Literature Reviews of Topology Optimal Design Methods and Applications in Magnetic Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Implementations of existing deterministic topology optimization methods and applications in magnetic devices are reviewed. The characteristics of topology optimization, such as convergence, searching accuracy, and scope of applications, are discussed.
- (2)
- To deal with uncertainties in electrical engineering, topology optimization, considering reliability and robustness, is analyzed. The problem of difficult manufacturability encountered after topology optimization is also considered, and the filtering strategies are summarized.
- (3)
- Challenges in the application of magnetic devices are discussed, and predictions are made about future solutions.
2. Topology Optimization
2.1. Theory of Topology Optimization Method
2.1.1. Homogenization Method
2.1.2. Variable Density Method
2.1.3. Evolutionary Structural Optimization Method
2.1.4. Normalized Gaussian Network Method
2.1.5. Level Set Method
2.1.6. Binary Structure Method
2.1.7. ON/OFF Method
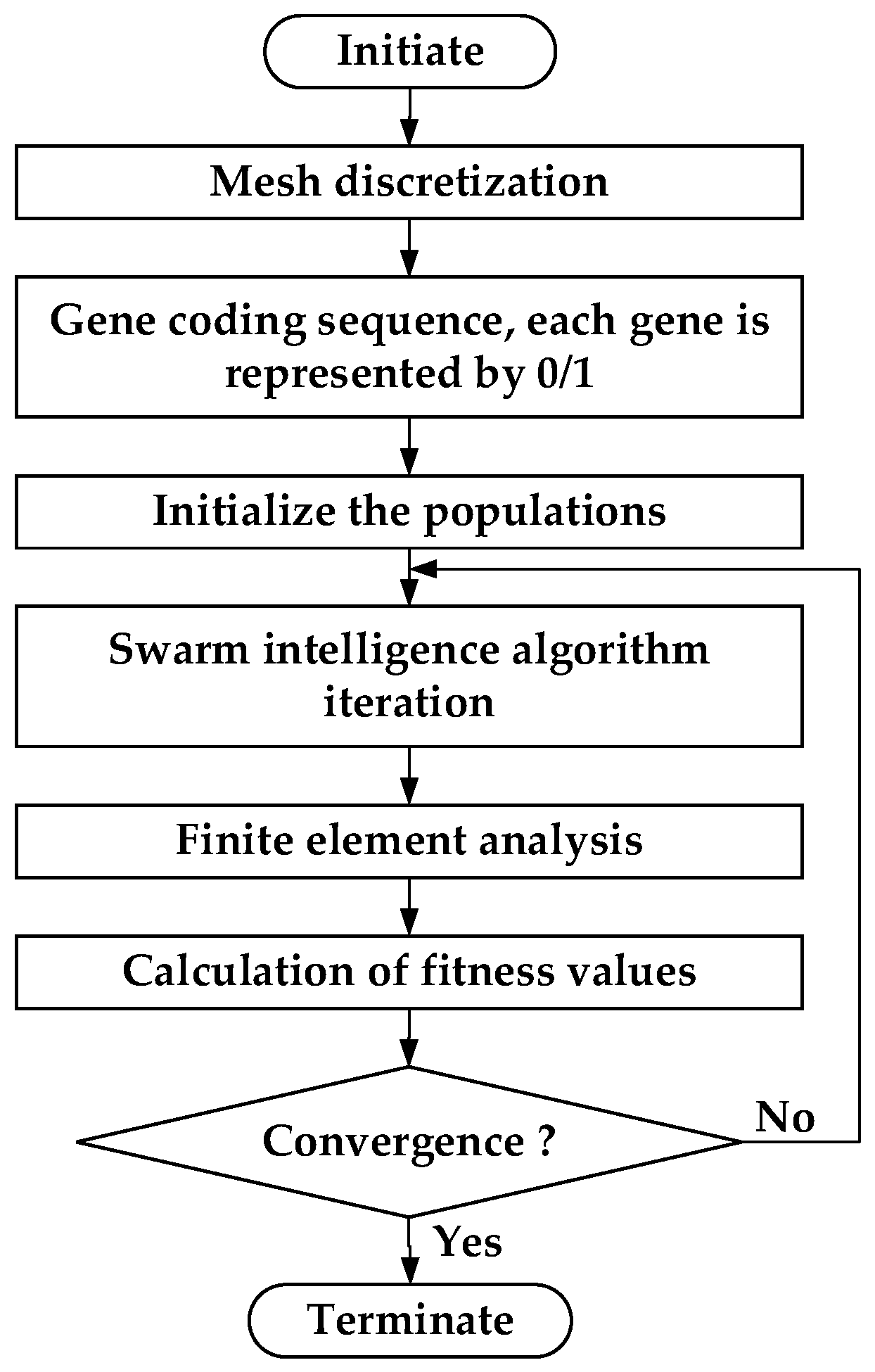
2.2. Implementation of Topology Optimization
3. Applications of Deterministic Topology Optimization in Magnetic Device
3.1. Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor
3.2. Magnetic Shielding System
3.3. Magnetic Recording Head
3.4. Brushless DC Motor
3.5. Synchronous Reluctance Motors
3.6. Electromagnetic Actuator
3.7. Electromagnetic Interference Filter
3.8. Induction Motor
3.9. Other Applications
4. Topology Optimization Considering Uncertainties
4.1. Reliability-Based Topology Optimization
- (1)
- Nested Optimization Method
- (2)
- Decoupling Method
- (3)
- Single-loop Method
- (4)
- Reliability Safety Factor Method
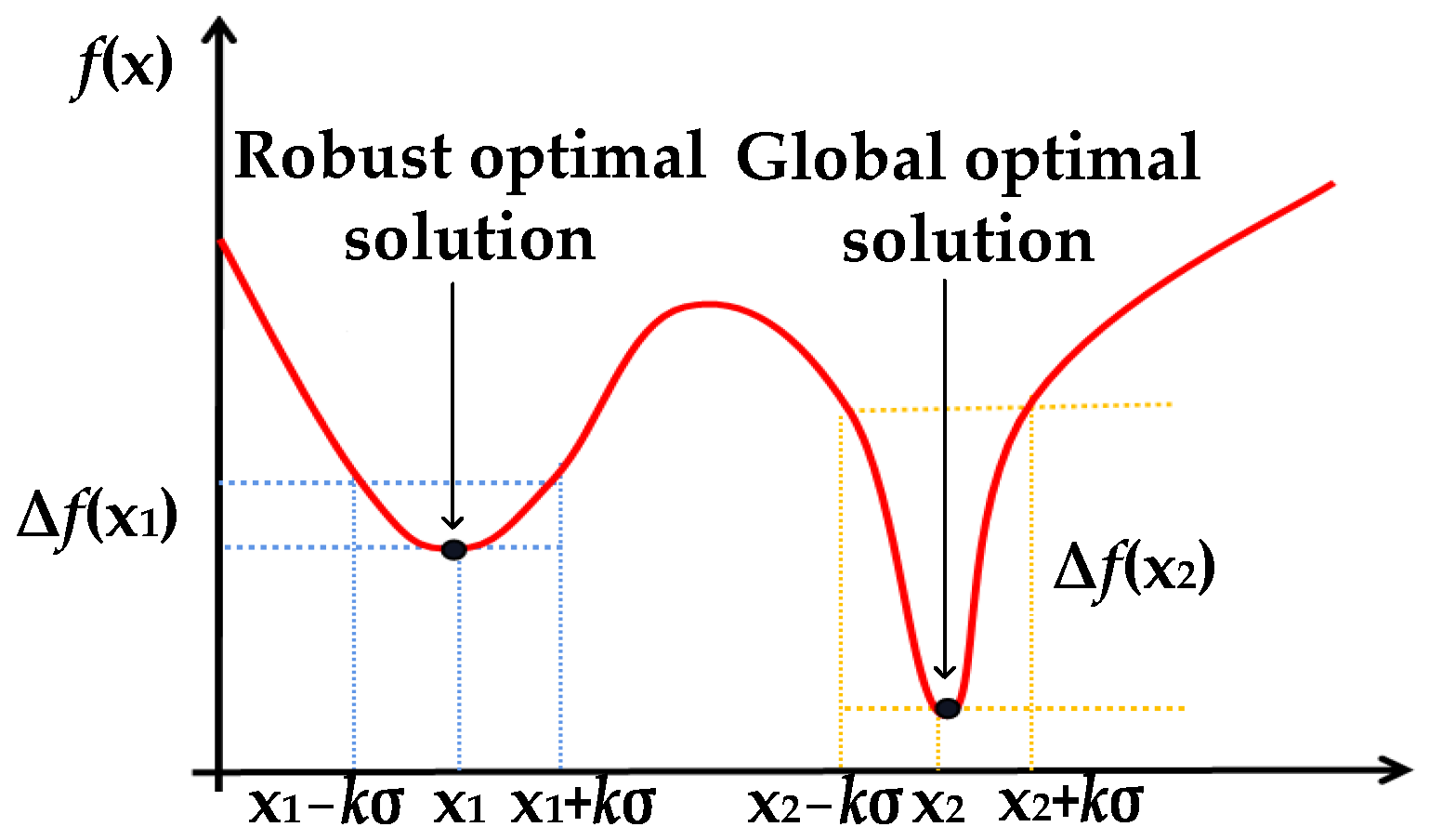
4.2. Robustness-Based Topology Optimization
- (1)
- Random Probability RTO Method
- (2)
- Non-probability RTO Method
- Variance Model
- Gradient Index Model
- Worst-case Model
5. Filtering Strategy
5.1. Density Filtering Method
5.2. Sensitivity Filtering Method
5.3. Morphology-Based Filtering Method
6. Challenges and Future Developments
6.1. The Complexity of Multi-Physics Field Coupling
6.2. Manufacturing Process Constraints
6.3. Material Nonlinearity
6.4. Computing Resource Bottleneck
6.5. Uncertainty
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Saidi, M.; Al-Badi, A.; Onen, A.; Elhaffar, A. Optimal location and size of static var compensators (SVC) to enhance the voltage profile on the main interconnected system in Oman. Energies 2023, 16, 6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.; Ferreira, J.; Martins, N. Geometry optimisation of a wave energy converter. Energies 2025, 18, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsavdaridis, K.D. Applications of topology optimization in structural engineering: High-rise buildings and steel components. Jorda. J. Civi. Eng. 2015, 9, 335–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korman, O.; Di Nardo, M.; Degano, M.; Gerada, C. On the use of topology optimization for synchronous reluctance machines design. Energies 2022, 15, 3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktay, E.; Akay, H.U.; Merttopcuoglu, O. Parallelized structural topology optimization and CFD coupling for design of aircraft wing structures. Comput. Fluids 2011, 49, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascino, A.; Meli, E.; Rindi, A. Development of a design procedure combining topological optimization and a multibody environment: Application to a tram motor bogie frame. Vehicles 2024, 6, 1843–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, M.; Wakao, S.; Murata, N.; Makino, H.; Takeuchi, K.; Matsushita, M. Multi-Objective topology optimization of synchronous reluctance motors using autoencoder-estimated flux barrier shapes. IEEJ J. Ind. Appl. 2025, 14, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, R.; Okamoto, Y. Reduction of memory consumption in time domain adjoint variable method for topology optimization of squirrel-cage induction motor driven by pulse width modulation inverter. IEEJ J. Ind. Appl. 2025, 14, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Kallaste, A.; Vaimann, T. Recent trends in additive manufacturing and topology optimization of reluctance machines. Energies 2023, 16, 3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, N.; North, D.J.; Collins, S.M.; Mellor, P.H. Additive manufacturing of shaped profile windings for minimal AC loss in electrical machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 2510–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sixel, W.; Liu, M.; Nellis, G.; Sarlioglu, B. Cooling of windings in electric machines via 3-D printed heat exchanger. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 4718–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendsøe, M.P.; Kikuchi, N. Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1988, 71, 197–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campelo, F.; Ramirez, J.; Igarashi, H. A survey of topology optimization in electromagnetics: Considerations and current trends. Acad. Manag. Ann. 2010, 46, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, G.U.; Cho, S.; Moon, J.; Jeon, K.; Kim, C.W. Topology optimization to reduce electromagnetic force induced vibration for the specific frequency of PMSM motor using electromagnetic-structural coupled analysis. Energies 2021, 14, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yoo, J.; Min, S.; Yoon, M. Topology optimization of anisotropic magnetic composites in actuators using homogenization design method. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2019, 60, 1423–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanogo, S.; Messine, F.; Henaux, C.; Vilamot, R. Topology optimization for magnetic circuits dedicated to electric propulsion. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 7401013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.D.; Li, X.R.; Guo, B.H.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, G.J. Topology optimization of truncated cone insulator with graded permittivity using variable density method. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2019, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, M.; Zhao, Y. Topology optimization of heat sink based on variable density method. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.M.; Steven, G.P.; Xie, Y.M.; Steven, G.P. Basic Evolutionary Structural Optimization; Springer: London, UK, 1997; pp. 12–29. [Google Scholar]
- Querin, O.M.; Steven, G.P.; Xie, Y.M. Evolutionary structural optimisation using an additive algorithm. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2000, 34, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Igarashi, H.; Takahashi, S.; Uchiyama, S.; Matsuhashi, D. Shape optimization of rotor in interior permanent magnet motor based on topology optimization method using normalized gaussian network. IEEJ Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 135, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarpour, R.; Pakdelian, S. Topology optimization of the reluctance coaxial magnetic gear. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 8001707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, H.; Igarashi, H. Topology optimization using basis functions for improvement of rotating machine performances. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 54, 8201504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.I.; Min, S. Optimal topology design of magnetic devices using level-set method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 1610–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Li, W.; Li, Q. Level-set based topology optimization for electromagnetic dipole antenna design. J. Comput. Phys. 2010, 229, 6915–6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, Y.; Masuda, H.; Kanda, Y.; Hoshino, R.; Wakao, S. Improvement of topology optimization method based on level set function in magnetic field problem. COMPEL–Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2018, 37, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivapuram, R.; Picelli, R. Topology optimization of binary structures using integer linear programming. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2018, 139, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Yoo, J. Structural topology optimization of magnetic actuators using genetic algorithms and ON/OFF sensitivity. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 2276–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Suga, T.; Kitabatake, S. Topology optimization based on the on/off method for synchronous motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 54, 7201104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Watanabe, K. A topology optimization of on-chip planar inductor based on evolutional on/off method and CMA-ES. COMPEL–Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2024, 43, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahla, S. Wind energy conversion system control: A multi-objective PSO approach based on improved on–off control. J. Electr. Syst. 2024, 20, 170–188. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, R.; Kumar, P.; El-Refaie, A. Minimization of rare-earth permanent magnets and demagnetization risk in PM-assisted synchronous reluctance motor with blended magnets. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Nashville, TN, USA, 29 October–2 November 2023; pp. 4257–4264. [Google Scholar]
- Arcentales, X.A.; Arcentales, D.A.; Montealegre, W. Design of rotors in centrifugal pumps using the topology optimization method and parallel computing in the cloud. Machines 2025, 13, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, H.; Zhao, Z.; Li, H.; Gan, T.H.; See, K.Y. A systematic three-stage safety enhancement approach for motor drive and gimbal systems in unmanned aerial vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 99, 9329–9342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wang, P.; Wang, W.; Xu, D. An electromagnetically integrated LCL-EMI filter for V2G power converters: Topology, analysis, and implementation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 72, 2746–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Lee, M.H.; Moon, J. Option-based deep reinforcement learning for topology control of power systems. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 26639–26650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Li, M. Structural topology optimization based on deep learning. J. Comput. Phys. 2025, 520, 113506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, R.; Sato, H.; Kujimichi, T.; Igarashi, H. Multiphysics deep learning for topology optimization of permanent magnet motor. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 21st Biennial Conference on Electromagnetic Field Computation (CEFC), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 2–5 June 2024; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka, Y. Multi-objective topology optimization method for hybrid-type motors combining combinatorial optimization and local search. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2023, 60, 8200404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizarribar, B.; Prieto, B.; Selema, A.; Ibrahim, M.N.; Sergeant, P.; Artetxe, G.; Martínez-Iturralde, M. Multiphysics topology optimization of aluminium and copper conductors for automotive electrical machines. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 9342–9350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L. An improved topology graph and ant colony optimization approach for optimizing electric vehicle travel path considering time and charging cost. Informatica 2025, 49, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahay, S.; Biswal, S.R.; Shankar, G.; Jha, A.V.; Appasani, B.; Srinivasulu, A.; Nsengiyumva, P. Optimized placement of distributed generators, capacitors, and EV charging stations in reconfigured radial distribution networks using enhanced artificial hummingbird algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, S.A.; Al-Sagar, Z.S.; Abdulsada, M.A.; Alruwaili, M.; Ibrahim, M.A. Design of an efficient MPPT topology based on a grey wolf optimizer-particle swarm optimization (GWO-PSO) algorithm for a grid-tied solar inverter under variable rapid-change irradiance. Energies 2025, 18, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhang, W. Isogeometric analysis (iga)-based topology optimization for 3d flexoelectric structures. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 2024, 37, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Wang, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, R.; Yao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wang, X.; Jiang, C.; Asare-Yeboah, K. Artificial neural network reinforced topological optimization for bionics-based tridimensional stereoscopic hydrogen sensor design and manufacture. International J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 53, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Duan, Z.; Yan, H.; Geng, D.; Du, H.; Yan, J.; Li, H. Deep learning-driven topology optimization for heat dissipation of integrated electrical components using dual temperature gradient learning and MMC method. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 2024, 20, 291–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Thabuis, A.; Belahcen, A.; Perriard, Y. Topology optimization for coils of electric machine with level-set method. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Harbin, China, 11–14 August 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Putek, P.; Paplicki, P.; Pałka, R. Topology optimization of rotor poles in a permanent-magnet machine using level set method and continuum design sensitivity analysis. COMPEL–Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2014, 33, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, B.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, L. Topology optimization of an interior PM motor for applying to refrigerant compressor. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Harbin, China, 11–14 August 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, T.; Watanabe, K.; Igarashi, H. A modified immune algorithm with spatial filtering for multiobjective topology optimisation of electromagnetic devices. COMPEL–Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2014, 33, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Watanabe, K.; Igarashi, H. Multimaterial topology optimization of electric machines based on normalized Gaussian network. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 7202604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidaka, Y.; Sato, T.; Igarashi, H. Topology optimization method based on on–off method and level set approach. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Yoo, J.; Choi, J.S. Simultaneous optimal design of the yoke and the coil in the perpendicular magnetic recording head. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 3668–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Yoo, J.; Choi, J.S. Optimal shape design of the perpendicular magnetic recording head. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 2272–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Akiyama, K.; Miyagi, D.; Kanai, Y. Advanced optimization of standard head model with higher writing field and higher field gradient using 3-D ON/OFF method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2008, 44, 966–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Yonetake, K.; Kurita, N. An optimal material distribution design of brushless DC motor by genetic algorithm considering a cluster of material. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 1310–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Sato, T.; Igarashi, H. Topology optimization of synchronous reluctance motor using normalized Gaussian network. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 8200904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthey, T.; Gangl, P.; Hassan, M.H. Multi-material topology optimization with continuous magnetization direction for motors design. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Valencia, Spain, 5–8 September 2022; pp. 483–489. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Jang, I.G. Topology optimization of multiple-barrier synchronous reluctance motors with initial random hollow circles. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2021, 64, 2213–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Lee, J.; Jang, I.G. Topology optimization for the manufacturable and structurally safe synchronous reluctance motors with multiple iron webs and bridges. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 70, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupertino, F.; Pellegrino, G.; Gerada, C. Design of synchronous reluctance motors with multiobjective optimization algorithms. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 3617–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Dede, E.M.; Nomura, T. Simultaneous design optimization of permanent magnet, coils, and ferromagnetic material in actuators. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 4712–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, H.; Zhao, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Chang, Y.; See, K.Y. Characterization and circuit modeling of electromagnetic interference filtering chokes in power electronics: A review. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 40, 920–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Chang, Y.; Fan, F.; Wang, C.; See, K.Y. A review of intentional electromagnetic interference in power electronics: Conducted and radiated susceptibility. IET Power Electron. 2024, 17, 1487–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, Z. Optimized design of three-phase EMI filter for electric vehicle onboard charging system. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meribout, M. Optimal design for a portable NMR-and MRI-based multiphase flow meter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 6354–6361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otomori, M.; Yamada, T.; Andkjær, J.; Izui, K.; Nishiwaki, S.; Kogiso, N. Level set-based topology optimization for the design of an electromagnetic cloak with ferrite material. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 2081–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Salameh, M.; Krishnamurthy, M.; Brown, I.P. Multimaterial magneto-structural topology optimization of wound field synchronous machine rotors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 3656–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Yang, S.; Choi, J.S. Optimal design of an electromagnetic coupler to maximize force to a specific direction. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2008, 44, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Devaraj, R.; Kavitha, R.; Geetha, K. Distributed energy resources with optimized power converter topology to improve load power quality. In Distributed Energy Storage Systems for Digital Power Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 221–238. [Google Scholar]
- Bazgir, E.; Samimi, A.; Salami, A. Multi-objective reliability-oriented optimal energy and reserve management in renewable-based microgrids in presence of demand response programs. J. Reliab. Stat. Stud. 2025, 18, 69–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, N.; Sharifian, M.B.B. Development and design of magnetic structures for improving reliability linear motors. Metall. Mater. Eng. 2024, 30, 391–403. [Google Scholar]
- Dechgummarn, Y.; Fuangfoo, P.; Kampeerawat, W. Reliability assessment and improvement of electrical distribution systems by using multinomial monte carlo simulations and a component risk priority index. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 111923–111935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Qudaih, Y.; Tang, D.; Liu, J.A.; Liu, T. Operational reliability assessment of distribution network with energy storage systems. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 17, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.R.; Lin, B.; Hsu, B.M.; Shu, M.H. Fault-tree analysis for liquefied natural gas terminal emergency shutdown system. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 11918–11924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, K.; Yoo, D.; Park, J.; Lee, K.D.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, C.W. Reliability-based robust design optimization for maximizing the output torque of brushless direct current (BLDC) motors considering manufacturing uncertainty. Machines 2022, 10, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Ma, J.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, D.; Koh, C.S. Managing uncertainties of permanent magnet synchronous machine by adaptive Kriging assisted weight index Monte Carlo simulation method. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 2162–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Cho, S.G.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, J.M.; Hong, J.P.; Lee, T.H. Reliability-based robust design optimization with kernel density estimation for electric power steering motor considering manufacturing uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 8001904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Kang, B.; Choi, K.K.; Kim, D.H. A comparative study on probabilistic optimization methods for electromagnetic design. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 52, 7201304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Haowen, L.; Pengcheng, W.; Guobiao, C.; Feng, H. Uncertainty analysis and design optimization of solid rocket motors with finocyl grain. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2020, 62, 3521–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Huang, M.; Liu, X. Reliability-based design optimization of a centrifugal compressor considering manufacturing uncertainties. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Reliability Systems Engineering (ICRSE), Beijing, China, 10–12 July 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Vaderobli, A.; Parikh, D.; Diwekar, U. Optimization under uncertainty to reduce the cost of energy for parabolic trough solar power plants for different weather conditions. Energies 2020, 13, 3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharmanda, G.; Olhoff, N.; Mohamed, A.; Lemaire, M. Reliability-based topology optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Mptimization 2004, 26, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Kim, C.; Wang, S. Reliability-based topology optimization for electromagnetic systems. COMPEL–Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2004, 23, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, K.R.; Wang, S. Reliability-based topology optimization. In Proceedings of the 9th AIAA/ISSMO Symposium on Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization, Atlanta, GA, USA, 4–6 September 2002; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Eom, Y.S.; Yoo, K.S.; Park, J.Y.; Han, S.Y. Reliability-based topology optimization using a standard response surface method for three-dimensional structures. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2011, 43, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalpour, M.; Tootkaboni, M. An efficient approach to reliability-based topology optimization for continua under material uncertainty. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2016, 53, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghias, K. Inverse optimum safety factor method for reliability-based topology optimization applied to free vibrated structures. Инженерные Mехнoлoгии Cистемы 2019, 29, 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghbeigi, O.M.; Razfar, M.R.; Wang, S. Reliability-based topology optimization design of a linear piezoelectric micromotor using an optimum finite element method. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part O J. Risk Reliab. 2013, 227, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Wang, S.; Hwang, I.; Lee, J. Application of reliability-based topology optimization for microelectromechanical systems. AIAA J. 2007, 45, 2926–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liang, J.; Wu, D. A non-probabilistic reliability-based topology optimization (NRBTO) method of continuum structures with convex uncertainties. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2018, 58, 2601–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Gu, W.; Liu, P.; Sun, Q.; Wu, Z.; Lu, X. Application of two-stage robust optimization theory in power system scheduling under uncertainties: A review and perspective. Energy 2022, 251, 123942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qin, D.; Ye, Y.; He, Y.; Fu, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H. Multi-time scale economic scheduling method based on day-ahead robust optimization and intraday MPC rolling optimization for microgrid. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 140315–140324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, K.Y.; Li, G.J. Robust unit commitment to improve the admissible region of wind power. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2018, 33, 523–532. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Shahidehpour, M.; Mei, S. Distribution system operation with renewables and energy storage: A linear programming based multistage robust feasibility approach. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2021, 37, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Wu, L.; Liu, T.; Bie, Z. Robust co-optimization planning of interdependent electricity and natural gas systems with a joint N-1 and probabilistic reliability criterion. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 33, 2140–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Li, P.; Ma, K.; Yang, B.; Yang, J. Robust energy management for industrial microgrid considering charging and discharging pressure of electric vehicles. Appl. Energy 2022, 325, 119846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, Z.; Ma, L.; Wang, L.; Zhou, K.; Feng, N. A robust optimization approach for optimal load dispatch of community energy hub. Appl. Energy 2020, 259, 114195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.L.; Yang, S.; Bai, Y.; Li, Y. A wind driven optimization-based methodology for robust optimizations of electromagnetic devices under interval uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 7001204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Song, L.; Qu, J.; Huang, Y.; Wu, X.; Lu, X.; Xia, S. A two-stage distributionally robust optimization model for wind farms and storage units jointly operated power systems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 111132–111142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, S.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, J.G.; Guo, Y.; Liu, D. Robust multilevel optimization of PMSM using design for six sigma. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 3248–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.C.; Park, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.G.; Lee, G.H.; Lim, M.S. Diagnosis and robust design optimization of SPMSM considering back EMF and cogging torque due to static eccentricity. Energies 2021, 14, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, G.; Bramerdorfer, G.; Ma, B.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, J. Robust design optimization of electrical machines: Multi-objective approach. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 36, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Sigmund, O. Topological design of electromechanical actuators with robustness toward over-and under-etching. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2013, 253, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Watanabe, K. An improved on/off method with a two-step surface smoother for topology optimization of electromagnetic devices. COMPEL–Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2023, 42, 1148–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, M.; Lombaert, G.; Schevenels, M.; Sigmund, O. Topology optimization of fail-safe structures using a simplified local damage model. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2014, 49, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Zhang, L.; Chen, N.; Zhang, S.; Liu, W.; Wu, D.O. Born this way: A self-organizing evolution scheme with motif for internet of things robustness. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2022, 30, 2644–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, Y.; Hoshino, R.; Wakao, S.; Tsuburaya, T. Improvement of torque characteristics for a synchronous reluctance motor using MMA-based topology optimization method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 54, 7203104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyaqout, S.F.; Papalambros, P.Y.; Ulsoy, A.G. Combined robust design and robust control of an electric DC motor. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2010, 16, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putek, P.; Pulch, R.; Bartel, A.; ter Maten, E.J.W.; Günther, M.; Gawrylczyk, K.M. Shape and topology optimization of a permanent-magnet machine under uncertainties. J. Math. Ind. 2016, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Han, X.; Liu, G.P. Uncertain optimization of composite laminated plates using a nonlinear interval number programming method. Comput. Struct. 2008, 86, 1696–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wu, D.; Song, C.; Tin-Loi, F.; Li, X. Hybrid probabilistic interval analysis of bar structures with uncertainty using a mixed perturbation Monte-Carlo method. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2011, 47, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Song, C.; Tin-Loi, F. Probabilistic interval analysis for structures with uncertainty. Struct. Saf. 2010, 32, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, T.E.; Tortorelli, D.A. Topology optimization of non-linear elastic structures and compliant mechanisms. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2001, 190, 3443–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdin, B. Filters in topology optimization. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2001, 50, 2143–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, T.E.; Tortorelli, D.A. An element removal and reintroduction strategy for the topology optimization of structures and compliant mechanisms. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2003, 57, 1413–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Wang, S. Bilateral filtering for structural topology optimization. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2005, 63, 1911–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmund, O.; Petersson, J. Numerical instabilities in topology optimization: A survey on procedures dealing with checkerboards, mesh-dependencies and local minima. Struct. Optim. 1998, 16, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmund, O. Morphology-based black and white filters for topology optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2007, 33, 401–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



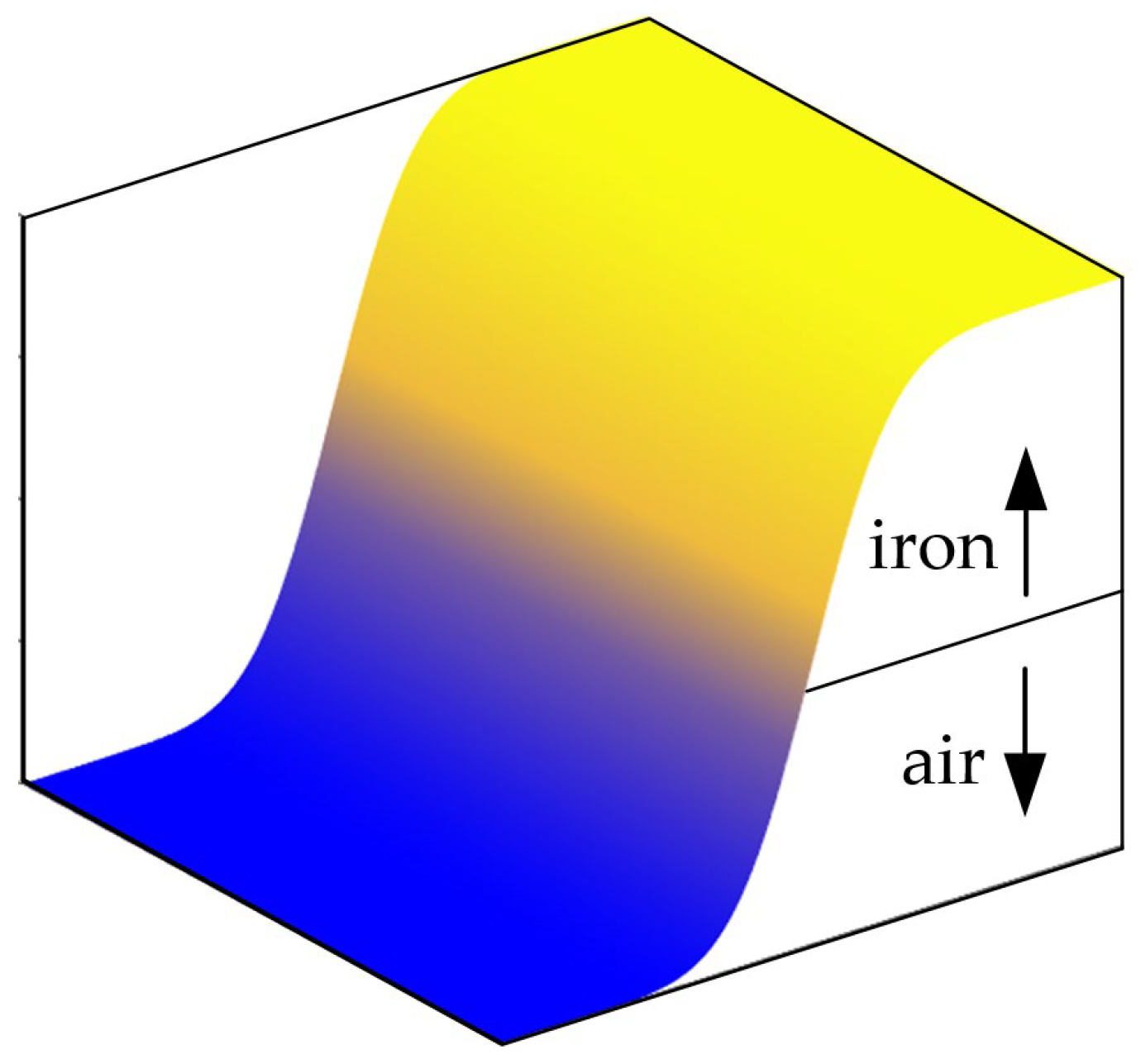

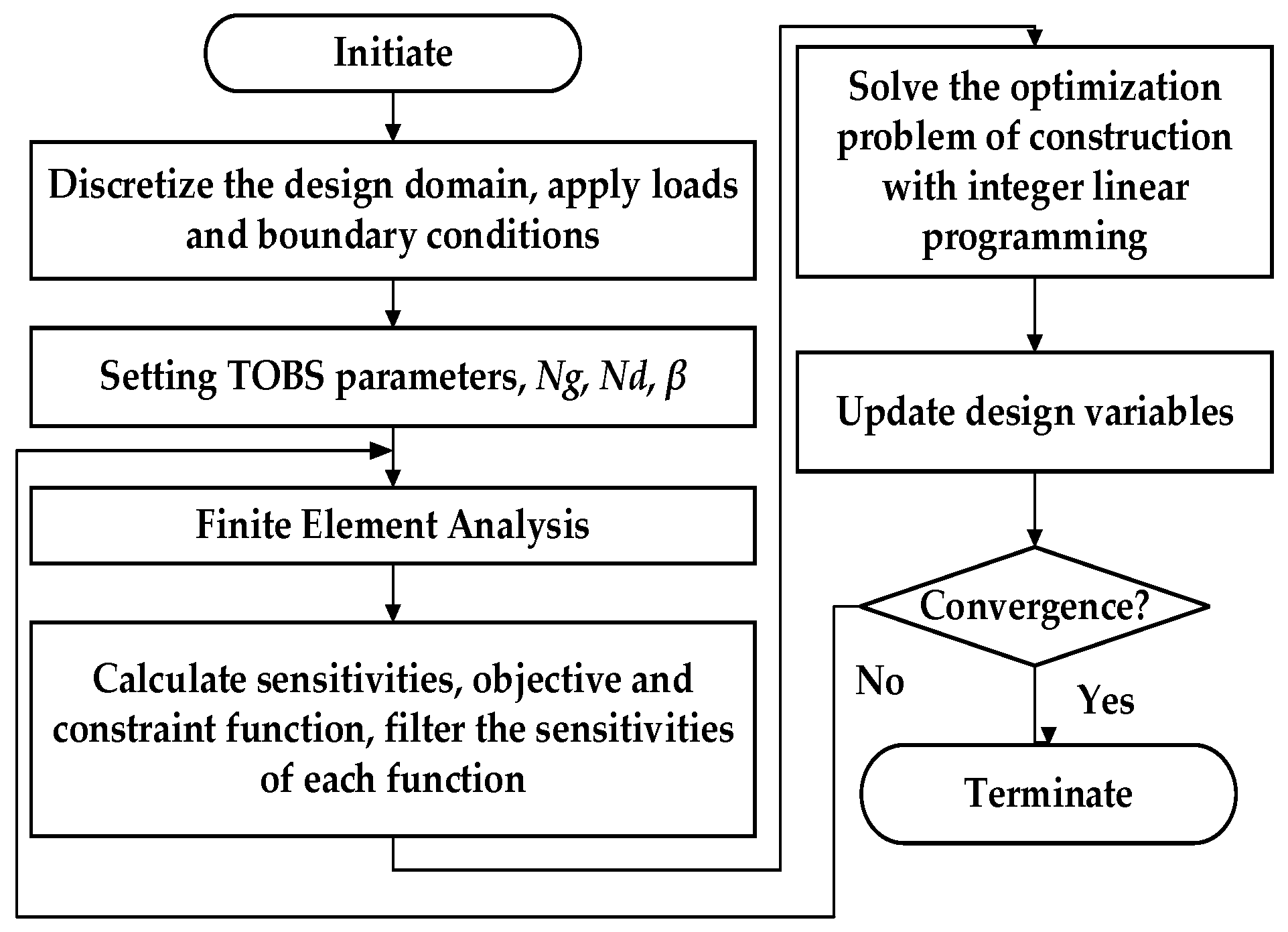
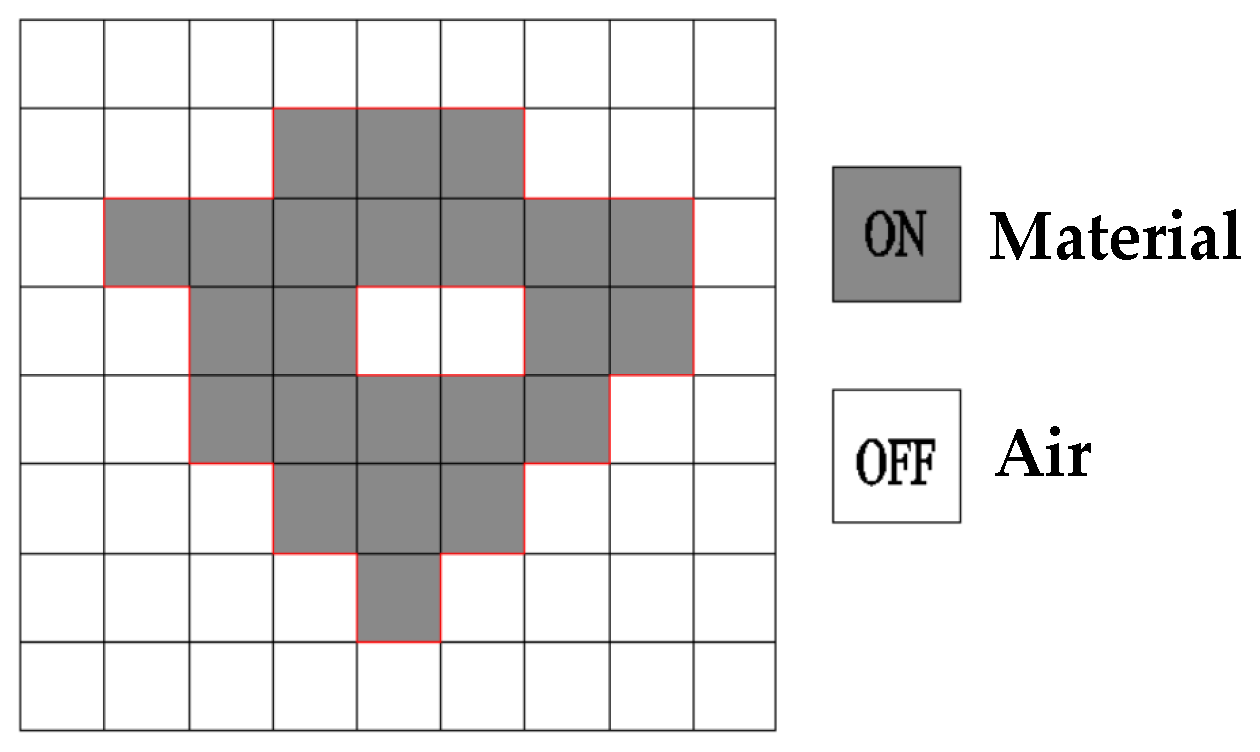



| Methods | Accuracy | Convergence | Complexity | Constraints | Speed | Applications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homogenization method | Moderate | Low | High | Volume constraint | Low | Truss/suspended beam structure, etc. | [12,13,14,15] |
| Variable density method | High | Stable | Moderate | Volume constraint | Fast | Motors/sensors/thermal management device, etc. | [16,17,18] |
| ESO | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Stress/displacement constraints | Moderate | Motor/sensor/electrical equipment structural components, etc. | [19,20] |
| NGnet | Higher | Moderate | High | Network weight constraint | Low | Motor/magnetic resonance system, etc. | [21,22,23] |
| LSM | Higher | Moderate | High | Volume/displacement constraints | Low | Microelectromechanical systems/sensors, etc. | [24,25,26] |
| TOBS | High | Unstable | Moderate | Geometric/topological constraints | Moderate | Motor/antenna design, etc. | [27] |
| ON/OFF | Moderate | Fast | Low | Material/geometric/topological constraints | Fast | Microelectromechanical systems/electromagnetic components, etc. | [28,29,30,31] |
| Devices | Method | Optimized Region | Objective | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMSM | LSM/improved LSM/NGnet/multi-objective topology optimization method based on the immune algorithm/improved NGnet/a two-step multi-material topology optimization method | Motor winding/rotor magnetic poles/rotor/rotor/rotor/rotor | Maximize motor torque/reduce cogging torque/improve torque performance without increasing iron loss/manufacturable with filtering/manufacturable without filtering/maximize motor average torque | [26,47,48,49,50,51] |
| Magnetic shielding system | ON/OFF and LSM | Magnetic shielding system | Facilitated practical engineering of manufacturable shapes | [52] |
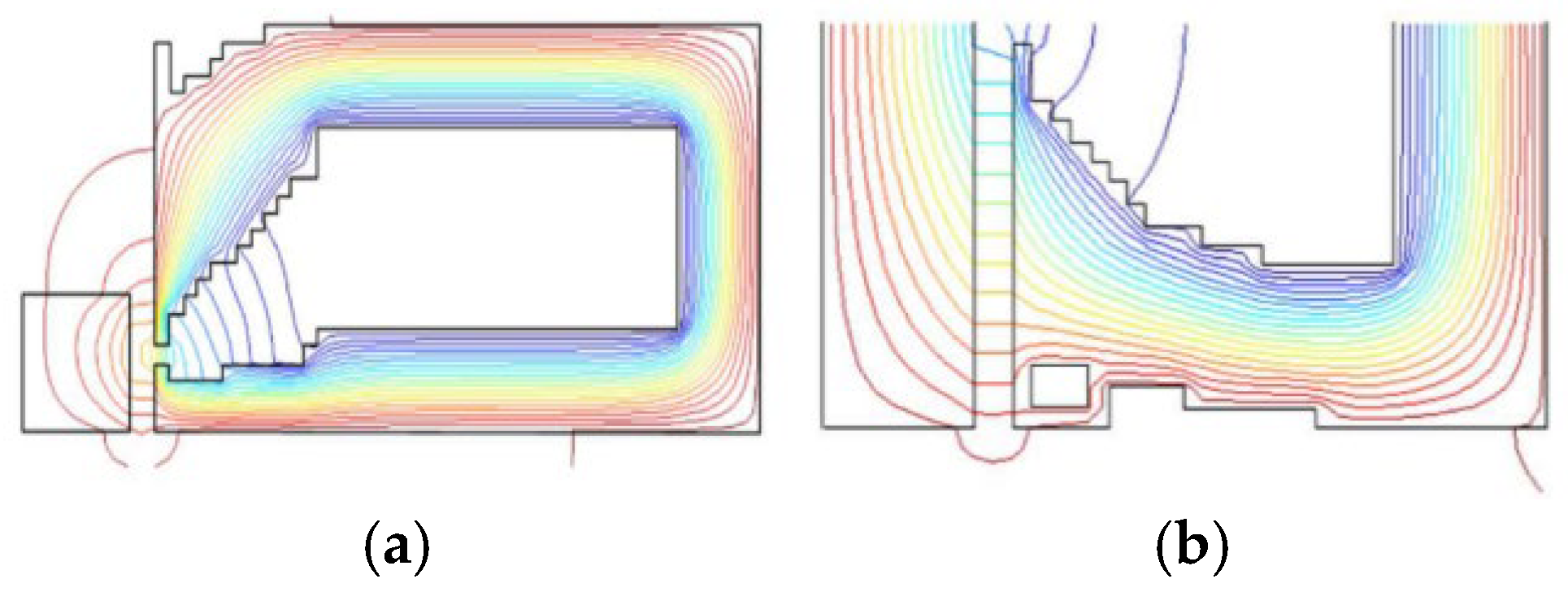
| Magnetic recording head | Variable density method/an improved ON/OFF method | The coil and magnetic yoke shapes/a pointed field monopole magnetic head with magnetic shielding | An increase in magnetic flux in the magnetic recording domain and a decrease in leakage flux in adjacent areas/the leakage flux in adjacent positions and lines decreased | [53,54,55] |
| Brushless DC motor | A micro-genetic algorithm | The stator teeth of brushless DC motor | Reduced the number of computations, increased the continuity of materials | [56] |
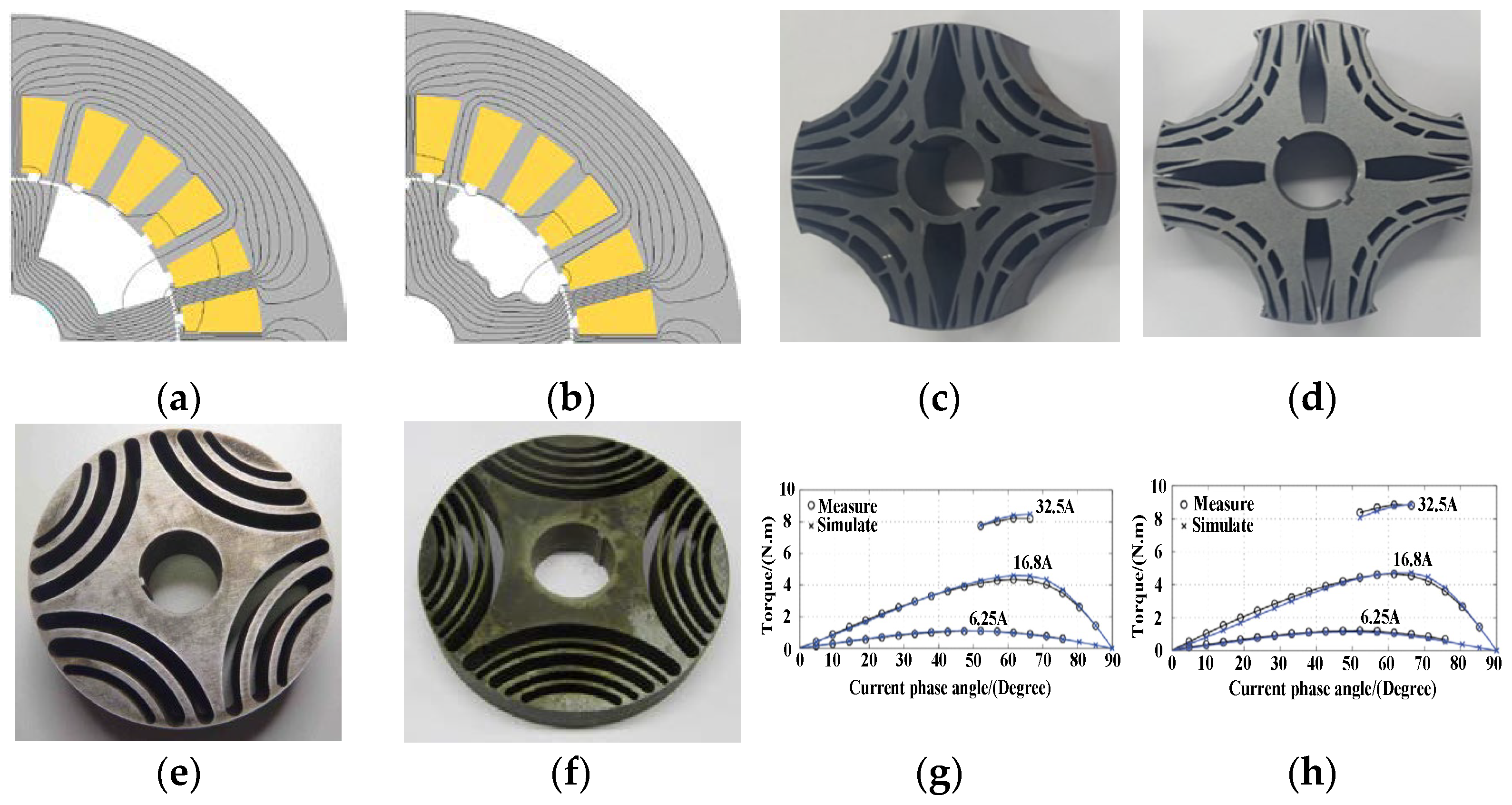
| SynRM | NGnet/an interpolation method/initial random hollow circles/a two-step topology optimization method/multi-objective genetic optimization algorithm based on FEA | Rotor silicon steel/the optimal distribution of air, iron, and magnets for SynRM/the flux barrier of rotor/rotor/rotor | Increase torque without increasing iron loss/reduction of magnet usage while simultaneously improving performance/lower torque ripple and higher average torque/enhance average torque/enhance torque | [57,58,59,60,61] |
| Electromagnetic actuator | Variable density method/improved genetic algorithms | Electromagnetic actuator/electromagnetic actuator | Maximizing the average magnetic force acting on the plunger while ensuring the optimal structural shape/maximizing the average magnetic force acting on the plunger | [28,62] |
| EMI filter | FEA | The layout and wiring rules of a three-phase EMI filter | Address electromagnetic compatibility issues of electric vehicle charging systems | [65] |
| Induction motor | A sensitivity-based PWM inverter voltage-driven induction motor time-domain topology optimization method | Induction motor | Consider the actual voltage waveform | [8] |
| Nuclear magnetic resonance magnet | FEA and particle swarm algorithm | Coils and magnets | Enhanced magnetic field uniformity | [66] |
| Electromagnetic cloaks | LSM | Electromagnetic cloaks | Achieving the optimal distribution of ferrite and air, finding a ferrite structure with electromagnetic invisibility cloak function | [67] |
| Wound synchronous motor | Integrates solid isotropy with material penalty | Rotor | Achieve the distribution of multi-materials in the rotor | [68] |
| Electromagnetic coupler | Variable density method | Electromagnetic coupler | Obtain optimal shape by maximizing the output force in a specified direction under constraint of power | [69] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, D. Literature Reviews of Topology Optimal Design Methods and Applications in Magnetic Devices. Energies 2025, 18, 3295. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18133295
Wu J, Ren Z, Zhang D. Literature Reviews of Topology Optimal Design Methods and Applications in Magnetic Devices. Energies. 2025; 18(13):3295. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18133295
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jiaqi, Ziyan Ren, and Dianhai Zhang. 2025. "Literature Reviews of Topology Optimal Design Methods and Applications in Magnetic Devices" Energies 18, no. 13: 3295. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18133295
APA StyleWu, J., Ren, Z., & Zhang, D. (2025). Literature Reviews of Topology Optimal Design Methods and Applications in Magnetic Devices. Energies, 18(13), 3295. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18133295









