Efficiency Testing of Pelton Turbines with Artificial Defects—Part 2: Needles and Seat Rings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Processing Steps of Needles and Seat Rings
3. Hill Chart Measurements
3.1. Test Rig and Procedure
3.2. Procedures for Measurement and Evaluation
3.3. Results of the Partially Grooved Needle and Seat Ring
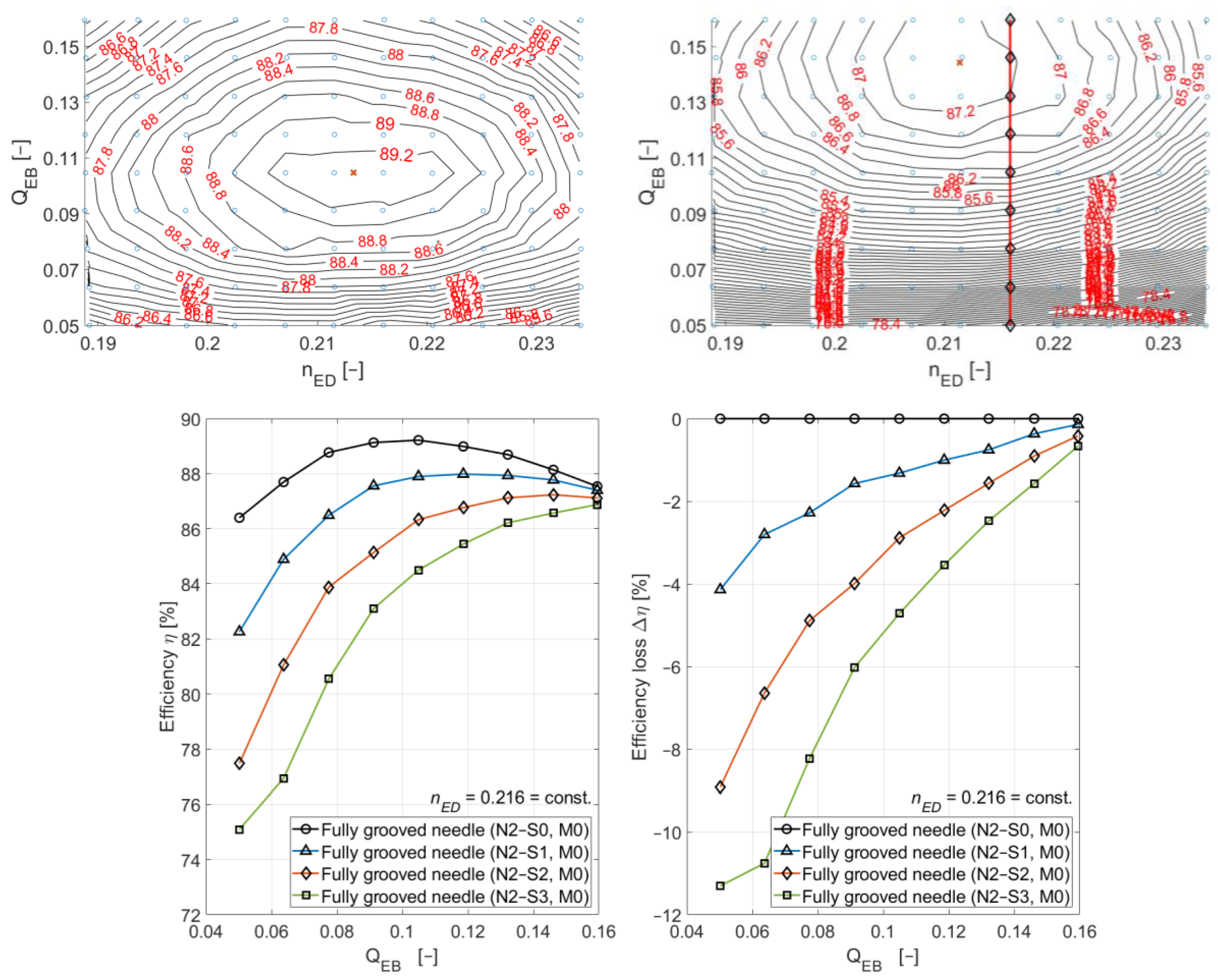
3.4. Results of the Fully Grooved Needle and Seat Ring
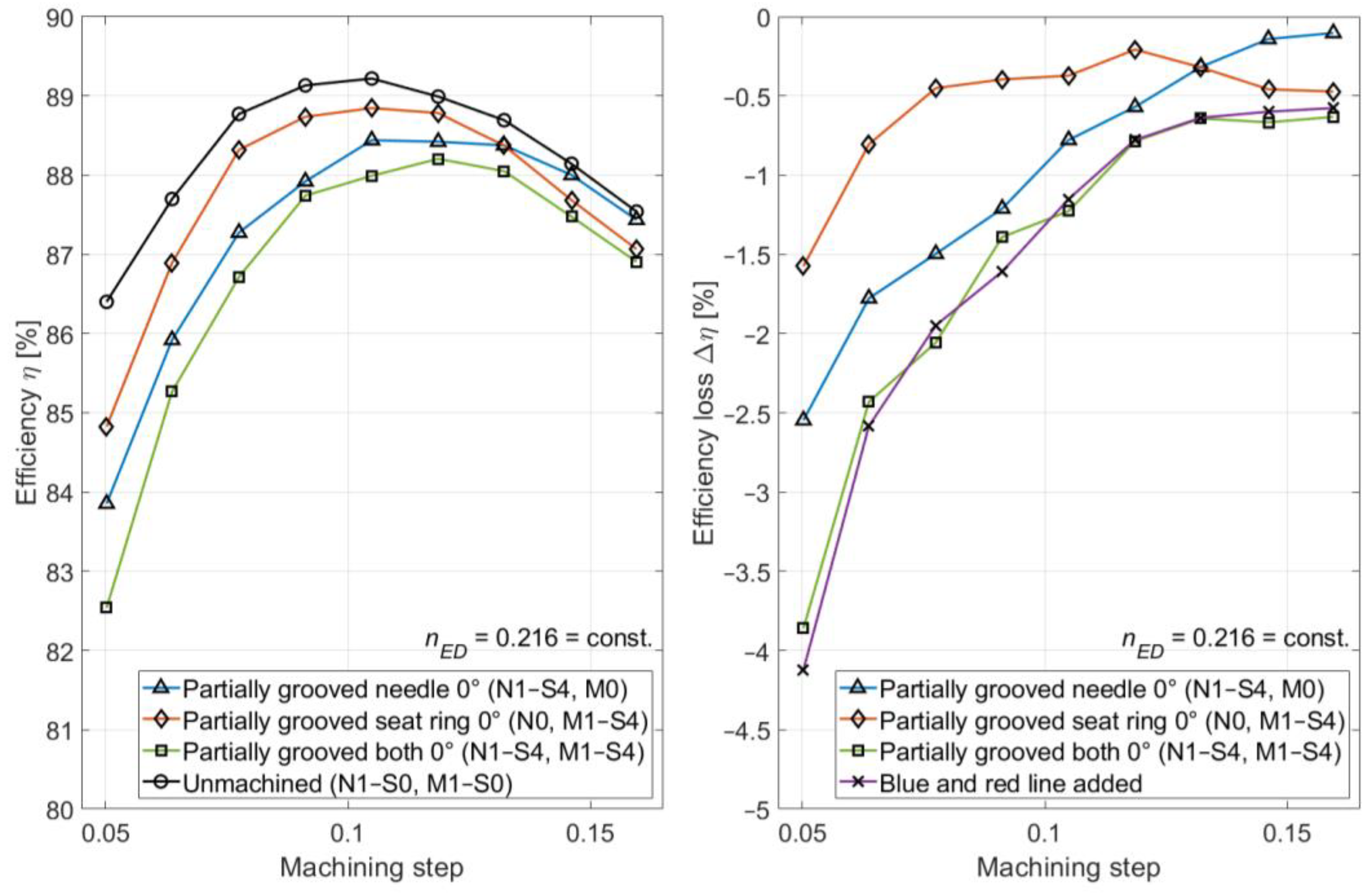
3.5. Combination of the Partially Machined Needle and Seat Ring
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ge, X.; Sun, J.; Chu, D.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Binama, M.; Zheng, Y. Sediment erosion on Pelton turbines: A review. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2023, 36, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, N.; Rai, A.K. Hydro-abrasive erosion in Pelton turbines: Comprehensive review and future outlook. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 207, 114957, ISSN 1364-0321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 62364:2019; Hydraulic Machines—Guidelines for Dealing with Hydro-Abrasive Erosion in Kaplan, Francis, and Pelton Turbines. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Guo, B.; Rai, A.K.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Q. Sediment-laden flow and erosion modeling in a Pelton turbine injector. Renew. Energy 2020, 163, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarodiya, R.; Khullar, S.; Levya, A. Particulate flow and erosion modeling of a Pelton turbine injector using CFD-DEM simulations. Powder Technol. 2022, 399, 117168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, N.; Rai, A.K. Parametric Investigation of Pelton Turbine Injector under Hydro-abrasive Erosion Conditions. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2024, 17, 89–104. [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava, N.; Rai, A.K.; Abbas, A.; Xiao, X. Analysis of hydro-abrasive erosion in a high-head Pelton turbine injector using a Eulerian-Lagrangian approach. Proc. IMechE Part A J. Power Energy 2024, 238, 495–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villacorta Benitez, R. Theoretische und experimentelle Untersuchungen an Einlaufdüsen von Freistrahlturbinen. Ph.D. Thesis, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule), Zurich, Switzerland, 1972. No. 4678. [Google Scholar]
- Brekke, H.; Wu, Y.L.; Cai, B.Y. Design of Hydraulic Machinery Working in Sand Laden Water. In Abrasive Erosion & Corrosion of Hydraulic Machinery; Duan, C.G., Karelin, V.Y., Eds.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2002; pp. 155–233. [Google Scholar]
- Thapa, B. Sand Erosion in Hydraulic Machinery. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Engineering & Technology, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bajracharya, T.R.; Acharya, B.; Joshi, C.B.; Saini, R.P.; Dahlhaug, O.G. Sand erosion of Pelton turbine nozzles and buckets: A case study of Chilime Hydropower Plant. Wear 2008, 264, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cateni, A.; Magri, L.; Grego, G. Optimization of Hydro Power Plants Performance—Importance of rehabilitation and maintenance in particular for the runner profiles. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Hydraulic Efficiency Measurements (IGHEM), Milan, Italy, 3–6 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, A.M.; Pachon, I.F.; Loboguerrero, J.; Medina, J.A.; Escobar, J.A. Development of a test rig to evaluate abrasive wear on Pelton turbine nozzles. A case study of Chivor Hydropower. Wear 2017, 372–373, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, M.Z.U.; Harmain, G.A. Assessment of erosive wear of Pelton turbine injector: Nozzle and spear combination–A study of Chenani hydro-power plant. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 116, 104695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messa, G.V.; Mandelli, S.; Malavasi, S. Hydro-abrasive erosion in Pelton turbine injectors: A numerical study. Renew. Energy 2019, 130, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyal, S.; Abregu, J.; Singh, B.; Nascimben, F.; Chitrakar, S.; Neopane, H.P.; Dahlhaug, O.G. Numerical Investigation of Effects of Ripple Type Needle Erosion on Pressure Inside a Pelton Nozzle. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1385, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, B.S.; Khatiwada1, A.; Vaidhya1, N.; Satyal, S.; Chitrakar, S. Numerical investigation of flow around the injector of a Pelton turbine due to eroded needle. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1385, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staubli, T.; Abgottspon, A.; Weibel, P.; Bissel, C.; Leduc, J.; Leboeuf, F. Jet quality and Pelton efficiency. In Proceedings of the Hydropower & Dams International, Hydro 2009, Lyon, France, 26–28 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fahrni, F.; Staubli, T.; Casartelli, E. Efficiency Testing of Pelton Turbines with Artificial Defects—Part 1: Buckets. Energies 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Abgottspon, A.; Staubli, T.; Bieri, E.; Felix, D. Economic optimization of maintenance measures based on continuous efficiency monitoring. In Proceedings of the 21st International Seminar on Hydropower Plants (Viennahydro 2022), Vienna, Austria, 9–11 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Staubli, T. Financial analysis for optimization of hydropower plants regarding hydro-abrasive erosion: A study from Indian Himalaya. In Proceedings of the 29th Symposium of Hydraulic Machinery and Systems, Kyoto, Japan, 16–21 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 4006; Measurement of Liquid Flow in Closed Conduits. Weighing Method. International Standardization Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1980.
- IEC 63461:2024; Pelton Hydraulic Turbines—Model Acceptance Tests. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024.
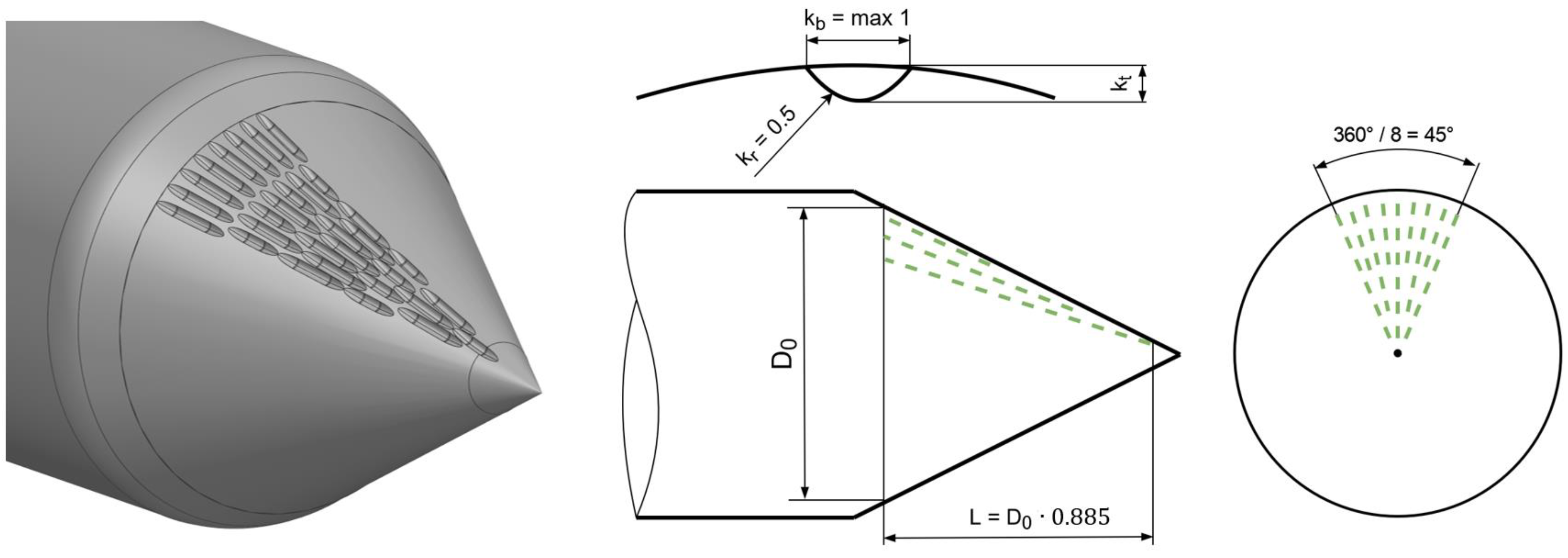
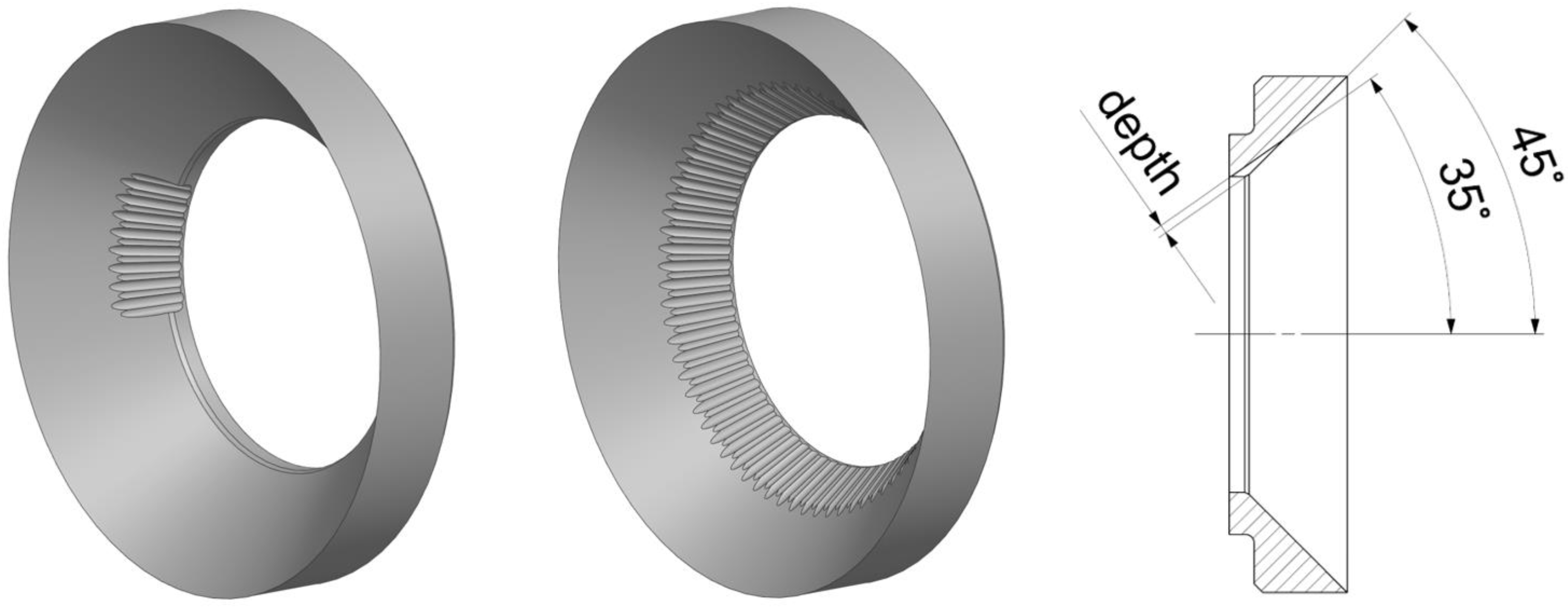

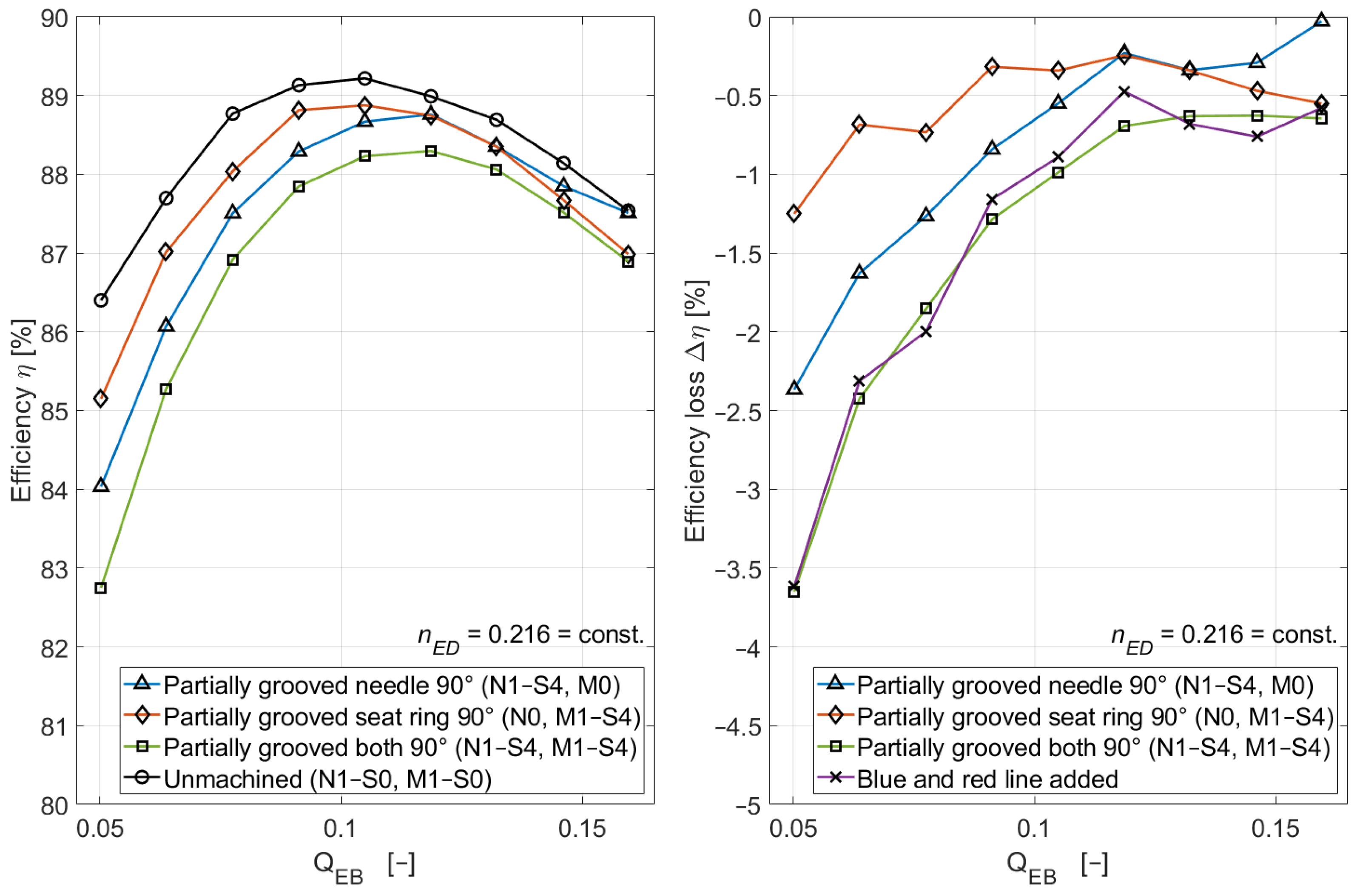

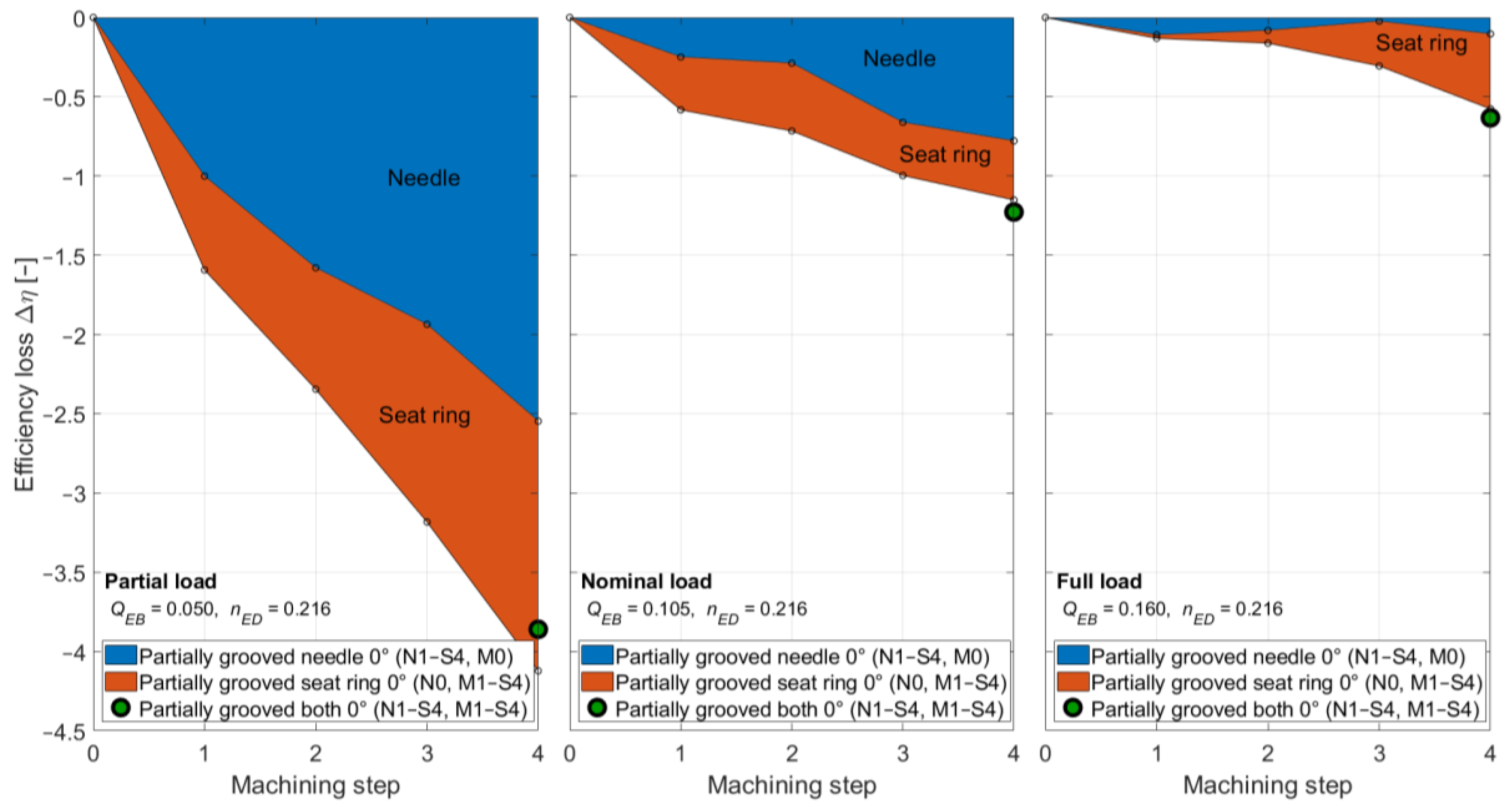
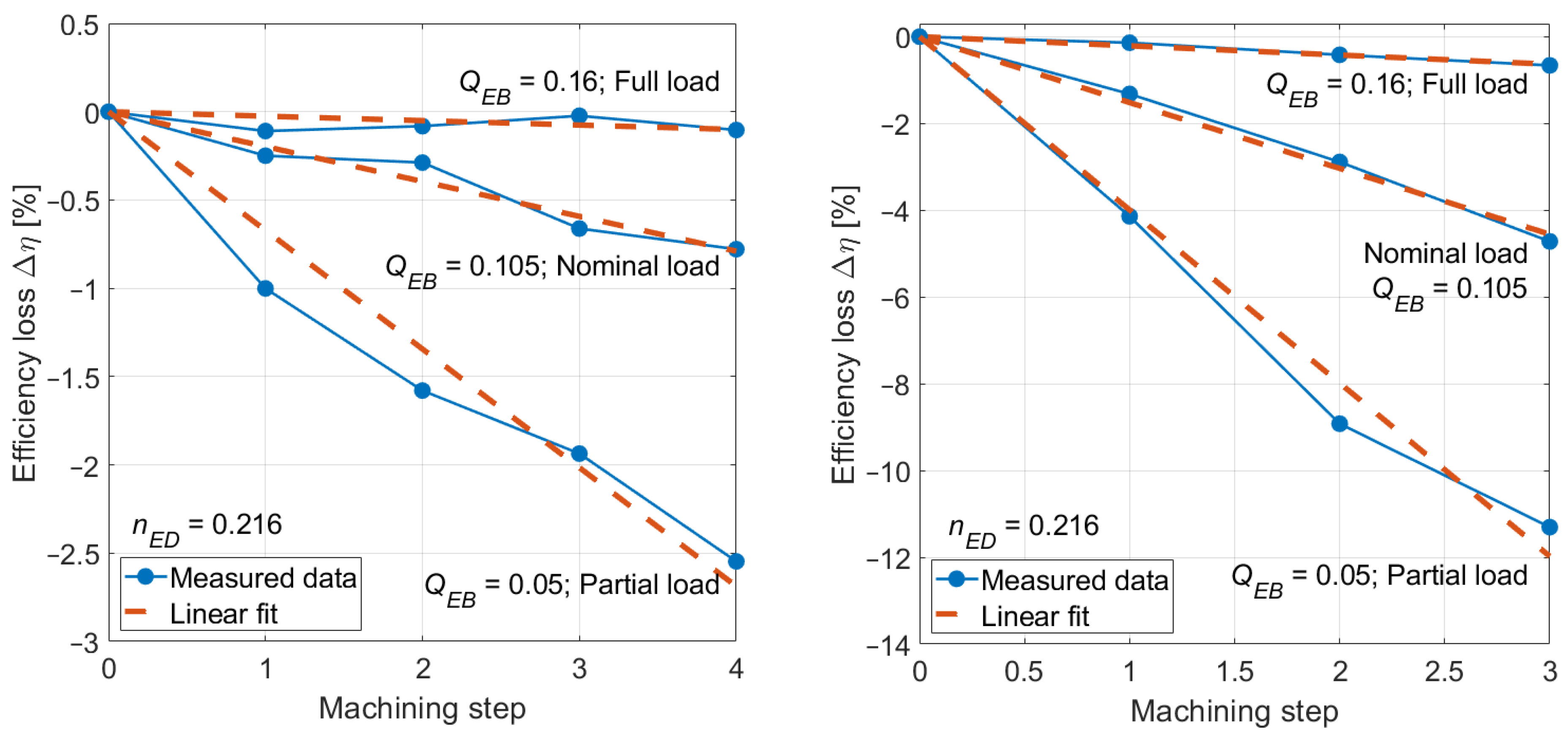
| Needle (N) Machining Step (S) | Seat Ring (M) Machining Step (S) | Comments | Number of Measured Hill Charts |
|---|---|---|---|
| N 1, S 0–4 | M 0 | Partial grooves at 0° | 5 |
| N 1, S 0–4 | M 0 | Partial grooves at 90° | 5 |
| N 0 | M 1, S 0–4 | Partial grooves at 0° | 5 |
| N 0 | M 1, S 0–4 | Partial grooves at 90° | 5 |
| N 1, S 4 | M 1, S 4 | Partial grooves at 0° (both) | 1 |
| N 1, S 4 | M 1, S 4 | Partial grooves at 90° (both) | 1 |
| N 2, S 0–3 | M 0 | Fully grooved needle | 4 |
| N 0 | M 2, S 0–4 | Fully grooved seat ring | 5 |
| N 2, S 3 | M 2, S 4 | Fully grooved both | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fahrni, F.; Staubli, T.; Casartelli, E. Efficiency Testing of Pelton Turbines with Artificial Defects—Part 2: Needles and Seat Rings. Energies 2025, 18, 2725. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18112725
Fahrni F, Staubli T, Casartelli E. Efficiency Testing of Pelton Turbines with Artificial Defects—Part 2: Needles and Seat Rings. Energies. 2025; 18(11):2725. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18112725
Chicago/Turabian StyleFahrni, Florian, Thomas Staubli, and Ernesto Casartelli. 2025. "Efficiency Testing of Pelton Turbines with Artificial Defects—Part 2: Needles and Seat Rings" Energies 18, no. 11: 2725. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18112725
APA StyleFahrni, F., Staubli, T., & Casartelli, E. (2025). Efficiency Testing of Pelton Turbines with Artificial Defects—Part 2: Needles and Seat Rings. Energies, 18(11), 2725. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18112725







