Soot Mass Concentration Prediction at the GPF Inlet of GDI Engine Based on Machine Learning Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Dataset Construction
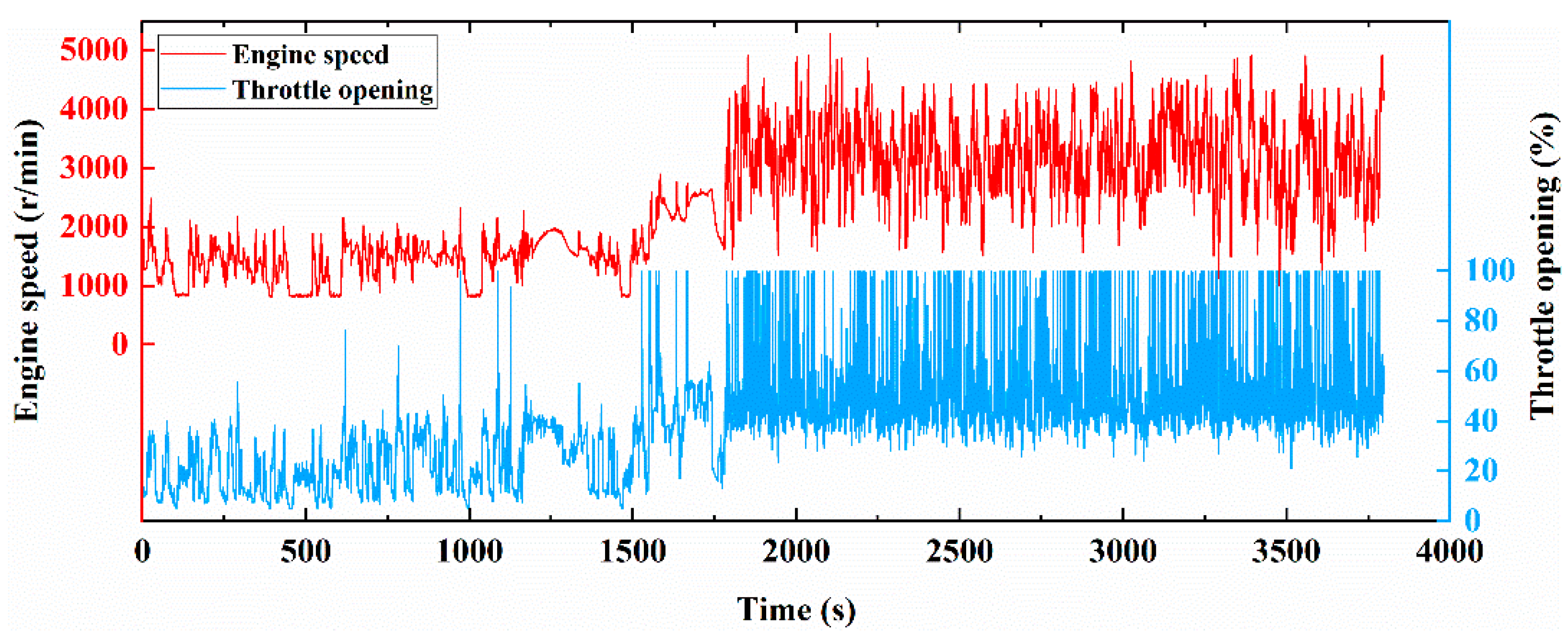
2.1. Data Collection
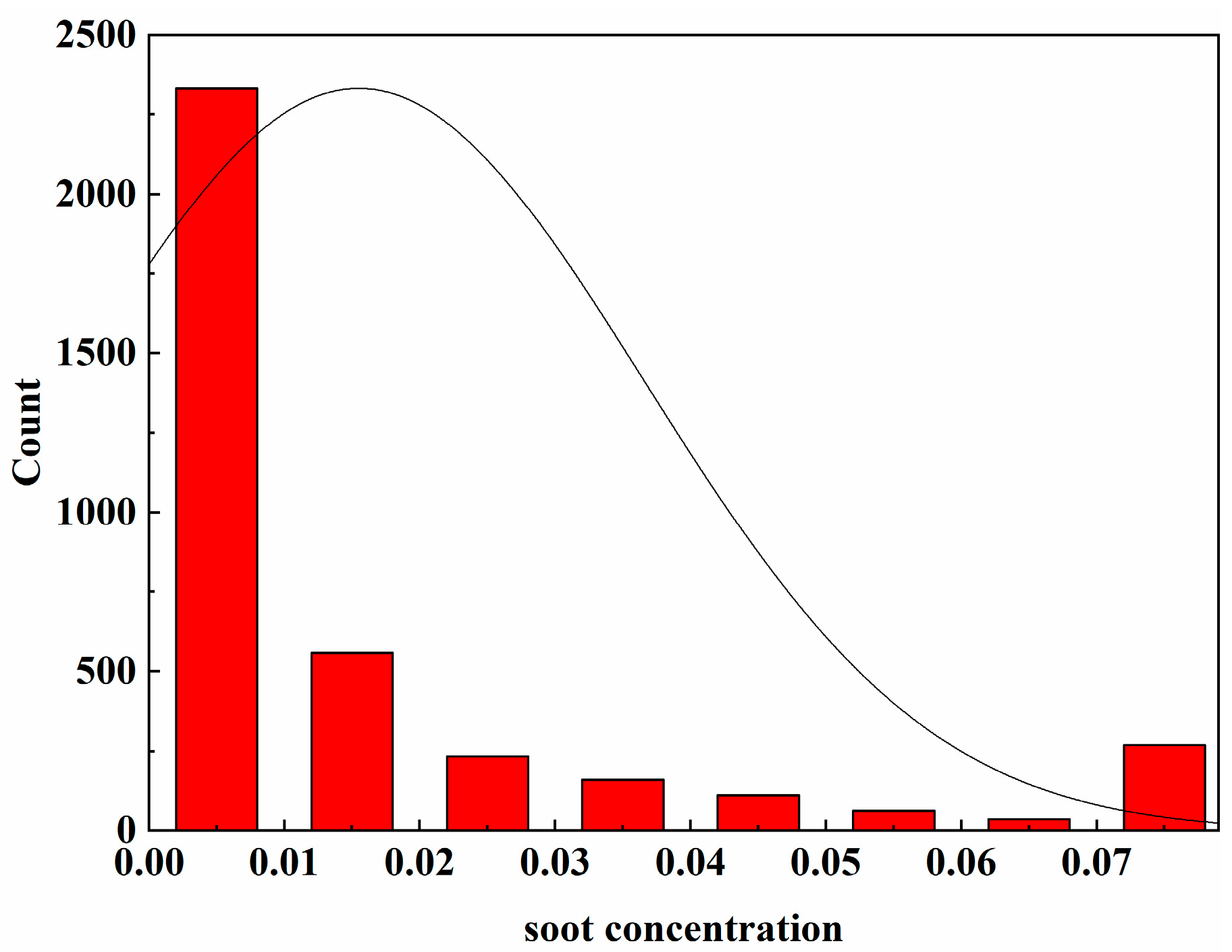
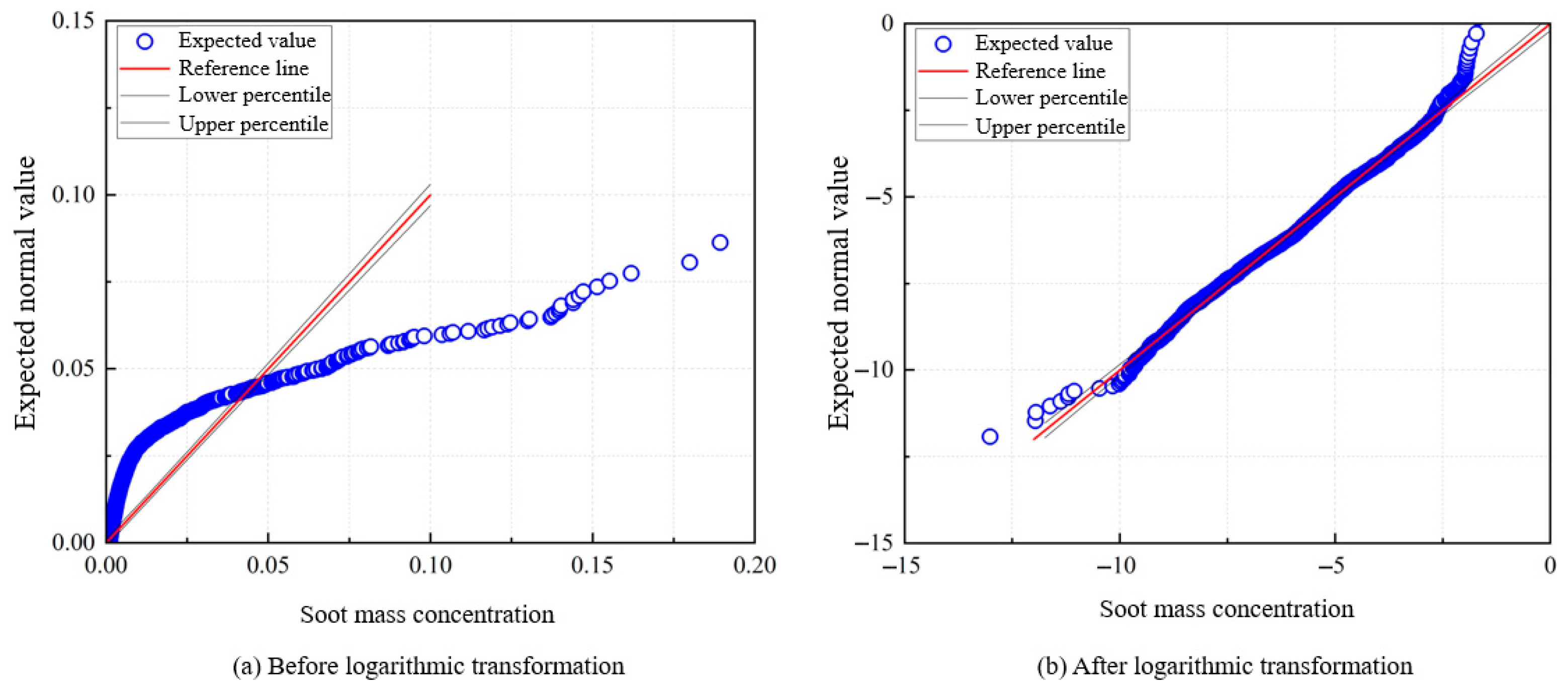
2.2. Data Normalization
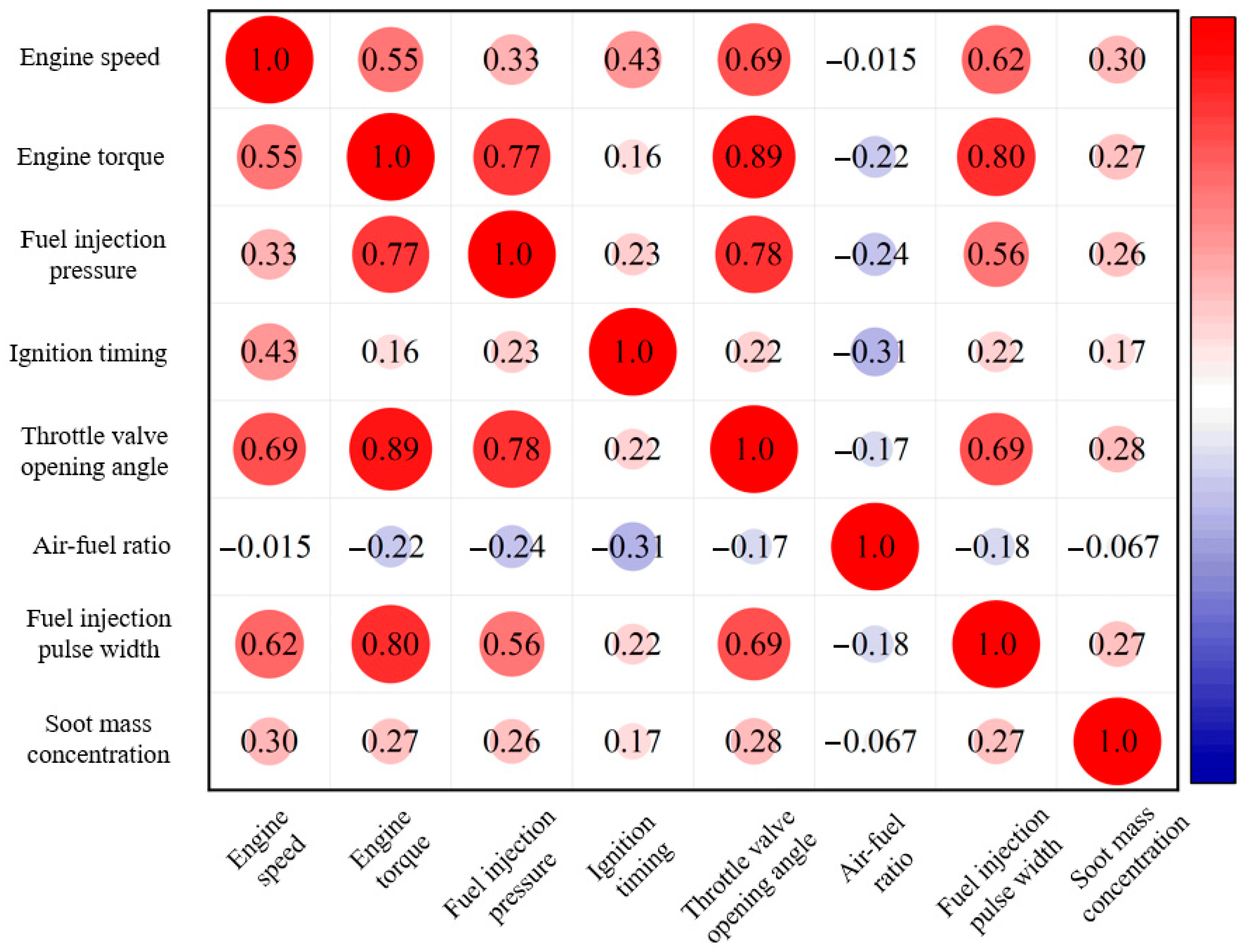
2.3. Data Correlation Analysis
3. Model Construction and Validation
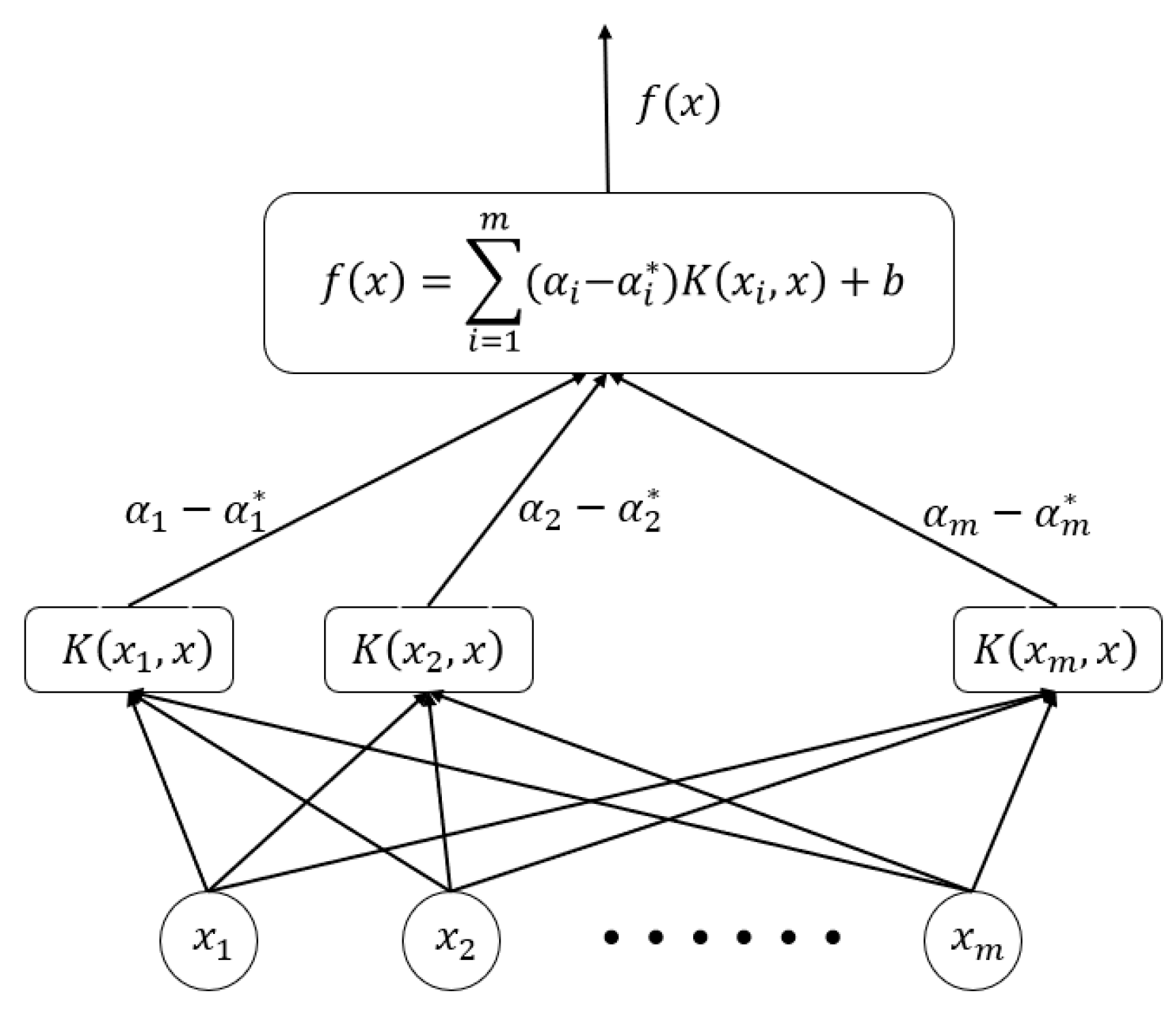
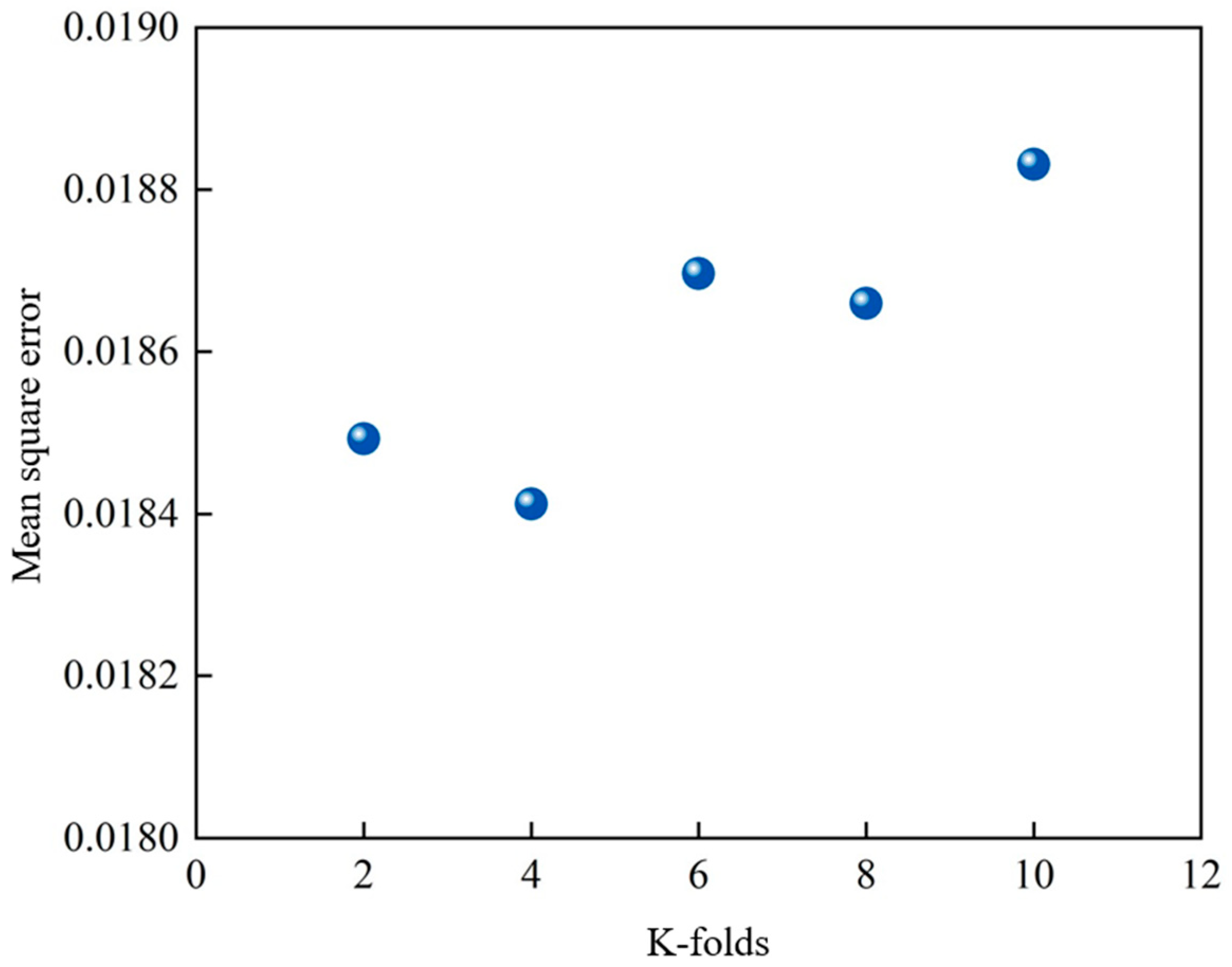
3.1. SVR Model
3.2. DNN Model
3.3. Integration Model of SVR and DNN Based on Stacking Algorithm
3.4. Analysis of Model Differences
4. Conclusions
- (1)
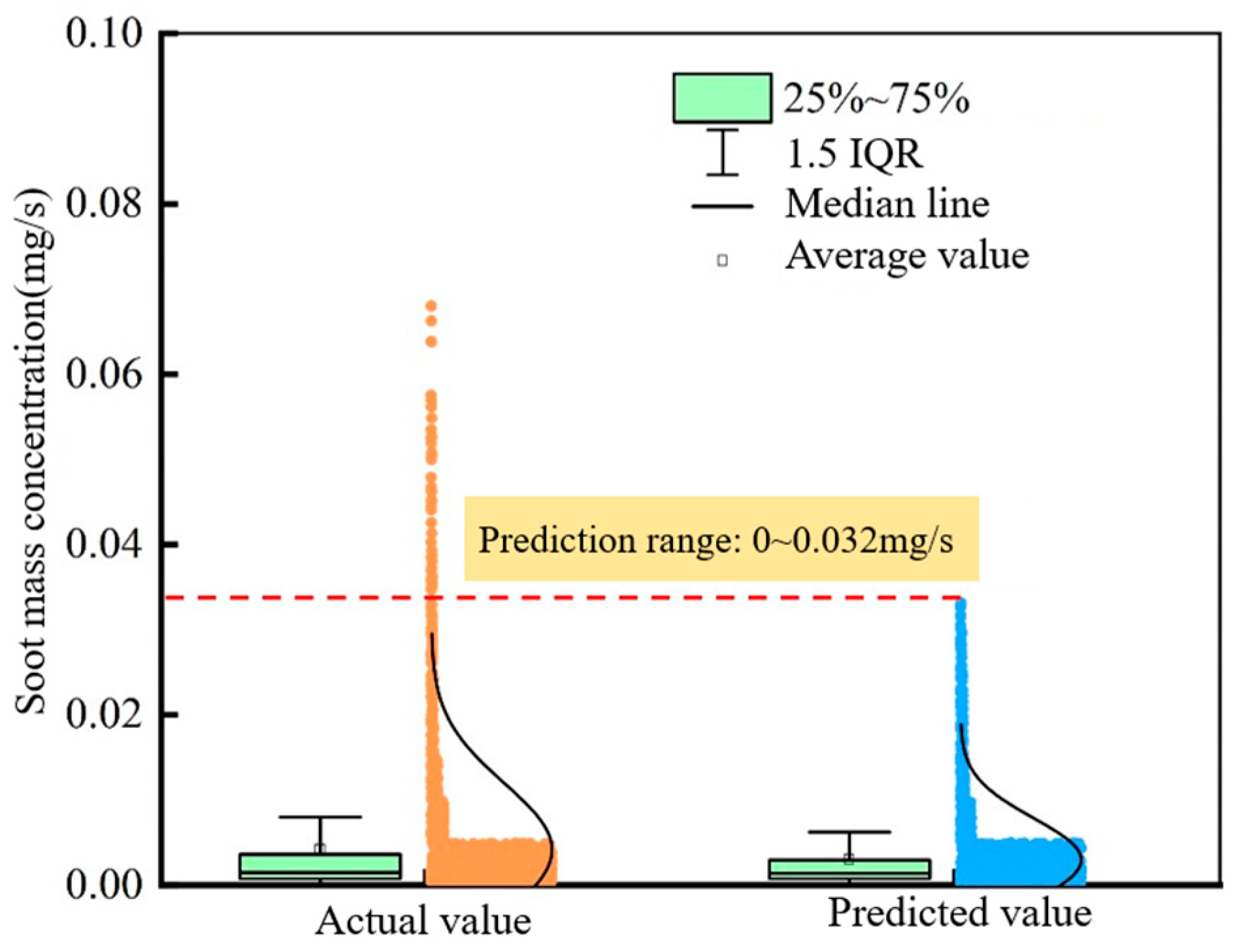
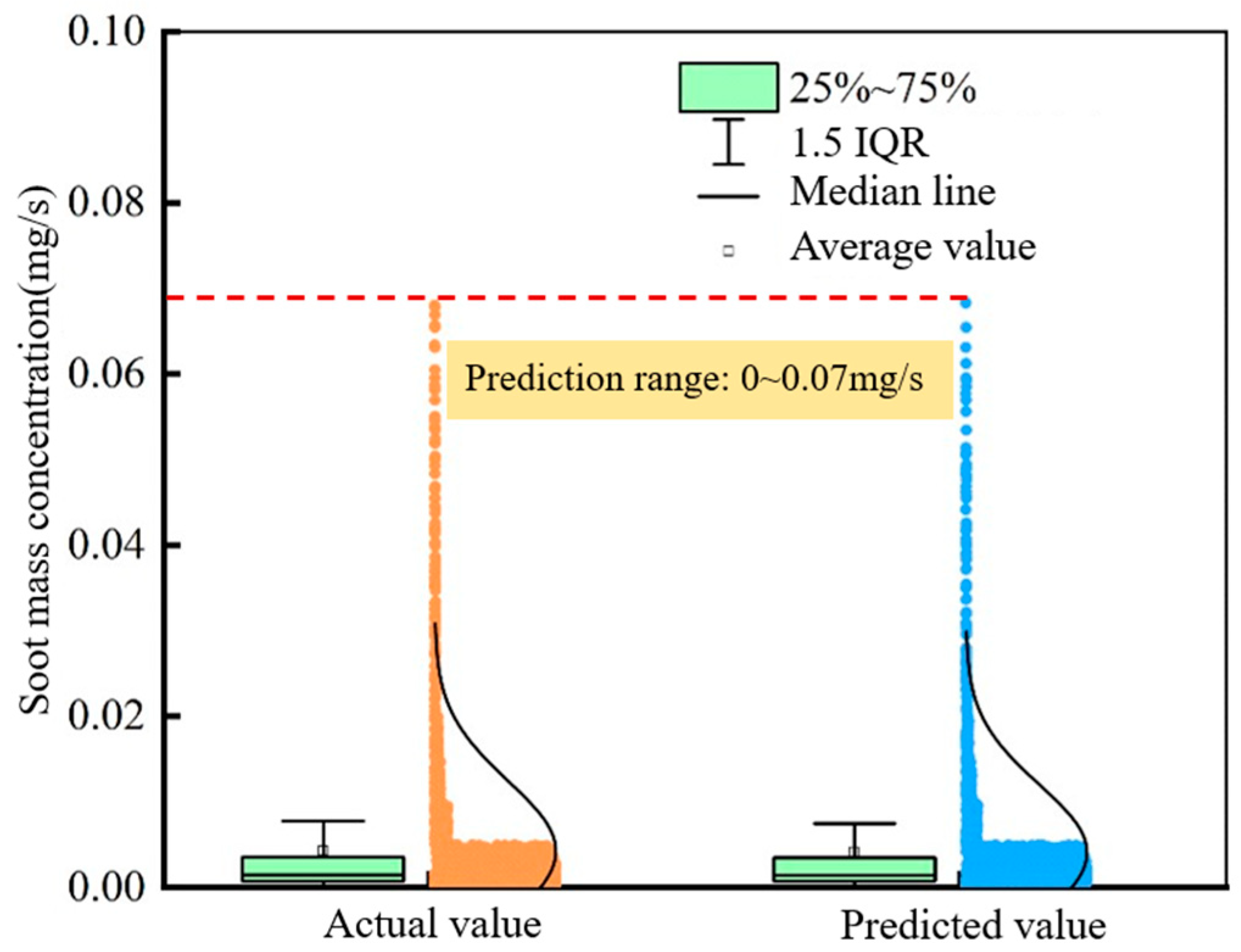
- The distribution, median, and data density of prediction results obtained by SVR, DNN, and the Stacking integration of SVR and DNN are all similar to that of the test results. The prediction ranges of soot mass concentration by using SVR, DNN, and the Stacking integration of SVR and DNN are 0–0.038 mg/s, 0–0.030 mg/s, and 0–0.07 mg/s, respectively.
- (2)
- The R2 of the SVR model is 0.937. The median of the prediction results obtained by the SVR model is a little higher the that of the test results, and the concentrated area of the prediction results is slightly smaller than that of the test results. The prediction effect of the SVR model is poor when the soot mass concentration is larger than 0.038 mg/s.
- (3)
- The R2 of the DNN model is 0.984. The median of the prediction results obtained by the DNN model is closer to that of the test results, especially within the range of the 25–75% dataset. And there exist a few negative prediction results on the test dataset due to overfitting.
- (4)
- The R2 of the Stacking integration model of SVR and DNN is 0.992. The integration model can effectively estimate the soot mass concentration over the entire range of 0–0.07 mg/s, and the overfitting of DNN is also avoided.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Description |
| GPF | gasoline particulate filter |
| GDI | gasoline direct injection |
| SVR | support vector regression |
| DNN | deep neural network |
| TWC | three-way catalyst |
| PN | particle number |
| WLTC | Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Cycle |
| MSE | mean square error |
| MAE | mean absolute error |
| R2 | correlation coefficient |
References
- Duronio, F.; De Vita, A.; Allocca, L.; Anatone, M. Gasoline direct injection engines—A review of latest technologies and trends. Part 2. Fuel 2020, 265, 116947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, Y.; Huang, H.; Cao, C. Review of particle filters for internal combustion engines. Processes 2022, 10, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Hartog, J.J.; Hoek, G.; Peters, A.; Timonen, K.L.; Ibald-Mulli, A.; Brunekreef, B.; Tiittanen, P.; Kreyling, W.; Kulmala, M. Effects of fine and ultrafine particles on cardiorespiratory symptoms in elderly subjects with coronary heart disease: The ULTRA study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 157, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yan, F.; Fang, N.; Yan, D.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W. An experimental investigation of the impact of washcoat composition on gasoline particulate filter (GPF) performance. Energies 2020, 13, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komori, A.; Sato, S.; Oryoji, K.; Koiwai, R. Study on Estimation Logic of GPF Temperature and Amount of Residual Soot. Int. J. Automot. Eng. 2021, 12, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamimoto, T.; Murayama, Y.; Minagawa, T.; Minami, T. Light scattering technique for estimating soot mass loading in diesel particulate filters. Int. J. Engine Res. 2009, 10, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Durve, A.; Barman, J.; Srinivasan, P. Evaluation of Different Methodologies of Soot Mass Estimation for Optimum Regeneration Interval of Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF); SAE Technical Paper No. 2021-26-0208; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Ren, F.; Gao, Z.; Zhu, L.; Huang, Z. Synergistic effect analysis on sooting tendency based on soot-specialized artificial neural network algorithm with experimental and numerical validation. Fuel 2022, 315, 122538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, J.M.; Alvarruiz, F.; Desantes, J.M.; Hernandez, L.; Hernandez, V.; Molto, G. Combining Neural Networks and Genetic Algorithms to Predict and Reduce Diesel Engine Emissions. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2007, 11, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, M.; Najafi, G.; Ghobadian, B.; Mamat, R.; Noor, M.M.; Moosavian, A. Support vector machine to predict diesel engine performance and emission parameters fueled with nano-particles additive to diesel fuel. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 100, 012069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, V.; Mahla, S.K.; Leekha, R.S.; Dhir, A.; Lee, K.; Ko, H. Intervention of Artificial Neural Network with an Improved Activation Function to Predict the Performance and Emission Characteristics of a Biogas Powered Dual Fuel Engine. Electronics 2021, 10, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seunghyup, S.; Jong-Un, W.; Minjeong, K. Comparative research on DNN and LSTM algorithms for soot emission prediction under transient conditions in a diesel engine. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2023, 37, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.R.; Shi, J.H.; Li, G.X. CRDI Engine Emission Prediction Models with Injection Parameters Based on ANN and SVM to Improve the SOOT-NOx Trade-Off. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2023, 16, 2041–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.N.; Kishore, P.; Raju, K.B.; Ashok, B.; Vignesh, R.; Jeevanantham, A.; Nanthagopal, K.; Tamilvanan, A. Decanol proportional effect prediction model as additive in palm biodiesel using ANN and RSM technique for diesel engine. Energy 2020, 213, 119072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaprakash, B.; Wilmer, B.; Northrop, W.F. Initial Development of a Physics-Aware Machine Learning Framework for Soot Mass Prediction in Gasoline Direct Injection Engines. SAE Int. J. Adv. Curr. Pract. Mobil. 2023, 6, 2005–2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, Y.-H.; Reddy, J.K.; Samuel, S. Machine learning for nano-scale particulate matter distribution from gasoline direct injection engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 125, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stangierska, M.; Bajwa, A.; Lewis, A.; Akehurst, S.; Turner, J.; Leach, F. Ensemble Machine Learning Techniques for Particulate Emissions Estimation from a Highly Boosted GDI Engine Fuelled by Different Gasoline Blends; 2024-01-4306; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, H.; Xiang, L.; Nie, X.; Ya, Y.; Gu, M. Laminar burning velocity and pollutant emissions of the gasoline components and its surrogate fuels: A review. Fuel 2020, 269, 117451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, S.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Qi, Y.; Xu, H. Recent Progress in Automotive Gasoline Direct Injection Engine Technology. Automot. Innov. 2018, 1, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Liu, S.; Tan, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, B. A review of the development and application of soot modelling for modern diesel engines and the soot modelling for different fuels. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 178, 836–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricq, M.M. Engine, aftertreatment, fuel quality and non-tailpipe achievements to lower gasoline vehicle PM emissions: Literature review and future prospects. Appl. Energy 2023, 886, 161225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsin, R.; Chen, L.F.; Felix, L.; Ding, S.T. A Review of Particulate Number (PN) Emissions from Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) Engines and Their Control Techniques. Energies 2018, 11, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Li, Z.; Yu, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, X. Review of the state-of-the-art of particulate matter emissions from modern gasoline fueled engines. Appl. Energy 2019, 238, 1269–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Liu, F.; Wu, H.; Lee, C.-F.; Li, Y. Effects of alcohol addition to traditional fuels on soot formation: A review. Int. J. Engine Res. 2021, 22, 1395–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catapano, F.; Di Iorio, S.; Luise, L.; Sementa, P.; Vaglieco, B.M. Influence of ethanol blended and dual fueled with gasoline on soot formation and particulate matter emissions in a small displacement spark ignition engine. Fuel 2019, 245, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, S.; Hagen, F.P.; Büttner, L.; Hartmann, J.; Velji, A.; Kubach, H.; Koch, T.; Bockhorn, H.; Trimis, D.; Suntz, R. Influence of Global Operating Parameters on the Reactivity of Soot Particles from Direct Injection Gasoline Engines. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 2022, 8, 9–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Q.; Rolf, D.R. The Effect of Operating Parameters on Soot Emissions in GDI Engines; 2015-01-1071; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, J.; Shao, L.; Zheng, R.; Peng, J.; Wang, W.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Shuai, S.; Hu, M. Individual particles emitted from gasoline engines: Impact of engine types, engine loads and fuel components. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alex, J.; Bernhard, S. A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat. Comput. 2004, 14, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshua, B.; Aaron, C.; Pascal, V. Representation Learning: A Review and New Perspectives. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1798–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskar, N.S.; Mudigere, D.; Nocedal, J.; Smelyanskiy, M.; Tang, P.T.P. On large-batch training for deep learning: Generalization gap and sharp minima. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2017-Conference Track Proceedings, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wolpert, D.H. Stacked generalization. Neural Netw. 1992, 5, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, Y.; Schapire, R.E. A desicion-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting. Eur. Conf. Comput. Learn. Theory 1997, 55, 119–139. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, K.; Witten, I. Issues in Stacked Generalization. J. Articial Intell. Res. 1999, 10, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Kernel Function | K-Folds | MSE | MAE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radial basis function | 4 | 0.018295 | 0.07249 | 0.937 |
| Activation Functions | Learning Rate | MSE | MAE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ReLU | 0.01 | 0.01349 | 0.06328 | 0.984 |
| Model | MSE | MAE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stacking | 0.00976 | 0.05948 | 0.992 |
| Model | First Cycle | Second Cycle | Third Cycle |
|---|---|---|---|
| SVR | 0.01912 | 0.01746 | 0.01824 |
| DNN | 0.01342 | 0.01260 | 0.01446 |
| Stacking | 0.00929 | 0.01065 | 0.00933 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Shen, J.; Wang, S.; Tan, P. Soot Mass Concentration Prediction at the GPF Inlet of GDI Engine Based on Machine Learning Methods. Energies 2025, 18, 3861. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143861
Hu Z, Liu Z, Shen J, Wang S, Tan P. Soot Mass Concentration Prediction at the GPF Inlet of GDI Engine Based on Machine Learning Methods. Energies. 2025; 18(14):3861. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143861
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Zhiyuan, Zeyu Liu, Jiayi Shen, Shimao Wang, and Piqiang Tan. 2025. "Soot Mass Concentration Prediction at the GPF Inlet of GDI Engine Based on Machine Learning Methods" Energies 18, no. 14: 3861. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143861
APA StyleHu, Z., Liu, Z., Shen, J., Wang, S., & Tan, P. (2025). Soot Mass Concentration Prediction at the GPF Inlet of GDI Engine Based on Machine Learning Methods. Energies, 18(14), 3861. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143861







