Abstract
Hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) is an effective method for processing wet sewage sludge without prior drying. This study investigates the influence of temperature (200 °C and 210 °C), residence time (15 and 30 min), and pH (neutral and acidic, pH = 2) on the properties of hydrochar and the liquid fraction. Increasing process severity enhanced carbonization, increasing carbon content from 36% in raw sludge to 43% in acidified samples. Under neutral HTC conditions, ash content exceeded 40%, while acidic conditions reduced it to 28%, indicating mineral dissolution and transfer into the liquid phase. Hydrogen and nitrogen contents remained within 3–6%, contributing to the fuel characteristics. The solid yield decreased from 1.04% in raw sludge to 0.22–0.37% after HTC, confirming intensified organic matter conversion. Acidic conditions significantly improved nutrient release to the liquid phase. PO43− concentration increased from 337 to 375 mg/L under neutral conditions to over 675 mg/L, while P2O5 exceeded 509 mg/L. Conductivity rose from approximately 2.0 to 4.25 mS/cm, reflecting high ionic content. These results highlight the potential of the liquid fraction as a nutrient-rich stream that can be used for fertilizer recovery, particularly via struvite precipitation, and confirm that precise HTC parameter control supports resource recovery in line with circular economy principles.
1. Introduction
Around the world, wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) operate at maximum capacity, serving large populations and generating thousands of tons of sewage sludge each day, which requires proper management [1]. It is estimated that more than 45 million dry tons of sewage sludge are produced annually, with Europe, East Asia, and North America as the leading contributors [2,3]. The volume of generated sludge is expected to increase further due to rapid urbanization, population growth, and the modernization of wastewater treatment technologies that improve water quality but simultaneously intensify sludge production.
Managing sewage sludge is a key environmental and public health issue, closely linked to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, particularly SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation), SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production), and SDG 13 (Climate Action) [4]. Beyond its volume, sludge contains harmful substances, including heavy metals (e.g., arsenic, lead), pharmaceutical residues, excess nutrients, and pathogenic microorganisms [5]. Improper handling can lead to soil and groundwater contamination, eutrophication, and health risks.
Undigested sewage sludge consists mainly of microbial biomass and organic matter such as fats, proteins, and cellulose [6]. This sludge often contains a diverse array of organic contaminants, such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, polychlorinated biphenyls, pesticides, hormones, and pharmaceutical residues [6]. It also accumulates toxic heavy metals, including zinc, copper, cadmium, lead, arsenic, nickel, mercury, selenium, and chromium, and can host various pathogenic microorganisms. Due to this complex and hazardous composition, the application of untreated sewage sludge to agricultural soils raises serious environmental and public health concerns. Contaminants can infiltrate the soil and groundwater, potentially disrupting ecosystems and entering the food chain, thus posing risks to human health [7,8,9]. The elevated levels of heavy metals and organic pollutants significantly hinder the safe and direct use of sewage sludge as fertilizer without prior treatment [7,10].
In response, the European Union and other authorities have tightened restrictions on land application and disposal, promoting sustainable and resource-efficient strategies. As a result, research increasingly focuses on thermochemical conversion methods that reduce sludge volume, destroy hazardous components, and recover energy and nutrients such as phosphorus and nitrogen.
Hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) offers a sustainable and energy-efficient solution to the environmental and health challenges posed by undigested sewage sludge. As a thermochemical process conducted at moderate temperatures (160–250 °C) under autogenous pressure, HTC allows the direct treatment of wet biomass without prior drying, making it particularly suitable for high-moisture waste such as sewage sludge [11,12]. Through HTC, sewage sludge is transformed into a carbon-rich solid product known as hydrochar, along with liquid and gaseous by-products. Hydrochar exhibits a higher energy content than that of the raw sludge, positioning it as a promising renewable biofuel [11,13,14]. Additionally, HTC significantly improves the dewaterability of sludge, which enhances its manageability during transportation and post-processing.
In addition to hydrochar, HTC produces a nutrient-rich liquid phase whose composition depends on temperature, pressure, and residence time [15,16,17]. It typically contains volatile fatty acids, nutrients (e.g., N, P, K), and metals (e.g., Ca, Fe, Zn). Due to its organic and metal contents, post-treatment such as distillation is required before reuse [18]. Nevertheless, the liquid’s nutrient profile makes it a potential secondary resource for fertilizer recovery or methane production via anaerobic digestion [15]. Likewise, hydrochar may be utilized in soil improvement, carbon sequestration, or pollutant adsorption [19,20]. However, further research is needed to optimize HTC for diverse feedstocks and to develop efficient, scalable post-treatment methods to enable the full valorization of both product phases.
Therefore, the objective of this study was to assess the effect of temperature and residence time on the properties of hydrochar and the accompanying liquid phase derived from undigested sewage sludge. The process was carried out at 200 °C and 210 °C for 15 and 30 min under acidic conditions (pH = 2) to evaluate how strong acidification influences phosphorus and metal behavior. Chemical and physical analyses were used to determine changes in energy content, ash content, and nutrient distribution, with particular attention to phosphorus dynamics in the liquid fraction.
The novelty of this study lies in the simultaneous evaluation of both solid (hydrochar) and liquid (post-HTC) products, providing a comprehensive understanding of how process parameters affect energy content, nutrient recovery, and contaminant partitioning. By analyzing both fractions under identical operating conditions, this research identifies interdependencies that are often overlooked when only the solid phase is examined. However, the simultaneous evaluation also revealed certain restrictions and challenges. The liquid phase, while rich in nutrients, may contain elevated concentrations of heavy metals and organic contaminants, necessitating post-treatment before reuse or discharge. Likewise, hydrochar requires assessment of its metal content and stability prior to application as a soil amendment or fuel. Therefore, further optimization of process conditions and purification methods is recommended to ensure safe and efficient resource recovery within the circular economy framework.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
Samples of undigested sewage sludge (SS) were collected from the Smolnica Wastewater Treatment Plant (Poland) and then stored in plastic containers at 4 °C to limit the biodegradation process. A portion of the raw sewage sludge was dried and prepared for further comparative analyses. The analysis of the collected sewage sludge was carried out by an external laboratory, WESSLING Poland Ltd., Kraków, Poland. The physicochemical properties of the collected material are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Physicochemical properties of sewage sludge.
2.2. Hydrothermal Carbonization
The hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) system employed in this study features a Zipperclave® batch mixing reactor (Parker Autoclave Engineers, Erie, PA, USA) with a volume capacity of 1000 mL. The apparatus includes a removable heating jacket, a cooling system, and a control panel enabling precise adjustment of temperature, pressure, and stirring speed (Figure 1). Further technical details of the setup can be found in a previous publication [21,22].
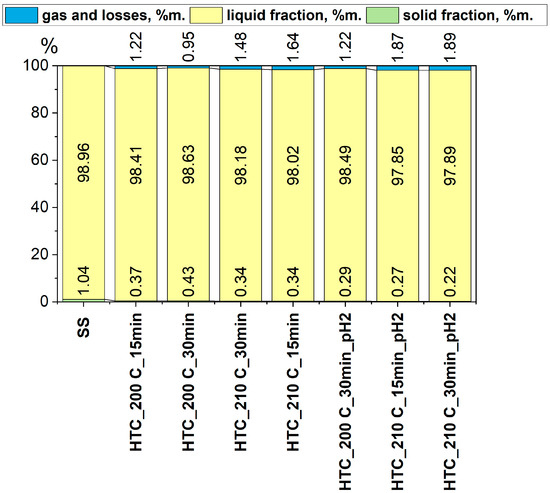
Figure 1.
Product distribution.
In each experiment, 750 g of sewage sludge was introduced into the reactor, and the system was hermetically sealed. The HTC process was conducted at two temperature levels, 200 °C and 210 °C, with reaction durations of 15 and 30 min. Tests were performed under both natural pH conditions and acidic conditions adjusted to pH = 2, to test if strong acidification significantly alters reaction pathways and thus indicate the potential relevance of pH control in process optimization. During the reaction, the contents were continuously stirred at a speed of 150 rpm.
After the reaction time had elapsed, the heating was stopped, the jacket was removed, and water cooling was activated to reduce the reactor temperature to ambient conditions. The processed material was then withdrawn from the reactor, and the solid and liquid phases were separated via filtration. The resulting hydrochar was dried and stored in plastic containers for subsequent analyses. Each hydrochar sample was labeled using a code that reflects the process temperature, residence time, and pH conditions; for instance, HTC_210C_30min_pH2 indicates a hydrochar sample obtained at 210 °C after 30 min of carbonization at pH 2.
2.3. Analytical Methods
The moisture content (M), ash content (Ash), and volatile matter content (VM) were analyzed using a 5E-MAC6710 Proximate Analyser-TGA (Changsha Kaiyuan Instruments Co., Ltd., Changsha, China), following the guidelines of ASTM D7582 [23] and ISO 17246:2010 [24]. The elemental composition—specifically carbon (C), nitrogen (N), hydrogen (H), and sulfur (S)—was measured using a Truespec CHNS625 elemental analyzer (LECO, St. Joseph, MI, USA), in accordance with the PKN-ISO/TS 12902:2007 [25] standard. Due to the limited amount of available sample material, the higher heating value (HHV) was calculated using the empirical correlation proposed by Channiwala and Parikh [26]. The lower heating value (LHV) was subsequently derived from the HHV using the methodology provided by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency [27].
For the liquid sample, the following parameters were analyzed: pH, conductivity, PO4-P, PO43−, P2O5, COD, and total nitrogen (Ntot). Measurements of pH and conductivity were carried out using a multifunctional analyzer CX 461 (Elmetron, Zabrze, Poland) equipped with dedicated electrodes. The pH was measured with the IJ44A electrode, while conductivity was assessed using the ECF-1 electrode (both from Elmetron).
The concentrations of PO4-P, PO43−, P2O5, COD, and Ntot were determined using a Spectroquant Prove 100 spectrophotometer (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany), following the manufacturer’s test procedures:
- Total nitrogen (Ntot)—test no. 1.14763, based on ISO 23697-1 [28], which outlines the small-scale sealed tube method. The digestion process is in accordance with EN ISO 11905-1 [29], and nitrate determination follows DIN 38405-9 [30].
- Phosphates (PO4-P, PO43−, P2O5)—test no. 1.00798, aligned with EPA 365.2 + 3 [31], APHA 4500-P E [32], and DIN EN ISO 6878 [33].
- Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD)—test no. 1.01797, corresponding to DIN ISO 15705 [34] and comparable to EPA 410.4 [35], APHA 5220 D [36], and ASTM D1252-06 B [37].
A Spectroquant® TR 420 thermoreactor (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) was used to heat the samples prior to COD and Ntot analysis.
3. Results and Discussion
The mass balance of the hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) process for sewage sludge showed that the majority of the mass after the process was in the liquid fraction, which accounted for between 97.85% and 98.96% in all trials. Compared to the raw material (SS), where the solid fraction content was 1.04%, the proportion of this fraction in the samples subjected to HTC was significantly reduced, ranging from 0.22% to 0.37%. The lowest yield of the solid fraction was observed in samples treated at 210 °C for 30 min in an acidic environment (pH = 2), suggesting that such conditions promote intense decomposition of the solid fraction and the transfer of organic matter to the liquid phase. These results are consistent with previous literature [37].
Meanwhile, the share of the gaseous fraction and losses ranged from 0.87% to 1.89%, with the highest values also recorded for samples processed under acidic conditions. The increase in gas and loss share in the balance may indicate intensified decarboxylation and deamination reactions, leading to the emission of gases such as CO2, NH3, and trace amounts of hydrogen sulfide. In samples processed under neutral conditions, gas losses were lower, which may suggest a lesser degree of thermochemical degradation and retention of a greater amount of substances in the liquid phase. In earlier studies conducted by Czerwińska et al. [21], a similar trend was observed; the share of the gaseous fraction and losses decreased under more acidic conditions. This consistency suggests that the acidified environment limits decarboxylation and deamination reactions, resulting in reduced gas formation and a higher retention of compounds in the liquid phase.
3.1. Hydrochar
Figure 2 presents eight hydrochar samples obtained from the hydrothermal carbonization process. Sample I represents the raw material (sewage sludge), characterized by a heterogeneous structure and the presence of visible organic residues, while samples II–VIII are hydrochars produced under varying process conditions, differing in temperature, residence time, and pH of the reaction environment.
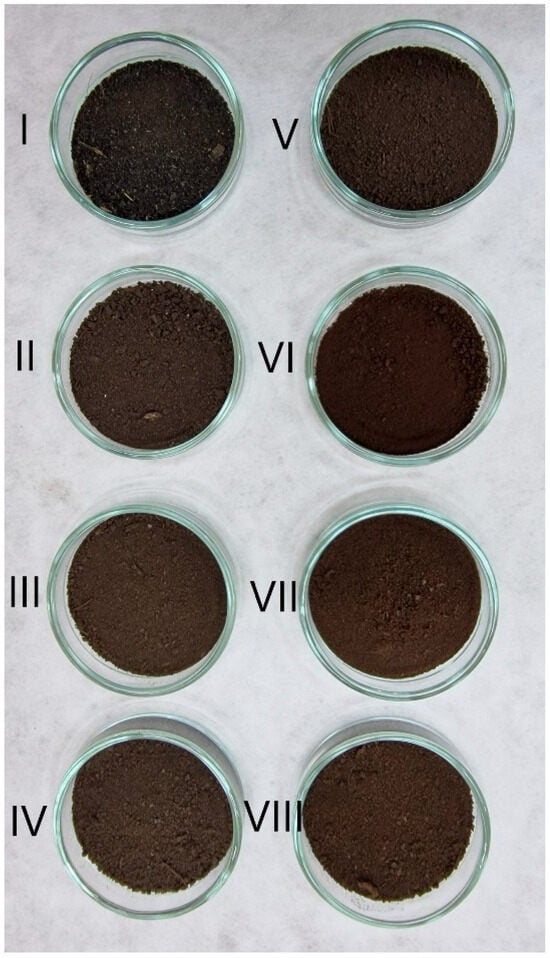

Figure 2.
Visual appearance of hydrochars and sewage sludge: I—SEWAGE SLUDGE, II—HTC_210C_30min; III—HTC_210C_15min; IV—HTC_200C_15min; V—HTC_200C_30min; VI—HTC_210C_30min_pH2; VII—HTC_210C_15min_pH2; VIII—HTC_200C_30min_pH2.
Samples processed under neutral conditions (II–V) show slight but noticeable variations in color and structure depending on process intensity. Increasing temperature and residence time resulted in progressively darker coloration and improved structural homogeneity, indicating a gradual increase in the degree of carbonization. The lightest material (sample IV) was obtained at 200 °C/15 min, whereas the darkest and most uniform one (sample II) resulted from treatment at 210 °C/30 min. Samples VI–VIII, produced under acidic conditions, show a finer, more compact structure and an even darker color, most pronounced in sample VI (210 °C/30 min/pH 2), suggesting more extensive degradation of organic matter. Lowering the pH enhances the overall efficiency of the HTC process, as confirmed by visible differences between acid-treated and neutral samples.
The observed differences in color, texture, and uniformity reflect the strong influence of HTC parameters on the degree of carbonization and the resulting physical properties of hydrochars. Beyond these visual changes, process conditions also affect the internal structure and surface characteristics of hydrochars. The porosity and specific surface area are closely related to hydrothermal parameters such as temperature, residence time, and water-to-biomass ratio. For instance, Feng et al. [38] reported that hydrochars produced at 200 °C demonstrated a significant increase in surface area and pore volume compared to raw sludge, with the surface area increasing by 7.66 times and pore volume by 1.73 times. Generally, higher process temperatures favor the formation of more porous structures, resulting in an increase in specific surface area and enhanced reactivity of hydrochars [39].
The elemental analysis of hydrochar samples obtained under various HTC conditions included the determination of basic elements (carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur), and the quantification of ash content, moisture, volatile matter (VM), fixed carbon (FC) (Figure 3), and calculated atomic ratios (O/C and H/C). The compilation of these parameters enables a comprehensive assessment of the influence of temperature, reaction time, and pH on the physicochemical properties of the resulting material.
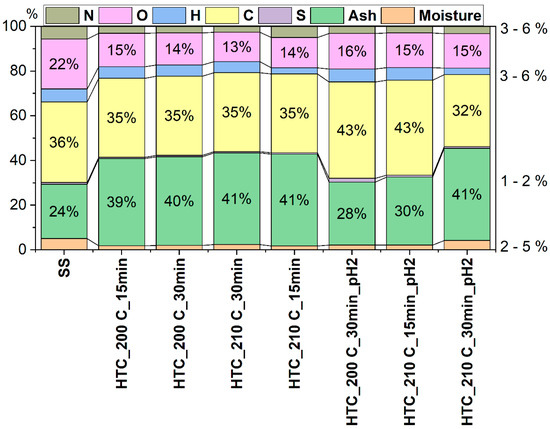
Figure 3.
Chemical and physical properties of hydrochars and sewage sludge.
Ash content increased with the intensification of HTC process conditions, reaching values above 40% in samples treated at 210 °C (e.g., HTC_210C_15min). This increase is a typical consequence of the concentration of inorganic components in the solid phase due to the loss of organic matter. Both temperature and reaction time strongly influenced this parameter—higher HTC temperatures and prolonged reaction times generally led to higher ash content in the hydrochar. This trend results from the enhanced decomposition of organic matter at elevated temperatures and longer residence times, which leaves behind a higher proportion of inorganic residues. Similar findings were reported by other authors. For instance, Huezo et al. [40] observed that higher HTC temperatures led to an increase in ash content due to the enhanced decomposition of organic matter and concentration of inorganics in the solid phase. Likewise, Wilk et al. [41] and Merzari et al. [42] confirmed that both increasing temperature and prolonged residence time resulted in a progressive enrichment of the hydrochar with mineral components, reaching ash contents exceeding 40–50%. This trend is commonly attributed to the loss of volatile organic compounds and the retention of thermally stable inorganic residues during the carbonization process.
However, it is worth noting that acidification of the reaction environment to pH = 2 significantly reduced the ash content. The lowest values (28.13% and 30.45%) were recorded for samples HTC_200C_30min_pH2 and HTC_210C_15min_pH2. This may be attributed to the dissolution of certain mineral components in the acidic medium and their transition into the liquid phase.
Although some studies indicate that higher HTC temperatures can increase ash content, others report that elevated temperatures promote dehydration and decarboxylation reactions, which enhance carbonization and can result in hydrochars with higher carbon content and lower ash content, improving their fuel properties such as higher heating value and reduced ash fraction [43,44].
Carbon (C) content systematically increased with the severity of the HTC process conditions. The highest values were observed in acidified samples, up to 43.13% for HTC_200C_30min_pH2—indicating effective decarboxylation and the concentration of the carbonaceous structure. The acidic environment may have further promoted selective removal of oxygen and hydrogen from organic matter, enriching the hydrochar in carbon and enhancing the degree of carbonization.
According to the literature, increasing the HTC temperature generally leads to higher carbon content in hydrochar. For example, the carbon content was found to increase from 30.02 wt.% to 37.53 wt.% when the temperature rose from 150 °C to 300 °C [45]. However, some studies reported a decrease in carbon retention with rising temperature, although the overall energy content of the hydrochar increased [46]. Extended reaction times may also reduce carbon retention, as prolonged exposure promotes secondary reactions that further degrade organic carbon—for instance, carbon retention decreased from 64 to 77% at 140–160 °C to 50–62% at 180–200 °C when the reaction time was prolonged [46]. In contrast, acidification of the process water (pH = 2) may favor higher carbon content and improved fuel properties due to enhanced dehydration and condensation reactions. Similarly, Czerwińska et al. [21] observed that longer residence times during the HTC process enhanced the hydrophobic character of hydrochar and slightly increased its carbon stability, as a result of more advanced dehydration and demethanation reactions leading to lower O/C and H/C ratios. In turn, Liu et al. [47] reported that under acidic conditions (pH = 2–5), hydrochar exhibited higher carbon quality and energy density. The acidified medium limited decarboxylation and deamination pathways, reduced gaseous losses, and promoted condensation and aromatization reactions, resulting in more carbon-rich, homogeneous hydrochars. These findings confirm that both temperature and process acidity significantly influence carbon retention and structural maturity of hydrochar, enhancing its potential as a solid biofuel.
Hydrogen (H) and nitrogen (N) contents ranged from approximately 2.6% to 5.9%, with no clear trends related to temperature, reaction time, or pH. Minor variations between samples may have resulted from partial migration of these elements into the liquid phase or their participation in gaseous products (e.g., NH3). Nevertheless, literature data indicate that increasing the HTC temperature and reaction time typically reduces hydrogen and oxygen contents as a result of intensified dehydration and decarboxylation reactions. For instance, hydrogen content decreased from 5.26 wt.% to 3.18 wt.% and oxygen content from 25.55 wt.% to 9.48 wt.% as temperature increased [45]. Both acidic and alkaline conditions tend to lower the atomic H/C and O/C ratios, increasing the degree of aromatization and thereby improving the hydrochar’s fuel characteristics [48,49].
Sulfur (S) content remained low in all analyzed samples (below 1%), with no significant variations observed. This aligns with literature observations indicating that higher HTC temperatures and longer reaction times facilitate the transformation of organic sulfur into more stable forms, such as sulfate-S in the aqueous phase [48]. The pH of the reaction environment also plays a role: acidic conditions favor cyclization of organic sulfur into aromatic or thiophenic forms, while alkaline conditions promote oxidation to sulfate-S [48].
Table 2 presents the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio (C:N) of the samples. This parameter is an important indicator when assessing the potential applicability of materials for soil amendment purposes, as the optimal C:N range for soil-conditioning substances is approximately 10:1–30:1. Values below 10 may promote nitrogen release and excessively rapid material decomposition, whereas values above 30 may lead to nitrogen immobilization in the soil and limit its availability to plants.

Table 2.
Carbon-to-nitrogen ratio in a sample.
The C:N ratios of most samples fall within the lower optimal range for soil-improving materials (10–30), which suggests their potential suitability as soil fertility enhancers, particularly for samples subjected to HTC at 210 °C for 30 min (C:N = 13.6–14.6). Only the raw sample (C:N = 6.4) exhibits a ratio that is too low, which may result in excessive nitrogen release in the soil.
The results presented in the Van Krevelen diagram (Figure 4) illustrate changes in the elemental composition of hydrochars, particularly in relation to the atomic H/C and O/C ratios. With an increase in temperature from 200 °C to 210 °C and an extension of the reaction time from 15 to 30 min, a systematic decrease in both ratios was observed, reflecting the intensification of dehydration and decarboxylation processes. The samples shift toward lower O/C and H/C values, indicating the formation of more condensed, aromatic structures with properties resembling those of solid fuels. Acidification of the reaction environment further enhanced this effect—acid-treated samples, especially HTC_210C_30min_pH2 and HTC_210C_15min_pH2, exhibited the lowest O/C values (0.27–0.28) and moderately low H/C ratios, confirming intensified reactions leading to carbon enrichment. A similar trend was reported by Parshetti et al. [50] and Saetea et al. [51]. A longer residence time and acidic conditions during the HTC process also induced changes: the H/C and O/C ratios of the hydrochars approached values similar to those associated with lignite, and the process likely involved further dehydration and demethanation effects.
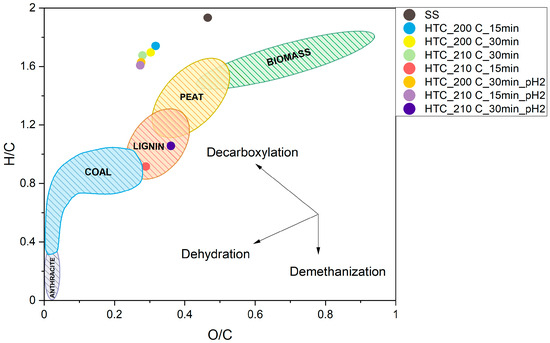
Figure 4.
Van Krevelen diagram.
The analysis of higher heating value (HHV) (Figure 5) revealed that the influence of process parameters on the calorific value of hydrochar was neither linear nor unambiguous. The highest HHVs (19.84 MJ/kg and 19.34 MJ/kg), were obtained for acidified samples, specifically HTC_200C_30min_pH2 and HTC_210C_15min_pH2, respectively. This indicates that under certain configurations, acidic conditions can significantly enhance the energy properties of the material. Although acidification generally enhances HHV through dehydration and condensation, excessively low pH values (pH = 2) promote over-decomposition of organic matter, leading to a reduction in carbon content and, consequently, HHV. At the same time, the sample HTC_210C_30min_pH2 exhibited the lowest HHV in the entire set (12.16 MJ/kg), suggesting that overly intense processing may lead to excessive structural degradation and a reduction in energy content.
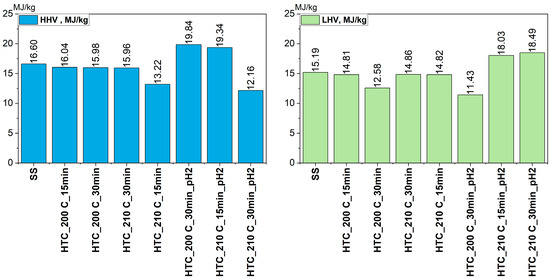
Figure 5.
The analysis of higher heating value (HHV) and lower heating value (LHV).
This sharp decline in HHV under the most severe acidic conditions (210C_30 min_pH2) can be attributed to the intensified hydrolysis and solubilization of carbon-rich organic fractions into the liquid phase, which-combined with a relative enrichment of mineral matter in the solid residue (as indicated by the increased ash fraction in Figure 3) resulted in a lower proportion of energy-dense carbon in the hydrochar. In such conditions, the formation of secondary decomposition products and their migration to the aqueous phase likely reduced the fixed carbon content and increased the oxygenated and ash-forming components, ultimately decreasing the calorific value.
The relationship between HHV, temperature, and time was complex—in some cases (e.g., HTC_210C_15min vs. HTC_210C_30min), higher temperature and extended reaction time resulted in increased HHV, while in others, no clear effect was observed. Therefore, optimizing HTC process parameters should account for the complex interactions between temperature, reaction time, and pH, with acidification appearing particularly significant. Under specific conditions, lowering the pH may lead to a notably higher heating value and greater carbon concentration in the solid product; however, excessively aggressive combinations of temperature, time, and low pH may instead promote carbon loss to the liquid phase and increase inorganic residue, adversely affecting the energy performance of the material.
A similar trend was observed for the lower heating value (LHV). The obtained values reflected the combined influence of temperature, reaction time, and acidity, showing that the same factors which enhanced HHV also positively affected the usable energy potential of the produced hydrochars. The highest LHVs were recorded for the acidified samples HTC_210C_30min_pH2 and HTC_210C_15min_pH2, which confirms that acidification promotes dehydration and partial aromatization reactions, improving the fuel quality of the solid product. Under the most severe process conditions (210 °C, 30 min, pH 2), the LHV remained relatively high and did not show the distinct decline observed for HHV, suggesting that despite partial degradation of organic structures, the resulting hydrochar retained a considerable fraction of combustible carbon.
The relationship between LHV and the HTC parameters, therefore, followed a non-linear pattern, consistent with HHV, indicating that a balanced combination of process temperature, reaction time, and pH can effectively enhance the energetic performance of the solid product.
3.2. Liquid Fraction
The analysis of the physicochemical properties of the post-processing liquid revealed a significant influence of process parameters—such as temperature, reaction time, and pH of the environment—on the chemical composition and quality of the resulting liquid fraction. The conducted studies included measurements of pH, electrical conductivity, chemical oxygen demand (COD), the content of phosphorus in the form of orthophosphates (PO43−), reactive phosphorus (PO4-P), calculated phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5), as well as total nitrogen (Ntot), potassium (K), and total chlorides (Cltot).
The image (Figure 6) shows fourteen vials containing post-processing liquids obtained from the hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) of sewage sludge, conducted under varying temperatures, reaction times, and pH conditions. The samples exhibit clear differences in color intensity and hue, reflecting changes in the chemical composition of the liquid fraction depending on the process parameters. The dark brown coloration of the samples produced under neutral conditions indicates a high concentration of dissolved organic compounds, including humic-like substances. In contrast, the lighter color of the samples obtained under acidic conditions may result from reduced formation of aromatic compounds and increased dissolution of mineral components. These visual differences confirm the significant impact of temperature, reaction time, and pH on the quality and composition of the post-processing liquid generated during HTC.

Figure 6.
Visual Appearance of liquids: I, II—HTC_210C_30min; III, IV—HTC_210C_15min; V, VI—HTC_200C_15min; VII, VIII—HTC_200C_30min; IX, X—HTC_210C_30min_pH2; XI, XII—HTC_210C_15min_pH2; XIII, XIV—HTC_200C_30min_pH2.
Based on the figure showing the concentrations of PO4-P, PO43−, and P2O5, a clear increasing trend in phosphate content in the post-processing liquid can be observed for samples treated under acidic conditions. Particularly high values were recorded for samples HTC_210C_15min_pH2 and HTC_200C_30min_pH2, where the PO43− concentrations reached 675.0 and 675.6 mg/L, respectively, and the calculated P2O5 content was as high as 506.3 and 509.4 mg/L. For PO4-P, values exceeding 200 mg/L were also noted, indicating a significant share of bioavailable phosphorus forms. In samples with natural pH, PO43− concentrations were significantly lower—ranging from 336.9 to 375.0 mg/L—while P2O5 content ranged from 251.9 to 280.0 mg/L. This variation clearly confirms that acidification promotes phosphorus mobilization, likely through the dissolution of inorganic phosphate fractions containing calcium, magnesium, or iron. According to a previous research study by Czerwińska et al. [21], lowering the pH to around 2 can increase phosphorus concentration in the liquid phase by up to 80%, highlighting the strong dependence of phosphorus solubility on the acidity of the reaction environment. Moreover, acidic conditions also affect the mobility of heavy metals such as zinc (Zn) and nickel (Ni), which tend to concentrate more in the post-processing liquid at lower pH values [21]. The high solubility of phosphorus in acidic samples provides a strong basis for its subsequent recovery from the post-processing liquid, for example, in the form of struvite (Figure 7).
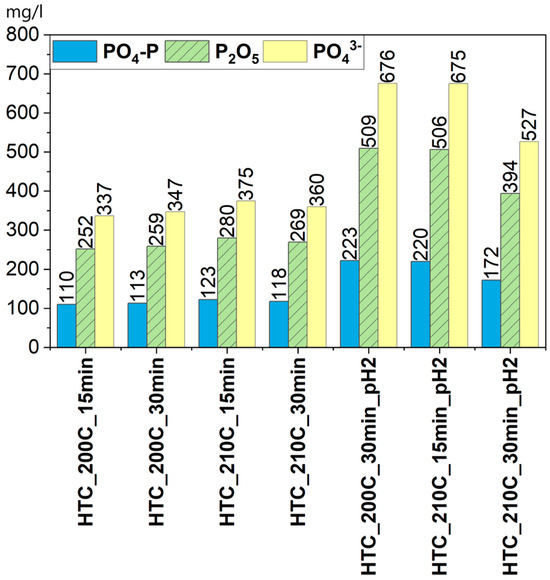
Figure 7.
Content of phosphorus compound.
A similar trend was observed for total nitrogen (Ntot), where the concentration in acidified samples was moderately higher, reaching a maximum of 631 mg/L in the HTC_210C_30min_pH2 sample compared with 563–581 mg/L under natural pH conditions. The slight increase in nitrogen concentration in the post-processing liquid may be attributed to the degradation of proteins and other nitrogen-containing compounds, as well as the formation of ammonia and soluble ammonium salts in the acidic reaction environment. Studies by Blach et al. [52] have shown that the concentration of ammonia nitrogen (NH4-N) increases with temperature, rising from 754 mg/L at 190 °C to 1230 mg/L at 250 °C, which further supports the observed increase in nitrogen content under intensified process conditions. This may affect both the fertilizing potential of the liquid fraction and the necessity of its treatment prior to potential utilization.
Chemical oxygen demand (COD) (Figure 8) exhibited higher values in non-acidified samples, reaching 6783 mg/L (HTC_210C_30min) and 6733 mg/L (HTC_210C_15min). The high COD concentration indicates a substantial presence of dissolved organic matter, including carboxylic acids, alcohols, phenols, and other degradation products of complex organic structures such as hemicellulose, lignin, or lipids. Higher temperatures generally enhance the solubilization of organic compounds, leading to increased COD values in the post-processing liquid [53]. For instance, at 200 °C, a marked rise in solubilized COD has been observed due to intensified decomposition of organic matter [44]. Reaction time also plays a key role—prolonged processing (e.g., 1 h at 200 °C) can significantly enhance the solubilization of COD and carbohydrates [53], thereby increasing the concentration of organic degradation products in the liquid phase. The elevated COD suggests the potential use of the post-processing liquid as a carbon source in biological processes, e.g., denitrification, but it may also pose an environmental concern if discharged directly into aquatic ecosystems.
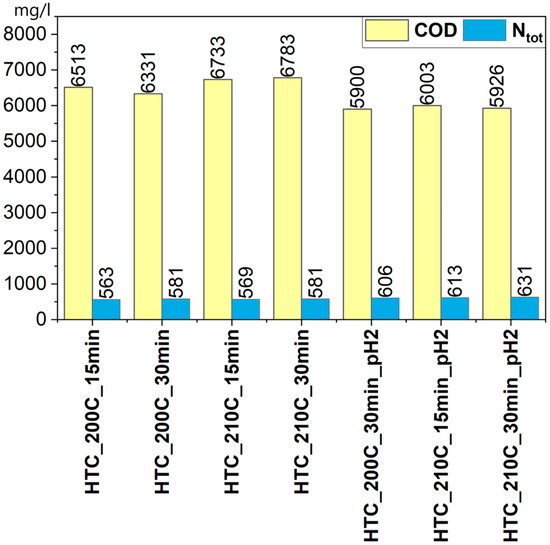
Figure 8.
COD and Ntot content in post-processing liquids.
The pH values (Figure 9) after the HTC process ranged from 3.60 (HTC_210C_30min_pH2) to 5.70 (HTC_210C_30min). Samples that were acidified prior to the process exhibited significantly lower final pH levels, indicating the persistence of acidification effects under high-temperature conditions and the possible formation of acidic by-products. Lower pH may contribute to increased solubility of both mineral and organic substances. This is also reflected in the electrical conductivity analysis—acidified samples showed significantly higher values, reaching 4.25 mS/cm (HTC_210C_30min_pH2) and 3.80 mS/cm (HTC_200C_30min_pH2), compared to 2.03–2.27 mS/cm for samples with natural pH. The elevated conductivity results from the presence of considerable amounts of dissolved ions in the solution, including phosphates, ammonium ions, potassium, chlorides, and organic residues. Higher temperatures and longer reaction times further contribute to increased ionic strength and conductivity, as they promote mineral dissolution and organic compound breakdown. Similar observations were reported by Rathika et al. [54], who found that increasing HTC temperature and residence time enhanced the release of inorganic constituents from sewage sludge, leading to elevated concentrations of nitrogen, phosphorus, and other ions in the process water. The resulting higher ionic content directly contributed to increased electrical conductivity, confirming the intensified mineral dissolution and organic matter degradation under more severe hydrothermal conditions. Likewise, Khoury et al. [55] demonstrated that the solubility of phosphorus species and the release of potassium and ammonium ions from waste-activated sludge were strongly influenced by reaction temperature, with milder conditions (200–250 °C) maintaining more soluble nutrient forms. These findings collectively support the idea that both acidification and elevated temperature enhance ionic strength in the liquid phase, primarily through the decomposition of organic matter and the transformation of mineral components into readily soluble forms.

Figure 9.
PH and conductivity of the post-processing liquids.
4. Conclusions
The conducted study demonstrated that the parameters of the hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) process of sewage sludge, particularly temperature, reaction time, and the pH of the environment, notably affect both the elemental composition and structure of the solid phase (hydrochar) and the properties of the post-processing liquid, which is consistent with previous findings reported by Czerwińska et al. [21]. Increasing the severity of the HTC process led to more advanced carbonization, reflected by higher carbon and ash content in the hydrochar and reduced moisture. While the hydrogen and nitrogen content remained relatively stable, their monitoring remains important in terms of the quality of the final solid fuel. However, further studies covering a broader range of process parameters are necessary to confirm these observed trends and to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the system.
The yield of the solid fraction was low and dependent on process conditions-higher temperature and acidification promoted the decomposition of organic matter and the transfer of components into the liquid or gaseous phase. Analysis of the post-processing liquid composition confirmed that acidic conditions significantly enhance the release of valuable elements—especially phosphorus, nitrogen, and potassium—leading to increased concentrations and higher conductivity of the solution. The resulting liquid, rich in nutrients and organic compounds, may serve as a potential source of fertilizer components, provided that appropriate treatment or further processing methods, such as struvite precipitation, are applied.
Overall, the obtained results indicate that conscious and precise modification of HTC allows for the adjustment of physical and chemical transformations and the redistribution of components between phases. This is important both for improving the quality and application of hydrochar as a fuel and for supporting the recovery of valuable elements from the post-processing liquid within a circular economy framework.
5. Prospects
Future research on the hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) of sewage sludge should focus on scaling up the process and developing integrated systems for energy and nutrient recovery. Optimization of operating parameters, particularly temperature, residence time, and pH, will be essential to balance energy efficiency, carbon retention, and nutrient release. Further studies should address the treatment and valorization of the liquid fraction, which, as shown, can serve as a rich source of phosphorus and nitrogen for fertilizer production, provided that potential contaminants are effectively removed.
In addition, combining HTC with complementary technologies such as anaerobic digestion, struvite precipitation, or advanced oxidation processes could create closed-loop solutions consistent with circular economy principles. From a practical perspective, future work should also assess the long-term stability, toxicity, and agronomic potential of hydrochars to ensure their safe use as soil amendments or renewable fuels. Life cycle assessments and techno-economic analyses will be necessary to evaluate the environmental and financial viability of implementing HTC at wastewater treatment plants.
Overall, the findings of this study highlight that precise control of HTC conditions can significantly enhance both energy recovery and resource circularity, making this technology a promising pathway for sustainable sludge management in the coming years.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.W., K.S. and A.P.; methodology, M.W. and K.S.; validation, K.S., J.M., A.P. and M.W.; formal analysis, K.S.; investigation, K.S. and J.M.; resources, M.W.; data curation, K.S. and M.W.; writing—original draft preparation, K.S.; writing—review and editing, M.W.; visualization, K.S.; supervision, M.W. and A.P.; project administration, M.W.; funding acquisition, M.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research project was supported by the program “Excellence initiative—research university” for the AGH University of Krakow, Poland (grant no. 501.696.7996, ID: 9714).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to project management.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge EKOPROD Ltd., the proprietor of the HTC apparatus used in the presented study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sun, X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, L.; Aketagawa, K.; Xue, B.; Ren, Y.; Bai, J.; Zhan, Y.; Chen, S.; Dong, B. Partial Ozonation of Returned Sludge via High-Concentration Ozone to Reduce Excess Sludge Production: A Pilot Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, K.; Zhu, Q.; Zhai, S.; Gao, Y.; Cao, H.; Tang, X.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Tian, L.; Sun, H. PPCPs and Heavy Metals from Hydrothermal Sewage Sludge-Derived Biochar: Migration in Wheat and Physiological Response. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 83234–83246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaddel, S.; Bakhtiary-Davijany, H.; Kabbe, C.; Dadgar, F.; Østerhus, S. Sustainable Sewage Sludge Management: From Current Practices to Emerging Nutrient Recovery Technologies. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkos, G.; Gkampoura, E.-C. Where Do We Stand on the 17 Sustainable Development Goals? An Overview on Progress. Econ. Anal. Policy 2021, 70, 94–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Pandey, A.K.; Udayan, A.; Kumar, S. Role of Microbial Community and Metal-Binding Proteins in Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 326, 124750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacprzak, M. Sewage Sludge as a Source of Organic to Be Used as Soil Improvement. In Water Management and Circular Economy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 303–316. [Google Scholar]
- Ayub, M.A.; Adnan, M.; Umar, W.; Farooqi, Z.U.R.; Awais, M.; Ahmad, H.R.; Imran Ch, B.; Siddique, A. Required Quality of Sewage Sludge as an Agricultural Soil Amendment. In Sustainable Management and Utilization of Sewage Sludge; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 247–262. [Google Scholar]
- Ammar, E.; Maury, H.; Morin, L.; Sghir, A. Environmental, Economic, and Ethical Assessment of the Treated Wastewater and Sewage Sludge Valorization in Agriculture. In Interaction and Fate of Pharmaceuticals in Soil-Crop Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 49–78. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, T.; Ali, I.; Khan, N.; Eash, N.S.; Qadir, M.F.; Jatav, H.S. Detoxification of Sewage Sludge by Natural Attenuation and Application as a Fertilizer. In Environmental Pollution Impact on Plants; Apple Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 245–270. [Google Scholar]
- Zorpas, A.A.; Arapoglou, D.; Panagiotis, K. Waste Paper and Clinoptilolite as a Bulking Material with Dewatered Anaerobically Stabilized Primary Sewage Sludge (DASPSS) for Compost Production. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chang, Y.; Li, A. Hydrothermal Carbonization for Energy-Efficient Processing of Sewage Sludge: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 108, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Li, R.; Wu, Y. Hydrothermal Carbonization and Liquefaction of Sludge for Harmless and Resource Purposes: A Review. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 13268–13290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslan, S.Z.; Zainudin, S.F.; Mohd Aris, A.; Chin, K.B.; Musa, M.; Mohamad Daud, A.R.; Syed Hassan, S.S.A. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Sewage Sludge into Solid Biofuel: Influences of Process Conditions on the Energetic Properties of Hydrochar. Energies 2023, 16, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, M.; Czerwińska, K.; Śliz, M.; Imbierowicz, M. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Sewage Sludge: Hydrochar Properties and Processing Water Treatment by Distillation and Wet Oxidation. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamil, J.A.; De la Rubia, M.A.; Diaz, E.; Mohedano, A.F. Technologies for Wastewater Sludge Utilization and Energy Production: Hydrothermal Carbonization of Lignocellulosic Biomass and Sewage Sludge. In Wastewater Treatment Residues as Resources for Biorefinery Products and Biofuels; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 133–153. [Google Scholar]
- Maniscalco, M.P.; Volpe, M.; Messineo, A. Hydrothermal Carbonization as a Valuable Tool for Energy and Environmental Applications: A Review. Energies 2020, 13, 4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, T.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Peng, H.; Li, D.; Zhu, Z. Volatile Fatty Acid Release and Metal Ion Concentration in Hydrothermal Carbonization Liquid. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2024, 183, 106815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwińska, K.; Śliz, M.; Wilk, M. Thermal Disposal of Post-Processing Water Derived from the Hydrothermal Carbonization Process of Sewage Sludge. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 15, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Xu, Q.; Abou-Elwafa, S.F.; Alshehri, M.A.; Zhang, T. Hydrothermal Carbonization Technology for Wastewater Treatment under the “Dual Carbon” Goals: Current Status, Trends, and Challenges. Water 2024, 16, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Valle, C.J.; Botet-Jiménez, A.B.; Omenat-Morán, D. Hydrothermal Carbonisation: An Eco-Friendly Method for the Production of Carbon Adsorbents. In Adsorption Processes for Water Treatment and Purification; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 77–108. [Google Scholar]
- Czerwińska, K.; Wierońska-Wiśniewska, F.; Bytnar, K.; Mikusińska, J.; Śliz, M.; Wilk, M. The Effect of an Acidic Environment during the Hydrothermal Carbonization of Sewage Sludge on Solid and Liquid Products: The Fate of Heavy Metals, Phosphorus and Other Compounds. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 365, 121637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwińska, K.; Mikusińska, J.; Błoniarz, A.; Śliz, M.; Wilk, M. The Effect of Residence Time during the Hydrothermal Carbonization Process of Sewage Sludge on the Properties of Hydrochar. Energies 2024, 17, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D7582; Standard Test Methods for Proximate Analysis of Coal and Coke by Macro Thermogravimetric Analysis. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023.
- ISO 17246:2010; Coal—Proximate Analysis to Determine Moisture (M), Ash (Ash) and Volatile Matter (VM) Contents. The Ultimate Analysis (Carbon (C), Nitrogen (N), Hydrogen (H), and Sulphur (S) Contents. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- Polish Committee for Standardization. PKN ISO/TS 12902: 2007; Solid Mineral Fuels—Determination of Total Carbon, Hydrogen and Nitrogen—Instrumental Methods. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2013.
- Channiwala, S.A.; Parikh, P.P. A Unified Correlation for Estimating HHV of Solid, Liquid and Gaseous Fuels. Fuel 2002, 81, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Methodology for Thermal Efficiency and Energy Input Calculations and Analysis of Biomass Cogeneration Unit Characteristics; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 23697; Water Quality—Determination of Total Bound Nitrogen (ST-TNb) in Water Using Small-Scale Sealed Tubes. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- ISO 11905-1:1997; Water Quality—Determination of Nitrogen Part 1: Method Using Oxidative Digestion with Peroxodisulfate. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- DIN 38405-9; German Standard Methods for Examination of Water, Waste Water and Sludge-Anions (Group D)—Part 9: Spectrometric Determination of Nitrate (D 9). DIN: Berlin, Germany, 2011.
- EPA 365.2+3; Hosphorous, All Forms (Colorimetric, Ascorbic Acid, Two Reagent). EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- APHA Method 4500-P; Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1992.
- ISO 6878:2004; Water Quality—Determination of Phosphorus—Ammonium Molybdate Spectrometric Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- O’Dell, J.W. (Ed.) EPA Method 410.4, Revision 2.0: The Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand by SemiAutomated Colorimetry; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association. APHA 5220 Chemical Oxygen Demand; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D1252-06; Standard Test Methods for Chemical Oxygen Demand (Dichromate Oxygen Demand) of Water. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012.
- Wilk, M.; Śliz, M.; Czerwińska, K.; Śledź, M. The Effect of an Acid Catalyst on the Hydrothermal Carbonization of Sewage Sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yu, T.; Ma, K.; Xu, G.; Hu, Y.; Chen, D. Effect of Hydrothermal Temperature on the Steam Gasification Performance of Sewage Sludge: Syngas Quality and Tar Formation. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 6834–6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Guo, C.; Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, H. Revealing Carbon-Iron Interaction Characteristics in Sludge-Derived Hydrochars under Different Hydrothermal Conditions. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huezo, L.; Vasco-Correa, J.; Shah, A. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Anaerobically Digested Sewage Sludge for Hydrochar Production. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 15, 100795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, M.; Gajek, M.; Śliz, M.; Czerwińska, K.; Lombardi, L. Hydrothermal Carbonization Process of Digestate from Sewage Sludge: Chemical and Physical Properties of Hydrochar in Terms of Energy Application. Energies 2022, 15, 6499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzari, F.; Goldfarb, J.; Andreottola, G.; Mimmo, T.; Volpe, M.; Fiori, L. Hydrothermal Carbonization as a Strategy for Sewage Sludge Management: Influence of Process Withdrawal Point on Hydrochar Properties. Energies 2020, 13, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, H.; Li, C.; Zhu, Y. Co-Hydrothermal Carbonization of Rape Straw and Microalgae: PH-Enhanced Carbonization Process to Obtain Clean Hydrochar. Energy 2022, 257, 124733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, C.; Wang, T.; Zhu, L.; Li, C.; Zeng, G. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Sewage Sludge: The Effect of Feed-Water PH on Fate and Risk of Heavy Metals in Hydrochars. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roslan, S.Z.; Zainol, M.M.; Bikane, K.; Syed-Hassan, S.S.A. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Sewage Sludge for Hydrochar Production: Optimization of Operating Conditions Using Box-Behnken Design Coupled with Response Surface Methodology. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2025, 15, 10109–10125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danso-Boateng, E.; Shama, G.; Wheatley, A.D.; Martin, S.J.; Holdich, R.G. Hydrothermal Carbonisation of Sewage Sludge: Effect of Process Conditions on Product Characteristics and Methane Production. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 177, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhai, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Li, C. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Sewage Sludge: Effect of Feed-Water PH on Hydrochar’s Physicochemical Properties, Organic Component and Thermal Behavior. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 122084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Y. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Sewage Sludge for Hydrochar Valorization: Role of Feedwater PH on Sulfur Removal and Transformation. Fuel 2024, 377, 132813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gu, J.; Yuan, S.; Dai, X. Improving Fuel Characteristics of Sludge-Derived Hydrochar through Acidic Thermal Hydrolysis Pretreatment by Promoting Dehydration, Decarboxylation, and Demethylation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 118891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartulistiyoso, E.; Farobie, O.; Anis, L.A.; Syaftika, N.; Bayu, A.; Amrullah, A.; Moheimani, N.R.; Karnjanakom, S.; Matsumura, Y. Co-Production of Hydrochar and Bioactive Compounds from Ulva Lactuca via a Hydrothermal Process. Carbon Resour. Convers. 2024, 7, 100183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Surface Roughness and Contact Angle. J. Phys. Colloid Chem. 1949, 53, 1466–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blach, T.; Engelhart, M. Optimizing the Hydrothermal Carbonization of Sewage Sludge—Response Surface Methodology and the Effect of Volatile Solids. Water 2021, 13, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, R.; Capannelli, G.; Bernardini, M.; Pagliero, M.; Comite, A. Effect of Varying Hydrothermal Temperature, Time, and Sludge PH on Sludge Solubilisation. Carbon Resour. Convers. 2023, 6, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathika, K.; Kumar, S.; Yadav, B.R. Enhanced Energy and Nutrient Recovery via Hydrothermal Carbonisation of Sewage Sludge: Effect of Process Parameters. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, O.; Gaur, R.; Zohar, M.; Erel, R.; Laor, Y.; Posmanik, R. Phosphorus Recycling from Waste Activated Sludge Using the Hydrothermal Platform: Recovery, Solubility and Phytoavailability. Waste Manag. 2023, 169, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).