Internet of Things Application in an Automated Irrigation Prototype Powered by Photovoltaic Energy
Abstract
1. Introduction
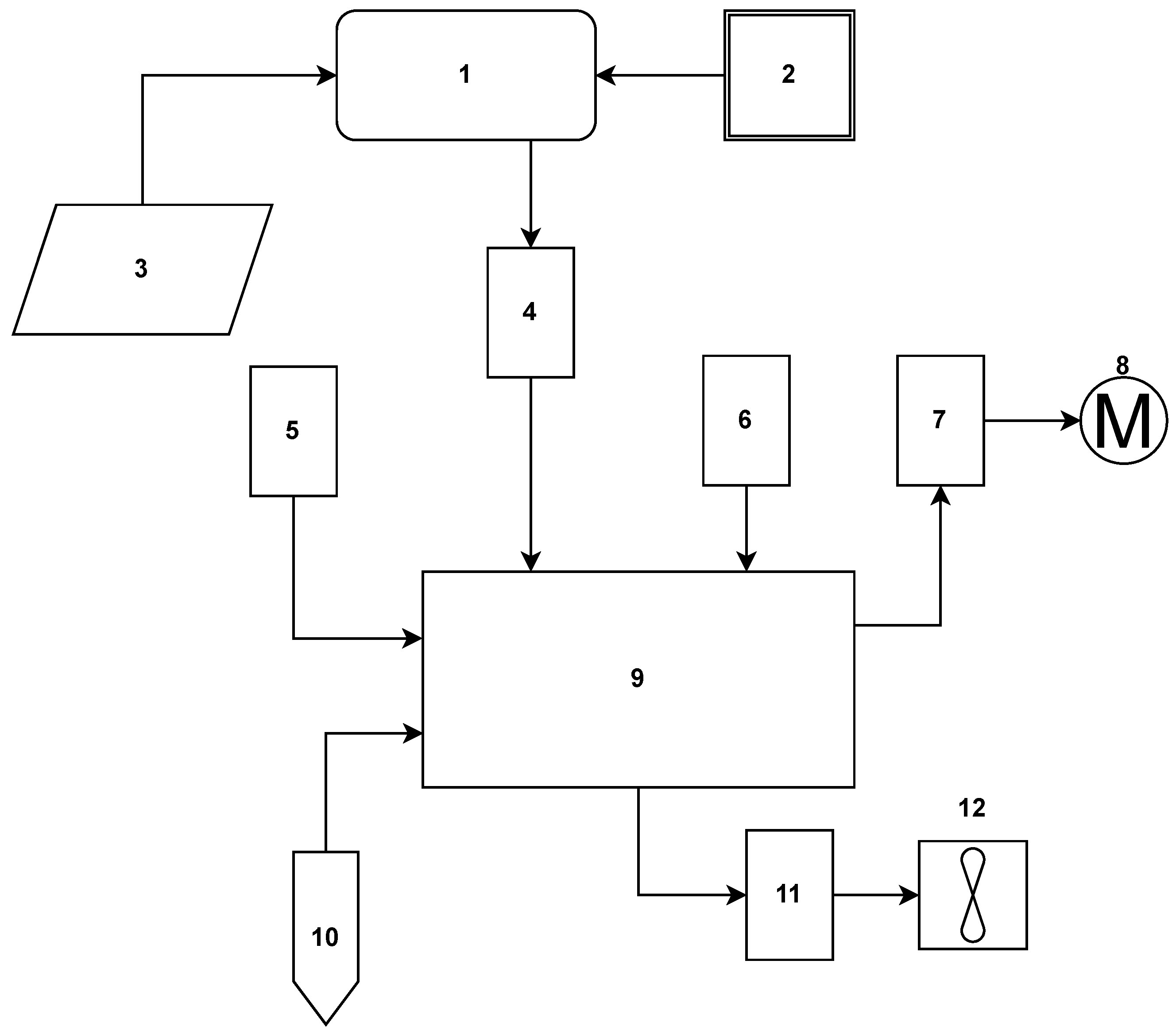
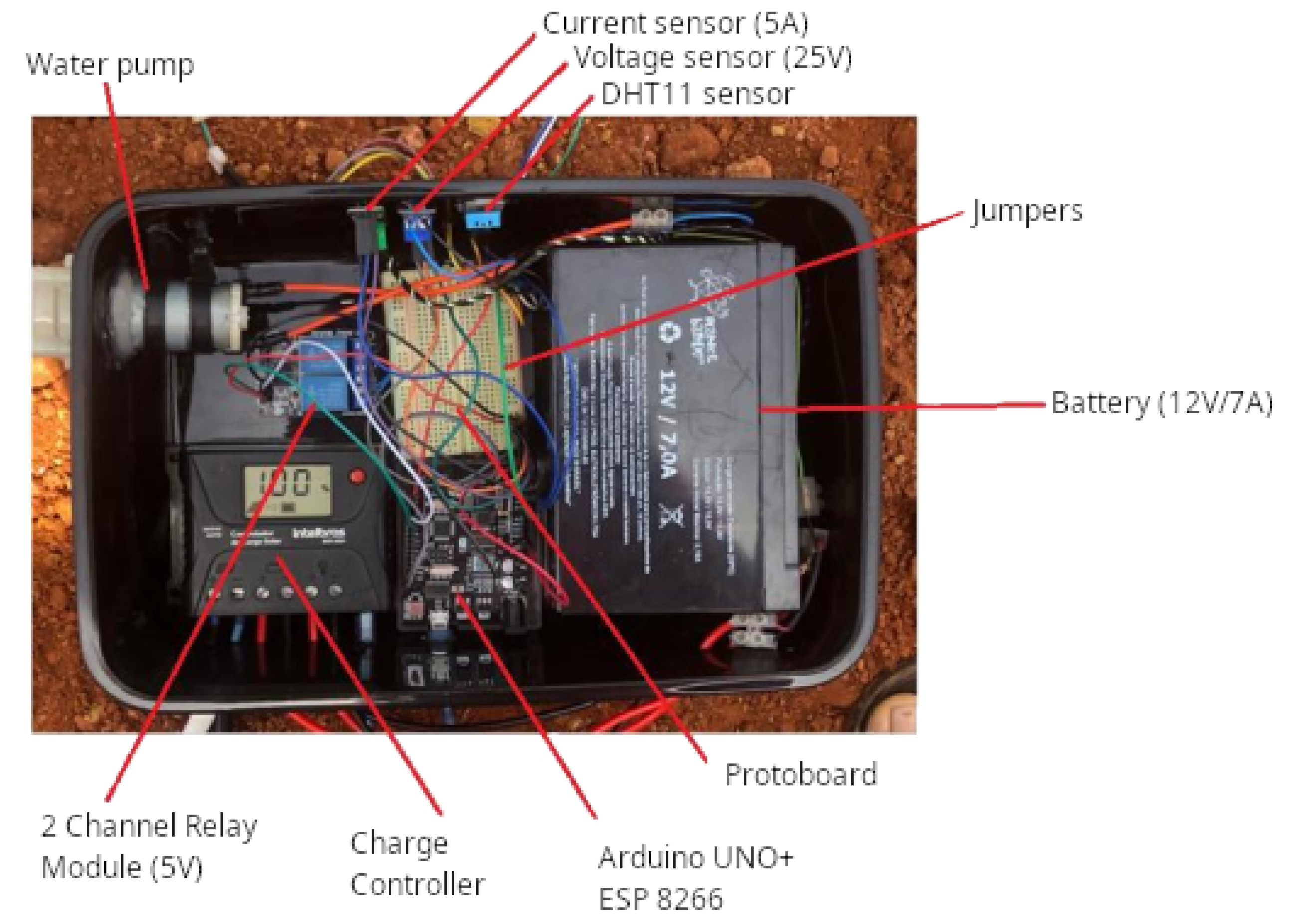
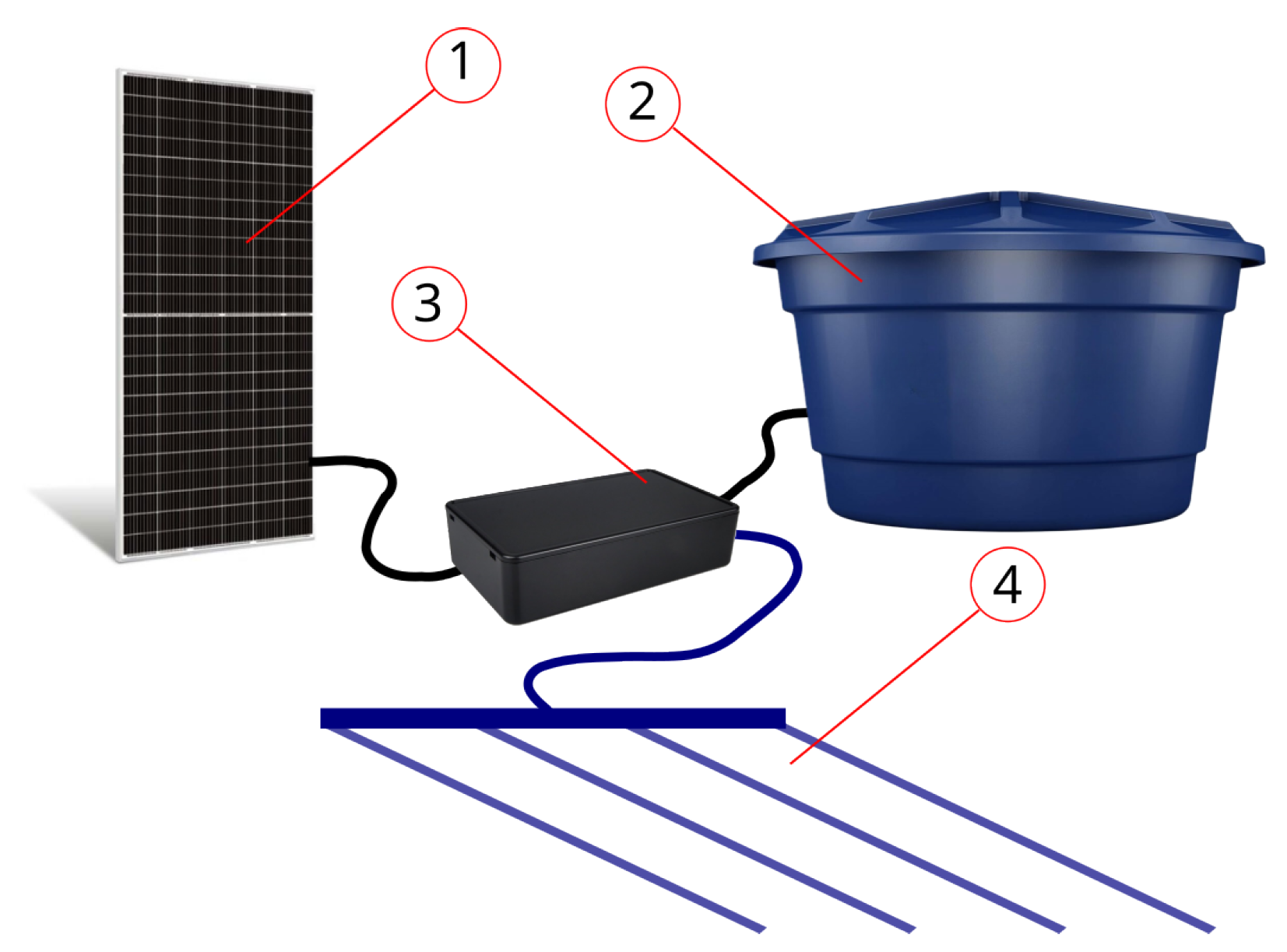
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussions
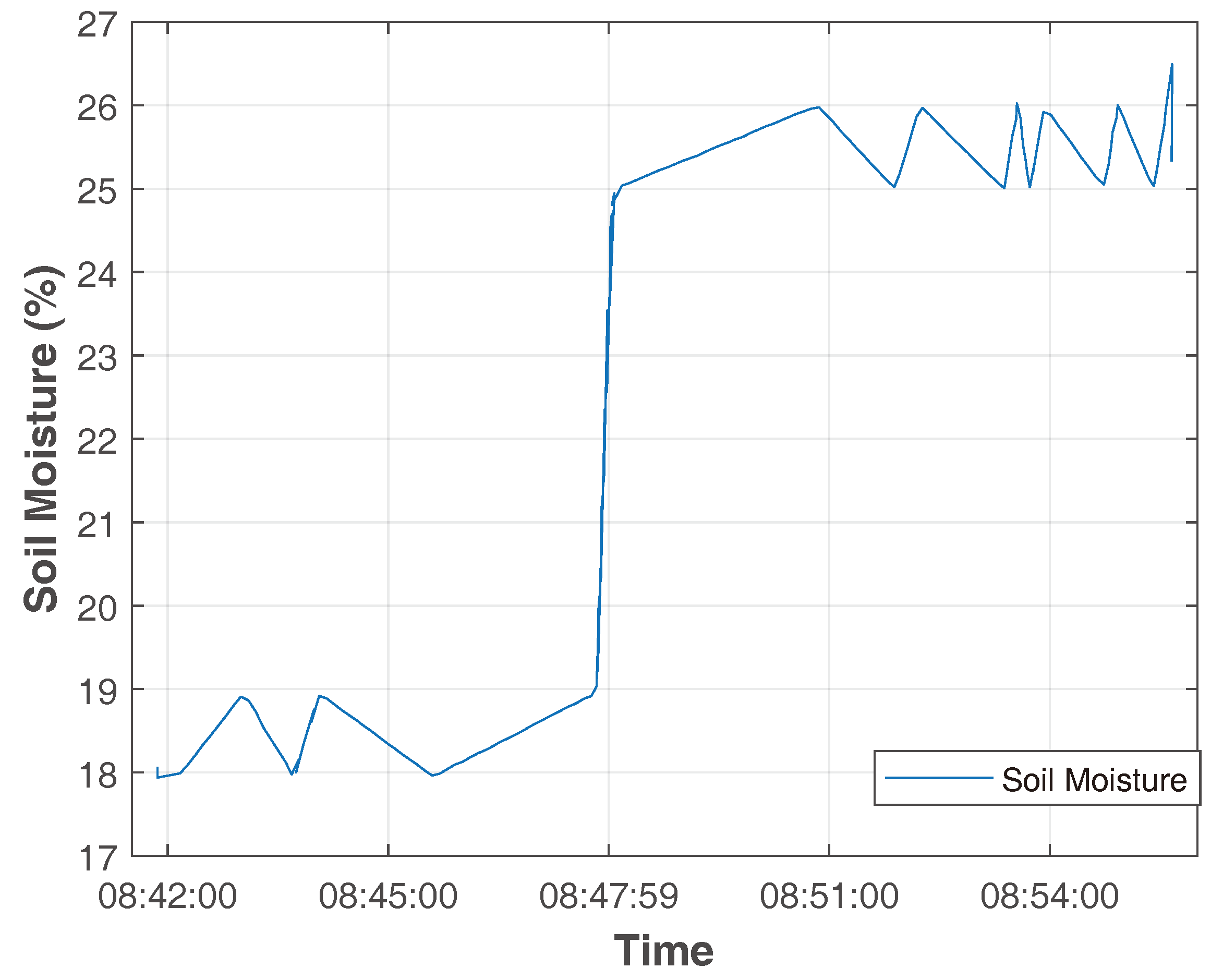
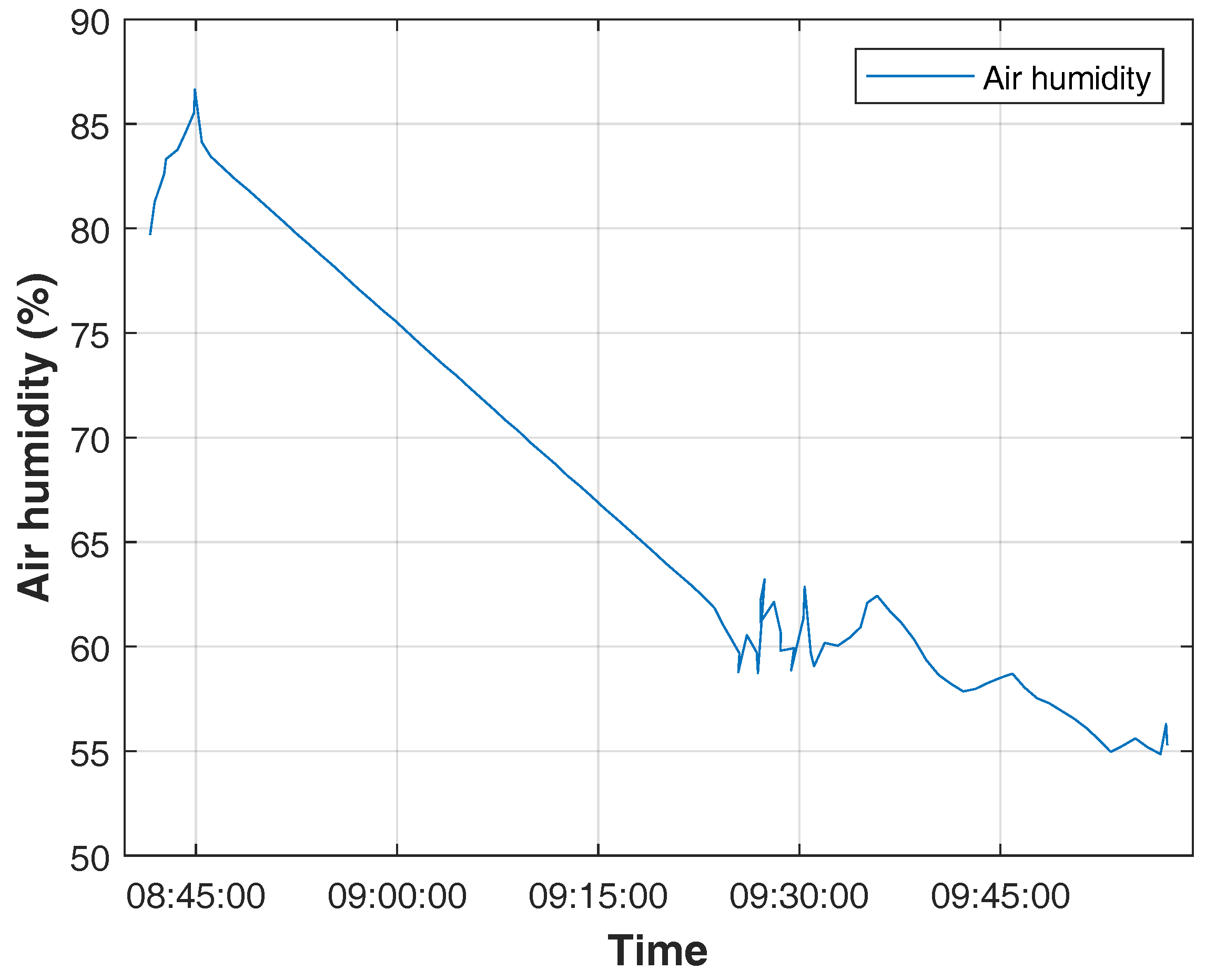
3.1. Resistive Humidity Sensor Calibration
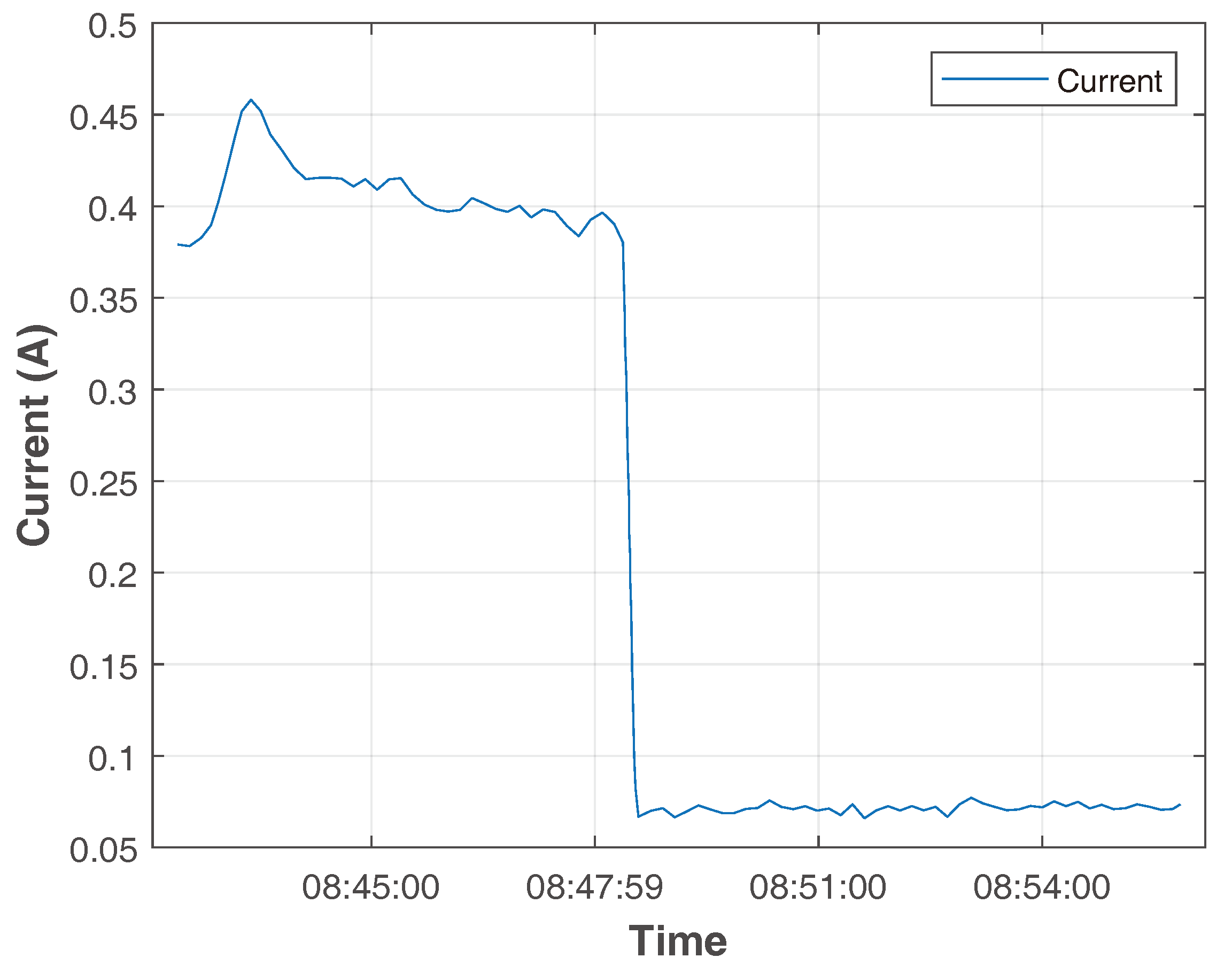
3.2. Calibration of ACS712 5A Current Sensor and 25 V Voltage Sensor
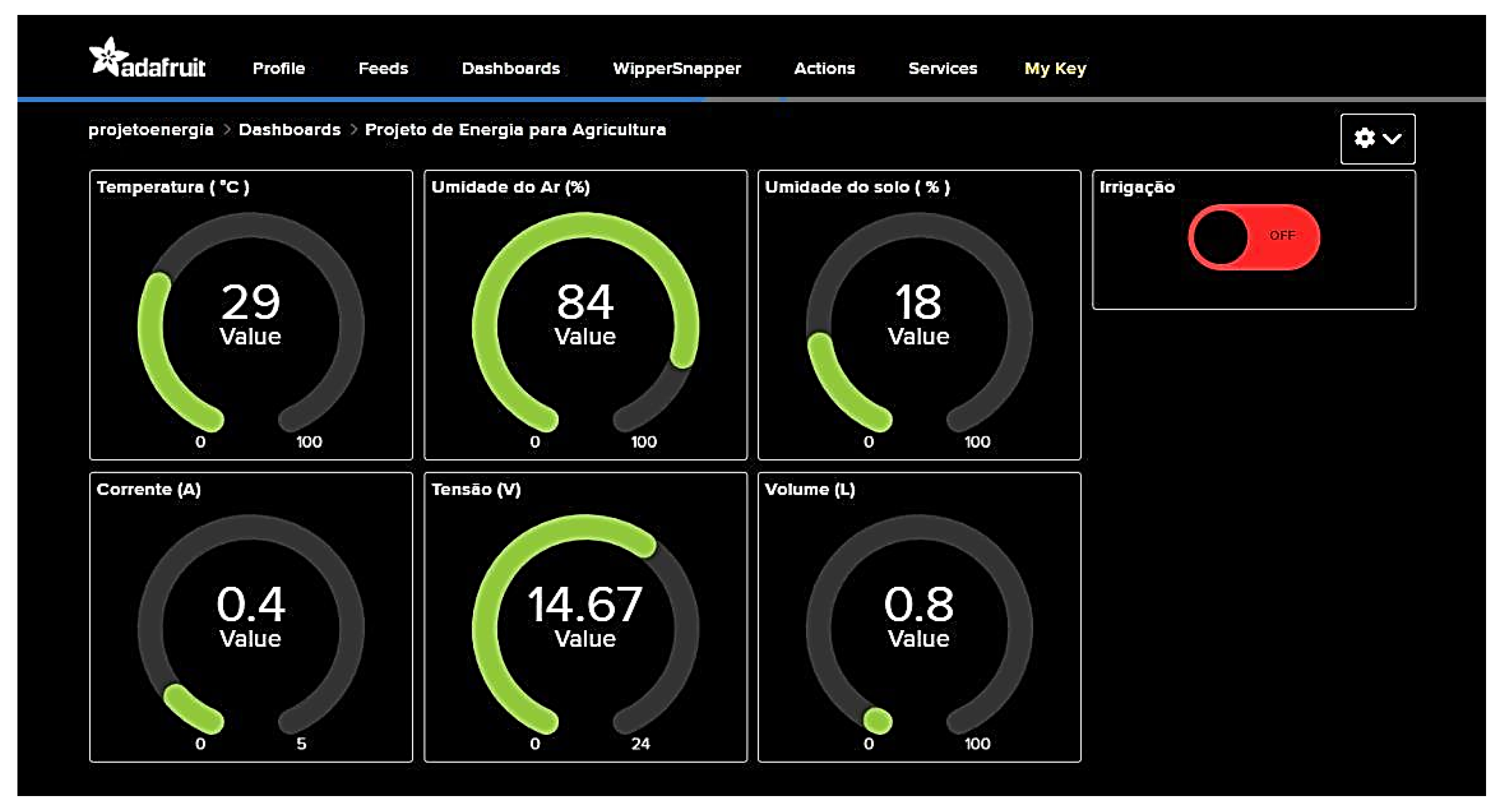
3.3. Adafruit IO Development Platform
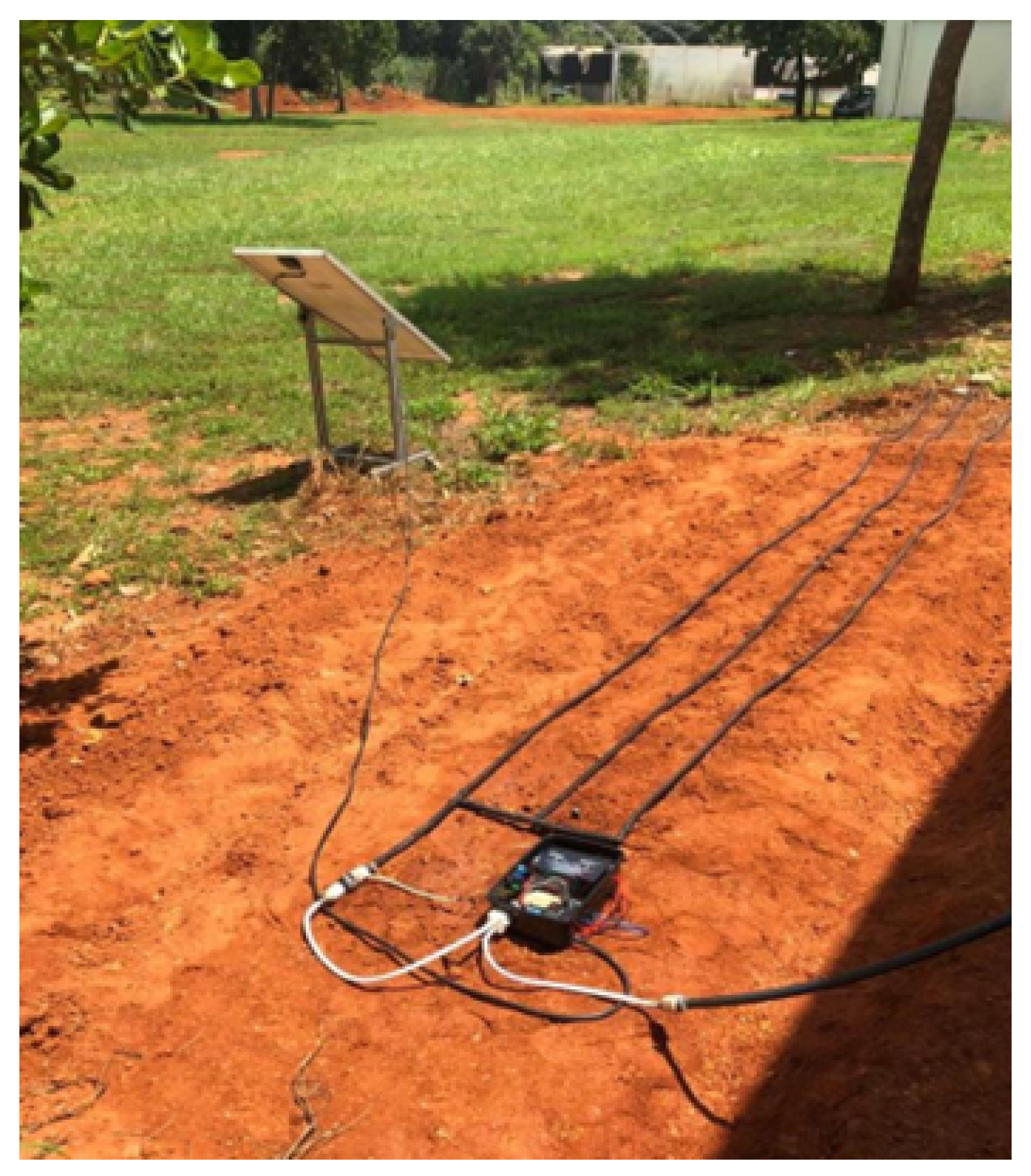
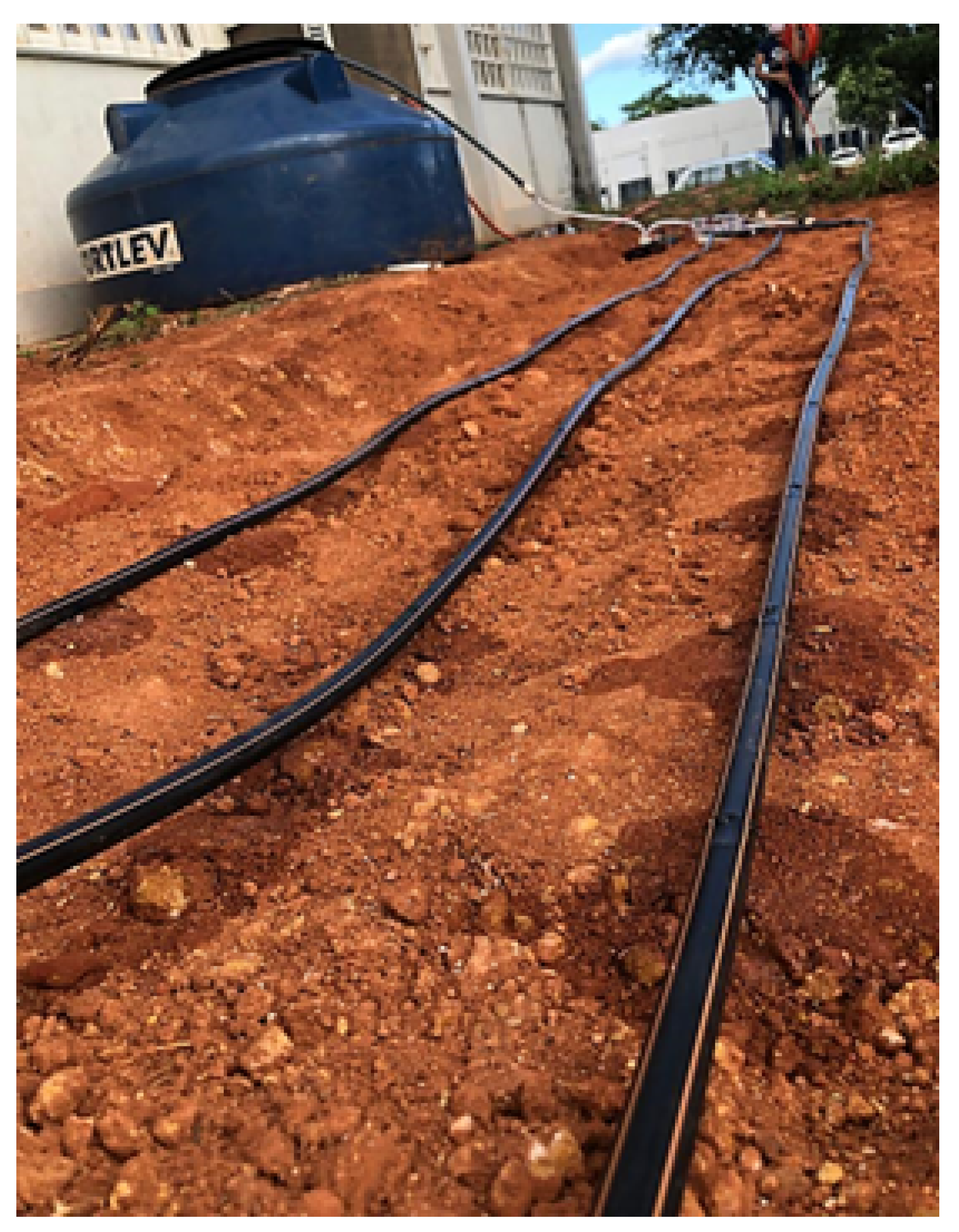
3.4. Implementation of the Prototype in the Experimental Area
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CSV | Comma Separated Values |
| GPIO | General Purpose Input/Output |
| i2C | Inter-Integrated Circuit |
| IO | Input and Output |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| PWM | Pulse Width Modulation |
| SCL | Serial Clock |
| SDA | Serial Data |
| UFR | Federal University of Rondonópolis |
References
- ONU. Perspectiva Global Reportagens Humanas. 2019. Available online: https://news.un.org/pt/story/2019/06/1676601 (accessed on 21 February 2022).
- Pawlak, K.; Kolodziejcczak, M. The Role of Agriculture in Ensuring Food Security in Developing Countries: Considerations in the Context of the Problem of Sustainable Food Production. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embrapa. Determinação de matéria seca e umidade em solos e plantas com forno de microondas doméstico. In Circular Técnica, 33rd ed.; Embrapa: São Carlos, Brazil, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pardossi, A.; Incrocci, L.; Incrocci, G.; Malorgio, F.; Battista, P.; Bacci, L.; Rapi, B.; Marzialetti, P.; Hemming, J.; Balendonck, J. Root Zone Sensors for Irrigation Management in Intensive Agriculture. Sensors 2009, 9, 2809–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha, K.C.B.; Da Rocha, R.V. Automação no processo de irrigação na agricultura familiar com plataforma Arduino. Rev. Eletrônica Competências Digit. Para Agric. Fam. 2015, 1, 62–74. [Google Scholar]
- Pinho, A.G.; Furtado, J.S.; Junior, J.A.; Ferreira, M.C.C.; AraúJo, S.D.F.A.; Albuquerque, R.D.N.O. Sistema de irrigação automatizado para uso em pequenas propriedades rurais. In Encontro Competências Digitais Para Agricultura Familiar; Tupã, Presidente Prudente, Belém, Anais eletrônicos; CoDAF: Tupã, Brazil, 2017; Volume 4, pp. 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, G.; de Sá, M.J.S.; da Silva, J.E.P.; Camargo, N. Plataforma arduino na automação da irrigação por gotejamento no cultivo da cana-deaçúcar. In Proceedings of the XXV CONIRD—Congresso Nacional de Irrigação e Drenagem, Ceres, Brazil, 8–13 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, D.; Oliveira, G.; Silva, R.; Fernandes, C.; Jesus, L.D.; Begier, I. Controle automático da umidade do solo com energia solar para pequenos produtores. Embrapa Pantanal—Artigo em anais de congresso (ALICE). In Proceedings of the Simpósio Sobre Recursos Naturais e Socioeconômicos do Pantanal, Corumbá, Brazil, 17–20 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Tariq, T.; Ahmer, M.F.; Sharma, G.; Bokoro, P.N.; Shongwe, T. Intelligent Control of Irrigation Systems Using Fuzzy Logic Controller. Energies 2022, 15, 7199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.S.; Alcantara, L.D.S. Sistema de bombeamento fotovoltaico para irrigação na agricultura familiar. Braz. J. Anim. Environ. Res. 2018, 1, 205–214. [Google Scholar]
- Izam, N.S.M.N.; Itam, Z.; Sing, W.L.; Syamsir, A. Sustainable Development Perspectives of Solar Energy Technologies with Focus on Solar Photovoltaic—A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, H.M.P.; Mendes, L.F.R. Análise de rendimento do sistema de bombeamento de água por energia solar fotovoltaica para irrigação de um 87 viveiro de mudas. Rev. Vértices 2019, 21, 463–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, M.E.C. Fixed Low-Order Wide-Area Damping Controller Considering Time Delays and Power System Operation Uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2020, 35, 3918–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvi, M.; Azadian, A. A comprehensive review and classified comparison of MPPT algorithms in PV systems. Energy Syst. 2022, 13, 281–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, K.Y.; Sarimuthu, C.R.; Lim, J.M.Y. Artificial Intelligence Based MPPT Techniques for Solar Power System: A review. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2020, 8, 1043–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, M.E.C. An approach for monitoring and updating the load margin of power systems in dynamic security assessment. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2021, 198, 107365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, M.E.C. A method for monitoring the load margin of power systems under load growth variations. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2022, 30, 100677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, M.E.C. Physics-Guided Neural Network for Load Margin Assessment of Power Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetita, I.; Zalhaf, A.S.; Mansour, D.E.A.; Han, Y.; Yang, P.; Wang, C. Modeling and protection of photovoltaic systems during lightning strikes: A review. Renew. Energy 2022, 184, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, M.; Koley, E.; Ghosh, S.; Mohanta, D.K.; Bansal, R.C. Spatio-temporal information based protection scheme for PV integrated microgrid under solar irradiance intermittency using deep convolutional neural network. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2020, 116, 105576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ola, S.R.; Saraswat, A.; Goyal, S.K.; Jhajharia, S.K.; Khan, B.; Mahela, O.P.; Alhelou, H.H.; Siano, P. A Protection Scheme for a Power System with Solar Energy Penetration. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenle, A.A. Assessment of solar energy technologies in Africa-opportunities and challenges in meeting the 2030 agenda and sustainable development goals. Energy Policy 2020, 137, 111180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dousari, A.; Al-Nassar, W.; Al-Hemoud, A.; Alsaleh, A.; Ramadan, A.; Al-Dousari, N.; Ahmed, M. Solar and wind energy: Challenges and solutions in desert regions. Energy 2019, 176, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, M.E.C. Monitoring of the power system load margin based on a machine learning technique. Electr. Eng. 2022, 104, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, M.E.C. Wide-Area Measurement-Based Two-Level Control Design to Tolerate Permanent Communication Failures. Energies 2023, 16, 5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, M.E.C. Load Margin Assessment of Power Systems Using Physics-Informed Neural Network with Optimized Parameters. Energies 2024, 17, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancevic, P.I.; Nunez, H.M.; Rosellon, J. Distributed photovoltaic power generation: Possibilities, benefits, and challenges for a widespread application in the Mexican residential sector. Energy Policy 2017, 110, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barnham, K.; Knorr, K.; Mazzer, M. Benefits of photovoltaic power in supplying national electricity demand. Energy Policy 2013, 54, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shahri, O.A.; Ismail, F.B.; Hannan, M.A.; Lipu, M.S.H.; Al-Shetwi, A.Q.; Begum, R.A.; Al-Muhsen, N.F.O.; Soujeri, E. Solar photovoltaic energy optimization methods, challenges and issues: A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 125465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, M.M.; Solangi, K.H.; Hossain, M.S.; Badarudin, A.; Jasmon, G.B.; Mokhlis, H.; Bakar, A.H.A.; Kazi, S.N. A review of Safety, Health and Environmental (SHE) issues of solar energy system. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 1190–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadori, A.; Nwaoha, C. A review on solar energy utilisation in Australia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 18, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firjan. INDÚSTRIA 4.0: Internet das Coisas. Federação das Indústrias do Estado do Rio de Janeiro. 2016. Available online: https://www.firjan.com.br/lumis/portal (accessed on 18 May 2021).
- Revell, S. Internet of Things (IoT) and Machine to Machine Communications (M2M)—Challenges and Opportunities. 2013. Available online: https://connect.innovateuk.org/documents/3077922/3726367/ (accessed on 21 February 2022).
- Farooq, M.S.; Riaz, S.; Abid, A.; Umer, T.; Zikria, Y.B. Role of IoT Technology in Agriculture: A Systematic Literature Review. Electronics 2020, 9, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.S.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, Y.J. A Review of the Applications of the Internet of Things (IoT) for Agricultural Automation. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 45, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gu, B.; Tian, G. Review of agricultural IoT technology. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2022, 6, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watthanawisuth, N.; Tuantranont, A.; Kerdcharoen, T. Microclimate real-time monitoring based on ZigBee sensor network. In Proceedings of the SENSORS, 2009 IEEE, Christchurch, New Zealand, 25–28 October 2009; pp. 1814–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-T.; Zhang, H.-H.; Wu, T.-T.; Hu, J.; Zhai, C.-Y.; Wang, D. Design of monitoring system for multilayer soil temperature and moisture based on WSN. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Wireless Communication and Sensor Network, Wuhan, China, 13–14 December 2014; pp. 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postolache, O.; Pereira, J.D.; Girao, P.S. Wireless sensor network-based solution for environmental monitoring: Water quality assessment case study. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2014, 8, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langendoen, K.; Baggio, A.; Visser, O. Murphy loves potatoes: Experiences from a pilot sensor network deployment in precision agriculture. In Proceedings of the 20th IEEE International Parallel & Distributed Processing Symposium, Rhodes, Greece, 25–29 April 2006; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandani, S.K.; Kalantari, M. Using field data to design a sensor network. In Proceedings of the 2009 43rd Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, Baltimore, MD, USA, 18–20 March 2009; pp. 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kang, H.; Bang, H.; Kang, S. Dynamic crop field analysis using mobile sensor node. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on ICT Convergence (ICTC), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 15–17 October 2012; pp. 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahi, M.E.E.; Xie, L.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Burkitt, L. A Temperature Compensated Smart Nitrate-Sensor for Agricultural Industry. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 7333–7341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, K.L.; Silver, O.; Malende, W.F.; Anuradha, K. Internet of Things application for implementation of smart agriculture system. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud) (I-SMAC), Palladam, India, 10–11 February 2017; pp. 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.D.L. Calibração de Sensores de Umidade do Solo de Baixo Custo. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidade Federal Rural de Pernambuco, Garanhuns, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, A.G. Sistema de Irrigação Automatizado Utilizando o Conceito de IOT Para Tomada de Decisão. Bachelor’s Thesis, UNESC, Criciúma, Brazil, 2020; p. 77. [Google Scholar]
- Dourado, V.C.; Ferreira, M.S.S.; Borges, R.C.; Beuter, C.H.; Silveira, M.H.D. Calibração de sensores de umidade resistivos HL-69 para uso no sistema automático de irrigação alimentado por energia solar. In Proceedings of the L Congresso Brasileiro de Engenharia Agrícola—CONBEA 2021, Online, 8–10 November 2021; Available online: https://conbea.org.br/anais/publicacoes/conbea-2021/livros-2021/energia-na-agricultura-eag-3/3053-calibracao-de-sensores-de-umidade-resistivos-hl-69-para-uso-no-sistema-automatico-de-irrigacao-alimentado-por-energia-solar/file (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Castro, G.D. Usando o Sensor de Fluxo de áGua. ROBOCORE. 2020. Available online: https://tecnoblog.net/responde/referencia-site-abnt-artigos/ (accessed on 25 April 2022).
- Martins, E.G.M. Coeficiente de determinação. Rev. Ciência Elem. 2018, 6, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, F.H.F.; Cunha, F.N.; Lopes Filho, L.C.; Vidal, V.M.; Soares, F.A.L.; Teixeira, M.B. Calibração de um sensor de umidade do solo de baixo custo. Rev. Bras. Agric. Irrig. 2017, 11, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gava, R.; da Silva, E.E.; Baio, F.H.R. Calibração de sensor eletrônico de umidade em diferentes texturas de solo. Rev. Bras. Eng. Biossistemas 2016, 10, 154–162. [Google Scholar]
- Leão, D.V.F.; Filho, G.S.T.; Freitas, D.L.A.; Oliveira, C.W.; Matias, S.S.R.; Barros, B.A.A. Avaliação e calibração de sensores de monitoramento da umidade superficial do solo/Evaluation and calibration of sensors for monitoring soil surface moisture. Braz. J. Dev. 2021, 7, 26294–26305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

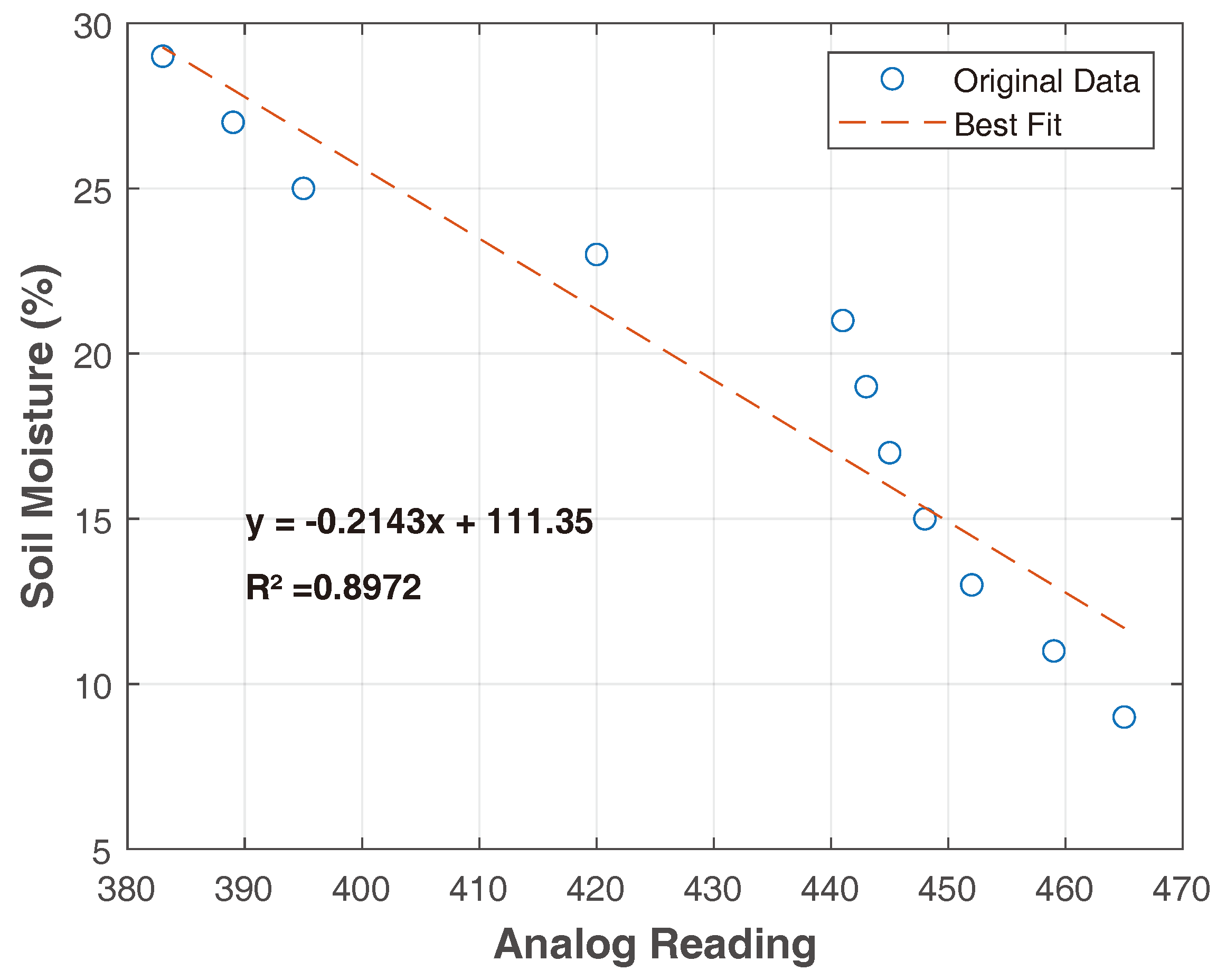


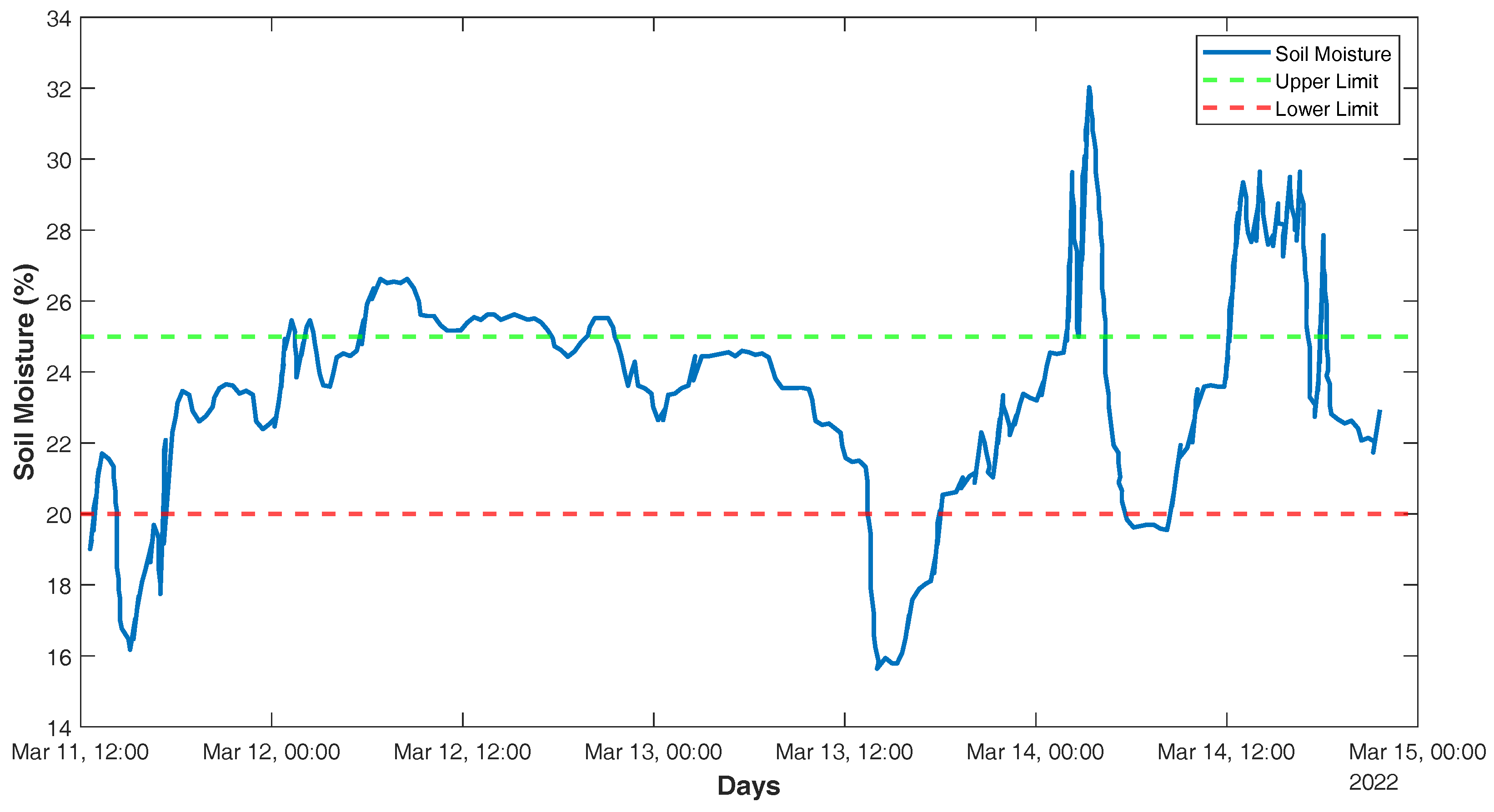



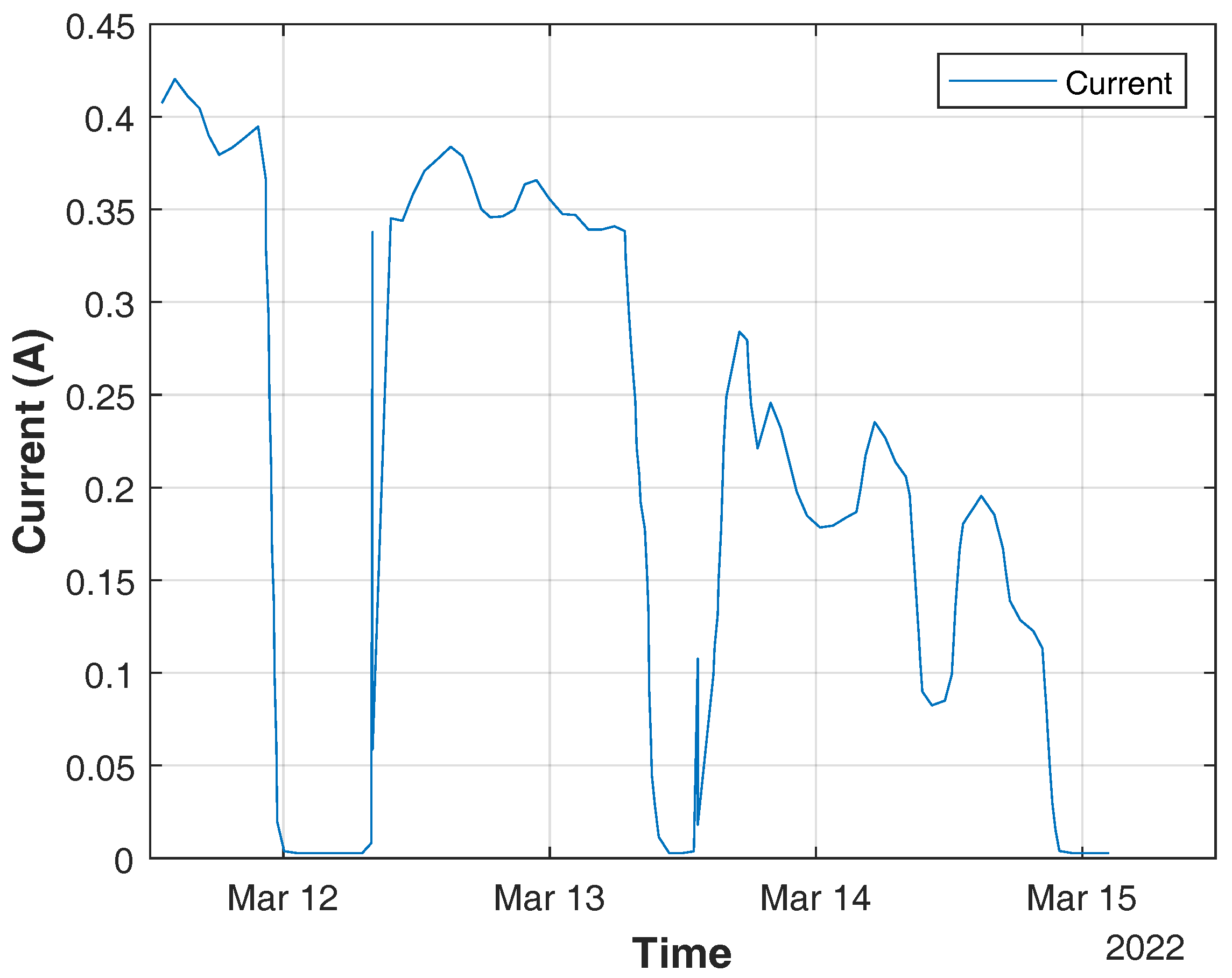


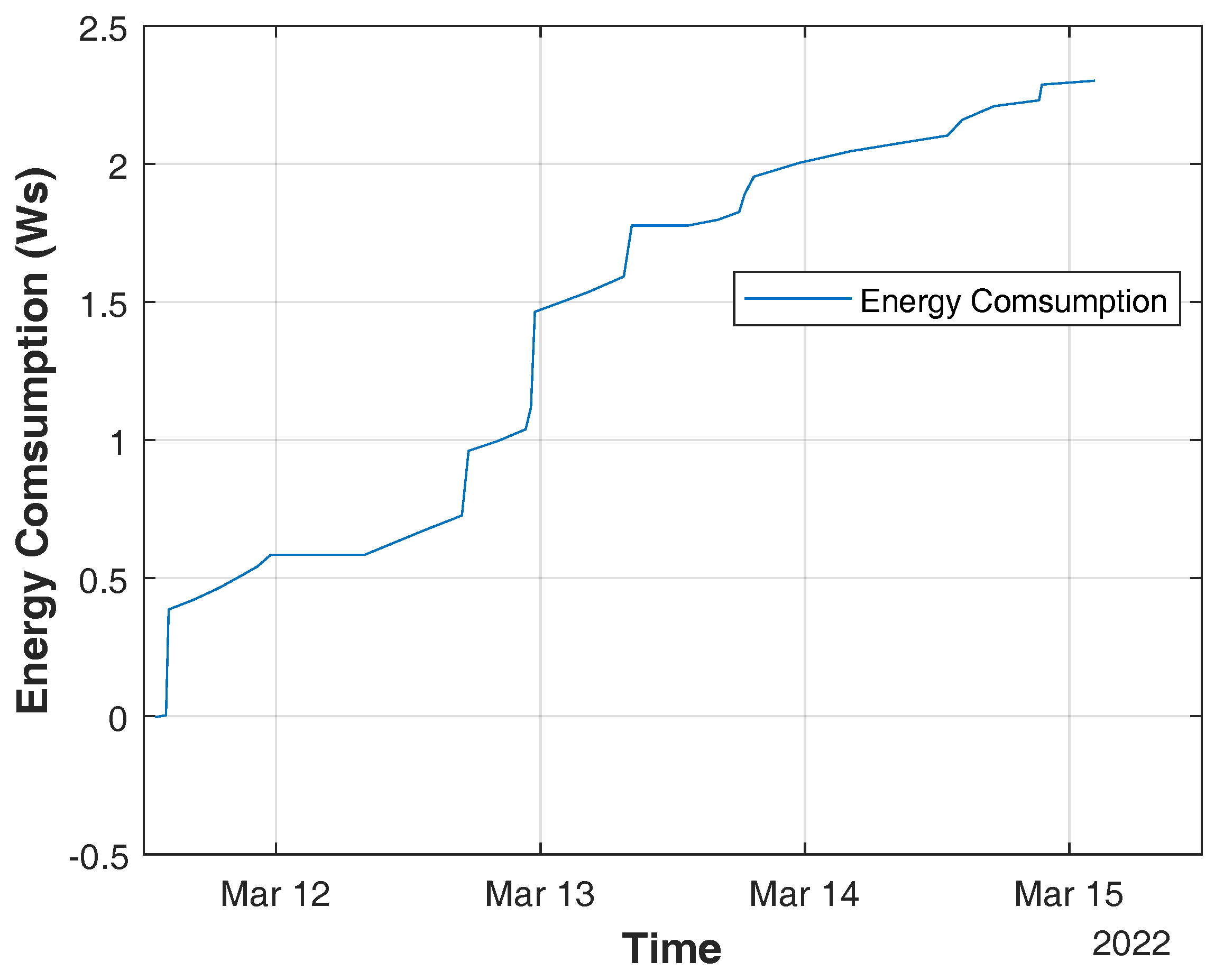
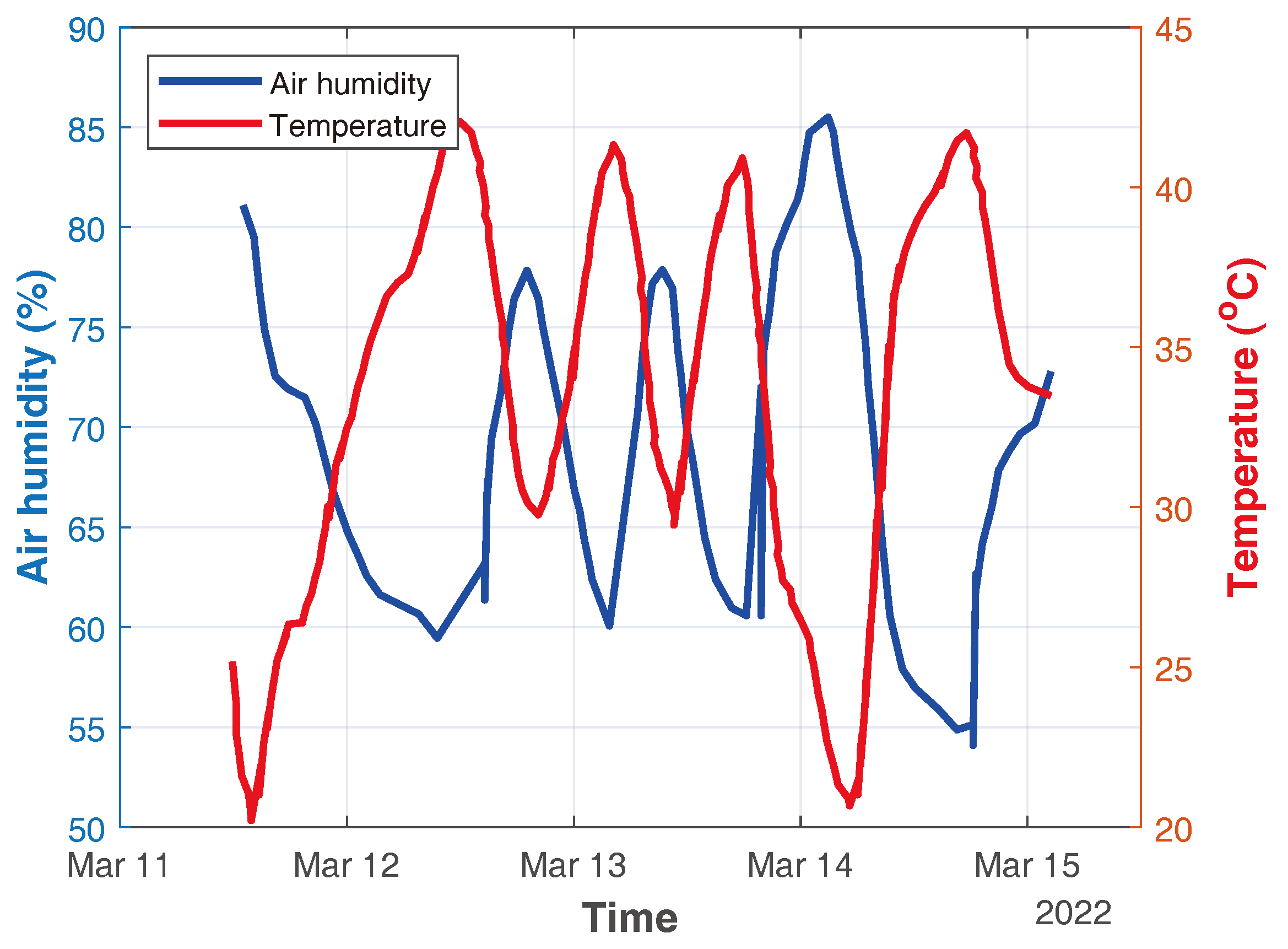
| Reading | Resistive Humidity Sensor | |
|---|---|---|
| Analog Reading | Soil Moisture | |
| 1° | 465 | 9% |
| 2° | 459 | 11% |
| 3° | 452 | 13% |
| 4° | 448 | 15% |
| 5° | 445 | 17% |
| 6° | 443 | 19% |
| 7° | 441 | 21% |
| 8° | 420 | 23% |
| 9° | 395 | 25% |
| 10° | 389 | 27% |
| 11° | 383 | 29% |
| Voltage | Current | Current | Current |
|---|---|---|---|
| Applied (V) | Source (A) | Multimeter (A) | Sensor (A) |
| 12 | 1.58 | 1.58 | 1.59 |
| 14 | 1.69 | 1.69 | 1.74 |
| 16 | 1.82 | 1.81 | 1.86 |
| 18 | 1.95 | 1.94 | 1.99 |
| 20 | 2.06 | 2.06 | 2.10 |
| 22 | 2.17 | 2.16 | 2.21 |
| 24 | 2.29 | 2.28 | 2.33 |
| Voltage | Current | Current | Current |
|---|---|---|---|
| Applied (V) | Source (A) | Multimeter (A) | Sensor (A) |
| 12 | 1.57 | 1.56 | 1.57 |
| 14 | 1.71 | 1.70 | 1.70 |
| 16 | 1.84 | 1.83 | 1.83 |
| 18 | 1.96 | 1.95 | 1.95 |
| 20 | 2.08 | 2.07 | 2.06 |
| 22 | 2.19 | 2.19 | 2.18 |
| 24 | 2.30 | 2.29 | 2.28 |
| Voltage | Voltage | Voltage | Analog |
|---|---|---|---|
| Applied (V) | Source (V) | Multimeter (V) | Sensor |
| 12 | 12 | 11.88 | 496 |
| 14 | 14 | 13.84 | 578 |
| 16 | 16 | 15.80 | 660 |
| 18 | 18 | 17.76 | 743 |
| 20 | 20 | 19.98 | 835 |
| 22 | 22 | 21.70 | 909 |
| 24 | 24 | 23.70 | 995 |
| Voltage | Voltage | Voltage | Analog |
|---|---|---|---|
| Applied (V) | Source (V) | Multimeter (V) | Sensor |
| 12 | 12 | 11.80 | 11.88 |
| 14 | 14 | 13.83 | 13.96 |
| 16 | 16 | 15.85 | 15.99 |
| 18 | 18 | 17.77 | 17.95 |
| 20 | 20 | 19.77 | 19.96 |
| 22 | 22 | 21.80 | 21.90 |
| 24 | 24 | 23.70 | 24.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borges, R.C.; Beuter, C.H.; Dourado, V.C.; Bento, M.E.C. Internet of Things Application in an Automated Irrigation Prototype Powered by Photovoltaic Energy. Energies 2024, 17, 2219. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092219
Borges RC, Beuter CH, Dourado VC, Bento MEC. Internet of Things Application in an Automated Irrigation Prototype Powered by Photovoltaic Energy. Energies. 2024; 17(9):2219. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092219
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorges, Rafael C., Carlos H. Beuter, Vitória C. Dourado, and Murilo E. C. Bento. 2024. "Internet of Things Application in an Automated Irrigation Prototype Powered by Photovoltaic Energy" Energies 17, no. 9: 2219. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092219
APA StyleBorges, R. C., Beuter, C. H., Dourado, V. C., & Bento, M. E. C. (2024). Internet of Things Application in an Automated Irrigation Prototype Powered by Photovoltaic Energy. Energies, 17(9), 2219. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092219








