Identifying the Impact of New Digital Infrastructure on Urban Energy Consumption: Evidence from the Broadband China Strategy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Research on Factors Affecting Energy Consumption
2.2. Research on the Effects for Broadband China Pilot Policy
2.3. Application Research of the DID Model
3. Policy Background and Research Hypothesis
3.1. Policy Background for BCPP
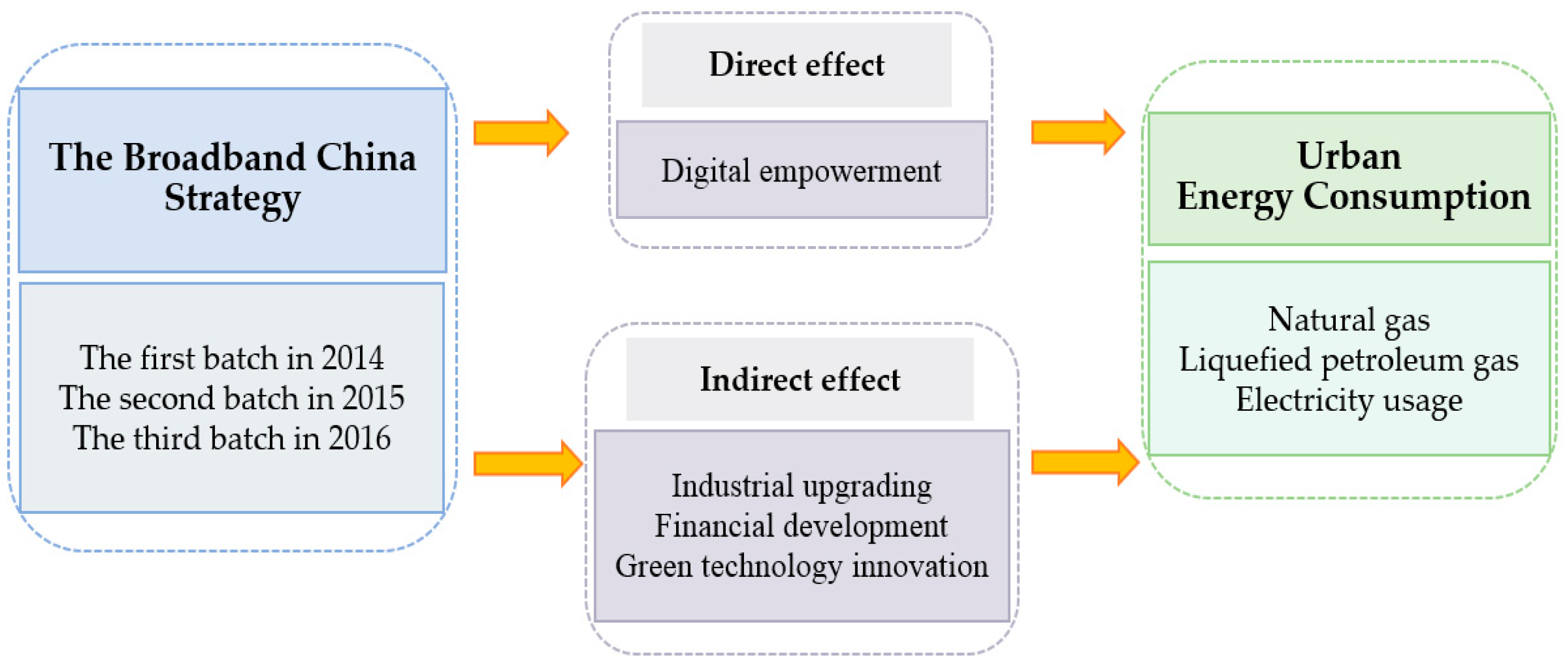
3.2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypothesis
4. Methodology, Variable Description, and Data Sources
4.1. The Framework of Multi-Phase DID Model
4.2. Variable Declaration
4.2.1. Explained Variable: Urban Energy Consumption (UEC)
4.2.2. Core Explanatory Variable: Broadband China Pilot Policy (BCPP)
4.2.3. Control Variables
4.3. Data Sources and Descriptive Statistics
5. Empirical Results and Analysis
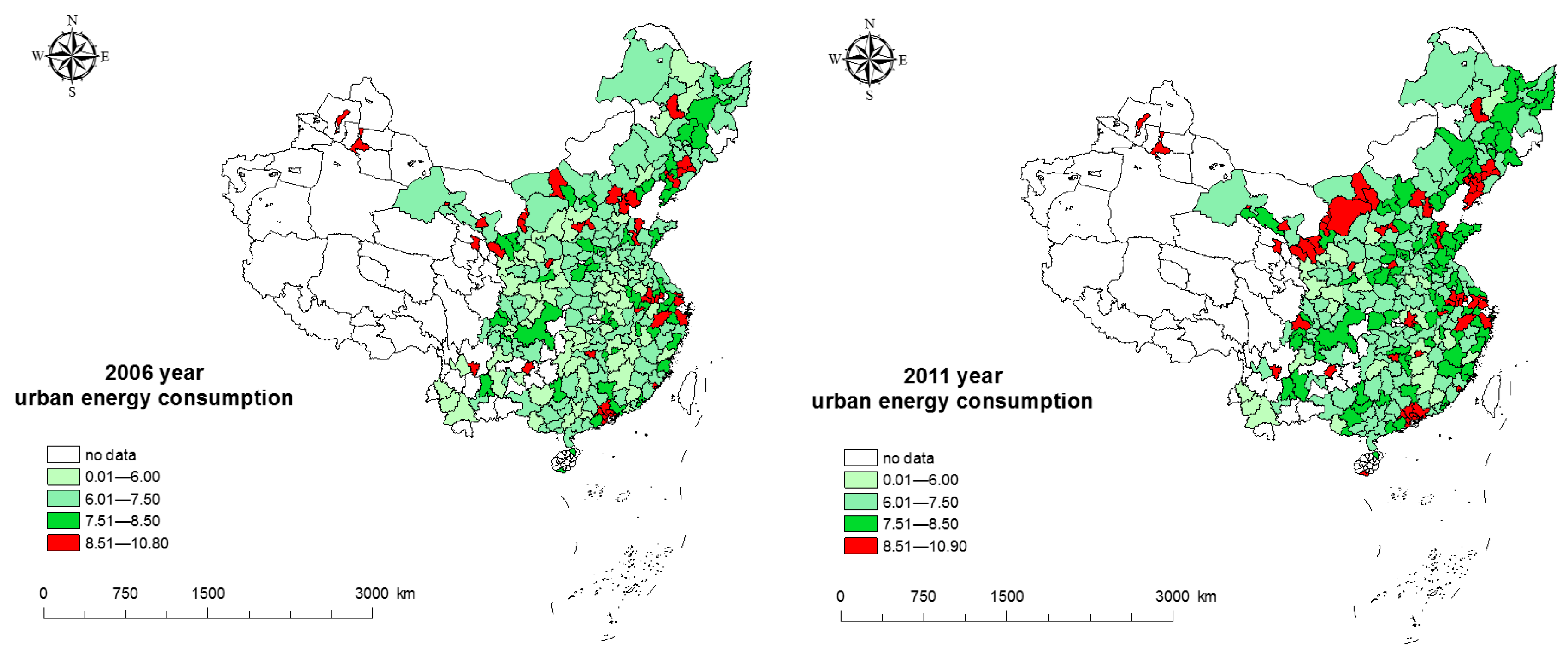
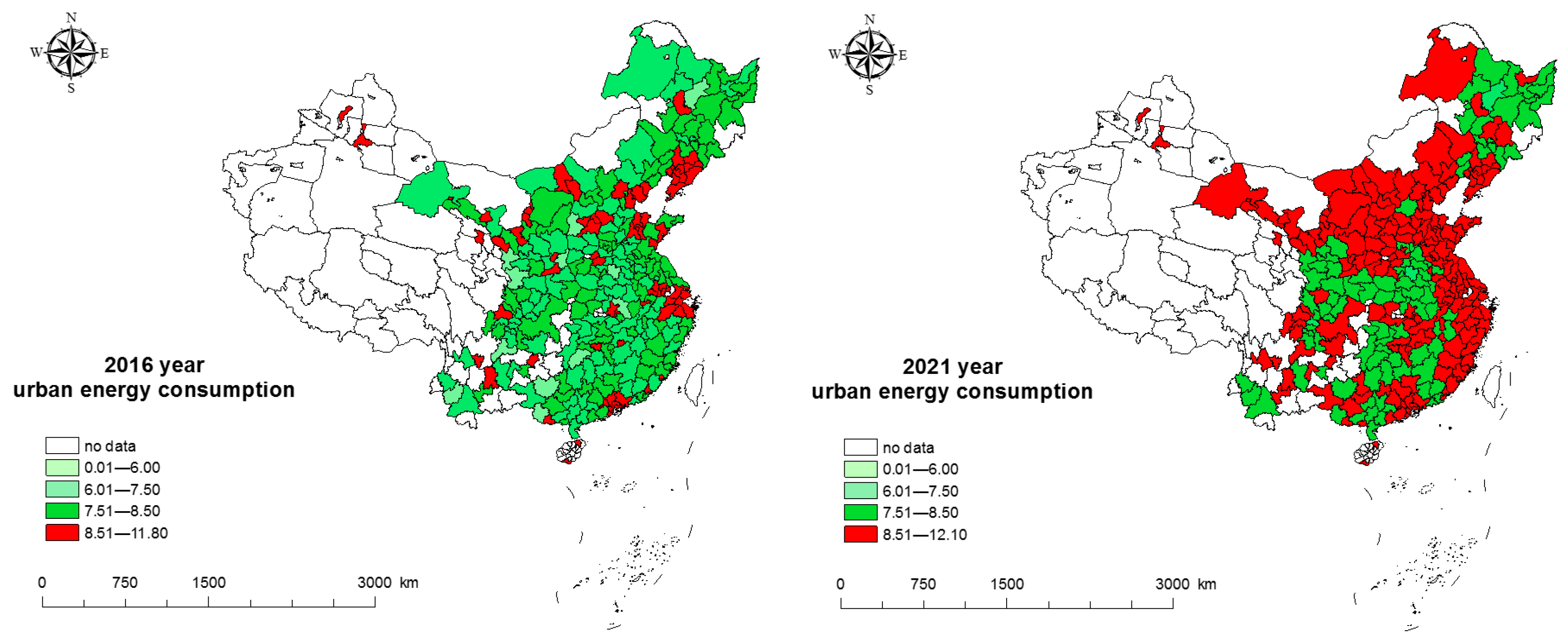
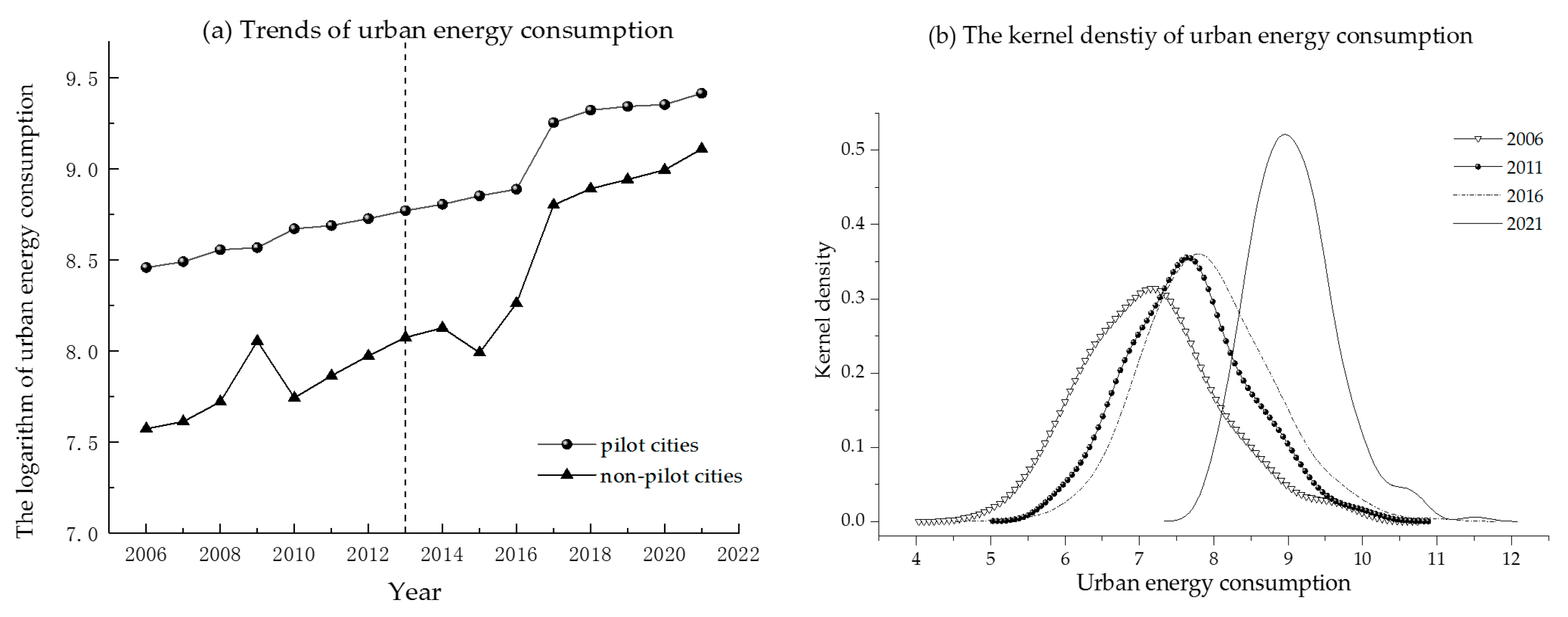
5.1. Temporal Evolution Trend for Urban Energy Consumption in China
5.2. Benchmark Regression Results
5.3. Robustness Tests
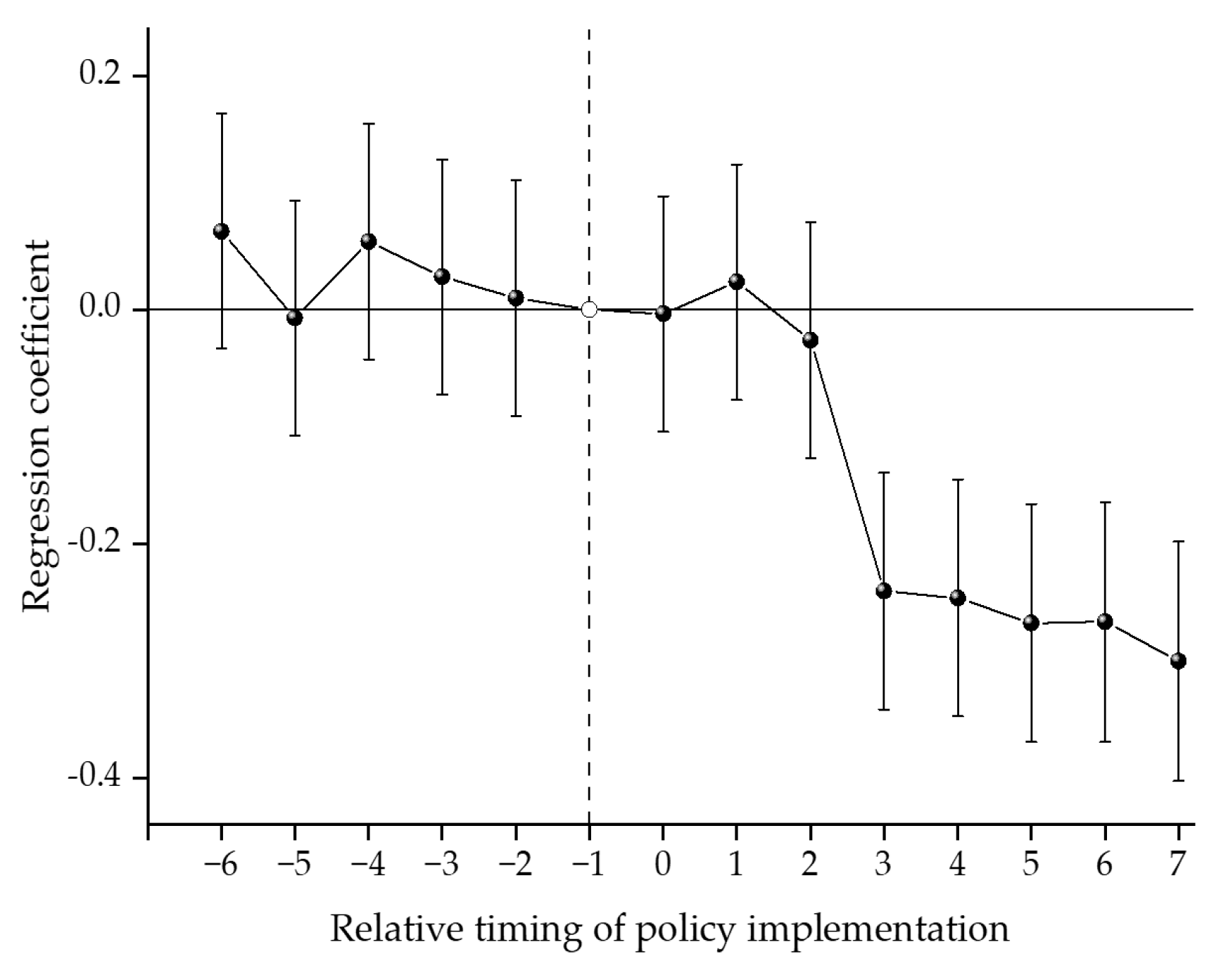
5.3.1. Parallel Trend Testing and Placebo Testing
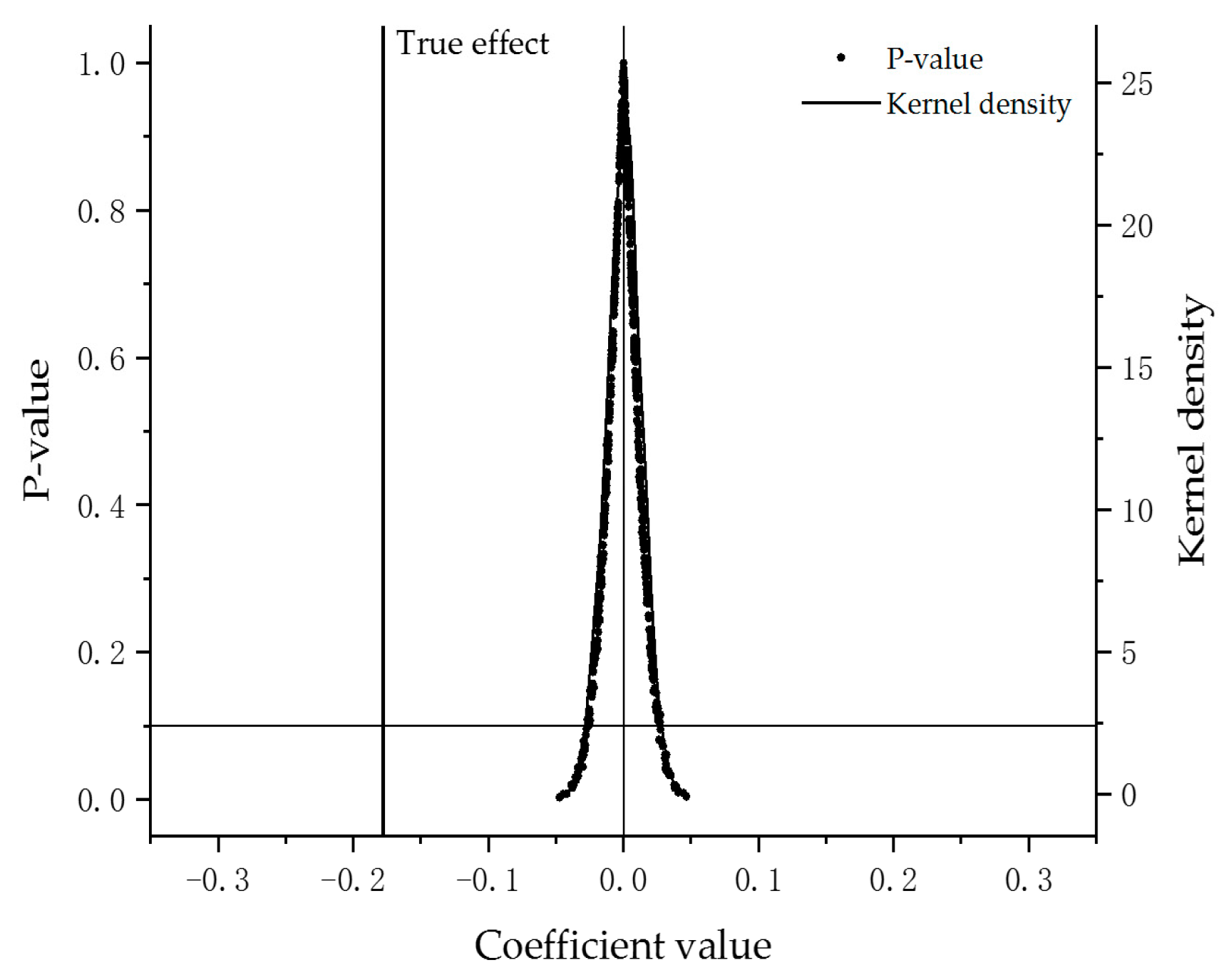
5.3.2. Policy Uniqueness Test
5.3.3. Other Robustness Tests
5.4. Heterogeneity Test
5.5. Mechanism Test
6. Conclusions and Policy Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Acheampong, A.O. Economic growth, CO2 emissions and energy consumption: What causes what and where? Energy Econ. 2018, 74, 677–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borck, R.; Mulder, P. Energy policies and pollution in two developing country cities: A quantitative model. J. Dev. Econ. 2024, 171, 103348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lai, Y.; Hu, H. The effect of technological factors and structural change on China’s energy intensity: Evidence from dynamic panel models. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 64, 101518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; He, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Wei, Z.; Li, K.; Li, M. A novel deep reinforcement learning-based predictive energy management for fuel cell buses integrating speed and passenger prediction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 100, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, S.; Jin, H.; Lu, Y. The impact of energy regulation on energy intensity and energy structure: Firm-level evidence from China. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 59, 101351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc-Ata, N.; Proskuryakova, L.N. The contribution of energy policies to green energy transition in the Asia-Pacific region. Renew Energy 2024, 237, 121797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Yu, Y.; Ge, L.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Z. The role of digital infrastructure construction on green city transformation: Does government governance matters? Cities 2024, 155, 105462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, L.; Gong, B.; Yan, Z.; Hu, P. Does broadband internet infrastructure mitigate firm-level economic policy uncertainty? Evidence from the Broadband China Pilot Policy. Econ. Lett. 2023, 232, 111325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Feng, C. How does internet development drive the sustainable economic growth of China? Evidence from internal-structural perspective of green total-factor productivity. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 887, 164125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulqadir, I.A.; Asongu, S.A. The asymmetric effect of internet access on economic growth in sub-Saharan Africa. Econ. Anal. Policy 2022, 73, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Hu, H.; Feng, D.; He, X. How does broadband infrastructure promote entrepreneurship in China: Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment. Telecommun. Policy 2022, 46, 102440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, M.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, J. Does New Digital Infrastructure Promote the Transformation of the Energy Structure? The Perspective of China’s Energy Industry Chain. Energies 2022, 15, 8784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Qing, H.; Hu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Wen, C. The impact of digital infrastructure on industrial ecology: Evidence from broadband China strategy. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 447, 141589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardi, I.; Afjal, M.; Can, M.; Idroes, G.M.; Noviandy, T.R.; Idroes, R. Shadow economy, energy consumption, and ecological footprint in Indonesia. Sustain. Futures 2024, 8, 100343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Mahalik, M.K.; Shah, S.H.; Sato, J.R. Time-varying analysis of CO2 emissions, energy consumption, and economic growth nexus: Statistical experience in next 11 countries. Energy Policy 2016, 98, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hondroyiannis, G.; Papapetrou, E.; Tsalaporta, P. Sustainable energy consumption and finance in the presence of risks: Towards a green economy. Renew. Energy 2024, 237, 121565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Shan, H. Impacts of industrial structures reconstructing on carbon emission and energy consumption: A case of Beijing. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodny, J.; Tutak, M. Analysis of the efficiency and structure of energy consumption in the industrial sector in the European Union countries between 1995 and 2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topcu, M.; Payne, J.E. The financial development–energy consumption nexus revisited. Energy Source Part B 2017, 12, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhou, X. Impact of green finance on renewable energy development: A spatiotemporal consistency perspective. Renew. Energy 2023, 204, 320–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Hoffmann, C. From investment to impact: The role of green finance and technological innovation on German energy transition. Renew. Energy 2024, 237, 121665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraparaju, S.K.; Samykano, M.; Dhivagar, R.; Natarajan, S.K.; Ghazali, M.F. Synergizing environmental and technological advances: Discarded transmission oil and paraffin wax as a phase change material for energy storage in solar distillation as a step towards sustainability. J. Energy Storage 2024, 85, 111046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamaruzzaman, M. Driving energy transition in BRI nations: The role of education, globalization, trade liberalization, and financial deepening—A comprehensive linear and nonlinear approach. Energy Strategy Rev. 2025, 57, 101620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voumik, L.C.; Rahman, M.H.; Md, H.; Md, M.; Ridwan, M.; Akter, S.; Raihan, A. Toward a sustainable future: Examining the interconnectedness among Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), urbanization, trade openness, economic growth, and energy usage in Australia. Reg. Sustain. 2023, 4, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraya, A.-A.S.; Handoyo, R.D.; Ibrahim, H.; Yusuf, A.A. Determinants of households’ energy consumption in Kebbi State Nigeria. Cogent. Econ. Financ. 2023, 11, 2242731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guta, D.; Zerriffi, H.; Baumgartner, J.; Jain, A.; Mani, S.; Jack, D.; Cater, E.; Shen, G.; Orgill-Meyer, J.; Rosenthal, J.; et al. The impact of LPG consumption on cooking energy efficiency: Evidence from rural Indian household panel data. World Dev. Perspect. 2024, 36, 100627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Liu, X.; Long, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, G. Spatial agglomeration and energy efficiency: Evidence from China’s manufacturing enterprises. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 135109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, T.; Tsai, P. Fuel poverty in Summer: An empirical analysis using microdata for Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X. Broadband and economic growth in China: An empirical study during the COVID-19 pandemic period. Telemat. Inform. 2021, 58, 101533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tao, Y.; Nie, C. Does broadband infrastructure boost firm productivity? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Financ. Res. Lett. 2022, 48, 102886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, L.; Li, X. Does digital infrastructure exacerbate income inequality? Evidence from the Broadband China Strategy. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2024, 72, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhong, S.; Sun, B. Blessing or curse? The effect of broadband Internet on China’s inter-city income inequality. Econ. Anal. Policy 2021, 72, 626–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zheng, S.; Zhou, L. Broadband internet and enterprise innovation. China Econ. Rev. 2022, 74, 101802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Shao, Y.; Liu, P. Research on the Impact of Digital Economy on Environmental Pollution Management—A Quasi-Natural Experiment from the “Broadband China” Pilot Policy. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2024, 33, 4311–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Wang, X.; Miao, M. Network infrastructure and corporate environmental performance: Empirical evidence from “Broadband China”. Energy Econ. 2024, 131, 107393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Guo, F. How digital infrastructure development affects residents’ health: A quasi-natural experiment based on the “Broadband China” strategy. Cities 2025, 157, 105611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Ma, B.; Zhang, H. Impact of fast internet access on employment: Evidence from a broadband expansion in China. China Econ. Rev. 2023, 81, 102038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Duan, Y.; Ward, M.R. The effect of broadband internet on divorce in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 139, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Wang, H.; Wei, J. Internet technology and regional financial fraud: Evidence from Broadband expansion in China. J. Appl. Econ. 2023, 26, 2281167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, D.; Dube, A.; Lindner, A.; Zipperer, B. The Effect of Minimum Wages on Low-Wage Jobs*. Q. J. Econ. 2019, 134, 1405–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hou, L.; Hu, L.; Cai, W.; Xiao, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, C. Do areas with a higher proportion of single-person households save more on electricity consumption? Evidence from the difference-in-differences model. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2023, 77, 101350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtele, E.; Beria, P.; Tolentino, S. The evaluation of competition effect on rail fares using the difference-in-difference method through symmetric and lagged spans. J. Rail Transp. Plan. Manag. 2024, 32, 100484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zeng, X.; Yu, H.; Chen, H. Big data development and labor income share: Evidence from China’s national big data comprehensive pilot zones. Econ. Anal. Policy 2024, 84, 1415–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, K.; Treku, D.; Sarnie, R.; Hoover, J. What does ESG risk premia tell us about mutual fund sustainability levels: A difference-in-differences analysis. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 57, 104262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zeng, D.; Lee, C.-C. Impact of smart city pilot on energy and environmental performance: China-based empirical evidence. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 97, 104731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Yu, F.; Ji, L.; Wang, X. New energy demonstration city and urban pollutant emissions: An analysis based on a spatial difference-in-differences model. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 91, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tan, X.; Liu, Y.; He, C. Exploring the effect of emission trading system on marginal abatement cost-based on the frontier synthetic difference-in-differences model. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Wang, M.; Pu, C. Effect of marine ecological compensation policy on coastal water pollution: Evidence from China based on a multiple period difference-in-differences approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 923, 171469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-S.; Lee, T.-H.; Park, I.-S. Net Effect of Short-Term Smoking Cessation on Mental Health Changes: Inverse Probability of Treatment Weighting and Difference-in-Differences Method. Int. J. Ment. Health Promot. 2024, 26, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zheng, J. Effective policy research of county and township health sector integration in China: Empirical evidence from the difference-in-differences model. Soc. Sci. Med. 2024, 348, 116797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braghieri, L.; Levy, R.; Makarin, A. Social Media and Mental Health. Am. Econ. Rev. 2022, 112, 3660–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, S. The impact of industrial transformation and upgrading on fossil energy elasticity in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, D.; Gu, J. Does increasing income have a positive impact on energy consumption? New evidence from China. Sustain. Futures 2024, 7, 100139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos, J.; Borunda, M.; Garduno, R.; García-Beltrán, C.D. Spatial Intelligent Estimation of Energy Consumption. Lect. Notes Comput. 2024, 15247, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, C.; Bai, T.; Xu, D. The impact of industry-favoring land allocation strategy on urban carbon emissions: A city-level empirical study in China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Huang, L. How Does Environmental Protection Tax Affect Urban Energy Consumption in China? New Insights from the Intensity Difference-in-Differences Model. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Sun, X. Research on Technology Spillover of Digital Economy Affecting Energy Consumption Intensity in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, T.; Levine, R.; Levkov, A. Big Bad Banks? The Winners and Losers from Bank Deregulation in the United States. J. Financ. 2012, 65, 1637–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman-Bacon, A. Difference-in-Differences with Variation in Treatment Timing. J. Econom. 2021, 225, 254–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Feng, Y.; Peng, D.Y. A green path towards sustainable development: The impact of low-carbon city pilot on energy transition. Energy Econ. 2022, 115, 106343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.B.; Wang, Y.J.; Luan, B.J.; Zou, H.; Wang, J. The energy intensity reduction effect of developing digital economy: Theory and empirical evidence from China. Energy Econ. 2023, 128, 107193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Definition | Sample Size | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UEC | Urban energy consumption | 4464 | 7.884 | 1.224 | 4.038 | 12.141 |
| Broad | Broadband China Pilot Policy | 4464 | 0.165 | 0.372 | 0 | 1 |
| GDP | Economic development level | 4464 | 10.496 | 0.709 | 8.150 | 13.056 |
| Exp | Total consumption expense | 4464 | 1.630 | 0.831 | 0.001 | 4.822 |
| Pop | Urban registered population | 4464 | 5.892 | 0.683 | 2.868 | 8.136 |
| Urban | Urbanization rate | 4464 | 0.418 | 0.107 | 0.109 | 0.693 |
| Gov | Government fiscal support | 4464 | 0.181 | 0.094 | 0.043 | 1.485 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broad | −0.254 *** | −0.201 *** | −0.187 *** | −0.178 *** | −0.178 *** |
| (0.023) | (0.023) | (0.022) | (0.023) | (0.054) | |
| GDP | 0.680 *** | 0.565 *** | 0.589 *** | 0.589 *** | |
| (0.037) | (0.038) | (0.039) | (0.081) | ||
| Exp | −0.171 *** | −0.75 * | −0.040 | −0.040 | |
| (0.037) | (0.039) | (0.040) | (0.075) | ||
| Pop | −0.654 *** | −0.626 *** | −0.626 *** | ||
| (0.100) | (0.101) | (0.201) | |||
| Urban | 1.542 *** | 1.532 *** | 1.532 *** | ||
| (0.167) | (0.167) | (0.299) | |||
| Gov | 0.488 *** | 0.488 | |||
| (0.151) | (0.302) | ||||
| _Cons | 7.081 *** | 0.750 *** | 5.042 *** | 4.552 *** | 4.552 *** |
| (0.023) | (0.345) | (0.720) | (0.735) | (1.466) | |
| Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 4464 | 4464 | 4464 | 4464 | 4464 |
| R2 | 0.729 | 0.750 | 0.758 | 0.758 | 0.758 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broad | −0.173 *** | −0.178 *** | −0.176 *** | −0.180 *** | −0.171 *** | −0.164 *** |
| (0.023) | (0.023) | (0.023) | (0.054) | (0.054) | (0.054) | |
| City_DID | −0.050 ** | −0.047 | ||||
| (0.023) | (0.048) | |||||
| Data_DID | 0.003 | 0.019 | ||||
| (0.025) | (0.066) | |||||
| Trade_DID | −0.058 * | −0.078 | ||||
| (0.033) | (0.063) | |||||
| Green_DID | −0.241 ** | −0.259 ** | ||||
| (0.117) | (0.111) | |||||
| Energy_DID | −0.118 * | −0.120 ** | ||||
| (0.061) | (0.061) | |||||
| _Cons | 4.535 *** | 4.548 *** | 4.413 *** | 4.452 *** | 4.365 *** | 4.031 *** |
| (0.735) | (0.736) | (0.739) | (1.484) | (1.464) | (1.455) | |
| Control variable | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 4464 | 4464 | 4464 | 4464 | 4464 | 4464 |
| R2 | 0.759 | 0.758 | 0.758 | 0.759 | 0.759 | 0.761 |
| Variable | PSM-DID | Replacing the Variable UEC | Excluding the Municipalities | Lagging Control Variables | Adjusting the Sample Period | Excluding the Expected Effect | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
| Broad | −0.167 *** | −0.146 *** | −0.175 *** | −0.024 *** | −0.178 *** | −0.189 *** | −0.140 *** | −0.058 ** |
| (0.023) | (0.028) | (0.023) | (0.004) | (0.023) | (0.023) | (0.024) | (0.023) | |
| Broad_F1 | −0.034 | |||||||
| (0.036) | ||||||||
| Broad_F2 | 0.007 | |||||||
| (0.032) | ||||||||
| _Cons | 3.448 *** | 8.362 *** | 4.120 *** | 0.642 | 4.509 *** | 4.622 *** | 7.575 *** | 2.229 *** |
| (0.775) | (0.992) | (0.756) | (0.121) | (0.737) | (0.776) | (0.900) | (0.493) | |
| Control variable | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 4407 | 2949 | 4458 | 4464 | 4400 | 4185 | 3348 | 4464 |
| R2 | 0.763 | 0.699 | 0.759 | 0.304 | 0.760 | 0.7537 | 0.711 | 0.749 |
| Testing Type | Estimator | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Treated earlier vs. later | −0.0596 | 0.0335 |
| Treated later vs. earlier | 0.2500 | 0.0254 |
| Treated vs. never treated | −0.2742 | 0.9410 |
| Population Size | Geographical Location | Resource Endowment | Digital Inclusive Finance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
| Large | Others | Hu_Line East | Hu_Line West | Non_Res | Res_Based | High_Fin | Low_Fin | |
| Broad | −0.151 *** | −0.134 | −0.215 *** | −0.776 | −0.219 *** | −0.098 | −0.206 *** | −0.112 |
| (0.057) | (0.123) | (0.056) | (0.270) | (0.062) | (0.105) | (0.066) | (0.096) | |
| _Cons | 7.282 *** | 0.359 | 4.354 *** | 1.030 | 8.935 *** | 0.235 | 8.837 *** | −4.721 * |
| (1.742) | (2.943) | (1.496) | (4.659) | (2.115) | (2.472) | (1.559) | (2.536) | |
| Control variable | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 2848 | 1616 | 4128 | 336 | 2688 | 1776 | 2224 | 2240 |
| R2 | 0.756 | 0.786 | 0.777 | 0.673 | 0.790 | 0.730 | 0.744 | 0.786 |
| Variable | Industrial Upgrading | Financial Development | Green Technology Innovation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indus | UEC | UEC | Finan | UEC | UEC | Green | UEC | UEC | |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | |
| Broad | 0.026 ** | 0.139 *** | 0.168 *** | ||||||
| (0.013) | (0.012) | (0.021) | |||||||
| Broad_high | −0.222 *** | −0.136 *** | −0.250 *** | −0.149 *** | −0.351 *** | −0.245 *** | |||
| (0.029) | (0.028) | (0.027) | (0.027) | (0.027) | (0.026) | ||||
| Broad_low | −0.059 | −0.009 | 0.079 | −0.072 | −0.011 | −0.033 | |||
| (0.060) | (0.057) | (0.106) | (0.101) | (0.073) | (0.070) | ||||
| _Cons | 6.928 *** | 7.081 *** | 4.498 *** | −2.875 *** | 7.081 *** | 4.417 *** | 0.093 *** | 7.081 *** | 4.564 *** |
| (0.423) | (0.023) | (0.739) | (0.378) | (0.023) | (0.738) | (0.681) | (0.023) | (0.734) | |
| Control variable | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 4464 | 4464 | 4464 | 4464 | 4464 | 4464 | 4464 | 4464 | 4464 |
| R2 | 0.618 | 0.725 | 0.756 | 0.382 | 0.727 | 0.756 | 0.692 | 0.733 | 0.756 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Meng, Q.; Huang, J. Identifying the Impact of New Digital Infrastructure on Urban Energy Consumption: Evidence from the Broadband China Strategy. Energies 2025, 18, 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18051072
Xu X, Meng Q, Huang J. Identifying the Impact of New Digital Infrastructure on Urban Energy Consumption: Evidence from the Broadband China Strategy. Energies. 2025; 18(5):1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18051072
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xianpu, Qiqi Meng, and Jing Huang. 2025. "Identifying the Impact of New Digital Infrastructure on Urban Energy Consumption: Evidence from the Broadband China Strategy" Energies 18, no. 5: 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18051072
APA StyleXu, X., Meng, Q., & Huang, J. (2025). Identifying the Impact of New Digital Infrastructure on Urban Energy Consumption: Evidence from the Broadband China Strategy. Energies, 18(5), 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18051072








