kelly, M.; Kar, N.C. Dual three-phase PMSM torque modelling and maximum torque per peak current control through optimized harmonic current injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 3356–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Zou, J.; Xu, Y.; Yu, G.; Wang, L.; Zanchetta, P. High-frequency current harmonic analysis and suppression in dual three-phase PMSMs with advanced carrier phase-shift PWM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karttunen, J.; Kallio, S.; Peltoniemi, P.; Silventoinen, P. Current harmonic compensation in dual three-phase PMSMs using a disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengoni, L.; Höchemer, S.; Wrzecionko, B.; Mayer, J.; Füchtner, M.; De Doncker, R. Comparison of PMSM and inverter efficiency for dual three-phase high performance powertrains including low order harmonics and voltage modulation. In Proceedings of the 2022 25th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 29 November–2 December 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rudden, I.; Li, G.; Padinharu, D.; Zhu, Z.; Duke, A.; Clark, R.; Thomas, A. Space harmonic cancellation in a dual three-phase SPM machine with star-delta windings. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 39, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, K. Study on winding design of dual three-phase electrical machines for circulating current harmonics and vibration suppression. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 71, 5063–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Feng, J.; Tao, T.; Wang, C.; Liu, S. High-frequency harmonics and vibration reduction for dual three-phase PMSM using multiple randomized SVPWM strategy. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 11455–11467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Li, J.; Qu, R.; Jiang, D.; Xiao, L.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J. Variable switching sequence PWM strategy of dual three-phase machine drive for high-frequency current harmonic suppression. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 35, 4984–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Rivera, M.; Golovanov, D.; Blissett, J.; Moran, J.; Davison, P.; Ramtharan, G.; Gerada, C.; Wheeler, P. Investigation of PWM techniques for high-frequency harmonics loss performance in dual-three phase asymmetrical machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Rivera, M.; Golovanov, D.; Blissett, J.; Moran, J.; Davison, P.; Ramtharan, G.; Gerada, C.; Wheeler, P. A hybrid PWM technique employing variable switching sequences for current ripple suppression in dual three-phase PMSMs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeeb, H.; Hackl, C.; Abdelrahem, M.; Abdel-Khalik, A.S. A unified SVPWM realization for minimizing circulating currents of dual three phase machines. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 12th International Conference on Power Electronics and Drive Systems (PEDS), Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–15 December 2017; pp. 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, C.; Guo, L.; Xu, G.; Xiao, F.; Wang, R.; Gao, S.; Liu, G.; Zhang, W. Current harmonic minimum pulse width modulation for dual three-phase PMSM system with 3L-NPC inverter and output filter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 2847–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarcos, A.; Robles, E.; Ugalde, U.; Elosegui, I.; Andreu, J. Output current ripple in electric vehicles with asymmetrical dual three-phase arrangement applying interleaved carrier-based PWM techniques. IEEE Access. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Sánchez, M.; Yepes, A.G.; López, Ó.; Doval-Gandoy, J. Assessment and exploitation of the minimum current harmonic distortion under overmodulation in five-phase induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 4289–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fan, H.; Zhao, J. Model-free predictive current control of DTP-PMSM based on ultra-local model considering back EMF harmonics. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2024, 13, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoro, S.; Husain, I. Model-free predictive current and disturbance rejection control of dual three-phase PMSM drives using optimal virtual vector modulation. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 11, 1432–1443. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Yang, G.; Deng, R. Synthetic vectors-based predictive control of dual three-phase PMSMs for current harmonics mitigation considering average deception effect. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2024, 12, 3103–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Song, Z.; Dong, Z. Harmonic current suppression for dual three-phase PMSM based on deadbeat control and disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 70, 3482–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, C. Direct harmonic current control scheme for dual three-phase PMSM drive system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 11647–11657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Ren, Y.; Gao, P.; Guo, K.; Wang, Z. Harmonic suppression strategy for dual three-phase permanent magnet synchronous machines based on a multi-input multi-output controller. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2024, 34, 5209305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lipo, T. Space vector PWM control of dual three-phase induction machine using vector space decomposition. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1995, 31, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karttunen, J.; Kallio, S.; Peltoniemi, P.; Silventoinen, P.; Pyrhönen, O. Decoupled vector control scheme for dual three-phase permanent magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 2185–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karttunen, J.; Kallio, S.; Honkanen, J.; Peltoniemi, P.; Silventoinen, P. Partial current harmonic compensation in dual three-phase PMSMs considering the limited available voltage. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhu, Z.; Qi, J.; Ren, Y.; Gan, C.; Brockway, S. Multiple synchronous reference frame current harmonic regulation of dual three phase PMSM with enhanced dynamic performance and system stability. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 8825–8838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Gui, X.; Xu, D. DTP-PMSM drive with proportional resonant regulator and dual zero injection PWM control method. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 1628–1633. [Google Scholar]
- Che, H.S.; Levi, E.; Jones, M.; Hew, W. Current control methods for an asymmetrical six-phase induction motor drive. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 29, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Y. Comparative study on harmonic current suppression of dual three-phase PMSM based on LMS adaptive linear neuron and resonant controller. In Proceedings of the 2023 26th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Zhuhai, China, 5–8 November 2023; pp. 2755–2760. [Google Scholar]
- An, Q.; Zhang, J.; An, Q.; Shamekov, A. Quasi-proportional-resonant controller based adaptive position observer for sensorless control of PMSM drives under low carrier ratio. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 2564–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepes, A.; Freijedo, F.; Doval-Gandoy, J.; López, Ó.; Malvar, J.; Fernandez-Comesaña, P. Effects of discretization methods on the performance of resonant controllers. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 1692–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Hua, W.; Huang, W.; Meng, J. Digital current control of an asymmetrical dual three-phase flux-switching permanent magnet machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 4281–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhu, Z.; Qi, J. Suppression of major harmonic currents for dual three-phase PMSMs by virtual multi three-phase systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 5478–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, Z. Harmonic currents and unbalance suppression of dual three-phase PMSM based on adaptive linear neuron controller. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 38, 2353–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, M.; Li, B.; Sun, X.; Jiang, F. Optimized fault-tolerant control of dual three-phase PMSM under open-switch faults. Energies 2024, 17, 5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

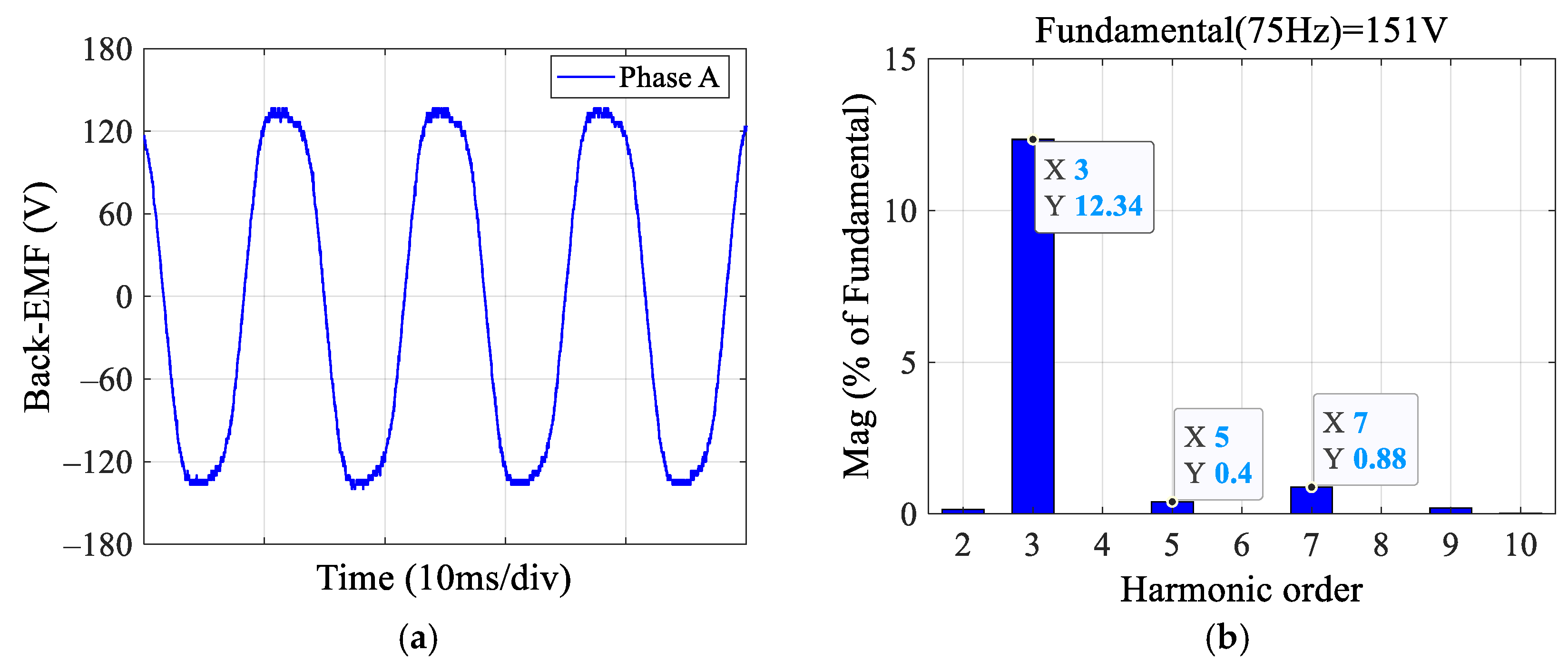

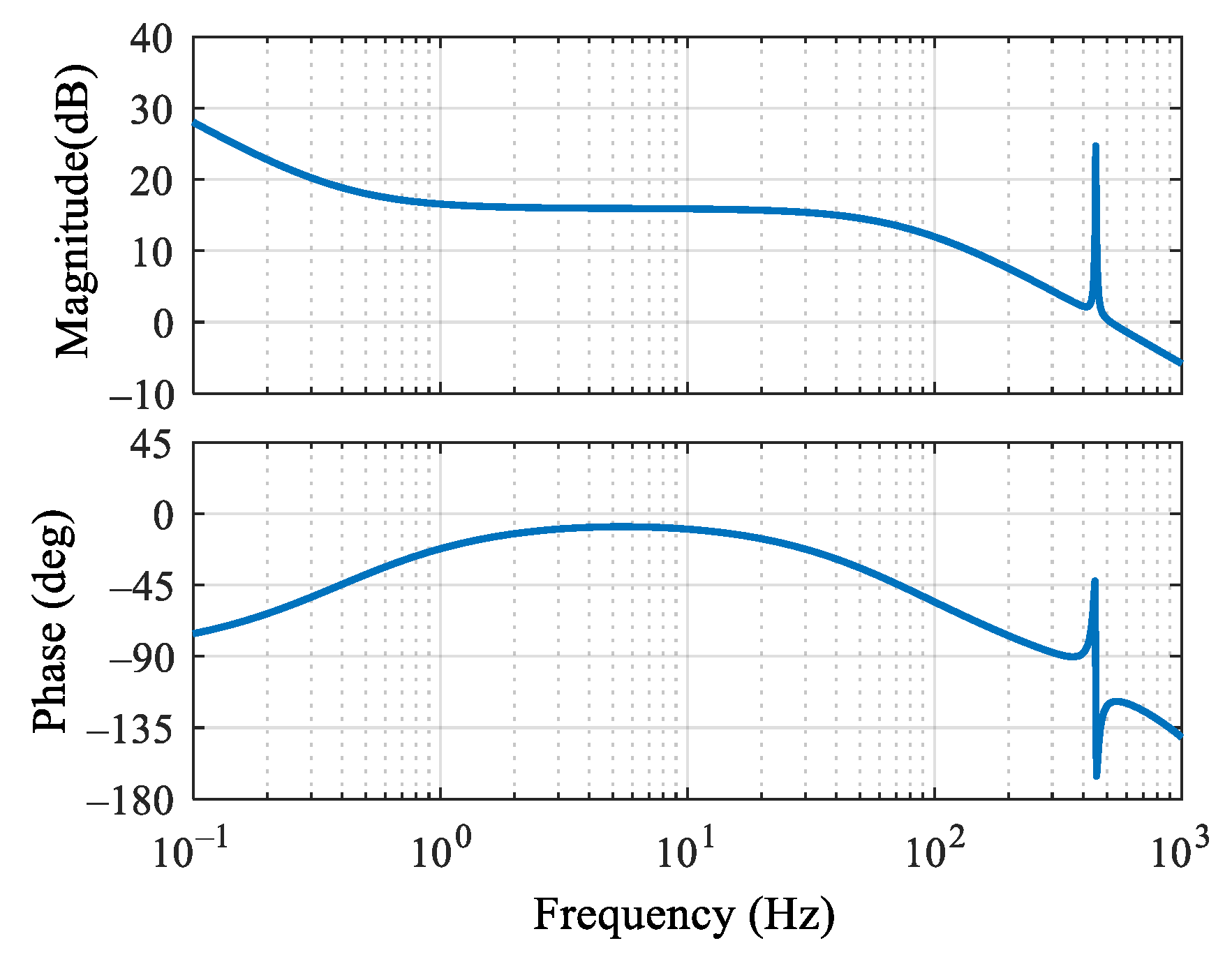
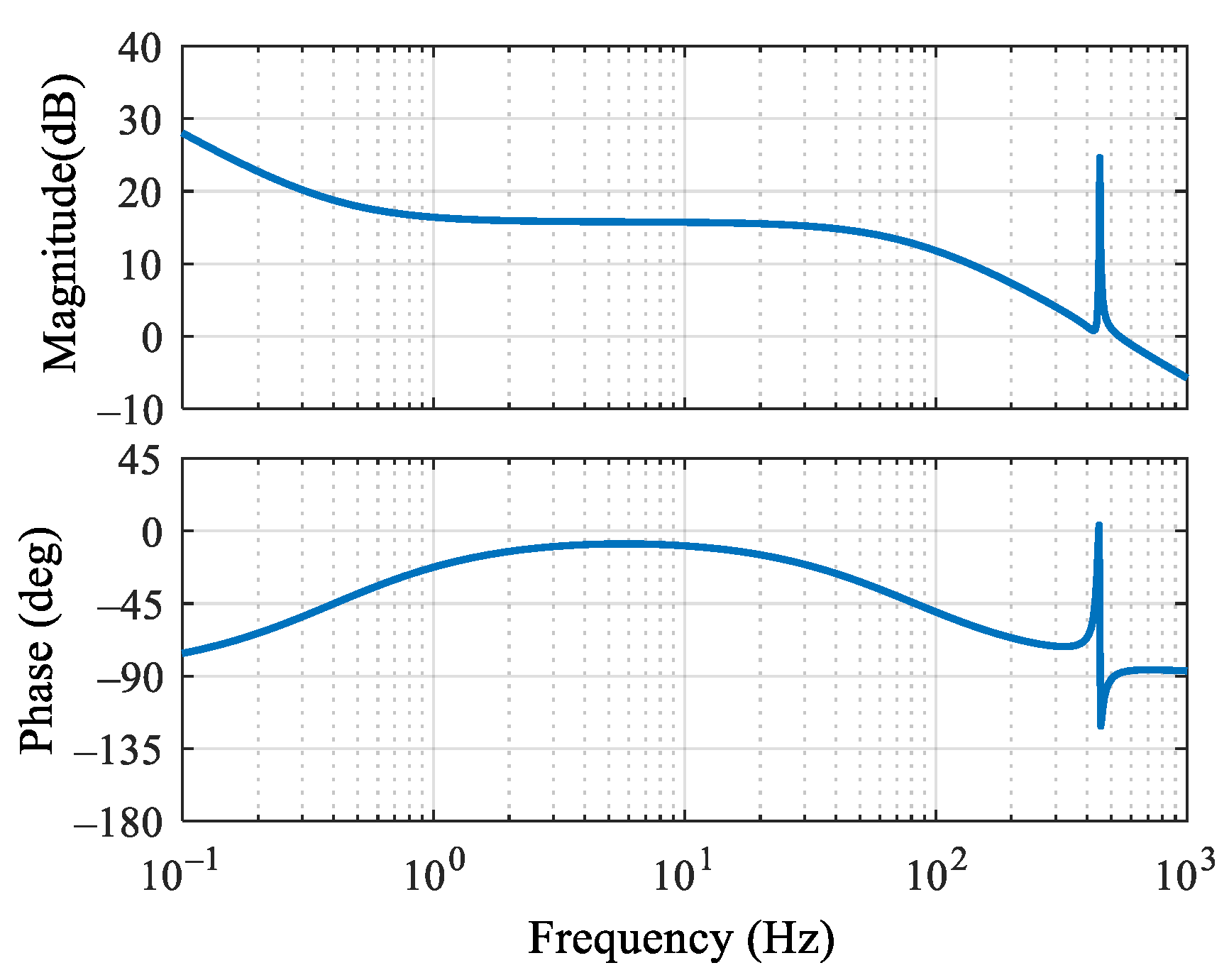
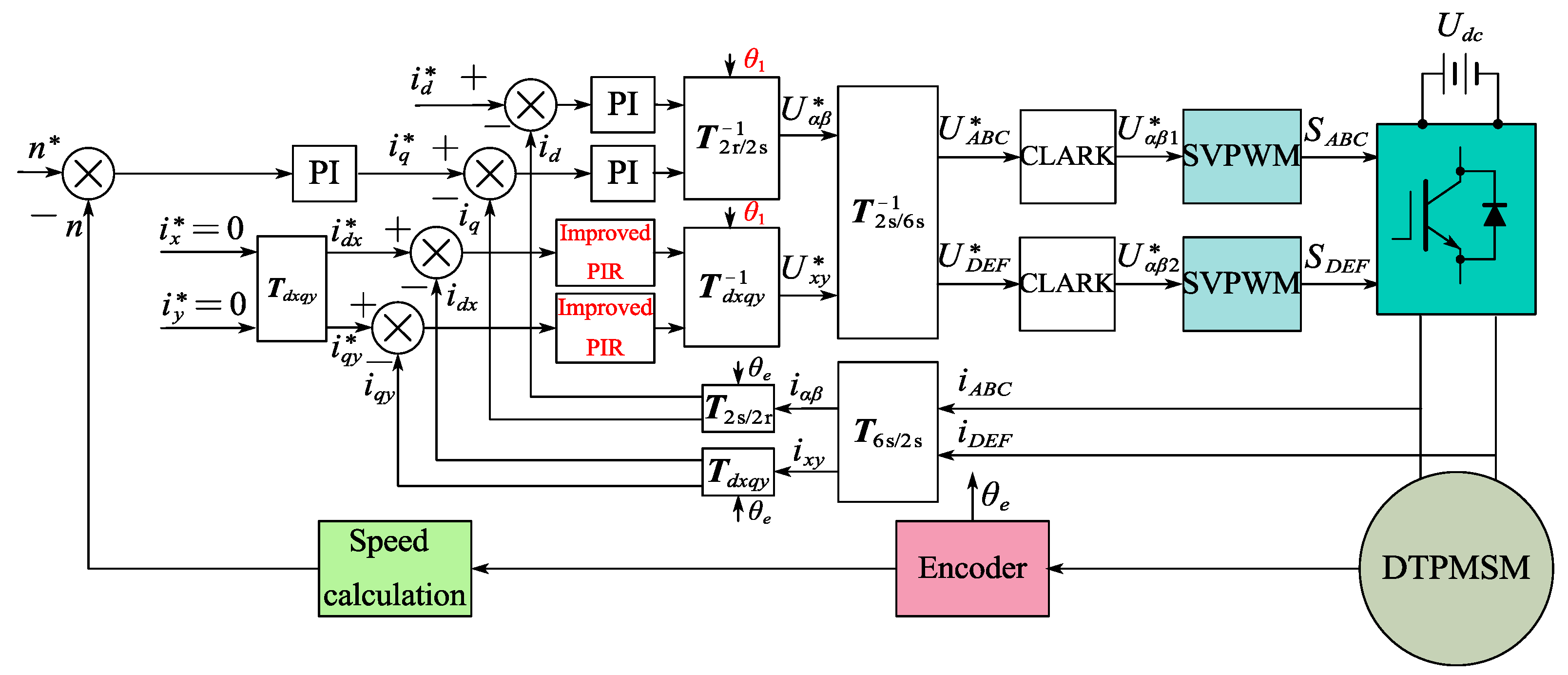

| Parameters | Value | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pole number | 3 | PM flux linkage | 0.316 Wb |
| d-axis inductance | 9.36 mH | Rated phase current | 4 A |
| q-axis inductance | 20.76 mH | Rated speed | 1500 r/min |
| Leakage inductance | 1.32 mH | Rated power | 2.5 kW |
| Stator resistance | 0.68 Ω |
| Controllers | Traditional Dual PI Controllers | Traditional Dual PIR Controllers | Proposed Dual Improved PIR Controllers | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load | Light Load | Medium Load | Heavy Load | Light Load | Medium Load | Heavy Load | Light Load | Medium Load | Heavy Load | |
| Speed | ||||||||||
| 500 r/min | 16.64% | 14.63% | 13.07% | 4.67% | 3.94% | 2.31% | 5.08% | 3.82% | 2.28% | |
| 1000 r/min | 39.33% | 36.51% | 32.88% | 7.95% | 5.60% | 4.19% | 5.68% | 5.61% | 4.17% | |
| 1500 r/min | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7.69% | 5.72% | 5.08% | |
| Controllers | rcu | Response Time |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Dual PI Controllers | 12.83% | 1.25 s |
| Traditional Dual PIR Controllers | 0.08% | 0.48 s |
| Proposed Dual Improved PIR Controllers | 0.09% | 0.71 s |
| Controllers | Traditional Dual PI Controllers | Traditional Dual PIR Controllers | Proposed Dual Improved PIR Controllers | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load | Light Load | Medium Load | Heavy Load | Light Load | Medium Load | Heavy Load | Light Load | Medium Load | Heavy Load | |
| Speed | ||||||||||
| 500 r/min | 0.26% | 0.80% | 0.46% | 0.18% | 0.21% | 0.37% | −0.01% | 0.64% | 0.45% | |
| 1000 r/min | −0.03% | 0.51% | 0.21% | 0.23% | 0.73% | 0.26% | 0.69% | 0.64% | 0.30% | |
| 1500 r/min | * | * | * | * | * | * | 0.72% | 0.57% | −0.06% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Chen, M.; Li, B.; Sun, X.; Jiang, F. Harmonic Current Suppression of Dual Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Improved Proportional-Integral Resonant Controller. Energies 2025, 18, 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061340
Chen L, Chen M, Li B, Sun X, Jiang F. Harmonic Current Suppression of Dual Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Improved Proportional-Integral Resonant Controller. Energies. 2025; 18(6):1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061340
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lei, Min Chen, Bodong Li, Xinnan Sun, and Feng Jiang. 2025. "Harmonic Current Suppression of Dual Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Improved Proportional-Integral Resonant Controller" Energies 18, no. 6: 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061340
APA StyleChen, L., Chen, M., Li, B., Sun, X., & Jiang, F. (2025). Harmonic Current Suppression of Dual Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Improved Proportional-Integral Resonant Controller. Energies, 18(6), 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061340







