In Search of the Proper Dimensions of the Optimum In-Wheel Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. What Is “Good Design” for In-Wheel BLDCM
3. Fundamental Equations Related to Main Dimensions
4. Essential Dimensions of In-Wheel BLDCM
5. QFD Methodology
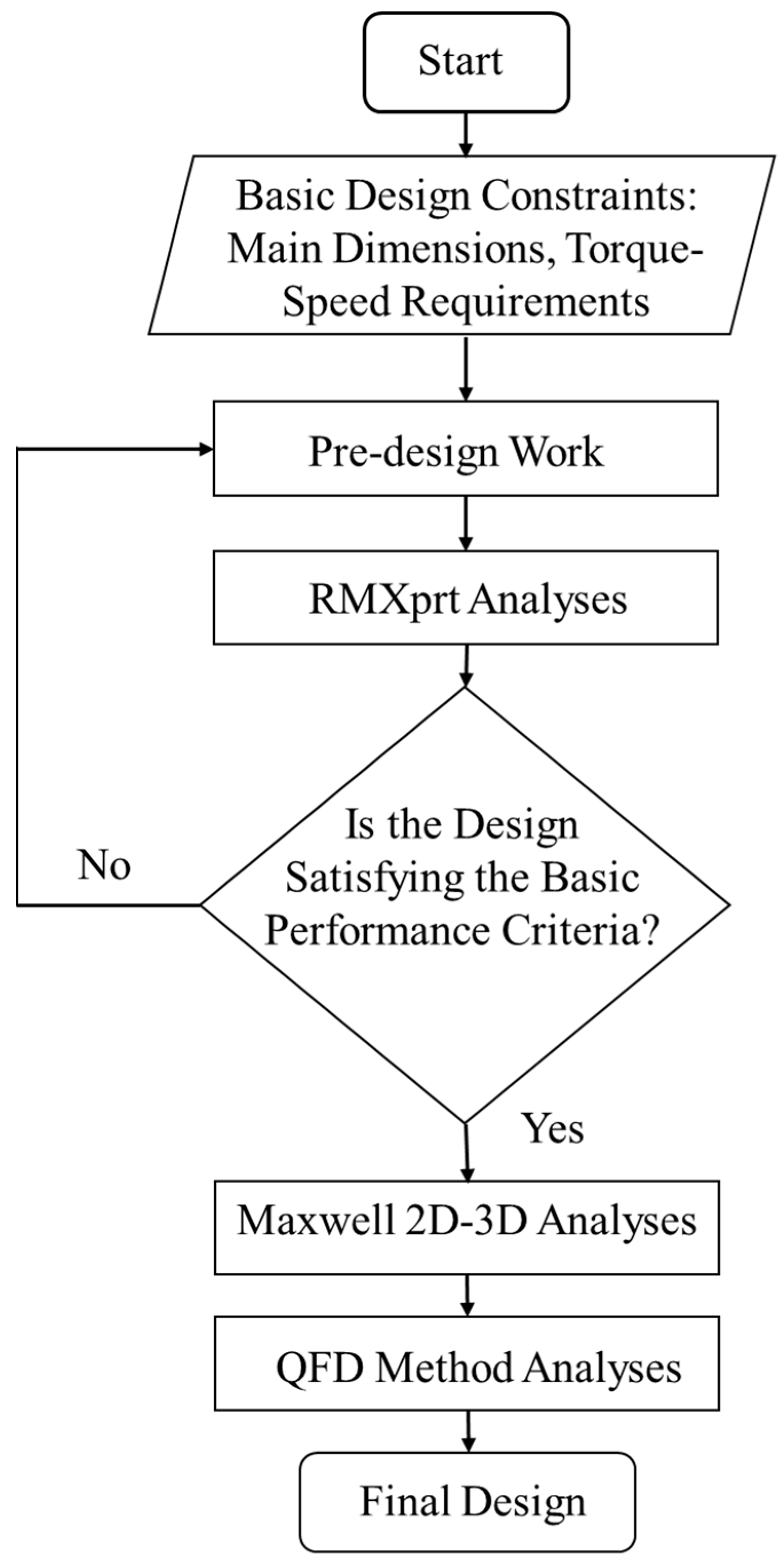
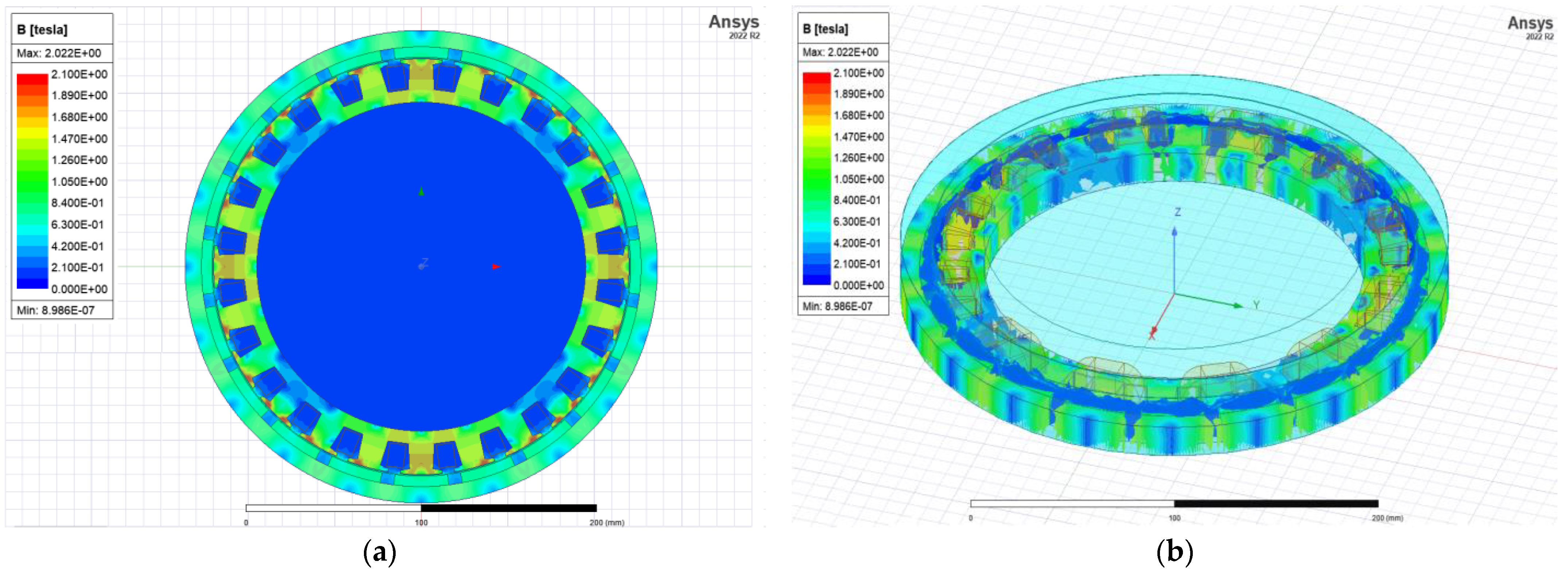
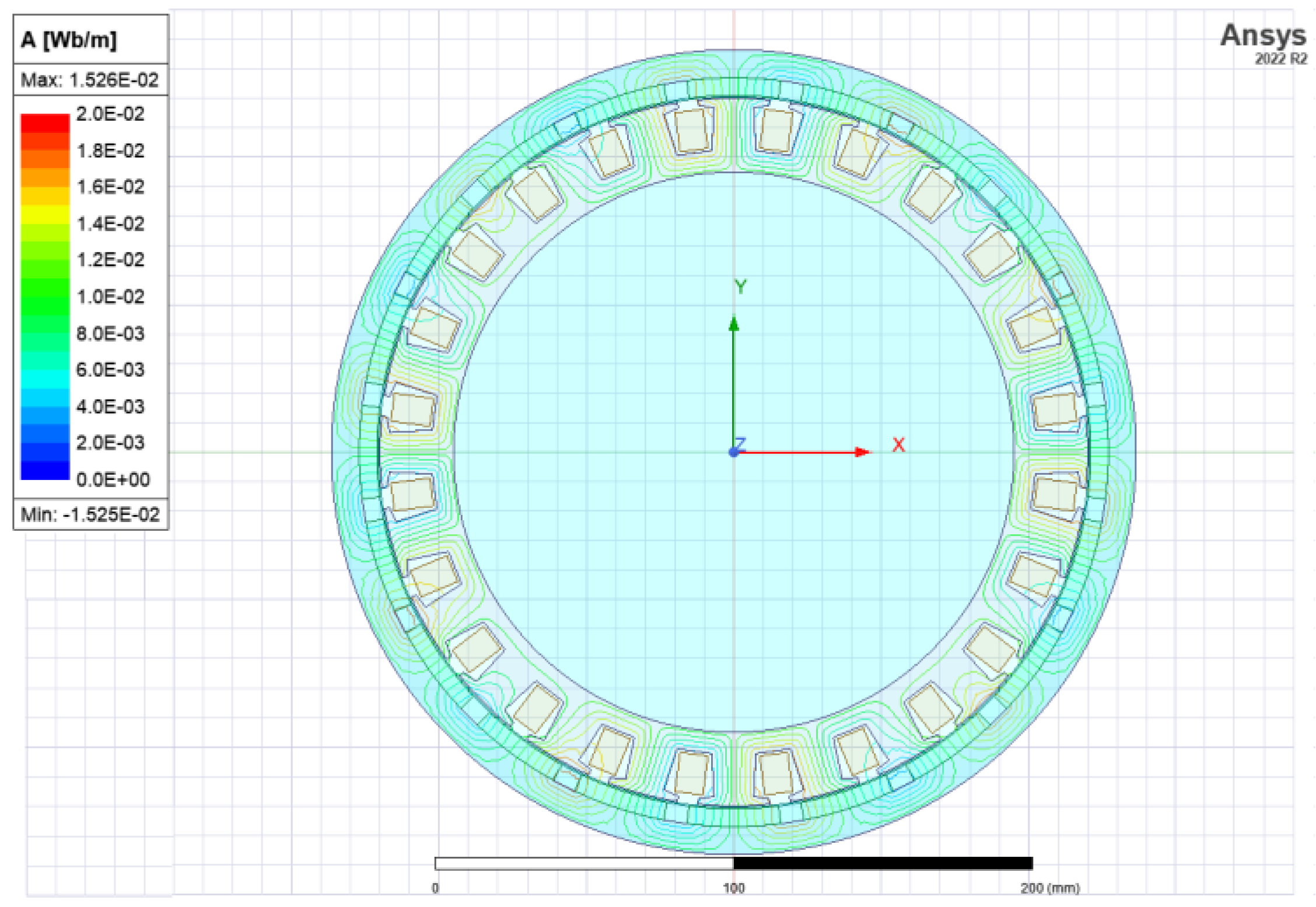
6. Analysis of In-Wheel BLDCM Performance with Different Design Parameters
7. Implementation of QFD
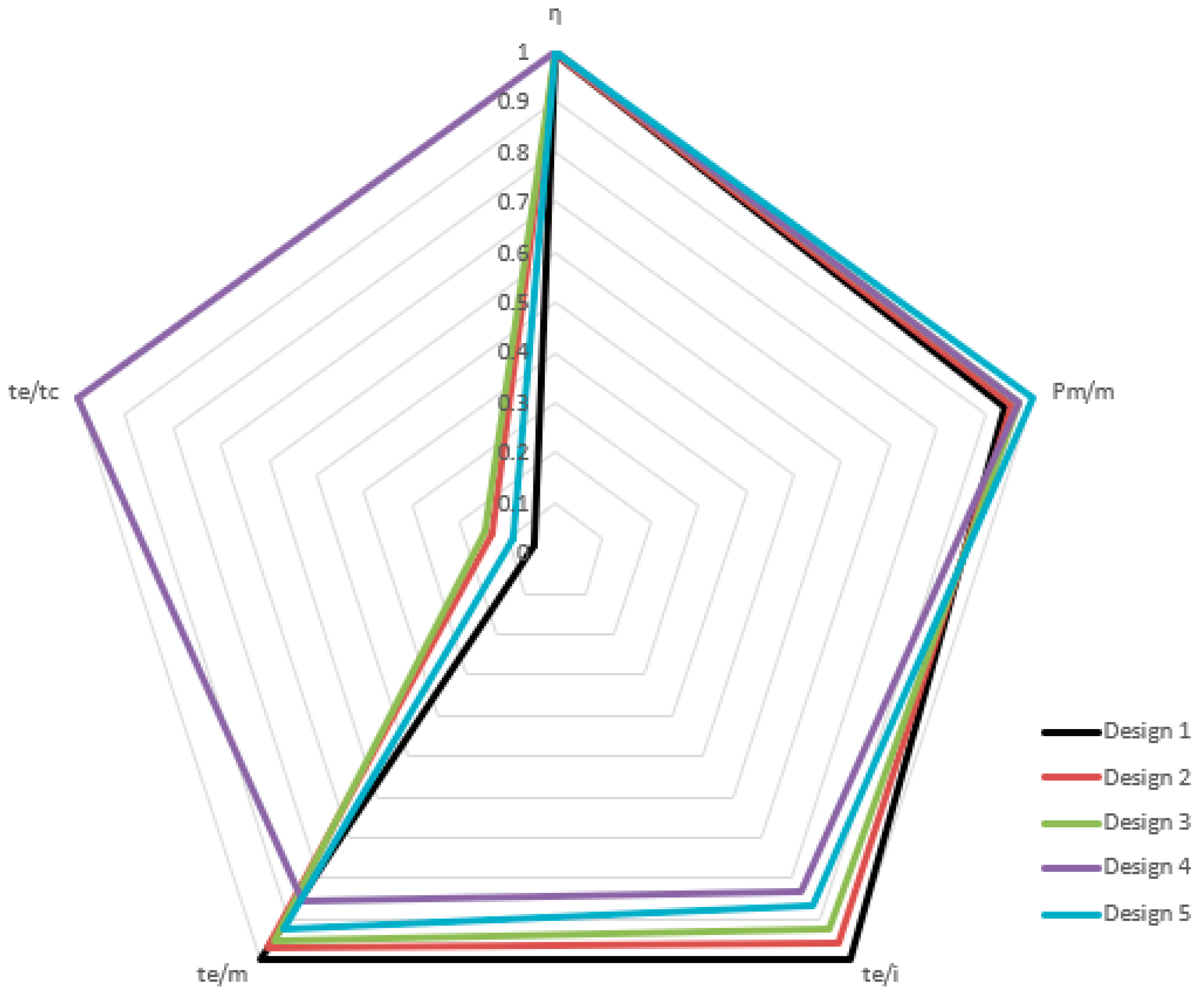
- The efficiency values of all designs are almost the same.
- The optimal result of the shaft power over the total weight belongs to Design 5.
- The optimal result of the rated torque over the input current belongs to Design 1.
- The optimal result of the rated torque over the total weight belongs to Design 1.
- The optimal result of the rated torque over the cogging torque belongs to Design 4.
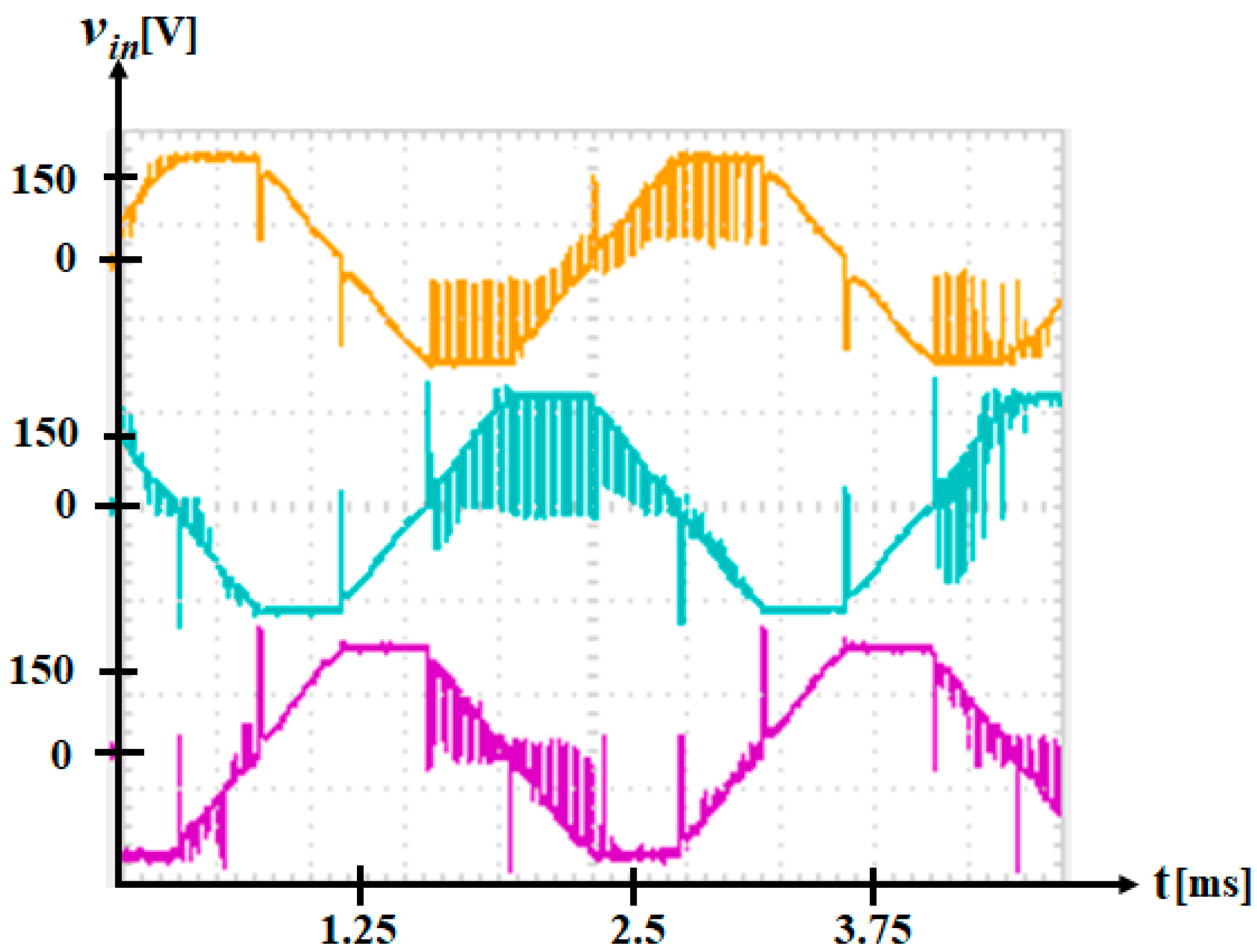
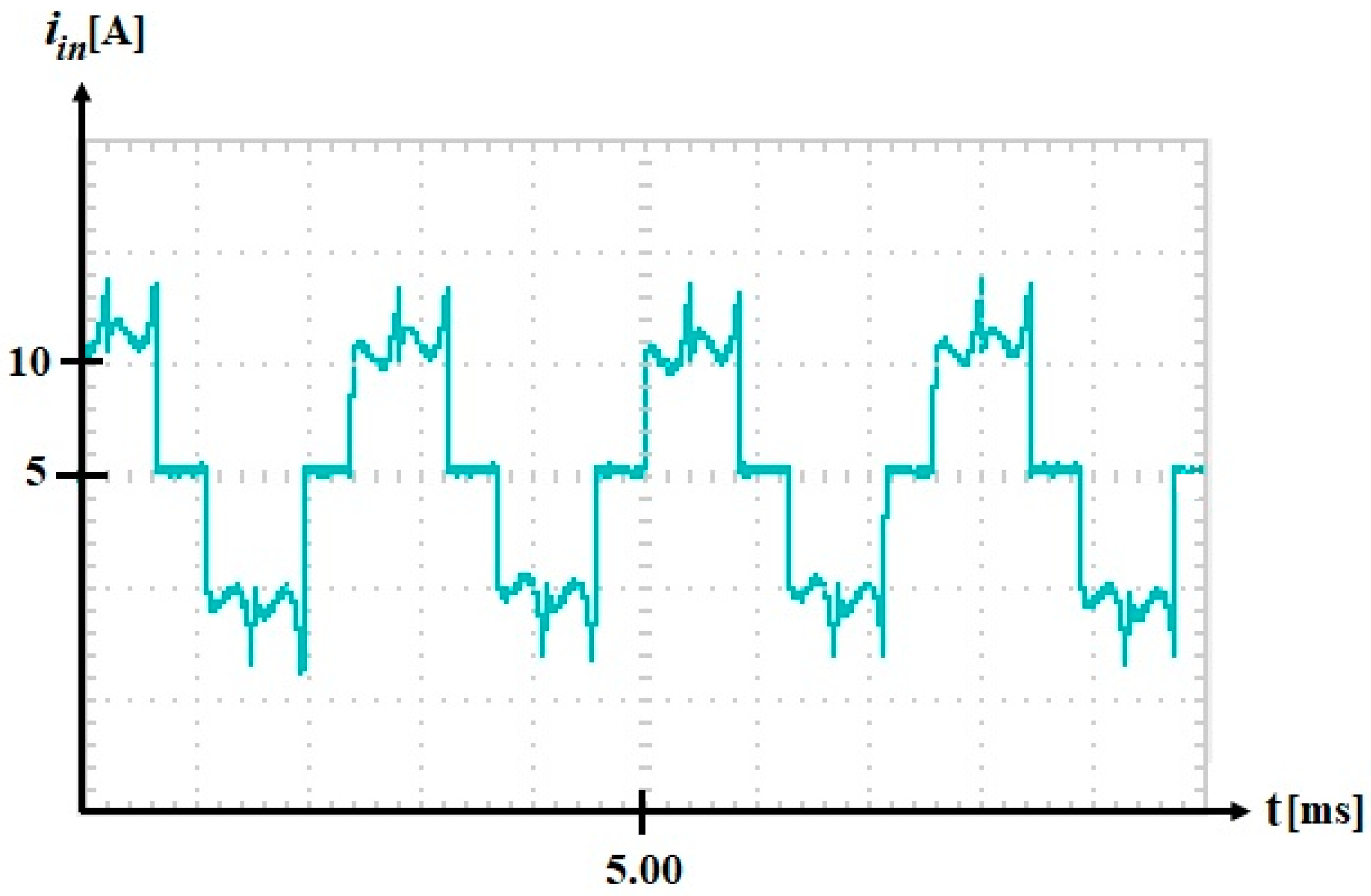
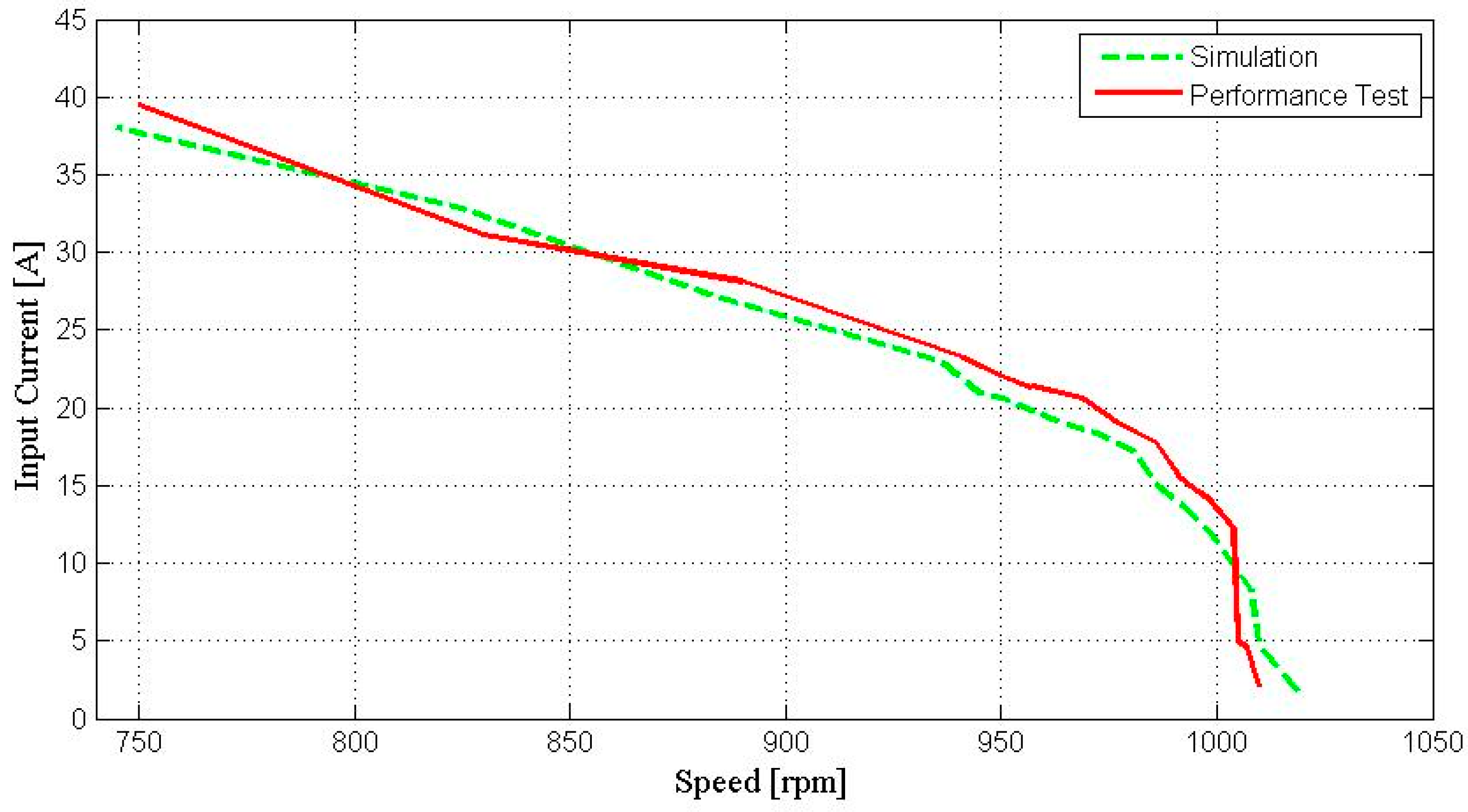
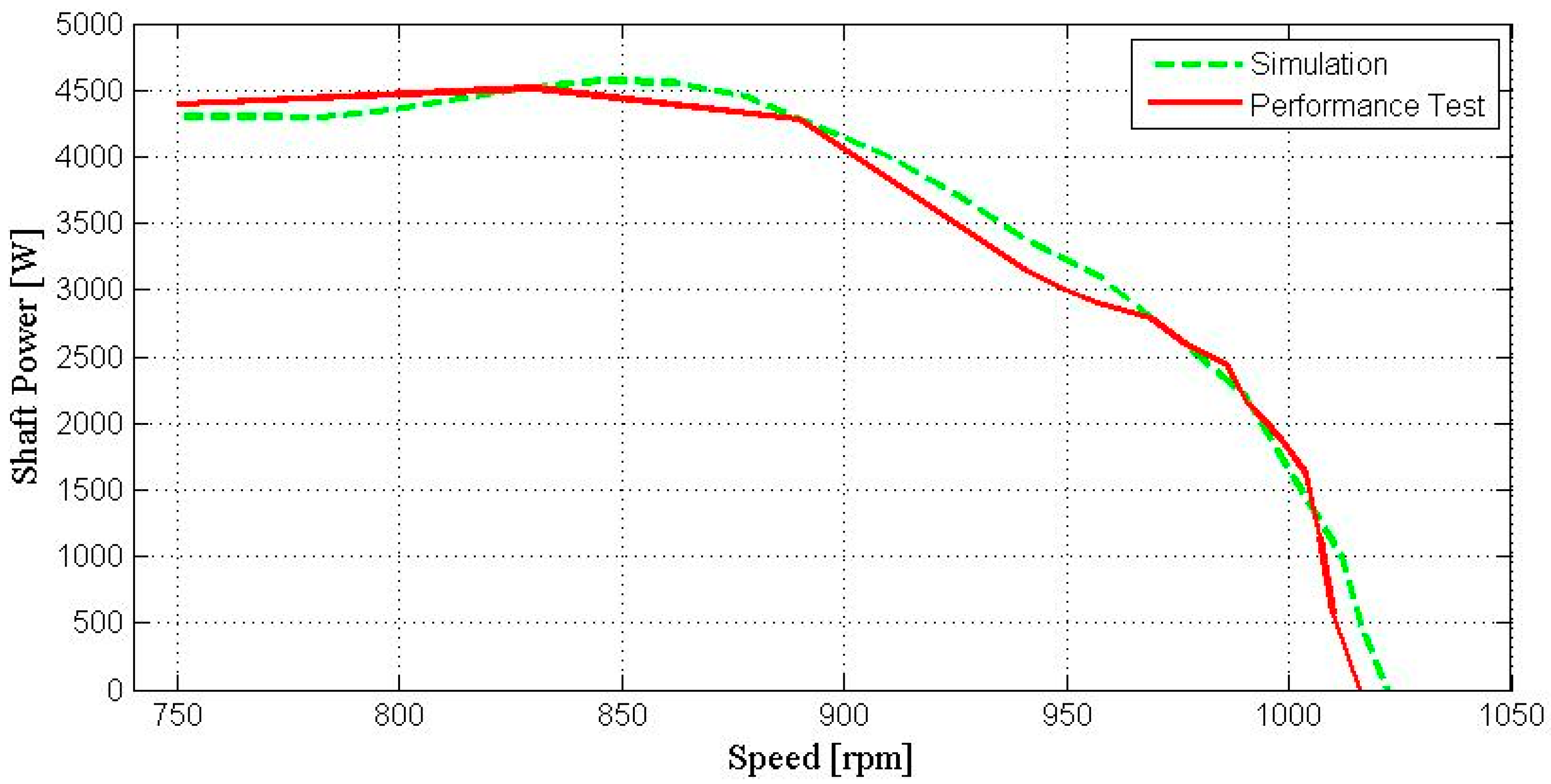
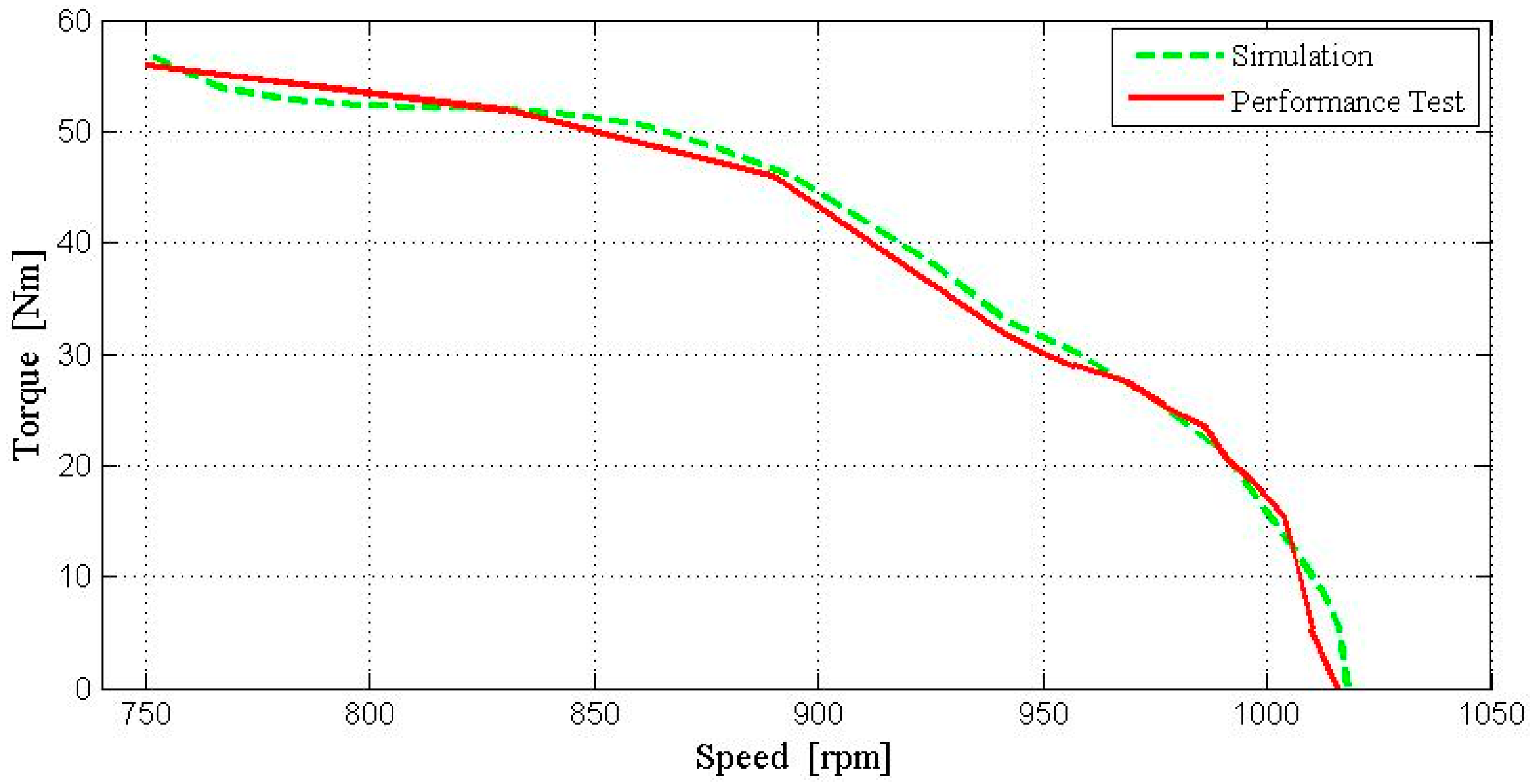
8. Prototyping and Experimental Results of In-Wheel BLDCM
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- König, P.; Sharma, D.; Konda, K.R.; Xie, T.; Höschler, K. Comprehensive Review on Cooling of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors and Their Qualitative Assessment for Aerospace Applications. Energies 2023, 16, 7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wei, Q.; Xiao, X.; Xia, Y.; Rivera, M.; Wheeler, P. Enhanced Dual–Vector Model Predictive Control for PMSM Drives Using the Optimal Vector Selection Principle. Energies 2023, 16, 7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Hung, C.H.; Le, T.-A. Intelligent Fault Diagnosis for BLDC With Incorporating Accuracy and False Negative Rate in Feature Selection Optimization. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 69939–69949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, B.S.K.K.; Azubir, N.A.M.; Ishak, N.H.M.; Hassan, M.K.; Toha, S.F.; Abidin, M.A.Z.; Ismail, H.F.; Zamzuri, H. PI-Fuzzy logic control for 3 phase BLDC motor for electric vehicle application. In Proceedings of the UKSim-AMSS 6th European Modelling Symposium, Valetta, Malta, 14–16 November 2012; pp. 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, P.R.; Rajagopa, K.R.; Singh, B.P. Effect of armature reaction on the performance of an axial-field permanent magnet brushless DC motor using FE method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2004, 40, 2023–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanraj, D.; Aruldavid, R.; Verma, R.; Sathiyasekar, K.; Barnawi, A.B.; Chokkalingam, B.; Mihet-Popa, L. A Review of BLDC Motor: State of Art, Advanced Control Techniques, and Applications. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 54833–54869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Yonetake, K.; Kurita, N. An optimal material distribution design of Brushless DC motor by genetic algorithm considering a cluster of material. In Proceedings of the Digests of the 2010 14th Biennial IEEE Conference on Electromagnetic Field Computation, Chicago, IL, USA, 9–12 May 2010; p. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmikanth, S.; Devarajaiah, R.M.; Chowdhury, A.; Krishna, S. Analytical Design of 3Kw BLDC Motor for Electric Vehicle Applications. In Proceedings of the 2023 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Technologies (CONIT), Hubli, India, 23–25 June 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabuk, A.S. Simulation of the effect of segmented axial direction magnets on the efficiency of in-wheel permanent magnet brushless DC motors used in light electric vehicles based on finite element method. Electr Eng 2021, 103, 3111–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, M.; Muller, V.; Hodder, A.; Perriard, Y. Optimal design of an in-wheel BLDC motor for kick scooter. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Atlanta, GA, USA, 12–16 September 2010; pp. 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhao, W.; Xu, L.; Ji, J. Design and analysis of a new partitioned stator flux-modulation motor for direct drive applications. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2020, 14, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chau, K.-T.; Lee, C.H.T.; Liu, C. Design and analysis of a new axial-field magnetic variable gear using pole-changing permanent magnets. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2015, 153, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.T.; Chau, K.-T.; Liu, C. Electromagnetic design and analysis of magnet less double-rotor dual-mode machines. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2013, 142, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suphama, M.; Seangwong, P.; Fernando, N.; Jongudomkarn, J.; Siritaratiwat, A.; Khunkitti, P. A Novel Asymmetric Hybrid-Layer Del-Shaped Rotor Interior Permanent Magnet Motor for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Access 2023, 12, 2793–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Liu, J. Parameter Optimization Design of PMSM. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2nd International Conference on Data Science and Computer Application (ICDSCA), Dalian, China, 28–30 October 2022; pp. 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Chen, D.; Lipo, T.A.; Kwon, B.I. Performance Improvement of Ferrite-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machines Using Asymmetrical Rotor Configurations. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.S.; Botre, B.A.; Krishan, K.; Kaushal, K.; Samarth, S.; Akbar, S.A.; Biradar, Y.; Prabhu, K.R. Modeling and implementation of intelligent commutation system for BLDC motor in underwater robotic applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 1st International Conference on Power Electronics, Intelligent Control and Energy Systems (ICPEICES), Delhi, India, 4–6 July 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, D.; Xu, G.; Wang, X. Design and Comparison of the Centralized Winding Permanent Magnet Motors for Robotic Joint. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Zhuhai, China, 5–8 November 2023; pp. 5317–5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohman, F.; Nurhadi; Martawati, M.E. Wireless Enabled Brushless DC Motor Controller for Robotic Application. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Electrical and Information Technology (IEIT), Malang, Indonesia, 14–15 September 2021; pp. 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindoriya, R.M.; Mishra, A.K.; Rajpurohit, B.S.; Kumar, R. An Analysis of Vibration and Acoustic Noise of BLDC Motor Drive. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Portland, OR, USA, 5–10 August 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.H.; An, Y.G.; Kim, G.T. The Characteristics of Noise and Vibration by Asymmetrical Overhang Effect of Permanent Magnet in BLDC Motor. In Proceedings of the 12th Biennial IEEE Conference on Electromagnetic Field Computation, Miami, FL, USA, 30 April–3 May 2006; p. 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saed, N.; Asgari, S.; Muetze, A. On the Effect of Claw Geometry on the Vibration of Single-Phase Claw-Pole BLDC Machines. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Power Electronics and ECCE Asia (ICPE 2023-ECCE Asia), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 22–25 May 2023; pp. 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Habetler, T.G. Static eccentricity fault detection of the BLDC motor inside the air handler unit (AHU). In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), Coeur d’Alene, ID, USA, 10–13 May 2015; pp. 1473–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, K.; Pei, Y.; Chen, T. Magnetic Field Analysis of Conical Shape External Rotor Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Equivalent Magnetic Network Method. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Zhuhai, China, 5–8 November 2023; pp. 4168–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Choi, J.; Ko, K.C.; Lee, J. Finite-element analysis of brushless DC motor considering freewheeling diodes and DC link voltage ripple. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2003, 39, 3274–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, V.K.; Rao, G.; Landge, B. Design of BLDC Based ISG for Aerial Application: Effect of Stator Slot Design Parameters on the Efficiency. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Advances in Communication and Computing Technology (ICACCT), Sangamner, India, 8–9 February 2018; pp. 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.S.; Lee, G.S.; Jang, H.; Cho, S.; Seo, J.H.; Bae, S.W.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, G.Y.; Lee, J. Analysis of Optimize Designing Small Size BLDC Motor Considering Air Gap Clearance. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.; Li, H.; Xiong, H. Calculation of gig air-gap magnetic field in poly-phase multi-pole BLDC motor. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Wuhan, China, 17–20 October 2008; pp. 3224–3227. [Google Scholar]
- Sangsefidi, Y.; Ziaeinejad, S.; Shoulaie, A. Torque ripple reduction of BLDC motors by modifying the non-commutating phase voltage. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical, Control and Computer Engineering 2011 (InECCE), Kuantan, Malaysia, 21–22 June 2011; pp. 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banović, M.; Iričanin, B.; Reljić, D.; Jerkan, D. Hybrid Iron Loss Model for IPMSMs in Wide-Speed Range Applications. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Symposium on Power Electronics (Ee), Novi Sad, Serbia, 25–28 October 2023; pp. 01–06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Cheng, S. Pole optimization of brushless DC motor. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 2004 IEEE Industry Applications Conference, 2004. 39th IAS Annual Meeting, Seattle, WA, USA, 3–7 October 2004; Volume 2, pp. 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abirami, S.; Bala, S.M.; Priya, R.J. Design of BLDC Hub Motor using FEM analysis. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Green Computing Communication and Electrical Engineering (ICGCCEE), Coimbatore, India, 6–8 March 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phyu, H.N.; Quan, J. Analysis of rotor eddy current loss with different magnetization directions in PM BLDC motor. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Pattaya, Thailand, 25–28 October 2015; pp. 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cros, J.; Viarouge, P. Synthesis of high-performance PM motors with concentrated windings. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2002, 17, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Xia, Z.P.; Wu, L.J.; Jewell, G.W. Influence of slot and pole number combination on radial force and vibration modes in fractional slot pm brushless machines having single- and double-layer windings. In Proceedings of the IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, San Jose, CA, USA, 20–24 September 2009; pp. 3443–3450. [Google Scholar]
- Friendly, M.; Andrews, R.J. The radiant diagrams of Florence Nightingale. SORT-Stat. Oper. Res. Trans. 2021, 45, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laithwaite, E.R. The goodness of a machine. Proc. Inst. Electr. Eng. 1965, 112, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendershot, J.R.; Miller, T.J.E. Design of Brushless Permanent-Magnet Machines, 2nd ed.; Motor Design Books LLC: Miami Beach, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nasiri-Zarandi, R.; Karami-Shahnani, A.; Toulabi, M.S.; Tessarolo, A. Design and Experimental Performance Assessment of an Outer Rotor PM-Assisted SynRM for the Electric Bike Propulsion. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 9, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.; Gumma, M.; Potarlanka, S.R. Virtual design optimization of a BLDC motor for a two wheeler electric cargo vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2nd Asian Conference on Innovation in Technology (ASIANCON), Ravet, India, 26–28 August 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitencourt, A.; Borba, B.; França, B.; Dias, D. Development and Analysis of an IPMSM Fea-Based Model for Electric Vehicle Application. In Proceedings of the 25th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’23 ECCE Europe), Aalborg, Denmark, 4–8 September 2023; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
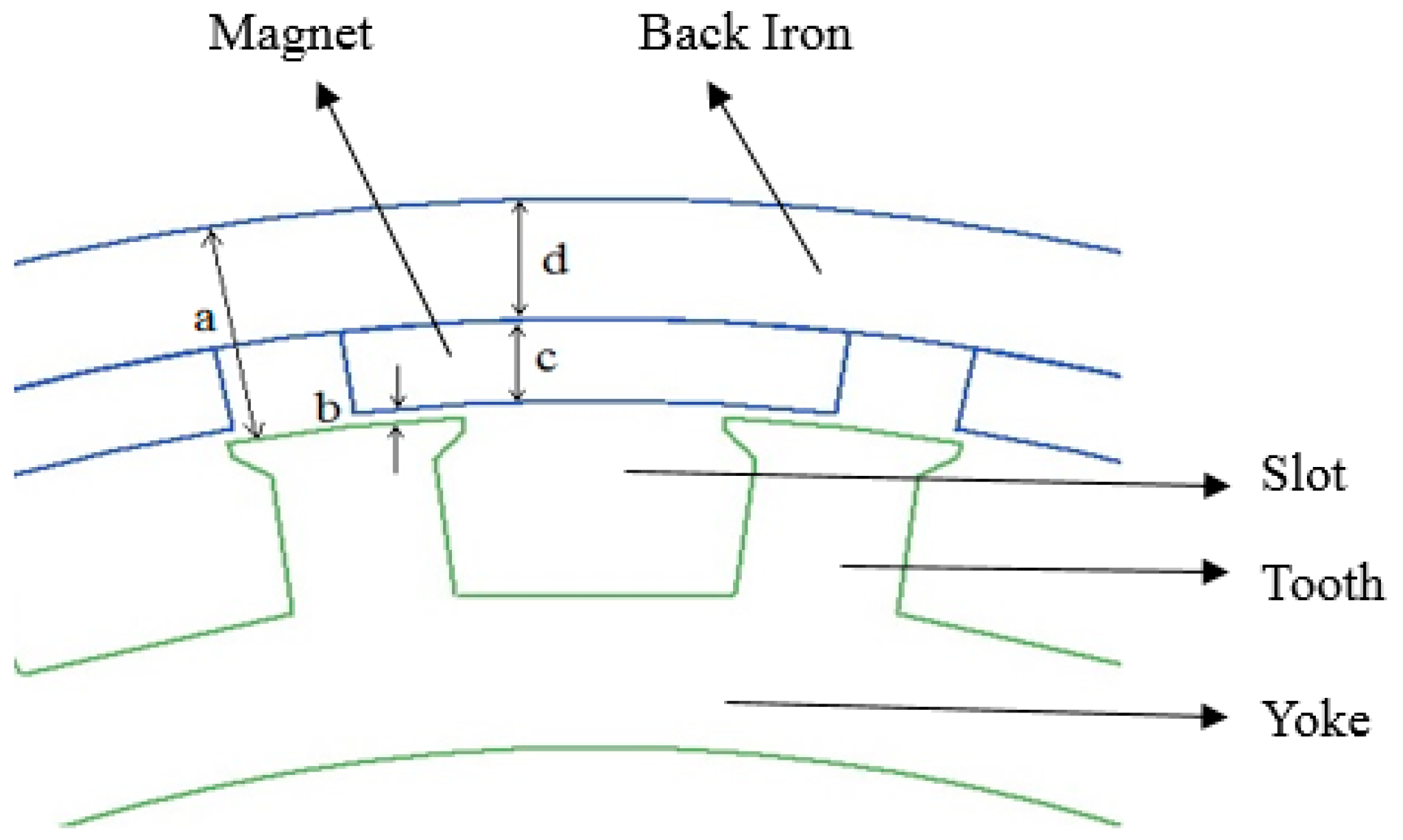
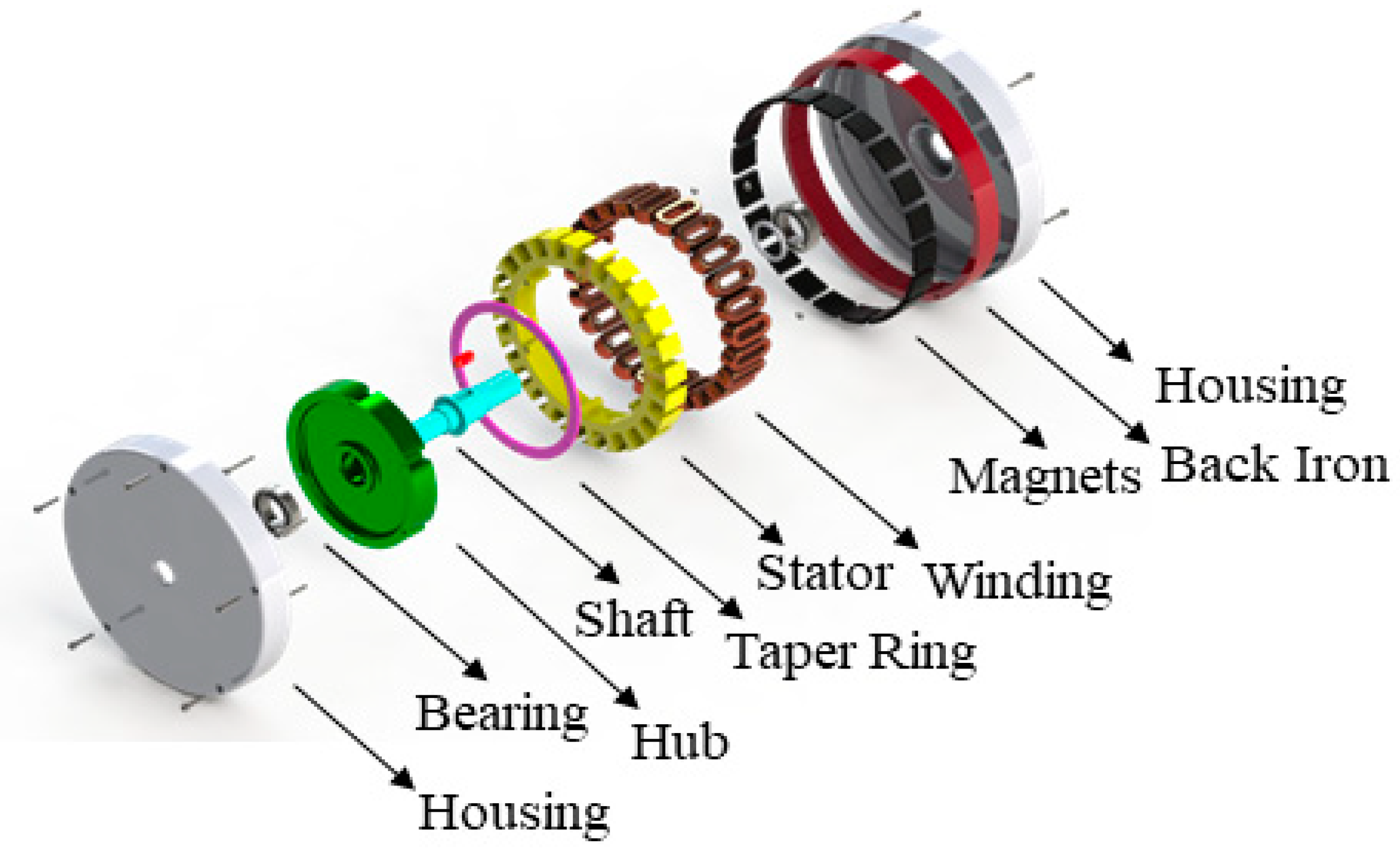
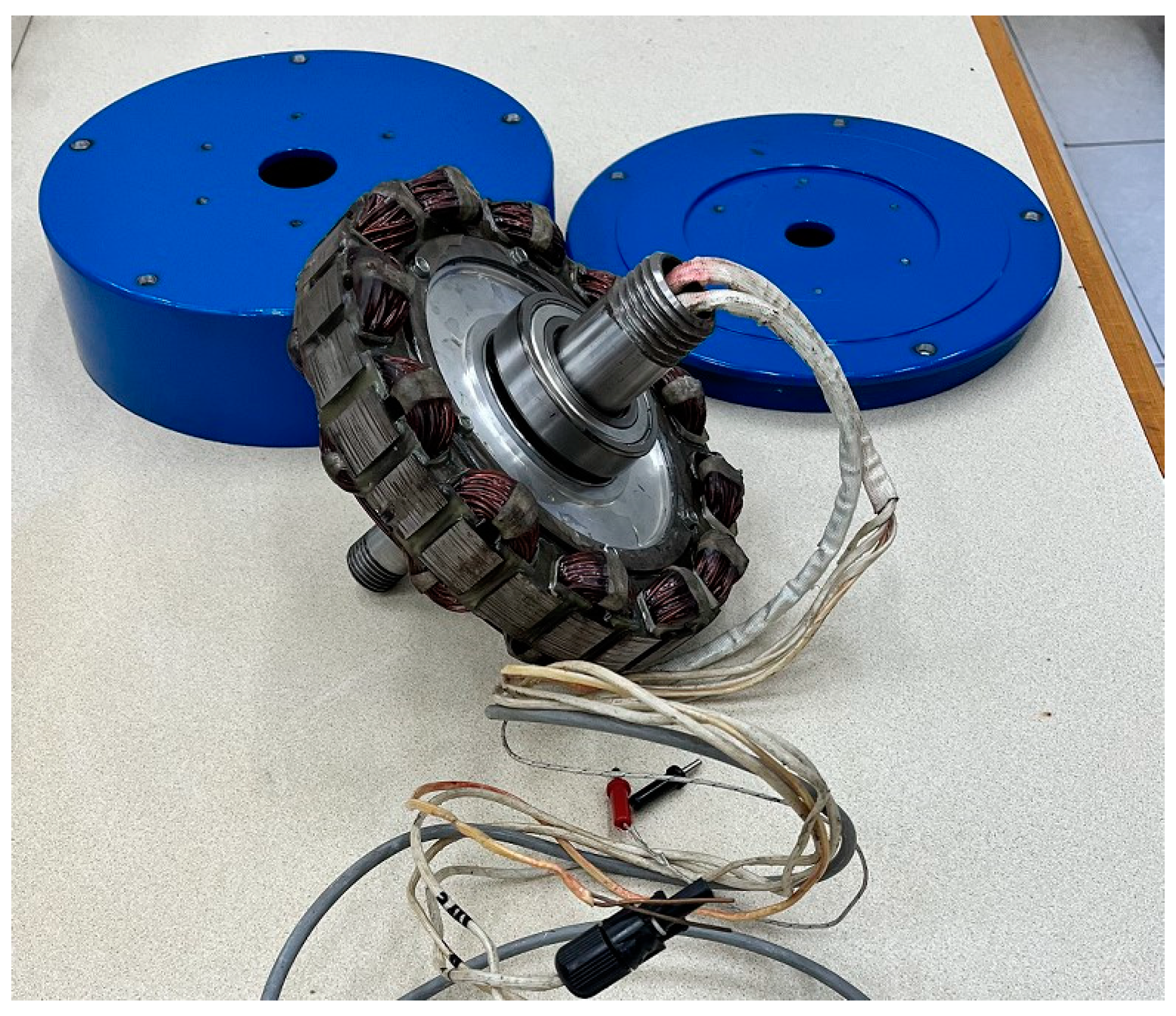



| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Rated Output Power | 2.5 | kW |
| Rated Voltage | 150 | V |
| Number of Poles | 20 | |
| Number of Stator Slots | 24 | |
| Given Rated Speed | 900 | rpm |
| Type of Steel | M15_29G | |
| Length of Rotor | 30 | mm |
| Type of Magnet | NdFe38 | |
| Outer Diameter of Stator | 234 | mm |
| Outer Diameter of Rotor | 265.8 | mm |
| Electrical Pole Embrace | 0.792 | mm |
| Data Name | Initial Data [mm] | Optimized Data Range [mm] Min–Max | Increment Step [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 15.9 | 15.9 | fixed |
| b | 1 | 1–3 | 0.5 |
| c | 3 | 3–7 | 1 |
| d | 11.9 | 5.9–11.9 | 0.5 or 1.0 * |
| Full Load Data | Design 1 | Design 2 | Design 3 | Design 4 | Design 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| η [%] | 94.9281 | 95.0341 | 95.1184 | 95.3568 | 95.2557 |
| Pm [W] | 2499.91 | 2499.8 | 2499.74 | 2499.98 | 2499.99 |
| te [Nm] | 22.0573 | 21.1043 | 20.3569 | 18.2489 | 19.1299 |
| i [A] | 17.5565 | 17.5361 | 17.5202 | 17.4781 | 17.4967 |
| tc [Nm] | 0.66704 | 0.22058 | 0.18830 | 0.02516 | 0.29259 |
| m [kg] | 5.63004 | 5.54567 | 5.46094 | 5.4496 | 5.29044 |
| Full Load Data | Design 1 | Design 2 | Design 3 | Design 4 | Design 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| η | 0.9955043 | 0.9966159 | 0.9974999 | 1 | 0.9989398 |
| Pm/m | 0.9396506 | 0.9539042 | 0.9686814 | 0.9707903 | 1 |
| te/i | 1 | 0.9579073 | 0.9248219 | 0.8310517 | 0.8702461 |
| te/m | 1 | 0.9713508 | 0.9514882 | 0.8547345 | 0.9229541 |
| te/tc | 0.0455905 | 0.1319103 | 0.1490511 | 1 | 0.0901421 |
| QFD | 1.4104799 | 1.4525340 | 1.4421132 | 2.0650991 | 1.3532123 |
| Test Number | Input Current [A] | Input Voltage [V] | Speed [min−1] | Rated Torque [Nm] | Input Power [W] | Shaft Power [W] | Efficiency [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.8 | 150.3 | 1010 | 5.4 | 721.44 | 571.10 | 79.16 |
| 2 | 12.3 | 148.9 | 1004 | 15.5 | 1831.47 | 1629.53 | 88.97 |
| 3 | 14.8 | 150.2 | 995 | 19.3 | 2222.96 | 2010.84 | 90.46 |
| 4 | 17.8 | 148.8 | 986 | 23.7 | 2648.64 | 2446.93 | 92.38 |
| 5 | 20.6 | 148.8 | 969 | 27.5 | 3065.28 | 2790.31 | 91.03 |
| 6 | 22.1 | 150.2 | 950 | 30.2 | 3319.42 | 3004.19 | 90.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cabuk, A.S.; Ustun, O. In Search of the Proper Dimensions of the Optimum In-Wheel Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Design. Energies 2024, 17, 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051106
Cabuk AS, Ustun O. In Search of the Proper Dimensions of the Optimum In-Wheel Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Design. Energies. 2024; 17(5):1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051106
Chicago/Turabian StyleCabuk, Ali Sinan, and Ozgur Ustun. 2024. "In Search of the Proper Dimensions of the Optimum In-Wheel Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Design" Energies 17, no. 5: 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051106
APA StyleCabuk, A. S., & Ustun, O. (2024). In Search of the Proper Dimensions of the Optimum In-Wheel Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Design. Energies, 17(5), 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051106






