A Graphical Tool for Predicting Class EF Inverter Behavior Including Non-Ideal Load Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Generalities
1.2. Challenges in Analytical Modeling and State of the Art
1.3. Contribution of This Work
- Comprehensive analytical modeling: time-domain and harmonic analysis of the class EF inverter with a quarter-wave transmission line, capturing nonlinear voltage and current dynamics under arbitrary loads.
- Practical design tool: a graphical design chart enabling rapid sizing and optimization without iterative simulations.
- Experimental validation: measurements with a 15 MHz, 25 VDC class EF inverter confirm close agreement between theory and practice.
- Applicability to lumped-element derivatives: the methodology is validated on the class inverter, showing its generality to discrete-element analogs of the class EF topology.
1.4. Paper Organization
- Section 2 introduces the comprehensive analytical modeling of the class EF inverter and presents two sizing equations derived from combined time-domain and frequency-domain approaches.
- Section 3 applies constraints for ZVS and ZdVS operation, resulting in a set of nonlinear equations describing inverter behavior under soft-switching conditions. These equations are then gathered in a single user-friendly design chart, enabling fast and visual sizing of the class EF inverter for any load conditions.
- Section 4 presents the experimental validation, first using a quarter-wave transmission line and then substituting it with discrete elements, confirming that waveform fidelity is maintained and demonstrating applicability to lumped-element equivalents (including class ).
- Section 5 concludes the paper and discusses future perspectives in high-frequency power electronics.
2. Generalized Equations of Class EF Inverter
2.1. Starting Assumptions and Theoretical Background
- A single switch whose source is connected to the ground.
- A capacitor placed in parallel with the switch, which in practice may include the switch’s output capacitance.
- A quarter-wavelength transmission line that is short-circuited at its extremity by the input DC voltage source.
- An output filter tuned to the switching frequency F of the inverter.
- A load that presents a impedance at the switching frequency F of the inverter where .
- (H1): the quarter-wavelength input transmission line is lossless.
- (H2): the input voltage is constant.
- (H3): the input DC voltage source presents an ideal short-circuit to the transmission line (ideal voltage source).
- (H4): all passive and active components are assumed to be perfect.
- (H5): the filter is tuned to the switching frequency F of the inverter.
- (H6): the quality factor of the output filter is supposed to be infinite.
2.2. Defining Variables
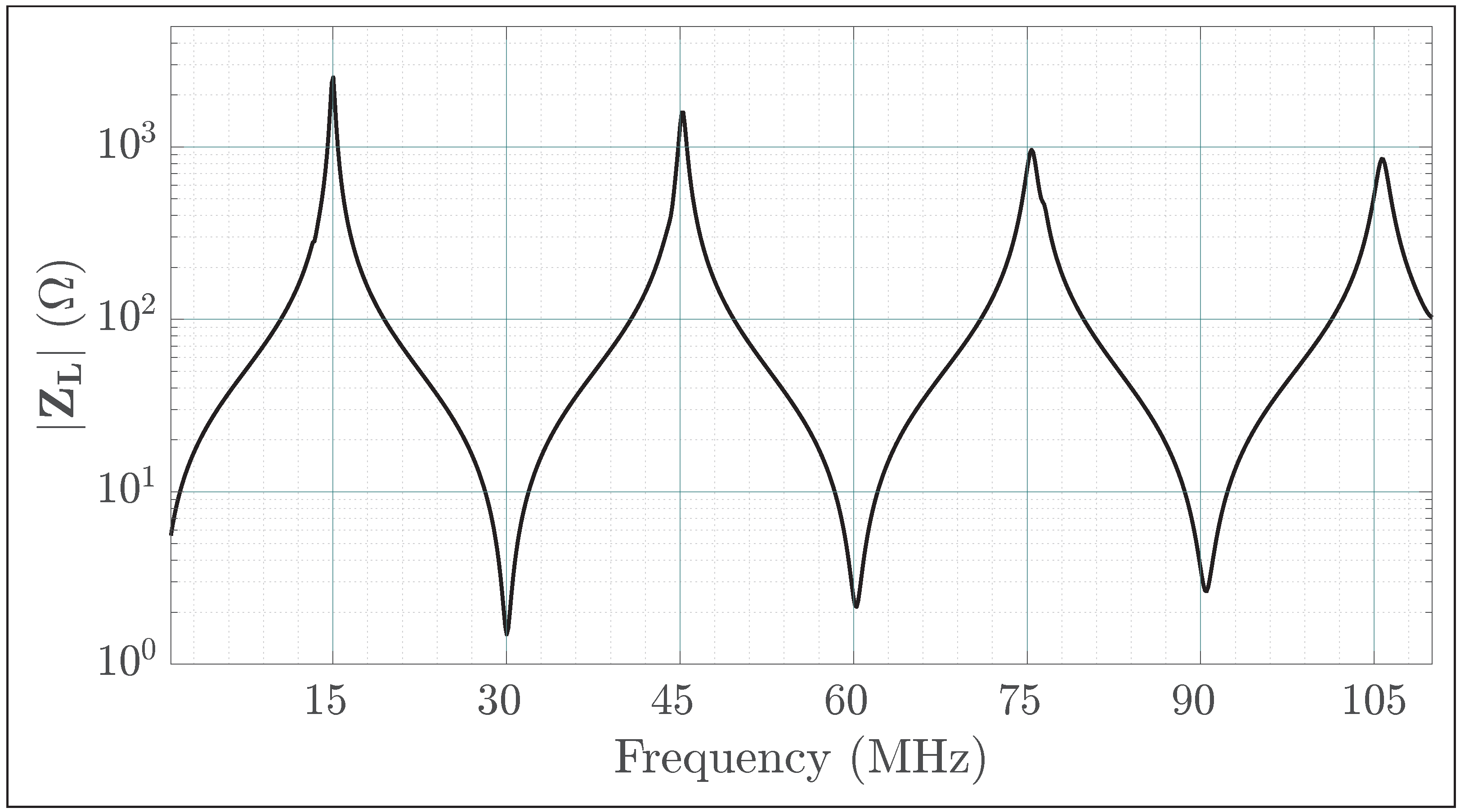
2.3. Frequency-Domain Analysis of the Impact of the Quarter-Wavelength Transmission Line on the Circuit
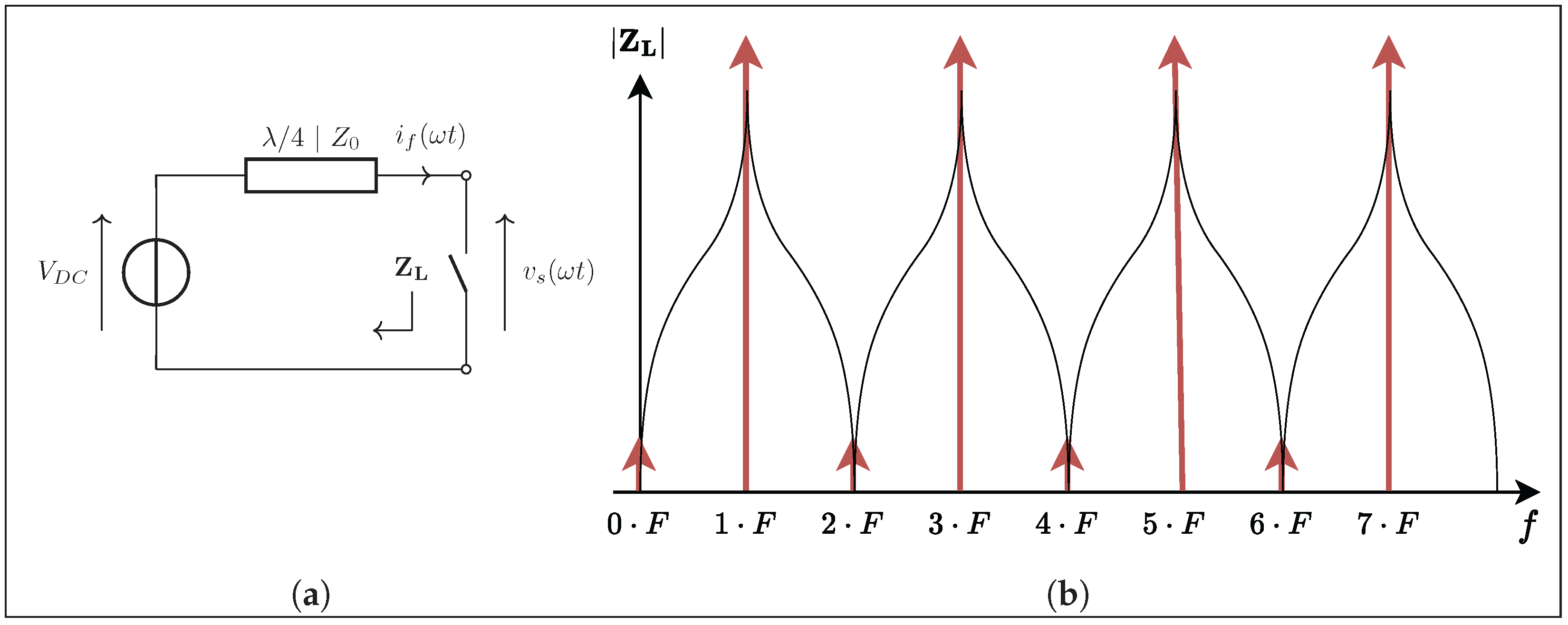
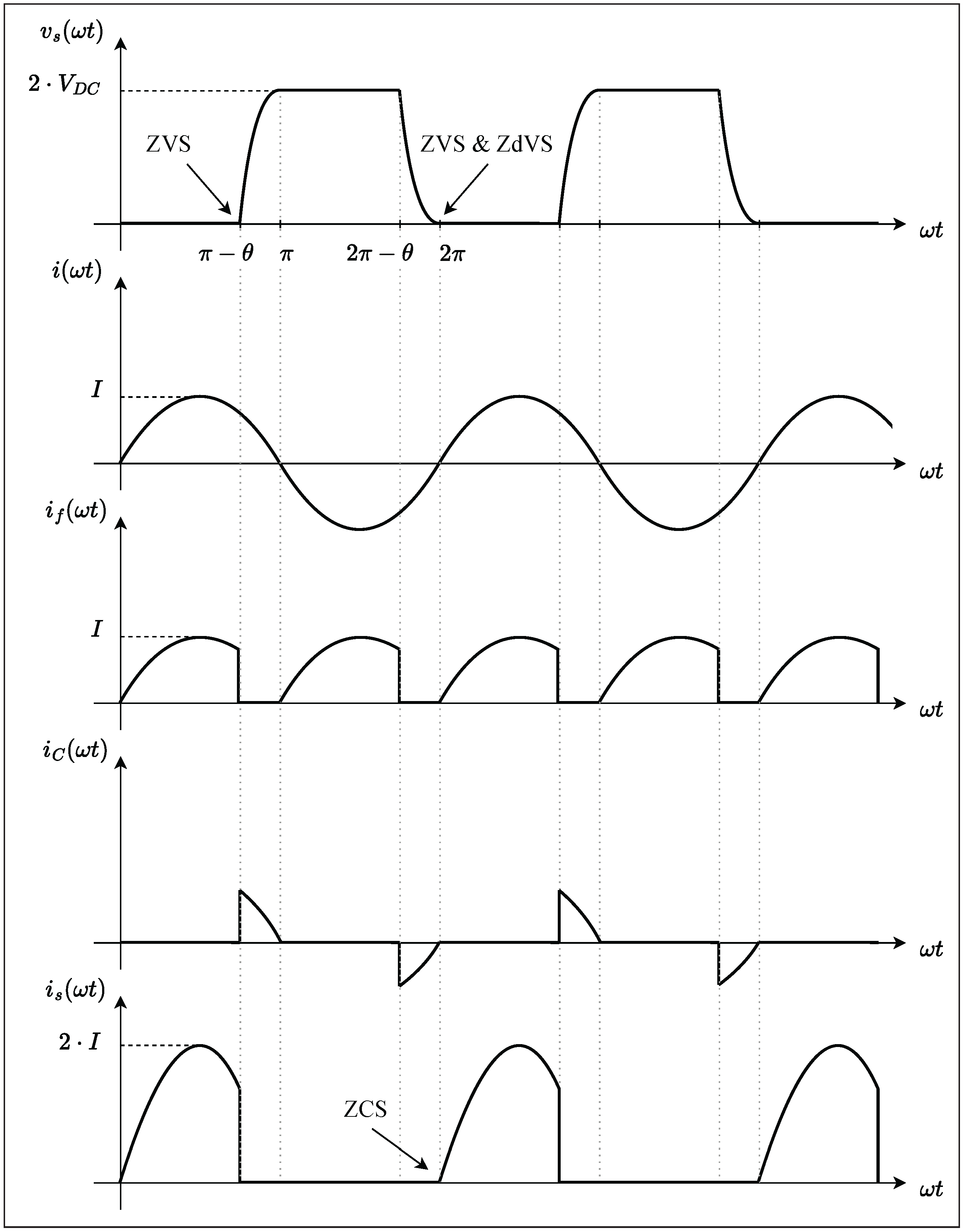
2.4. Operating Phases of the Inverter
| S | ON | OFF | OFF | OFF |
2.5. Soft-Switching Conditions
2.6. Output Stage
- Two design equations, given by (40) and (41), which characterize the inverter’s behavior for a given load.
3. Optimal and Non-Optimal Behavior of the Class EF Inverter
3.1. Optimally Loaded Class EF Inverter
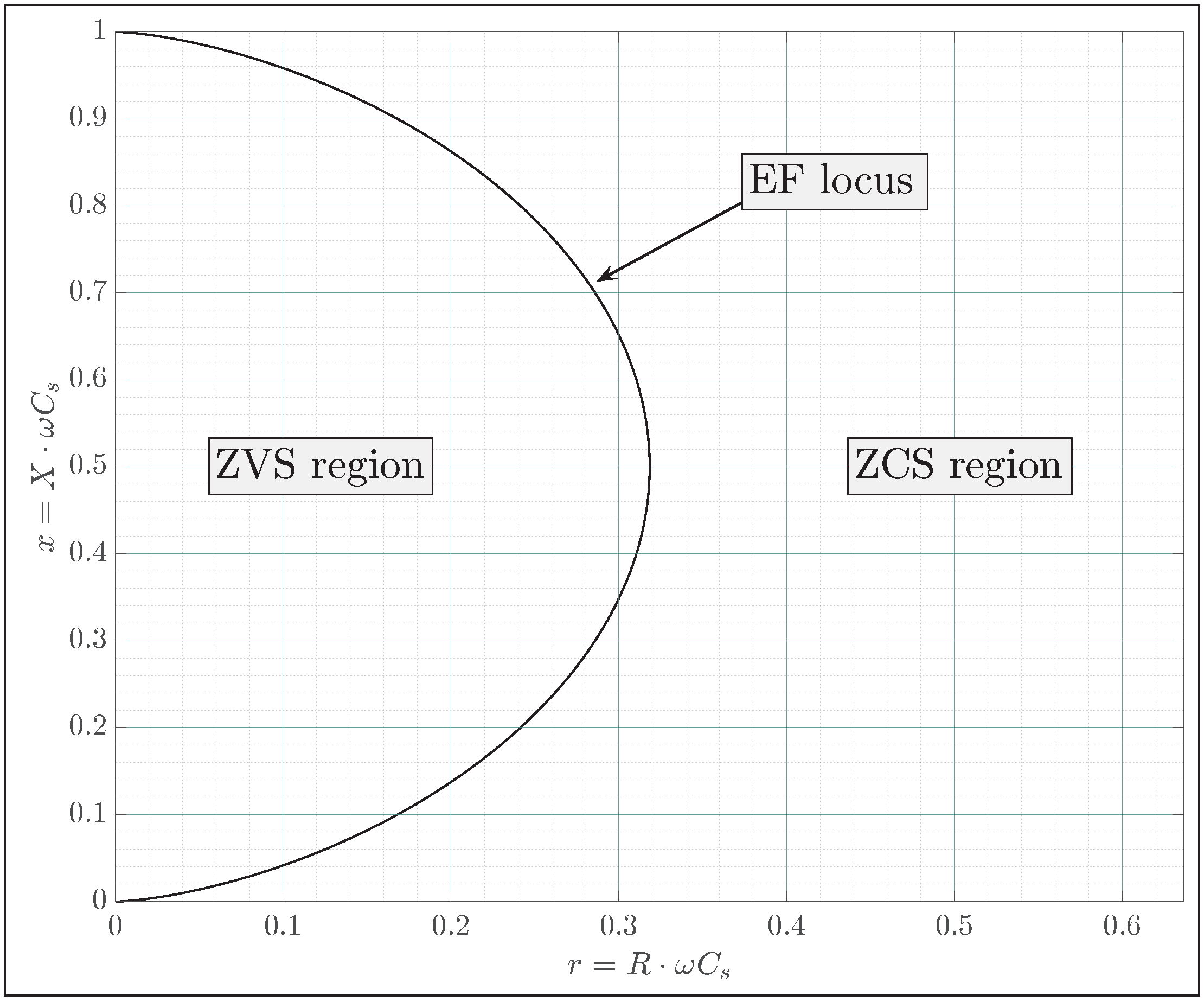
- ZCS region: occurs when the product exceeds the optimal value.
- ZVS region: occurs when the product is below the optimal value.
3.2. ZCS Region
3.3. ZVS Region
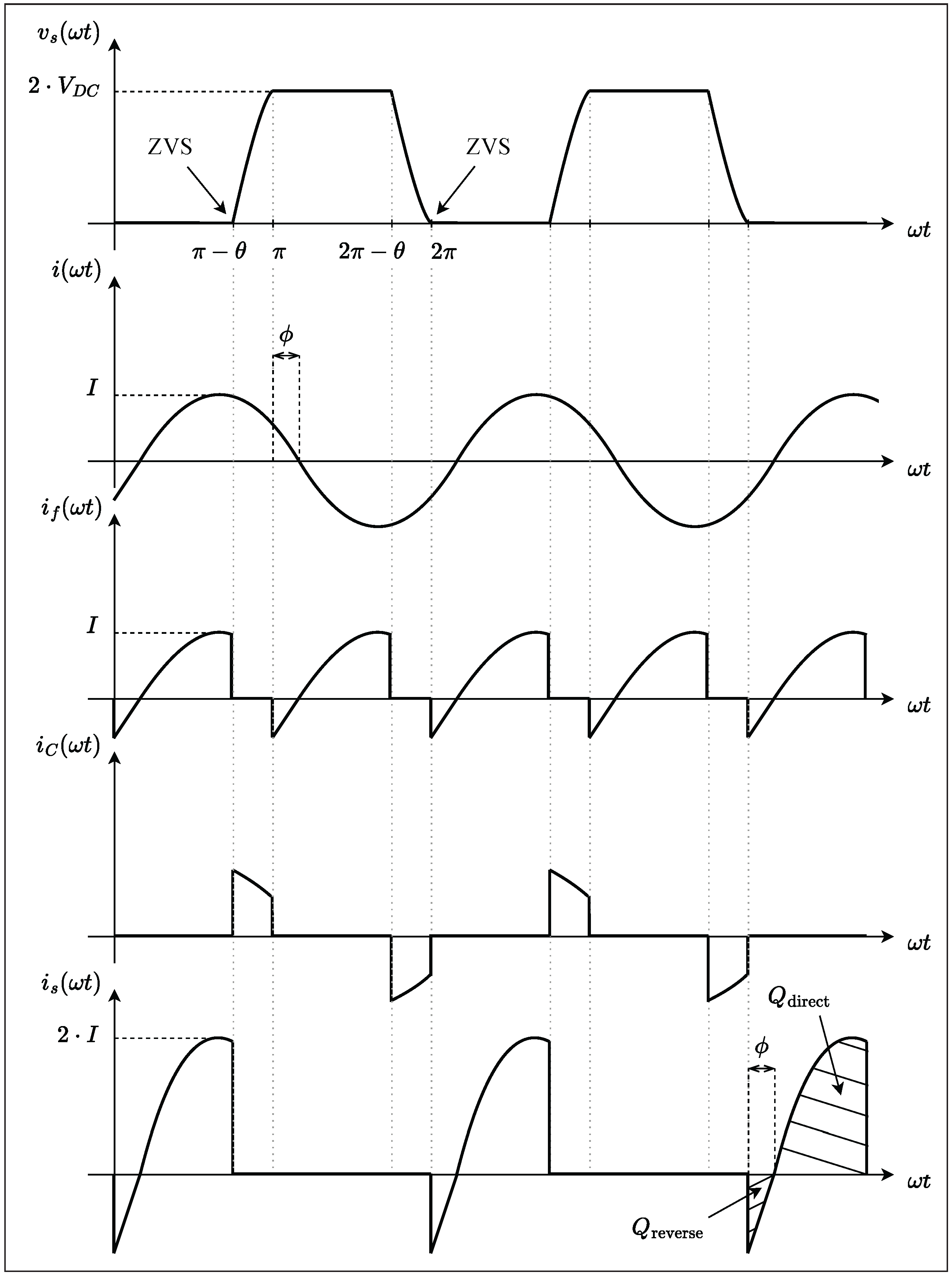
4. Experimental Validation
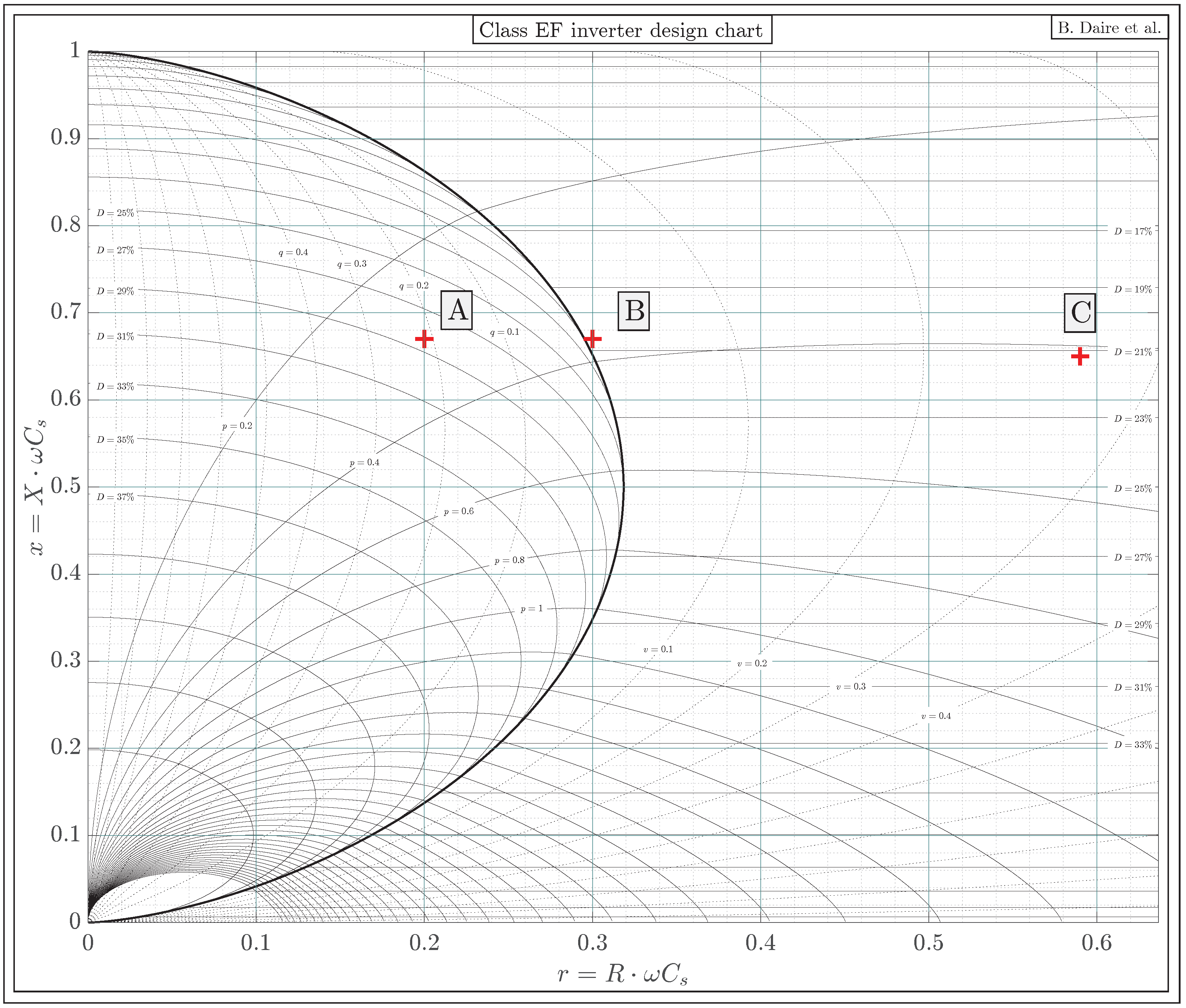
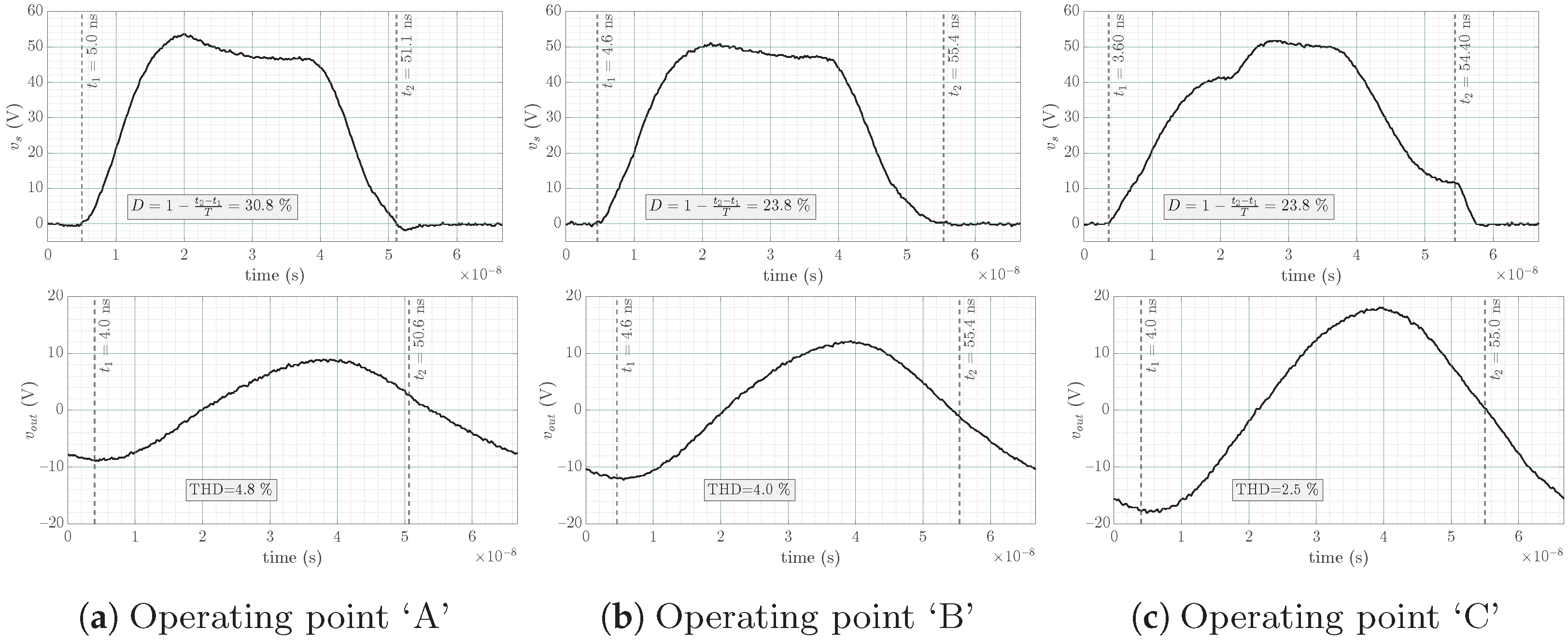
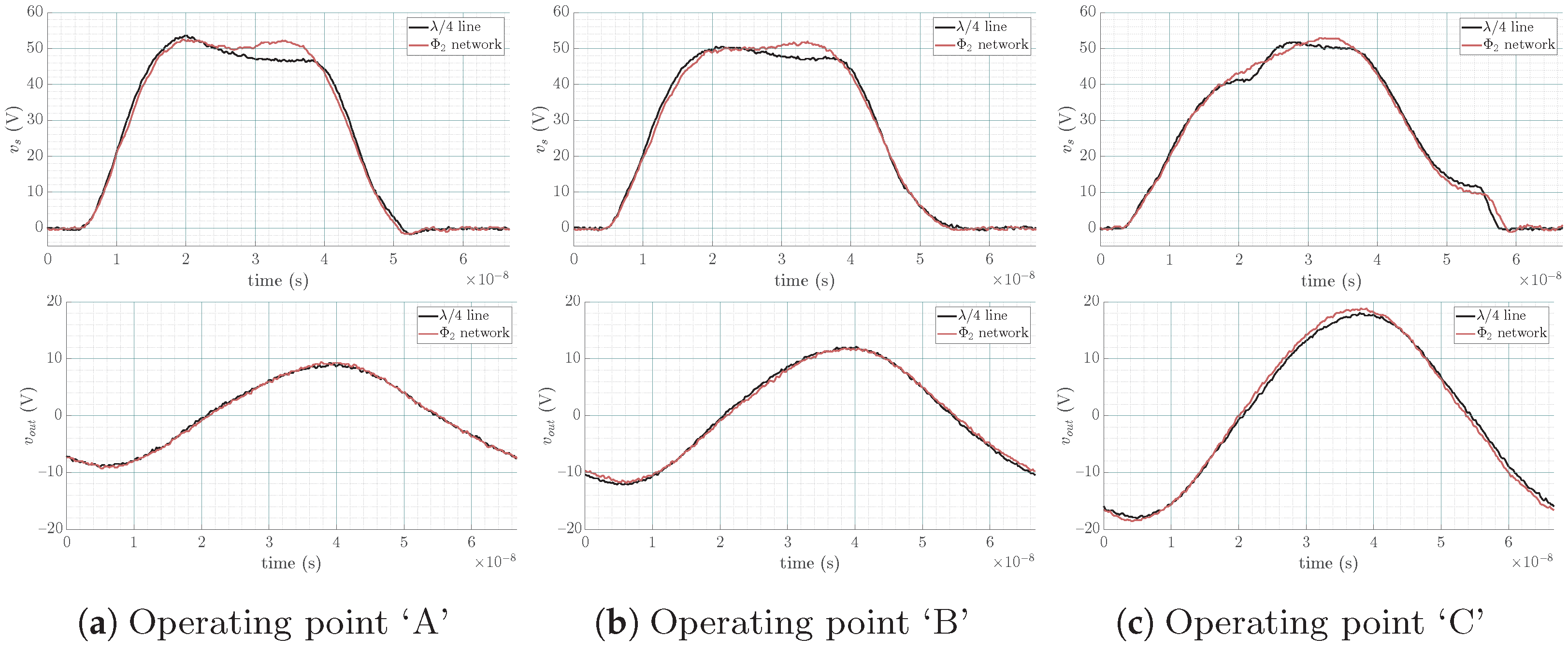
- Operating point ‘A’: located in the ZVS region
- Operating point ‘B’: located on the EF locus
- Operating point ‘C’: located in the ZCS region
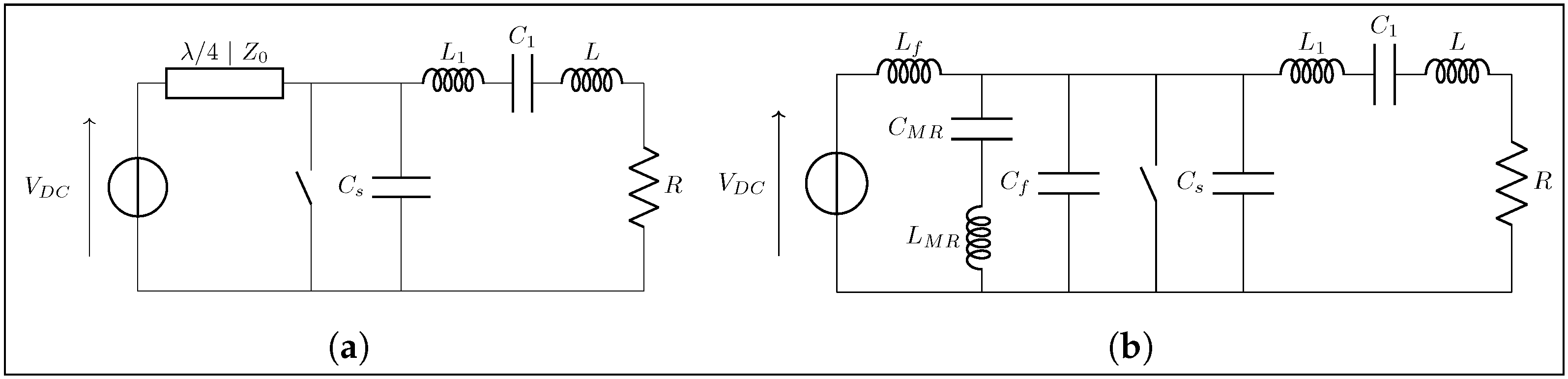
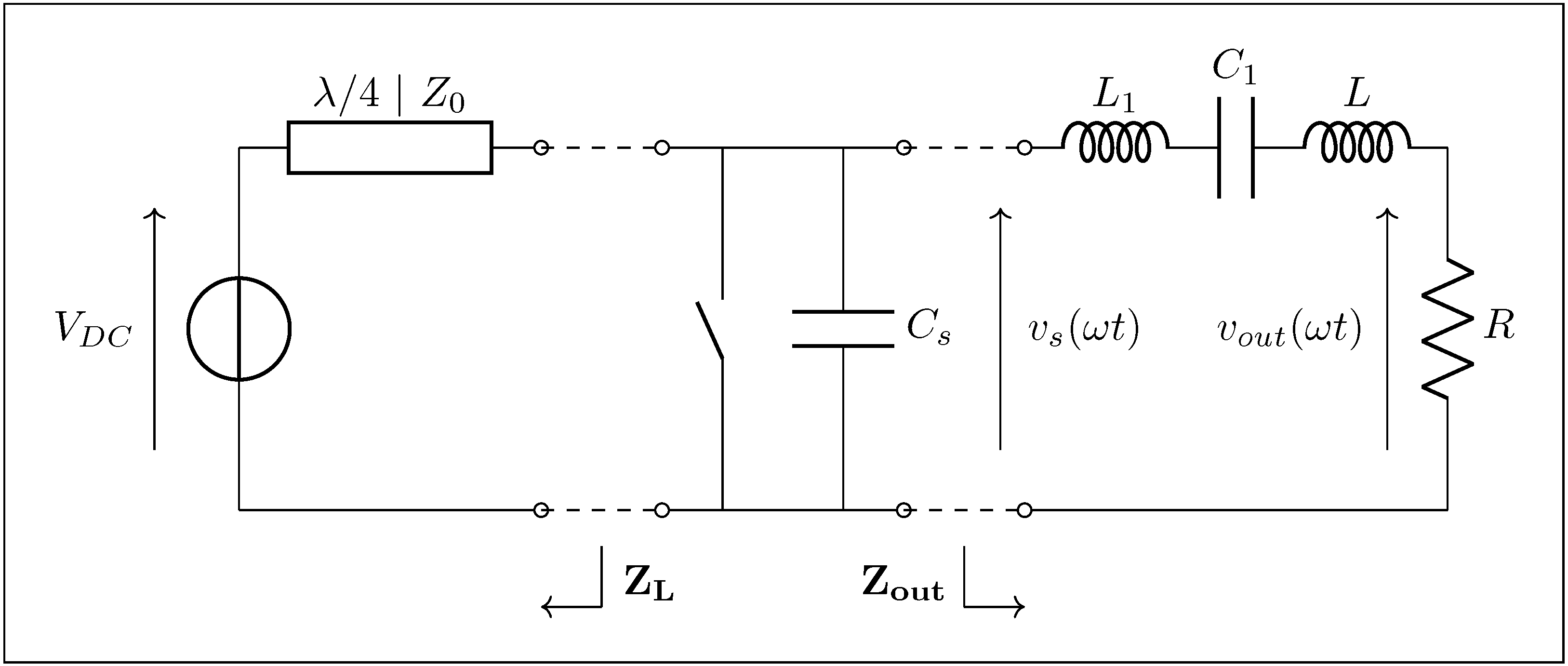
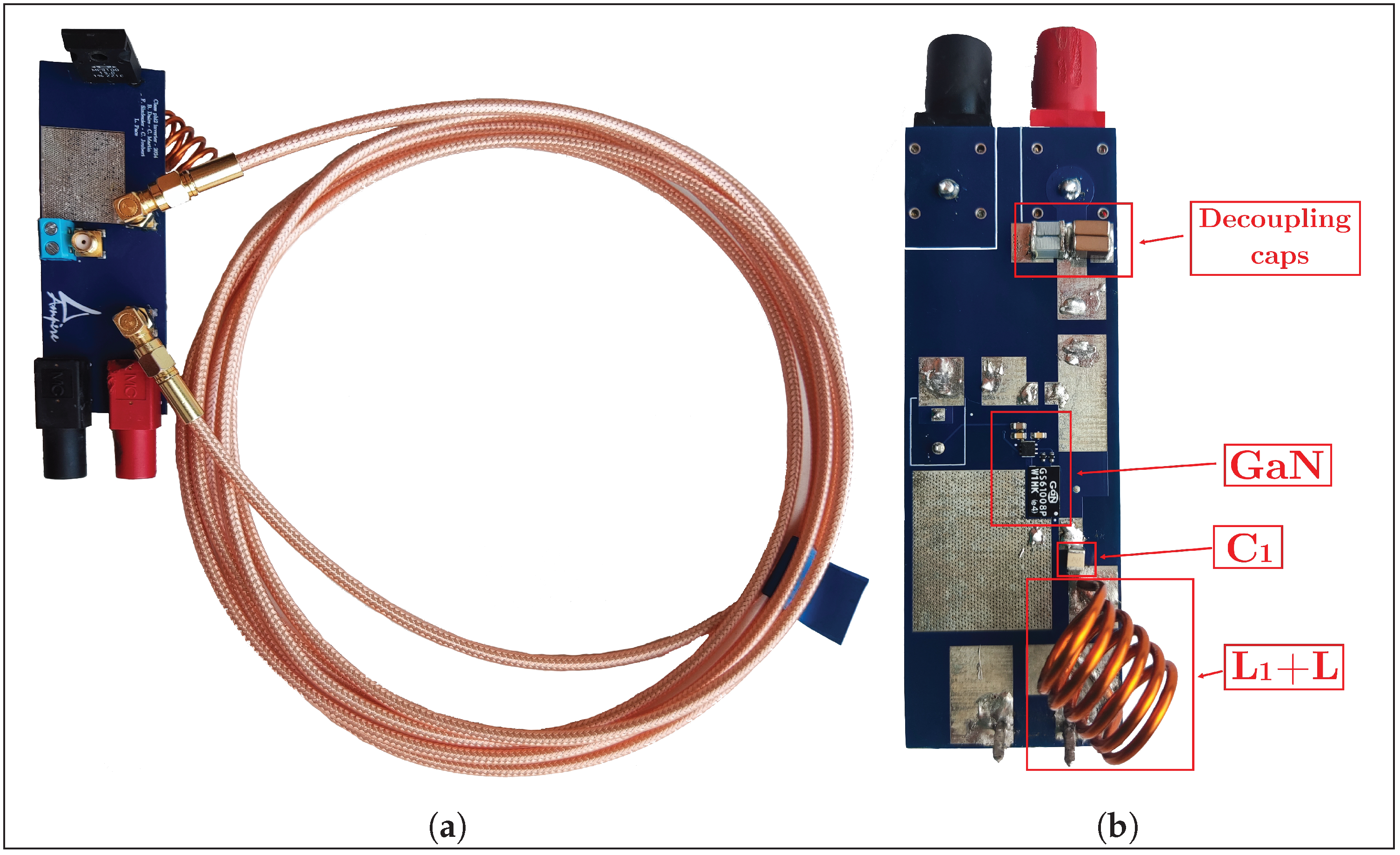
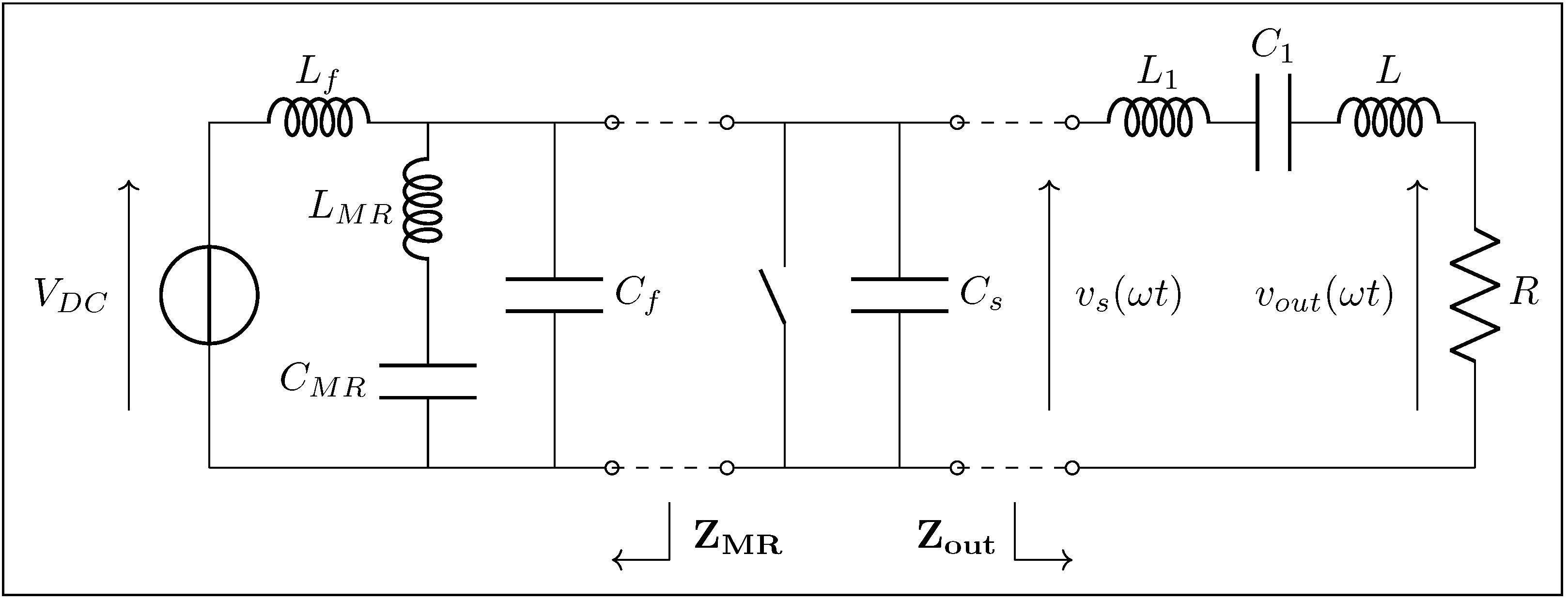
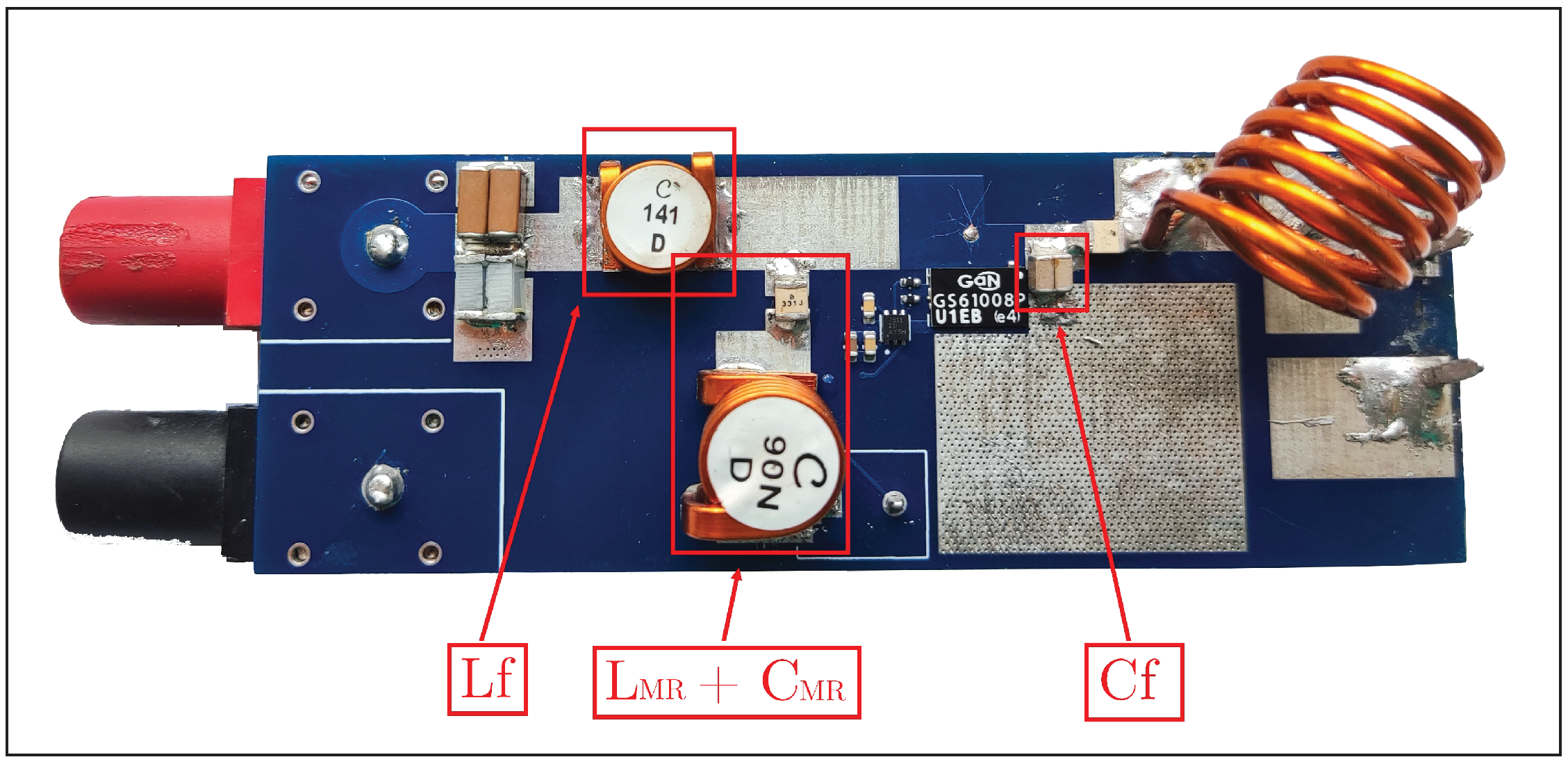
4.1. Implementation of the Class EF Inverter
- The need to validate the analytical derivation under quarter-wavelength conditions, while staying within the bandwidth of our oscilloscope.
- The opportunity to present, to the best of our knowledge, unprecedented experimental waveforms of this type
- Providing a direct justification for the substitution with discrete reactive components: the line is often replaced by an equivalent network made of lumped-elements, as detailed in Section 4.4.
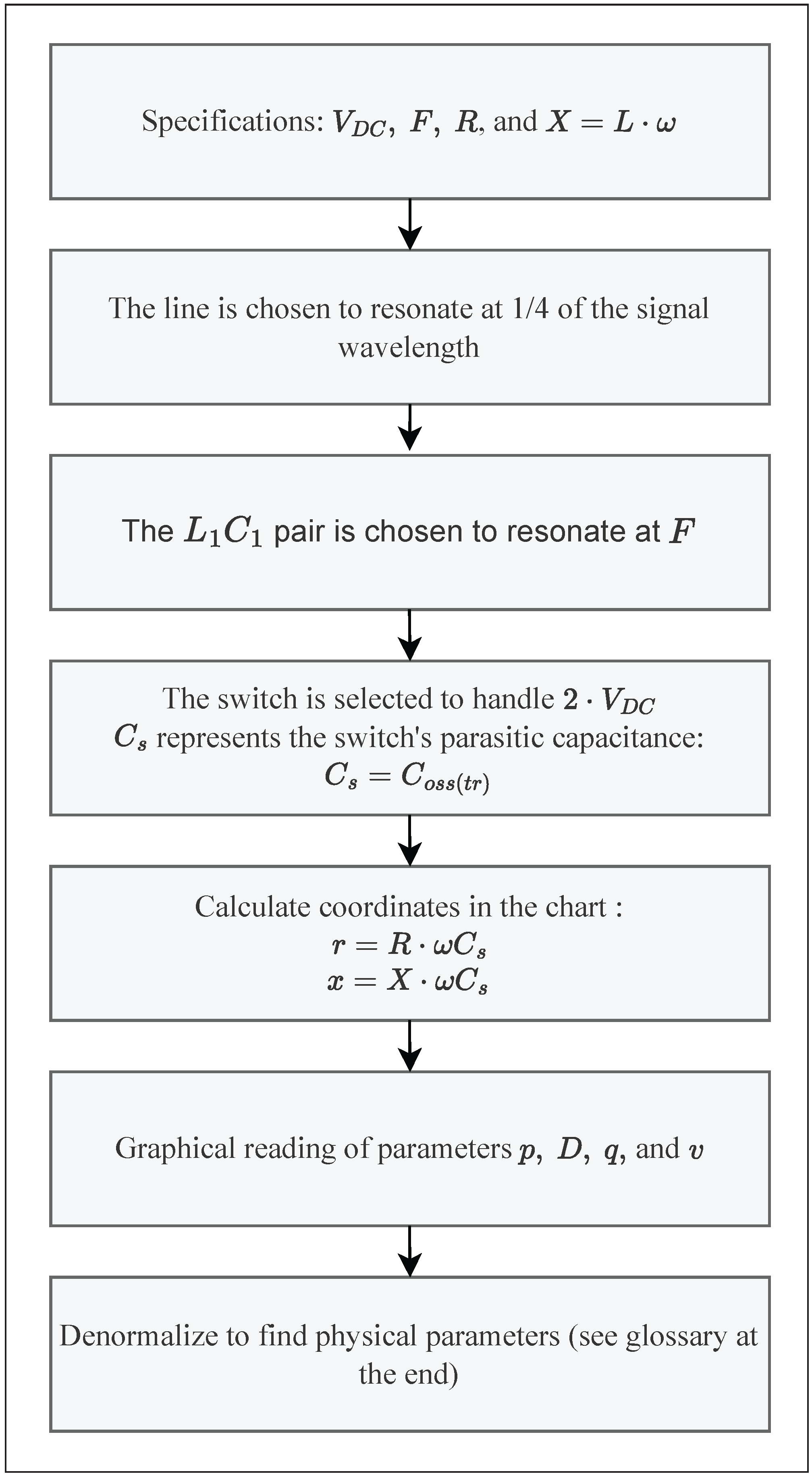
4.2. Extraction of Key Parameters Using the Design Chart
- The value of the duty cycle D, using the D-curves, that must be used in order to maintain soft switching;
- The value of p, using p-curves, from which can be deduced the corresponding power delivered to the load using Equation (5);
- The value of v or q, using the v-curves or q-curves whether the operating point is located in the ZVS region or in the ZCS region. These values can be used in order to calculate the value of the voltage at which the switch is turned on or the amount of electrical charges that are reverse-conducted through the switch using Equations (52) or (58).
4.3. Experimental Results
- Only ZVS is performed at operating point ‘A’ as predicted using the chart since this operating point is located in the ZVS region.
- Only ZCS, which is structurally equivalent to zero derivative voltage switching (ZdVS or ZDS) operation, is performed at operating point ‘C’ as predicted using the chart since this operating point is located in the ZCS region.
- Both ZVS and ZCS (⇔ZdVS) are performed at operating point ‘B’ as predicted using the chart, since this operating point is located on the EF locus.
4.4. Lumped Analogs
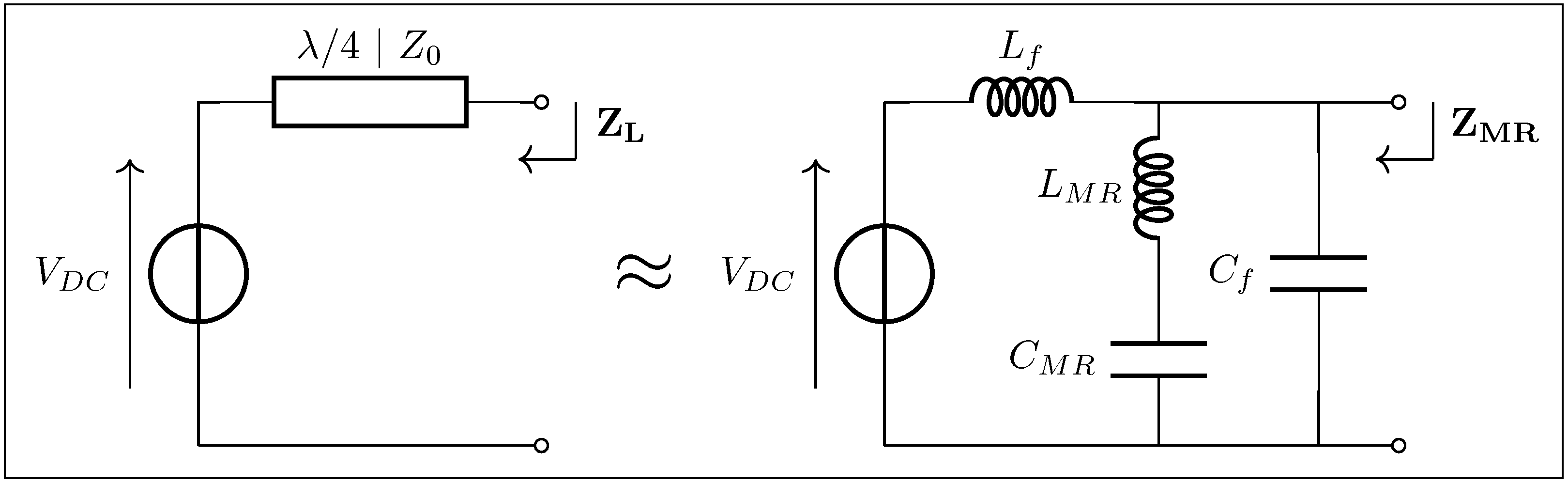
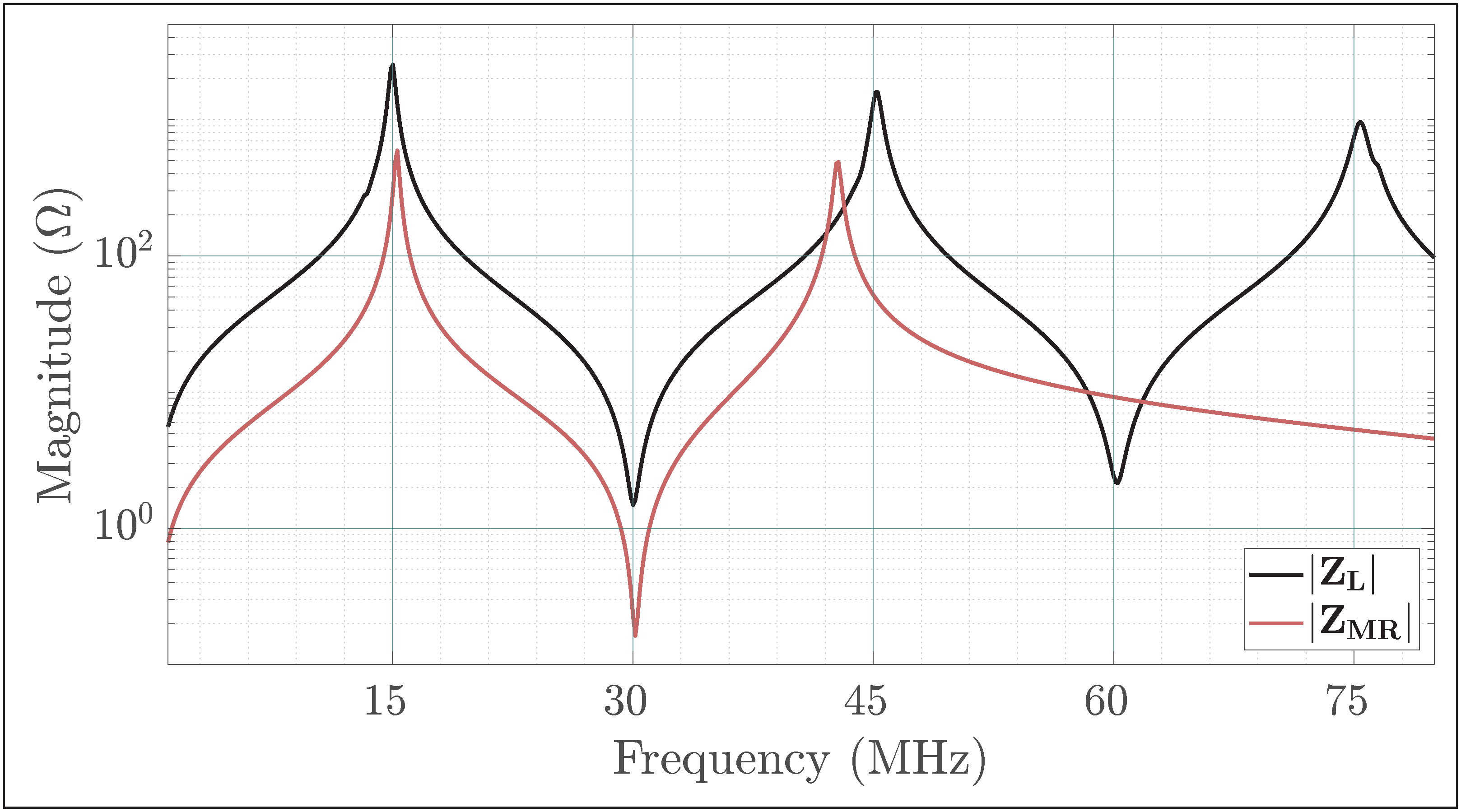
Figure 17 depicts the overall circuit of the class inverter, with its key impedances annotated.“Figure 3 shows the proposed switched-mode resonant inverter, which we term the inverter. It is closely related to the class Φ [EF in this work] inverter of [5], [25] [respectively [4,35] in this work], but has the high-order transmission-line network replaced by the low-order resonant network illustrated in Figure 4 [Figure 16 in this work] (or an equivalent network).”J. Rivas in [7]
5. Discussion
5.1. Limitations
5.1.1. Sensitivity to Parasitic Elements and Component Tolerances
- Negligible parasitic elements (e.g., stray inductance, ON-state resistance).
- Fixed transistor capacitance , representing the full switching range from 0 to .
- Infinite quality factor for the output filter.
5.1.2. Generality of the Design Chart
- Restricted coverage of the design chart: extreme regions of the chart were not experimentally validated. However, the tested conditions reflect realistic operating scenarios.
- Fixed design parameters: experiments were conducted at a single input voltage ( V), transistor capacitance (), and switching frequency (15 MHz). Accuracy outside this parameter set is not guaranteed.
5.2. Expected Benefits and Perspectives
5.2.1. Comparison with Existing Design Methodologies
5.2.2. Design of Novel Conversion Architectures
- Align with a -curve in the ZVS or ZCS region, enabling soft switching over a wide load range without modifying the duty cycle.
- Align with the EF locus to maintain simultaneous ZVS and ZCS, with duty cycle adjustment per load as needed.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Name | Definition | Expression |
|---|---|---|
| r | Normalized resistance | |
| x | Normalized reactance | |
| i | Normalized output current | |
| p | Normalized output power | |
| v | Normalized voltage | |
| q | Normalized reverse charge |
References
- Perreault, D.J.; Hu, J.; Rivas, J.M.; Han, Y.; Leitermann, O.; Pilawa-Podgurski, R.C.; Sagneri, A.; Sullivan, C.R. Opportunities and Challenges in Very High Frequency Power Conversion. In Proceedings of the 2009 Twenty-Fourth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, Washington, DC, USA, 15–19 February 2009; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lucia, O.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, S.; Guan, Y.; Xu, D. A Review of High Frequency Power Converters and Related Technologies. IEEE Open J. Ind. Electron. Soc. 2020, 1, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Guan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W. Topologies and control strategies of very high frequency converters: A survey. CPSS Trans. Power Electron. Appl. 2017, 2, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinney, J.W.; Perreault, D.J.; Lang, J.H. Radio-Frequency Inverters with Transmission-Line Input Networks. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2007, 22, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebennikov, A. High-Efficiency Class-FE Tuned Power Amplifiers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2008, 55, 3284–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thian, M.; Barakat, A.; Fusco, V. High-efficiency harmonic-peaking class-EF power amplifiers with enhanced maximum operating frequency. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2015, 63, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, J.M.; Han, Y.; Leitermann, O.; Sagneri, A.; Perreault, D.J. A High-Frequency Resonant Inverter Topology with Low Voltage Stress. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 17–21 June 2007; pp. 2705–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, Y.; Miura, Y.; Handa, H.; Ueda, T.; Ise, T. Characteristics of Isolated DC–DC Converter with Class Phi-2 Inverter Under Various Load Conditions. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 10887–10897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Hirokawa, M. A Class Φ2 Resonant Buck Converter with Ripple Injection Burst Control Method. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Power Electronics Conference (IPEC-Niigata 2018 -ECCE Asia), Niigata, Japan, 20–24 May 2018; pp. 4133–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.-Y.; He, J.-P.; Li, Z.-F. Resonant DC/DC converter with Class Φ2 inverter and Class DE rectifier based on GaN HEMT. In Proceedings of the 2020 22nd European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’20 ECCE Europe), Lyon, France, 7–11 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laha, A.; Kalathy, A.; Pahlevani, M.; Jain, P. A comprehensive review on wireless power transfer systems for charging portable electronics. Eng 2023, 4, 1023–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaechele, K.D.; Kocher, K.; Ulmer, S.; Soenmez, E.; Schullerus, G. Class Phi2 Amplifier using GaN HEMTs at 13.56MHz with Tuned Transformer for Wireless Power Transfer. In Proceedings of the PCIM Europe 2022—International Exhibition and Conference for Power Electronics, Intelligent Motion, Renewable Energy and Energy Management, Nürnberg, Germany, 10–12 May 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Xu, J.; Makhoul, R.; Davila, J.M.R. Implementing an impedance compression network to compensate for misalignments in a wireless power transfer system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 4173–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczuk, M.K.; Czarkowski, D. Resonant Power Converters, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Corti, F.; Grasso, F.; Reatti, A.; Ayachit, A.; Saini, D.K.; Kazimierczuk, M.K. Design of class-E ZVS inverter with loosely-coupled transformer at fixed coupling coefficient. In Proceedings of the IECON 2016—42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Florence, Italy, 23–26 October 2016; pp. 5627–5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surakitbovorn, K.N.; Rivas-Davila, J.M. On the Optimization of a Class-E Power Amplifier with GaN HEMTs at Megahertz Operation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 4009–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jayathurathnage, P.; Kyyrä, J.; Zhang, Y. Data-Driven Design of MHz Resonant Converters for Full-Freedom Soft-Switching Optimization. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jayathurathnage, P.; Kyyrä, J. A New Simplified Method and Design Guidelines for the Optimization of Push–Pull Class Φ2 Converters for Wireless Power Transfer Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 10442–10459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Guan, Y.; Yao, T.; Zong, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D. A Family of Class EF Resonant Inverters with Constant AC Voltage Output and Load-Independent Characteristics. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 7029–7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Xu, D. Analytical Derivation and Design of 20-MHz DC–DC Soft-Switching Resonant Converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Asiya; Wei, X.; Nguyen, K.; Sekiya, H. Analysis and Design of Generalized Class-E/F2 and Class-E/F3 Inverters. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 61277–61288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kyyrä, J.; Blaabjerg, F. Data-Based Circuit Design Method for Class Φ Resonate Converters. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Design Methodologies Conference (DMC), Grenoble, France, 18–20 November 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Lyu, D.; Zhang, M.; Dong, M.; Min, R.; Zhang, Q.; Tong, Q.; Zou, X. Linear Equivalent Model for VHF Class Φ2 Inverter Based on Spectrum Quantification Method to Reduce GaN Reverse Conduction Loss. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 61635–61645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Lu, L.; Tong, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Min, R.; Peng, H.; Zou, X. Harmonic Weighting and Target Function Design Strategy to Minimize Switch Voltage Stress of Class Φ2 Inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 12289–12300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Jin, K.; Tan, R. Resonant-Linear Hybrid Structure for Power Amplifier at Radio Frequency Band. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 5113–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforidis, I.; Arteaga, J.M.; Kwan, C.H.; Pucci, N.; Yates, D.C.; Mitcheson, P.D. Generalized Multistage Modeling and Tuning Algorithm for Class EF and Class Φ Inverters to Eliminate Iterative Retuning. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 12877–12900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Zulauf, G.; Zhang, Z.; Chakraborty, S.; Rivas-Davila, J. Push–Pull Class Φ2 RF Power Amplifier. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 10515–10531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslaniec, L.; Jurkov, A.S.; Bastami, A.A.; Perreault, D.J. Design of Single-Switch Inverters for Variable Resistance/Load Modulation Operation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 3200–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Kai, Y.; Lao, Y.; Wang, J.; Meng, F. Demonstration of Low DV/DT Class-Φ2 DC-DC Converter with 50% Duty Cycle. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 15759–15767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, J.S.; Rivas, J.M. A 500 W push-pull dc-dc power converter with a 30 MHz switching frequency. In Proceedings of the 2010 Twenty-Fifth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Palm Springs, CA, USA, 21–25 February 2010; pp. 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panov, Y.; Huber, L.; Jovanović, M.M. Design Optimization and Performance Evaluation of Class Φ2 VHF DC/DC Converter. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), New Orleans, LA, USA, 15–19 March 2020; pp. 2170–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, N.; Komiyama, Y.; Zhu, W.; Xie, Y.; Komanaka, A.; Konishi, A.; Nguyen, K.; Sekiya, H. ML-Based Fully-Numerical Design Method for Load-Independent Class-EF WPT Systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, M.; Burkart, R.M.; Deboy, G.; Kolar, J.W. ZVS of Power MOSFETs Revisited. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 8063–8067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daire, B.; Martin, C.; Sixdenier, F.; Joubert, C.; Pace, L. Experimental Investigation of Class Phi Inverter Under Various Load Conditions. In Proceedings of the PCIM Europe 2024—International Exhibition and Conference for Power Electronics, Intelligent Motion, Renewable Energy and Energy Management, Nürnberg, Germany, 11–13 June 2024; pp. 3105–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinney, J.W. Multi-Resonant Passive Components for Power Conversion. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Grebennikov, A. Circuit design technique for high efficiency Class F amplifiers. In Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest (Cat. No.00CH37017), Boston, MA, USA, 11–16 June 2000; Volume 2, pp. 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhoul, R.; Maynard, X.; Perichon, P.; Frey, D.; Jeannin, P.O.; Lembeye, Y. A Comprehensive Sensitivity Evaluation of a GaN Based Class Φ2 Inverter at Very High Frequency (VHF). In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Melbourne, Australia, 13–15 February 2019; pp. 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

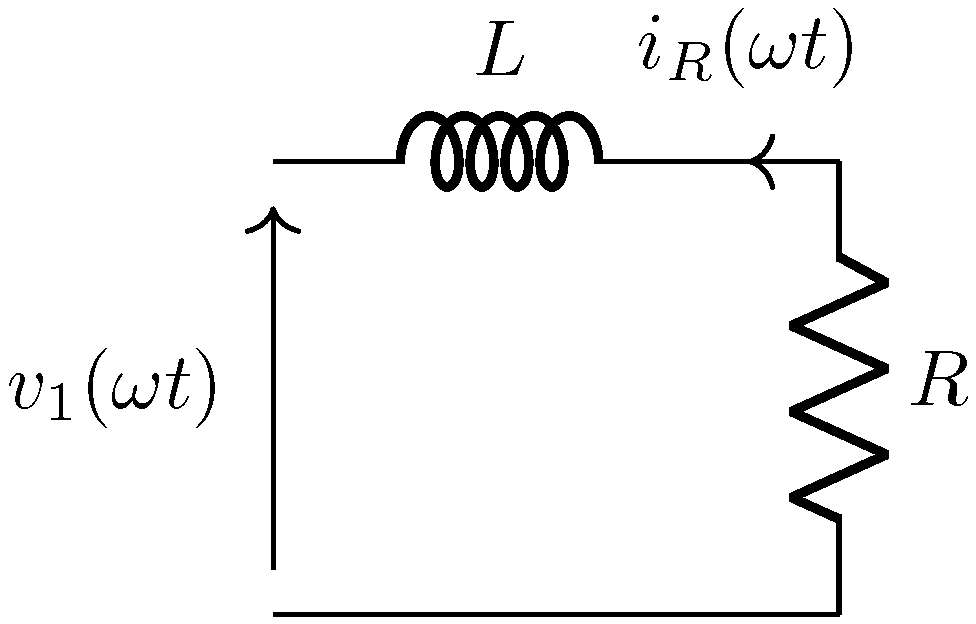


| S | ON | OFF | OFF | OFF |
| 0 | 0 | |||
| 0 | 0 | |||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 0 | ||||
| Point | A | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Homemade AWG16 inductance | |||
| 100B471JT300XT (KYOCERA AVX) (470 pF—300 V) | |||
| R | MP9100-5.00-1% | MP9100-7.50-1% | MP9100-15.0-1% |
| () | () | R () | X () | r | x | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 19.33 | 73.36 | 5.53 | 18.52 | 0.20 | 0.67 |
| B | 20.14 | 65.98 | 8.20 | 18.40 | 0.30 | 0.67 |
| C | 24.17 | 47.98 | 16.18 | 17.96 | 0.59 | 0.65 |
| D (%) | p | P (W) | v | (V) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 28.4 | 0.3 | 6.80 | 0 (ZVS) | 0.22 | |
| B | 20.7 | 0.38 | 8.62 | 0 (ZVS & ZCS) | ||
| C | 21.1 | 0.41 | 9.30 | 0.26 | 13 | 0 (ZCS) |
| D | P | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted | Measured | Error | Predicted | Measured | Error | |
| A | 28.4% | 30.8% | 7.8% | 6.80 W | 7.29 W | 7.2% |
| B | 20.7% | 23.8% | 15.0% | 8.62 W | 9.21 W | 6.8% |
| C | 21.1% | 23.8% | 12.8% | 9.30 W | 10.34 W | 11.2% |
| Name | Reference | Value | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| VJ1111D181JXLAJ | 2 × 180 pF | Vishay | |
| 1010VS-141 | 146 nH | Coilcraft | |
| 100B331JW600XC100 | 330 pF | KYOCERA AVX | |
| 1212VS-90N | 90 nH | Coilcraft |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daire, B.; Martin, C.; Sixdenier, F.; Joubert, C.; Pace, L. A Graphical Tool for Predicting Class EF Inverter Behavior Including Non-Ideal Load Conditions. Energies 2025, 18, 5409. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205409
Daire B, Martin C, Sixdenier F, Joubert C, Pace L. A Graphical Tool for Predicting Class EF Inverter Behavior Including Non-Ideal Load Conditions. Energies. 2025; 18(20):5409. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205409
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaire, Baptiste, Christian Martin, Fabien Sixdenier, Charles Joubert, and Loris Pace. 2025. "A Graphical Tool for Predicting Class EF Inverter Behavior Including Non-Ideal Load Conditions" Energies 18, no. 20: 5409. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205409
APA StyleDaire, B., Martin, C., Sixdenier, F., Joubert, C., & Pace, L. (2025). A Graphical Tool for Predicting Class EF Inverter Behavior Including Non-Ideal Load Conditions. Energies, 18(20), 5409. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205409






