1. Introduction
Liquid metal cooled reactors can be considered the future of nuclear plants due to of their potential for breeding efficiency and, consequently, economic advantages. This type of reactor can achieve high coolant temperatures. Metal coolants remove heat from the reactor core more rapidly, allowing for much higher power density. In other words, using this type of reactor offers several advantages, including economic viability, high power density, and high coolant temperature.
The first experimental fast reactor was built in 1946 at Los Alamos. It was operated until 1953. The reactor was fueled with 2.5 L of metallic plutonium, and the reactor core was cooled by mercury [
1]. In 1951, first experimental fast breeder reactor, EBR-I, which generated practical amount of useful power of 200 kWe, was constructed at the National Reactor Testing Station in Idaho [
1]. Eutectic sodium-potassium served as the coolant of the reactor. Unfortunately, there are only about 20 experimental and commercial fast neutron reactors in operation worldwide [
2,
3]. One reason for this limited number is that fast reactors are typically cooled by liquid metal and have positive α
V coefficient value, it is difficult to reduce this coefficient.
A negative value of αV is a fundamental property of passive safety of all types of nuclear reactors. The second important property is the passive removal of shutdown heat after a loss of coolant accident.
In recent years there has been stagnation in the development of liquid metal cooled fast reactors. However, interest in fast reactors has been renewed due to necessity of limiting CO2 emission and addressing global warming.
Fast reactors have nuclear characteristics that enable the efficient use of uranium fuel and the ability to burn the long-lived actinides found in nuclear waste [
2]. The authors of [
2] presented the results of their calculations of reactivity feedback for a Sodium Fast Reactor (SFR) with a U-cycle. Their study provided a detailed description of neutron physics and included calculation results obtained using the perturbation method for voided condition in the SFR. Unfortunately, the study did not provide an estimated value for α
V.
To mitigate the overall reactivity increase during an accident, different concepts are used, including axial fuel expansion and radial core expansion. Core shape expansion is a passive method that utilizes thermal expansion and bowing of the ducts [
4,
5]. Additionally, there are other methods, such as control rod driveline expansion or a special coolant cavity over core to reduce the α
V, as well as passive shutdown systems with hydraulically suspended rods [
4,
5].
The European Lead Cooling System (ELSY) is a research project aimed developing nuclear reactors cooled using lead [
6,
7]. Lead Fast Reactors (LFRs) (1530 MWth) have a core composed of MOX fuel and a lead reflector [
6]. The heterogeneous reactor core consists of a square fuel lattice. The core has three fuel zones, i.e., inner, intermediate and outer, with enrichment of 13.4 vol. %, 15 vol. %, 18.5 vol. %, respectively. The authors of [
6] presented interesting results of the void reactivity effect, which was significantly positive in the inner zone and near zero in the outer zone.
The estimation of the value of α
V was studied in a water-cooled reactor with a flexible fuel cycle, which is a type of Boiling Water Reactor (BWR) [
8]. In that work, exact perturbation calculations were applied, which quantitatively estimated α
V as a function of fuel rod diameter.
The effect on α
V of distribution of voids inside a reactor was studied in the Na-cooled FBR-IME reactor, based on the Japanese JOYO experimental reactor. The central part of the reactor consists of 95 heterogeneous fuel assemblies, while peripheral part (outer/fertile) consists 295 assemblies of U-238 [
9,
10]. The peripheral part is used for the conversion of U-238 to Pu-239. Unfortunately, it also plays a role as a reflector, which increases α
V. This work provides the exact result of α
V for several distributions of no-sodium assemblies in central part of reactor.
The void reactivity was studied as the effect of an unprotected loss of flow event (ULOF) in a MOX-fueled core based on the MONJU prototype reactor [
11,
12]. This reactor also utilized an inner core and an outer/fertile region.
The saturation concentration of U-233 in Th-cycle achieved 0.11 in fast reactor, while in in thermal reactor, it was only 0.0137 [
13,
14]. Breeding and criticality in Th-cycle occured simultaneously in the fast reactor only [
15]. In other words, to achieve the most effective and safe thorium reactor, a fast reactor with a negative value of α
V should be constructed [
13,
14,
15,
16].
Two large FSRs (3600 MWth), i.e., MOX-3600 and CAR-3600, and two medium FSRs (1000 MWth), i.e., MET-1000 and MOX-1000, with different fuel types were compared in [
17]. This excellent work presented various technical parameters of these reactors including numerical values for α
v for 100% void. All values of α
v were positive.
Reactors with a low value of αv, referred to as “the low void worth core” (CFV) possess relatively complex core geometries [
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24]. The cores are designed with radially or axially heterogeneous geometries, incorporating sodium plenums, fuel zones, fertile zones, and absorbing zones. There are several reactors based on low void worth cores including the Russian BN-800 reactor [
18,
23], the Japanese concepts of Takeda [
21,
22,
23] and Saito [
20,
23] and the French concepts CFV of Sciora [
23] and ASTRID CFV of Beck [
24]. For the CFV concept, the value of α
v is positive when a decrease in coolant density occurs in central part of the core (fissile and fertile zone) and negative when it occurs in the upper sodium plenum zone. This concept does not eliminate the risk of sodium boiling.
A characteristic feature of CFV cores is the leakage of neutrons primarily through the upper sodium plenum, during the voided conditions. This concept restricts the neutron leakage to the top of core base, which, in turn limits, the height of the active core.
This paper presents a concept for a hybrid reactor in which neutron leakage primarily occurs through the radial side area of the core. This approach allows for a higher value of neutron leakage rate that is proportional to the height of the core. The hybrid concept consists of two kinds of fuel assemblies; assemblies with high enrichment fuel placed in the peripheral region, and with low enrichment fuel located in central part of core. The study focuses on the influence of the average fuel density and coolant volume fraction in the fuel cell on the decrease the value of αv.
Additionally, the calculation results from hybrid model and FBR-IME reactor are compared (
Section 8, [
9,
10]).
2. Materials and Methods
Current Fast Reactors have a low height of the active core (about 1 m) and large reflectors. This geometry makes it difficult to increase neutron leakage through the radial side of the core when it is in a voided state. The amount of radial leakage is proportional to the area of the radial side of the core, which is proportional to the height of the core. For this reason, a modified geometry of the European Pressurized Reactor (EPR) [
25,
26] was used for our computer simulation. This modified geometry was selected as it provides a sufficiently wide and high reactor core without a reflector, which is necessary for a comprehensive study of the α
V in a general context.
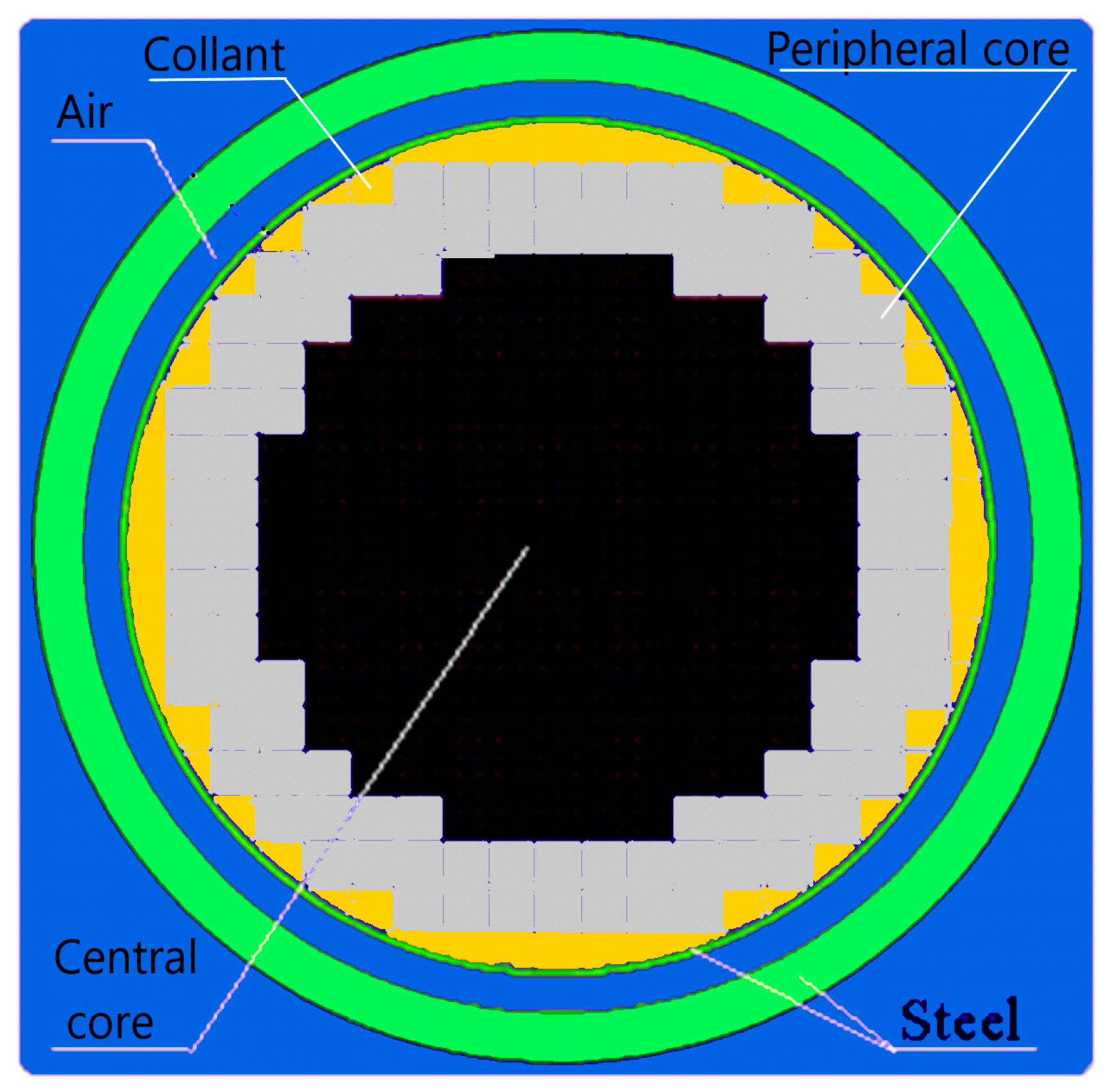
The modified model incorporates various type of coolants i.e., liquid sodium (Na) or lead (Pb). Additionally, it accounts for changeable volumes of fuel and coolant (
Figure 1,
Figure 2,
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5 and
Table 1,
Table 2 and
Table 3), as well as different numbers of fuel assemblies [
15,
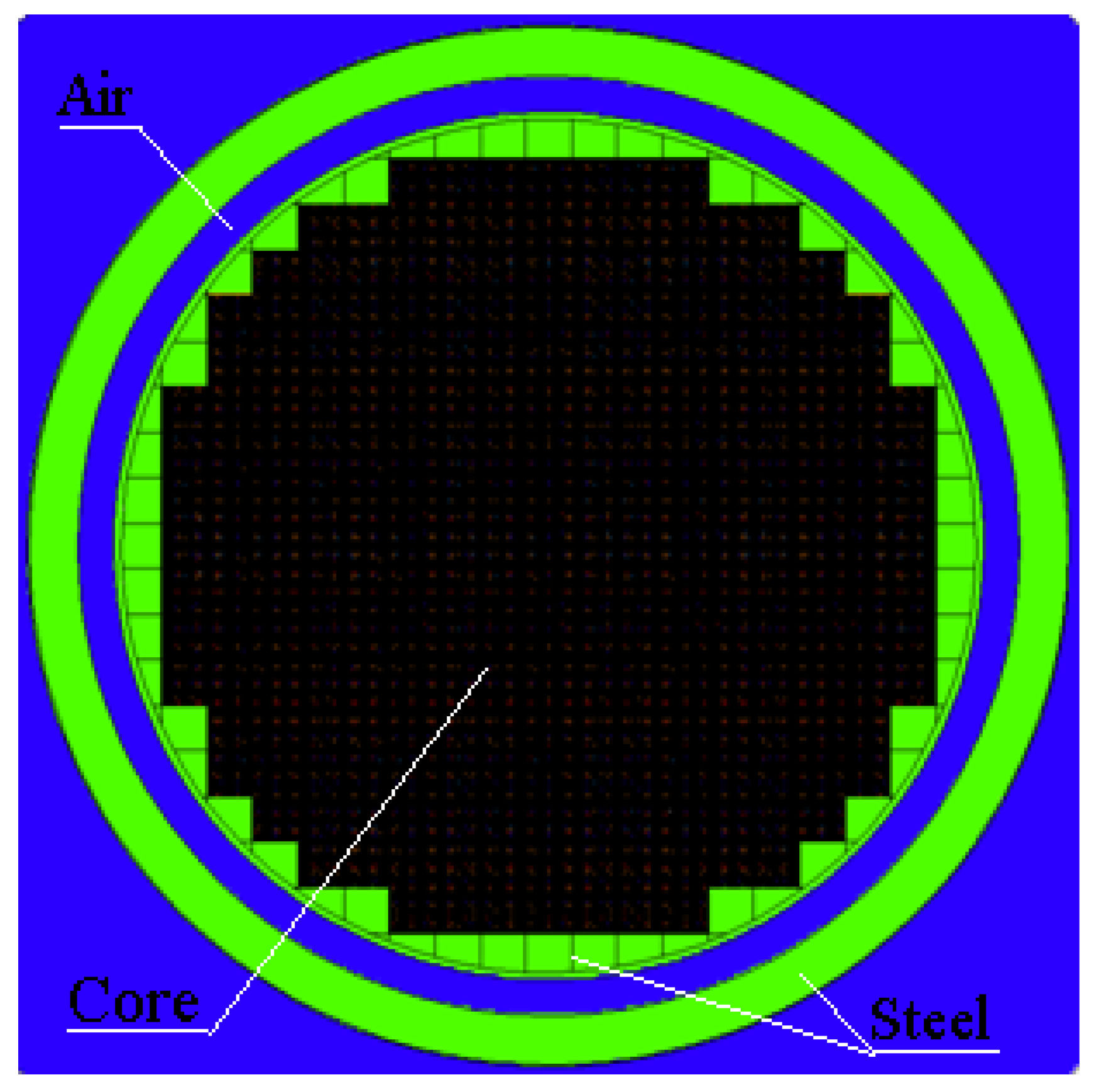
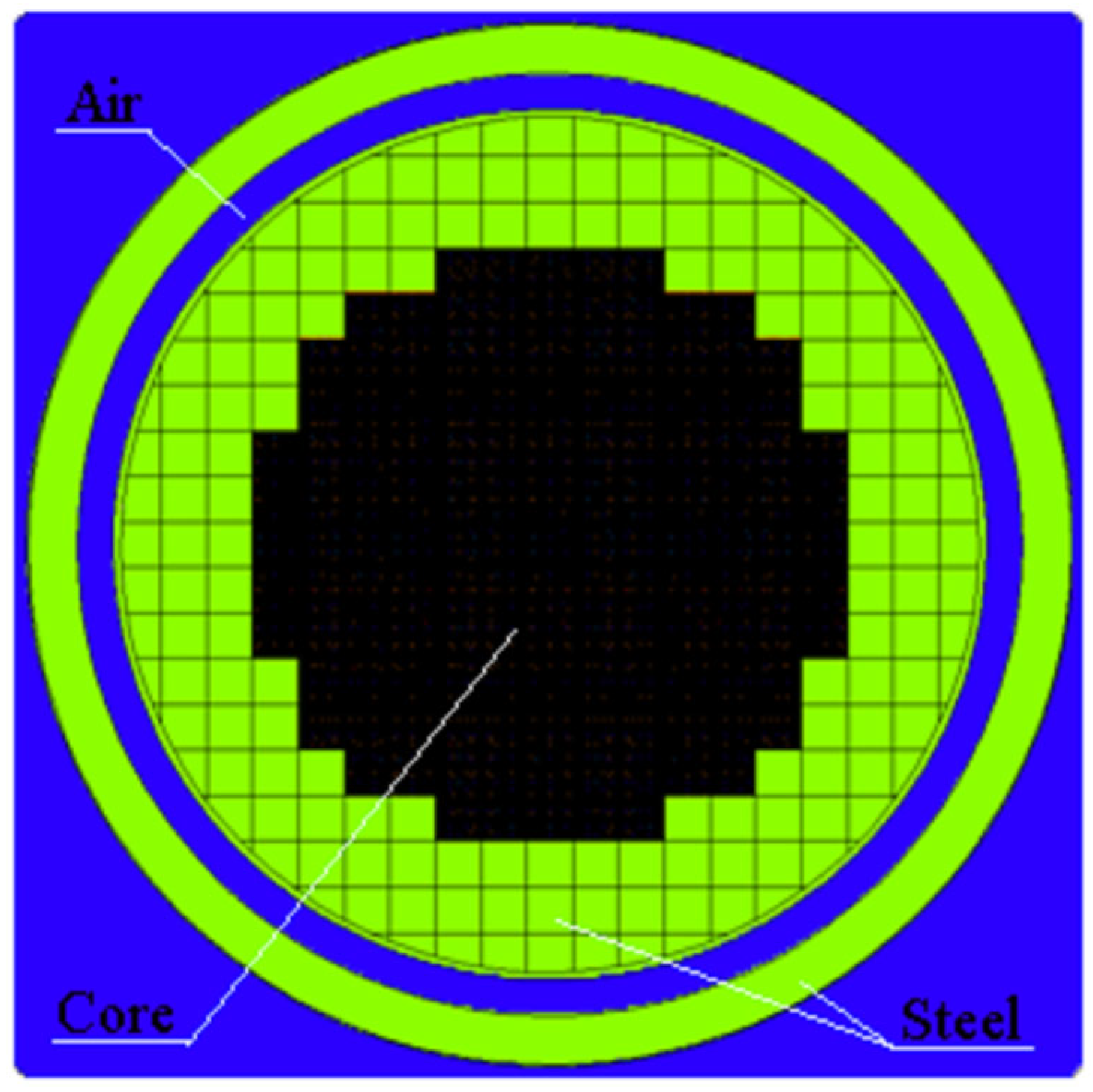
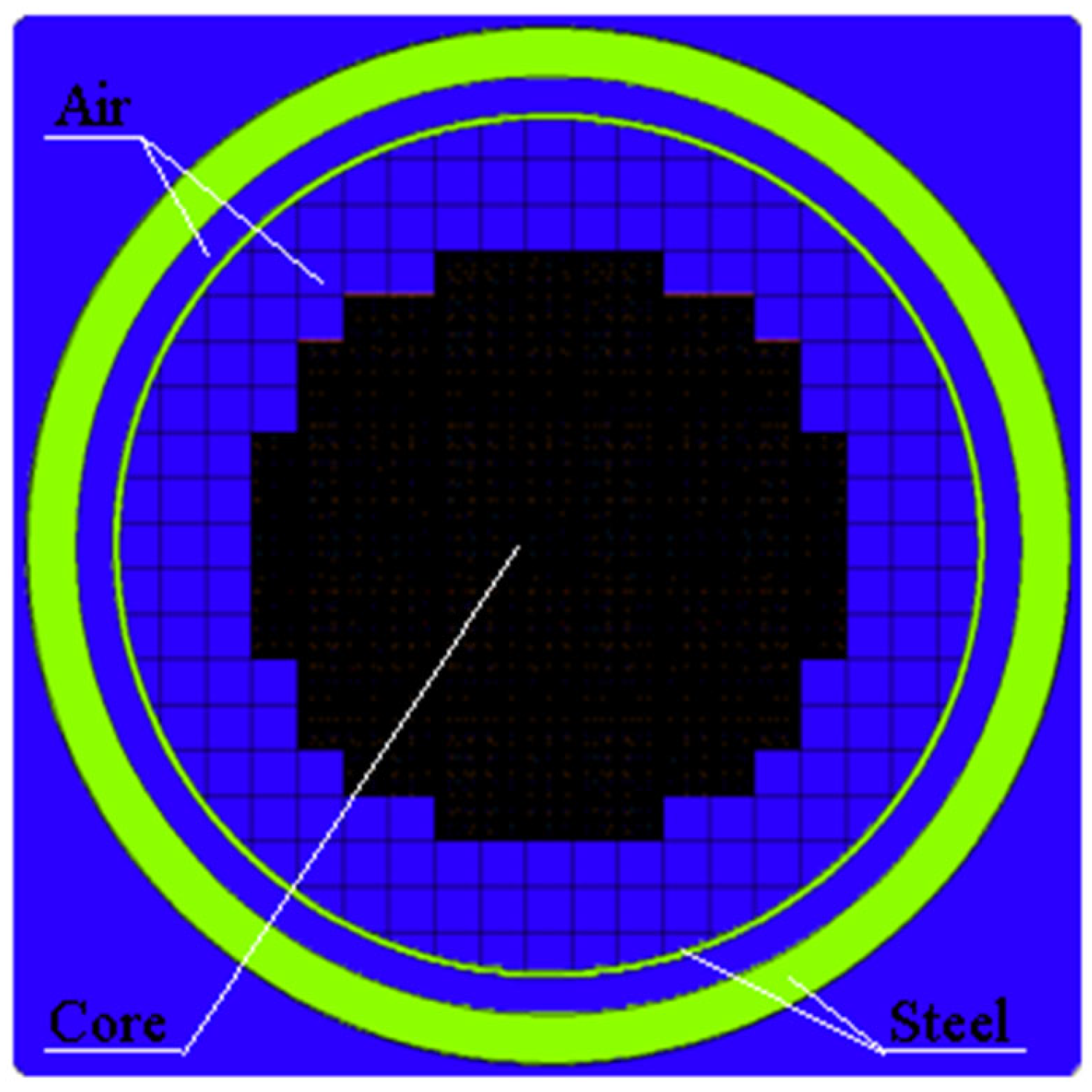
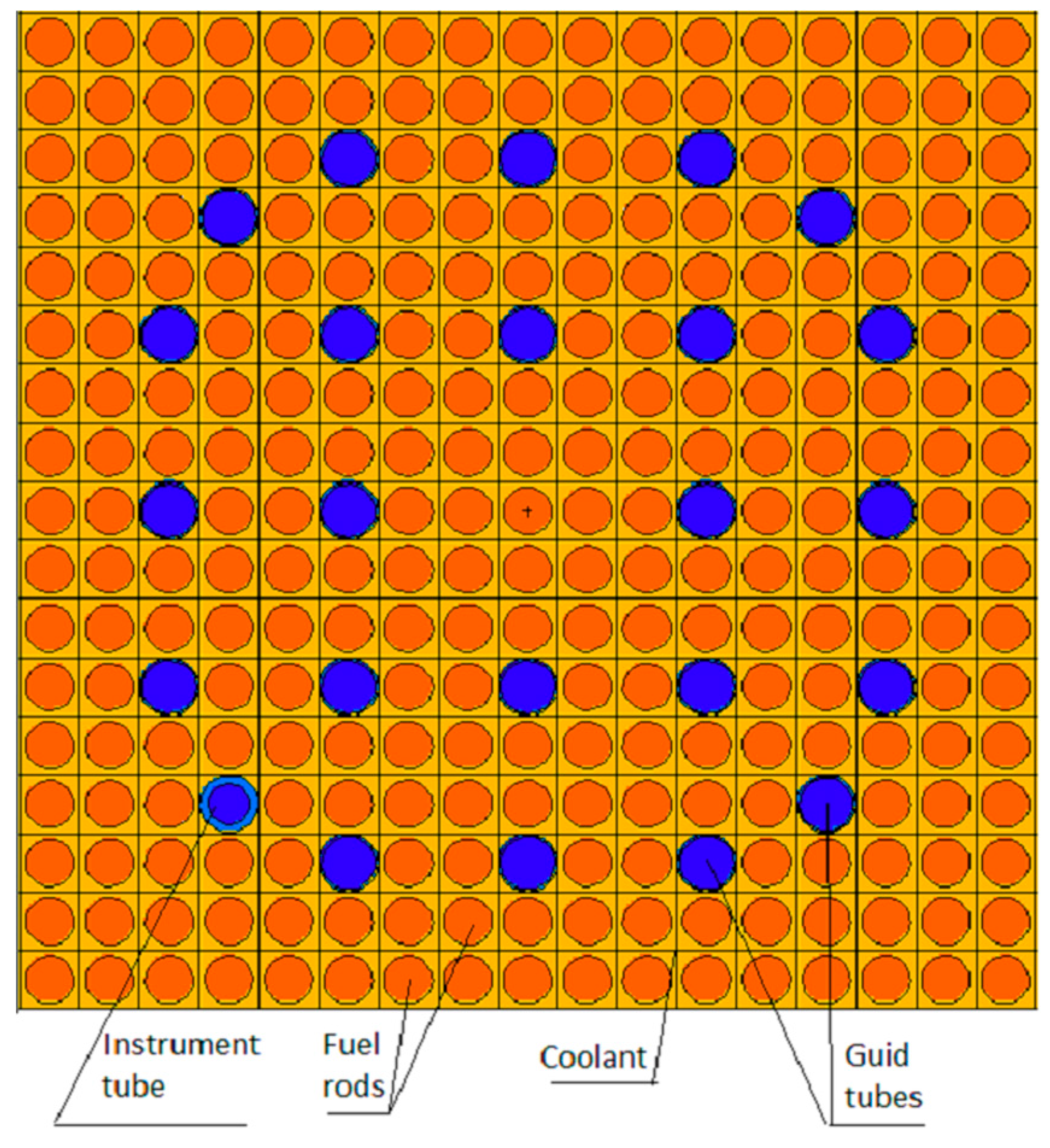
16]. The reactor core model consists of 241, 137 or 101 assemblies (
Figure 1,
Figure 2,
Figure 3 and
Figure 4). We use the A1 assembly in the reactor model, which employs a single type of fuel rod (
Figure 6, [
25]). The fuel is a mixture of U-238 and Pu-239 or Th-232 and U-233 to study the U-cycle and Th-cycle, respectively. Furthermore, three different values of fuel density are applied.
The reactor model has a changeable fraction of coolant in the volume of the fuel cell (
VCR)
The width values of the VCR parameters are in the range of <0.239, 0.976>.
Other parameter often used in the literature are the volume ratio of coolant and fuel (
VCFR)
It is assumed that, the thickness of cladding of the fuel rods is equal to zero. For this reason, VCFR = VCR/(1 − VCR). This assumption is made to reduce the number of computations. It is a simplified model, intended solely for computational purposes, rather than for experimental research.
The wide range of values of the
VCR or
VCFR (
Table 1) parameters allowed us to study a broad range of neutron flux spectrum (
Section 4). However, in the hybrid reactor, we used only practical values of these parameters. This reactor model can achieve neutron flux characteristics typical of a fast reactor. For example, the average neutron energy (ANE) in fuel rods reaches 0.5 MeV, while the average neutron energy causing fission (ANFE) for the hybrid reactor based on a Na-cooled U-cycle is approximately 0.9 MeV in normal operating conditions and 1.1 MeV for voided core state (
Section 6).
The change of the
VCR or
VCFR parameter of the reactor model can be achieved by using assemblies with appropriate cell configurations, which entail the suitable fuel and coolant volumes (
Figure 5,
Table 1).
To reduce the density of fuel, one can utilize porous materials or fill part of the fuel volume with air, for example. The simplest method for decreasing the average fuel density of fuel rods is to fill the central part of the rods with air. The calculation results in this work utilize a homogeneous fuel density distribution within the fuel rods. However, the homogeneous distribution is compared with a method featuring an empty central part of the fuel rod. The differences between these methods are found to be less than the standard deviation of αv.
The initial value of the effective multiplication factor (k
eff) is in the range of 1.05 ± 0.02 for all cases. The uncertainty of α
V is discussed in
Section 7. In other words, the initial enrichment of fuel is determined for each case before the reactor is voided for all values of the
VCR parameter, fuel type and geometry. Herein, the reactor core may contain fuel assemblies of a single type (
Figure 1,
Figure 2 and
Figure 3) or a two types (hybrid reactor, see
Figure 4). The base parameters of the reactor cores are presented in
Table 3. The core configuration presented in
Figure 3 consists of 137 assemblies, referred to as the ‘small core’, or 101 assemblies, referred as the ‘very small core’.
The calculation results are obtained using Monte Carlo method, specifically employing the MCNP6.2 code [
27]. The MCNP 6.2 code was developed by Los Alamos National Laboratory (USA) and is designed to track various particle types over a wide range of energies. For the calculations, only tabulated corresponding neutron cross sections from ENDF/B-VII.1 nuclear data library are used.
3. Definitions
There are different definitions for the void reactivity coefficient [
8]. For example, the void reactivity coefficient for BWR is defined as the α
V at which the coolant flow rate reaches 90% of the nominal value [
8]. In other case, the coolant has fully flowed out, and the reactor vessel is filled with saturated steam. The latter case is named as “the 100% void reactivity coefficient”. The following definition of α
V is presented in [
8].
where,
αV: void reactivity coefficient
k1, k0: effective multiplication factor at void fraction of V1 and V0, respectively:
V1, V0: void fraction under varied and nominal conditions [%], respectively:
The definition in Equation (3) suggests that αV is a linear function of the void fraction.
However, this is not accurate, as
αV is not generally a linear function (see
Section 4 and
Section 5).
For this reason, we employed the following definition of
αV:
where,
void [%] is an average value of the void fraction in the fuel cells,
knorm, kvoid are effective multiplication factors in a normally working and voided reactor core, respectively.
The following definition often is used in the literature:
where,
, indicate the reactivity of the reactor under normal operating condition and in a voided reactor core, respectively.
The definitions of
αV and
are compared in
Section 7.
The definitions provided by Equations (4) and (5) are more general than that of Equation (3), because they do not assume a linear void dependence of on the void fraction. In other words, all values of are calculated directly for each specific value of void parameter value.
means 0% of coolant density, i.e., the volume of coolant is filled by air at atmospheric pressure. This case simulates a Loss of Coolant Accident (LOCA).
means that the n% of part of the coolant is evaporated and the average density of the coolant is equal to (100 − n)% of its normal value. The normal value of the coolant density is equal to the density of liquid metal.
Magnitude
depends on a various parameters, such as the
VCR or the type of fuel, and the size and shape of the reactor core (See
Section 4). If we are interested in
as a function of the
VCR parameter and a constant void value, we can write it in the following form:
Meanwhile, if we are interested in
as a function of the void parameter and with a constant value of the
VCR parameter we can express it in the following form:
Both function
and
are not linear functions of the void and
VCR parameters (See
Section 4 and
Section 5).
4. Calculation Results for the Reactor Core Filled with Single-Type of Assemblies
This section presents
for the geometry of reactor cores depicted in the
Figure 1,
Figure 2 and
Figure 3, considering different parameter values as
VCR, type of fuel, type of coolant, geometry and fuel assembly (
Table 3). In this section we assume that the reactors consist of a single type of fuel assembly. The initial values of fuel enrichments are the same for both normal operation and during the reactor void condition.
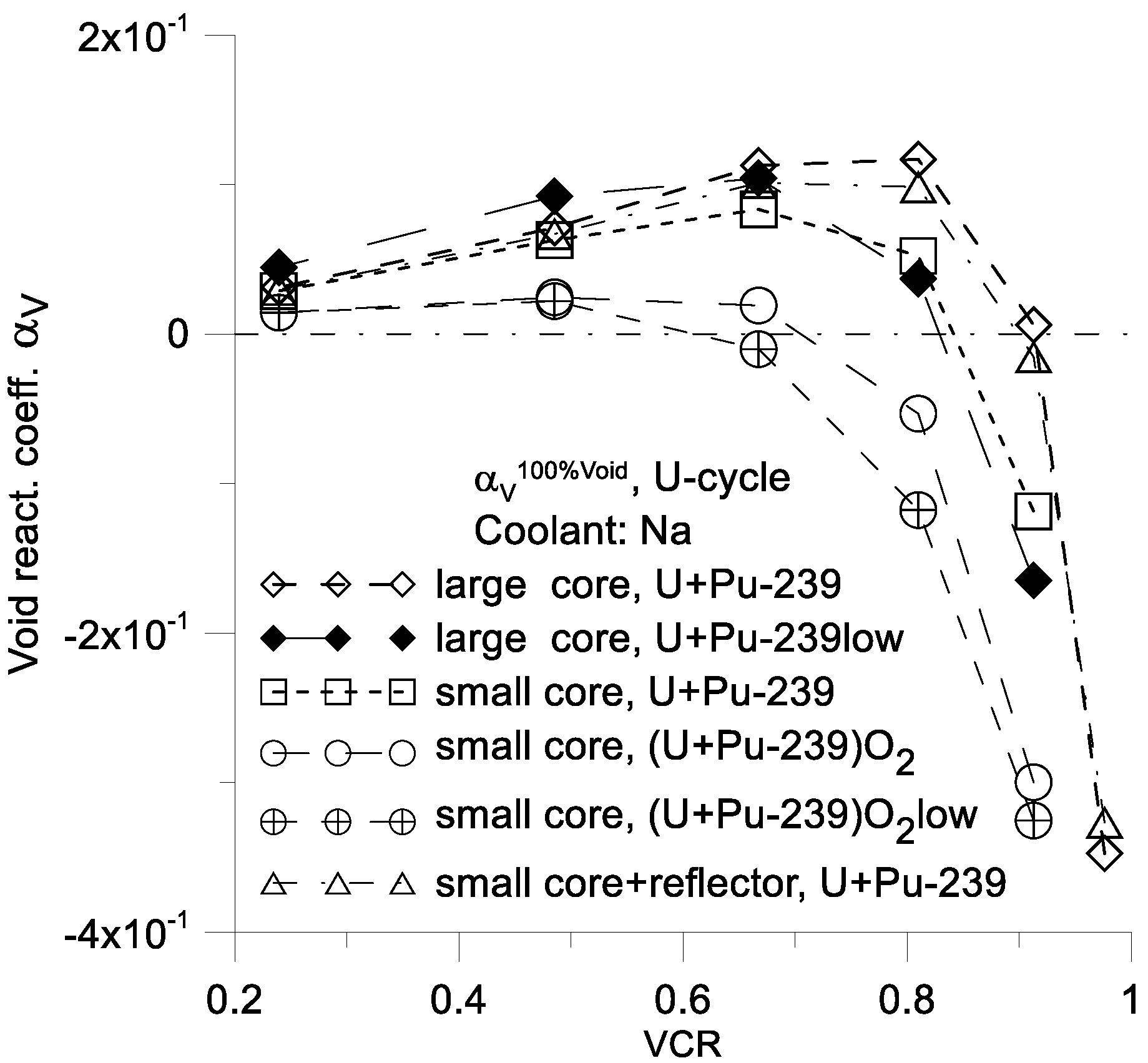
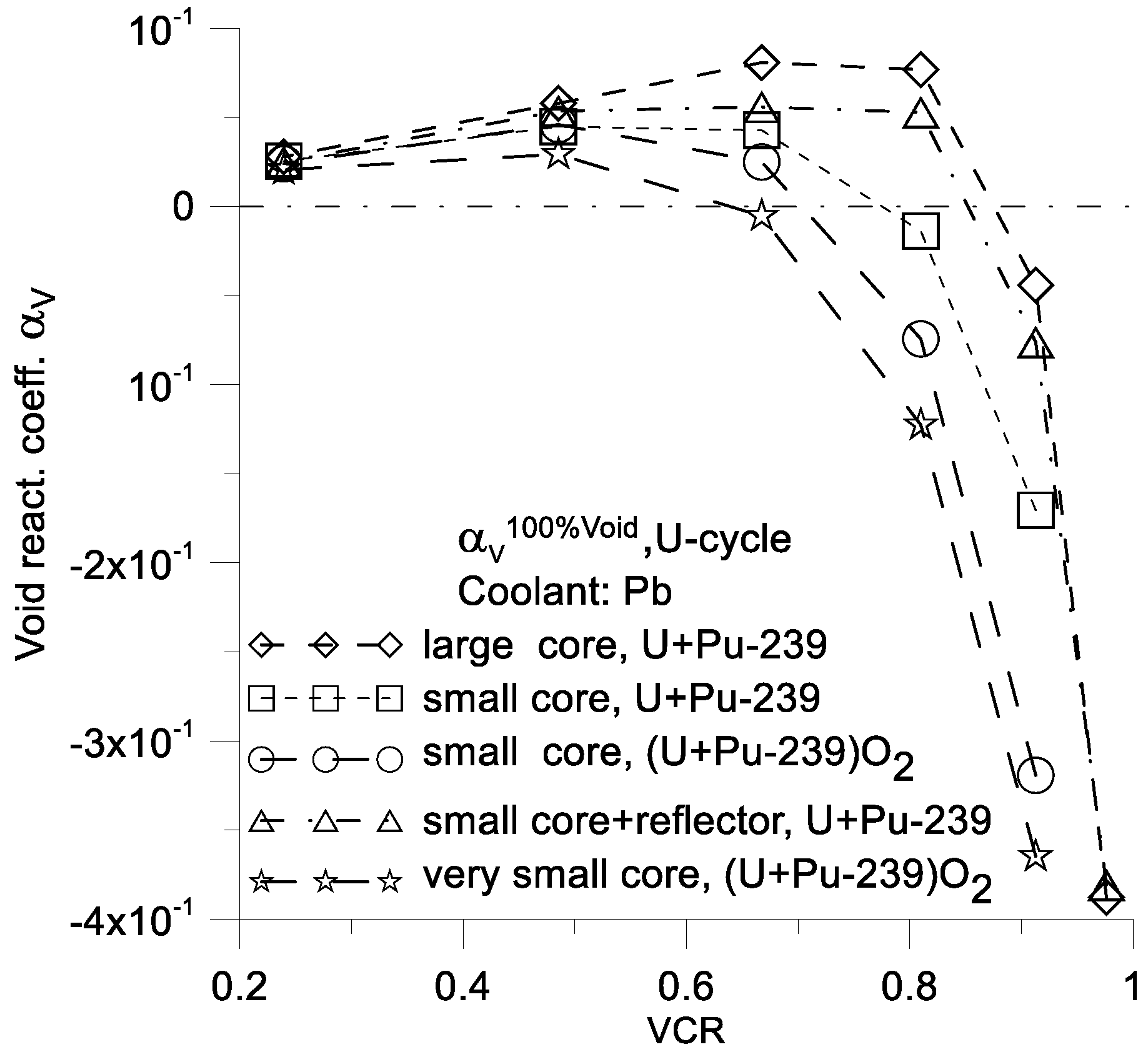
The
Figure 7,
Figure 8,
Figure 9 and
Figure 10 present values of
for different types of cores (
Figure 1,
Figure 2 and
Figure 3) and various combinations of fuel and coolant (from
Table 3). These values can be both positive and negative. The values of
(
VCR) are important because they indicate the maximal positive value of
and minimal negative value for the maximal value of the void parameter.
The value of , for which () = 0, is very important. In other words, the parameter is the zero (root) of a function (VCR). This is significant because for VCR < , it is not possible to obtain a negative value of . For these values of the VCR, the reactor does not passively decrease the number of neutrons during a LOCA accident. In contrast, for reactors with a VCR greater than , the value of becomes negative, indicating that the reactor should be turned off during such an accident. Please note that is a characteristic parameter of a class (set) of reactors that differ only in the VCR parameter.
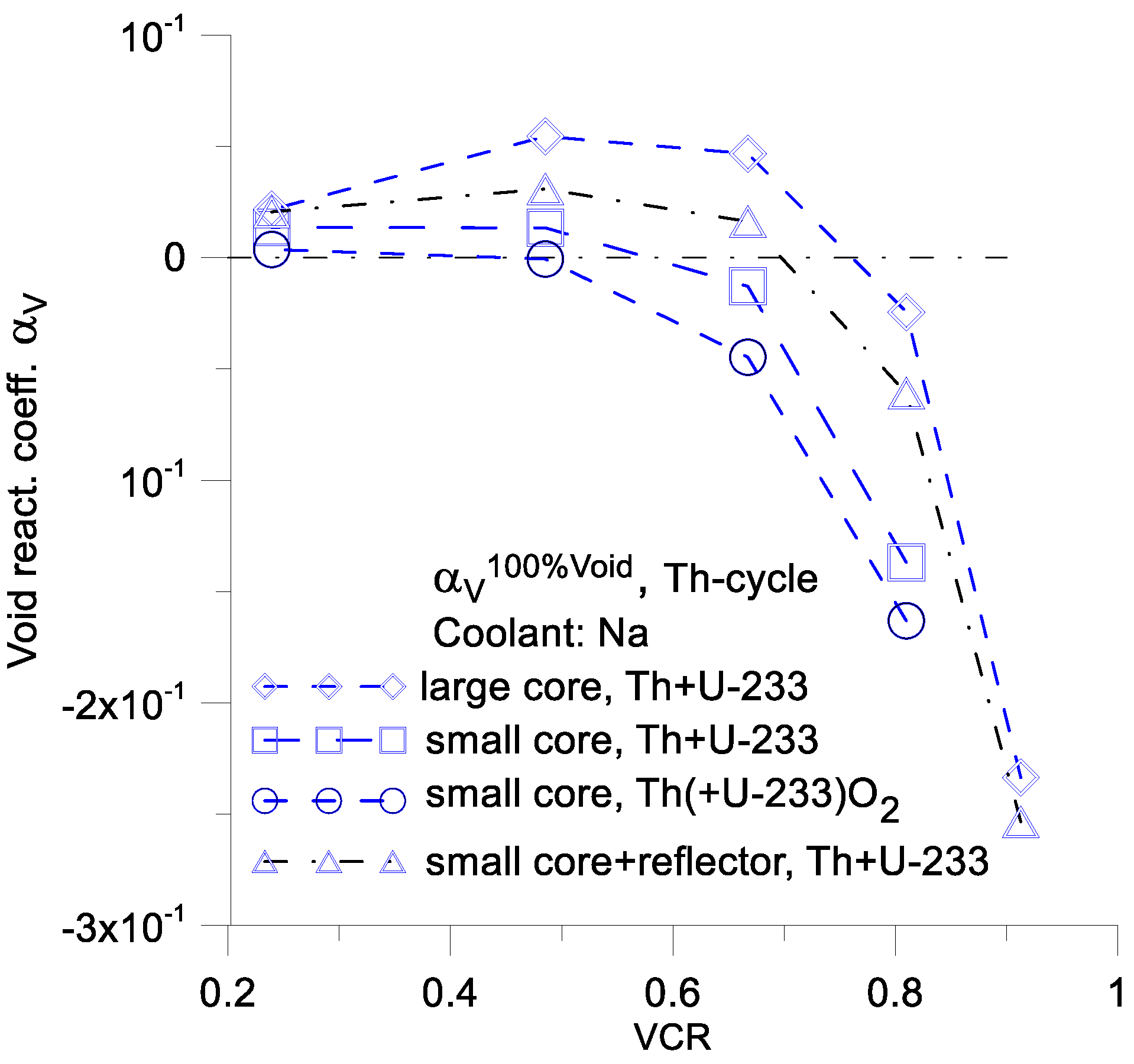
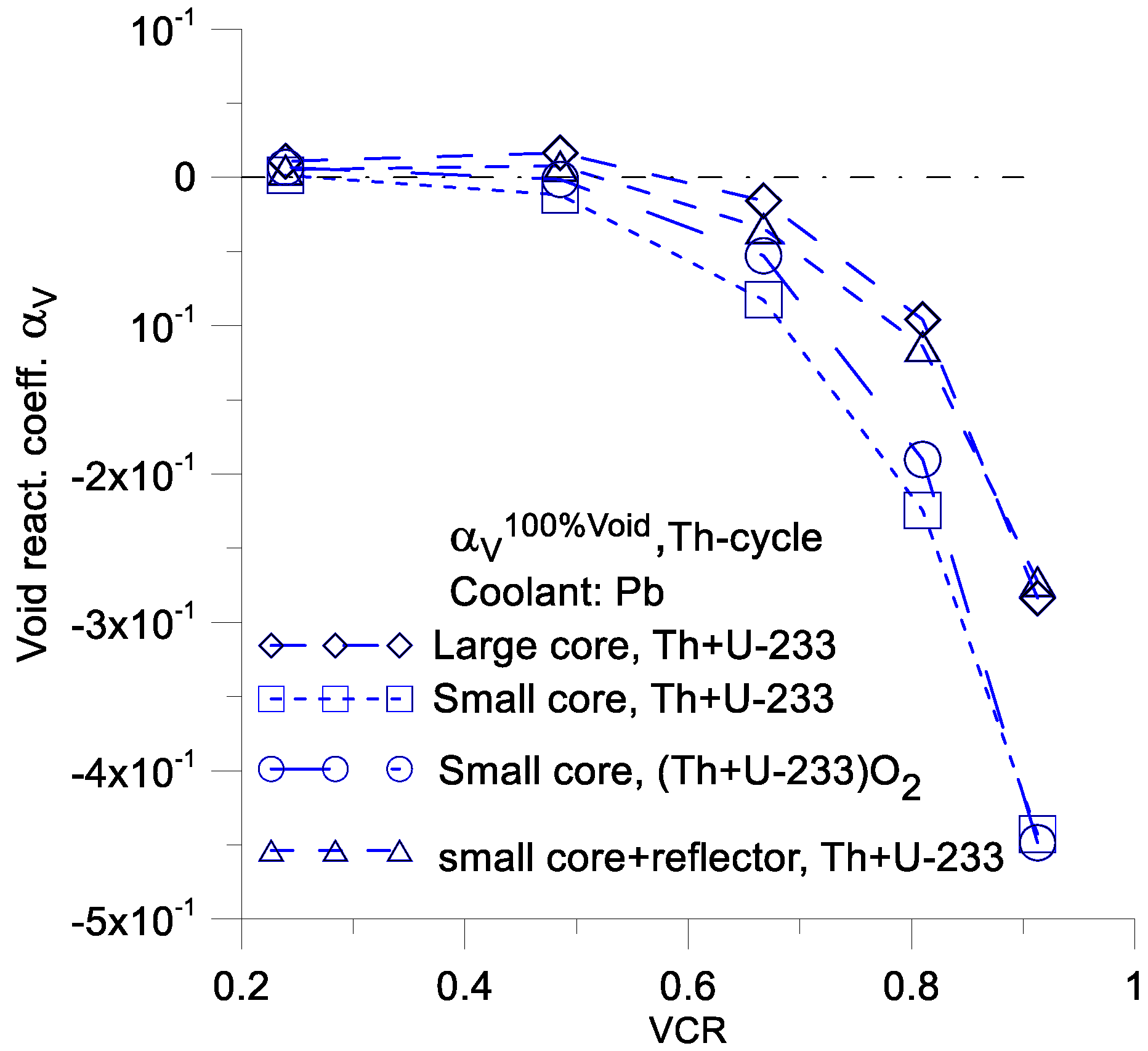
All the functions have negative values for sufficiently high values of VCR. For this reason, VCR is the most important factor to reduce the value of .
The greatest positive values of
one can be achieved with large cores or small cores that incorporate a reflector and use metallic fuel of type U-238 + Pu-239 (
Figure 7,
Figure 8,
Figure 9 and
Figure 10). For this reason, both a reflector and high value of a fuel density are unfavorable when the goal is to reduce the value of
.
Lower positive values of
are obtained for the thorium cycle (
Figure 9 and
Figure 10), the primary reason for this result is the lower density of metallic thorium compared to metallic uranium (see
Section 6).
A negative value of
one can easily be obtained with a Pb-cooled Th-cycle (
Figure 10). For this type of reactor, it is possible to obtain a negative value of
over a wide range of VCR parameter values.
The
function increases or decreases with low and high values of
VCR, respectively. The absorption and leakage components of α
v are responsible for the increasing and decreasing part of the α
v function, respectively. To obtain a negative α
v value, than the leakage component must be greater than the sum of absorption and spectrum components α
v [
23].
The components mentioned above are closely interconnected. A high value of VCR indicates a high positive value of the absorption component; however, this does not necessarily imply a higher value of αv. In fact, a high value of VCR parameter generally corresponds to lower value of fuel mass in the fuel cell which increases the leakage component. As the VCR value becomes sufficiently high, αv tends to decrease.
A small core makes it easier to obtain a negative value of
for in different type of reactors cores without reflectors (
Figure 7,
Figure 8,
Figure 9 and
Figure 10). This finding extends the existing literature [
2,
3,
4,
5,
17]. However, another significant parameter that decreases the value of
is the density of the fuel (
Figure 7). The most effective method of reducing of
is to apply the three methods simultaneously: reducing fuel density, decreasing the size of core, and increasing the value of
VCR (
Figure 7,
Figure 8,
Figure 9,
Figure 10 and
Figure 11).
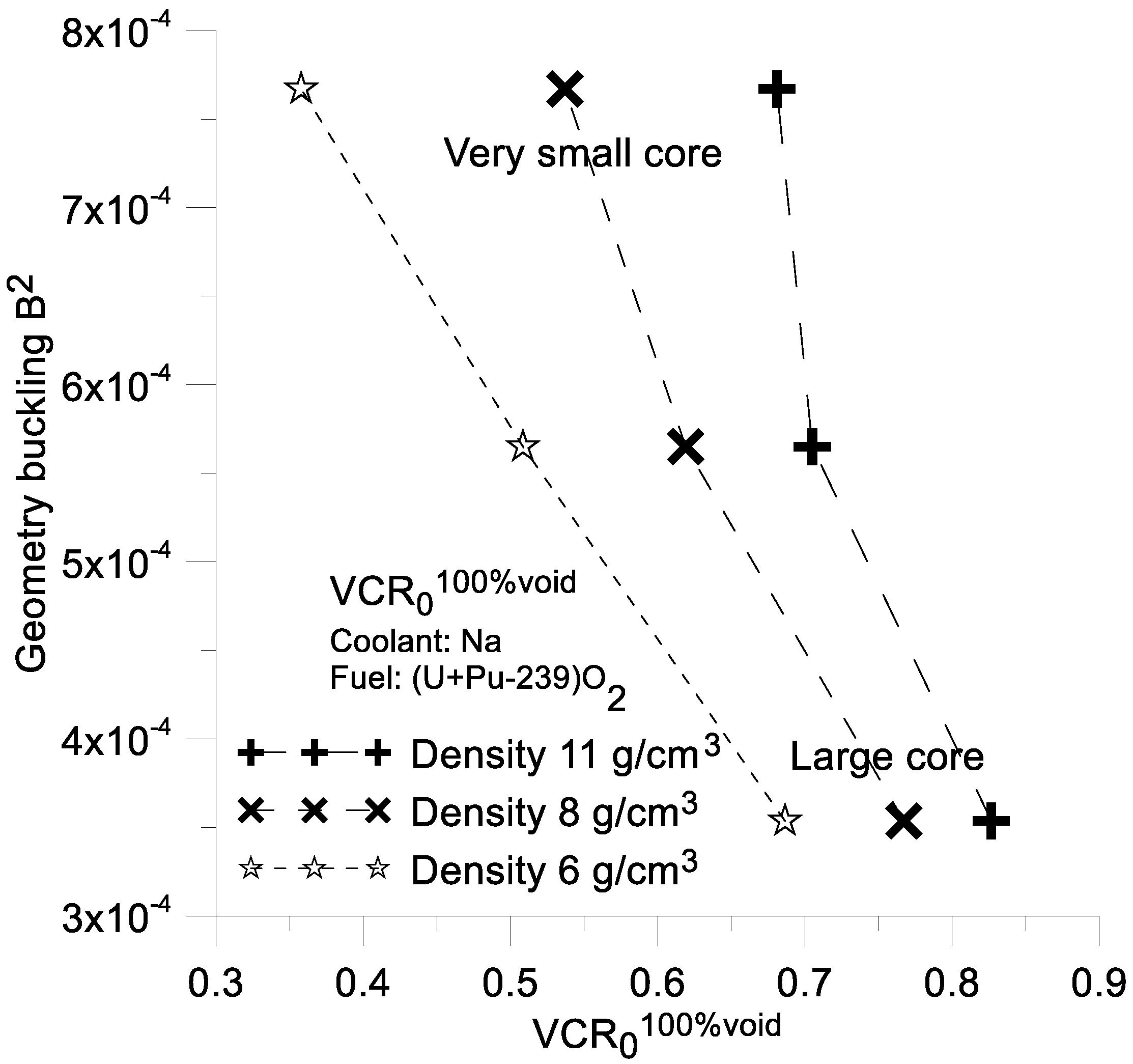
The average fuel density plays important role in decreasing the value of
. Unfortunately, only a very small core with a fuel density of 6 g/cm
3 achieves a
value of less than 0.5. The method of reducing the average density of the fuel does not practically allow for the construction of a large reactor filled solely with a single-type of fuel assembly with a negative
(
Figure 11).
Please note that the above conclusion applies to reactor core containing only a single-type of fuel assembly using the U-cycle.
The large and medium reactors presented in Reference [
17] have reflectors and positive α
v values.
The results in this section predict that large reactors without the reflectors also exhibit a positive value of αv. Why it is so difficult to obtain a low value of ? This is because decreasing this value simultaneously increases the fuel mass in the fuel cell, which, in turn, decreases the neutron flux leakage.
Unfortunately, the results presented in this section exhibit a high value of
. However, they provide guidance on how to significantly reduce this quantity (see
Section 6).
5. Loss of Neutrons
This section presents the relationship between α
v and neutron loss coefficient
Loss Equation (8), and
βv Equation (10) as a functions of
VCR. The fraction of lost neutrons can be defined in the following form:
where:
Absorption—means the absorption fraction without absorption neutrons inducing fissions i.e., (n,γ)
Escape—means the total escaped fraction of neutrons,
Fission—means the fraction of all actinides fission reactions.
Loss is a function of VCR and the void parameter.
The
βv function can be defined as relative change in the
Loss(VCR) function
where
Lossnorm, Lossvoid—mean the loss neutrons fraction at 0% void (normal work) and n% void, respectively.
The
Incore(
VCR) function can be defined as the neutron fraction inside the core in the following form:
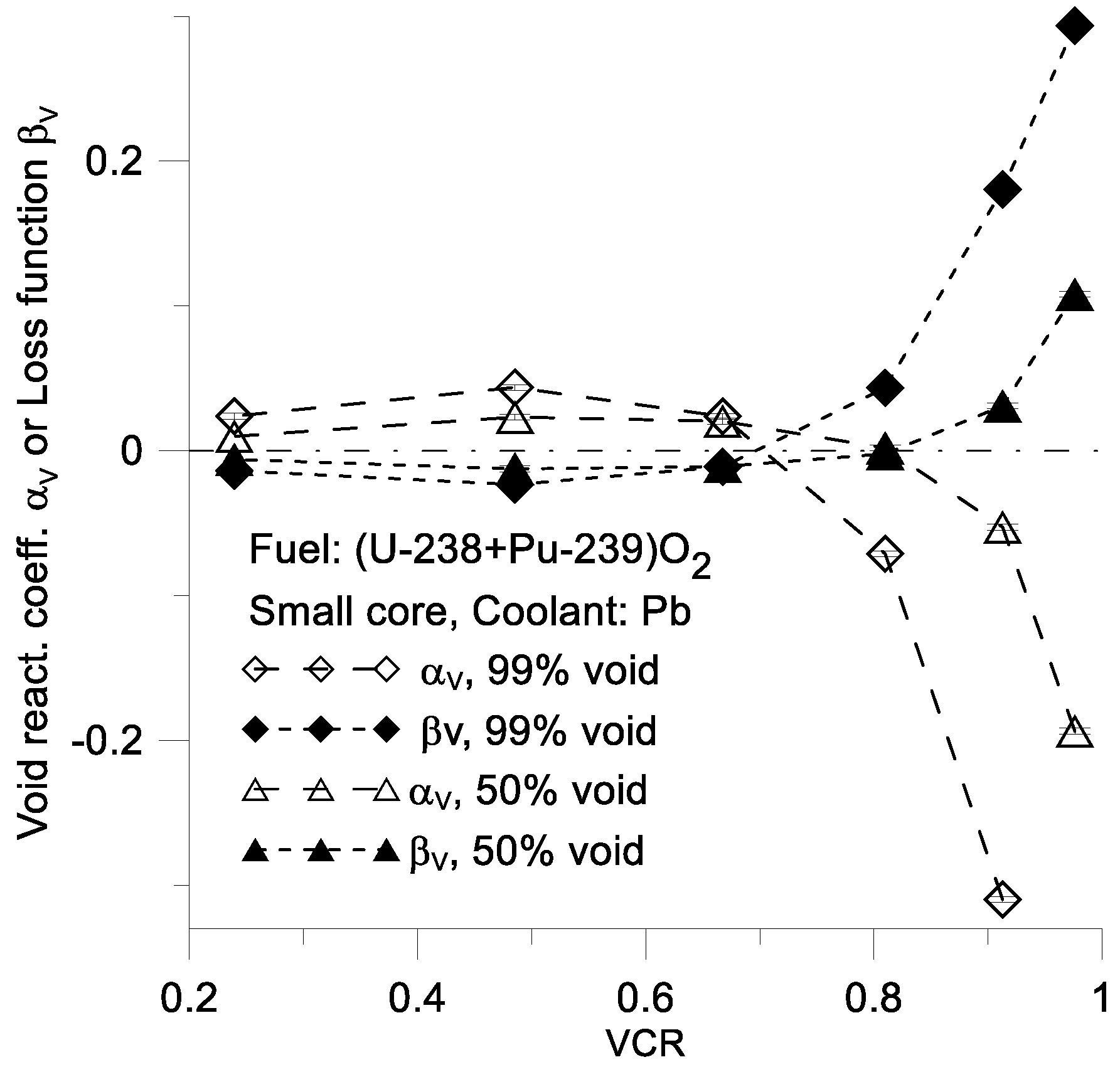
Comparisons between
and
for the Pb-cooled U-cycle in a small core reactor as a function of
VCR are presented in
Figure 12. Similarly, we determined the relationships between
and
for all cases discussed in this work.
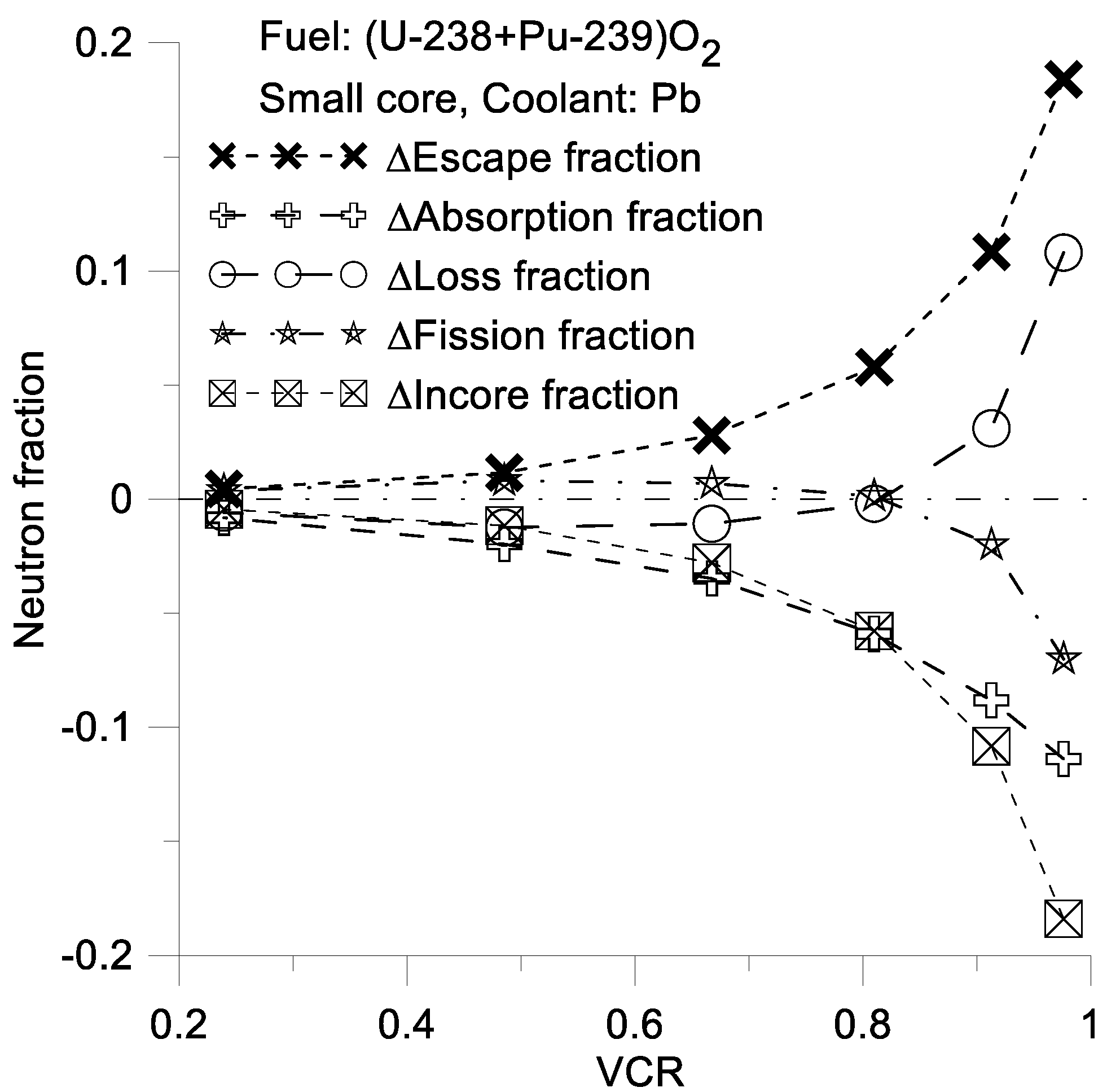
It is important to note, that has negative and positive values. A positive values means positive values of and a decreasing number of neutrons in the core. Conversely, a negative value of suggests an increase in the number of neutrons in the reactor core. In other words, the presence of a void can either increase or decrease the neutron populations in the core, which, in turn, changes the value of .
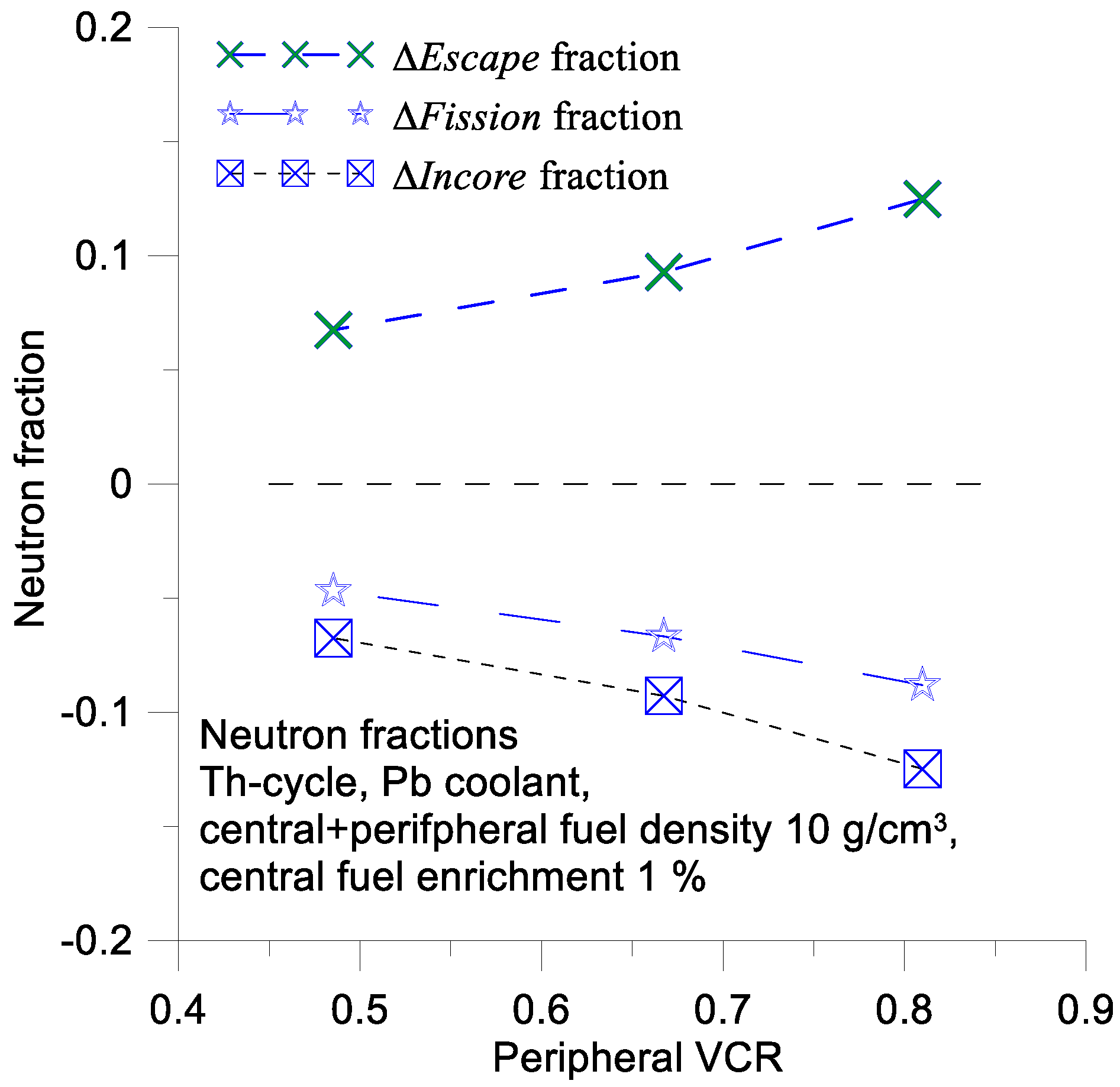
Note that the Δ
Loss fraction is equal to the negative value of the Δ
fission fraction (
Figure 13). In other words, a positive value of the Δ
Loss fraction indicates a decrease in the fission fraction and a negative value of
. The primary reason for this is the high value of the Δ
Escape fraction during evaporative cooling. These calculations results take into account changes in the neutron flux energy distribution and cross sections of the corresponding reactions during reactor voiding. Specifically, the results consider the increase in fission cross sections induced by an increase in the average neutron energy. However, such an increase in the fission cross section can be mitigated by a decrease in the neutron fraction within the reactor core, which is caused by neutron escape. The
Incore(
VCR) function can be useful for illustrating this effect (
Figure 13).
The results obtained in this section help us to get negative value of
for a hybrid reactor (see
Section 6).
6. Calculation Results for Hybrid Reactor
The primary physical phenomenon that reduces the number of neutrons in the core in a voided state is their escape from the core. This can be achieved using the appropriate reactor geometry and material properties. Since the main goal of the present work is to increase the neutron leakage through the radial side surface of the core, a reactor should be designed without a radial reflector. The fuel arrangement in the reactor is also crucial, i.e., highly enriched fuel should be placed in the peripheral region of the reactor. In addition, the assemblies in the peripheral zone of the reactor should employ an increased VCR value and a reduced fuel density. These parameters contribute to an additional increase in neutron leakage.
Using the results from the previous sections, we can derive intriguing outcomes for the hybrid reactor (
Figure 4,
Table 3). In this study, the hybrid reactor core contains two parts: the central core and the peripheral core. The central core contains the fuel assembly with an optimal value for
VCR, i.e., 0.485 (
VCFR = 0.94), a standard fuel density and a low value of fuel enrichment. In contrast, the peripheral core is composed of a fuel assembly with a high level of fuel enrichment and three values of both the
VCR parameter and fuel density. By simultaneously utilizing these three parameters and characteristics for the peripheral assemblies, we achieve the smallest values for
. The calculations were conducted with central fuel enrichments of 1 and 5 at. % for both U-cycle and Th-cycle reactors. The enrichment of peripheral fuel was adjusted to ensure k
eff = 1.05 ± 0.02.
Herein two examples of hybrid reactors are presented: Na-cooled U-cycle and Pb-cooled Th-cycle. It is important to note that the Na-cooled U-cycle predicts maximal values of
whereas the Pb-cooled Th-cycle exhibits minimal values of
when the reactor core is filled with a single type of assembly (compare
Figure 7,
Figure 8,
Figure 9 and
Figure 10).
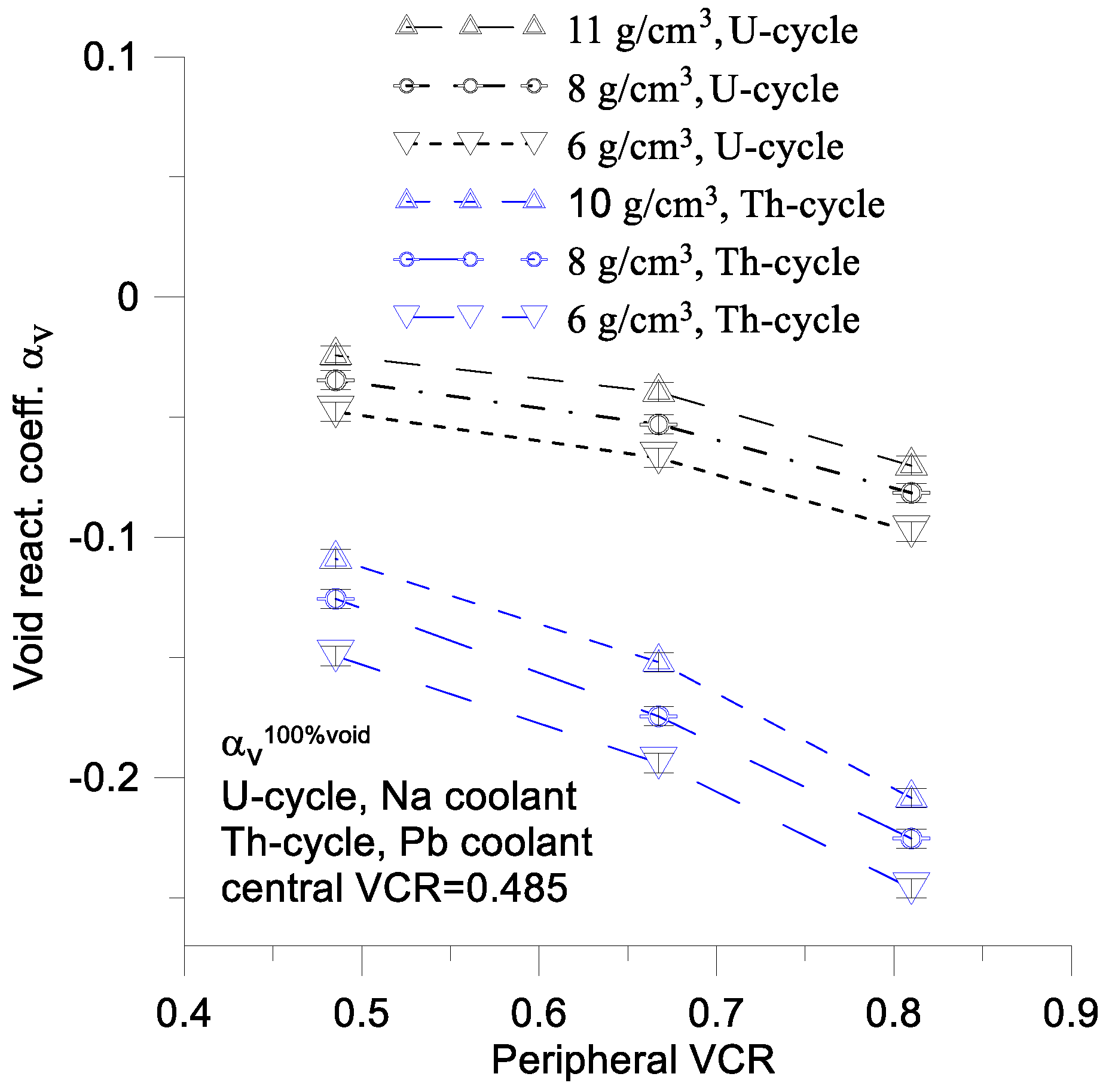
The Pb-cooled Th-cycle hybrid reactor has significantly lower value of
compared to the Na-cooled U-cycle reactor (
Figure 14 and
Figure 15). This indicates that Th-cycle reactors are characterized by substantially greater passive safety than U-cycle reactors.
The values of
are significantly less than 0.485 for all presented cases. While the exact values of
were not calculated, they can be easily estimated using the
function and extrapolation method (
Figure 14,
Figure 16 and
Figure 17). It is important to note that the values of
VCR for the central and peripheral parts are significantly greater than
. This can be expressed in the following inequalities:
VCRcentral >
and
VCRperipheral >
. These results indicate that
has a negative value (see
Section 5).
The negative value of
can be explained in another way. Note that the value of
is positive for all the cases presented in this section (
Figure 16); a positive value of
always corresponds to negative value of
(
Section 5). The primary reason of the positive value of
is the high value of Δ
Escape quantity, which indicates an increase of escaping neutrons in a voided reactor core; an increase in Δ
Escape leads to a decrease in Δ
Incore, that is, it reduces the fraction of neutrons in the core. The relative increase in Δ
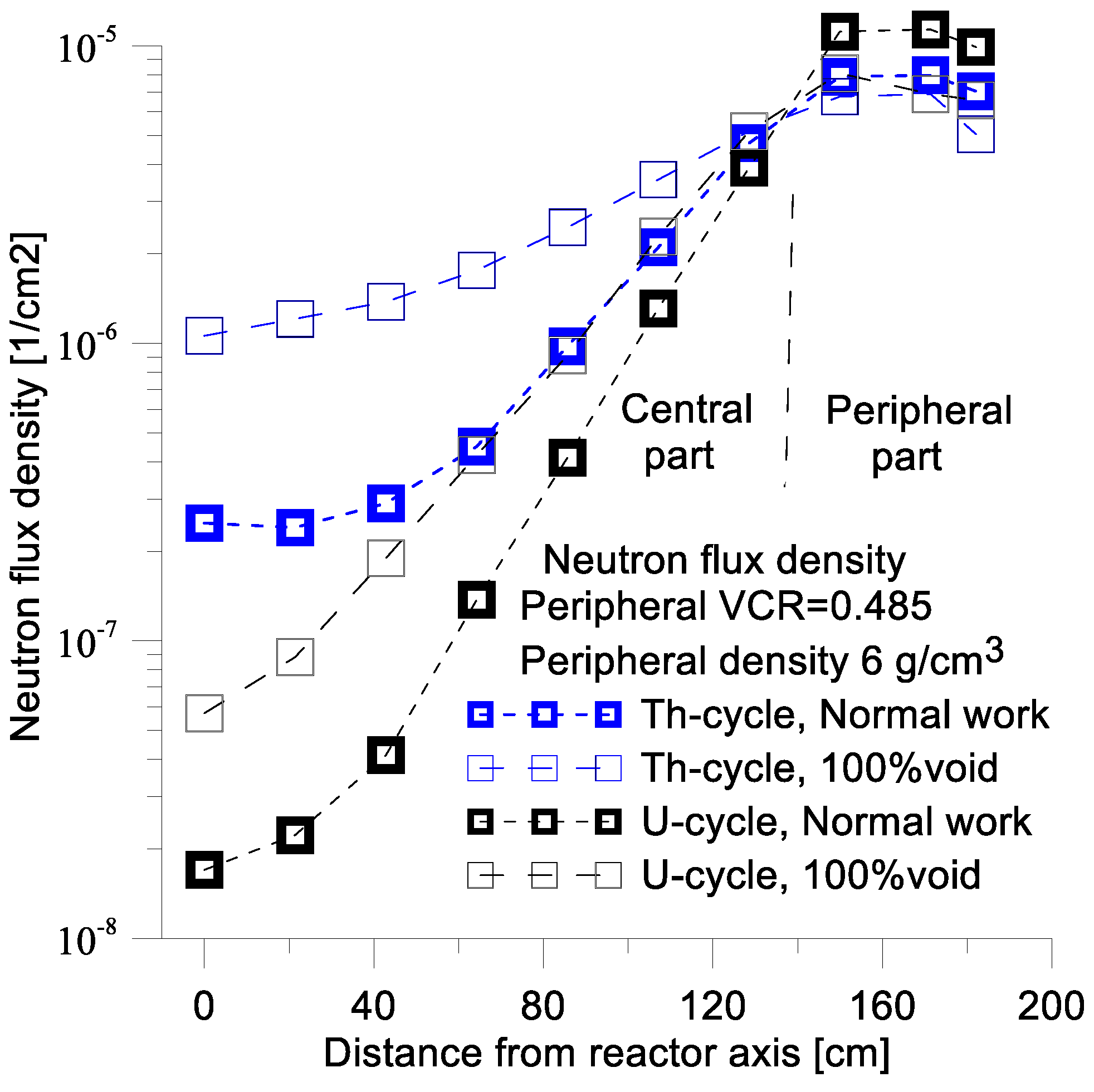
Escape exceeds 60% and the average energy of the escaping neutrons increases by more than 20%. This results in a reduction in the average value of neutron flux density in the peripheral part of the core (
Figure 17), leading to a decrease in fission reaction within the core, as evidenced by the negative value of Δ
fission (
Figure 18). The Δ
fission fraction is negative for all samples presented in this section.
Note that in cases of VCR = 0.485 with a normal fuel density value for both central and peripheral assemblies, a significant difference in fuel enrichment between the peripheral and center segments is sufficient to obtain a negative value of . This phenomenon occurs because the hybrid reactor undertakes high fuel enrichment in the peripheral region and reaches a high value of leakage neutrons under the condition of a voided reactor. Note also that an analogical large reactor Na-cooled U-cycle reactor based on a single type of assembly has = 0.827 and .
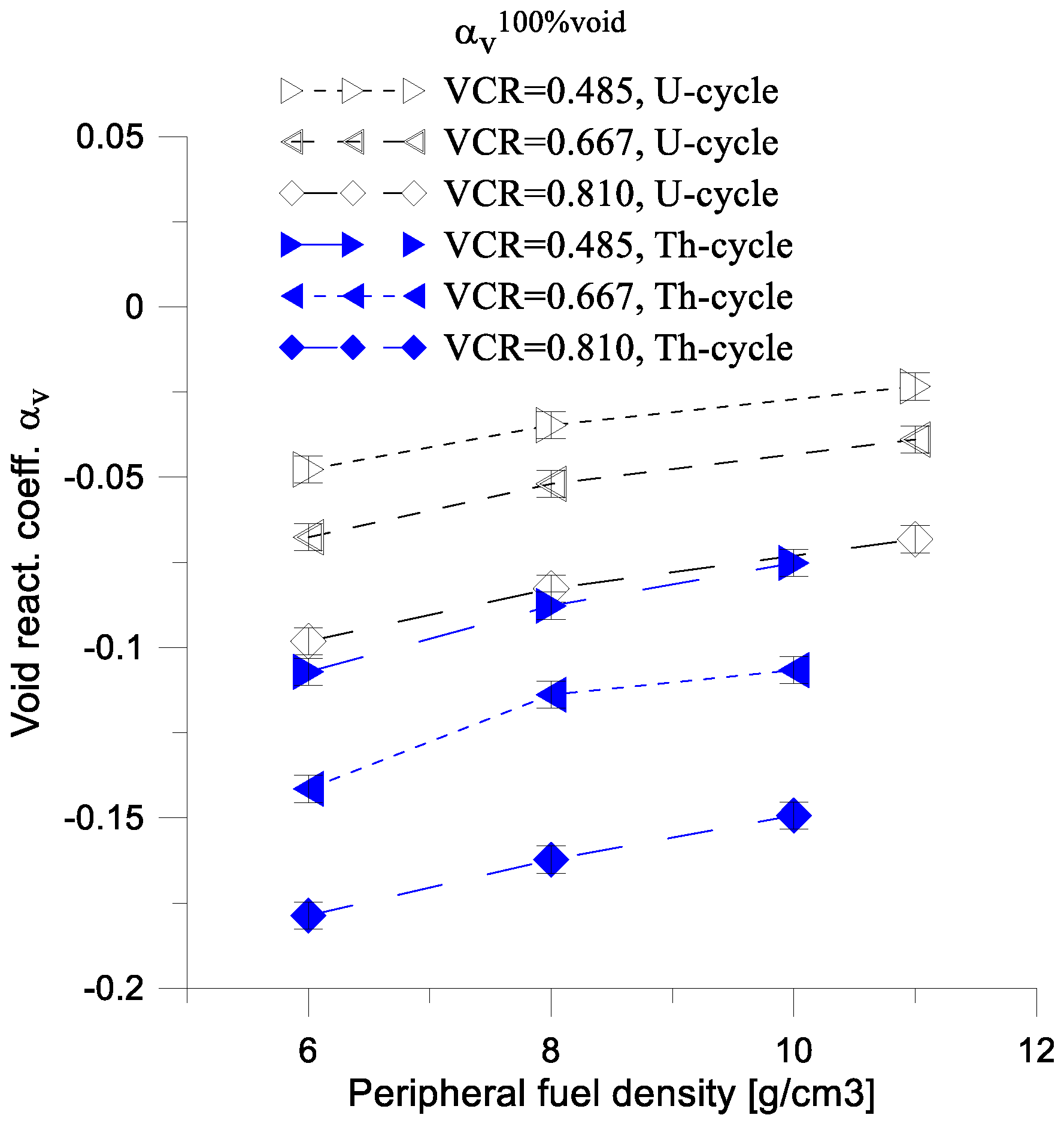
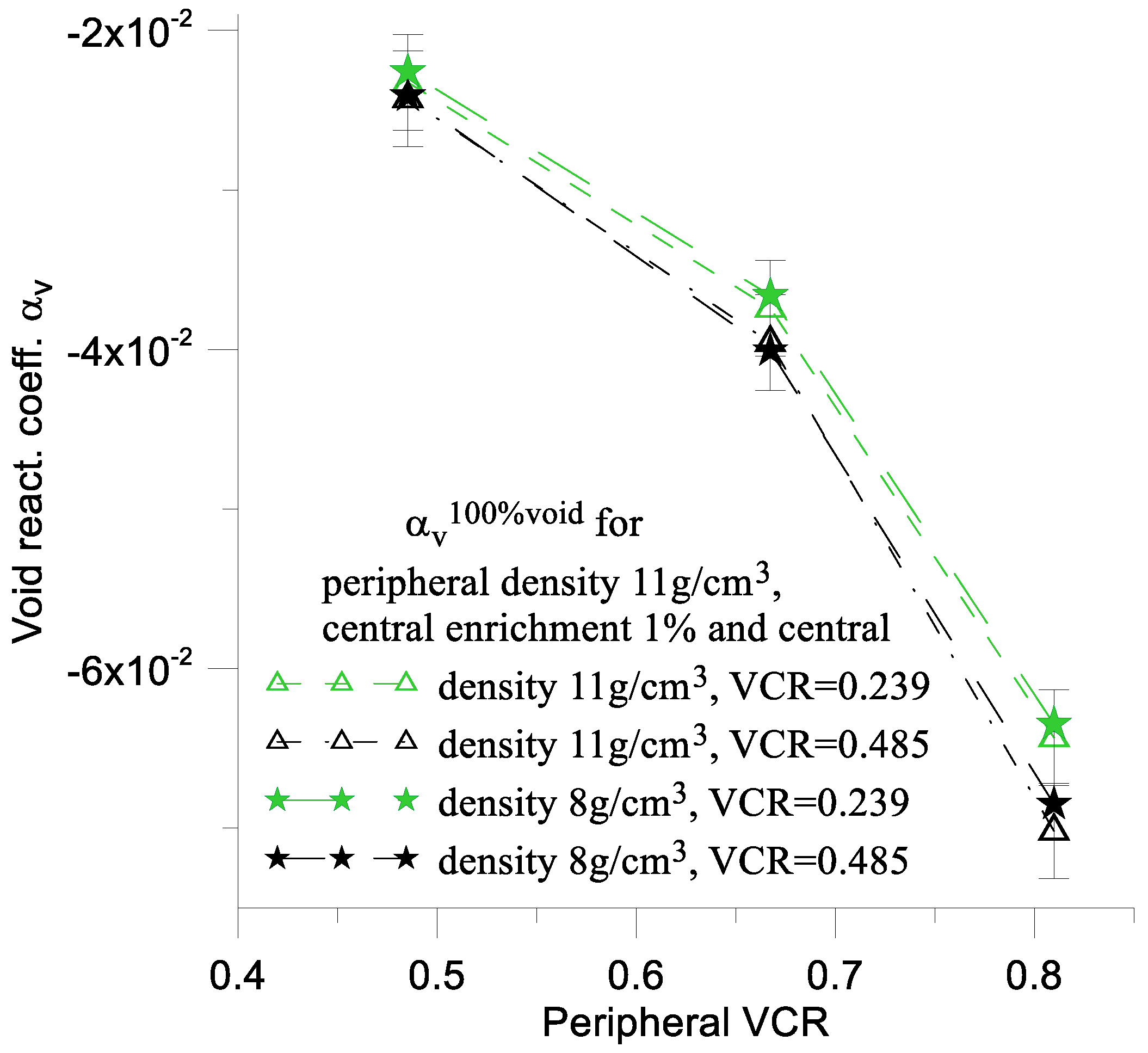
One can observe that
is a decreasing function of peripheral
VCR (
Figure 14) and an increasing function of peripheral fuel density (
Figure 15). In other words, the negative value of
is a decreasing function of the difference in fuel enrichment and the fuel density, as well as the
VCR between the central and peripheral parts (
Table 4 and
Table 5,
Figure 15).
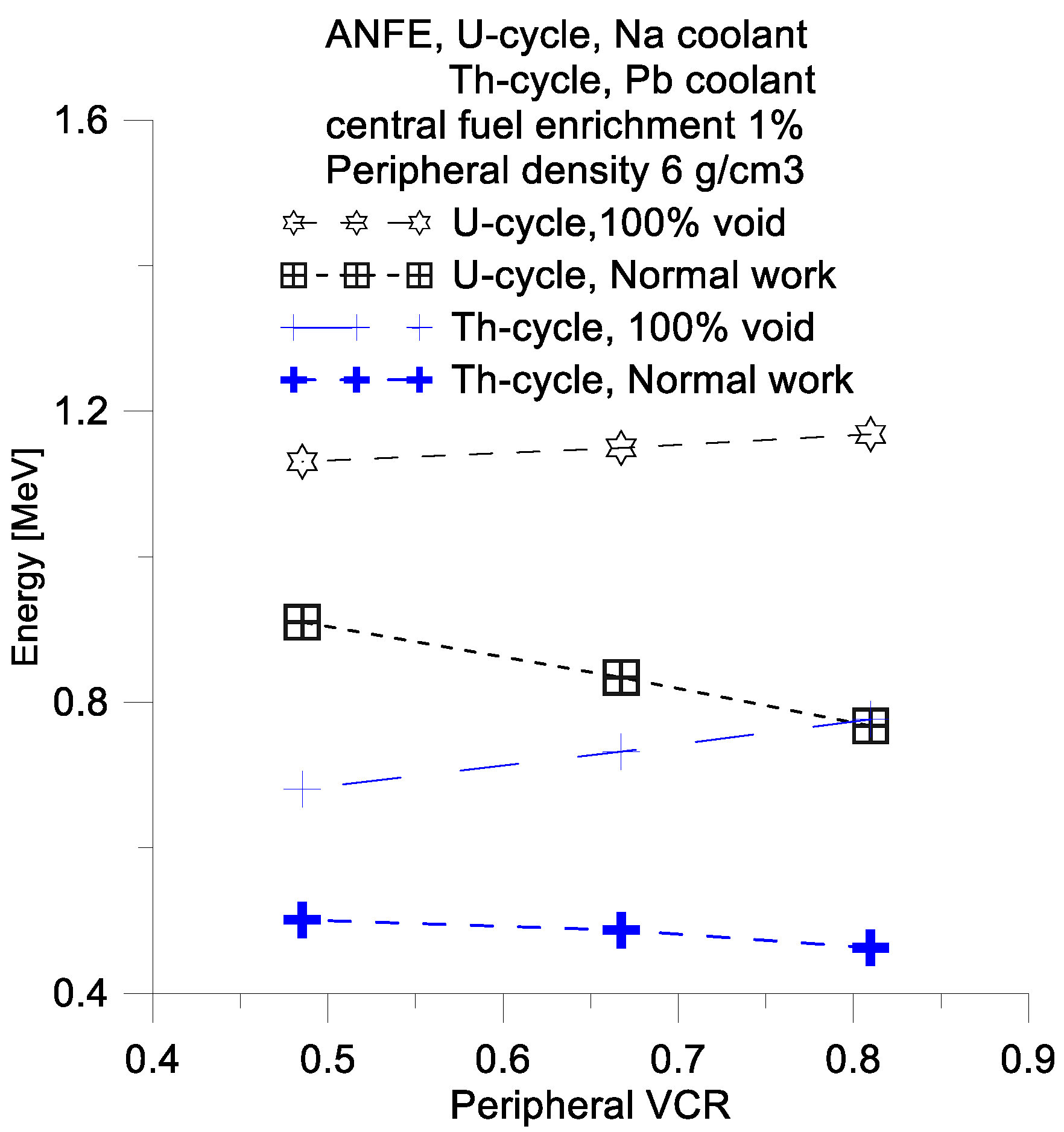
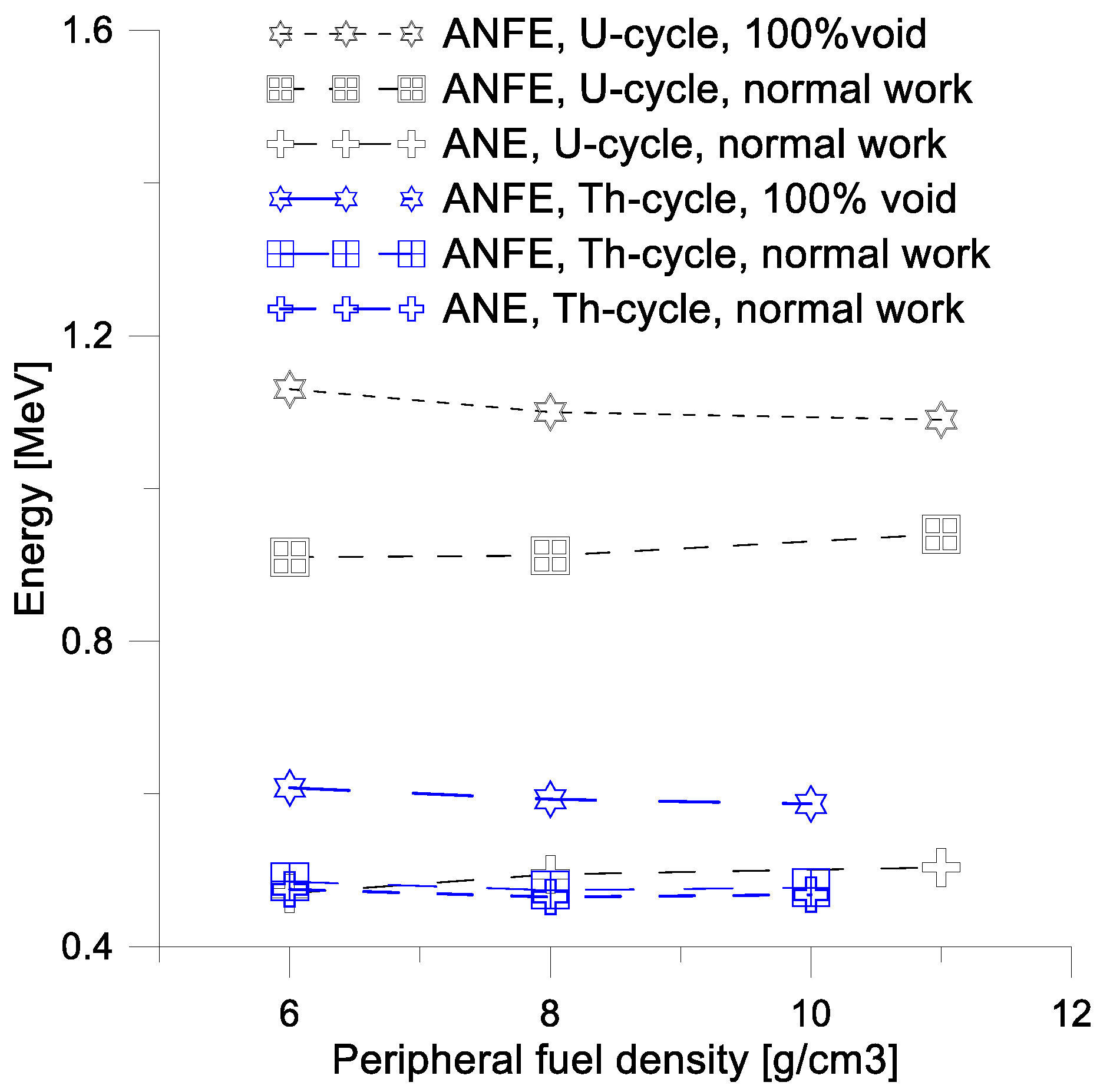
The ANE and ANFE have a weak dependence on the peripheral fuel density (
Figure 16). However,
is an increasing function of peripheral fuel density. For these reasons, it is advantageous to reduce the peripheral fuel density.
The type of coolant and fuel has a significant impact on
value, i.e., a higher value for the cross section of the neutron absorption of the coolant increases of
value. An important factor contributing to an increase in
is the increase in the number of fission reactions induced by fast neutrons (
Table 6) and ANFE for a voided reactor core (
Figure 19 and
Figure 20). These magnitudes have significantly greater values for the U-cycle compared to the Th-cycle reactor. The reason for this is that the fission cross section (FCS) for U-233 is higher than that of Pu-239 in the intermediate neutron energy range (
Table 6). Additionally, the FCS for Th-232 is lower than that of U-238 for neutron energies higher than 0.5 MeV. The number of directly fission events with U-238 is significantly greater than that with Th-232.
The geometry of the hybrid reactor presented in this section is not yet optimized. Furthermore, reducing of the value of can be achieved by increasing the outer surface area of the peripheral part at the top and bottom of the core, for example.
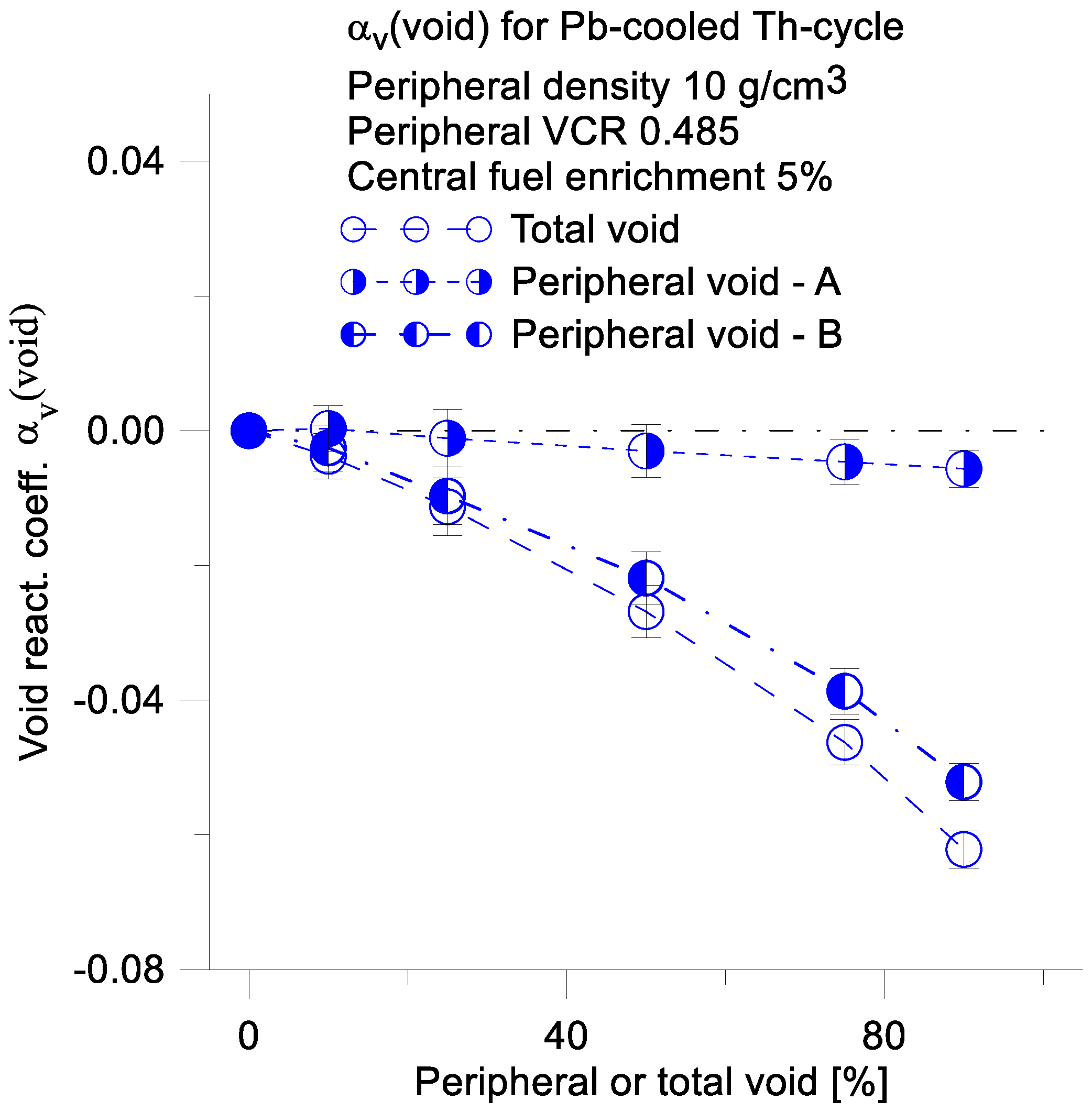
Herein, is , is calculated. However, neutron flux density, power density and the evaporation rate of the coolant in the peripheral region are significantly greater than in the central region. For these reasons, the rate of decrease in the coolant density in the peripheral region will be greater than in the central region. For this reason, the functions are calculated for both total void and peripheral void. The αv for the peripheral void is calculated for two cases: Partial Void-A and Partial Void-B.
Partial Void–A refers to the case in which the average coolant density is changed only in the peripheral assemblies. In this scenario, the thin layer of coolant between the fuel assemblies and core barrel has a constant normal density. This situation does not reflect a real case.
Partial Void–B, on the other hand, describes the case in which the average coolant density is modified in the peripheral region of the reactor, specifically in the peripheral assemblies and the thin layer of coolant between the fuel assemblies and the core barrel. This represents a more realistic scenario.
The difference between Partial Void-A and Partial Void-B predicts the significant impact of the peripheral thin layer of coolant on the αv.
The concept of a hybrid reactor allows for the construction of a large and efficient reactor with a negative
value. A low value for central fuel enrichment facilitates the use of natural uranium or thorium, as the criticality of the hybrid reactor is determined by the peripheral part of reactor. In other words the central region should contain blanket/fertile assemblies for the conversion of fuel. The fuel conversion ratio (CR) is a decreasing function of fuel enrichment. For this reason, the CR for peripheral region should be less than 1 [
14,
15].
Influence of the Central Region Parameters on αv
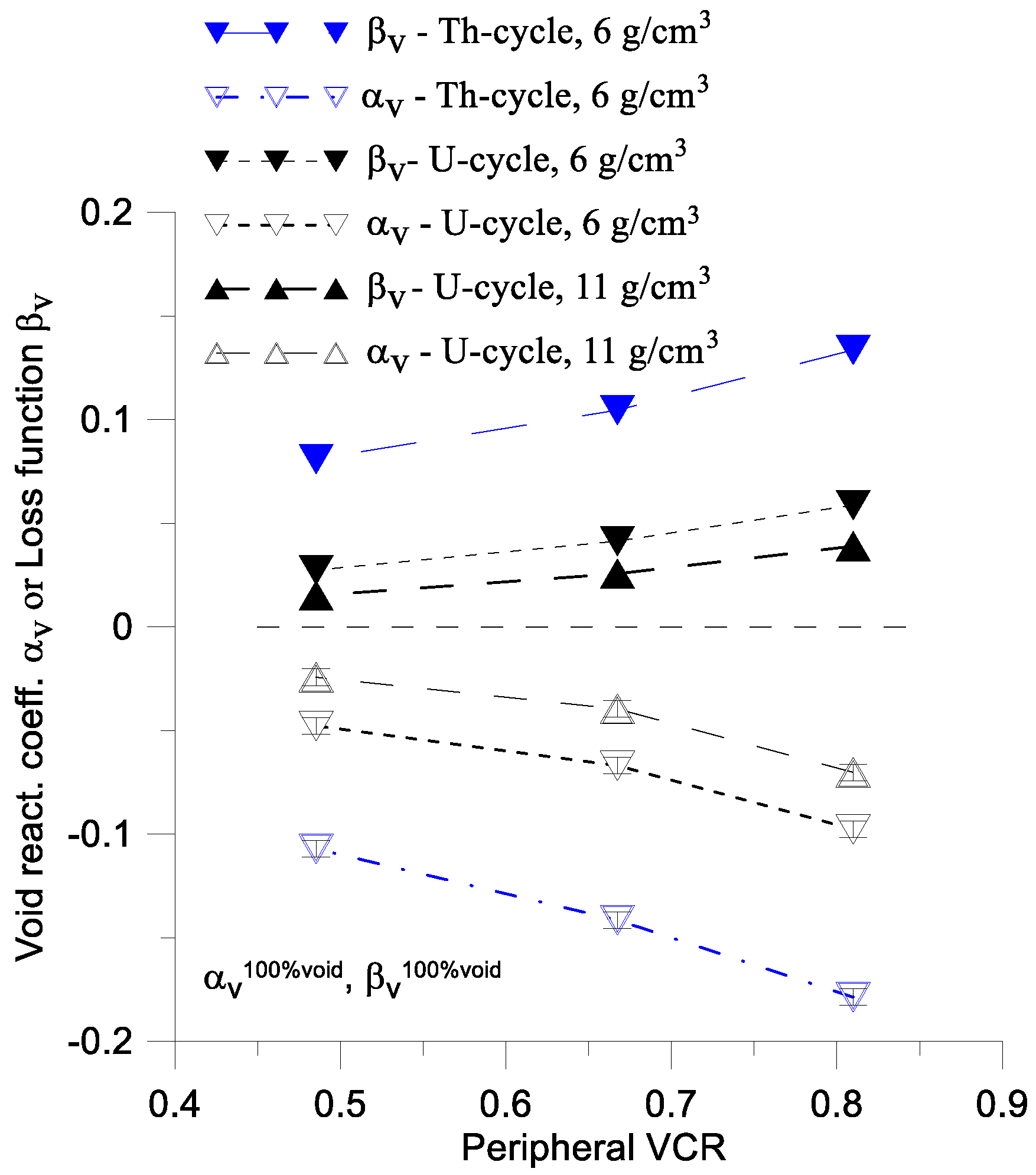
In this section, we examine the influence of the central region parameters, i.e., the average fuel density and the central VCR parameter on αv, while the central fuel enrichment is maintained at a stable level of 1%.
The peripheral fuel density is set to 11 g/cm3, and the peripheral VCR values are 0.485, 0.667 and 0.810.
We compare the
functions for central fuel densities of 11 g/cm
3 and 8 g/cm
3, as well as central
VCR values of 0.239 and 0.485 (
Figure 22).
The fuel density of the central core region does not influence α
v (
Figure 22). However, the central
VCR has a weak influence on α
v. Strictly speaking, a decrease in the central
VCR parameter of about 50% induces an increase in the relative value of α
v of approximately 4–9%. A decrease in the value of the central
VCR parameter decreases the absorption component of α
v, which should lead to a decrease in α
v. A slight increase in α
v suggests that the absolute value of the leakage component of α
v should simultaneously decrease. In other words, from the point of view of α
v, there is no need to employ very low values of central
VCR in the a hybrid reactor; however, one could employ them to increase the average neutron energy.
7. Calculation Uncertainties
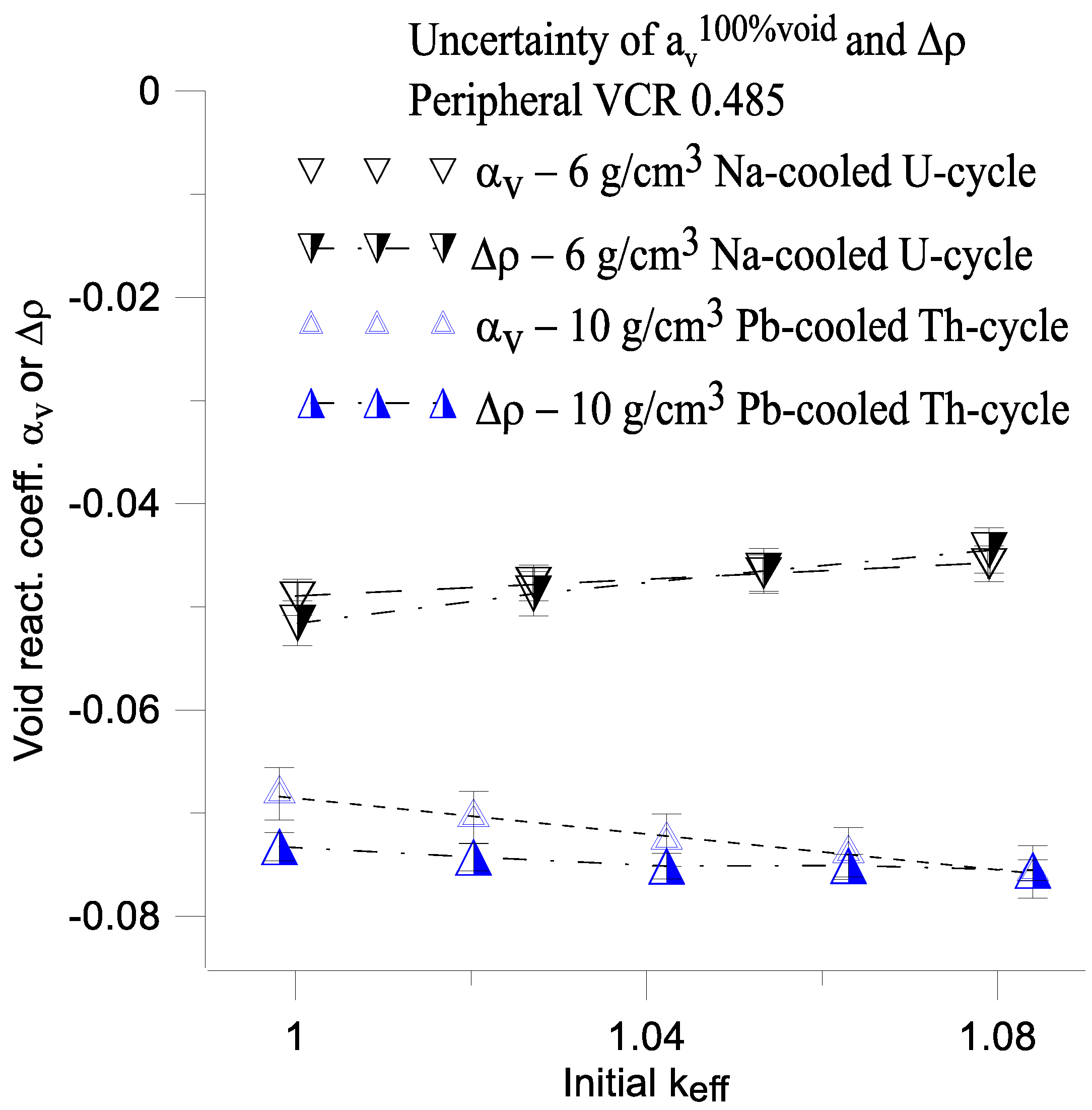
This section presents the values of the uncertainties for both the αv (Equation (4)) and the difference in reactivity defined by Δρ (Equation (5)).
Here, Δρ and α
v are functions of the initial value of k
eff (
Figure 23). The calculated uncertainties of α
v and Δρ include both the systematic error due to the uncertainty of the initial value of k
eff and standard deviation resulting from the statistical errors of the initial values of k
eff (
Figure 23).
A value of the systematic error (MSE) in the range Δkeff = 0.02 is calculated using the corresponding fitting function of αV(keff) and Δρ(keff) for Na-coolled U-cycle and Pb-cooled Th-cycle reactors respectively.
The standard deviation of reactivity σ(ρ) was determined using the standard deviation σ
keff of k
eff and the following formula:
The standard deviation of Δρ is calculated using the following formula:
The standard deviation of α
v is calculated from the following equation:
The total uncertainties of α
v and Δρ for 100% void are equal to the sum of the standard deviation and MSE. These are denoted as Δ
Tot(α
v) and Δ
Tot(Δρ), respectively (
Table 7).
The total uncertainty
of the
αv(void) function (
Figure 21) is determined by perturbation effective multiplicity factor
and its standard deviation
and MSE. The perturbation error is calculated for 10% of the average coolant density using PERT command of MCP6.2 code. The maximal value of
achieves is 0.004 for void = 20%.
8. FBR-IME Reactor Versus Hybrid Model
The main aim of this section is to compare the difference in reactivity Δρ of FBR-IME [
9,
10] and hybrid reactors with low average void values. The hybrid reactor is based on a
VCR parameter of 0.485, a fuel density of 11 g/cm
3, and a central fuel enrichment of 1%. Here, a hybrid-inverse reactor is presented. The geometry of this model is identical to that of the hybrid reactor, but assemblies with fuel enrichment of 1% are placed in peripheral region, while assemblies with high fuel enrichment are positioned in the central part of the reactor (likely as in FBR_IME, (see
Table 8).
The FBR-IME reactor consists of a simple core with 91 fuel assemblies and an outer/fertile blanket with 295 assemblies. The fuel assemblies are designed based on the geometry of the assembly used in the Japanese experimental reactor named JOYO. The core consists of 75 fuel assemblies, nine control rods and seven inner blanket assemblies. The fuel assemblies are arrangement in special way: two inner layers are blanket assemblies, followed by two layers of MOX at 25% enrichment, one layer of MOX at 33% and one layer of MOX at 42%. In other words, the enrichment of the fuel assemblies increases with the distance from the center of the core. This specific arrangement of enrichment is a method involving decresing of α
v. A similary method was used in the LFR-ELSY reactor [
6].
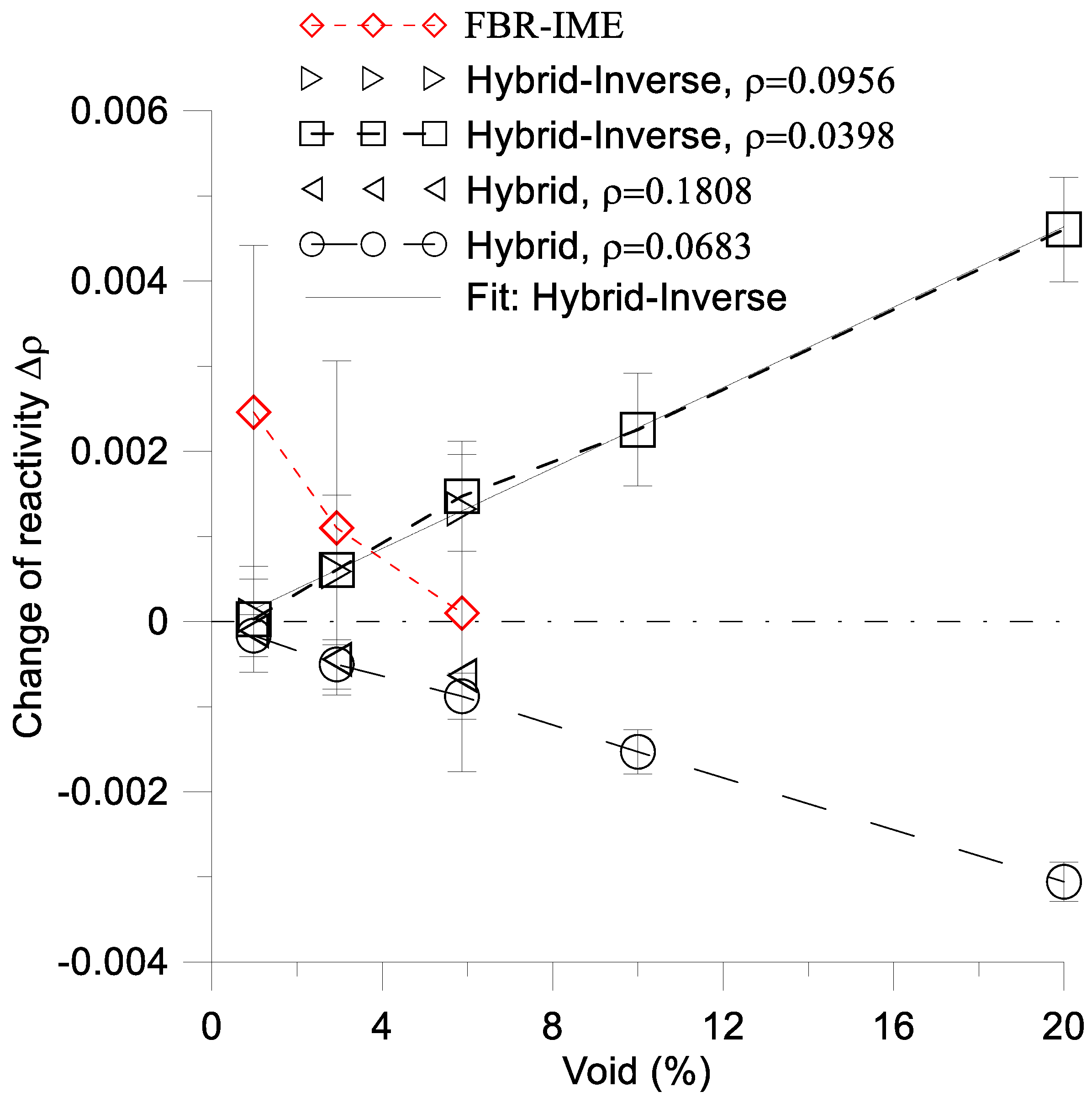
The Δρ for hybrid reactors are calculated for two different values of ρ. The difference between them is less than the corresponding standard deviation value (
Figure 24 and
Table 8).
The low void value indicates a low value of difference in reactivity Δρ and requires a high value of the corresponding statistics. For this reason, measurement of Δρ is a difficult task. The standard deviations of Δρ for voids of 2.93% and 5.87% for FBR_IME are significantly greater than the corresponding values of Δρ (
Table 8,
Figure 24) and exceed the corresponding values for the hybrid-inverse reactor. However, the results of Δρ are likely applicable to both FBR-IME and hybrid-inverse reactors. Despite the many differences between FBR-IME and hybrid-inverse reactors, the results are practically the same, i.e., with in the range of calculation errors. Strictly speaking, the differences between Δρ for voids of 2.93% and 5.87% are approximately to 0.0005 and 0.0014, respectively. These differences are both less than the corresponding standard deviation of FBR-IME. Meanwhile, the difference for a void of 0.98% is approximately 0.0024, which is less than the sum of the corresponding deviation of FBR-IME and hybrid-inverse reactors.
These reactors have a low value of fuel enrichment in the peripheral region (blanket/fertile) (
Table 8, [
9,
10]).
Here, Δρ (void) is a decreasing function of the void for both the FBR-IME and hybrid reactors within the range of (0.98%, 5.87%) void. However, the FBR-IME exhibits a positive value of of Δρ, whereas the hybrid reactor shows a negative one. A special arrangement of high enrichment MOX fuel assemblies in the central part of the FBR-IME is insufficient to achieve a negative value of Δρ.
The hybrid model results in a negative value of Δρ in all cases. In this scenario the average coolant density is modified in the total peripheral region of reactor, which includes the peripheral assemblies and thin layer of coolant between the assemblies and the reactor barrel.
It is important to note, that blanket/fertile assemblies placed in central part of the reactor significantly decrease Δρ (
Figure 24,
Table 8), while those placed in the peripheral part acts as reflectors and increase Δρ (see
Section 4).
This section is important, because it compares two methods of reducing αv based on the distribution of high enrichment fuel assemblies in the reactor cores of significantly different reactors. The FBR-IME method involves increasing the enrichment of fuel assemblies with a distance from the center of the active zone, located in the central part reactor core. In contrast, the hybrid method uses a constant value of enrichment of the fuel assemblies within the active zone, positioned in the peripheral part of the reactor core. This section shows that the hybrid method is significantly more effective. Of course, these methods can be combined, and the results of such combination would be even more interesting.
The is calulated using Equation (13).
The standard deviation σ(α
v) of
should may be determined from the following formula:
If we assume that = 0 then .
Using the above equations one can easy show that . This means that the relative values of of αv and of for are the same. In a real reactor, the uncertainty of Δv can be significantly greater than 0. This implies, that the total relative uncertainty of αV can be considerably greater than the total uncertainty of Δρ. For this reasons we compare Δρ in this section.
9. Discussion
The choice of the hybrid reactor geometry was made due to its large core without both a reflector and an upper sodium plenum (compare Ref. [
24]). The hybrid reactor has all the features of fast reactor with negative α
v (see
Section 6 and
Section 8). Its core has a relatively simple geometry, and the special arrangement of the fuel assemblies are optimized for leakage neutron flux during void conditions.
The purpose of this section is to present the main differences between a fast reactor core and a PWR core, as well as to explain their influence on the value of αv.
On top of that, the active fuel zone in SFRs and LFRs should only be about 1 m, due to significant concerns about the core void reactivity, which is much shorter than in conventional PWRs.
The high value of the active zone is intentional and is chosen to show that a negative value can still be achieved, even with an elevated core height.
Reducing the height of the active fuel zone to about 1 m is advantageous from the perspective of αv and can be applied in a hybrid concept, as it increases the neutron leakage fraction and decreases αv.
In the case of a sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), the fuel lattice should be very tight to minimize the void reactivity; all SFR designs are based on a hexagonal lattice.
The neutron flux spectrum and average value of neutron energy do not depend on the type of lattice. Instead, they are influenced mainly by the
VCR or
VCFR parameters. A hybrid reactor is designed based on the values of these parameters, i.e., central region VCR = 0.485 or 0.239 (
Figure 22) and an average value of neutron energy of approximately 0.5 MeV. A square fuel lattice is used in a LFR-ELSY reactor in [
6]. In other words, a hexagonal lattice can be used in a hybrid reactor without changing α
v. The minimal value of the
VCR parameters for FBR-IME and hybrid reactor are 0.374 and 0.239, respectively.
In addition, there should be thick steel reflectors on both the radial and bottom sides of the core.
Excessive core height affects αv in a manner similar to that of a thick bottom and top reflector. This means that the thick bottom reflector is included in the calculation results for the hybrid reactor. However, the thick radial side reflector presents a challenge that needs to be addressed; as such, this reflector should be removed. Additionally, the blanket/fertile should be positioned at the center of the core.
As such, there are significant differences in the core configurations between fast reactors and PWRs.
While there are many technical distinctions between the cores of fast reactors and PWRs, the neutron flux spectrum and neutron physics in the hybrid reactor in this study are similar to those in fast reactors. Many technical concepts from fast reactors, such as bending fuel assembly or upper gas plenum, can be applied in hybrid reactors. In other words, future fast reactors will integrate the hybrid concept based on the technology of present-day fast reactors.
10. Conclusions
The hybrid reactor concept offers a very effective passive and promising method for achieving a negative α
v value under a wide range of basic reactor parameters (
Section 6).
The fuel density and
VCR parameter are important reactor parameters in terms of reducing the value of α
v (
Section 6); decreasing the average fuel density and increasing the
VCR parameter in peripheral fuel assemblies induces a decrease of α
v. (
Section 6,
Figure 14 and
Figure 15).
The
parameter is a very convenient parameter for determining the reduction value of α
v; reducing this parameter is crucial for decreasing the value of α
v. Additionally, this parameter can be used to compare different methods of reducing α
v. To achieve a negative α
v value, the reactor must have a
VCR value exceeding
(
Section 4). In other words, a positive value of the difference between
VCR and
is the most important when seeking to achieve a negative value of α
v.
Particularly noteworthy is the low value of α
v for the Pb-cooled Th-cycle hybrid reactor in this study (
Section 6).
Herein, only the calculated results for liquid Pb and Na cooled reactors are presented. However, the hybrid concept could be useful for obtaining a negative value of αv in reactors cooled using other liquids.