Reactive Power Compensation for Single-Phase AC Motors Using Integral Power Theory
Abstract
1. Introduction
- power quality assessment,
- the detection of main waveform distortion sources, and
- theoretical calculations for the design of active filters and compensators.
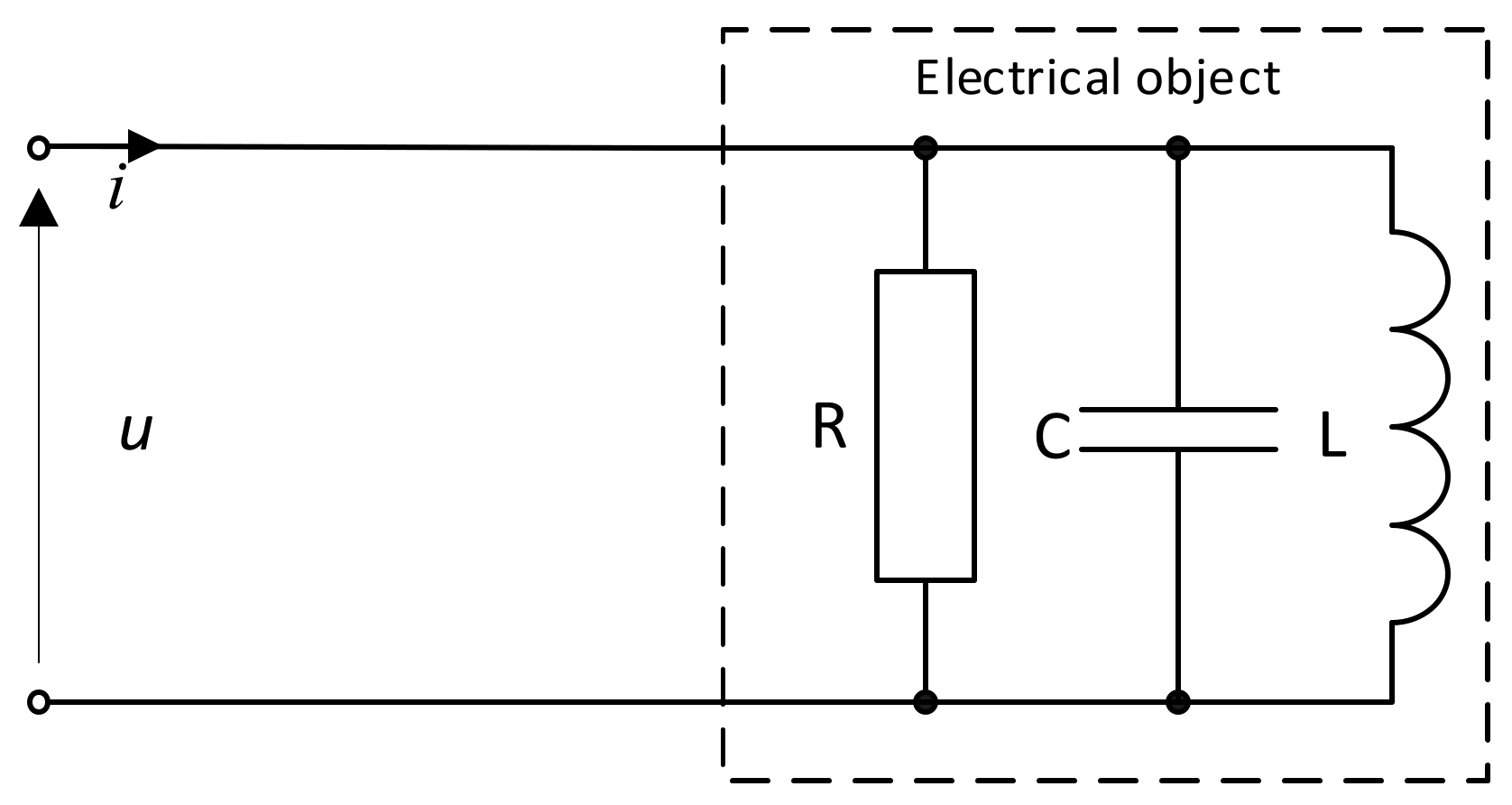
2. Integral Definitions of Reactive Power
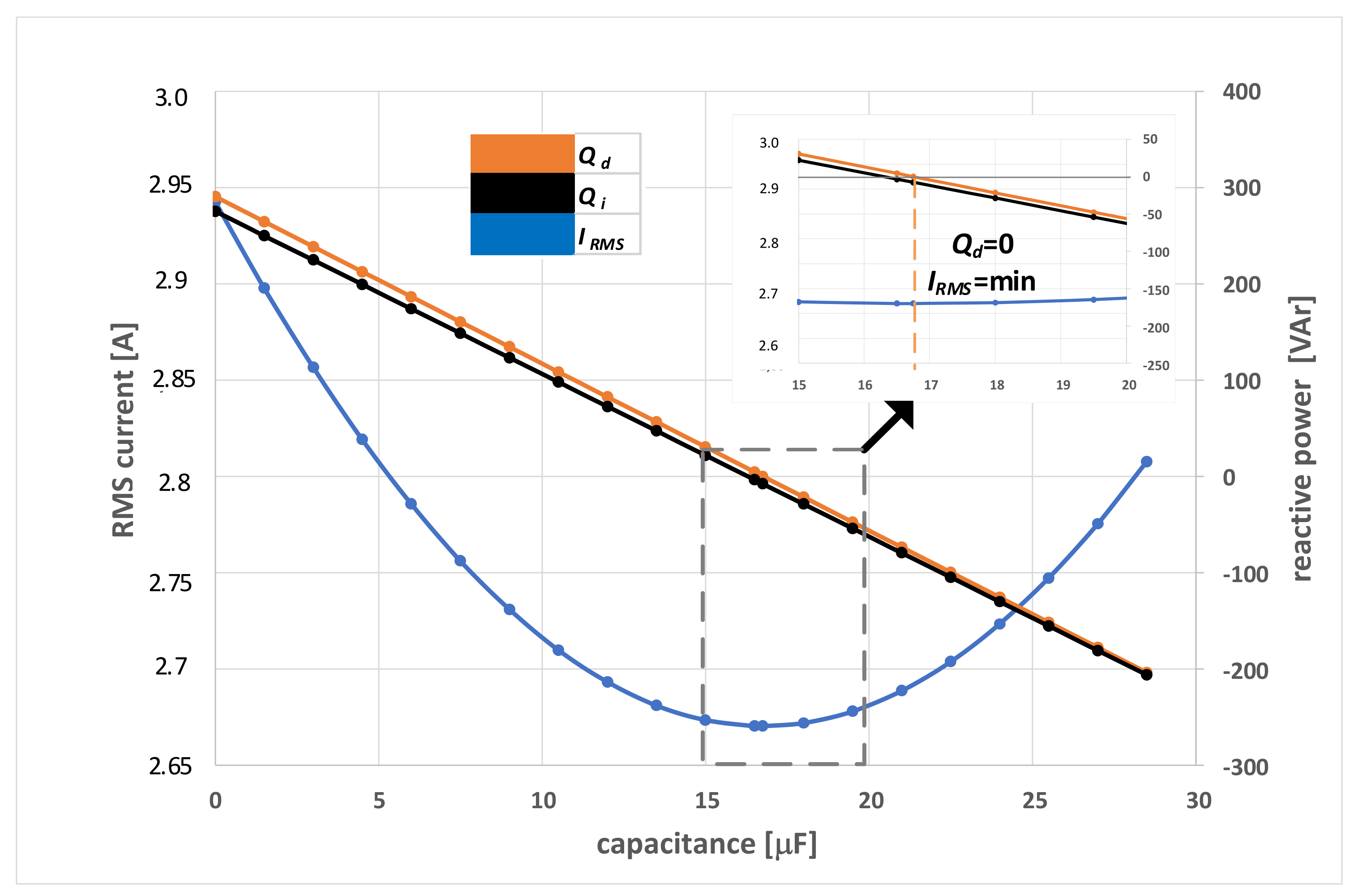
3. Minimization of the RMS Value of the Load Current or Voltage

3.1. Minimization of the RMS Current Value with a Parallel-Connected Capacitor
3.2. Minimization of the RMS Current Value with a Parallel-Connected Inductor
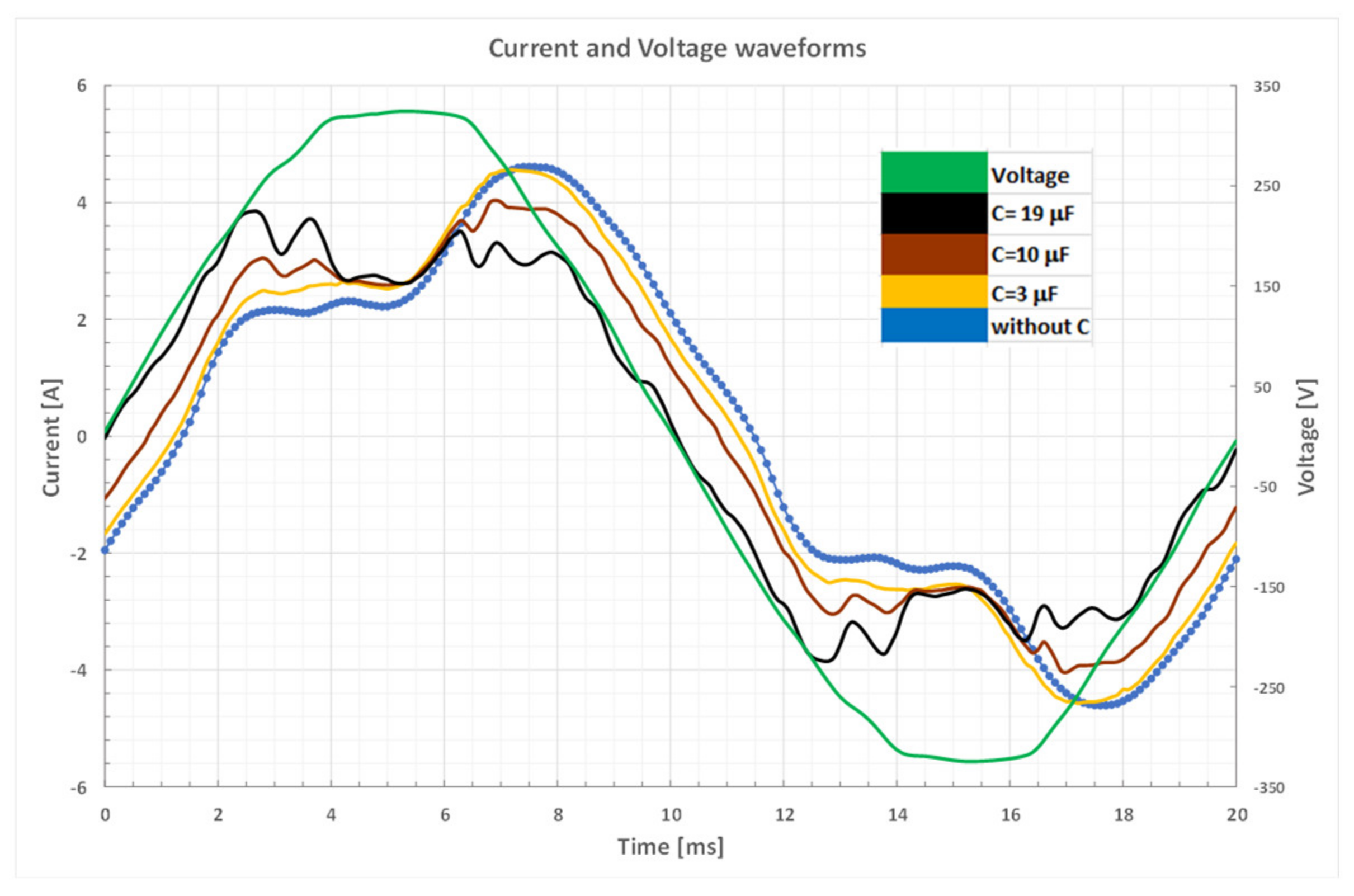
4. Results and Discussion
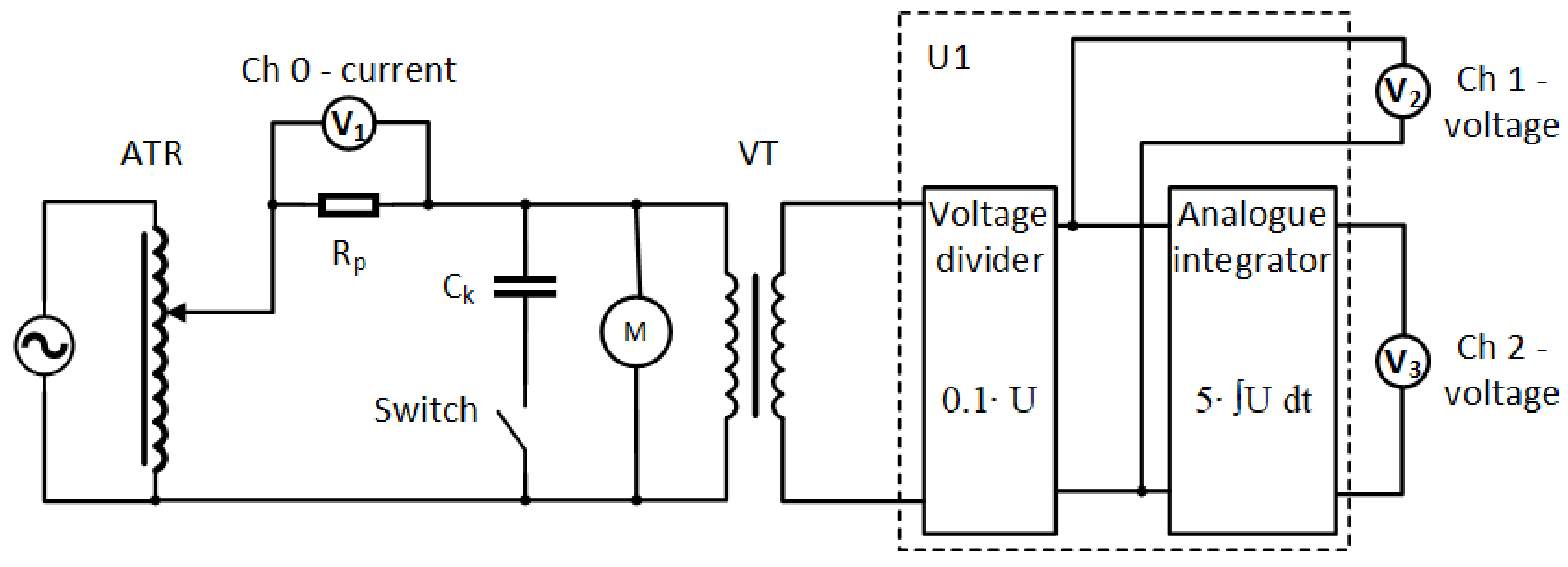
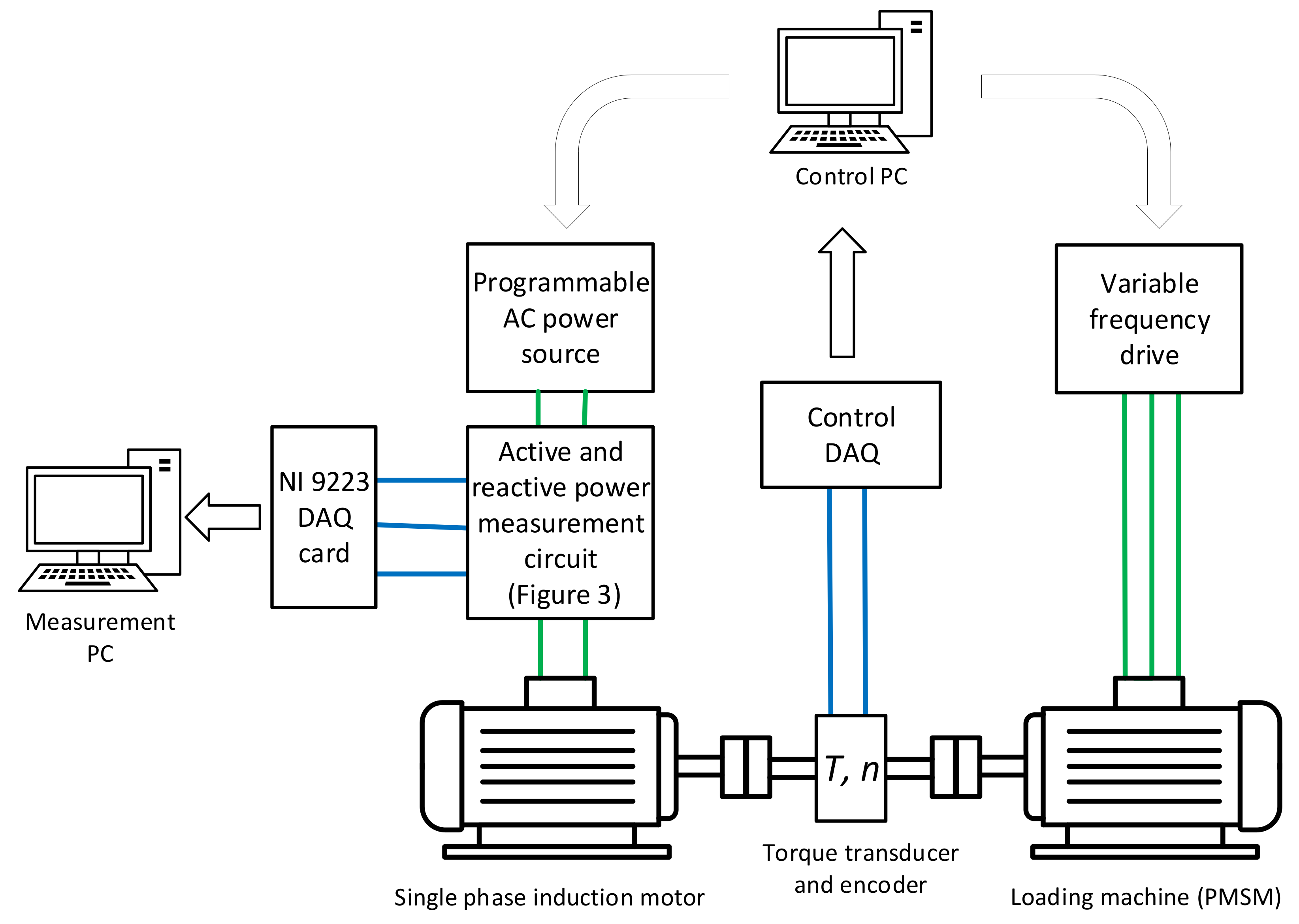
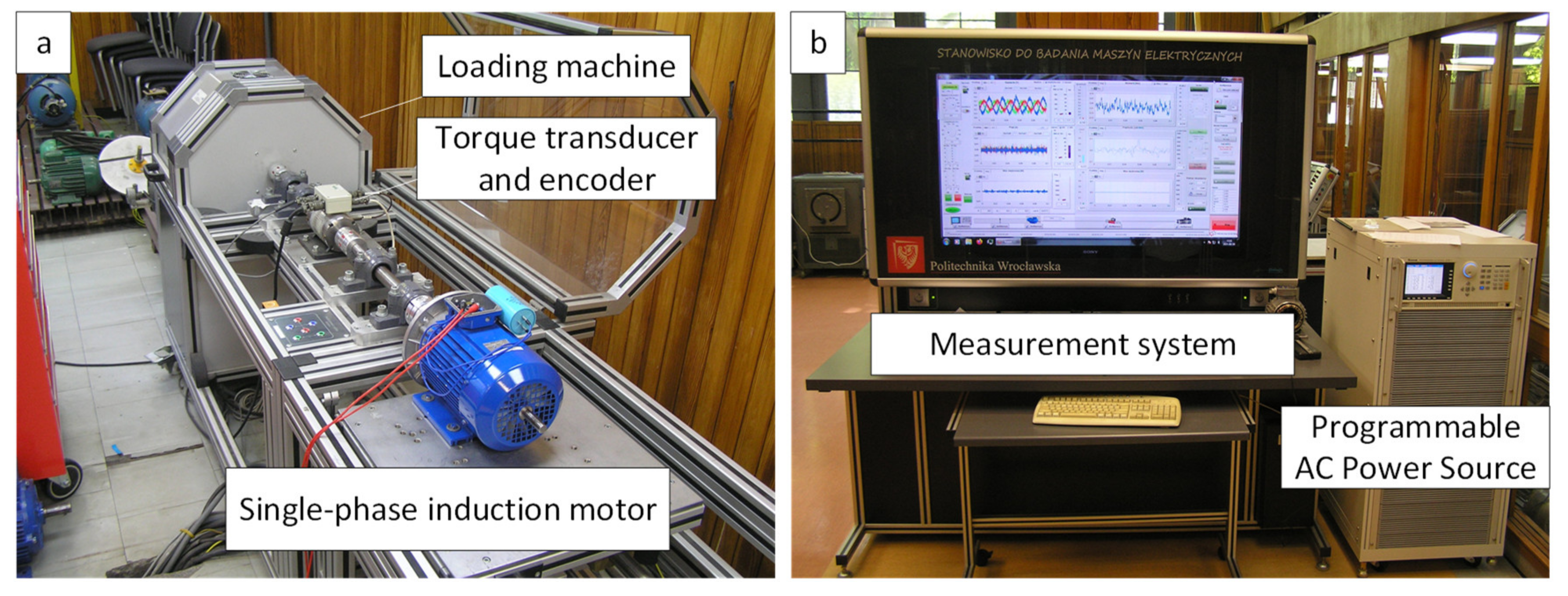
4.1. Description of the Research Object and Measurement Setups
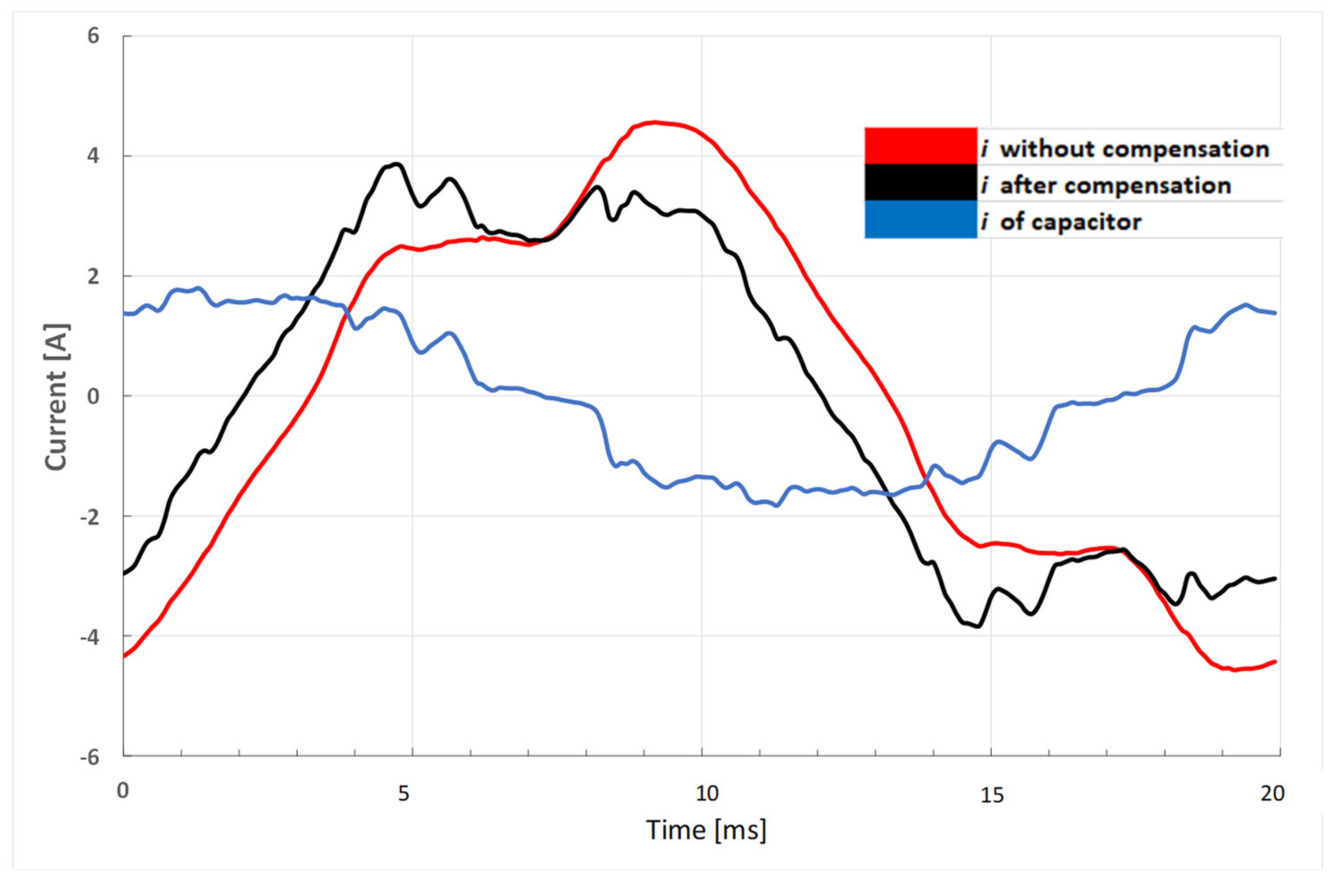
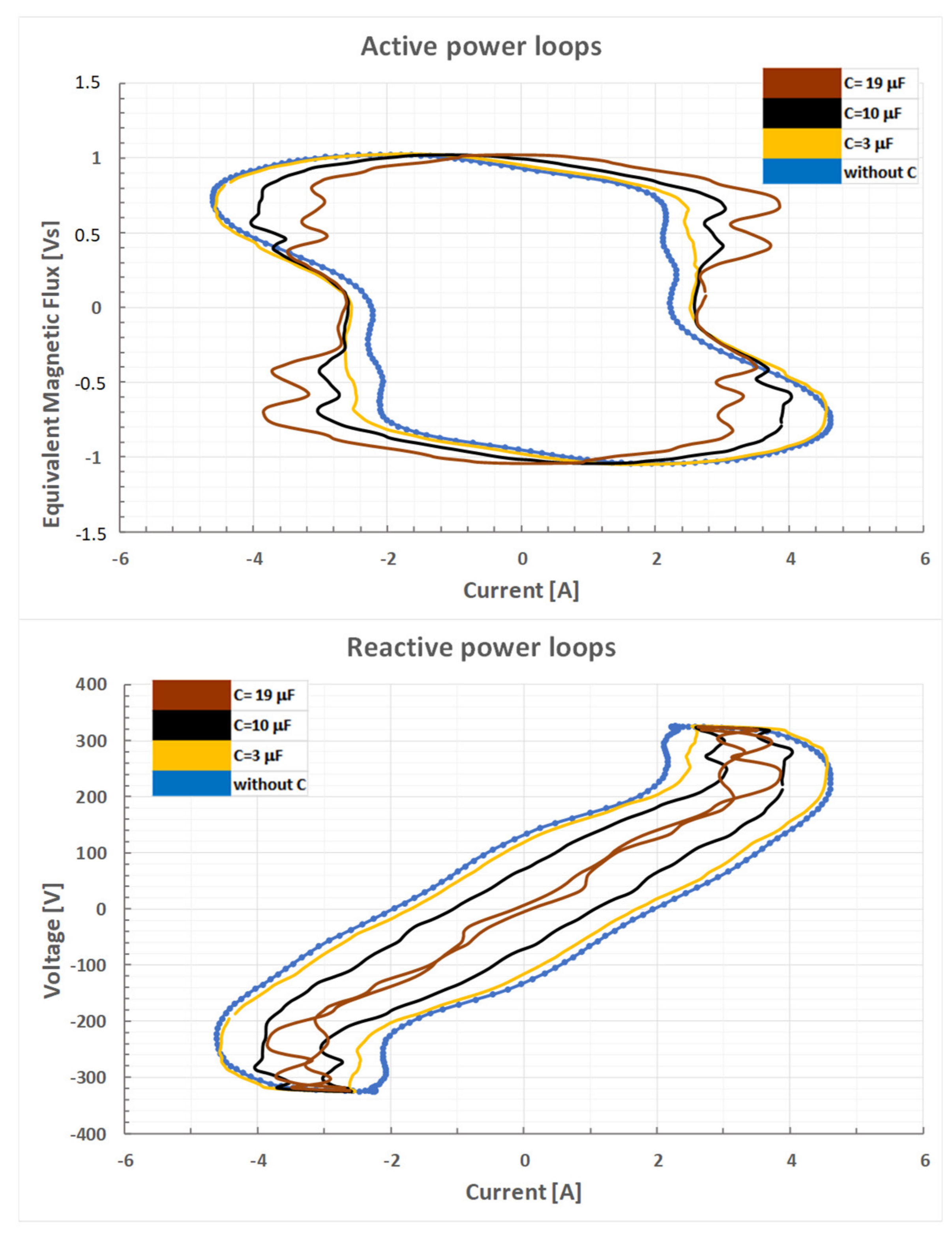
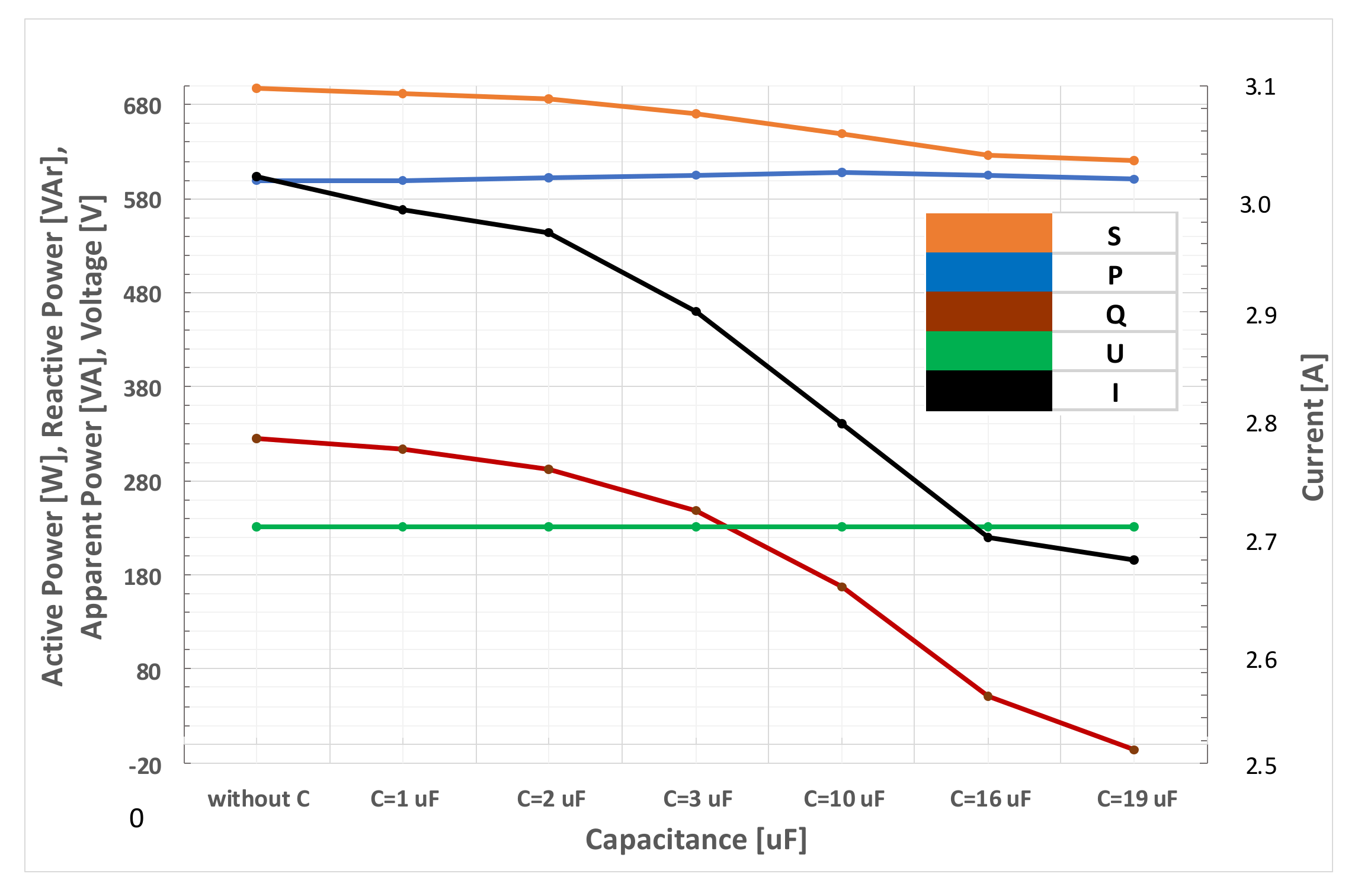
4.2. Reactive Power Compensation of the Load
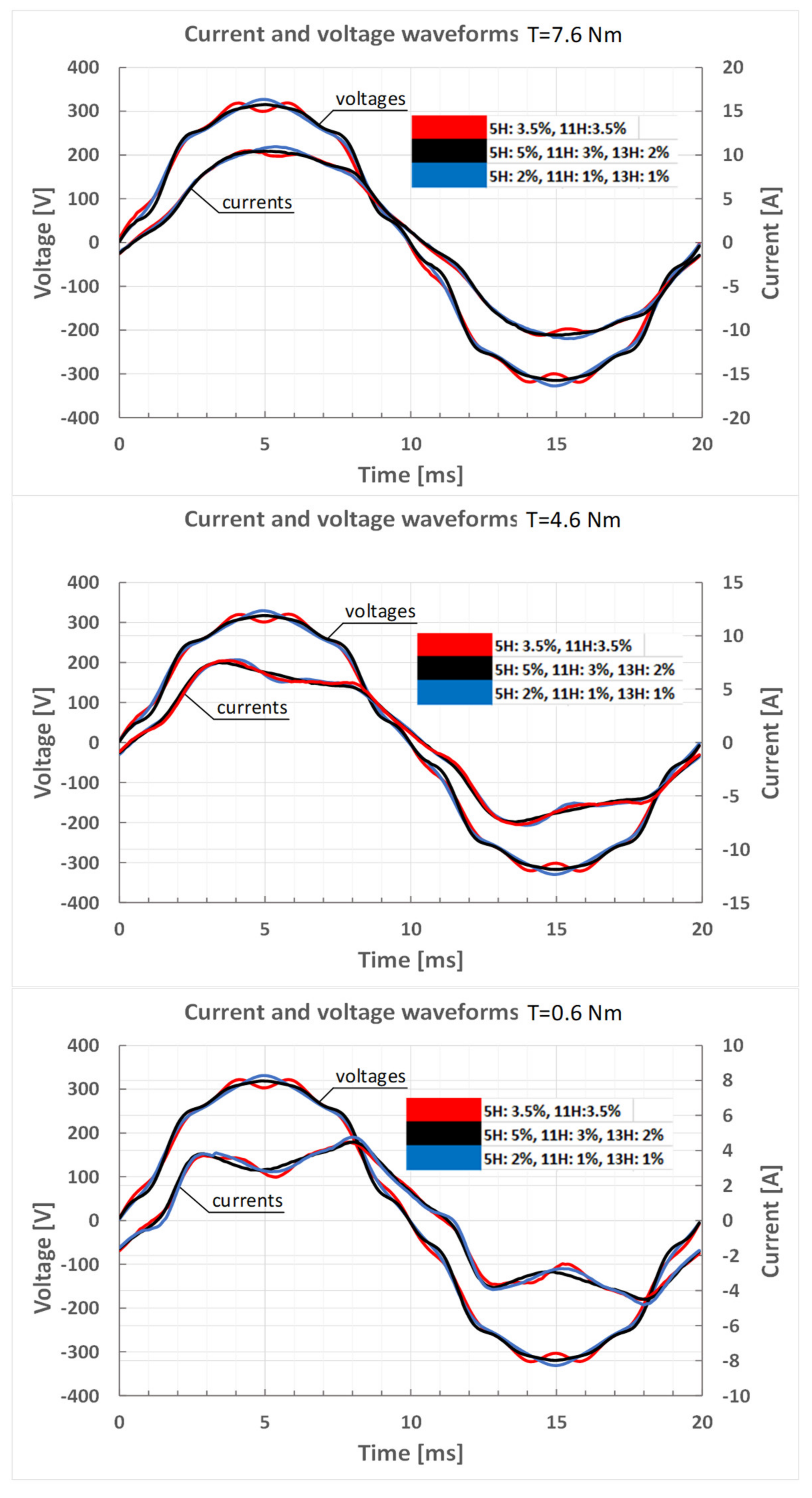
4.3. Effects of Distorted Voltage on Power Values
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balci, M.E.; Hocaoglu, M.H. Comparison of power definitions for reactive power compensation in nonsinusoidal conditions. In Proceedings of the 2004 11th International Conference on Harmonics and Quality of Power (IEEE Cat. No.04EX951), Lake Placid, NY, USA, 12–15 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Czarnecki, L.S. Considerations on the Reactive Power in Nonsinusoidal Situations. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1985, IM-34, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, W.; Zakikhani, P. Suggested definition and power factor improvement in nonlinear systems. Proc. Inst. Electr. Eng. 1972, 119, 1361–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusters, N.L.; Moore, W.J.M. On the definition of rectiwe power under nonsinusoidal conditions. IEEE Trans. Pow. Appl. Syst. 1980, PAS-99, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnecki, L.S. What is wrong with the Budeanu Concept of reactive and distortion power and why it should be abandoned. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1987, IM-36, 834–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnecki, S.; Pearce, S.S. CPC-based comparison of compensation goals in systems with nonsinusoidal voltages and currents. In Proceedings of the 2010 International School on Nonsinusoidal Currents and Compensation, Lagow, Poland, 15–18 June 2010; pp. 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnecki, L.S. Currents’ Physical Components (CPC)-based power theory a review part II: Filters and reactive, switching and hybrid compensators. Prz. Elektrotechniczny 2020, 20, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sołjan, Z.; Zajkowski, M.; Borusiewicz, A. Reactive Power Compensation and Distortion Power Variation Identification in Extended Budeanu Power Theory for Single-Phase Systems. Energies 2024, 17, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulović, J.Č.; Šekara, T.B. Power Definitions for Nonsinusoidal Unbalanced Three-Phase Four-Wire Systems with Different Neutral Conductor Resistance. In Proceedings of the 2025 24th International Symposium INFOTEH-JAHORINA (INFOTEH), East Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 19–21 March 2025; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE 1459-2010; IEEE Standard Definitions for the Measurement of Electric Power Quantities Under Sinusoidal, Nonsinusoidal, Balanced or Unbalanced Conditions. IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2010.
- Xavier, G.L.; Miyasaka, G.; Silvério, E.T.; da Silva, H.R.J.; Braz, L.L.; de Oliveira, R.F.B.; Lima, R.N.C.; Macedo, J.R., Jr. An update on the performance of reactive energy meters under non-sinusoidal conditions. Electr. Eng. 2020, 102, 1881–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anu, G.; Francis, M. Fernandez, Reactive Power Measurement in Power Systems with Harmonic Currents. In Proceedings of the 2024 Third International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Information and Communication Technologies (ICEEICT), Trichirappalli, India, 24–26 July 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Abreu, A.-D.; Osornio-Rios, R.-A.; Jaen-Cuellar, A.-Y.; Delgado-Prieto, M.; Antonino-Daviu, J.-A.; Karlis, A. Advances in Power Quality Analysis Techniques for Electrical Machines and Drives: A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepliński, M.; Adamczak, D.; Gnaciński, P. Single-Phase Induction Motor Under Voltage Fluctuations. Sci. J. Gdyn. Marit. Univ. 2022, 123, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnaciński, P.; Hallmann, D.; Muc, A.; Klimczak, P.; Pepliński, M. Induction Motor Supplied with Voltage Containing Symmetrical Subharmonics and Interharmonics. Energies 2022, 15, 7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elphick, S.; Crawford, M.; Perera, S.; Ciufo, P. Laboratory investigation of the impact of PQ on induction motor performance. In Proceedings of the 2018 18th International Conference on Harmonics and Quality of Power (ICHQP), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 13–16 May 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Parida, S. Performance of single phase induction motor under different supply quality. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 6th International Conference on Power Systems (ICPS), New Delhi, India, 4–6 March 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donolo, P.; Pezzani, C.; Bossio, G.; De Angelo, C.; Donolo, M. Derating of Induction Motors Due to Power Quality Issues Considering the Motor Efficiency Class. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogburn, A.; Bhattarai, P. Reactive Power Compensation of Induction Motors Supplied with Unbalanced Voltage. In Proceedings of the 2024 56th North American Power Symposium (NAPS), El Paso, TX, USA, 13–15 October 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.R.L.; Soares, L.T.F.; Coelho, A.L.M. Back-to-Back Inverter for Induction Machine Drive with Harmonic Current Compensation and Reactive Power Tolerance to Voltage Sags. Energies 2024, 17, 4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhong, L.; Zhao, J.; Gao, G. Single-Phase Reactive Power Compensation Control for STATCOMs via Unknown System Dynamics Estimation. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8394513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkowski, T.; Nowak, M.; Piróg, S. Power Supply and Reactive Power Compensation of a Single-Phase Higher Frequency On-Board Grid with Photovoltaic Inverter. Energies 2022, 15, 2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliovici, M. Definition et Measure de la Puissance et de L’Energie Reactives (The definition and measurement reactive power and energy). Bull. Soc. Franc. Electr. 1925, 5, 931–956. [Google Scholar]
- Kosobudzki, G.; Nawrocki, Z.; Nowak, J. Measure of electric reactive power. Metrol. Meas. Syst. 2005, 12, 131–149. Available online: http://www.metrology.pg.gda.pl/full/2005/M&MS_2005_131.pdf (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Schurov, N.I.; Myatezh, S.V.; Myatezh, A.V.; Malozyomov, B.V.; Shtang, A.A. Inactive power detection in AC network. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2021, 11, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosobudzki, G.; Dusza, D. Reactive Power Measurements Based on its Geometrical Interpretation. In Proceedings of the 2018 14th Selected Issues of Electrical Engineering and Electronics (WZEE), Szczecin, Poland, 19–21 November 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, M.T.; Wojciechowski, D. Emanuel’s method versus Iliovici’s method for reactive power compensation in passive-active power conditioning scheme. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference-Workshop Compatibility and Power Electronics, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 5–7 June 2013; pp. 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated power | 1.1 kW |
| Rated voltage | 230 V |
| Rated frequency | 50 Hz |
| Rated current | 7.5 A |
| Rated efficiency | 70% |
| Rated power factor | 0.96 |
| Rated speed | 1380 rpm |
| Rated torque | 7.6 N∙m |
| Breakdown torque ratio | 1.4 |
| Starting torque ratio | 0.4 |
| Starting current ratio | 2.5 |
| Run capacitor | 30 μF |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kosobudzki, G.; Dusza, D.; Ciurys, M.P.; Leicht, A. Reactive Power Compensation for Single-Phase AC Motors Using Integral Power Theory. Energies 2025, 18, 2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102641
Kosobudzki G, Dusza D, Ciurys MP, Leicht A. Reactive Power Compensation for Single-Phase AC Motors Using Integral Power Theory. Energies. 2025; 18(10):2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102641
Chicago/Turabian StyleKosobudzki, Grzegorz, Daniel Dusza, Marek Pawel Ciurys, and Aleksander Leicht. 2025. "Reactive Power Compensation for Single-Phase AC Motors Using Integral Power Theory" Energies 18, no. 10: 2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102641
APA StyleKosobudzki, G., Dusza, D., Ciurys, M. P., & Leicht, A. (2025). Reactive Power Compensation for Single-Phase AC Motors Using Integral Power Theory. Energies, 18(10), 2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102641






