An Ultra-Throughput Boost Method for Gamma-Ray Spectrometers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
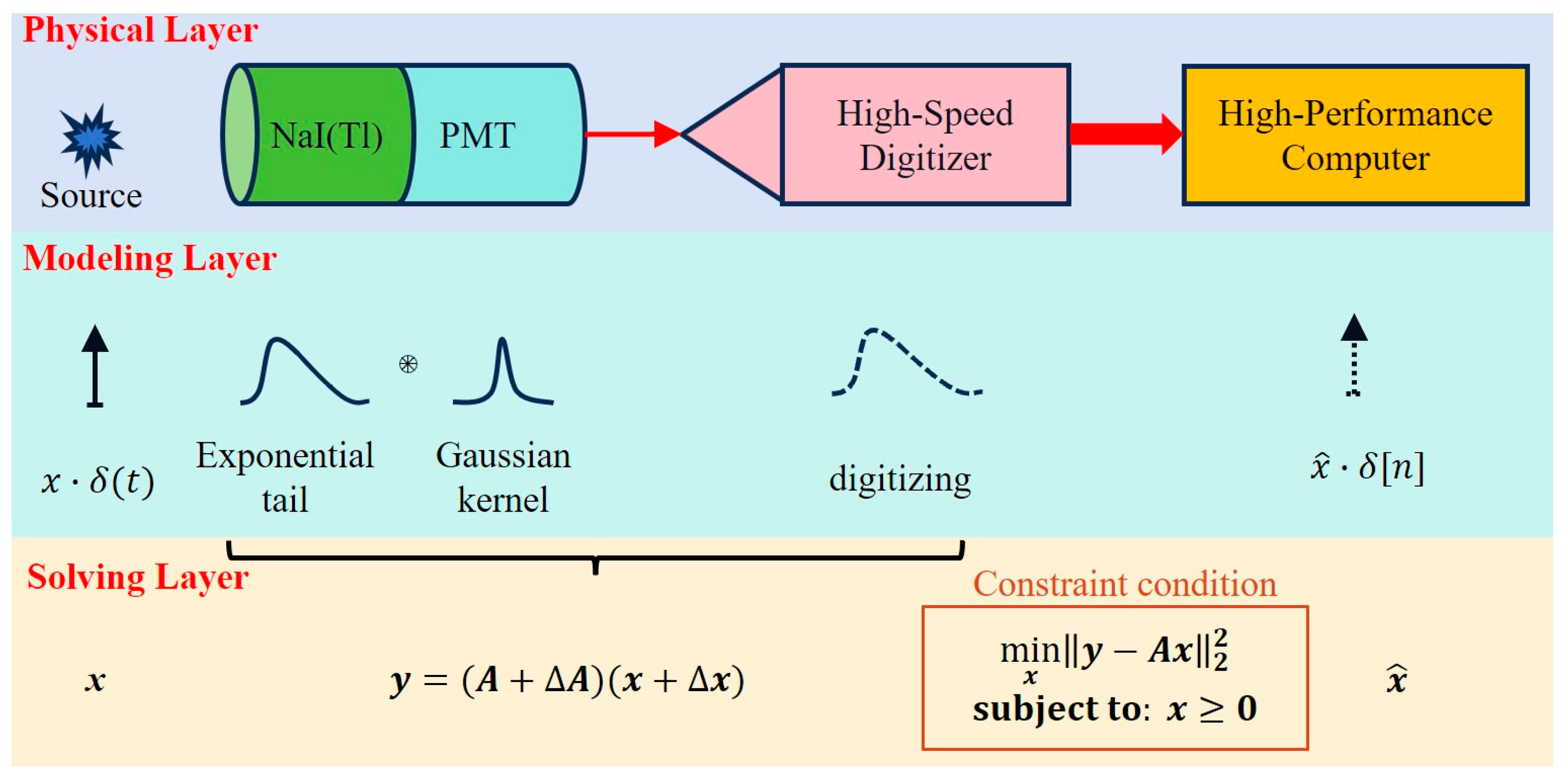
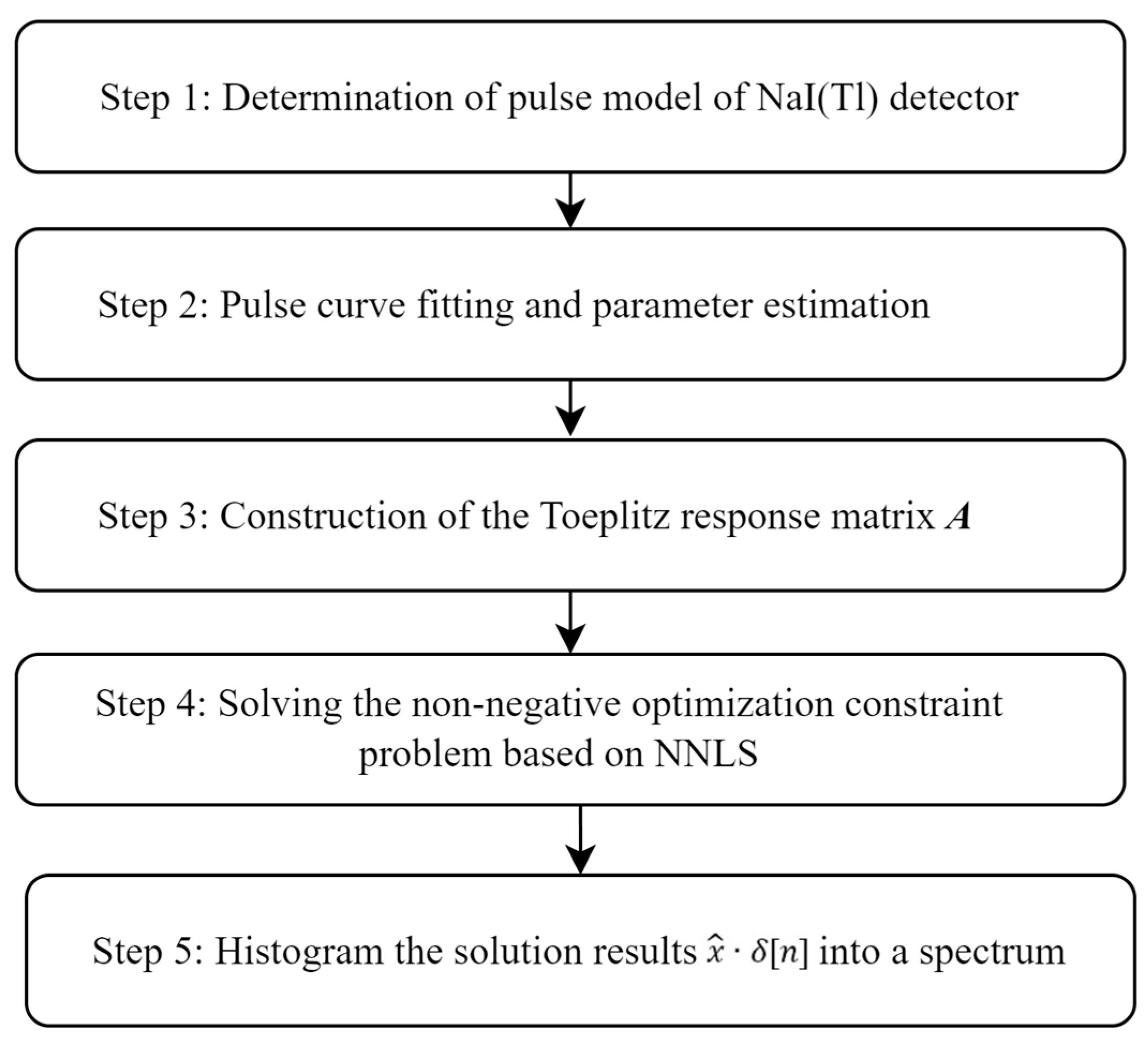
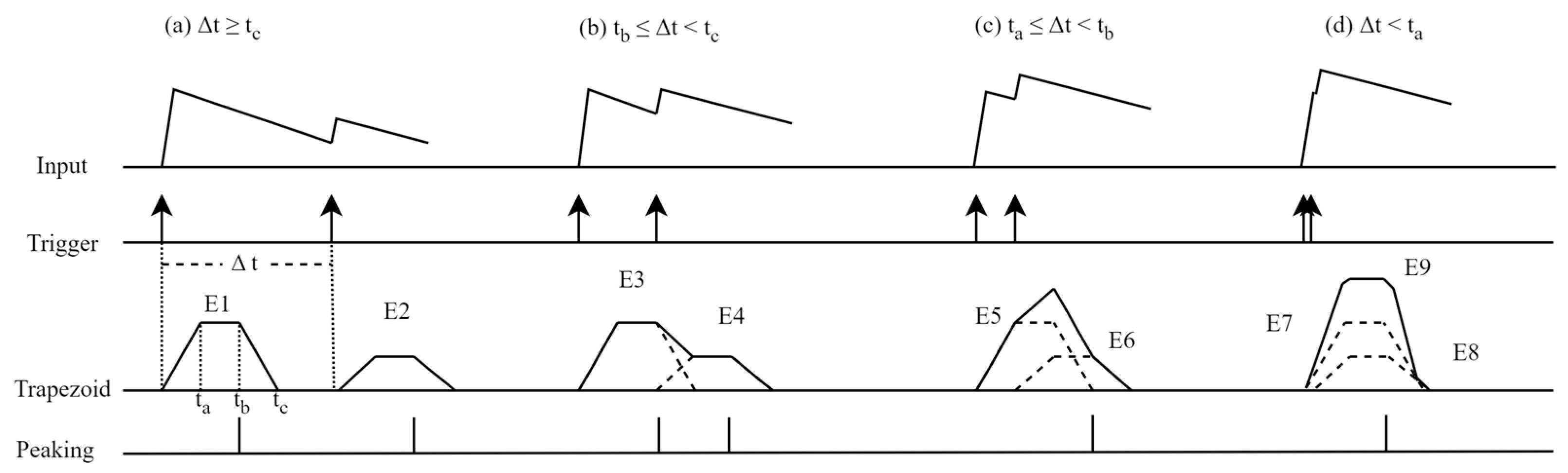
2.1. Description of the UTB Method
| Algorithm 1. The NNLS Algorithm | |
| Step | Description |
| 1 | Set , , and . |
| 2 | Compute the n-vector . |
| 3 | If the set is empty or if for all , go to Step 12. |
| 4 | Find an index such that . |
| 5 | Move the index from set to set |
| 6 | Let denote the matrix defined by column of Compute the n-vector as a solution of the least squares problem . Note that only the components , are determined by this problem. Define for . |
| 7 | If for all , set and go to Step 2. |
| 8 | Find an index such that . |
| 9 | Set . |
| 10 | Set . |
| 11 | Move from set to set all indices for which . Go to Step 6. |
| 12 | Comment: the computation is completed. |
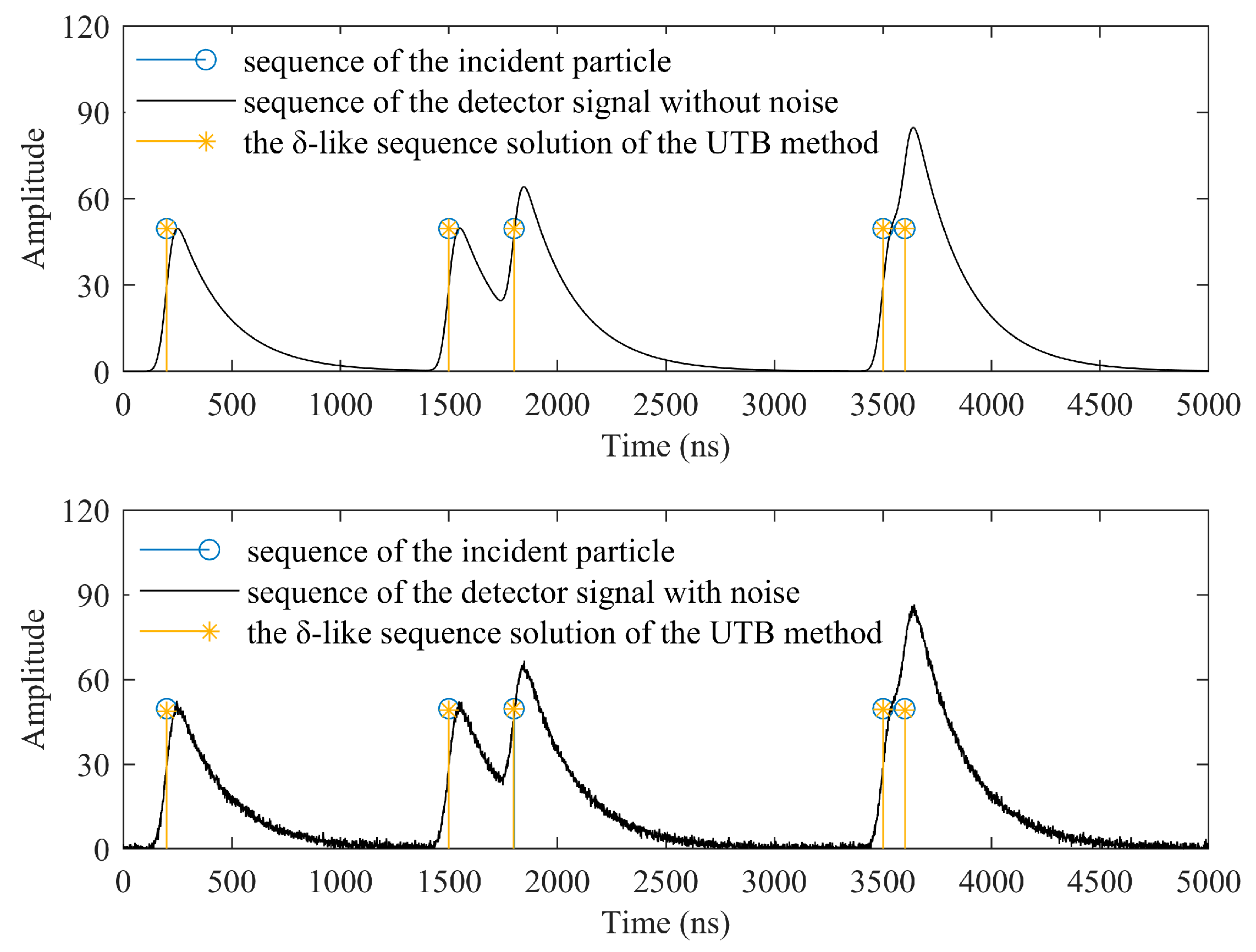
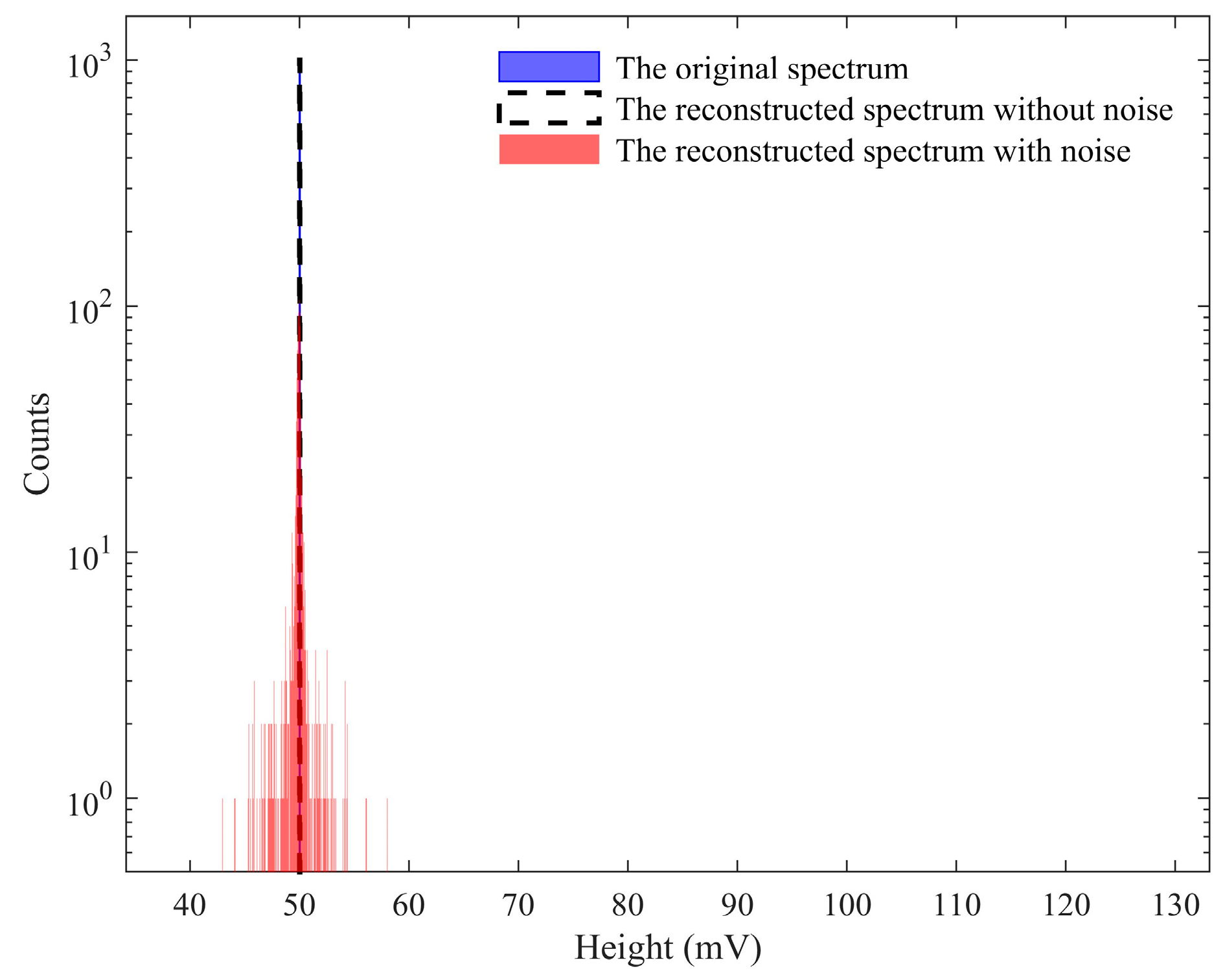
2.2. Simulation and Verification of the UTB Method
3. Results
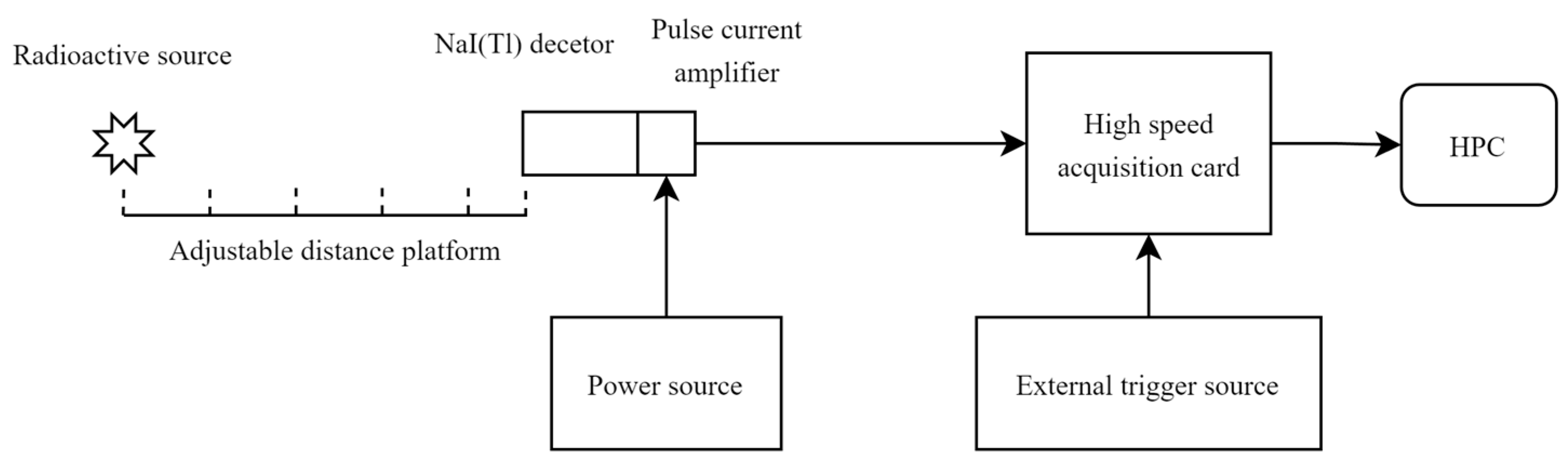
3.1. Setup of the Experiment
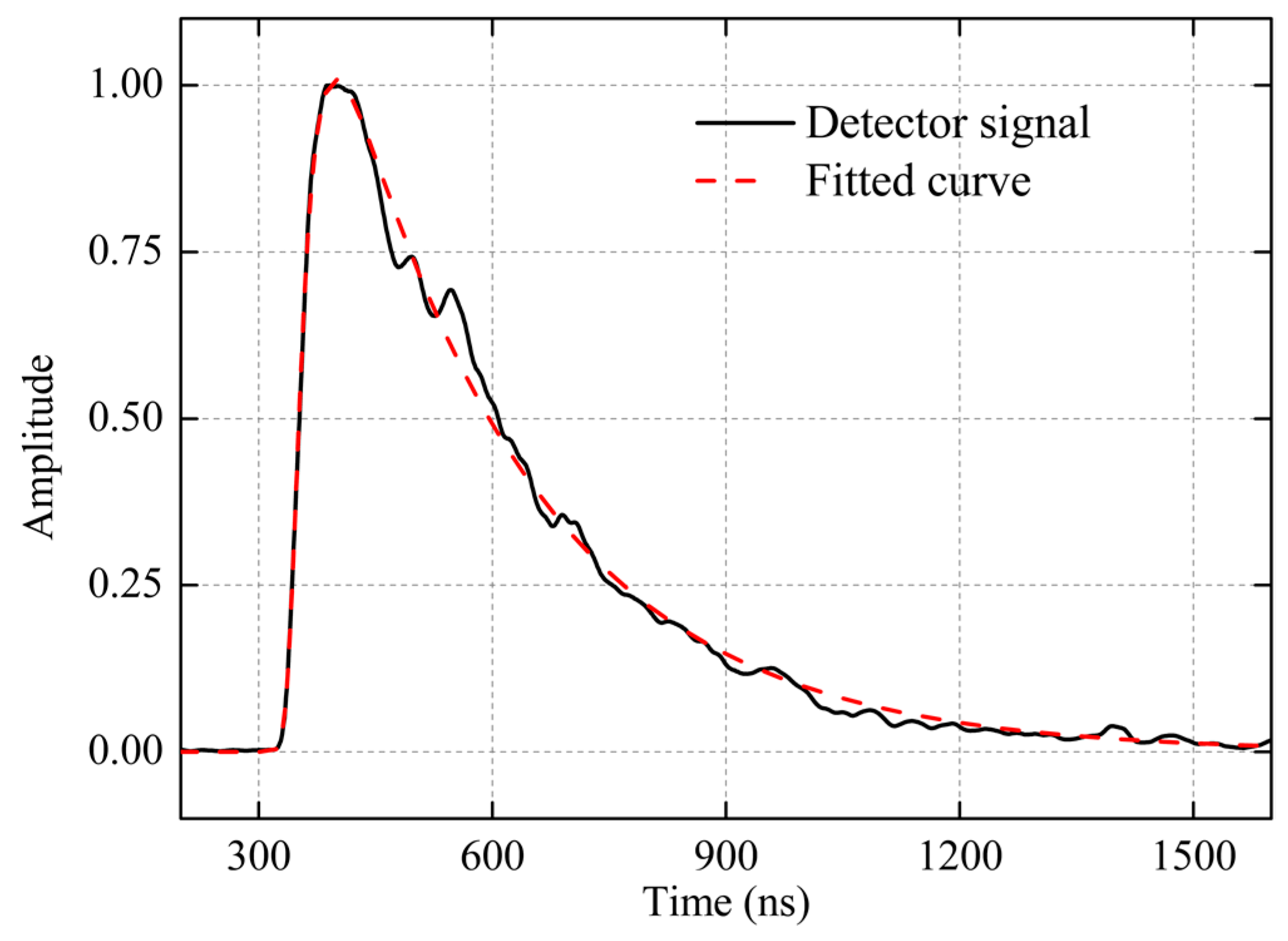
3.2. Parameter Estimation
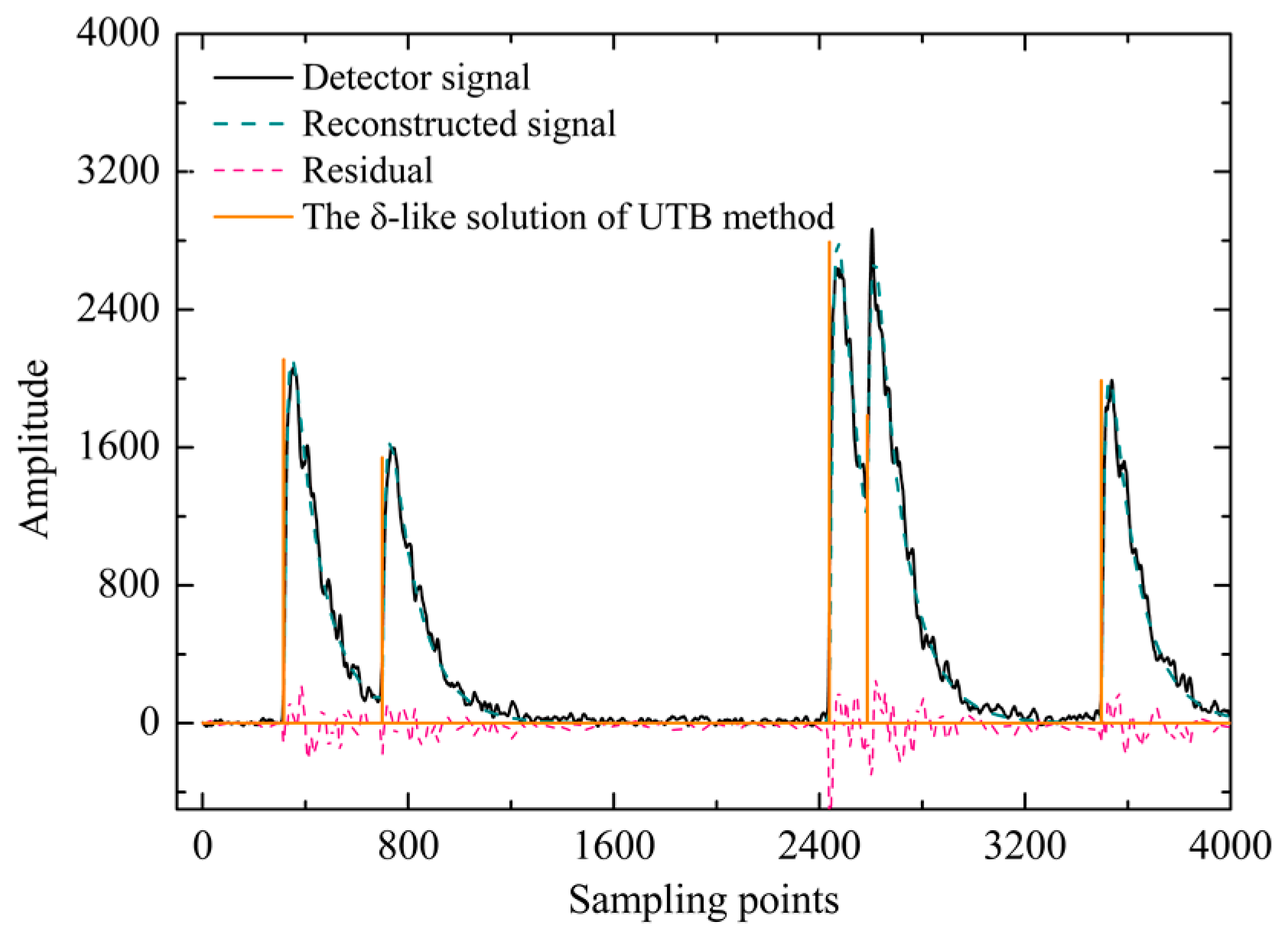
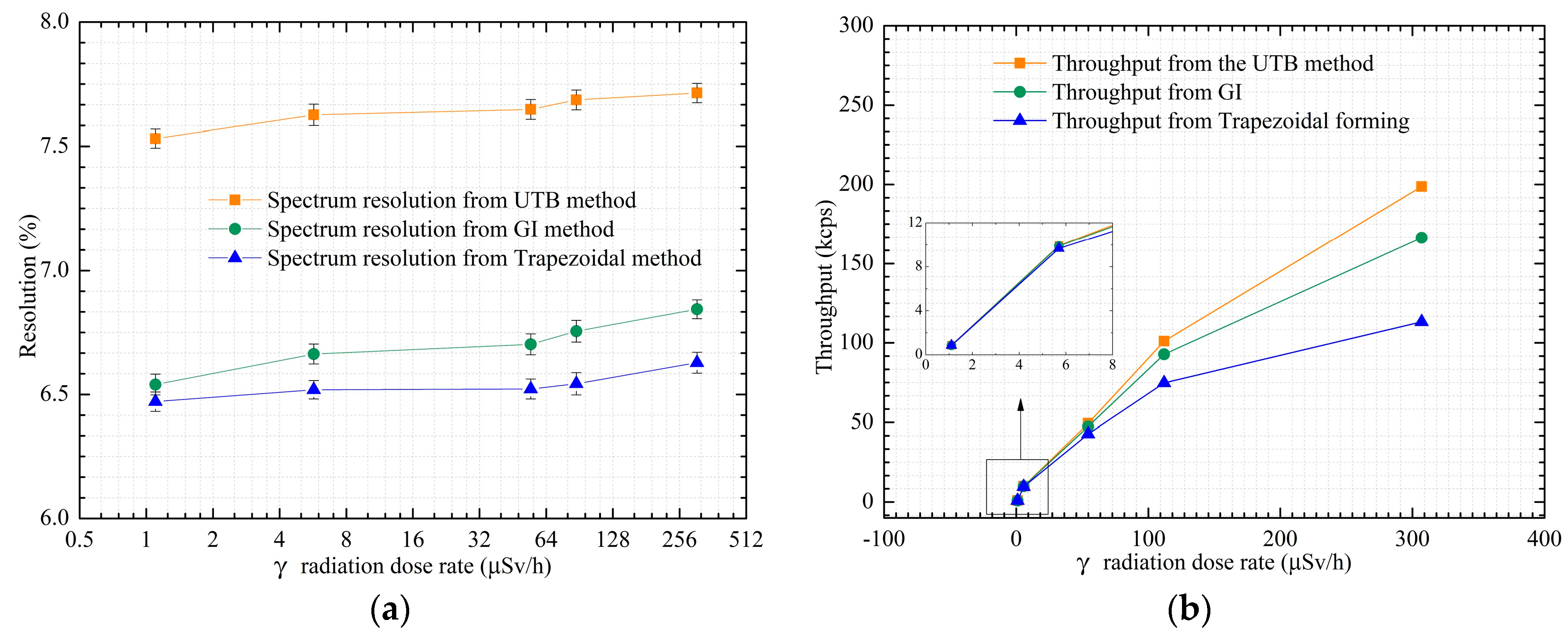
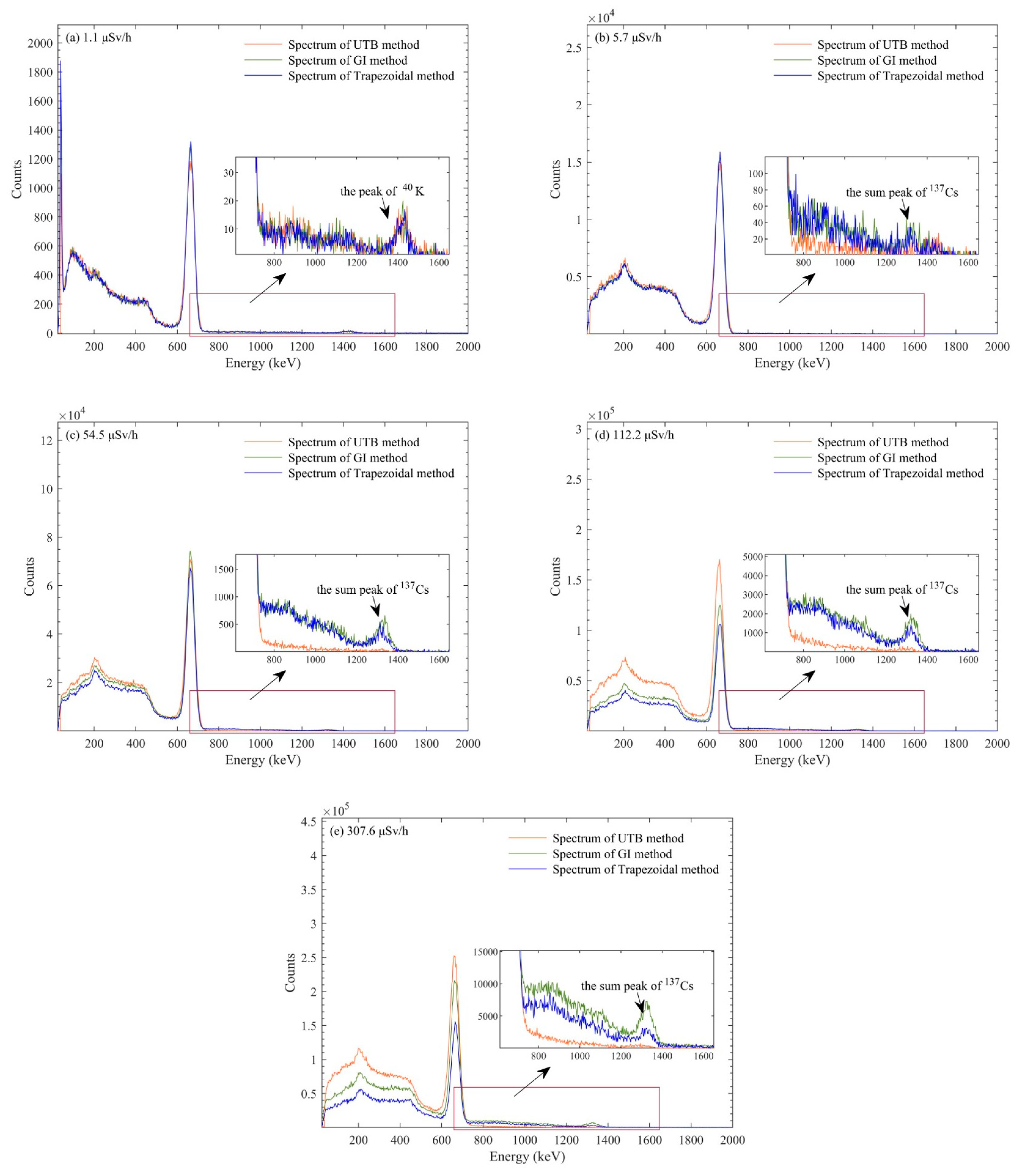
3.3. Verification Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Convolution Integral Formula
References
- Radeka, V.; Karlovac, N. Least-Square-Error Amplitude Measurement of Pulse Signals in Presence of Noise. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 1967, 52, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radeka, V. Trapezoidal Filtering of Signals from Large Germanium Detectors at High Rates. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 1972, 99, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordanov, V.T.; Knoll, G.F. Digital Synthesis of Pulse Shapes in Real Time for High Resolution Radiation Spectroscopy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 1994, 345, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordanov, V.T. Deconvolution of Pulses from a Detector-Amplifier Configuration. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 1994, 351, 592–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raad, M.W.; Deriche, M.; Noras, J.; Shafiq, M. A Novel Approach for Pileup Detection in Gamma-Ray Spectroscopy Using Deconvolution. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 065601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingefors, N.; Bouvier, S.; Gadomski, S.; Hall, G.; Høgh, T.S.; Jalocha, P.; Vd. Lippe, H.; Michel, J.; Nygård, E.; Raymond, M.; et al. A Novel Technique for Fast Pulse-Shaping Using a Slow Amplifier at LHC. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 1993, 326, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Scoullar, P.A.B.; Evans, R.J. Maximum Likelihood Estimation Techniques for High Rate, High Throughput Digital Pulse Processing. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record, Dresden, Germany, 19–25 October 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 1668–1672. [Google Scholar]
- Miklavec, M.; Loher, B.; Savran, D.; Novak, R.; Sirca, S.; Vencelj, M. Pile-up Correction Techniques for Real-Time Dosimetry in Photon Radiotherapy. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference Record (NSS/MIC), Anaheim, CA, USA, 29 October–3 November 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 3880–3882. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.; Farsoni, A.T.; Yang, H.; Hamby, D.H. A New Pulse Model for NaI(Tl) Detection Systems. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2014, 763, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Farsoni, A.T.; Yang, H.; Hamby, D.M. Model-Based Pulse Deconvolution Method for NaI(Tl) Detectors. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2015, 769, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafaee, M.; Goodarzi, M.M. Pile-Up Correction in Spectroscopic Signals Using Regularized Sparse Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2020, 67, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rooi, J.; Eilers, P. Deconvolution of Pulse Trains with the L0 Penalty. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 705, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xiao, W.; Ai, X.; Chen, Y. Nonnegative Constraint Quadratic Program Technique to Enhance the Resolution of γ Spectra. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2018, 887, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morháč, M.; Matoušek, V. High-Resolution Boosted Deconvolution of Spectroscopic Data. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2011, 235, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.-K.; Huang, H.-Q.; Wang, Q.-C.; Zhao, J.; Yang, F.; Jiang, K.-M.; Ding, W.-C.; Zhou, W. Estimation of Gaussian Overlapping Nuclear Pulse Parameters Based on a Deep Learning LSTM Model. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2019, 30, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.-K.; Huang, H.-Q.; Ji, X.; Dai, H.-Y.; Wu, J.-H.; Zhao, J.; Yang, F.; Tang, L.; Jiang, K.-M.; Ding, W.-C.; et al. Estimation of Trapezoidal-Shaped Overlapping Nuclear Pulse Parameters Based on a Deep Learning CNN-LSTM Model. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2021, 28, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, H.; Ma, X.; Shen, Z.; Zhong, C.; Ding, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, J. Trapezoidal Pile-up Nuclear Pulse Parameter Identification Method Based on Deep Learning Transformer Model. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2022, 190, 110515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, P.; Deng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shen, C. Universal Uncertainty Estimation for Nuclear Detector Signals with Neural Networks and Ensemble Learning. J. Instrum. 2022, 17, P02032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, C.; Baghaei, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ramirez, R.; Liu, S.; An, S.; Wong, W.-H. A New Statistics-Based Online Baseline Restorer for a High Count-Rate Fully Digital System. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2010, 57, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gray, R.M. Toeplitz and Circulant Matrices: A Review. Found. Trends® Commun. Inf. Theory 2005, 2, 155–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.P.; Vandenberghe, L. Convex Optimization; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-0-521-83378-3. [Google Scholar]

| Dose Rate (μSv/h) | UTB | GI | Trapezoidal | GI * | Trapezoidal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acquisition Time (s) | Real Time (s) | Rise Time/Flat Top (μs) | |||
| 1.1 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 0.016/1 | 1/1 |
| 5.7 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 0.016/1 | 1/1 |
| 54.5 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 0.016/1 | 1/1 |
| 112.2 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 0.016/1 | 1/1 |
| 307.6 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 0.016/1 | 1/1 |
| Model Parameters (ns) | ) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | 5.7 | 54.5 | 112.2 | 307.6 | |
| 12.678 | 12.759 | 12.749 | 12.761 | 12.752 | |
| 31.106 | 31.532 | 31.432 | 31.653 | 31.591 | |
| 230.108 | 231.302 | 230.985 | 231.689 | 231.762 | |
| R-square | 0.9991 | 0.9988 | 0.9989 | 0.9985 | 0.9985 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Cui, H. An Ultra-Throughput Boost Method for Gamma-Ray Spectrometers. Energies 2024, 17, 1456. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17061456
Li W, Zhou Q, Zhang Y, Xie J, Zhao W, Li J, Cui H. An Ultra-Throughput Boost Method for Gamma-Ray Spectrometers. Energies. 2024; 17(6):1456. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17061456
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wenhui, Qianqian Zhou, Yuzhong Zhang, Jianming Xie, Wei Zhao, Jinglun Li, and Hui Cui. 2024. "An Ultra-Throughput Boost Method for Gamma-Ray Spectrometers" Energies 17, no. 6: 1456. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17061456
APA StyleLi, W., Zhou, Q., Zhang, Y., Xie, J., Zhao, W., Li, J., & Cui, H. (2024). An Ultra-Throughput Boost Method for Gamma-Ray Spectrometers. Energies, 17(6), 1456. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17061456





