Non-Isolated High Step-Up DC-DC Interleaved Boost Converter Based on Coupled Inductors and Voltage Multiplier Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Topologies with high or ultra-high voltage gain and rated power in the range of a few hundred watts, available in thousands of publications.
- (2)
- Topologies with low voltage gain and power levels ranging from a few kilowatts to tens of kilowatts, as seen in conventional interleaved converters without high step-up capability.
- (3)
- Topologies with high voltage gain and rated power in the range of a few kilowatts, which are addressed in a significantly smaller number of works.
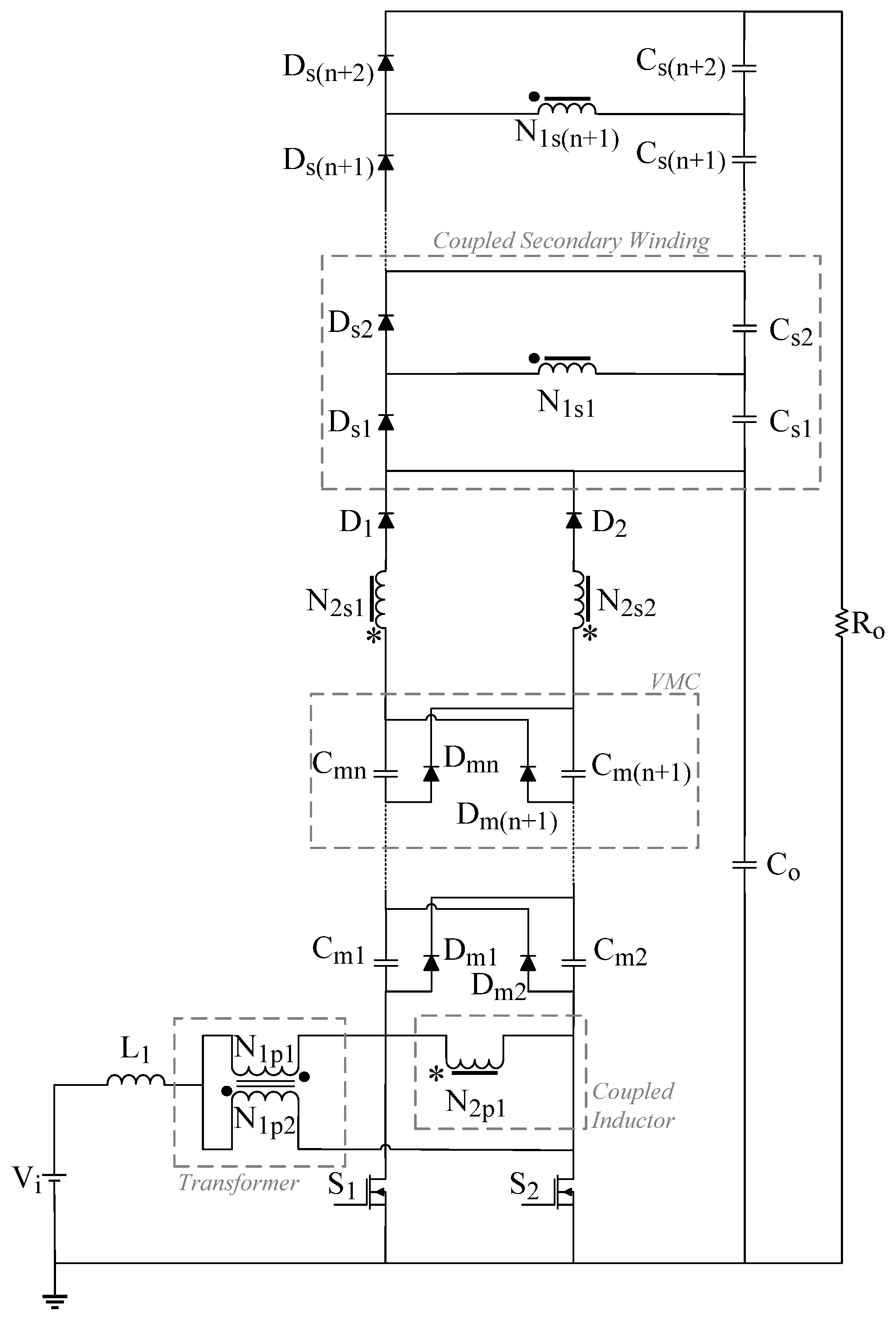
2. Proposed Non-Isolated High Step-Up Interleaved Boost Converter
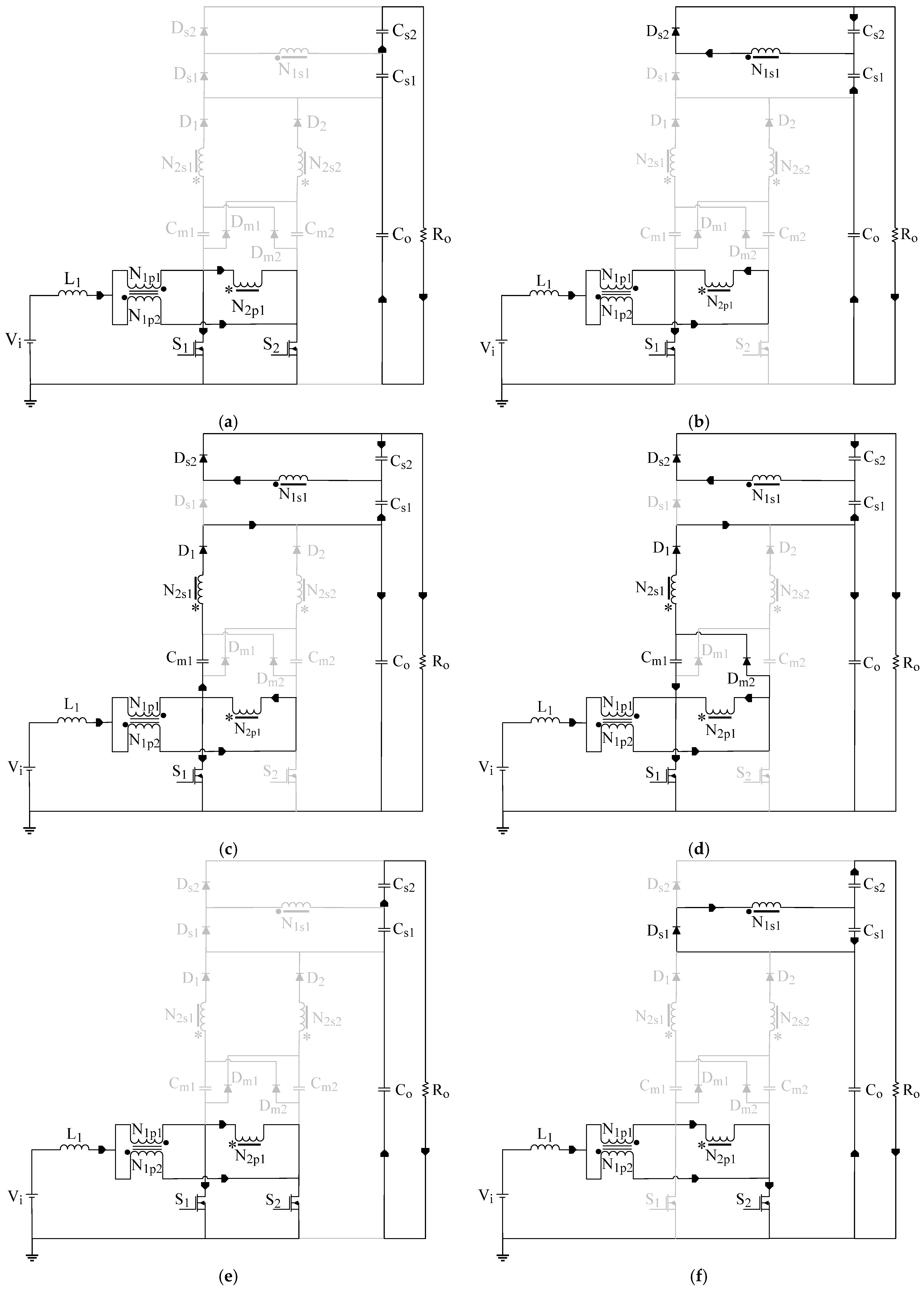
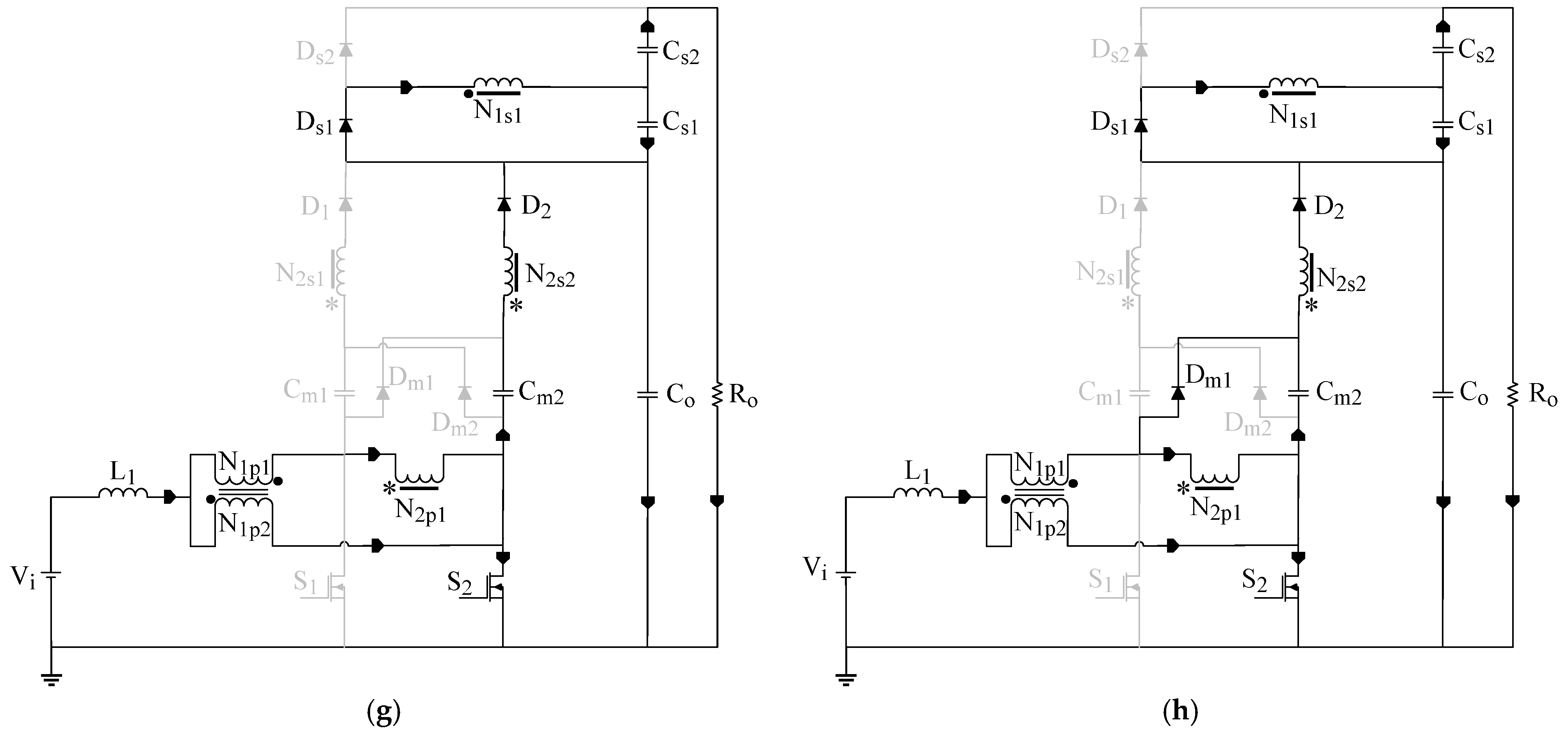
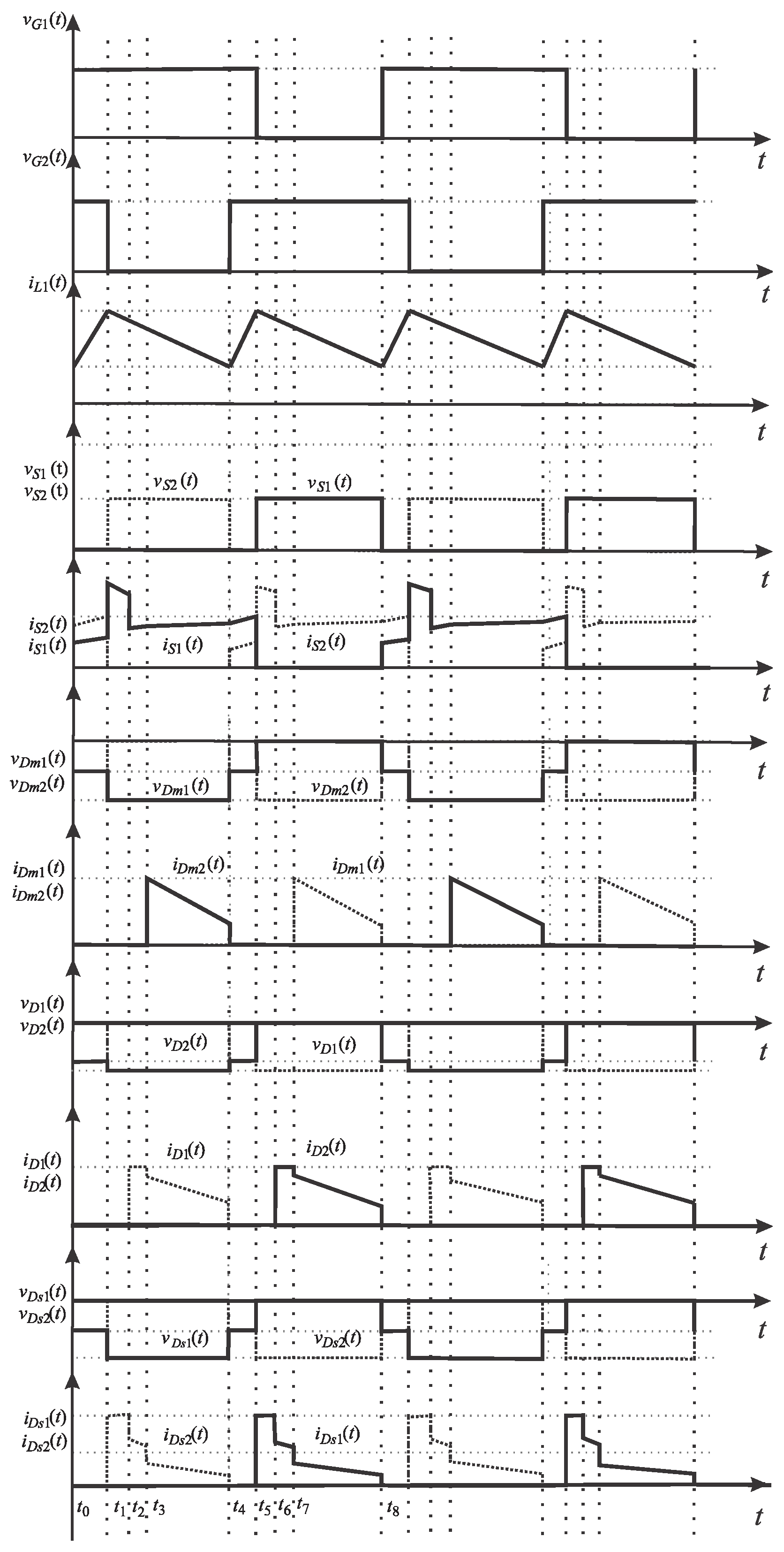
2.1. Qualitative Analysis
2.2. Quantitative Analysis
2.3. Small-Signal Modeling
3. Comparison with Other Non-Isolated High Step-Up Interleaved Boost Converters
4. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farajdadian, S.; Hajizadeh, A.; Soltani, M. Recent developments of multiport dc/dc converter topologies, control strategies, and applications: A comparative review and analysis. Energy Rep. 2024, 11, 1019–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, K.; Arif, M.S.B.; Masud, M.I.; Ahmad, M.F.; Alqarni, M. Optimal selection of extensively used non-isolated dc–dc converters for solar PV applications: A review. Energies 2025, 18, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikkumar, S.; Sheela, A.; Talluri, M.T.; Krishna, B. Single switch hybrid network-based large step-up dc-dc converter for solar PV applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2024, 71, 3573–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guepfrih, M.F.; Waltrich, G.; Lazzarin, T.B. Quadratic-boost-double-flyback converter. IET Power Electron. 2019, 12, 3166–3177. [Google Scholar]
- Forouzesh, M.; Siwakoti, Y.P.; Gorji, S.A.; Blaabjerg, F.; Lehman, B. Step-up dc–dc converters: A comprehensive review of voltage boosting techniques, topologies, and applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 9143–9178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Ruan, X.; Ye, Z. High step-up dc–dc converter based on switched capacitor and coupled inductor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 5572–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Cheng, K.W.E.; Chen, S. A high step-up PWM dc–dc converter with coupled-inductor and resonant switched-capacitor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 7739–7749. [Google Scholar]
- Costa da Silva Bernardo Loureiro, P.H.; Klein Faistel, T.M.; Toebe, A.; Spencer Andrade, A.M.S. Generation and comparative analysis of high voltage gain non-isolated dc–dc converters with ladder switched capacitor and coupled inductor. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 10, 6742–6753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshkati, E.; Packnezhad, M.; Farzanehfard, H.; Khajehoddin, S.A. Soft switched high step-up multi-port converter with single magnetic core and auxiliary switch for renewable energy applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025, 72, 288–298. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, W.; Mallik, A. Modeling and design optimization of a bidirectional ultrahigh gain dc/dc converter for cell-integrated power electronics. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2025, 13, 3297–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarzamni, H.; Gohari, H.S.; Sabahi, M.; Kyyrä, J. Nonisolated high step-up dc–dc converters: Comparative review and metrics applicability. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 582–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valarmathy, A.S.; Prabhakar, M. High gain interleaved boost-derived dc-dc converters—A review on structural variations, gain extension mechanisms and applications. e-Prime—Adv. Electr. Eng. Electron. Energy 2024, 8, 100618. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, Q.; Zheng, J.; Liu, X.; Huangfu, Y.; Li, Z.-p. Design and control studies of six-phase interleaved boost converter for integrated energy efficiency improvement of green ship. J. Energy Storage 2024, 96, 112549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-J.; Yang, S.-P.; Huang, C.-M.; Hu, P.-Y. High step-up interleaved dc–dc converter with voltage-lift capacitor and voltage multiplier cell. Electronics 2025, 14, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghela, M.A.; Mulla, M.A. High step-up gain converter based on two-phase interleaved coupled inductor without right-hand plane zero. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 5911–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Rezvanyvardom, M.; Mekhilef, S. High step-up interleaved zero-voltage transition dc–dc converter with coupled inductors. IET Power Electron. 2020, 13, 4518–4531. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, T.J.; Lee, J.H.; Chen, S.M.; Chen, J.F.; Yang, L.S. Novel isolated high-step-up dc–dc converter with voltage lift. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Lin, M.; Ai, J. High step-up interleaved dc–dc converter with asymmetric voltage multiplier cell and coupled inductor. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 8, 4209–4222. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Fu, D.; Kan, J.; Wang, T. Dual switches dc/dc converter with three-winding-coupled inductor and charge pump. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 461–469. [Google Scholar]
- Guepfrih, M.F.; Waltrich, G.; Lazzarin, T.B. High step-up dc-dc converter using built-in transformer voltage multiplier cell and dual boost concepts. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 6700–6712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Lin, W.C.; Liang, R.H. An interleaved high step-up dc-dc converter with double boost paths. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2015, 43, 967–983. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, L.; Siadatan, A.; Afjei, E.; Javadi, S. An efficient interleaved boost dc–dc converter with high-voltage gain based on switched capacitor. Electr. Eng. 2024, 107, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarsan Reddy, D.V.; Thangavel, S. A non-isolated high step up interleaved boost converter with coupled inductors. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2022, 50, 3153–3170. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.A.; Prajapati, A.; Chaudhary, K. High-gain compact interleaved boost converter with reduced voltage stress for PV application. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 10, 4763–4770. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemzadeh, S.M.; Al-Hitmi, M.A.; Aghaei, H.; Marzang, V.; Iqbal, A.; Babaei, E.; Hosseini, S.H.; Islam, S. An ultra-high voltage gain interleaved converter based on three-winding coupled inductor with reduced input current ripple for renewable energy applications. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2024, 18, 141–151. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, S.W.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Choi, H.H. Transformerless quadruple high step-up dc/dc converter using coupled inductors. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 26501–26513. [Google Scholar]
- Nouri, T.; Kurdkandi, N.V.; Shaneh, M. A novel interleaved high step-up converter with built-in transformer voltage multiplier cell. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 4988–4999. [Google Scholar]
- Alizadeh, D.; Babaei, E.; Sabahi, M.; Cecati, C. A family of high step-up interleaved dc-dc converters based on the coupled inductors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025, 72, 345–355. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimi, R.; Habibi, S.; Ferdowsi, M.; Shamsi, P. An interleaved high step-up dc-dc converter based on integration of coupled inductor and built-in-transformer with switched-capacitor cells for renewable energy applications. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 34–45. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, S.W.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.B. Ultra-high step-up interleaved converter with low voltage stress. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 37167–37178. [Google Scholar]
- Denholm, I.K.; Hassan, W.; Negnevitsky, M.; Lu, D.D.C. Optimized interleaved ultra-high gain dc-dc power converter with low ripple input current and voltage stress for fuel cell systems. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 121052–121063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasian, S.; Farsijani, M.; Tavakoli Bina, M.; Abrishamifar, A.; Hosseini, A.; Shahirinia, A. An interleaved non-isolated high gain soft switching DC–DC converter with small input current ripple. IET Power Electron. 2023, 16, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Goetz, S.M. A general modeling and analysis of impacts of unbalanced inductance on PWM schemes for two-parallel interleaved power converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 12235–12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrique Feretti, P.; Franco de Souza, A.; Custódio Gomes, A.; Silva de Morais, A.; Tofoli, F.L. A step-up/step-down direct current to direct current converter for high-power, high-current applications. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2019, 47, 445–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlebrook, R.D.; Cuk, S. A general unified approach to modelling switching-converter power stages. In Proceedings of the 1976 IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Cleveland, OH, USA, 8–10 June 1976; pp. 18–34. [Google Scholar]
- Alcazar, Y.J.A.; Lessa, T.F.; Souza, O.J.D.D.; Torrico-Bascopé, R.P. Modelling of nonisolated high-voltage gain boost converters using the PWM switch model. Int. J. Electron. 2014, 101, 1134–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, T.C.; Tofoli, F.L.; de Souza Oliveira Júnior, D.; Ribeiro, E.R. Nonisolated high step-up dc-dc interleaved SEPIC converter based on voltage multiplier cells. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2022, 50, 2735–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



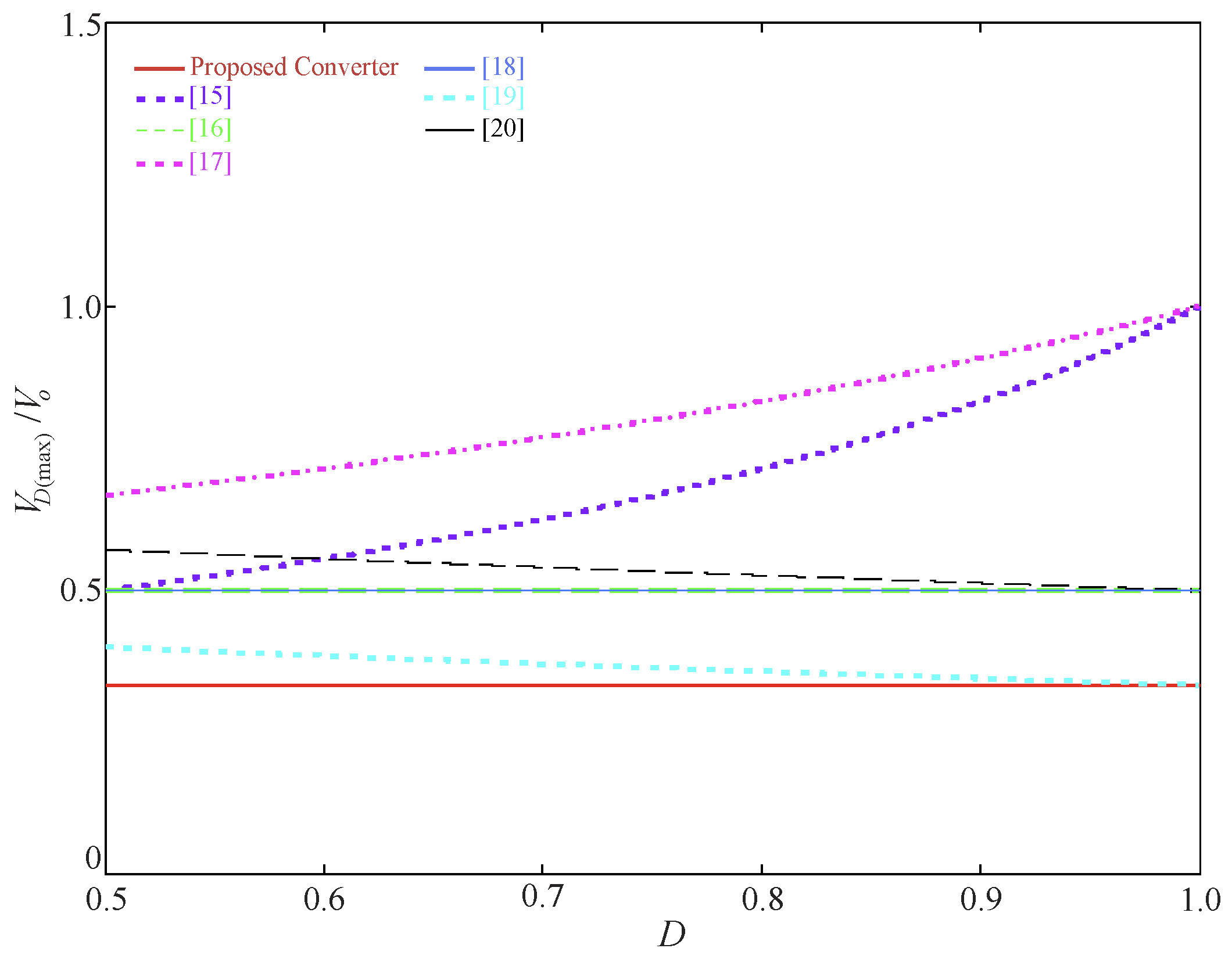






| Parameter | Proposed Converter | [15] | [16] | [17] | [18] | [19] | [20] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Switches | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Diodes | 4 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 | |
| Capacitors | 3 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6 | |
| Cores | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 |
| Windings | 4 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 6 | |
| Gain (Vo/Vi) | |||||||
| VS(max.)/Vo | |||||||
| VD(max.)/Vo | |||||||
| Specifications | 48 V/400 V | 24 V/100 V | 40 V/420 V | 24 V/200 V | 40 V/400 V | 40 V/400 V | 48 V/800 V |
| 25 kHz | 50 kHz | 100 kHz | 50 kHz | 50 kHz | 50 kHz | 50 kHz | |
| 1 kW | 200 W | 210 W | 200 W | 400 W | 500 W | 1 kW | |
| 95.12% | 95.8% | 96.5% | 96.2% | 97% | 94.5% | 93% | |
| Common ground | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| Modularity | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Isolated drive circuitry | No | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Improved current sharing | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Electrolytic capacitors | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Input voltage | Vi = 48 V |
| Output voltage | Vo = 400 V |
| Rated output power | Po = 1000 W |
| Switching frequency | fs = 25 kHz |
| Rated duty cycle | D = 0.58 |
| Input filter inductor ripple | ΔIL1 = 15%·IL1 |
| Voltage ripple across C1, C2, and C3 | ΔVC = 0.25%·Vo |
| Voltage ripple across Cm1 and Cm2 | ΔVCm = 0.5%·Vo |
| Output voltage ripple | ΔVo = 0.25%·Vo |
| Switches S1 and S2 | MOSFET IRFP90N20 by Infineon |
| Diodes D1, D2, Ds1, Ds2, Dm1, and Dm2 | Ultrafast diode U860 by ON Semiconductor |
| Capacitor C1 | 33 μF/250 V polypropylene capacitor |
| Capacitors C2 and C3 | Two parallel-connected 33 μF/250 V polypropylene capacitors |
| Capacitors Cm1 and Cm2 | Two parallel-connected polypropylene capacitors, rated at 10 μF/250 V and 33 μF/250 V |
| Filter inductor L1 | L1 = 50 µF Core: MMT052T7725 by Magmattec 18 turns, 21 × AWG22 |
| Transformer | Core: NEE-65/33/26 by Thornton N1p1 = N1p2 = 10 turns − 12 × AWG22 N1s1 = 15 turns − 8 × AWG22 (n1 = N1s1/N1p1 = 1.50) |
| Three-winding coupled inductor | Core: NEE-55/28/21 by Thornton N2p1 = 17 turns − 4 × AWG22 N2s1 = N2s2 = 21 turns − 2 × AWG22 (n2 = N2s1/N2p1 = 1.24) |
| Parameter | Calculated | Measured |
|---|---|---|
| Average inductor current (IL1) | 20.83 A | 20.90 A |
| Inductor current ripple (ΔIL1) | 3.13 A | 3.11 A |
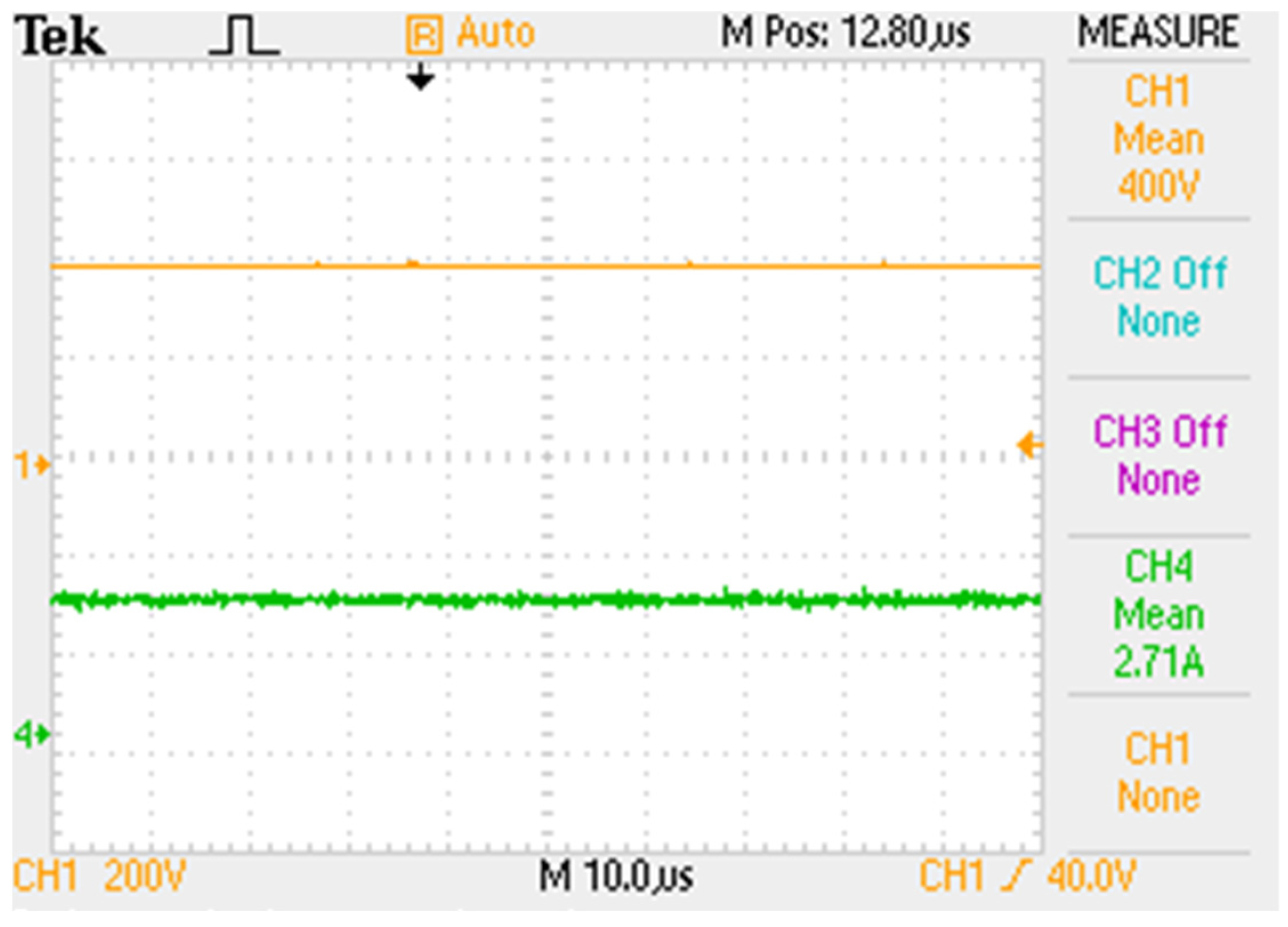
| Average output voltage (Vo) | 400.00 V | 400 V |
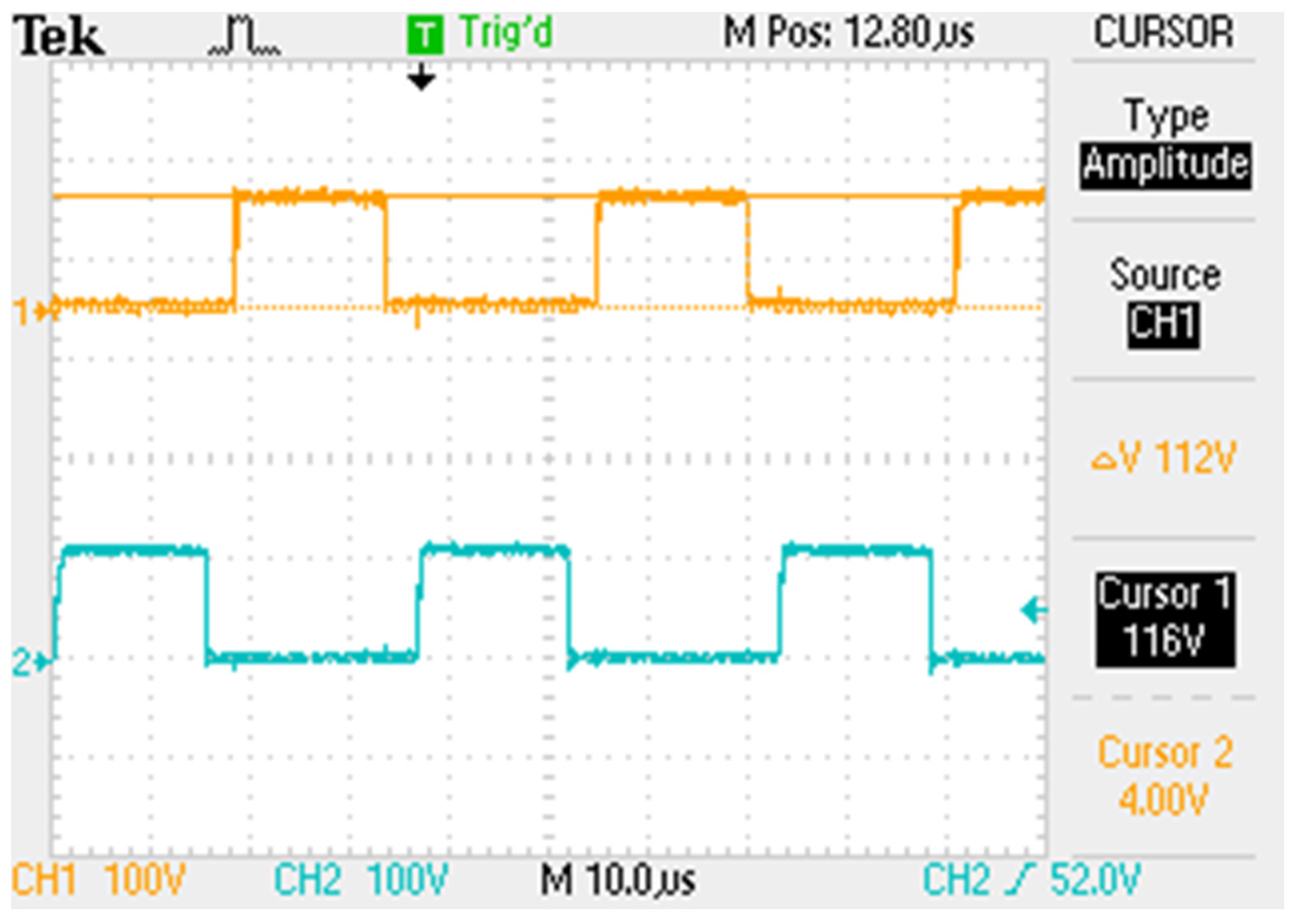
| Maximum voltage across the switches (VS1(max), VS2(max)) | 114.49 V | 112 V |
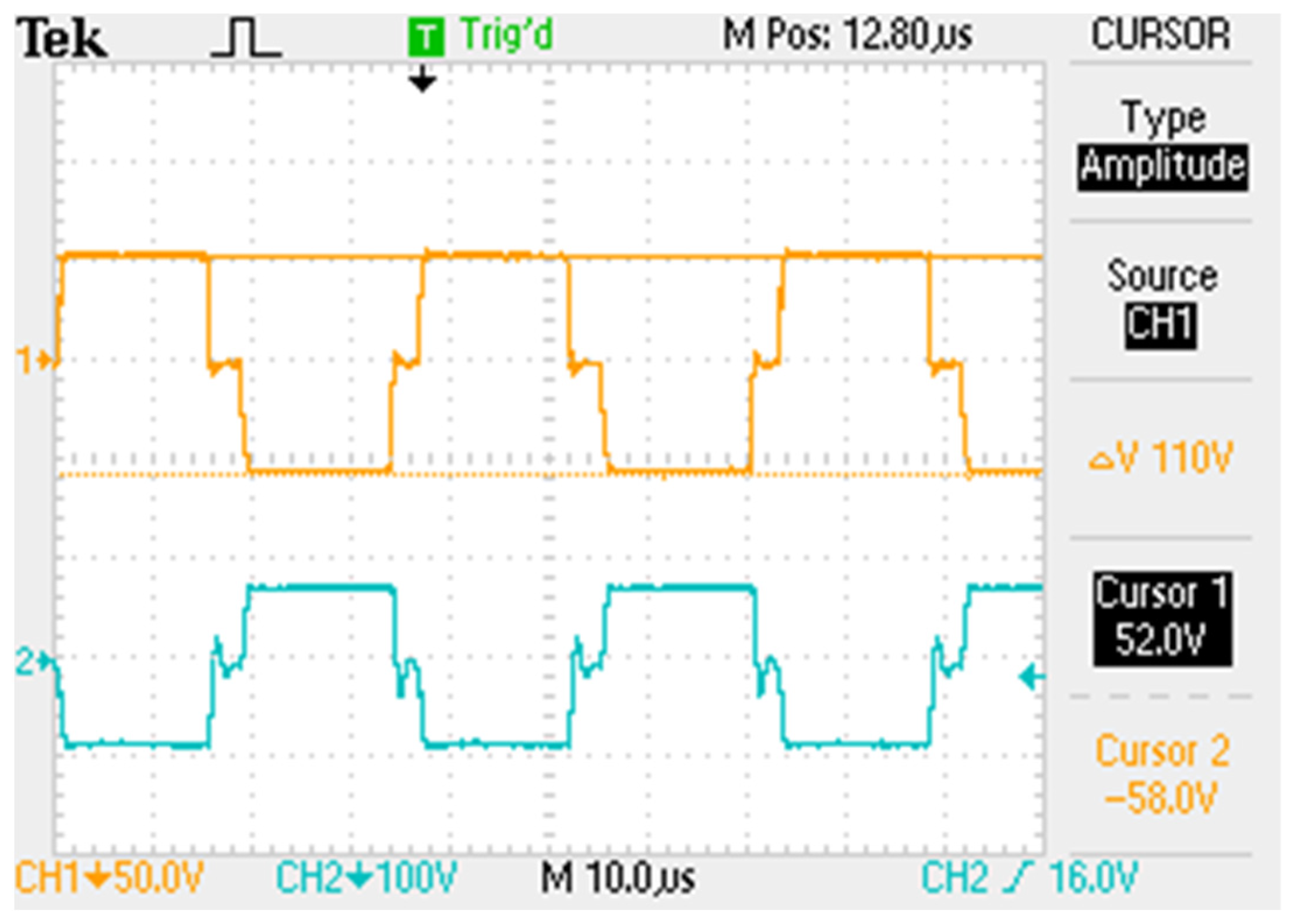
| Maximum reverse voltage across the output diodes (VD1(max), VD2(max)) | −133.84 V | −148 V |
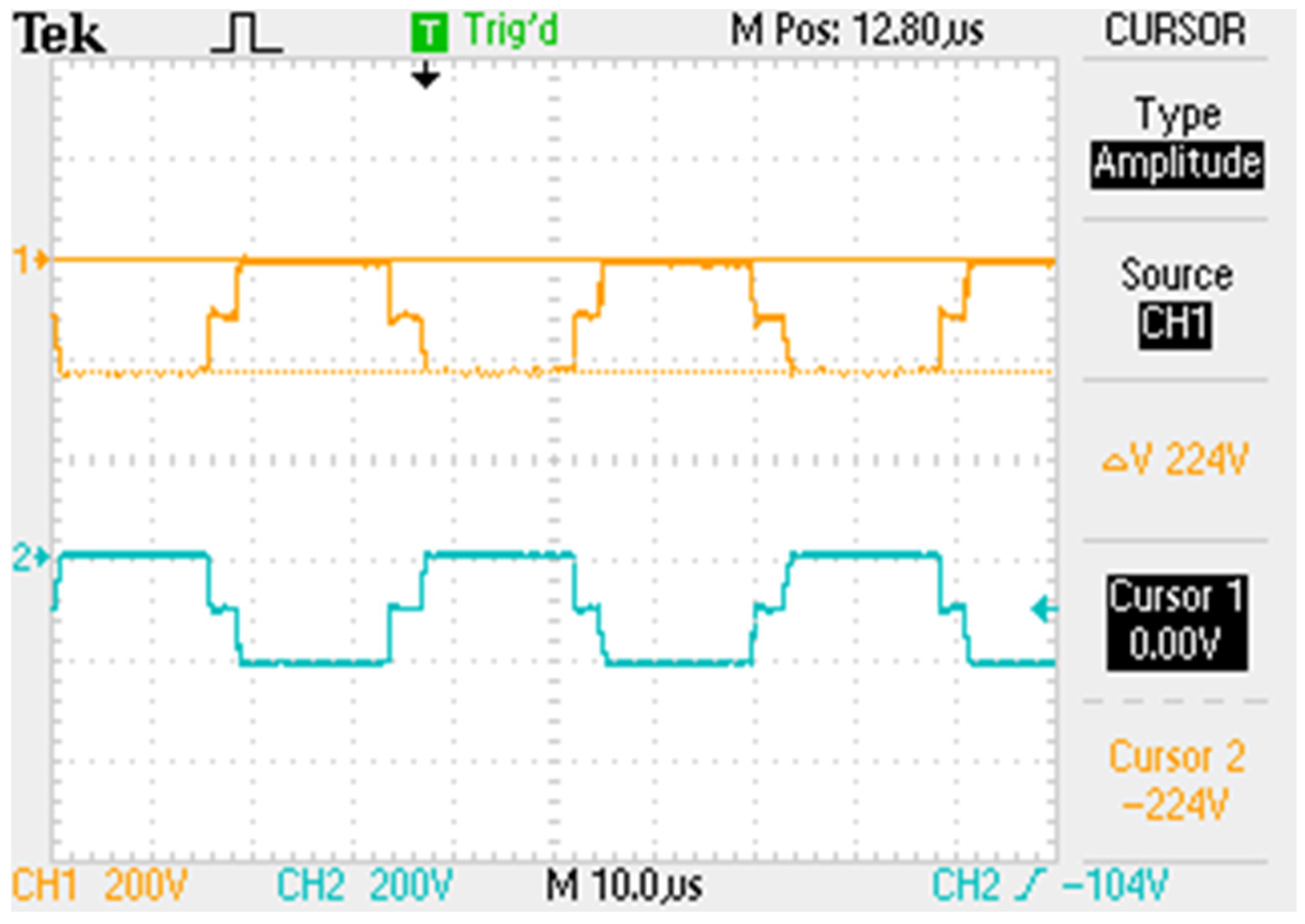
| Maximum reverse voltage across the multiplier diodes (VDm1(max), VDm2(max)) | −228.93 V | −224 V |
| Maximum reverse voltage across the secondary diodes (VDs1(max), VDs2(max)) | −161.50 V | −164 V |
| Maximum voltage across the multiplier capacitors (VCm1(max), VCm2(max)) | 114.49 V | 112 V |
| Maximum voltage across the output filter capacitor (VCo(max)) | 238.68 V | 246 V |
| Maximum voltage across the secondary capacitors (VCs1(max), VCs2(max)) | 80.96 V | 84 V |
| Maximum voltage on the primary windings of the transformer (VN1p1(max), VN1p2(max)) | 57.24 V | 56 V |
| Maximum voltage on the secondary winding of the transformer (VN1p1(max)) | 80.96 V | 80 V |
| Maximum voltage on the primary winding of the coupled inductor (VN2p1(max)) | 114.49 V | 112 V |
| Maximum voltage on the secondary windings of the coupled inductor (VN221(max), VN2s2(max)) | 124.18 V | 130 V |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salvador, T.C.; Mario da Silva, R.; Silva, W.W.A.G.; Maia, N.J.; Tofoli, F.L.; Ribeiro, E.R. Non-Isolated High Step-Up DC-DC Interleaved Boost Converter Based on Coupled Inductors and Voltage Multiplier Cells. Energies 2025, 18, 5199. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18195199
Salvador TC, Mario da Silva R, Silva WWAG, Maia NJ, Tofoli FL, Ribeiro ER. Non-Isolated High Step-Up DC-DC Interleaved Boost Converter Based on Coupled Inductors and Voltage Multiplier Cells. Energies. 2025; 18(19):5199. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18195199
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalvador, Thaís Carvalho, Rafael Mario da Silva, Waner Wodson Aparecido Goncalves Silva, Nedson Joaquim Maia, Fernando Lessa Tofoli, and Enio Roberto Ribeiro. 2025. "Non-Isolated High Step-Up DC-DC Interleaved Boost Converter Based on Coupled Inductors and Voltage Multiplier Cells" Energies 18, no. 19: 5199. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18195199
APA StyleSalvador, T. C., Mario da Silva, R., Silva, W. W. A. G., Maia, N. J., Tofoli, F. L., & Ribeiro, E. R. (2025). Non-Isolated High Step-Up DC-DC Interleaved Boost Converter Based on Coupled Inductors and Voltage Multiplier Cells. Energies, 18(19), 5199. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18195199







