Impact of Sweep Gas on the Degradation of an La0.6Sr0.4Co0.8Fe0.8O3 Anode in a Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Reference Performance of the Cells
3.2. Degradation Experiments
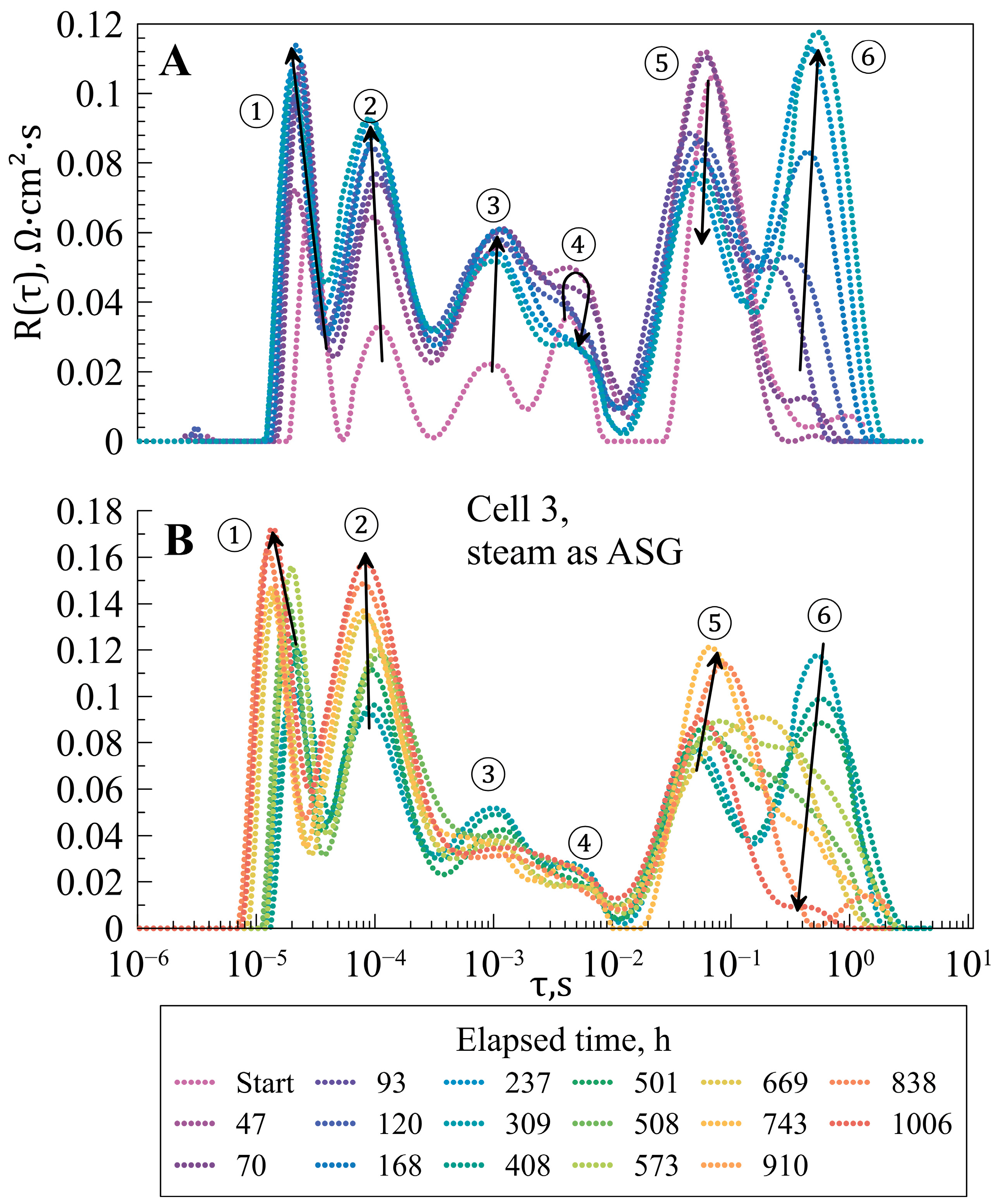
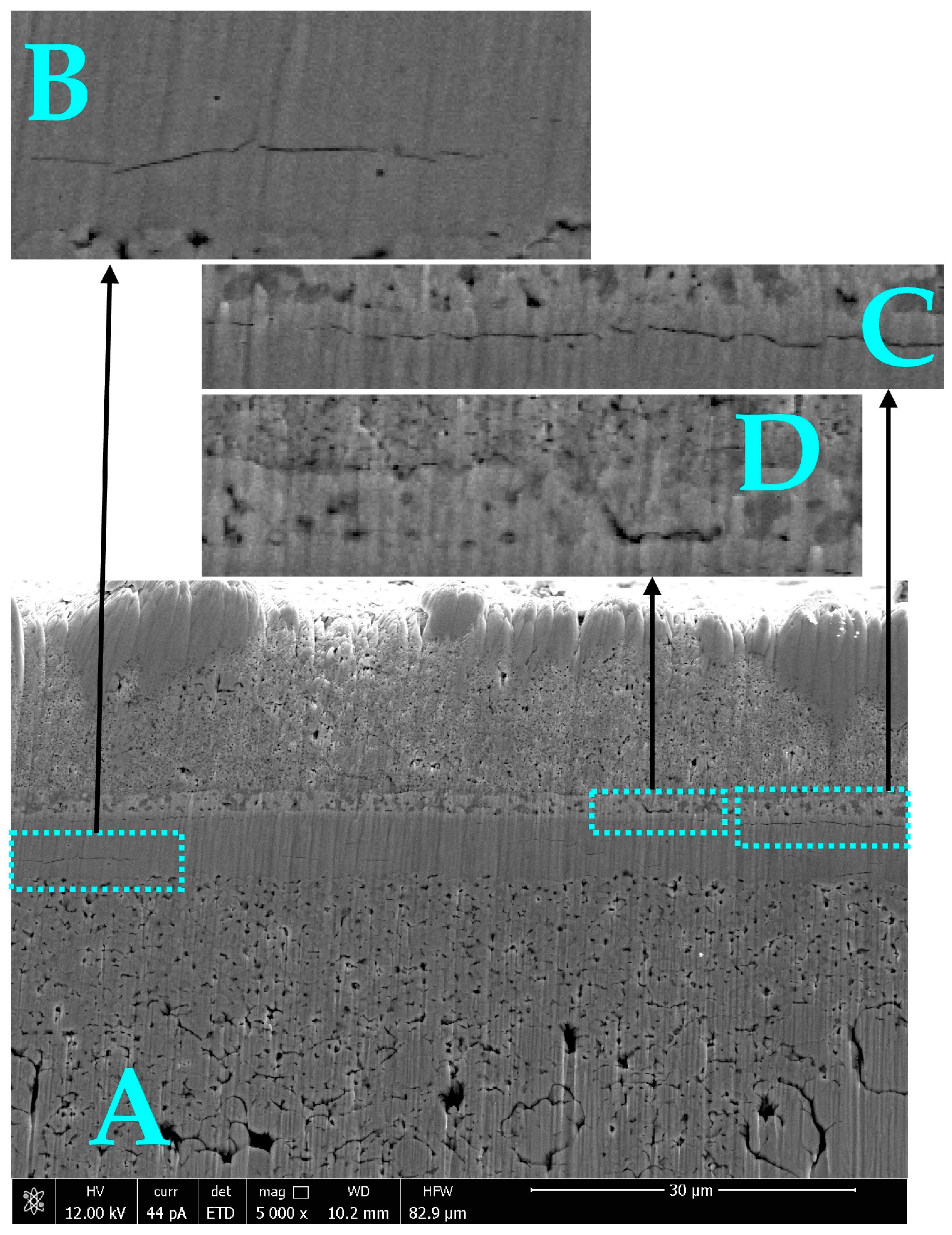
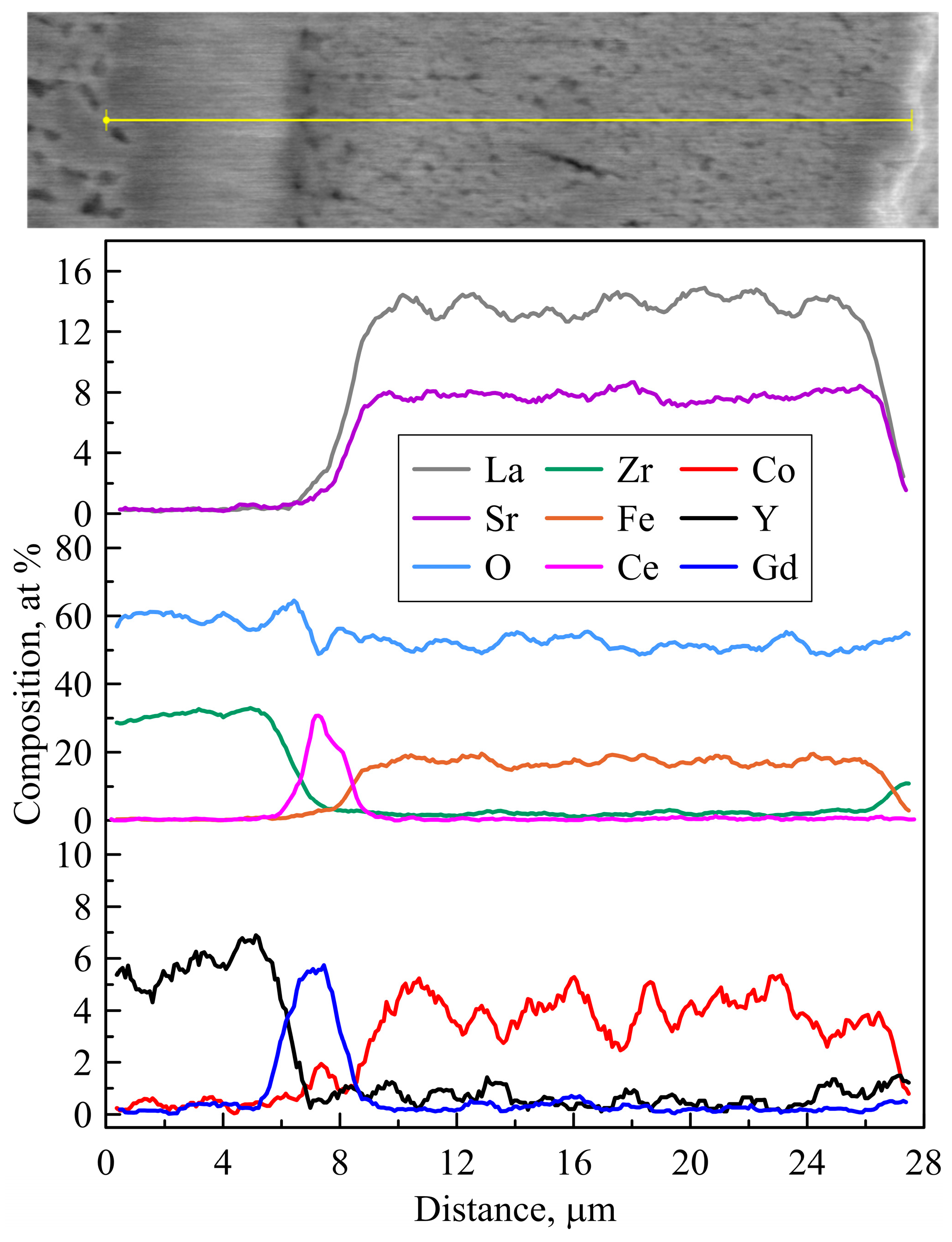
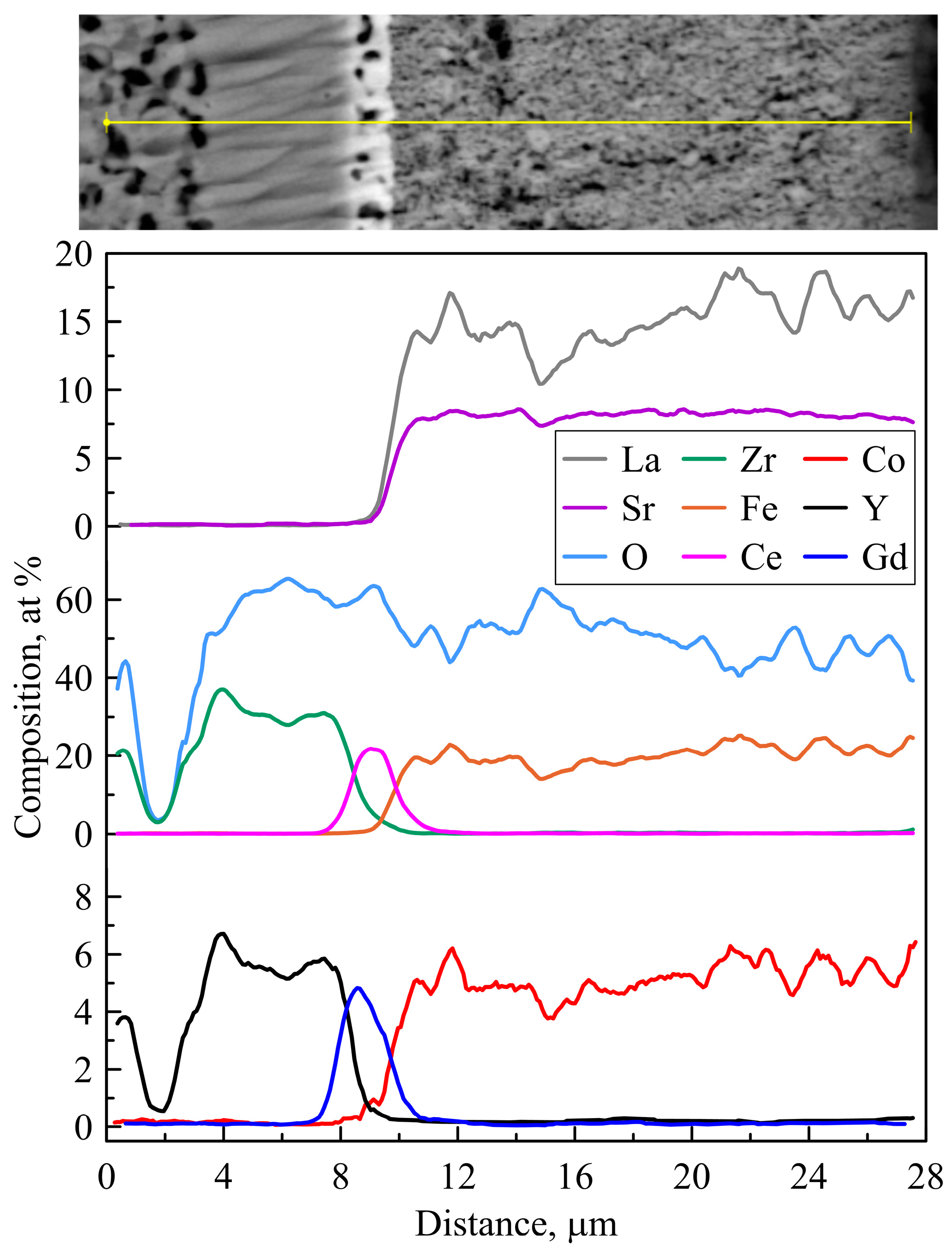
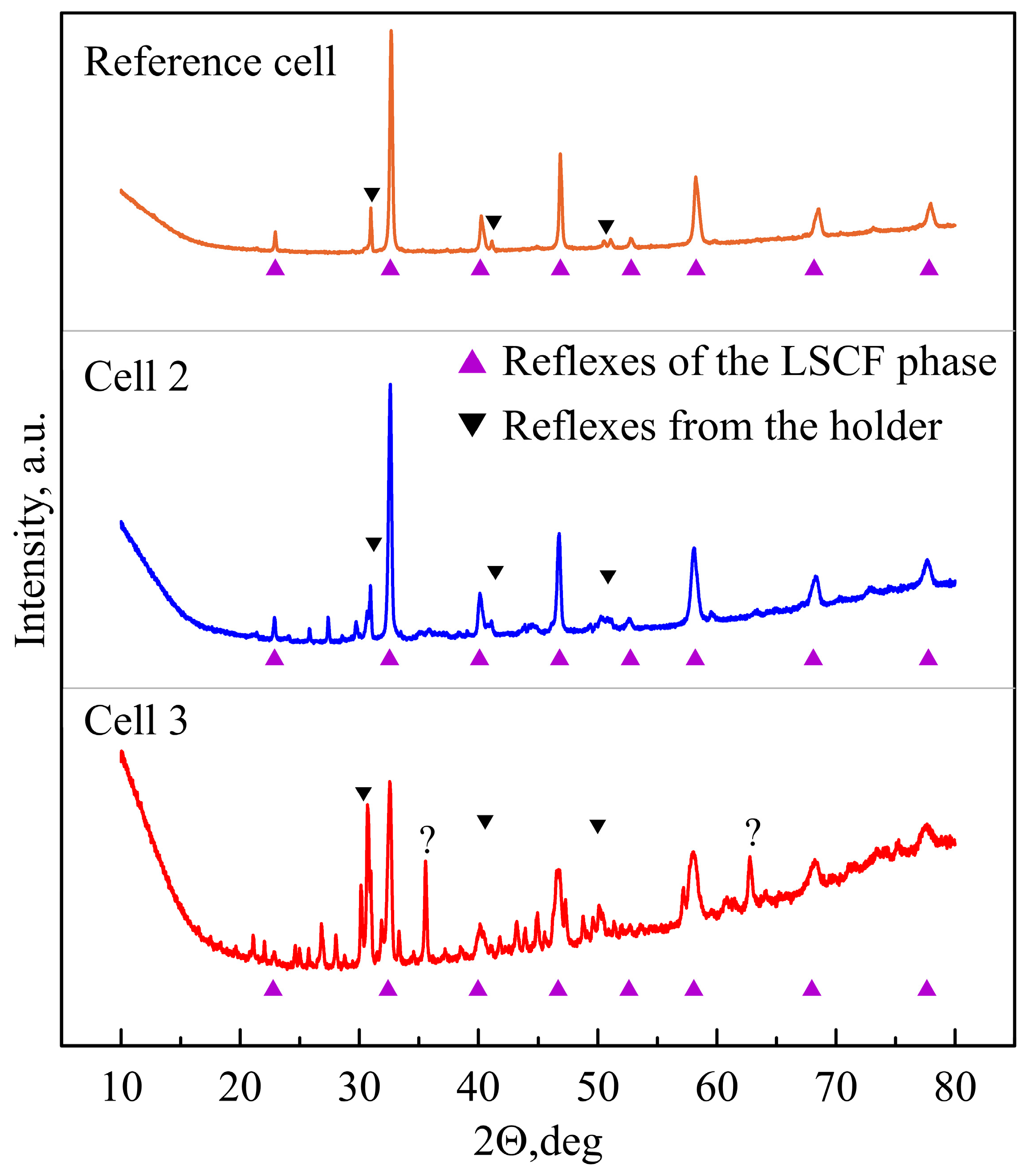
3.3. Post-Mortem
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kupecki, J.; Hercog, J.; Motyliński, K.; Malesa, J.; Muszyński, D.; Skrzypek, E.; Skrzypek, M.; Boettcher, A.; Tchorek, G. Advancing production of hydrogen using nuclear cycles—Integration of high temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGR) with solid oxide electrolyzers (SOE). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 53, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRENA. Geopolitics of the Energy Transformation: The Hydrogen Factor; International Renewable Energy Agency: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2022; ISBN 978-92-9260-370-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kupecki, J.; Motylinski, K.; Jagielski, S.; Wierzbicki, M.; Brouwer, J.; Naumovich, Y.; Skrzypkiewicz, M. Energy analysis of a 10 kW-class power-to-gas system based on a solid oxide electrolyzer (SOE). Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 199, 111934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauch, A.; Küngas, R.; Blennow, P.; Hansen, A.B.; Hansen, J.B.; Mathiesen, B.V.; Mogensen, M.B. Recent advances in solid oxide cell technology for electrolysis. Science 2020, 370, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Kupecki, J.; Deng, Z.; Li, X. Efficiency analysis of a novel reversible solid oxide cell system with the secondary utilization of the stack off-gas: A model-based study. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 397, 136570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, Z.; Kupecki, J.; Fu, X.; Li, X. Control-oriented performance prediction of solid oxide electrolysis cell and durability improvement through retard oxygen electrode delamination with reverse operation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 277, 116596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udagawa, J.; Aguiar, P.; Brandon, N.P. Hydrogen production through steam electrolysis: Control strategies for a cathode-supported intermediate temperature solid oxide electrolysis cell. J. Power Sources 2008, 180, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barelli, L.; Bidini, G.; Cinti, G. Steam as sweep gas in SOE oxygen electrode. J. Energy Storage 2018, 20, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aphale, A.; Liang, C.; Hu, B.; Singh, P. Cathode Degradation From Airborne Contaminants in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: A Review. In Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Lifetime and Reliability; Brandon, N.P., Ruiz-Trejo, E., Boldrin, P., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2017; pp. 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, A.; Neufeld, K.; Liu, Y.L. Effect of Humidity in Air on Performance and Long-Term Durability of SOFCs. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, B1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Muroyama, H.; Matsui, T.; Eguchi, K. Influence of Water Vapor on Performance Degradation and Microstructural Change of (La,Sr)(Co,Fe)O3−δ Cathode. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, F1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, A.; Perz, M.; Bucher, E.; Gspan, C.; Sitte, W. Effect of Microstructure on the Degradation of La0.6Sr0.4CoO3–δ Electrodes in Dry and Humid Atmospheres. Fuel Cells 2019, 19, 458–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, A.; Schrödl, N.; Sitte, W. Evaluation of oxide ceramics as anodes for SOECs. Faraday Discuss. 2015, 182, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Hendriksen, P.V.; Hauch, A.; Clausen, A.K.; Lehtinen, T.; Noponen, M. Effect of Anode Side Purge Gas on the Degradation of Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells. ECS Trans. 2021, 103, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solid Oxide Fuel Cells—Elcogen | Solid Oxide Cells and Stacks. Available online: https://elcogen.com/products/solid-oxide-fuel-cells/ (accessed on 8 December 2023).
- Saccoccio, M.; Wan, T.H.; Chen, C.; Ciucci, F. Optimal Regularization in Distribution of Relaxation Times applied to Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy: Ridge and Lasso Regression Methods—A Theoretical and Experimental Study. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 147, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, J.R.; Potter, L.D. A flexible procedure for analyzing impedance spectroscopy results: Description and illustrations. Solid State Ion. 1987, 24, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukamp, B.A. Distribution (function) of relaxation times, successor to complex nonlinear least squares analysis of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy? J. Phys. Energy 2020, 2, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GSL—GNU Scientific Library—GNU Project—Free Software Foundation. Available online: https://www.gnu.org/software/gsl/ (accessed on 27 December 2023).
- OpenBLAS: An Optimized BLAS Library. Available online: https://www.openblas.net/ (accessed on 27 December 2023).
- Johnson, S.G. The NLopt Nonlinear-Optimization Package. Available online: http://github.com/stevengj/nlopt (accessed on 27 December 2023).
- Wang, Y.; Marchetti, B.; Zhou, X.-D. Call attention to using DRT and EIS to quantify the contributions of solid oxide cell components to the total impedance. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 35437–35448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, Y.L.; Bentzen, J.J.; Zhang, W.; Sun, X.; Hauch, A.; Tao, Y.; Bowen, J.R.; Hendriksen, P.V. Microstructural Degradation of Ni/YSZ Electrodes in Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells under High Current. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, F883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietz, F.; Sebold, D.; Brisse, A.; Schefold, J. Degradation phenomena in a solid oxide electrolysis cell after 9000 h of operation. J. Power Sources 2013, 223, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorato, L.; Shang, Y.; Yang, S.; Hubert, M.; Couturier, K.; Zhang, L.; Vulliet, J.; Chen, M.; Laurencin, J. Understanding the Ni Migration in Solid Oxide Cell: A Coupled Experimental and Modeling Approach. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2023, 170, 034504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmeester, H.J.M.; Den Otter, M.W.; Boukamp, B.A. Oxygen transport in La0.6Sr0.4Co1−yFeyO3−δ. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2003, 9, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashiro, K.; Nakano, I.; Kuhn, M.; Hashimoto, S.; Sato, K.; Mizusaki, J. Electrical Conductivity and Oxygen Diffusivity of Perovskite-Type Solid Solution La0.6Sr0.4Co1-yFeyO3-δ (y = 0.2, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.8). ECS Trans. 2011, 35, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, S.; Fukuda, Y.; Kuhn, M.; Sato, K.; Yashiro, K.; Mizusaki, J. Oxygen nonstoichiometry and thermo-chemical stability of La0.6Sr0.4Co1-yFeyO3-δ (y = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8). Solid State Ion. 2010, 181, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virkar, A.V. Mechanism of oxygen electrode delamination in solid oxide electrolyzer cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 9527–9543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.; Miguel-Pérez, V.; Tarancón, A.; Slodczyk, A.; Torrell, M.; Ballesteros, B.; Ouweltjes, J.P.; Bassat, J.M.; Montinaro, D.; Morata, A. Multi-scale analysis of the diffusion barrier layer of gadolinia-doped ceria in a solid oxide fuel cell operated in a stack for 3000 h. J. Power Sources 2017, 344, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Railsback, J.; Choi, S.H.; Barnett, S.A. Effectiveness of dense Gd-doped ceria barrier layers for (La,Sr)(Co,Fe)O3 cathodes on Yttria-stabilized zirconia electrolytes. Solid State Ion. 2019, 335, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubeyroux, J.L.; Courbin, P.; Fournes, L.; Fruchart, D.; Le Flem, G. La phase SrLaFeO4: Structures cristalline et magnétique. J. Solid State Chem. 1980, 31, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shinawi, H.; Greaves, C. Synthesis and characterization of the K2NiF4 phases La1+xSr1−xCo0.5Fe0.5O4−δ (x = 0, 0.2). J. Solid State Chem. 2008, 181, 2705–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, K.-T.; Kim, Y.N.; Manthiram, A. Crystal chemistry and electrochemical properties of Ln(Sr,Ca)3(Fe,Co)3O10 intergrowth oxide cathodes for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 2482–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.A.S.; Waerenborgh, J.C.; Mendonça, M.H.R.M.; Nunes, M.R.; Costa, F.M. Structural and morphological characterization of FeCo2O4 and CoFe2O4 spinels prepared by a coprecipitation method. Solid State Sci. 2003, 5, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horita, T. Chromium poisoning for prolonged lifetime of electrodes in solid oxide fuel cells—Review. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 7293–7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crofer 22APU—Material Data Sheet No. 4046. ThyssenKrupp VDM, 2010. Available online: https://www.vdm-metals.com/fileadmin/user_upload/Downloads/Data_Sheets/Data_Sheet_VDM_Crofer_22_APU.pdf (accessed on 3 June 2023).
- Hilpert, K.; Das, D.; Miller, M.; Peck, D.H.; Weiß, R. Chromium Vapor Species over Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Interconnect Materials and Their Potential for Degradation Processes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, 3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


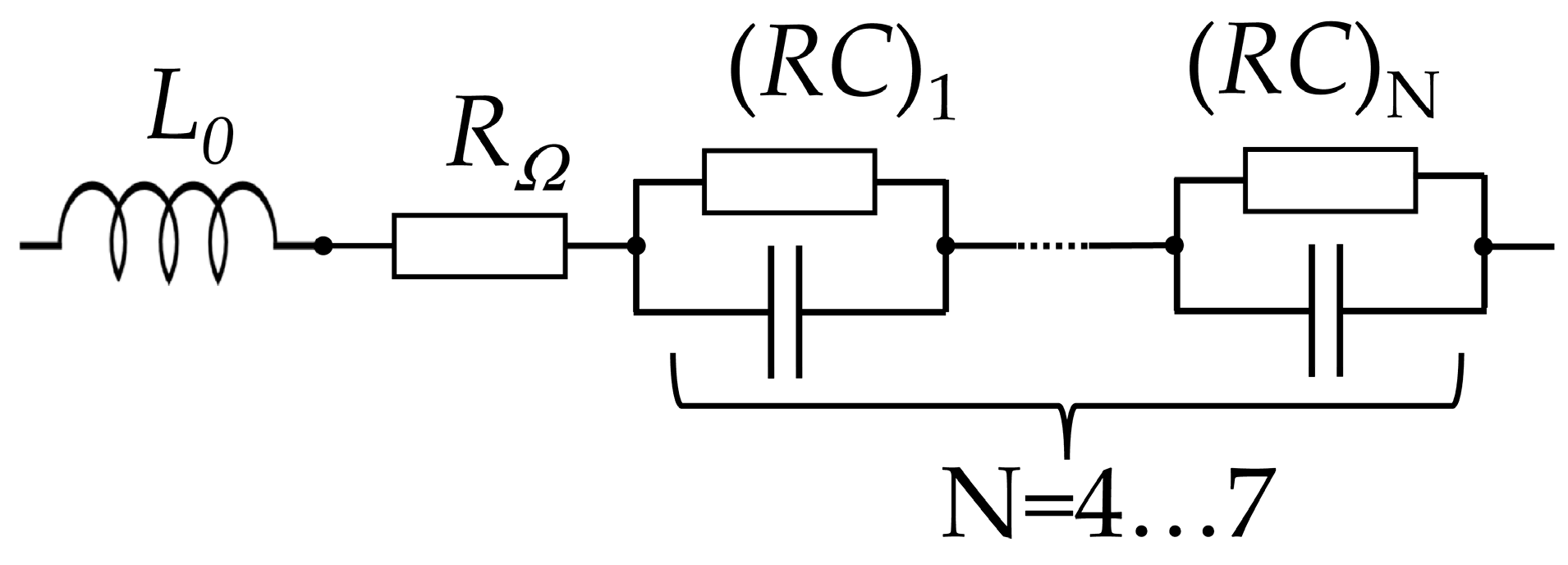
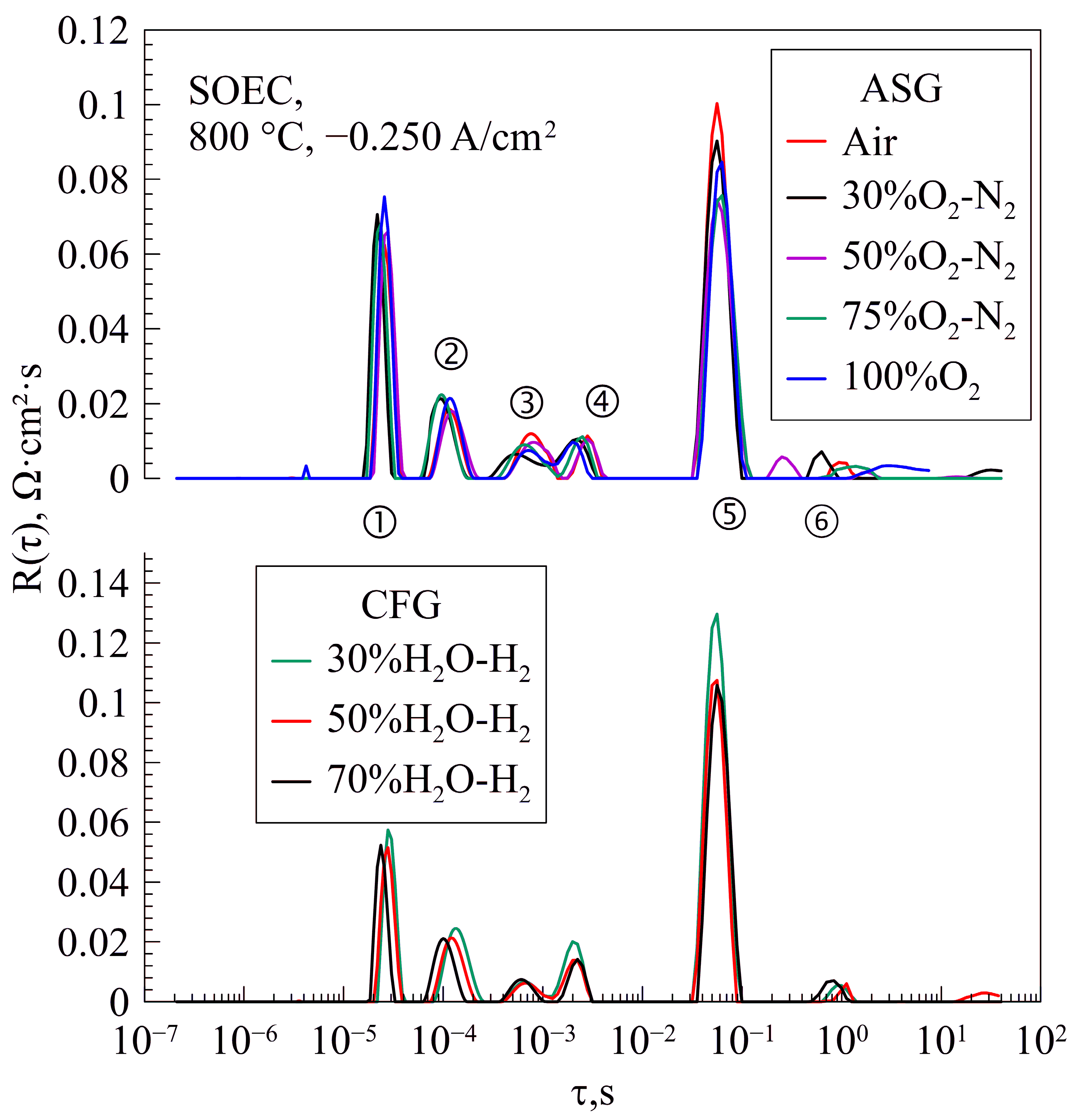


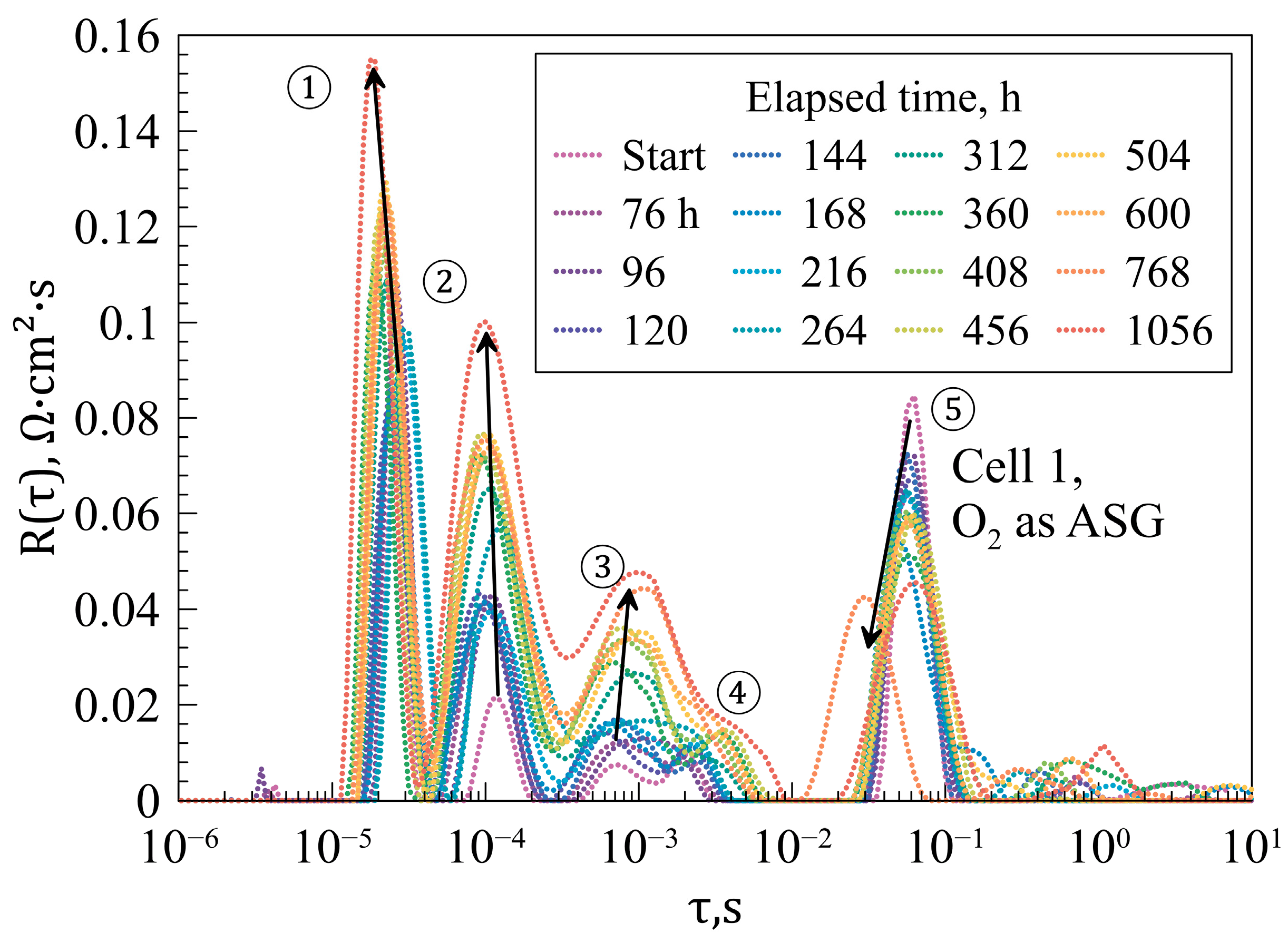
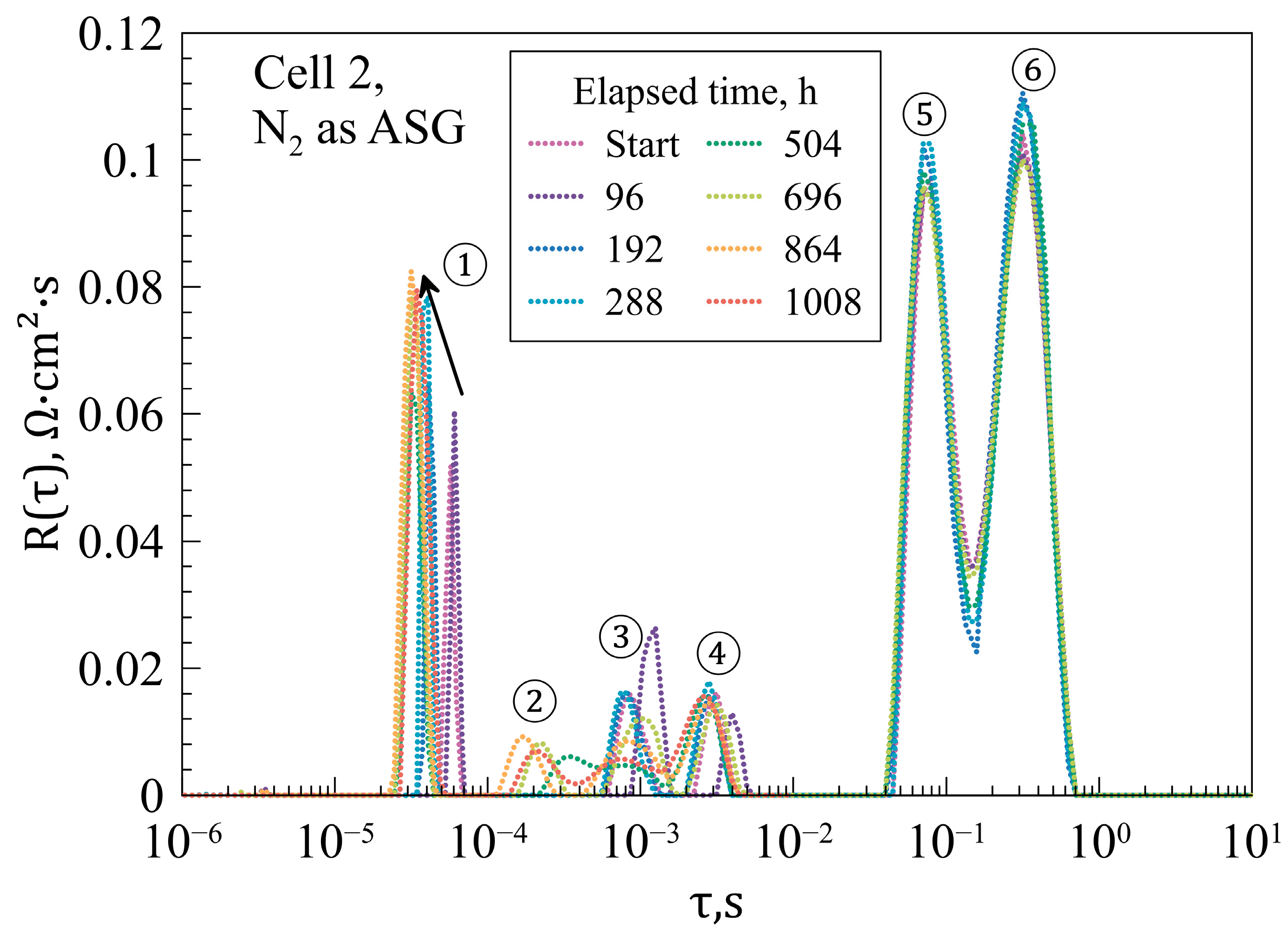


| Layer | Material | Thickness, μm |
|---|---|---|
| Anode (oxygen electrode) | La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.8Co0.2O3−δ | 30 |
| Strontium diffusion barrier | Gd0.1Ce0.9O2 | 3 |
| Electrolyte | 8YSZ | 3–6 1 |
| Cathode (fuel electrode) | NiO/8YSZ | 10 |
| Fuel electrode support | NiO/8YSZ | 300 |
| Contact layer | NiO | 3 |
| Cell Label | Long-Term ASG, mLN/min | Initial RΩ, Ω cm2 | Initial Rp, Ω cm2 | Initial OCV *, V |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell 1 | O2, 500 | 0.150 | 0.105 | 1.233 |
| Cell 2 | N2, 1000 | 0.126 | 0.107 | 1.190 |
| Cell 3 | Steam, 500 | 0.135 | 0.140 | 1.201 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wierzbicki, M.; Jagielski, S.; Naumovich, Y.; Niemczyk, A.; Skrzypkiewicz, M.; Kupecki, J. Impact of Sweep Gas on the Degradation of an La0.6Sr0.4Co0.8Fe0.8O3 Anode in a Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell. Energies 2024, 17, 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051144
Wierzbicki M, Jagielski S, Naumovich Y, Niemczyk A, Skrzypkiewicz M, Kupecki J. Impact of Sweep Gas on the Degradation of an La0.6Sr0.4Co0.8Fe0.8O3 Anode in a Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell. Energies. 2024; 17(5):1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051144
Chicago/Turabian StyleWierzbicki, Michał, Stanisław Jagielski, Yevgeniy Naumovich, Anna Niemczyk, Marek Skrzypkiewicz, and Jakub Kupecki. 2024. "Impact of Sweep Gas on the Degradation of an La0.6Sr0.4Co0.8Fe0.8O3 Anode in a Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell" Energies 17, no. 5: 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051144
APA StyleWierzbicki, M., Jagielski, S., Naumovich, Y., Niemczyk, A., Skrzypkiewicz, M., & Kupecki, J. (2024). Impact of Sweep Gas on the Degradation of an La0.6Sr0.4Co0.8Fe0.8O3 Anode in a Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell. Energies, 17(5), 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051144








