A Data-Driven Iterative Feedforward Tuning Strategy with a Variable-Gain Feedback Controller for Linear Servo Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
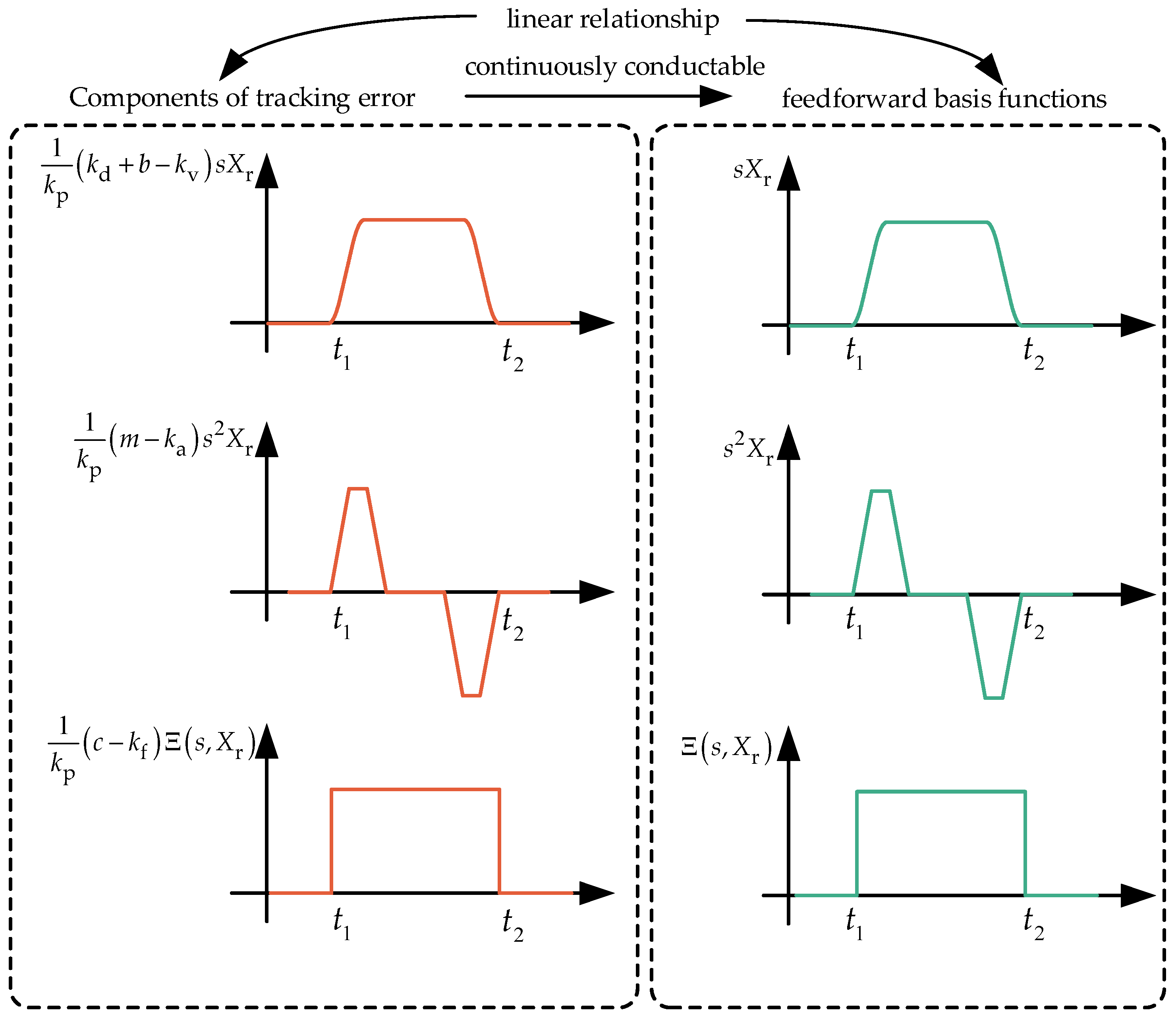
2. Analysis of the Tracking Error of the Linear Servo System
3. The Process of Iterative Feedforward Tuning
4. Effect of Feedback Controller DC Gain on Tracking Error in Iterative Feedforward Tuning
4.1. The DC Gain of the Feedback Controller Is Finite σ
4.2. The DC Gain of the Feedback Controller Is Infinite ∞
5. Iterative Feedforward Tuning with the Variable-Gain Feedback Controller
5.1. Iterative Feedforward Tuning with the Variable-Gain Feedback Controller
5.2. The Proof of the Stability of a System with the Variable-Gain Feedback Controller
6. Experimental Validation
6.1. Introduction of the System Experimental Platform
6.2. Operational Stability Verification of the System Based on the Variable-Gain Feedback Controller
6.3. Verification of the Tracking Errors with Various Orders of Elevation Under the Action of Feedback Controllers with Different DC Gains
6.4. Performance Verification of Efficient and Highly Accurate Iterative Feedforward Tuning with the Variable-Gain Feedback Controller
6.5. Verification of Trajectory Adaptation of Iterative Feedforward Tuning Results
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Erwinski, K.; Wawrzak, A.; Paprocki, M. Real-Time Jerk Limited Feedrate Profiling and Interpolation for Linear Motor Multiaxis Machines Using NURBS Toolpaths. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 7560–7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Shi, T.N.; Gao, X.M.; Lei, Y.X.; Yan, D.; Guo, L.Y.; Yan, Y. Electromagnetic characteristic analysis and design of a linear motor used for ultra-high-speed EMS maglev train. Sci. China-Technol. Sci. 2024, 67, 1957–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.M.; Xiao, Q.H.; Wang, X.S.; Yang, M.L.; Wang, Y.Q. Optimal Design of Doubly-Fed Linear Motor for High Speed Maglev Train Based on Improved Genetic Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Harbin, China, 6–9 August 2023; pp. 2089–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, M.; Seki, K.; Maeda, Y. High-Precision Motion Control Techniques: A Promising Approach to Improving Motion Performance. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2012, 6, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Hu, C.; Ou, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y. Intelligent GRU-RIC position-loop feedforward compensation control method with application to an ultraprecision motion stage. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 20, 5609–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Tomizuka, M. Real-time iterative compensation control using plant-injection feedforward architecture with application to ultraprecision wafer stage. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 11708–11719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, K.M.; Yang, L.H.; Hu, C.X. Data-based switching feedforward control for repeating and varying tasks: With application to an ultraprecision wafer stage. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 8670–8680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.Y.; Li, L.; Liu, Y. Iterative Control Decoupling Tuning by Feedforward Compensation for Precision Motion Stage. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 12th Data Driven Control and Learning Systems Conference, Xiangtan, China, 12–14 May 2023; pp. 1812–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.X.; Yang, X.F.; He, P.; Yang, Z.L. Iterative Learning Identification and Compensation of Space-Periodic Disturbance in PMLSM Systems With Time Delay. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 7579–7589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.X.; Yang, X.F.; Zhu, Q. Data-Driven Iterative Feedforward Tuning for a Wafer Stage: A High-Order Approach Based on Instrumental Variables. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 3106–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meulen, S.V.D.; Tousain, R.; Bosgra, O. Fixed Structure Feedforward Controller Tuning Exploiting Iterative Trials, Applied to a High-Precision Electromechanical Servo System. In Proceedings of the 2007 American Control Conference, New York, NY, USA, 9–13 July 2007; pp. 4033–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.J.; Hinze, C.; Iannelli, A.; Verl, A. Robust Inversion-Based Feedforward Control with Hybrid Modeling for Feed Drives. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2024, 33, 858–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.Z.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Chen, X.K.; Tan, J.B. Motion Control of Wafer Scanners in Lithography Systems: From Setpoint Generation to Multistage Coordination. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 7508040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.W.; Yang, X.F.; Zanchetta, P.; Tang, M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.Y. An Adaptive Data-Driven Iterative Feedforward Tuning Approach Based on Fast Recursive Algorithm: With Application to a Linear Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 19, 6160–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeren, F.; Oomen, T.; Steinbuch, M. Iterative motion feedforward tuning: A data-driven approach based on instrumental variable identification. Control Eng. Pract. 2015, 37, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeren, F.; Bruijnen, D.; Oomen, T. Enhancing feedforward controller tuning via instrumental variables: With application to nanopositioning. Int. J. Control 2017, 90, 746–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.Z.; Liu, Y.; Jin, W.; Tan, J.B.; He, W. Data-Driven Feedforward Learning with Force Ripple Compensation for Wafer Stages: A Variable-Gain Robust Approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 1594–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Liu, Y.; Song, F.Z. Data-driven Rational Feedforward Tuning Algorithm Based on Self-adaptive Hybrid Self-learning TLBO. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 12th Data Driven Control and Learning Systems Conference, Xiangtan, China, 12–14 May 2023; pp. 1516–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.Y.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, M. Auto-tuning of model-based feedforward controller by feedback control signal in ultraprecision motion systems. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2020, 142, 106764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.Y.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hu, C.X. The Generation Mechanism of Tracking Error During Acceleration or Deceleration Phase in Ultraprecision Motion Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 7109–7119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.X.; Li, X.Q.; Luo, Y.; Chen, X.D.; Zeng, L.Z. Iterative Tuning of Feedforward Controller with Precise Time-Delay Compensation for Precision Motion System. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 9391526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.Y.; Tan, J.B. Kalman-Filtering-Based Iterative Feedforward Tuning in Presence of Stochastic Noise: With Application to a Wafer Stage. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 5816–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Li, M.; Yao, X.Y. Data-driven tuning of feedforward controller structured with infinite impulse response filter via iterative learning control. IET Control Theory Appl. 2019, 13, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.Y.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, M. Feedforward tuning by fitting iterative learning control signal for precision motion systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 8412–8421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.H.; Wang, M.Y.; Li, J.C.; Sun, Q.W.; Zhang, C.M.; Li, L.Y. Adaptive Feedforward Control Based on Recursive Least Squares Algorithm for the Biaxial Maglev Planar-Motor-Driven Gantry System. In Proceedings of the 2024 27th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Fukuoka, Japan, 26–29 November 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marton, L. On analysis of limit cycles in positioning systems near Striebeck velocities. Mechatronics 2008, 18, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marton, L.; Lantos, B. Modeling, Identification, and Compensation of Stick-Slip Friction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brian, A.H. Control of Machines with Friction. Tribol.-Trans. ASME 1991, 114, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.N.; Liang, W.Y.; Tan, K.K. Intelligent Friction Compensation: A Review. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 1763–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.F.; Li, Z.C.; Zhang, X.K.; Li, Y.H.; Zhu, M.C. A Semi-linearized Approach for Dynamic Identification of Manipulator Based on Nonlinear Friction Model. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 7503520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatoorehchi, H.; Abolghasemi, H. Computation of analytical Laplace transforms by the differential transform method. Math. Comput. Model. 2012, 56, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascetta, L.; Paolo, R.; Gianantonio, M. Force Ripple Compensation in Linear Motors Based on Closed-Loop Position-Dependent Identification. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2010, 15, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| φ | the basis function vector |
| Ψ | the sampling matrix of the basis function vector |
| Ψ | the specific sampling data in the sampling matrix of the feedforward basis function vector |
| Item | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Rated voltage, Vn | 220 | V |
| Rated power, Pn | 103.9 | W |
| Thrust constant, KT | 10.355 | N/A |
| Action mass, mm | 1.1 | kg |
| Limit of current | 12 | A |
| Reference Trajectory | Maximum Displacement xmax | Maximum Velocity vmax | Maximum Acceleration amax | Maximum Jerk jmax |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 0.045 (m) | 0.2 (m/s) | 5 (m/s2) | 250 (m/s3) |
| R2 | 0.045 (m) | 0.3 (m/s) | 6 (m/s2) | 240 (m/s3) |
| Number of iterations | IFFT with the Fixed-Gain Feedback Controller (LS) (µm) | IFFT with the Fixed-Gain Feedback Controller (GD) (µm) | IFFT with the Variable-Gain Feedback Controller (LS) (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 291.95 | 292.24 | 619.97 |
| 2 | 237.86 | 238.65 | 158.13 |
| 3 | 232.87 | 232.04 | 39.64 |
| 4 | 208.47 | 181.14 | 13.83 |
| 5 | 168.45 | 143.52 | 8.00 |
| ··· | ··· | ··· | ··· |
| 30 | 11.89 | 11.49 | 8.00 |
| Number of iterations | IFFT with the Fixed-Gain Feedback Controller (LS) (µm) | IFFT with the Fixed-Gain Feedback Controller (GD) (µm) | IFFT with the Variable-Gain Feedback Controller (LS) (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 113.98 | 113.84 | 443.28 |
| 2 | 91.55 | 91.40 | 105.093 |
| 3 | 82.03 | 76.20 | 23.40 |
| 4 | 68.25 | 63.21 | 5.54 |
| 5 | 58.64 | 52.93 | 2.79 |
| ··· | ··· | ··· | ··· |
| 30 | 4.23 | 3.83 | 2.74 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, J.; Li, S. A Data-Driven Iterative Feedforward Tuning Strategy with a Variable-Gain Feedback Controller for Linear Servo Systems. Energies 2025, 18, 3284. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18133284
Fu J, Li S. A Data-Driven Iterative Feedforward Tuning Strategy with a Variable-Gain Feedback Controller for Linear Servo Systems. Energies. 2025; 18(13):3284. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18133284
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Jiaqian, and Shanhu Li. 2025. "A Data-Driven Iterative Feedforward Tuning Strategy with a Variable-Gain Feedback Controller for Linear Servo Systems" Energies 18, no. 13: 3284. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18133284
APA StyleFu, J., & Li, S. (2025). A Data-Driven Iterative Feedforward Tuning Strategy with a Variable-Gain Feedback Controller for Linear Servo Systems. Energies, 18(13), 3284. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18133284







