A Review of Electricity Price Forecasting Models in the Day-Ahead, Intra-Day, and Balancing Markets
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Point Forecasting Methods
1.2. Related Work and Literature Gap
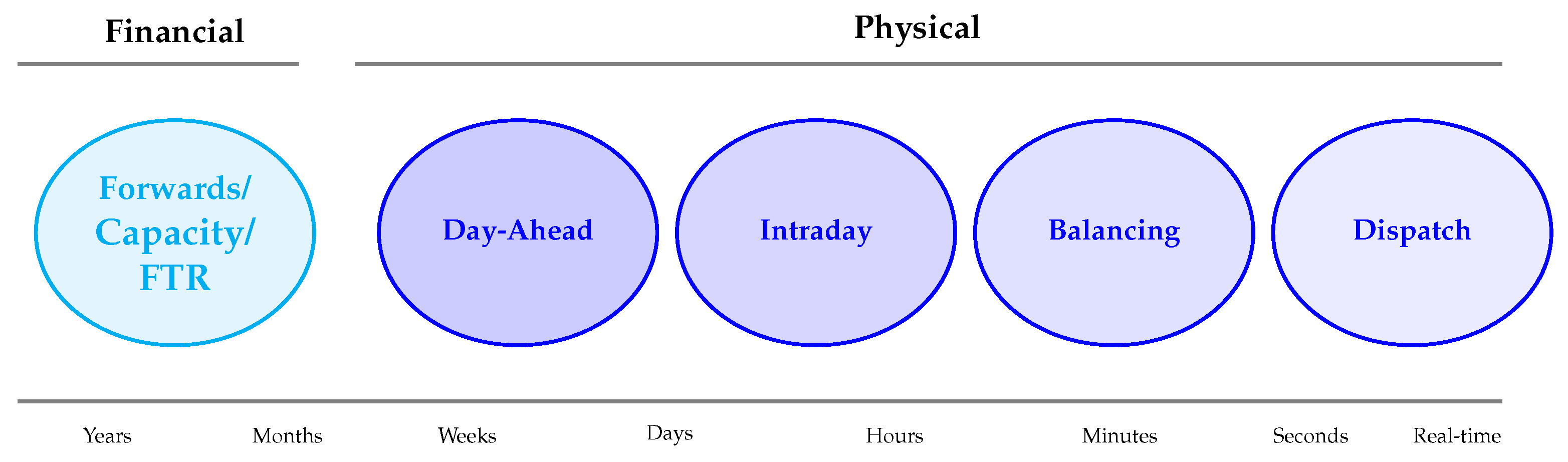
2. Background: Electricity Market Structure
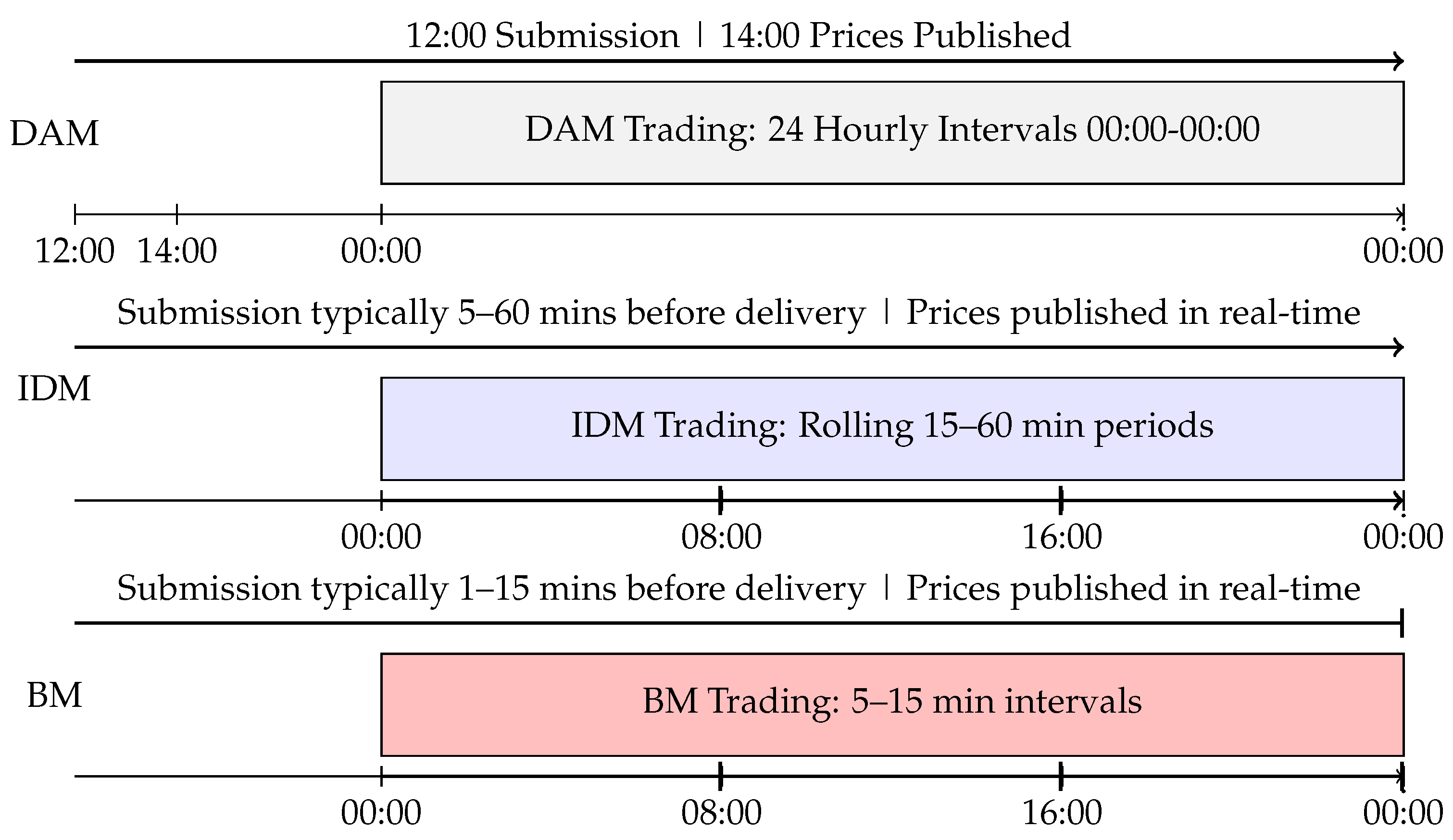
2.1. Day-Ahead Market
2.2. Intra-Day Market
2.3. Balancing Market
2.4. Other Electricity Markets
- Forward market: Allows participants to hedge positions in DAM, IDM, and BM through contracts-for-difference [37]. Contracts-for-difference enable participants to lock in a strike price, providing protection against price volatility. Forecasting in this market requires predicting long-term price trends and movements.
- Ancillary markets: Support the power grid’s stability and reliability through services like frequency regulation, spinning reserve, voltage control, and black start capabilities. Accurate forecasting in ancillary markets ensures the availability of resources needed to maintain grid stability. This involves sophisticated models considering real-time operational data and dynamic supply and demand conditions [38].
- Capacity market: Ensures sufficient generation capacity to meet peak demand. Capacity providers receive payments for committing to supply electricity or reduce demand during peak periods, incentivising investment in new capacity [39]. Forecasting in the capacity market involves predicting peak demand periods and capacity resource availability.
- Financial transmission rights auctions: Manage congestion costs and provide financial hedges against price differences across market zones. Financial transmission rights entitle holders to payments based on price differences between locations. Forecasting in this market involves predicting congestion patterns and price differentials, requiring an understanding of grid operations and transmission constraints [40].
3. Predictive Models
3.1. Statistical Methods Without Exogenous Inputs
3.1.1. Autoregressive Model
3.1.2. Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average Model
3.1.3. Generalised Autoregressive Conditional Heteroscedasticity Model
3.1.4. Exponential Smoothing Model
3.1.5. Naive Model
3.2. Statistical Methods with Exogenous Inputs
3.2.1. ARX-Type Models
3.2.2. ARIMAX Model
3.2.3. LASSO Models
3.2.4. LEAR Models
3.2.5. Transfer Function Model
3.2.6. Copula Model
3.3. Machine Learning Methods
3.3.1. K-Nearest Neighbours
3.3.2. Support Vector Regression
3.3.3. Random Forest
3.3.4. Gradient Boosting
3.4. Deep Learning Methods
3.4.1. Deep Neural Networks
3.4.2. Convolutional Neural Networks
3.4.3. Long Short-Term Memory
3.4.4. Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs)
3.4.5. Temporal Fusion Transformers
3.4.6. DeepAR
3.4.7. Prophet
3.5. Hybrid Models
3.5.1. Statistical Hybrid Models
3.5.2. Machine Learning Hybrid Models
3.5.3. Deep Learning Hybrid Models
4. Discussion
4.1. Overview
4.2. Forecasting Methods
4.2.1. Statistical Models
4.2.2. Machine Learning Models
4.2.3. Deep Learning Models
4.2.4. Hybrid Models
4.3. Input Data Requirements and Model Sensitivities
4.4. Forecasting Across the Day-Ahead, Intra-Day, and Balancing Markets
4.5. Regional Trends in Model Usage
4.6. Evaluation Metrics—Persistent Issues
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Ortner, A.; Totschnig, G. The future relevance of electricity balancing markets in Europe-A 2030 case study. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019, 24, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koecklin, M.T.; Longoria, G.; Fitiwi, D.Z.; DeCarolis, J.F.; Curtis, J. Public acceptance of renewable electricity generation and transmission network developments: Insights from Ireland. Energy Policy 2021, 151, 112185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meles, T.H.; Ryan, L. Adoption of renewable home heating systems: An agent-based model of heat pumps in Ireland. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 169, 112853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, J.; Marcjasz, G.; De Schutter, B.; Weron, R. Forecasting day-ahead electricity prices: A review of state-of-the-art algorithms, best practices and an open-access benchmark. Appl. Energy 2021, 293, 116983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ce, L.; Lian, L. Electricity price forecasting by a hybrid model, combining wavelet transform, ARMA and kernel-based extreme learning machine methods. Appl. Energy 2017, 190, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, J.; De Ridder, F.; Vrancx, P.; De Schutter, B. Forecasting day-ahead electricity prices in Europe: The importance of considering market integration. Appl. Energy 2018, 211, 890–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Baldick, R. Day-ahead price forecasting in ERCOT market using neural network approaches. In Proceedings of the Tenth ACM International Conference on Future Energy Systems, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 June 2019; pp. 486–491. [Google Scholar]
- Zahid, M.; Ahmed, F.; Javaid, N.; Abbasi, R.A.; Zainab Kazmi, H.S.; Javaid, A.; Bilal, M.; Akbar, M.; Ilahi, M. Electricity price and load forecasting using enhanced convolutional neural network and enhanced support vector regression in smart grids. Electronics 2019, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarpanah, M.; Hooshyaripor, F.; Fazeli, M. Daily electricity price forecasting using artificial intelligence models in the Iranian electricity market. Energy 2023, 263, 126011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.K.; Saini, L.M.; Kumar, A. Electricity price forecasting in deregulated markets: A review and evaluation. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2009, 31, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weron, R. Electricity price forecasting: A review of the state-of-the-art with a look into the future. Int. J. Forecast. 2014, 30, 1030–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Fleyeh, H. A review of single artificial neural network models for electricity spot price forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th International Conference on the European Energy Market (EEM), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 18–20 September 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Acaroğlu, H.; García Márquez, F.P. Comprehensive review on electricity market price and load forecasting based on wind energy. Energies 2021, 14, 7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jędrzejewski, A.; Lago, J.; Marcjasz, G.; Weron, R. Electricity price forecasting: The dawn of machine learning. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2022, 20, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbery, D.; Strbac, G.; Viehoff, I. The benefits of integrating European electricity markets. Energy Policy 2016, 94, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilea, V.; Bovo, C. European day-ahead electricity market coupling: Discussion, modeling, and case study. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 155, 80–92. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Anido, C.B.; Brinkman, G.; Hodge, B.M. The impact of wind power on electricity prices. Renew. Energy 2016, 94, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugurlu, U.; Oksuz, I.; Tas, O. Electricity price forecasting using recurrent neural networks. Energies 2018, 11, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, J.; De Ridder, F.; De Schutter, B. Forecasting spot electricity prices: Deep learning approaches and empirical comparison of traditional algorithms. Appl. Energy 2018, 221, 386–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Jin, Q. BRIM: An accurate electricity spot price prediction scheme-based bidirectional recurrent neural network and integrated market. Energies 2019, 12, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Becker, D.M. Day-ahead electricity price prediction applying hybrid models of LSTM-based deep learning methods and feature selection algorithms under consideration of market coupling. Energy 2021, 237, 121543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, P.; Amelin, M. A literature review of intraday electricity markets and prices. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Milan PowerTech, Milan, Italy, 23–27 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, C.; Ramirez-Rosado, I.J.; Fernandez-Jimenez, L.A.; Conde, P. Short-term price forecasting models based on artificial neural networks for intraday sessions in the Iberian electricity market. Energies 2016, 9, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, J.R.; Filipe, J.; Reis, M.; Bessa, R.J. Probabilistic price forecasting for day-ahead and intraday markets: Beyond the statistical model. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uniejewski, B.; Marcjasz, G.; Weron, R. Understanding intraday electricity markets: Variable selection and very short-term price forecasting using LASSO. Int. J. Forecast. 2019, 35, 1533–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narajewski, M.; Ziel, F. Ensemble forecasting for intraday electricity prices: Simulating trajectories. Appl. Energy 2020, 279, 115801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.; Hirth, L. Short-term electricity trading for system balancing: An empirical analysis of the role of intraday trading in balancing Germany’s electricity system. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 113, 109275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkeland, D.; AlSkaif, T. Research areas and methods of interest in European intraday electricity market research—A systematic literature review. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2024, 38, 101368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachmann, G.; Hirth, L.; Heussaff, C.; Schlecht, I.; Mühlenpfordt, J.; Eicke, A. The Design of the European Electricity Market–Current Proposals and Ways Ahead; European Parliament: Luxembourg, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Dumas, J.; Boukas, I.; de Villena, M.M.; Mathieu, S.; Cornélusse, B. Probabilistic forecasting of imbalance prices in the belgian context. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th International Conference on the European Energy Market (EEM), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 18–20 September 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Narajewski, M. Probabilistic forecasting of German electricity imbalance prices. Energies 2022, 15, 4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, C.; Collins, J.; Prestwich, S.; Visentin, A. Electricity Price Forecasting in the Irish Balancing Market. Energy Strategy Rev. 2024, 54, 101436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Veen, R.A.; Hakvoort, R.A. The electricity balancing market: Exploring the design challenge. Util. Policy 2016, 43, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicke, A.; Ruhnau, O.; Hirth, L. Electricity balancing as a market equilibrium. Energy Econ. 2021, 102, 105455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEMO. Markets and Timelines. Available online: https://www.sem-o.com/markets (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- Silva-Rodriguez, L.; Sanjab, A.; Fumagalli, E.; Virag, A.; Gibescu, M. Short term wholesale electricity market designs: A review of identified challenges and promising solutions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 160, 112228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peura, H.; Bunn, D.W. Renewable power and electricity prices: The impact of forward markets. Manag. Sci. 2021, 67, 4772–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancilio, G.; Rossi, A.; Falabretti, D.; Galliani, A.; Merlo, M. Ancillary services markets in europe: Evolution and regulatory trade-offs. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 154, 111850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramton, P.; Ockenfels, A.; Stoft, S. Capacity market fundamentals. Econ. Energy Environ. Policy 2013, 2, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, V.; Khaparde, S.A. A comprehensive assessment of the evolution of financial transmission rights. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2008, 23, 1783–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejowska, K.; Weron, R. Short-and mid-term forecasting of baseload electricity prices in the UK: The impact of intra-day price relationships and market fundamentals. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 31, 994–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popławski, T.; Dudek, G.; Łyp, J. Forecasting methods for balancing energy market in Poland. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 65, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klæboe, G.; Eriksrud, A.L.; Fleten, S.E. Benchmarking time series based forecasting models for electricity balancing market prices. Energy Syst. 2015, 6, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girish, G.P. Spot electricity price forecasting in Indian electricity market using autoregressive-GARCH models. Energy Strategy Rev. 2016, 11, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, K.G.; Challu, C.; Marcjasz, G.; Weron, R.; Dubrawski, A. Neural basis expansion analysis with exogenous variables: Forecasting electricity prices with NBEATSx. Int. J. Forecast. 2023, 39, 884–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billé, A.G.; Gianfreda, A.; Del Grosso, F.; Ravazzolo, F. Forecasting electricity prices with expert, linear, and nonlinear models. Int. J. Forecast. 2023, 39, 570–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziel, F. Forecasting electricity spot prices using lasso: On capturing the autoregressive intraday structure. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 4977–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özen, K.; Yıldırım, D. Application of bagging in day-ahead electricity price forecasting and factor augmentation. Energy Econ. 2021, 103, 105573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englund, A. Evaluation of Machine Learning Models for Intraday Price Forecasting in the Renewable Energy Sector. Master’s Thesis, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Contreras, J.; Espinola, R.; Nogales, F.J.; Conejo, A.J. ARIMA models to predict next-day electricity prices. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2003, 18, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuaresma, J.C.; Hlouskova, J.; Kossmeier, S.; Obersteiner, M. Forecasting electricity spot-prices using linear univariate time-series models. Appl. Energy 2004, 77, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conejo, A.J.; Plazas, M.A.; Espinola, R.; Molina, A.B. Day-ahead electricity price forecasting using the wavelet transform and ARIMA models. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2005, 20, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Yang, H.; Ruan, G.; Zhong, H.; Liu, F. Short-term electricity price forecasting based on graph convolution network and attention mechanism. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2022, 16, 2481–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggi, A.; Di Persio, L.; Ehrhardt, M. Electricity price forecasting via statistical and deep learning approaches: The german case. AppliedMath 2023, 3, 316–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, D.K.; Nielsen, P.; Thibbotuwawa, A. Intraday Electricity Price Forecasting via LSTM and Trading Strategy for the Power Market: A Case Study of the West Denmark DK1 Grid Region. Energies 2024, 17, 2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knittel, C.R.; Roberts, M.R. An empirical examination of restructured electricity prices. Energy Econ. 2005, 27, 791–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diongue, A.K.; Guegan, D.; Vignal, B. Forecasting electricity spot market prices with a k-factor GIGARCH process. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, G.; Wichitaksorn, N. Electricity price forecasting in New Zealand: A comparative analysis of statistical and machine learning models with feature selection. Appl. Energy 2023, 347, 121446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, I.; Othman, N.S.; Harun, N.H. Forecasting electricity consumption of Malaysia’s residential sector: Evidence from an exponential smoothing model. F1000Research 2022, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, G.; Liu, C.; Sahoo, D.; Kumar, A.; Hoi, S. Etsformer: Exponential smoothing transformers for time-series forecasting. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.01381. [Google Scholar]
- Karabiber, O.A.; Xydis, G. Electricity price forecasting in the Danish day-ahead market using the TBATS, ANN and ARIMA methods. Energies 2019, 12, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellert, A.; Fiore, U.; Florea, A.; Chis, R.; Palmieri, F. Forecasting electricity consumption and production in smart homes through statistical methods. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 76, 103426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, R.; Mokhlis, H.; Khairuddin, A.S.M.; Ismail, S.; Muhammad, M.A. Optimized Gated Recurrent Unit for Mid-Term Electricity Price Forecasting. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2022, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, J.; Xiao, X.; Goh, M. Energy demand forecasting in China: A support vector regression-compositional data second exponential smoothing model. Energy 2023, 263, 125955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisi, F.; Shah, I. Joint component estimation for electricity price forecasting using functional models. Energies 2024, 17, 3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigaite, R.; Krilavičius, T.; Man, K.L. Electricity Price Forecasting for Nord Pool Data. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Platform Technology and Service (PlatCon), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 29–31 January 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcjasz, G.; Uniejewski, B.; Weron, R. Beating the naïve—Combining LASSO with naïve intraday electricity price forecasts. Energies 2020, 13, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksuz, I.; Ugurlu, U. Neural network based model comparison for intraday electricity price forecasting. Energies 2019, 12, 4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kath, C.; Ziel, F. The value of forecasts: Quantifying the economic gains of accurate quarter-hourly electricity price forecasts. Energy Econ. 2018, 76, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickelsen, D.; Müller, G. Bayesian hierarchical probabilistic forecasting of intraday electricity prices. Appl. Energy 2025, 380, 124975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejowska, K.; Nitka, W.; Weron, T. Day-ahead vs. Intraday—Forecasting the price spread to maximize economic benefits. Energies 2019, 12, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsias, P.C. Forecasting Electricity Prices for Intraday Markets with Machine Learning: An exploratory comparison of the state of the art. IET Conf. Proc. 2022, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Uniejewski, B. Regularization for electricity price forecasting. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.03968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakaša, T.; Andročec, I.; Sprčić, P. Electricity price forecasting—ARIMA model approach. In Proceedings of the 2011 8th international conference on the European energy market (EEM), Zagreb, Croatia, 25–27 May 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 222–225. [Google Scholar]
- Lehna, M.; Scheller, F.; Herwartz, H. Forecasting day-ahead electricity prices: A comparison of time series and neural network models taking external regressors into account. Energy Econ. 2022, 106, 105742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozlak, Ç.B.; Yaşar, C.F. An optimized deep learning approach for forecasting day-ahead electricity prices. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2024, 229, 110129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsatoglou, A.; Georgopoulos, G.; Papadopoulos, P.; Antonopoulos, H. An ensemble approach for enhanced Day-Ahead price forecasting in electricity markets. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 256, 124971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narajewski, M.; Ziel, F. Econometric modelling and forecasting of intraday electricity prices. J. Commod. Mark. 2020, 19, 100107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafin, T.; Marcjasz, G.; Weron, R. Trading on short-term path forecasts of intraday electricity prices. Energy Econ. 2022, 112, 106125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agakishiev, I.; Härdle, W.K.; Kopa, M.; Kozmik, K.; Petukhina, A. Multivariate probabilistic forecasting of electricity prices with trading applications. Energy Econ. 2025, 141, 108008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uniejewski, B.; Nowotarski, J.; Weron, R. Automated variable selection and shrinkage for day-ahead electricity price forecasting. Energies 2016, 9, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschora, L.; Pierre, E.; Plantevit, M.; Robardet, C. Electricity price forecasting on the day-ahead market using machine learning. Appl. Energy 2022, 313, 118752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcjasz, G.; Narajewski, M.; Weron, R.; Ziel, F. Distributional neural networks for electricity price forecasting. Energy Econ. 2023, 125, 106843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, S.; Ugurlu, U.; Oksuz, I. Transfer learning for electricity price forecasting. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2023, 34, 100996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J. Forecasting day-ahead electricity prices with spatial dependence. Int. J. Forecast. 2024, 40, 1255–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, C.; Bahloul, M.; Rossi, R.; Prestwich, S.; Visentin, A. Conformal Prediction for Electricity Price Forecasting in the Day-Ahead and Real-Time Balancing Market. arXiv 2025, arXiv:cs.LG/2502.04935. [Google Scholar]
- Nogales, F.J.; Contreras, J.; Conejo, A.J.; Espínola, R. Forecasting next-day electricity prices by time series models. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2002, 17, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García González, J.; Barquín Gil, J.; Dueñas Martínez, P. A Hybrid Approach for Modeling Electricity Price Series in the Medium Term. 2008. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/255586295_A_hybrid_approach_for_modeling_electricity_price_series_in_the_medium_term (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- Durante, F.; Gianfreda, A.; Ravazzolo, F.; Rossini, L. A multivariate dependence analysis for electricity prices, demand and renewable energy sources. Inf. Sci. 2022, 590, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta-Prieto, M.; Schell, K.R. Spatio-temporal probabilistic forecasting of wind power for multiple farms: A copula-based hybrid model. Int. J. Forecast. 2022, 38, 300–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijoo, F.; Silva, W.; Das, T.K. A computationally efficient electricity price forecasting model for real time energy markets. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 113, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Khan, Z.A.; Mujeeb, S.; Abbas, S.; Javaid, N. Short-term electricity price and load forecasting using enhanced support vector machine and K-nearest neighbor. In Proceedings of the 2019 Sixth HCT Information Technology Trends (ITT), Ras Al Khaimah, United Arab Emirates, 20–21 November 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ashfaq, T.; Javaid, N. Short-term electricity load and price forecasting using enhanced KNN. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology (FIT), Islamabad, Pakistan, 16–18 December 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 266–2665. [Google Scholar]
- Johannesen, N.J.; Kolhe, M.; Goodwin, M. Deregulated electric energy price forecasting in nordpool market using regression techniques. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Sustainable Power and Energy Conference (iSPEC), Beijing, China, 21–23 November 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1932–1938. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Xu, K.; Ding, Z.; Du, Y.; Liu, W.; Sun, B.; Zhu, Z.; Tang, H. An online electricity market price forecasting method via random forest. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 7013–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, S.; Castro, A.; Irizar, I.; Naveran, G.; Yeregui, I. Framework for collaborative intelligence in forecasting day-ahead electricity price. Appl. Energy 2022, 306, 118049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Castillo, I.; LaGrande, G.; Jiang, S. A New Modeling Framework for Real-Time Extreme Electricity Price Forecasting. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2024, 58, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansom, D.C.; Downs, T.; Saha, T.K. Evaluation of support vector machine based forecasting tool in electricity price forecasting for Australian national electricity market participants. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. Aust. 2003, 22, 227–233. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, S.; Mao, C.; Chen, L. Next-day electricity-price forecasting using a hybrid network. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2007, 1, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Wang, J. Short-term electricity prices forecasting based on support vector regression and auto-regressive integrated moving average modeling. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Fleyeh, H.; Bales, C. A hybrid model based on bidirectional long short-term memory neural network and Catboost for short-term electricity spot price forecasting. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2022, 73, 301–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantillo-Luna, S.; Moreno-Chuquen, R.; Chamorro, H.R.; Riquelme-Dominguez, J.M.; Gonzalez-Longatt, F. Locational marginal price forecasting using svr-based multi-output regression in electricity markets. Energies 2022, 15, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Inekwe, J.; Smirnov, V.; Wait, A.; Wang, C. Seasonality in deep learning forecasts of electricity imbalance prices. Energy Econ. 2024, 137, 107770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, C.; Mira, J.M.; Ojeda, J.A. Applying Multi-Output Random Forest Models to Electricity Price Forecast. 2016. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/308384009_Applying_Multi-Output_Random_Forest_Models_to_Electricity_Price_Forecast (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- Kara, M.; Atici, K.B.; Ulucan, A. Price and volatility forecasting in electricity with support vector regression and random forest. In Applied Operations Research and Financial Modelling in Energy: Practical Applications and Implications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 101–124. [Google Scholar]
- Alkawaz, A.N.; Abdellatif, A.; Kanesan, J.; Khairuddin, A.S.M.; Gheni, H.M. Day-ahead electricity price forecasting based on hybrid regression model. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 108021–108033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Chen, S.; Lai, C.; Ma, G.; Huang, W. Forecasting the clearing price in the day-ahead spot market using eXtreme Gradient Boosting. Electr. Eng. 2022, 104, 1607–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; He, D.; Harley, R.; Habetler, T.; Qu, G. A random forest method for real-time price forecasting in New York electricity market. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE PES General Meeting|Conference & Exposition, Chicago, IL, USA, 14–17 April 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, C.; Collins, J.; Prestwich, S.; Visentin, A. Optimising quantile-based trading strategies in electricity arbitrage. Energy AI 2025, 20, 100476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Shi, J.; Wang, B.; An, N.; Li, L.; Hou, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Li, H.; et al. A hybrid framework for day-ahead electricity spot-price forecasting: A case study in China. Appl. Energy 2024, 373, 123863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Xie, S.; Wang, B.; Yang, R.; Xu, D.; He, Y. Wind speed forecasting based on extreme gradient boosting. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 175063–175069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qinghe, Z.; Wen, X.; Boyan, H.; Jong, W.; Junlong, F. Optimised extreme gradient boosting model for short term electric load demand forecasting of regional grid system. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafi, S.H.; Mahdi, M.M. A short-term load forecasting technique using extreme gradient boosting algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies-Asia (ISGT Asia), Brisbane, Australia, 5–8 December 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Suvarna, M.; Pravin, P.; Yap, K.S.; Wang, X. Application of machine learning and big data for smart energy management in manufacturing. In Computer Aided Chemical Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 49, pp. 1699–1704. [Google Scholar]
- Malakouti, S.M. Use machine learning algorithms to predict turbine power generation to replace renewable energy with fossil fuels. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2023, 41, 836–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A.; Pegios, K.; Kotsakis, E.; Clarke, D. Price forecasting for the balancing energy market using machine-learning regression. Energies 2020, 13, 5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, C.; Prestwich, S.; Visentin, A. Conformal Prediction Techniques for Electricity Price Forecasting. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Advanced Analytics and Learning on Temporal Data, Vilnius, Lithuania, 9–13 September 2024; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E.; Osindero, S.; Teh, Y.W. A Fast Learning Algorithm for Deep Belief Nets. Neural Comput. 2006, 18, 1527–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.; Deng, L.; Yu, D.; Dahl, G.E.; Mohamed, A.r.; Jaitly, N.; Senior, A.; Vanhoucke, V.; Nguyen, P.; Sainath, T.N.; et al. Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: The shared views of four research groups. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2012, 29, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.0473. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Li, G.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y. Deep belief network based deterministic and probabilistic wind speed forecasting approach. Appl. Energy 2016, 182, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, I.M.; Coelho, V.N.; Luz, E.J.d.S.; Ochi, L.S.; Guimaraes, F.G.; Rios, E. A GPU deep learning metaheuristic based model for time series forecasting. Appl. Energy 2017, 201, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atef, S.; Eltawil, A.B. A comparative study using deep learning and support vector regression for electricity price forecasting in smart grids. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 6th International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Applications (ICIEA), Tokyo, Japan, 12–15 April 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 603–607. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.; Weng, Y. A two-stage supervised learning approach for electricity price forecasting by leveraging different data sources. Appl. Energy 2019, 242, 1497–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujeeb, S.; Javaid, N. ESAENARX and DE-RELM: Novel schemes for big data predictive analytics of electricity load and price. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 51, 101642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnürch, S.; Wagner, A. Machine learning on epex order books: Insights and forecasts. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.06248. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.A.; Fareed, S.; Anwar, M.; Naeem, A.; Gul, H.; Arif, A.; Javaid, N. Short term electricity price forecasting through convolutional neural network. In Web, Artificial Intelligence and Network Applications: Proceedings of the Workshops of the 34th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications (WAINA-2020); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1181–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Schell, K.R. QCAE: A quadruple branch CNN autoencoder for real-time electricity price forecasting. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 141, 108092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourdaryaei, A.; Mohammadi, M.; Mubarak, H.; Abdellatif, A.; Karimi, M.; Gryazina, E.; Terzija, V. A new framework for electricity price forecasting via multi-head self-attention and CNN-based techniques in the competitive electricity market. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 235, 121207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S. Long Short-Term Memory; Neural Computation MIT-Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Chinnathambi, R.A.; Plathottam, S.J.; Hossen, T.; Nair, A.S.; Ranganathan, P. Deep neural networks for day-ahead electricity price markets. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Electrical Power and Energy Conference (EPEC), Toronto, ON, Canada, 10–11 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Memarzadeh, G.; Keynia, F. Short-term electricity load and price forecasting by a new optimal LSTM-NN based prediction algorithm. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2021, 192, 106995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, A.; Wang, P.; Zhai, G.; Zeng, C.; Chen, S.; Yang, X.; Yin, H. Electricity price forecasting with high penetration of renewable energy using attention-based LSTM network trained by crisscross optimization. Energy 2022, 254, 124212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Dai, R.; Liu, G.; Wang, Z.; Lu, S. Power market price forecasting via deep learning. In Proceedings of the IECON 2018-44th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Washington, DC, USA, 21–23 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 4935–4939. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Zhou, L.; Mao, M.; Tai, H.M.; Wan, Y. An optimized heterogeneous structure LSTM network for electricity price forecasting. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 108161–108173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.H.; Huang, C.J. An electricity price forecasting model by hybrid structured deep neural networks. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W. Effective adam-optimized LSTM neural network for electricity price forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 9th International Conference on Software Engineering and Service Science (ICSESS), Beijing, China, 23–25 November 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 245–248. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, N.; Rajabi, R.; Estebsari, A. Electricity price forecasting model based on gated recurrent units. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2022 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe (EEEIC/I&CPS Europe), Prague, Czech Republic, 28 June–1 July 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Molin, L. Predicting Electricity Imbalance Prices. Ph.D. Thesis, Tilburg University, Tilburg, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, W.; Wang, F.K.; Amogne, Z.E. Electricity Load and Price Forecasting Using a Hybrid Method Based Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory with Attention Mechanism Model. Int. J. Energy Res. 2023, 2023, 3815063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Robinson, E.; Basu, M. Wind power forecasting based on a novel gated recurrent neural network model. Wind. Energy Eng. Res. 2024, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Qing, G. A hybrid day-ahead electricity price forecasting framework based on time series. Energy 2023, 264, 126099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, Y.F. A robust electricity price forecasting framework based on heteroscedastic temporal Convolutional Network. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 161, 110177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Santos, M.; García-Santiago, X.; Echevarría Camarero, F.; Blázquez Gil, G.; Carrasco Ortega, P. Application of temporal fusion transformer for day-ahead PV power forecasting. Energies 2022, 15, 5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, A.; Shaikh, A.K.; Shah, A.S.; Khalil, A. Forecasting Energy Consumption Demand of Customers in Smart Grid Using Temporal Fusion Transformer. Results Eng. 2023, 17, 100888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Pan, S.; Dong, Y.; Wang, J. Probabilistic electricity price forecasting based on penalized temporal fusion transformer. J. Forecast. 2024, 43, 1465–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, D.; Flunkert, V.; Gasthaus, J.; Januschowski, T. DeepAR: Probabilistic forecasting with autoregressive recurrent networks. Int. J. Forecast. 2020, 36, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Seman, L.O.; Mariani, V.C.; Coelho, L.d.S. Aggregating prophet and seasonal trend decomposition for time series forecasting of Italian electricity spot prices. Energies 2023, 16, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shohan, M.J.A.; Faruque, M.O.; Foo, S.Y. Forecasting of electric load using a hybrid LSTM-neural prophet model. Energies 2022, 15, 2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Du, Y.; Wang, P.; Tian, X.; Xu, Z.; Yang, F.; Chen, L.; Wan, J. A hybrid forecasting method considering the long-term dependence of day-ahead electricity price series. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2024, 235, 110841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyangon, J.; Akintunde, R. Principal component analysis of day-ahead electricity price forecasting in CAISO and its implications for highly integrated renewable energy markets. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Energy Environ. 2024, 13, e504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapnken, F.E.; Tazehkandgheshlagh, A.K.; Diboma, B.S.; Hamaidi, M.; Noumo, P.G.; Wang, Y.; Tamba, J.G. A whale optimization algorithm-based multivariate exponential smoothing grey-holt model for electricity price forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 255, 124663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Tang, Z.; Wu, J.; Du, X.; Chen, K. Short term electricity price forecasting using a new hybrid model based on two-layer decomposition technique and ensemble learning. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 205, 107762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielli, P.; Wüthrich, M.; Blume, S.; Sansavini, G. Data-driven modeling for long-term electricity price forecasting. Energy 2022, 244, 123107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizad, B.; Ranjbarzadeh, H.; Jamali, A.; Khayyam, H. An intelligent hybrid machine learning model for sustainable forecasting of home energy demand and electricity price. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, B.; Du, C.; Yang, C.; Gui, W. Outlier-adaptive-based non-crossing quantiles method for day-ahead electricity price forecasting. Appl. Energy 2025, 382, 125328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.; Johnson, M.; Smith, J.; Rodriguez, S.; Deshmukh, A.; Brown, E. Developing a Hybrid Price Forecasting Model using Machine Learning and Time Series Analysis. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/388960526 (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- Bashir, T.; Haoyong, C.; Tahir, M.F.; Liqiang, Z. Short term electricity load forecasting using hybrid prophet-LSTM model optimized by BPNN. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 1678–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xiao, J.; Xu, W. A hybrid stacking method for short-term price forecasting in electricity trading market. In Proceedings of the 2024 8th International Conference on Information Technology, Information Systems and Electrical Engineering (ICITISEE), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 29–30 August 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Laitsos, V.; Vontzos, G.; Bargiotas, D.; Daskalopulu, A.; Tsoukalas, L.H. Data-driven techniques for short-term electricity price forecasting through novel deep learning approaches with attention mechanisms. Energies 2024, 17, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsani, B.; Pineau, P.O.; Charlin, L. Price forecasting in the Ontario electricity market via TriConvGRU hybrid model: Univariate vs. multivariate frameworks. Appl. Energy 2024, 359, 122649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belenguer, E.; Segarra-Tamarit, J.; Pérez, E.; Vidal-Albalate, R. Short-term electricity price forecasting through demand and renewable generation prediction. Math. Comput. Simul. 2025, 229, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Wang, P.; Xu, R.; Han, R.; Chen, E.; Han, Y.; Zhang, X. A novel mid-and long-term time-series forecasting framework for electricity price based on hierarchical recurrent neural networks. J. Frankl. Inst. 2025, 362, 107590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cu, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Mo, L. A Time Series Decomposition-Based Interpretable Electricity Price Forecasting Method. Energies 2025, 18, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, H.; Abdellatif, A.; Ahmad, S.; Islam, M.Z.; Muyeen, S.; Mannan, M.A.; Kamwa, I. Day-Ahead electricity price forecasting using a CNN-BiLSTM model in conjunction with autoregressive modeling and hyperparameter optimization. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 161, 110206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.A.; Ullah, M.H.; Tabassum, R.; Kabir, M.F. A transformer-BILSTM based hybrid deep learning approach for day-ahead electricity price forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Kansas Power and Energy Conference (KPEC), Manhattan, KS, USA, 25–26 April 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L. A novel multivariate electrical price bi-forecasting system based on deep learning, a multi-input multi-output structure and an operator combination mechanism. Appl. Energy 2024, 366, 123233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajigholam Saryazdi, A. A Novel Hybrid Deep learning Model for Electricity Price Forecasting. 2024. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5166713 (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- Zhou, M.; Yan, Z.; Ni, Y.; Li, G.; Nie, Y. Electricity price forecasting with confidence-interval estimation through an extended ARIMA approach. IEE Proc.-Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2006, 153, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.M.; Gow, H.J.; Tsai, M.T. An enhanced radial basis function network for short-term electricity price forecasting. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 3226–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Hu, G. Day-ahead price forecasting for electricity market using long-short term memory recurrent neural network. In Proceedings of the 2018 15th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision (ICARCV), Singapore, 18–21 November 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 949–954. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Cheema, F.; Srinivasan, D. Forecasting of electricity prices using deep learning networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE PES Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference (APPEEC), Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 7–10 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 451–456. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W. Electricity price prediction based on hybrid model of adam optimized LSTM neural network and wavelet transform. Energy 2019, 187, 115804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, S.; Deo, R.C.; Casillas-Pérez, D.; Salcedo-Sanz, S. Two-step deep learning framework with error compensation technique for short-term, half-hourly electricity price forecasting. Appl. Energy 2024, 353, 122059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Statistical | ML | DL | Hybrid | DAM | IDM | BM | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nogales et al. 2002 [87] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Contreras et al. 2003 [50] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Sansom et al. 2003 [98] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Cuaresma et al. 2004 [51] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Conejo et al. 2005 [52] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Knittel et al. 2005 [56] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Zhou et al. 2006 [171] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Fan et al. 2007 [99] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Garcia et al. 2008 [88] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Diongue et al. 2009 [57] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Lin et al. 2010 [172] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Che et al. 2010 [100] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Jakavsa et al. 2011 [74] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Mei et al. 2014 [108] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Klaeboe et al. 2015 [43] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Poplawski et al. 2015 [42] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Ziel et al. 2016 [47] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Uniejewski et al. 2016 [81] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Girish et al. 2016 [44] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Feijoo et al. 2016 [91] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Gonzalez et al. 2016 [104] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Yang et al. 2017 [5] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Lago et al. 2018 [19] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Rita et al. 2018 [66] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Ugurlu et al. 2018 [18] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Kuo et al. 2018 [138] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Chinnathambi et al. 2018 [133] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Jiang et al. 2018 [173] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Chang et al. 2018 [139] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Zhang et al. 2018 [174] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Kath et al. 2018 [69] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Zhu et al. 2018 [136] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Johannesen et al. 2019 [94] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Zhou et al. 2019 [137] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Xu et al. 2019 [7] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Zahid et al. 2019 [8] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Chang et al. 2019 [175] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Zahid et al. 2019 [8] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Atef et al. 2019 [125] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Luo et al. 2019 [126] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Lago et al. 2019 [6] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Karabiber et al. 2019 [61] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Johannesen et al. 2019 [94] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Schnurch et al. 2019 [128] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Oksuz et al. 2019 [68] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Uniejewski et al. 2019 [25] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Maciejowska et al. 2019 [71] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Ali et al. 2019 [92] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Schnurch et al. 2019 [128] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Reference | Statistical | ML | DL | Hybrid | DAM | IDM | BM | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marcjasz et al. 2020 [67] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Lucas et al. 2020 [116] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Khan et al. 2020 [129] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Narajewski et al. 2020 [78] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Li et al. 2021 [21] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Lago et al. 2021 [4] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Kara et al. 2021 [105] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Ozen et al. 2021 [48] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Wang et al. 2022 [95] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Lehna et al. 2022 [75] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Narajewski et al. 2022 [31] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Tschora et al. 2022 [82] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Xie et al. 2022 [107] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Zhang et al. 2022 [101] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Meng et al. 2022 [135] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Yang et al. 2022 [53] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Kotsias et al. 2022 [72] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Iqbal et al. 2022 [63] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Beltran et al. 2022 [96] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Jkedrzejewski et al. 2022 [14] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Alkawaz et al. 2022 [106] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Rezaei et al. 2022 [140] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Yang et al. 2022 [130] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Serafin et al. 2022 [79] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Heidarpanah et al. 2023 [9] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Bille et al. 2023 [46] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Xiong et al. 2023 [144] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Kapoor et al. 2023 [58] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Marcjasz et al. 2023 [83] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Olivares et al. 2023 [45] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Gunduz et al. 2023 [84] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Stefenon et al. 2023 [150] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Poggi et al. 2023 [54] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Molin et al. 2023 [141] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Yang et al. 2024 [85] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Kilicc et al. 2024 [55] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Ghimire et al. 2024 [176] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Bozlak et al. 2024 [76] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Lisi et al. 2024 [65] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Kitsatoglou et al. 2024 [77] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Peng et al. 2024 [97] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Huang et al. 2024 [110] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Pourdaryaei et al. 2024 [131] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Shi et al. 2024 [145] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Englund et al. 2024 [49] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| O’Connor et al. 2024 [32] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Uniejewski et al. 2024 [73] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Bozlak et al. 2024 [76] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Yang et al. 2024 [85] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Deng et al. 2024 [103] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Jiang et al. 2024 [148] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Guo et al. 2024 [152] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Nyangon et al. 2024 [153] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Sapnken et al. 2024 [154] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Chen et al. 2024 [161] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Laitsos et al. 2024 [162] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Ehsani et al. 2024 [163] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Mubarak et al. 2024 [167] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Khan et al. 2024 [168] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Nie et al. 2024 [169] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Hajigholam et al. 2024 [170] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Nickelsen et al. 2025 [70] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Agakishiev et al. 2025 [80] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| O’Connor et al. 2025 [86] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| O’Connor et al. 2025 [109] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Chen et al. 2025 [158] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Yan et al. 2025 [165] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Cu et al. 2025 [166] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Reference | Statistical | ML | DL | Hybrid | DAM | IDM | BM | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhu et al. 2018 [136] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Ali et al. 2019 [92] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Mujeeb et al. 2019 [127] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Ashfaq et al. 2019 [93] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Cai et al. 2020 [111] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Salinas et al. 2020 [149] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Rafi et al. 2021 [113] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Memarzadeh et al. 2021 [134] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Lopez et al. 2022 [146] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Ishak et al. 2022 [59] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Cantillo et al. 2022 [102] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Arrieta et al. 2022 [90] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Durante et al. 2022 [89] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Qinghe et al. 2022 [112] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Suvarna et al. 2022 [114] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Lopez et al. 2022 [146] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Shohan et al. 2022 [151] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Bashir et al. 2022 [160] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Woo et al. 2022 [60] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Gellert et al. 2022 [62] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Seyed et al. 2023 [115] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Nazir et al. 2023 [147] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Rao et al. 2023 [64] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Gomez et al. 2023 [142] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Parizad et al. 2024 [157] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Zhang et al. 2024 [143] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Williams et al. 2025 [159] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Belenguer et al. 2025 [164] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
O’Connor, C.; Bahloul, M.; Prestwich, S.; Visentin, A. A Review of Electricity Price Forecasting Models in the Day-Ahead, Intra-Day, and Balancing Markets. Energies 2025, 18, 3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123097
O’Connor C, Bahloul M, Prestwich S, Visentin A. A Review of Electricity Price Forecasting Models in the Day-Ahead, Intra-Day, and Balancing Markets. Energies. 2025; 18(12):3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123097
Chicago/Turabian StyleO’Connor, Ciaran, Mohamed Bahloul, Steven Prestwich, and Andrea Visentin. 2025. "A Review of Electricity Price Forecasting Models in the Day-Ahead, Intra-Day, and Balancing Markets" Energies 18, no. 12: 3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123097
APA StyleO’Connor, C., Bahloul, M., Prestwich, S., & Visentin, A. (2025). A Review of Electricity Price Forecasting Models in the Day-Ahead, Intra-Day, and Balancing Markets. Energies, 18(12), 3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123097








