Regression Modeling of Daily PM2.5 Concentrations with a Multilayer Perceptron
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
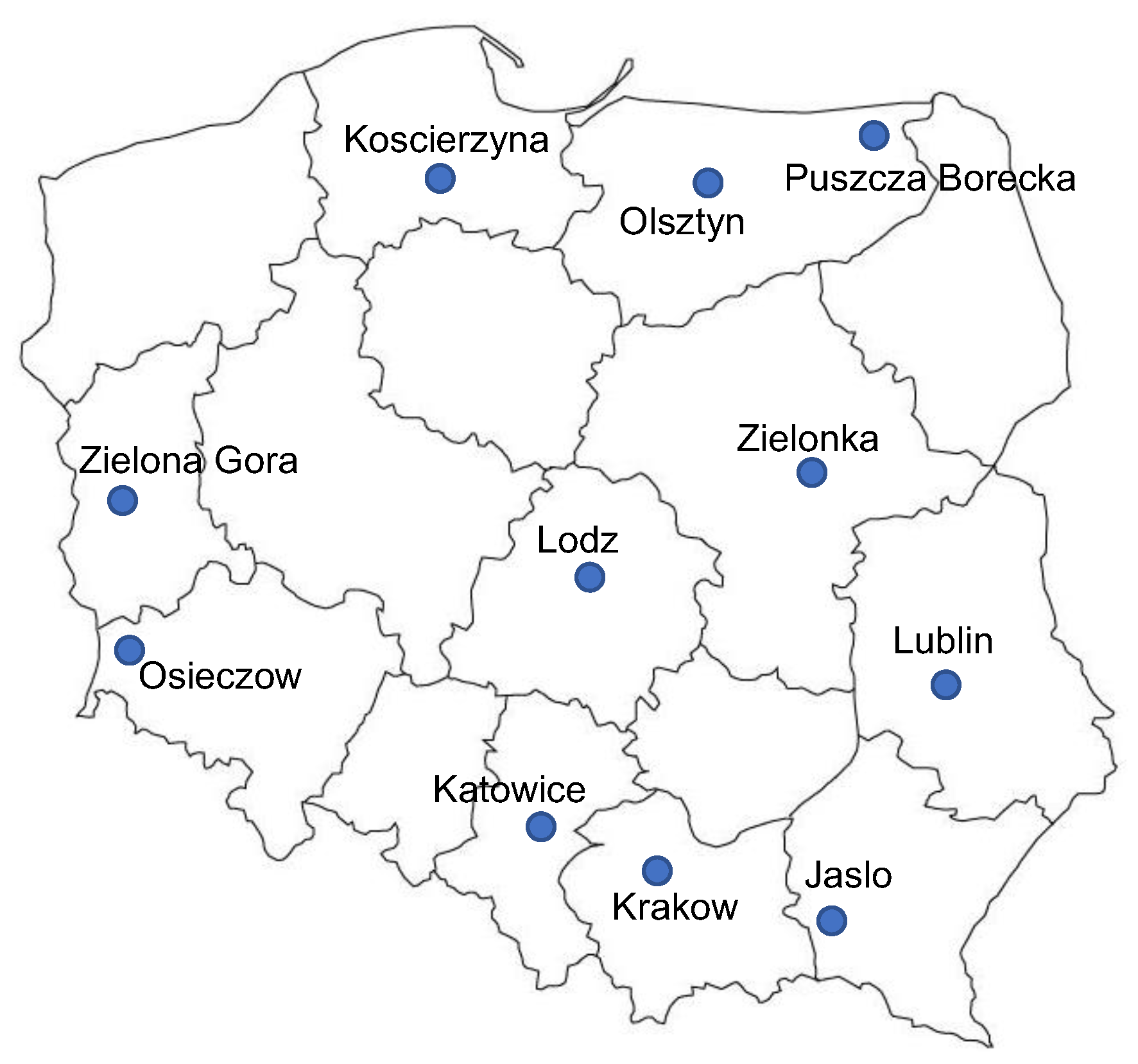
2.1. Air Monitoring Sites
- Their location was diverse enough to cover various regions of Poland;
- Daily concentrations of both PM10 and PM2.5 fractions were simultaneously measured at each station for at least several years.
2.2. Air Monitoring Data
- PM10—daily averaged concentration of particles up to 10 μm in size.
- PM2.5—daily averaged concentration of particles up to 2.5 μm in size.
- D—date in the numerical form.
2.3. Temporal Variable’s Transformation
2.4. Data Preparation
2.5. Regression Models
2.6. Assessment of the Prediction Accuracy
2.7. Verification of Models
3. Results
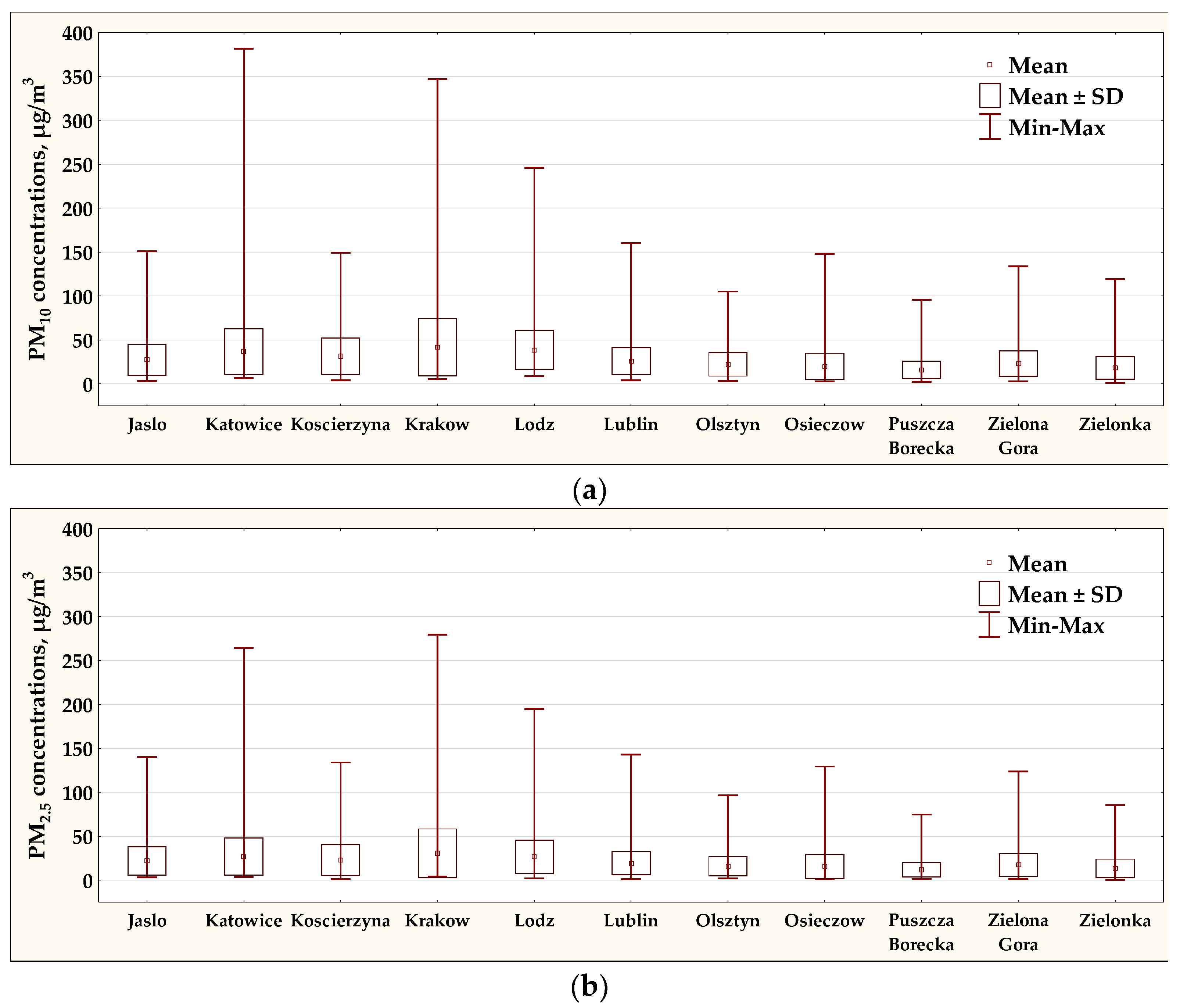
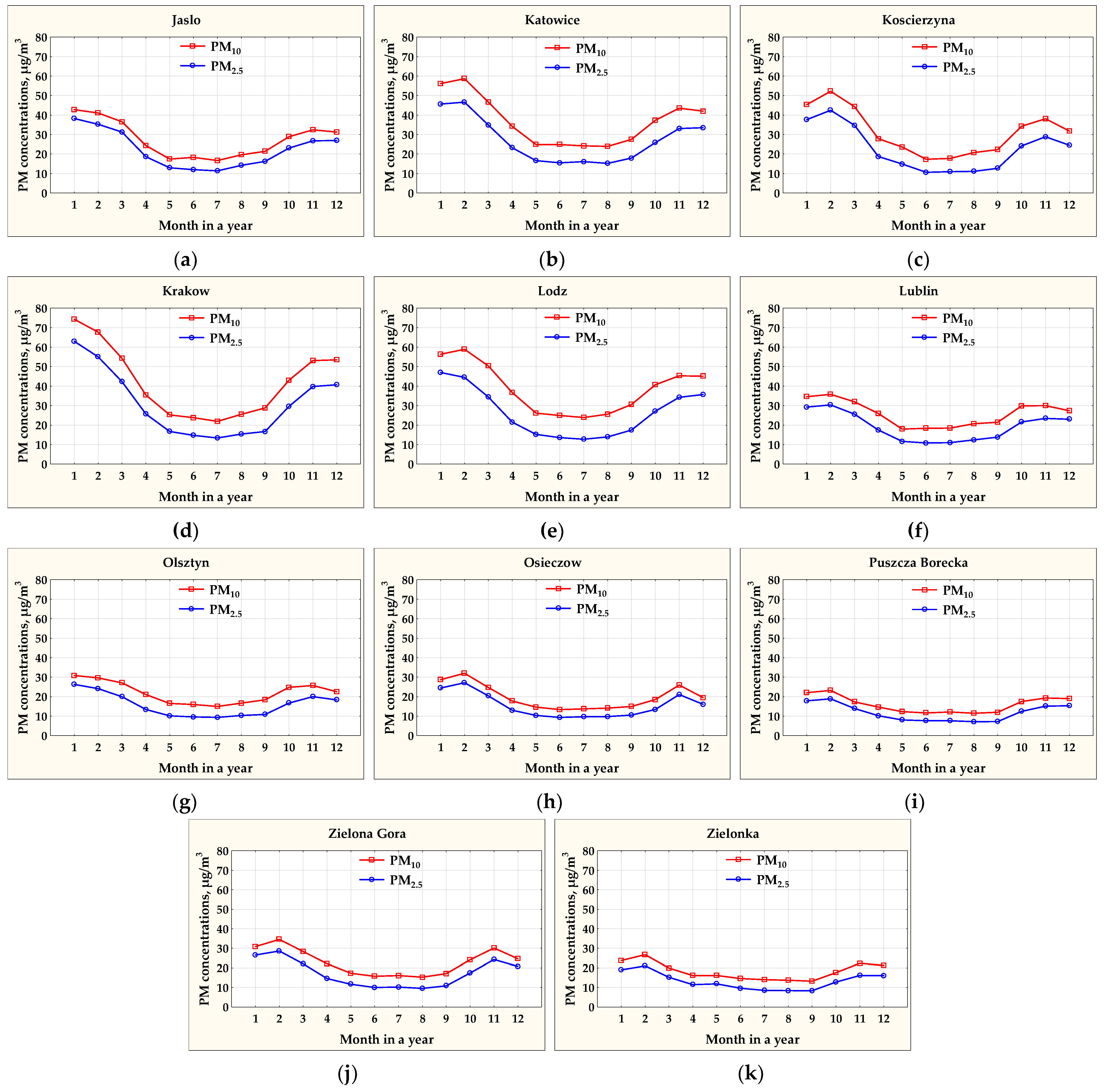
3.1. Annual Courses of PM10 and PM2.5 Concentrations
3.2. Correlations of Variables
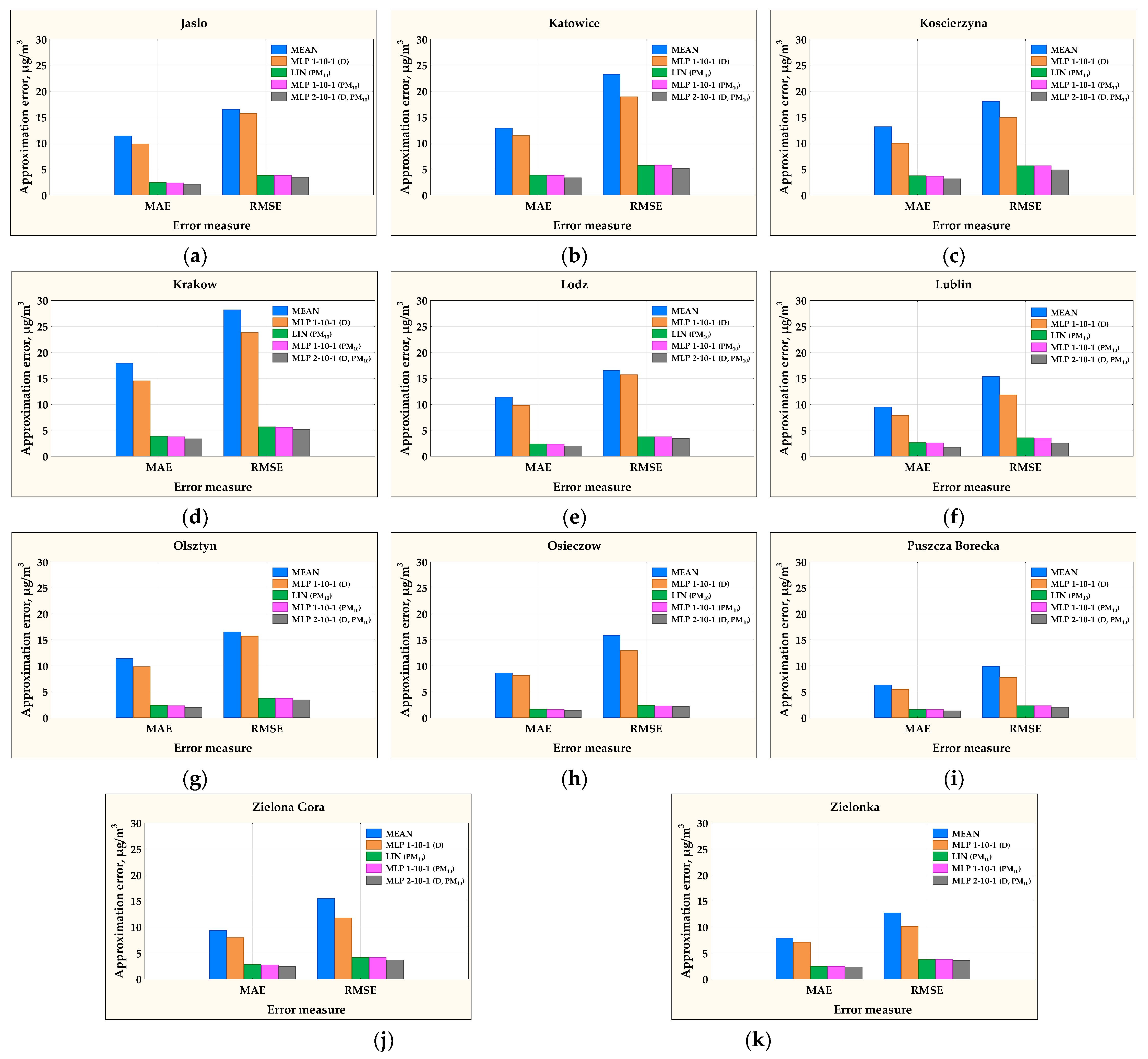
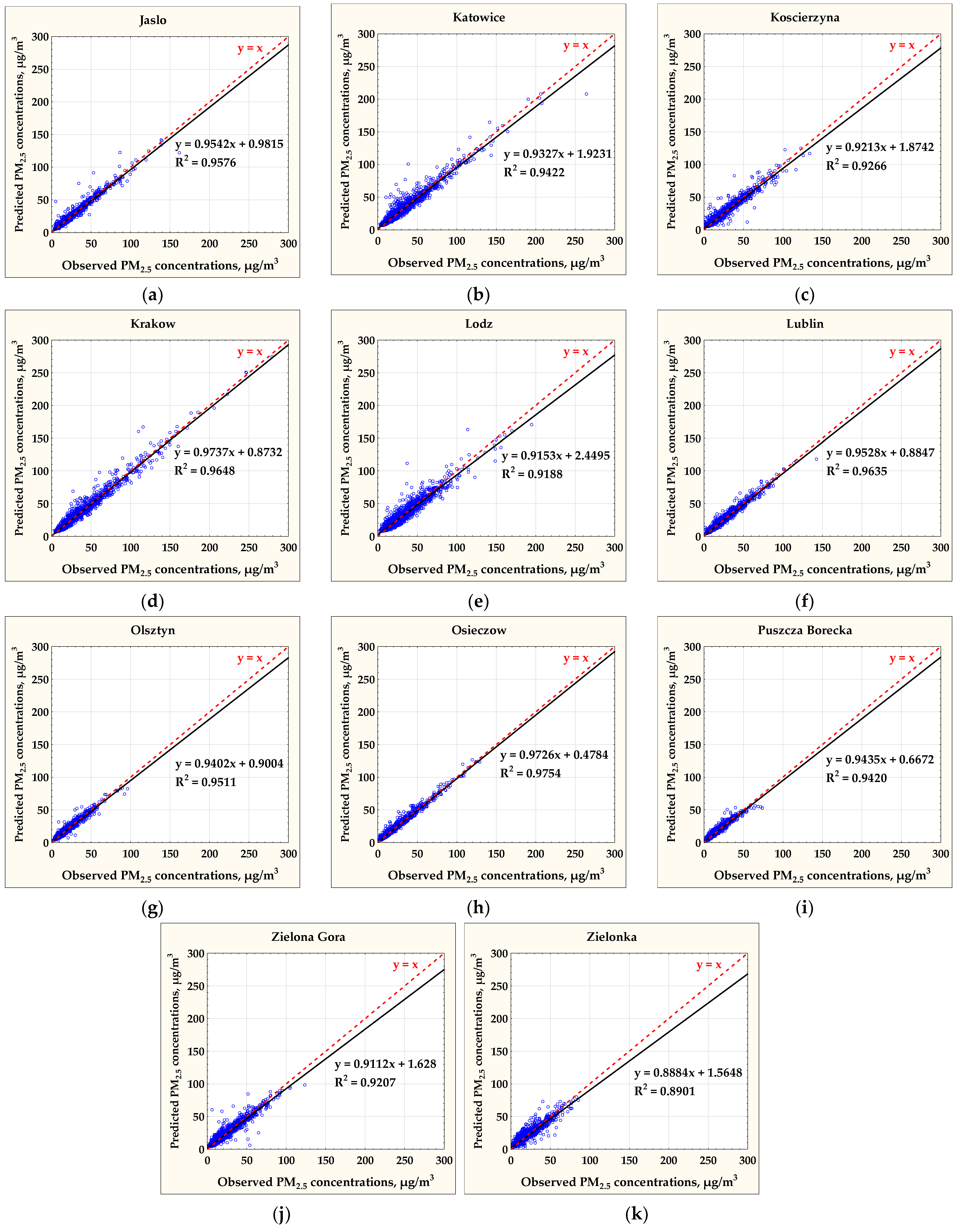
3.3. Results of Predicting PM2.5 Concentrations
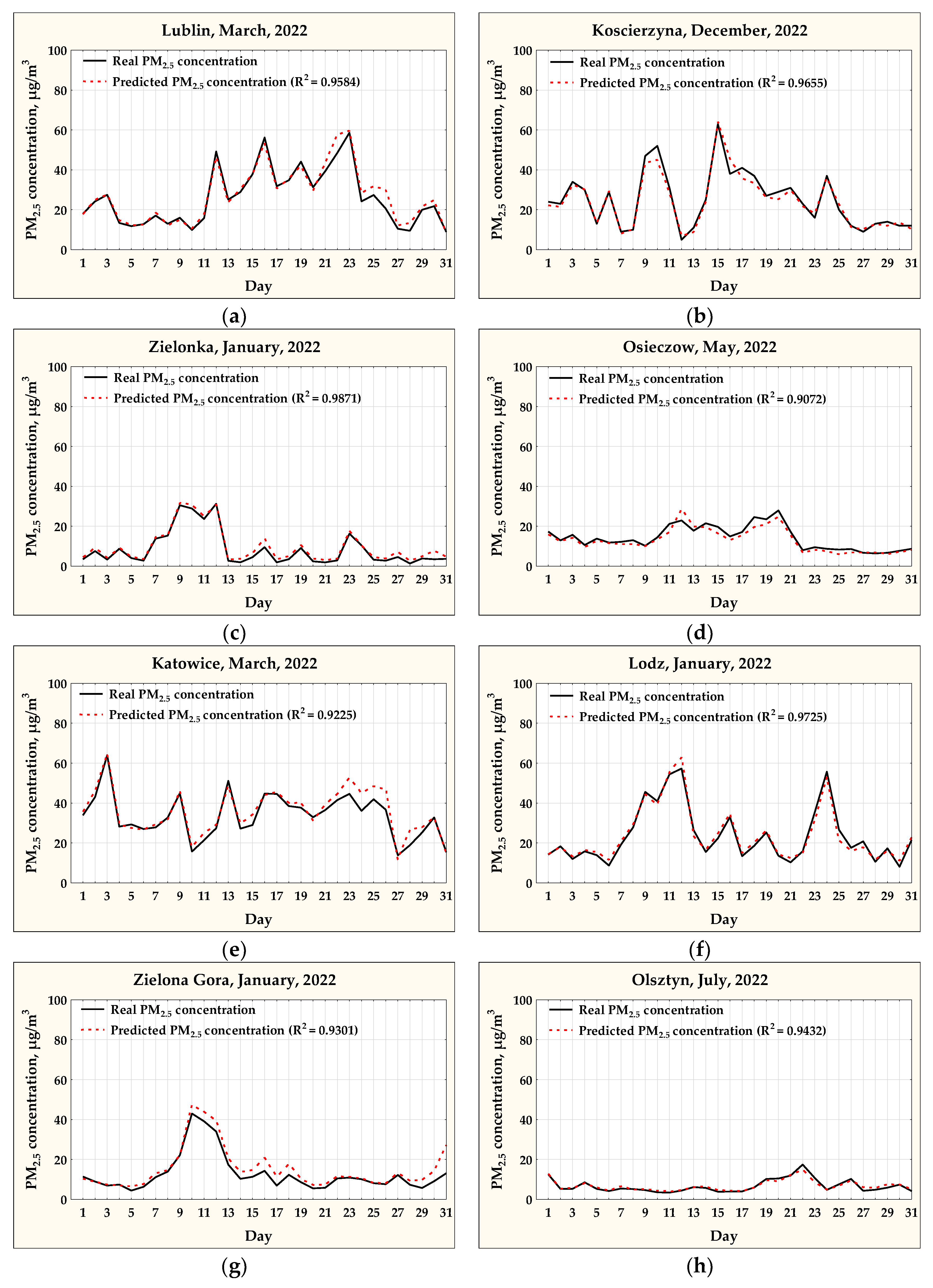
3.4. Verification of the Models
4. Summary and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gurjar, B.R.; Molina, L.T.; Ojha, C.S.P. Air Pollution: Health and Environmental Impacts; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P. Airborne Particles: Origin, Emissions and Health Impacts; Nova Science Publisher’s, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, B.; Roebbel, N.; Gumy, S.; Forastiere, F.; Brunekreef, B.; Jarosinska, D.; Walker, K.D.; van Erp, A.M.; O’Keefe, R.; Greenbaum, D.; et al. A joint workshop report of ERS, WHO, ISEE and HEI. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2002575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandya, S.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Maddikunta, P.K.R.; Sharma, R. A Study of the Impacts of Air Pollution on the Agricultural Community and Yield Crops (Indian Context). Sustainability 2022, 14, 13098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Wang, Z. Impact of Industrial Air Pollution on Agricultural Production. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathokleous, E.; Frei, M.; Knopf, O.M.; Muller, O.; Xu, Y.; Nguyen, T.H.; Gaiser, T.; Liu, X.; Liu, B.; Saitanis, C.J.; et al. Adapting crop production to climate change and air pollution at different scales. Nat. Food 2023, 4, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.; Zivin, J.G.; Gross, T.; Neidell, M. Particulate Pollution and the Productivity of Pear Packers. Am. Econ. J. Econ. Policy 2016, 8, 141–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff-Zivin, J.; Neidell, M. The Impact of Pollution on Worker Productivity. Am. Econ. Rev. 2012, 102, 3652–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, R.; Oliva, P. The Effect of Pollution on Labor Supply: Evidence from a Natural Experiment in Mexico City. J. Public Econ. 2015, 122, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragon, F.; Miranda, J.; Oliva, P. Particulate Matter and Labor Supply: The Role of Caregiving and Non-linearities. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2017, 86, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, S.; Ferrara, P.; D’Angiolella, L.S.; Lorelli, S.C.; Agazzi, G.; Fornari, C.; Cesana, G.; Mantovani, L.G. The economic impact of air pollution: A European assessment. Eur. J. Public Health 2020, 30 (Suppl. 5), ckaa165.084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallero, D.A. Fundamentals of Air Pollution, 4th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, J. Great Smog of London. Encyclopedia Britannica, Article History. 27 February 2024. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/event/Great-Smog-of-London (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Maesano, I. The Air of Europe: Where Are We Going? Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 170024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiotiu, A.I.; Novakova, P.; Nedeva, D.; Chong-Neto, H.J.; Novakova, S.; Steiropoulos, P.; Kowal, K. Impact of Air Pollution on Asthma Outcomes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, F.F.; Gimeno, P.M.; Sánchez, J.F.; García, J.A.L.; Arias, T.A.; Ardanaz, J.M.U. Air Pollution and Asthma. In The Dangers of Allergic Asthma; García-Menaya, J.M., Ed.; Nova Science Publisher’s, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumawardani, I.A.J.D.; Indraswari, G.; Komalasari, N.L.G.Y. Air Pollution and Lung Cancer. J. Respirasi 2023, 9, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, C.D.; Schiller, J.H.; Boffetta, P.; Cai, J.; Connolly, C.; Kerpel-Fronius, A.; Kitts, A.B.; Lam, D.C.; Mohan, A.; Myers, R.; et al. Air Pollution and Lung Cancer: A Review by International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Early Detection and Screening Committee. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, R.D.; Rajagopalan, S.; Pope, C.A., 3rd; Brook, J.R.; Bhatnagar, A.; Diez-Roux, A.V.; Holguin, F.; Hong, Y.; Luepker, R.V.; Mittleman, M.A.; et al. Particulate matter air pollution and cardiovascular disease: An update to the scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010, 121, 2331–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Münzel, T.; Hahad, O.; Daiber, A.; Lelieveld, J. Luftverschmutzung und Herz-Kreislauf-Erkrankungen [Air pollution and cardiovascular diseases]. Herz 2021, 46, 120–128. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bont, J.; Jaganathan, S.; Dahlquist, M.; Persson, Å.; Stafoggia, M.; Ljungman, P. Ambient air pollution and cardiovascular diseases: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 291, 779–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xin, Y. Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, B.S.; Rauh, V.A.; Bansal, R.; Hao, X.; Toth, Z.; Nati, G.; Walsh, K.; Miller, R.L.; Arias, F.; Semanek, D.; et al. Effects of Prenatal Exposure to Air Pollutants (Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons) on the Development of Brain White Matter, Cognition, and Behavior in Later Childhood. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Manley, J.; Radoias, V. Air Pollution and Long Term Mental Health. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Ayala, A. Air Pollution, Ultrafine Particles, and Your Brain: Are Combustion Nanoparticle Emissions and Engineered Nanoparticles Causing Preventable Fatal Neurodegenerative Diseases and Common Neuropsychiatric Outcomes? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 6847–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.; Ee, N.; Peters, J.; Booth, A.; Mudway, I.; Anstey, K.J. Air Pollution and Dementia: A Systematic Review. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 70, S145–S163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clean Air Act. UK Public General Acts, 5 July 1956. Available online: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/Eliz2/4-5/52/enacted (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Knox, A.; Evans, G.J.; Lee, C.J.; Brook, J.R. Air Pollution Monitoring and Sustainability. In Encyclopedia of Sustainability Science and Technology; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spandana, G.; Shanmughasundram, R. Design and Development of Air Pollution Monitoring System for Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 14–15 June 2018; pp. 1640–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.F.; Xu, Y.H.; Shi, M.H.; Lian, Y.X. The impact of PM2.5 on the human respiratory system. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E69–E74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xu, J.; Yang, B. PM2.5 deregulated microRNA and inflammatory microenvironment in lung injury. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 91, 103832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behinaein, P.; Hutchings, H.; Knapp, T.; Okereke, I.C. The growing impact of air quality on lung-related illness: A narrative review. J. Thorac. Dis. 2023, 15, 5055–5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Environment Agency. Air Quality in Europe-2020 Report. No. 12/2018; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020.
- World Health Organization. New WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines Aim to Save Millions of Lives from Air Pollution. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/22-09-2021-new-who-global-air-quality-guidelines-aim-to-save-millions-of-lives-from-air-pollution (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- EN 12341:2014; Ambient Air—Standard Gravimetric Measurement Method for the Determination of the PM10 or PM2.5 Mass Concentration of Suspended Particulate Matter. iTeh, Inc.: Newark, DE, USA, 2014.
- Hammitt, J.K.; Morfeld, P.; Tuomisto, J.T.; Erren, T.C. Premature Deaths, Statistical Lives, and Years of Life Lost: Identification, Quantification, and Valuation of Mortality Risks. Risk Anal. 2020, 40, 674–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Climate and Environment (Polish Government). Regulation on the Evaluation of Levels of Substances in the Air. 11 December 2020. Available online: http://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=WDU20200002279 (accessed on 12 March 2024). (In Polish)
- Milionis, A.E.; Davies, T.D. Regression and Stochastic Models for Air Pollution-I. Review, Comments and Suggestions. Atmos. Environ. 1994, 28, 2801–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manly, B.F.J. Statistics for Environmental Science and Management; Chapman & Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, G.; Leslie, L.M.; Shao, Y. Environmental Modeling and Prediction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Plaia, A.; Bondi, A.L. Single Imputation Method of Missing Values in Environmental Pollution Data Sets. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 7316–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, M.W.; Dorling, S.R. Artificial Neural Networks (the Multilayer Perceptron)-A Review of Applications in the Atmospheric Sciences. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 2627–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorling, S.R.; Gardner, M.W. Statistical Surface Ozone Models: An Improved Methodology to Account for Non-linear Behaviour. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, S. Short-Time forecasting of atmospheric NOx concentration by neural networks. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2006, 23, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentili, S.; Magnaterra, L.; Passerini, G. Handling Missing Data: Applications to Environmental Analysis; Latini, G., Passerini, G., Eds.; Wit Press: Southampton, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, S. Missing data completing in the air monitoring systems by forward and backward prognosis methods. Environ. Protec. Eng. 2006, 32, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, S. Treating missing data at air monitoring stations. In Environmental Engineering; Pawłowski, L., Dudzińska, M., Pawłowski, A., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2007; pp. 349–353. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, S. Approximation of Imission Level at Air Monitoring Stations by Means of Autonomous Neural Models. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2012, 38, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.C.; Tsai, C.F. Missing value imputation: A review and analysis of the literature (2006–2017). Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 1487–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, S.R.; Jahani, A.; Kalantary, S.; Moeinaddini, M.; Khorasani, N. The evaluation on artificial neural networks (ANN) and multiple linear regressions (MLR) models for predicting SO2 concentration. Urban Clim. 2021, 37, 100837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijal, N.; Gutta, R.T.; Cao, T.; Lin, J.; Bo, Q.; Zhang, J. Ensemble of Deep Neural Networks for Estimating Particulate Matter from Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE 3rd International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), Chongqing, China, 27–29 June 2018; pp. 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, S.; Shin, J.; Kwon, S.; Lee, S.; Kang, S.; Lee, D. PM10 and PM2.5 real-time prediction models using an interpolated convolutional neural network. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Rong, Y.; Yong, R.; Qin, D.; Li, M.; Zou, G.; Pan, J. Deep learning for air pollutant concentration prediction: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 290, 119347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, S.; Jasiński, R. The Use of Multilayer Perceptrons to Model PM2.5 Concentrations at Air Monitoring Stations in Poland. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Chen, Y.; Fang, W.; Su, Z. Characteristics and Relationship of PM, PM10, PM2.5 Concentration in a Polluted City in Northern China. Procedia Eng. 2015, 102, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangeli, C.; Palermi, S.; Bianco, S.; Aruffo, E.; Chiacchiaretta, P.; Di Carlo, P. The Relationship between PM2.5 and PM10 in Central Italy: Application of Machine Learning Model to Segregate Anthropogenic from Natural Sources. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chief Inspectorate of Environmental Protection (Poland)—Measurement Data Bank. Available online: https://powietrze.gios.gov.pl/pjp/archives (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Statistica. Electronic Textbook, 1984–2017, Available in the STATISTICA 13.3 Program.
- Fletcher, R. Practical Methods of Optimization, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Broyden, C.G. The convergence of a class of double-rank minimization algorithms. J. Inst. Math. Its Appl. 1970, 6, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, R. A New Approach to Variable Metric Algorithms. Comput. J. 1970, 13, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfarb, D. A Family of Variable Metric Updates Derived by Variational Means. Math. Comput. 1970, 24, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanno, D.F. Conditioning of quasi-Newton methods for function minimization. Math. Comput. 1970, 24, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J. On the validation of models. Phys. Geogr. 1981, 2, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Peng, L.; Hu, Y.; Shao, J.; Chi, T. Deep learning architecture for air quality predictions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 22408–22417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, S. Assessment of Prediction Accuracy in Autonomous Air Quality Models. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 57, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, S. Estimation of Prediction Error in Regression Air Quality Models. Energies 2021, 14, 7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, S.; Filak, M.; Jasiński, R. Air Quality Modeling with the Use of Regression Neural Networks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

|
Air Monitoring Station | Address |
International Code |
Geographical Coordinates, WGS84 | Type of Station | Area Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaslo | Sikorskiego Str. | PL0518A | Φ 49.744886, λ 21.454617 | background | urban |
| Katowice | 6 Kossutha Str. | PL0008A | Φ 50.264611, λ 18.975028 | background | urban |
| Koscierzyna | Targowa Str. | PL0558A | Φ 54.120694, λ 17.975861 | background | urban |
| Krakow | Bujaka Str. | PL0501A | Φ 50.010575, λ 19.949189 | background | urban |
| Lodz | 1 Legionow Str. | PL0100A | Φ 51.776417, λ 19.452936 | background | urban |
| Lublin | 5 Sliwińskiego Str. | PL0085A | Φ 51.273078, λ 22.551675 | background | urban |
| Olsztyn | 16 Puszkina Str. | PL0175A | Φ 53.789233, λ 20.486075 | background | urban |
| Osieczow | (no street) | PL0505A | Φ 51.317630, λ 15.431719 | background | rural |
| Puszcza Borecka | Diabla Gora | PL0005R | Φ 54.124819, λ 22.038056 | background | rural |
| Zielona Gora | Krotka Str. | PL0213A | Φ 51.939783, λ 15.518861 | background | urban |
| Zielonka | Bory Tucholskie | PL0077A | Φ 53.662136, λ 17.933986 | background | rural |
| Air Monitoring Station | Total Number of Observations (Cases) | Completeness of the Annual Series | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 % | 2011 % | 2012 % | 2013 % | 2014 % | 2015 % | 2016 % | 2017 % | 2018 % | 2019 % | 2020 % | 2021 % | ||
| Jaslo | 2043 | - | - | - | - | 91.5 | 91.5 | 99.5 | 97.3 | 81.4 | 98.4 | - | - |
| Katowice | 2731 | - | - | - | - | 89.0 | 89.3 | 89.6 | 95.9 | 92.1 | 97.3 | 99.5 | 95.1 |
| Koscierzyna | 1709 | - | - | - | - | 90.1 | 84.4 | 98.4 | 95.6 | 99.5 | - | - | - |
| Krakow | 2102 | - | - | - | - | 91.0 | 96.7 | 97.3 | 94.2 | 97.0 | 99.5 | - | - |
| Lodz | 2813 | - | - | - | - | 91.0 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.7 | 95.1 | 99.7 | 96.7 | 89.0 |
| Lublin | 3229 | - | - | - | 96.7 | 90.4 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 97.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Olsztyn | 2438 | - | - | - | - | - | 95.9 | 95.6 | 94.0 | 89.0 | 97.3 | 97.3 | 98.4 |
| Osieczow | 3412 | - | 95.3 | 95.6 | - | 88.8 | 94.8 | 86.3 | 91.5 | 97.0 | 89.9 | 97.0 | 97.8 |
| Puszcza Borecka | 3413 | - | - | 92.9 | 91.8 | 87.1 | 94.8 | 91.3 | 95.1 | 97.5 | 96.2 | 93.4 | 94.2 |
| Zielona Gora | 3849 | - | 89.9 | 92.9 | 94.8 | 92.9 | 91.8 | 99.7 | 97.5 | 100.0 | 99.7 | 96.4 | 98.1 |
| Zielonka | 3767 | 96.4 | 100.0 | 89.1 | 99.2 | 89.0 | - | 89.1 | 87.1 | 98.4 | 96.4 | 92.9 | 93.7 |
| Air Monitoring Station | Variable | D | PM10 | PM2.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaslo | D | 1.0000 | ||
| PM10 | 0.4201 | 1.0000 | ||
| PM2.5 | 0.4768 | 0.9735 | 1.0000 | |
| Katowice | D | 1.0000 | ||
| PM10 | 0.3842 | 1.0000 | ||
| PM2.5 | 0.4450 | 0.9639 | 1.0000 | |
| Koscierzyna | D | 1.0000 | ||
| PM10 | 0.4441 | 1.0000 | ||
| PM2.5 | 0.5069 | 0.9487 | 1.0000 | |
| Krakow | D | 1.0000 | ||
| PM10 | 0.4689 | 1.0000 | ||
| PM2.5 | 0.5048 | 0.9792 | 1.0000 | |
| Lodz | D | 1.0000 | ||
| PM10 | 0.4755 | 1.0000 | ||
| PM2.5 | 0.5661 | 0.9339 | 1.0000 | |
| Lublin | D | 1.0000 | ||
| PM10 | 0.3319 | 1.0000 | ||
| PM2.5 | 0.4553 | 0.9646 | 1.0000 | |
| Olsztyn | D | 1.0000 | ||
| PM10 | 0.3432 | 1.0000 | ||
| PM2.5 | 0.4519 | 0.9493 | 1.0000 | |
| Osieczow | D | 1.0000 | ||
| PM10 | 0.3219 | 1.0000 | ||
| PM2.5 | 0.3443 | 0.9852 | 1.0000 | |
| Puszcza Borecka | D | 1.0000 | ||
| PM10 | 0.3478 | 1.0000 | ||
| PM2.5 | 0.4329 | 0.9611 | 1.0000 | |
| Zielona Gora | D | 1.0000 | ||
| PM10 | 0.3725 | 1.0000 | ||
| PM2.5 | 0.4434 | 0.9487 | 1.0000 | |
| Zielonka | D | 1.0000 | ||
| PM10 | 0.2662 | 1.0000 | ||
| PM2.5 | 0.3176 | 0.9387 | 1.0000 |
| Air Monitoring Station | Regression Model | Explanatory Variable (Predictors) | MAE μg/m3 | RMSE μg/m3 | MARE | R2 | d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaslo | MEAN | - | 11.43 | 16.55 | 0.6893 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| LIN | PM10 | 2.43 | 3.79 | 0.1400 | 0.9477 | 0.9864 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | D | 9.85 | 15.74 | 0.5515 | 0.2373 | 0.6155 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | PM10 | 2.36 | 3.80 | 0.1321 | 0.9491 | 0.9867 | |
| MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 2.04 | 3.47 | 0.1148 | 0.9576 | 0.9890 | |
| Katowice | MEAN | - | 12.90 | 23.28 | 0.4161 | 0.0000 | 0.3162 |
| LIN | PM10 | 3.87 | 5.73 | 0.1691 | 0.9292 | 0.9814 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | D | 11.50 | 18.95 | 0.5165 | 0.2236 | 0.5760 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | PM10 | 3.84 | 5.81 | 0.1683 | 0.9274 | 0.9805 | |
| MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 3.35 | 5.18 | 0.1509 | 0.9422 | 0.9848 | |
| Koscierzyna | MEAN | - | 13.18 | 18.04 | 0.9755 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| LIN | PM10 | 3.74 | 5.70 | 0.2668 | 0.9000 | 0.9732 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | D | 10.01 | 14.97 | 0.6693 | 0.3050 | 0.6807 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | PM10 | 3.67 | 5.67 | 0.2675 | 0.9014 | 0.9735 | |
| MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 3.15 | 4.89 | 0.2339 | 0.9266 | 0.9805 | |
| Krakow | MEAN | - | 17.96 | 28.20 | 0.7839 | 0.0000 | 0.1307 |
| LIN | PM10 | 3.91 | 5.69 | 0.1576 | 0.9588 | 0.9894 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | D | 14.56 | 23.83 | 0.6539 | 0.2780 | 0.6492 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | PM10 | 3.80 | 5.63 | 0.1497 | 0.9598 | 0.9897 | |
| MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 3.38 | 5.26 | 0.1340 | 0.9648 | 0.9910 | |
| Lodz | MEAN | - | 13.11 | 21.32 | 0.4614 | 0.0000 | 0.3499 |
| LIN | PM10 | 4.86 | 6.94 | 0.2269 | 0.8722 | 0.9648 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | D | 10.05 | 15.63 | 0.4580 | 0.3522 | 0.7073 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | PM10 | 4.74 | 6.86 | 0.2183 | 0.8754 | 0.9659 | |
| MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 3.76 | 5.54 | 0.1821 | 0.9188 | 0.9783 | |
| Lublin | MEAN | - | 9.50 | 15.38 | 0.4408 | 0.0000 | 0.3713 |
| LIN | PM10 | 2.65 | 3.58 | 0.1692 | 0.9304 | 0.9817 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | D | 7.91 | 11.84 | 0.5503 | 0.2369 | 0.6047 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | PM10 | 2.62 | 3.56 | 0.1640 | 0.9310 | 0.9820 | |
| MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 1.79 | 2.59 | 0.1161 | 0.9635 | 0.9905 | |
| Olsztyn | MEAN | - | 7.77 | 12.02 | 0.5267 | 0.0000 | 0.3059 |
| LIN | PM10 | 2.51 | 3.58 | 0.1793 | 0.9012 | 0.9734 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | D | 7.02 | 9.98 | 0.6197 | 0.2315 | 0.6118 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | PM10 | 2.42 | 3.52 | 0.1683 | 0.9049 | 0.9742 | |
| MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 1.72 | 2.52 | 0.1301 | 0.9511 | 0.9872 | |
| Osieczow | MEAN | - | 8.64 | 15.89 | 0.4456 | 0.0000 | 0.3434 |
| LIN | PM10 | 1.70 | 2.43 | 0.1457 | 0.9705 | 0.9925 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | D | 8.18 | 12.95 | 0.7748 | 0.1621 | 0.5094 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | PM10 | 1.58 | 2.31 | 0.1302 | 0.9733 | 0.9932 | |
| MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 1.48 | 2.22 | 0.1239 | 0.9754 | 0.9937 | |
| Puszcza Borecka | MEAN | - | 6.35 | 9.96 | 0.4845 | 0.0000 | 0.3940 |
| LIN | PM10 | 1.62 | 2.36 | 0.1692 | 0.9237 | 0.9798 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | D | 5.52 | 7.79 | 0.6995 | 0.2188 | 0.5910 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | PM10 | 1.61 | 2.34 | 0.1702 | 0.9255 | 0.9801 | |
| MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 1.38 | 2.06 | 0.1458 | 0.9420 | 0.9849 | |
| Zielona Gora | MEAN | - | 9.33 | 15.50 | 0.4389 | 0.0000 | 0.3829 |
| LIN | PM10 | 2.84 | 4.21 | 0.2107 | 0.9001 | 0.9732 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | D | 7.95 | 11.76 | 0.5897 | 0.2252 | 0.5708 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | PM10 | 2.78 | 4.17 | 0.2058 | 0.9023 | 0.9734 | |
| MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 2.45 | 3.76 | 0.1812 | 0.9207 | 0.9787 | |
| Zielonka | MEAN | - | 7.87 | 12.75 | 0.5603 | 0.0000 | 0.3856 |
| LIN | PM10 | 2.51 | 3.77 | 0.2376 | 0.8811 | 0.9675 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | D | 7.11 | 10.12 | 0.9410 | 0.1295 | 0.4835 | |
| MLP 1-10-1 | PM10 | 2.50 | 3.77 | 0.2445 | 0.8815 | 0.9676 | |
| MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 2.38 | 3.63 | 0.2385 | 0.8901 | 0.9701 |
| Air Monitoring Station | Regression Model | Explanatory Variable (Predictors) | MAE μg/m3 | RMSE μg/m3 | MARE | R2 | d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaslo | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 3.01 | 4.53 | 0.1463 | 0.9533 | 0.9796 |
| Katowice | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 3.40 | 5.38 | 0.1481 | 0.9401 | 0.9845 |
| Koscierzyna | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 3.30 | 5.10 | 0.2514 | 0.9204 | 0.9785 |
| Krakow | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 3.38 | 5.26 | 0.1340 | 0.9648 | 0.9910 |
| Lodz | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 4.13 | 6.21 | 0.2072 | 0.9046 | 0.9730 |
| Lublin | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 2.11 | 2.88 | 0.1369 | 0.9597 | 0.9877 |
| Olsztyn | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 2.04 | 2.84 | 0.1676 | 0.9408 | 0.9829 |
| Osieczow | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 2.17 | 3.18 | 0.1786 | 0.9707 | 0.9852 |
| Puszcza Borecka | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 1.76 | 2.35 | 0.2461 | 0.9307 | 0.9784 |
| Zielona Gora | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 2.63 | 3.95 | 0.1913 | 0.9203 | 0.9746 |
| Zielonka | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 2.66 | 3.81 | 0.3325 | 0.8800 | 0.9663 |
| Air Monitoring Station | Regression Model | Explanatory Variable (Predictors) | MAE μg/m3 | RMSE μg/m3 | MARE | R2 | d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaslo | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 2.19 | 3.81 | 0.1215 | 0.9503 | 0.9872 |
| Katowice | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 4.24 | 7.76 | 0.1823 | 0.8886 | 0.9675 |
| Koscierzyna | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 3.84 | 6.25 | 0.2864 | 0.9158 | 0.9720 |
| Krakow | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 4.84 | 9.34 | 0.1790 | 0.9006 | 0.9712 |
| Lodz | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 5.69 | 8.43 | 0.2825 | 0.8826 | 0.9551 |
| Lublin | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 2.27 | 3.36 | 0.1514 | 0.9532 | 0.9853 |
| Olsztyn | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 2.26 | 3.47 | 0.1720 | 0.9315 | 0.9779 |
| Osieczow | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 1.48 | 2.22 | 0.1239 | 0.9754 | 0.9937 |
| Puszcza Borecka | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 1.48 | 2.32 | 0.1611 | 0.9366 | 0.9823 |
| Zielona Gora | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 2.61 | 4.03 | 0.1999 | 0.9150 | 0.9768 |
| Zielonka | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 2.53 | 4.09 | 0.2490 | 0.8842 | 0.9667 |
| Air Monitoring Station | Regression Model | Explanatory Variable (Predictors) | MAE μg/m3 | RMSE μg/m3 | MARE | R2 | d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaslo | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 3.31 | 5.76 | 0.1572 | 0.9134 | 0.9661 |
| Katowice | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 4.61 | 11.34 | 0.1630 | 0.7371 | 0.9061 |
| Koscierzyna | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 3.48 | 5.97 | 0.2360 | 0.8925 | 0.9692 |
| Krakow | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 6.03 | 15.86 | 0.1598 | 0.7119 | 0.8815 |
| Lodz | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 4.35 | 8.22 | 0.1910 | 0.8226 | 0.9472 |
| Lublin | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 2.14 | 3.76 | 0.1247 | 0.9281 | 0.9788 |
| Olsztyn | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 1.72 | 2.52 | 0.1301 | 0.9511 | 0.9872 |
| Osieczow | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 2.06 | 3.63 | 0.1433 | 0.9500 | 0.9811 |
| Puszcza Borecka | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 1.48 | 2.17 | 0.1594 | 0.9360 | 0.9832 |
| Zielona Gora | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 2.54 | 4.07 | 0.1761 | 0.9097 | 0.9741 |
| Zielonka | MLP 2-10-1 | D, PM10 | 2.46 | 3.87 | 0.2405 | 0.8788 | 0.9678 |
| Air Monitoring Station | PM10, μg/m3 | PM2.5, μg/m3 | PM2.5/PM10 Ratio, % | r-Pearson PM2.5/PM10 | RMSE, μg/m3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Variant I (MLP 1-10-1) | Variant III (MLP 2-10-1) | |||
| Jaslo | 27.2 | 18.3 | 21.9 | 16.6 | 0.79 | 0.9735 | 15.74 | 3.47 |
| Katowice | 36.6 | 26.5 | 26.7 | 21.5 | 0.71 | 0.9639 | 18.95 | 5.18 |
| Koscierzyna | 31.4 | 21.1 | 22.8 | 18.0 | 0.70 | 0.9487 | 14.97 | 4.89 |
| Krakow | 41.7 | 33.2 | 30.6 | 28.0 | 0.70 | 0.9792 | 23.83 | 5.26 |
| Lodz | 38.8 | 22.5 | 26.5 | 19.4 | 0.66 | 0.9339 | 15.63 | 5.54 |
| Lublin | 26.0 | 15.8 | 19.2 | 13.6 | 0.72 | 0.9646 | 11.84 | 2.59 |
| Olsztyn | 22.0 | 13.6 | 15.7 | 11.4 | 0.70 | 0.9493 | 9.98 | 2.52 |
| Osieczow | 19.9 | 15.3 | 15.5 | 14.1 | 0.74 | 0.9852 | 12.95 | 2.22 |
| Puszcza Borecka | 16.0 | 10.3 | 11.7 | 8.6 | 0.71 | 0.9611 | 7.79 | 2.06 |
| Zielona Gora | 23.0 | 14.7 | 17.2 | 13.3 | 0.72 | 0.9487 | 11.76 | 3.76 |
| Zielonka | 18.4 | 13.3 | 13.3 | 10.9 | 0.71 | 0.9387 | 10.12 | 3.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoffman, S.; Jasiński, R.; Baran, J. Regression Modeling of Daily PM2.5 Concentrations with a Multilayer Perceptron. Energies 2024, 17, 2202. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092202
Hoffman S, Jasiński R, Baran J. Regression Modeling of Daily PM2.5 Concentrations with a Multilayer Perceptron. Energies. 2024; 17(9):2202. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092202
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoffman, Szymon, Rafał Jasiński, and Janusz Baran. 2024. "Regression Modeling of Daily PM2.5 Concentrations with a Multilayer Perceptron" Energies 17, no. 9: 2202. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092202
APA StyleHoffman, S., Jasiński, R., & Baran, J. (2024). Regression Modeling of Daily PM2.5 Concentrations with a Multilayer Perceptron. Energies, 17(9), 2202. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092202






