Position Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Improved Model Reference Adaptive Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
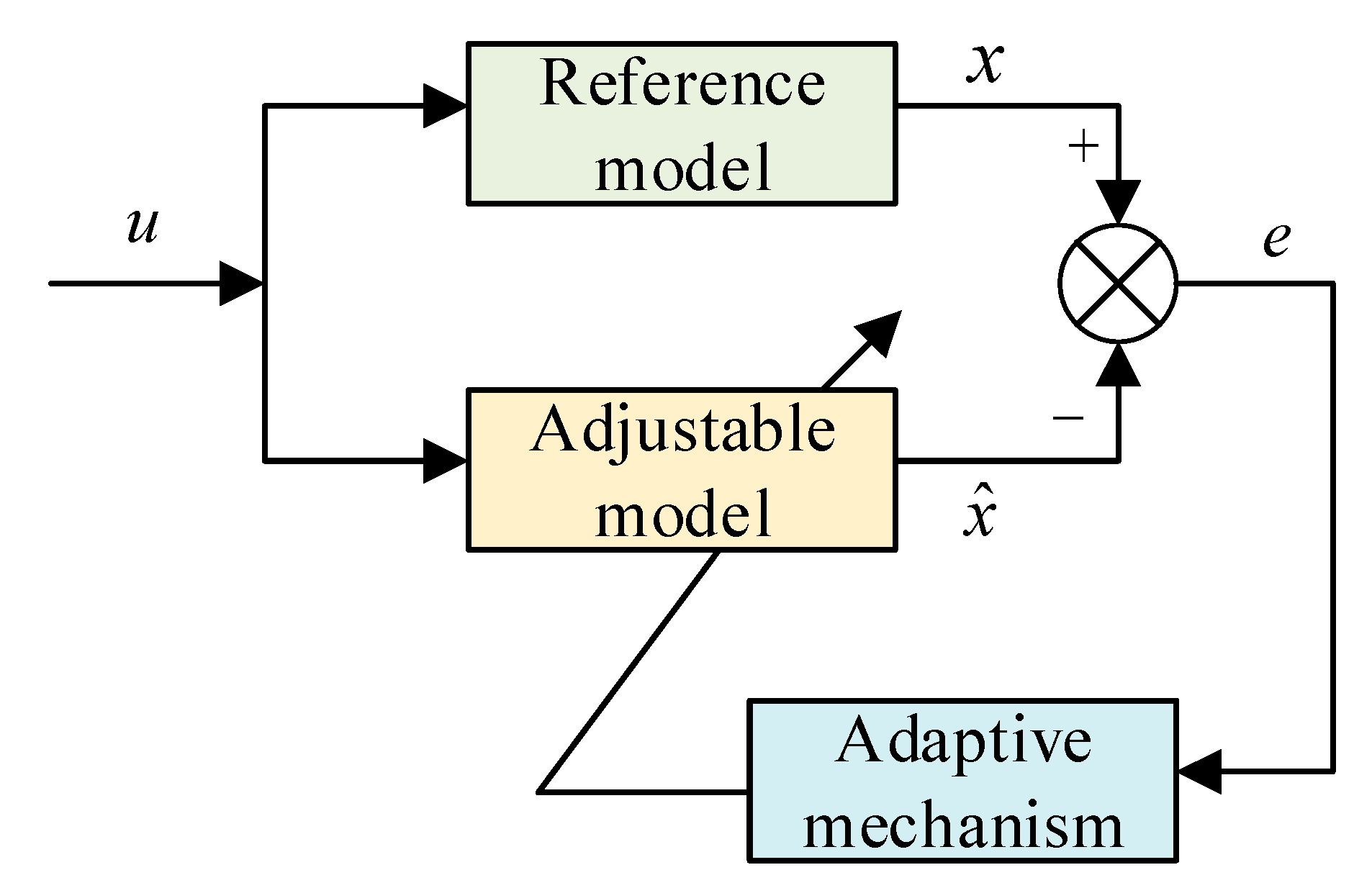
2. PMSM Model Reference Adaptive System
2.1. Selection of Reference Model and Adjustable Model
2.2. Selection of the Adaptive Law
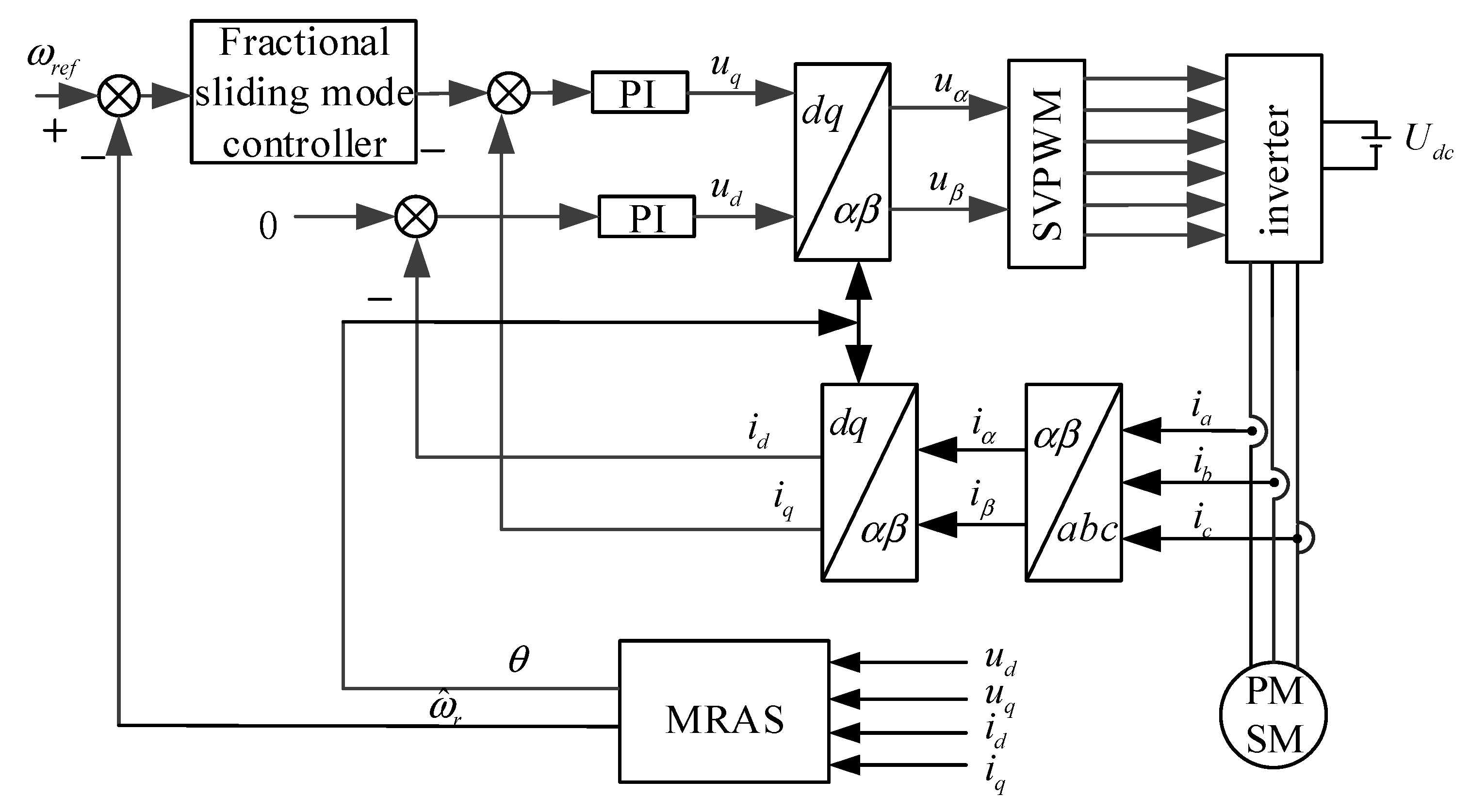
3. Design of the Sliding Mode Controller
3.1. Construction of the Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Surface
3.2. Design of the Reaching Law
3.3. Design of the Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Controller
4. Simulation and Experimental Results Analysis
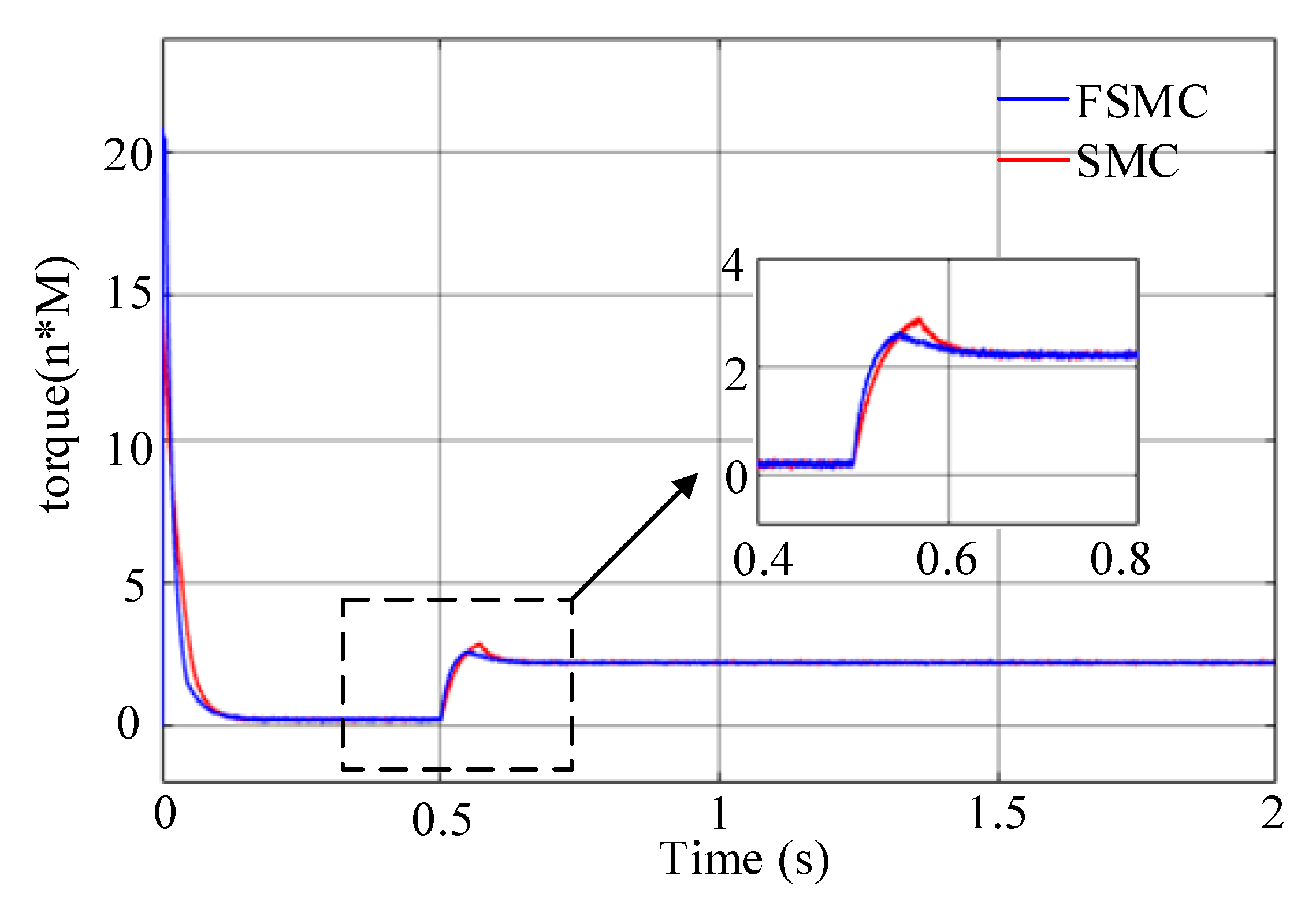
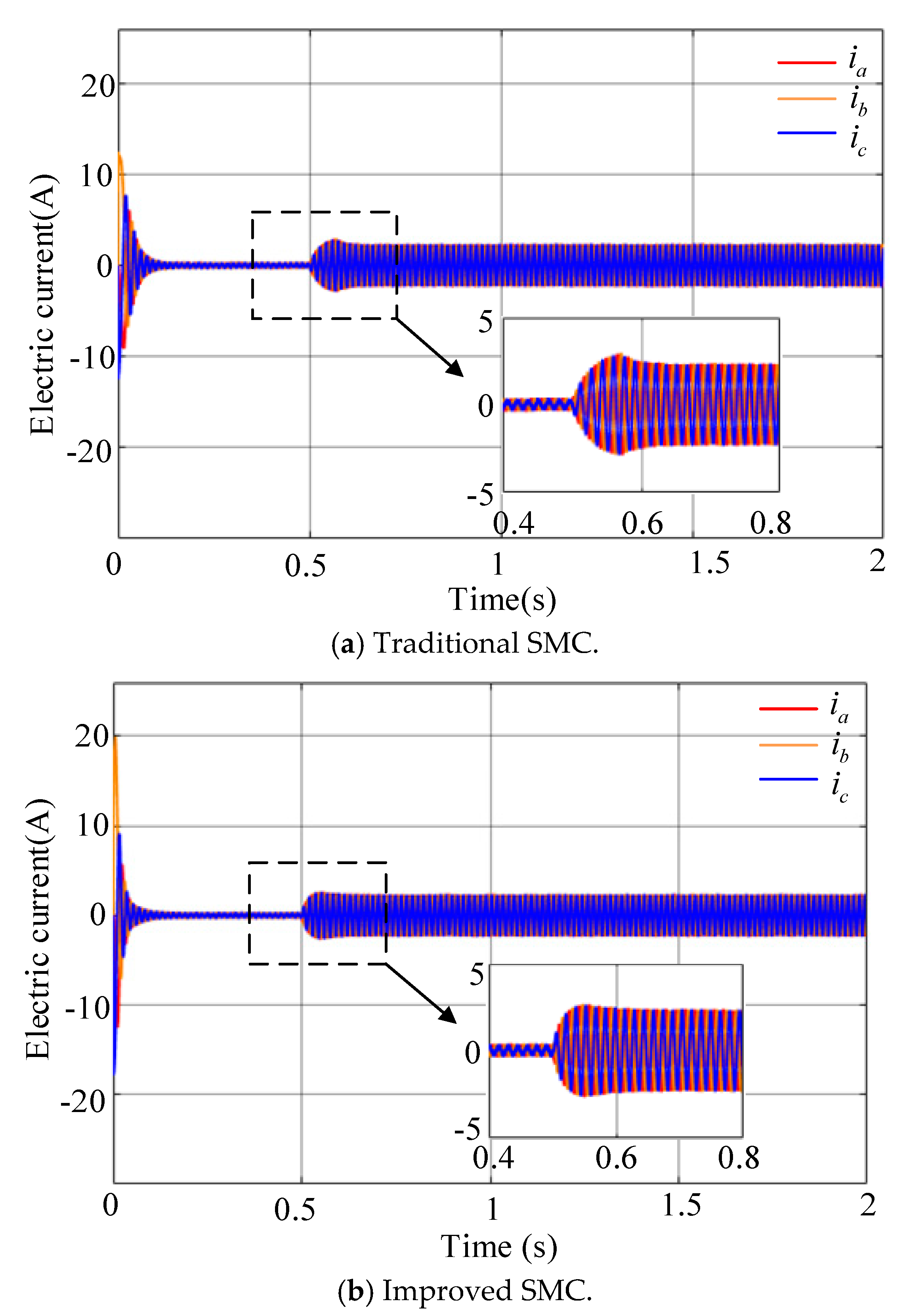
4.1. Simulation Analysis
4.2. Experimental Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wen, H.; Feng, K.; Yu, F.; Liu, C. A Novel Winding Connection Sequence of Dual Three-Phase Series-End Winding PMSM Drive for Speed Range Extension. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2023, 59, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Qu, R.; Shi, H.; Ni, J. Review of high-efficiency control dtrategy for permanent magnet synchronous motors under wide speed range. Proceeding CSEE 2023, 43, 2496–2512. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Song, C.; Chen, G. Research on speed sensorless control of permanent magnet synchronous motor. Modul. Mach. Tool Autom. Manuf. Tech. 2023, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Dong, D. Dynamic performance enhancement method based on improved model reference adaptive system for SPMSM sensorless drives. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 135012–135023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Lian, W. Research on control of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on high frequency quadrature square wave injection method. Electr. Mach. Control 2024, 28, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J. Winding condition monitoring for inverter-fed PMSM using high-frequency current injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 5818–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.L.; Li, J.; Qu, R.H. Sensorless control of permanent magnet synchronous machine based on second-order sliding-mode observer with online resistance estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 3672–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhu, X.; Niu, F.; Liu, X.; Li, S. Position sensorless control of PMSM based on improved integrated sliding mode observer. Proc. CSEE 2024, 44, 3269–3277. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Z.; Li, Y.; Luo, J.; Li, F.; Dai, Q. Position sensorless vector control of permanent magnet synchronous motor with adaptive extended Kalman filter. Electr. Mach. Control 2024, 28, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Yang, R.; Hu, W.; Huang, Z. FPGA-based sensorless speed control of PMSM using enhanced performance controller based on the reduced-order EKF. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2019, 9, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, H.; Xu, Y. PMSM model predictive torque control based on extended Kalman filter parameter identification. Electr. Mach. Control 2023, 27, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, F.; Xie, Y.; Wang, M.; Lin, H. Sensorless control of PMSM based on improved ADRC. Electr. Mach. Control 2024, 28, 50–60. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, B.; Wei, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, W. The new model refers to adaptive PMSM beat free current predictive control. Electr. Mach. Control 2023, 27, 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, F.; Xu, B.; Shi, G.; Ji, W.; Ding, S. Sensorless Vector Control of PMSM Based on Improved Sliding Mode Observer. In Proceedings of the Chinese Intelligent Systems Conference 2016, Xiamen, China, 28 January–4 February 2016; pp. 23–334. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, G.; Yan, Y.; Jun, W.; Ru, Z.Y.; Peng, Z.X. Rotor Position Estimation of Sensorless PMSM Based on Extented Kalman Filter. In Proceedings of the2018 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics Robotics and Automation (ICMRA), Hefei, China, 18–21 May 2018; pp. 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, A.; Husain, M.A. MRAS based Sensorless Control of Induction Motor based on Rotor Flux. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Computational and Characterization Techniques in Engineering & Sciences (CCTES), Lucknow, India, 14–15 September 2018; pp. 152–155. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Q.; Li, Z. Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Improved Model Reference Adaptive System. In Proceedings of the 2019 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Hangzhou, China, 22–24 November 2019; pp. 2422–2426. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Fan, C.; Xu, Q. Control strategy of new sliding mode variable structure on sped regulation system of permanent magnet synchronous motor. Automob. Technol. 2022, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Cao, J.; Lei, G.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, J. A composite sliding mode control for SPMSM drives based on a new hybrid reaching law with disturbance compensation. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Cheng, M.; Hua, W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, W. Sensorless control of electric continuously variable transmission based on sliding mode variable structure model reference adaptive. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2015, 30, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Wu, Y.; Meng, X.; Li, Z. Sensorless control of PMSM based on SMC and AFEKF. Transducer Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 38, 97–100, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.; Jin, M.; Shen, J. Sensorless control of the full speed range of model reference adaptive permanent magnet synchronous motor based on segmented PI regulator. Proc. CSEE 2018, 38, 1203–1211+1297. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C. Double Sliding-mode Model Reference Adaptive System Speed Identification forVector Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. Proc. CSEE 2014, 34, 897–902. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, P.; Wan, Z. Fractional-order sliding mode position tracking control for servo system with disturbance. ISA Trans. 2020, 105, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

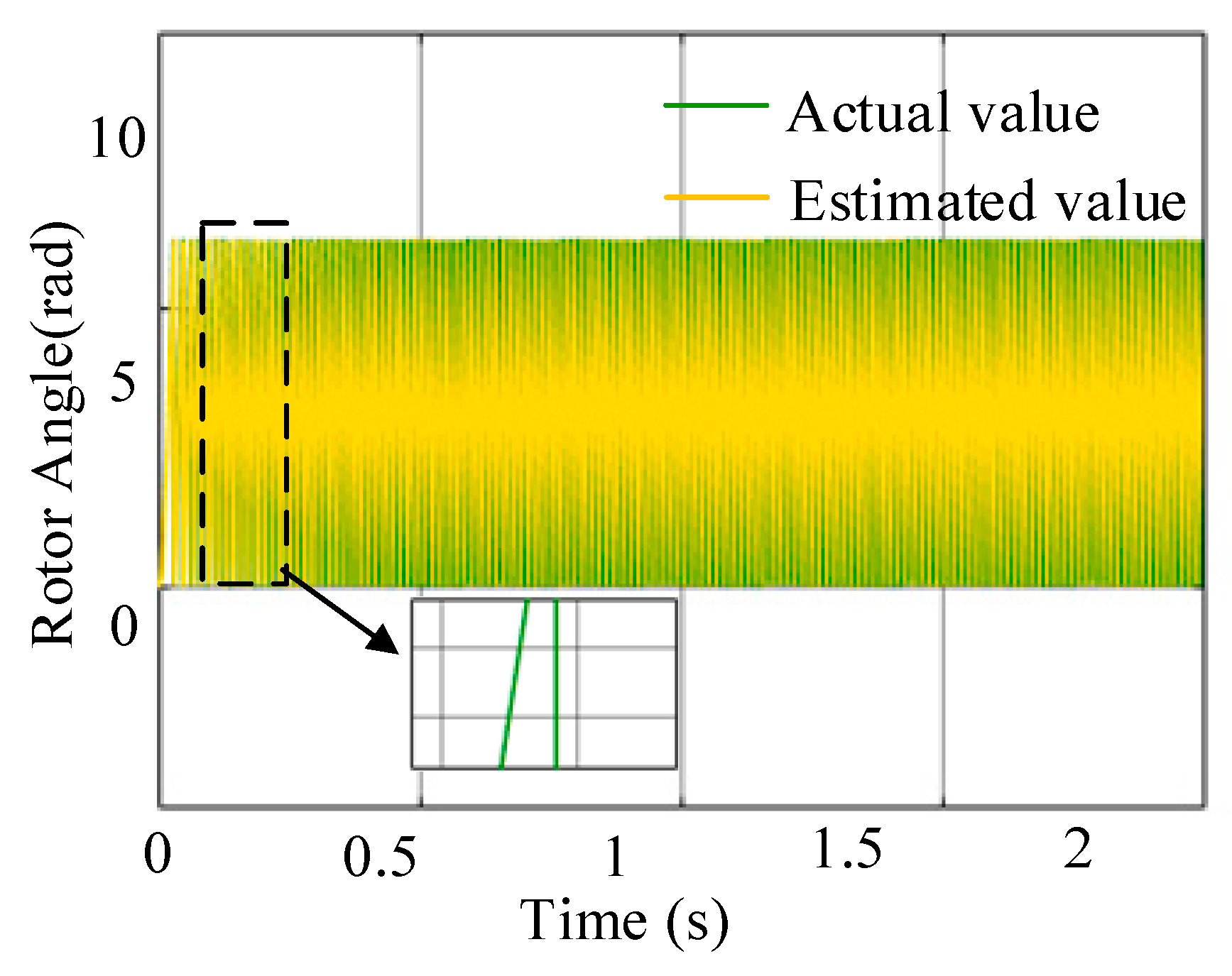


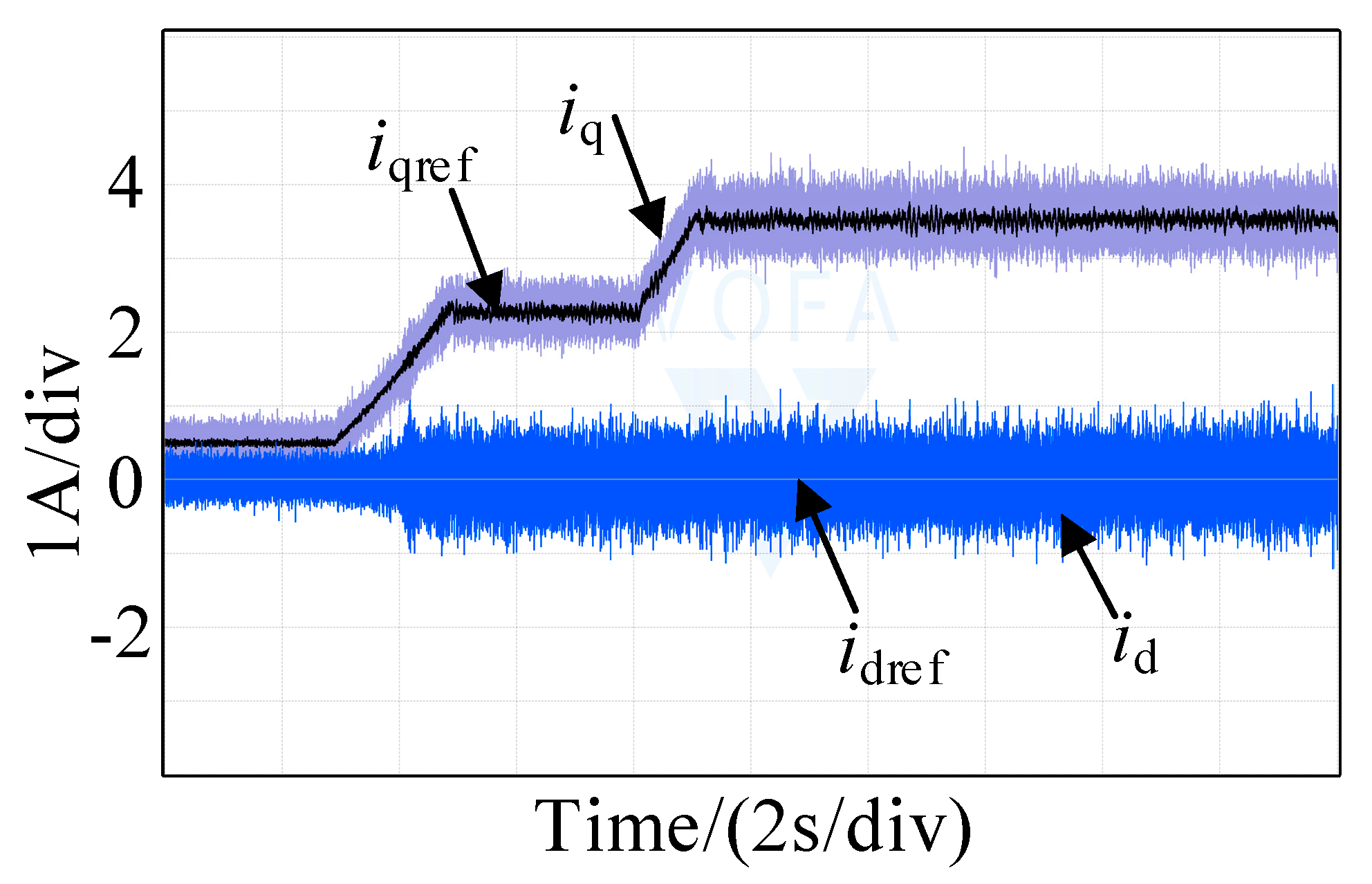



| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Stator resistance Rs/Ω | 0.117 |
| Stator inductance Ls/mH | 0.63 |
| Flux linkage Ψf/Wb | 0.041 |
| Moment of inertia J/(kg ∗ mg2) | 1.75 × 10−5 |
| Number of pole pairs pn | 1 |
| Reference speed ωref | 10000 |
| Damping coefficient B | 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Jiang, L.; Tan, K.; Wang, Y. Position Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Improved Model Reference Adaptive Systems. Energies 2025, 18, 2531. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102531
Wang M, Liu J, Jiang L, Tan K, Wang Y. Position Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Improved Model Reference Adaptive Systems. Energies. 2025; 18(10):2531. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102531
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Meng, Jian Liu, Lijun Jiang, Kun Tan, and Yiyong Wang. 2025. "Position Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Improved Model Reference Adaptive Systems" Energies 18, no. 10: 2531. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102531
APA StyleWang, M., Liu, J., Jiang, L., Tan, K., & Wang, Y. (2025). Position Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Improved Model Reference Adaptive Systems. Energies, 18(10), 2531. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102531




