A Survey of Quantitative Techniques in Electricity Consumption—A Global Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
- This paper provides an extensive and in-depth evaluation of earlier cutting-edge research on electricity consumption forecasting, considering the methodologies employed, the time framework including period and frequency, and the accuracy metrics utilized in the forecast.
- This study provides a succinct synopsis of the practical features of the compared methods for forecasting electricity consumption/loading/demand.
- This study determines the obstacles and prospects for additional research in forecasting electricity consumption/load/demand.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Information Extraction
2.2. Data Analysis
2.3. Study Framework
3. Comprehensive Review for Electricity Consumption Forecasting
3.1. Review of Electricity Consumption Based on Time Span
3.1.1. Short-Term Forecasting
3.1.2. Medium-Term Forecasting
3.1.3. Long-Term Forecasting
3.2. Review of Electricity Consumption Based on Quantitative Methods
3.2.1. Time Series Econometric Forecast Models
3.2.2. Grey Forecasting Forecast Models
3.2.3. Machine Learning Forecast Models
3.2.4. Deep Learning Forecast Models
3.2.5. Hybrid Forecast Models
3.3. Advantages and Disadvantages of Selected Quantitative Models
3.3.1. Time Series Models
3.3.2. Grey Models
3.3.3. Machine Learning Models
3.3.4. Deep Learning Models
3.3.5. Hybrid Models
3.4. The Accuracy Metrics
- Mean Absolute Error (MAE);
- Mean Squared Error (MSE);
- Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE);
- Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE);
- R-squared (R2).
3.5. Role of ChatGPT and Generative AI in Forecasting
3.6. Obstacles to Additional Research in Forecasting Electricity Consumption
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holmes, G.; Clemoes, J.; Marriot, K.; Wynne-Jones, S. The Politics of the Rural and Relational Values: Contested Discourses of Rural Change and Landscape Futures in West Wales. Geoforum 2022, 133, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EIU. Energy Outlook 2024. Available online: https://www.eiu.com/n/campaigns/energy-in-2024/#:~:text=Global%20energy%20consumption%20will%20grow,by%20strong%20demand%20in%20Asia (accessed on 26 August 2024).
- Griffiths, S.; Sovacool, B.K.; Kim, J.; Bazilian, M.; Uratani, J.M. Decarbonizing the Oil Refining Industry: A Systematic Review of Sociotechnical Systems, Technological Innovations, and Policy Options. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2022, 89, 102542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leavy, P. Research Design: Quantitative, Qualitative, Mixed Methods, Arts-Based, and Community-Based Participatory Research Approaches, 2nd ed.; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2022; ISBN 978-1-4625-4897-2. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.; Ser, Y.; Selvachandran, G.; Thong, P.; Cuong, L.; Son, L.; Tuan, N.; Gerogiannis, V. A Comparative Study of Forecasting Electricity Consumption Using Machine Learning Models. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgili, M.; Pinar, E. Gross Electricity Consumption Forecasting Using LSTM and SARIMA Approaches: A Case Study of Türkiye. Energy 2023, 284, 128575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaytez, F.; Taplamacioglu, M.C.; Cam, E.; Hardalac, F. Forecasting Electricity Consumption: A Comparison of Regression Analysis, Neural Networks and Least Squares Support Vector Machines. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 67, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannakkong, W.; Harncharnchai, T.; Buddhakulsomsiri, J. Forecasting Daily Electricity Consumption in Thailand Using Regression, Artificial Neural Network, Support Vector Machine, and Hybrid Models. Energies 2022, 15, 3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutun, S.; Chou, C.-A.; Caniyilmaz, E. A New Forecasting Framework for Volatile Behavior in Net Electricity Consumption: A Case Study in Turkey. Energy 2015, 93, 2406–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzia, R.; Rubio, L.; Velasquez, C.E. Sensitivity Analysis for Forecasting Brazilian Electricity Demand Using Artificial Neural Networks and Hybrid Models Based on Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average. Energy 2023, 274, 127365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filgueiras, D.B.; Coelho da Silva, F.L. A Study on the Prediction of Electricity Consumption Considering the Energy Efficiency Measures—Applied in Case of the Brazilian Public Sector. Energy Effic. 2023, 16, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahpour, A.; Wong, K.Y.; Rajoo, S.; Tian, G. An Evolutionary-Based Predictive Soft Computing Model for the Prediction of Electricity Consumption Using Multi Expression Programming. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 125287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstev, S.; Forcan, J.; Krneta, D. An Overview of Forecasting Methods for Monthly Electricity Consumption. Teh. Vjesn. 2023, 30, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutun, S.; Tosyali, A.; Sangrody, H.; Khasawneh, M.; Johnson, M.; Albizri, A.; Harfouche, A. Artificial Intelligence in Energy Industry: Forecasting Electricity Consumption through Cohort Intelligence & Adaptive Neural Fuzzy Inference System. J. Bus. Anal. 2023, 6, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosanu, D.M. Designing, Developing and Validating a Forecasting Method for the Month Ahead Hourly Electricity Consumption in the Case of Medium Industrial Consumers. Processes 2019, 7, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaleck, P.; Massucco, S.; Mosaico, G.; Saviozzi, M.; Serra, P.; Silvestro, F. Electrical Consumption Forecasting in Sports Venues: A Proposed Approach Based on Neural Networks and ARIMAX Models. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 100, 105019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuster, C.; Rezgui, Y.; Mourshed, M. Electrical Load Forecasting Models: A Critical Systematic Review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 35, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panklib, K.; Prakasvudhisarn, C.; Khummongkol, D. Electricity Consumption Forecasting in Thailand Using an Artificial Neural Network and Multiple Linear Regression. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2015, 10, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjout, D.; Sebaa, A.; Torres, J.F.; Martínez-Álvarez, F. Electricity Consumption Forecasting with Outliers Handling Based on Clustering and Deep Learning with Application to the Algerian Market. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 227, 120123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guefano, S.; Tamba, J.G.; Azong, T.E.W.; Monkam, L. Forecast of Electricity Consumption in the Cameroonian Residential Sector by Grey and Vector Autoregressive Models. Energy 2021, 214, 118791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukseltan, E.; Yucekaya, A.; Bilge, A.H. Forecasting Electricity Demand for Turkey: Modeling Periodic Variations and Demand Segregation. Appl. Energy 2017, 193, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasali, F.; Nusair, K.; Alhmoud, L.; Zarour, E. Impact of the Covid-19 Pandemic on Electricity Demand and Load Forecasting. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amber, K.P.; Ahmad, R.; Aslam, M.W.; Kousar, A.; Usman, M.; Khan, M.S. Intelligent Techniques for Forecasting Electricity Consumption of Buildings. Energy 2018, 157, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyuev, R.V.; Morgoev, I.D.; Morgoeva, A.D.; Gavrina, O.A.; Martyushev, N.V.; Efremenkov, E.A.; Mengxu, Q. Methods of Forecasting Electric Energy Consumption: A Literature Review. Energies 2022, 15, 8919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Dubey, A.; Kumar, A.; García-Díaz, V.; Kumar Sharma, A.; Kanhaiya, K. Study and Analysis of SARIMA and LSTM in Forecasting Time Series Data. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 47, 101474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, W.; Dwijantari, S.; Hartati, A. Time Series Machine Learning: Implementing ARIMA and Hybrid ARIMA-ANN for Electricity Forecasting Modeling. In Soft Computing in Data Science; Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer: Singapore, 2017; Volume 788, pp. 126–139. ISBN 978-981-10-7241-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiğit, S.; Turgay, S.; Cebeci, Ç.; Kara, E.S. Time-Stratified Analysis of Electricity Consumption: A Regression and Neural Network Approach in the Context of Turkey. Wseas Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 19, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakkas, N.; Yfanti, S.; Shah, P.; Sakkas, N.; Chaniotakis, C.; Daskalakis, C.; Barbu, E.; Domnich, M. Explainable Approaches for Forecasting Building Electricity Consumption. Energies 2023, 16, 7210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Wen, M.; Luo, J. A Short-Term Electricity Consumption Forecasting Approach Based on Feature Processing and Hybrid Modelling. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2022, 16, 2003–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Tian, Z.; Jin, H. Appling an Improved Method Based on ARIMA Model to Predict the Short-Term Electricity Consumption Transmitted by the Internet of Things (IoT). Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2021, 2021, 6610273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, N.; Hossain, S.M.Z.; Almuhaini, S.; Düştegör, D. Bayesian Optimization Algorithm-Based Statistical and Machine Learning Approaches for Forecasting Short-Term Electricity Demand. Energies 2022, 15, 3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.U.M.; Khan, N.; Hussain, T.; Lee, M.Y.; Baik, S.W. Diving Deep into Short-term Electricity Load Forecasting: Comparative Analysis and a Novel Framework. Mathematics 2021, 9, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, A.; Ismail, I.; Jameel, S.M.; Harindran, V.R. Electrical Load Forecasting Models for Different Generation Modalities: A Review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 142239–142263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahajjam, M.A.; Bonilla Licea, D.; Ghogho, M.; Kobbane, A. Experimental Investigation of Variational Mode Decomposition and Deep Learning for Short-Term Multi-Horizon Residential Electric Load Forecasting. Appl. Energy 2022, 326, 119963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-J.; Lin, J.-Y.; Chang, M.-J. Extended Modeling Procedure Based on the Projected Sample for Forecasting Short-Term Electricity Consumption. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2016, 30, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.-F.; Yu, M.; Dong, S.-Q.; Yeh, Y.-H.; Hong, W.-C. Forecasting Short-Term Electricity Load Using Hybrid Support Vector Regression with Grey Catastrophe and Random Forest Modeling. Util. Policy 2021, 73, 101294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsi, B.; Amayri, M.; Bouguila, N.; Eicker, U. On Short-Term Load Forecasting Using Machine Learning Techniques and a Novel Parallel Deep LSTM-CNN Approach. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 31191–31212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Peng, S.; Lao, Y.; Su, Q.; Sun, Q. Short-Term Electricity Consumption Forecasting Based on the EMD-Fbprophet-LSTM Method. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6613604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapirain, I.; Etxegarai, G.; Hernández, J.; Boussaada, Z.; Aginako, N.; Camblong, H. Short-Term Electricity Consumption Forecasting with NARX, LSTM, and SVR for a Single Building: Small Data Set Approach. Energy Sources Part Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2022, 44, 6898–6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El khantach, A.; Hamlich, M.; Belbounaguia, N. eddine. Short-Term Load Forecasting Using Machine Learning and Periodicity Decomposition. AIMS Energy 2019, 7, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyrwa, A.; Suwała, W.; Pluta, M.; Raczyński, M.; Zyśk, J.; Tokarski, S. A New Approach for Coupling the Short- and Long-Term Planning Models to Design a Pathway to Carbon Neutrality in a Coal-Based Power System. Energy 2022, 239, 122438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Weeks, M. Dynamic Tariffs, Demand Response, and Regulation in Retail Electricity Markets. Energy Econ. 2022, 106, 105774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cen, S.; Hur, J.G.; Lim, C.G. Energy Demand and Renewable Energy Generation Forecasting for Optimizing Dispatching Strategies of Virtual Power Plants Using Time Decomposition-Based DLinear. In Proceedings of the Advances in Systems Engineering; Selvaraj, H., Chmaj, G., Zydek, D., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanrisever, F.; Derinkuyu, K.; Heeren, M. Forecasting Electricity Infeed for Distribution System Networks: An Analysis of the Dutch Case. Energy 2013, 58, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, A.A.; Anderson, B.; Nachtigall, D.; Ngom, F. Long-Term Low Emissions Development Strategies: Cross-Country Experience; OECD: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, M.G.; Madeira, S.C.; Francisco, A.P. Short-Term Electricity Load Forecasting—A Systematic Approach from System Level to Secondary Substations. Appl. Energy 2023, 332, 120493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Zhang, S.; Duan, Q.; Gong, Y.; Li, Y.; Xie, X.; Bai, J.; Huang, C.; Zhao, X. Short- and Medium-Term Power Demand Forecasting with Multiple Factors Based on Multi-Model Fusion. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Reiner, D.M. What Is the Effect of Weather on Household Electricity Consumption? Empirical Evidence from Ireland. Energy Econ. 2022, 111, 106023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; O’Hanley, J.R.; Gibson, S. Predicting Residential Electricity Consumption Patterns Based on Smart Meter and Household Data: A Case Study from the Republic of Ireland. Util. Policy 2022, 79, 101446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumiran, T.; Sarjiya, S.; Putranto, L.M.; Nugraha Putra, E.; Setya Budi, R.F.; Febri Nugraha, C. Long-Term Electricity Demand Forecast Using Multivariate Regression and End-Use Method: A Study Case of Maluku-Papua Electricity System. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Technology and Policy in Energy and Electric Power (ICT-PEP), Jakarta, Indonesia, 29–30 September 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Su, J.; Ma, T.; Liu, D. Research on Long-Term Electricity Demand Forecasting Based on Adaboost-ANN Combined Model. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Seminar on Artificial Intelligence, Networking and Information Technology (AINIT), Nanjing, China, 16–18 June 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, A.; Lau, K.; Ren, C.; Chan, P.; Ng, E. Predicting Long-Term Monthly Electricity Demand under Future Climatic and Socioeconomic Changes Using Data-Driven Methods: A Case Study of Hong Kong. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 70, 102936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, G.S.; Hasan, M.B.; Phoumin, H.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F.; Ahmed, A.; Troster, V. Exploring the Critical Demand Drivers of Electricity Consumption in Thailand. Energy Econ. 2023, 125, 106875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.; Cardeira, C.; Calado, J.M.F.; Melicio, R. Short-Term Load Forecasting of Electricity Demand for the Residential Sector Based on Modelling Techniques: A Systematic Review. Energies 2023, 16, 4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, G.R.T.; Bastos, B.Q.; Cyrino, F.L.; Calili, R.F.; Souza, R.C. Long Term Electricity Forecast: A Systematic Review. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 55, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Citation-Based Clustering of Publications Using CitNetExplorer and VOSviewer. Scientometrics 2017, 111, 1053–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, R.; Ahmi, A.; Ahmad, A.H.; Othman, Z. Worldwide Melatonin Research: A Bibliometric Analysis of the Published Literature between 2015 and 2019. Chronobiol. Int. 2021, 38, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyoud, S.H. Global Scientific Trends on Aflatoxin Research during 1998–2017: A Bibliometric and Visualized Study. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2019, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Alessandro, L.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; A Stewart, L. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 Statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albhirat, M.M.; Rashid, A.; Rasheed, R.; Rasool, S.; Zulkiffli, S.N.A.; Zia-ul-Haq, H.M.; Mohammad, A.M. The PRISMA Statement in Enviropreneurship Study: A Systematic Literature and a Research Agenda. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2024, 18, 100721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mburamatare, D.; Gboney, W.K.; Hakizimana, J.D.D.; Mutemberezi, F. Analyzing and Forecasting Electricity Consumption in Energy-Intensive Industries in Rwanda. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 2022, 12, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, L.P.C.; Lin, K.-H.; Molnár, P. Electricity Consumption Modelling: A Case of Germany. Econ. Model. 2016, 55, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranaweera, D.K.; Karady, G.G.; Farmer, R.G. Economic Impact Analysis of Load Forecasting. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1997, 12, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzadi, N.; Nizami, A.; Khazen, M.; Nik-Bakht, M. Medium-Term Regional Electricity Load Forecasting through Machine Learning and Deep Learning. Designs 2021, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, N.; Shin, Y. Short- and Medium-Term Electricity Consumption Forecasting Using Prophet and GRU. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, K.; Yang, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhao, N. SARIMA-Based Medium- and Long-Term Load Forecasting. Strateg. Plan. Energy Environ. 2023, 42, 283–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, E.M.; Cyrino Oliveira, F.L. Forecasting Mid-Long Term Electric Energy Consumption through Bagging ARIMA and Exponential Smoothing Methods. Energy 2018, 144, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, N.; Collier, W.; Kiley, F.; Caulker, D.; Blyth, W.; Howells, M.; Brown, E. Long-Term Forecasting: A MAED Application for Sierra Leone’s Electricity Demand (2023–2050). Energies 2024, 17, 2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H.; Rubel, R.I.; Alam, M.A. Time Series Long-Term Forecasting of per Capita Electricity Consumption for Bangladesh. ASM Sci. J. 2021, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, Q.; Xia, Q.; Kang, C.; Zhang, X. A Monthly Electricity Consumption Forecasting Method Based on Vector Error Correction Model and Self-Adaptive Screening Method. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2018, 95, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cabral, J.A.; Legey, L.F.L.; de Freitas Cabral, M.V. Electricity Consumption Forecasting in Brazil: A Spatial Econometrics Approach. Energy 2017, 126, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasquez, C.E.; Zocatelli, M.; Estanislau, F.B.G.L.; Castro, V.F. Analysis of Time Series Models for Brazilian Electricity Demand Forecasting. Energy 2022, 247, 123483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delima, A.J.P. Application of Time Series Analysis in Projecting Philippines’ Electric Consumption. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Comput. 2019, 9, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sarkodie, S.A. Estimating Ghana’s Electricity Consumption by 2030: An ARIMA Forecast. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2017, 12, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Rahman, M.; Memon, J.A. Forecasting Electricity Consumption in Pakistan: The Way Forward. Energy Policy 2016, 90, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadri, R.; Kahoui, H.; Sahed, A. Electricity Consumption Forecasting in Algeria: A Comparison of ARIMA and GM (1,1) Models. Glob. Bus. 2023, 8, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, R. Hydroelectricity Consumption Forecast for Pakistan Using ARIMA Modeling and Supply-Demand Analysis for the Year 2030. Renew. Energy 2020, 154, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedokun, A. Nigeria Electricity Forecast and Vision 20: 2020: Evidence from ARIMA Model. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2016, 11, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, M.S.E.; Ahmed, F.; Durani, F.; Bojnec, Š.; Ghareeb, M.M. Predicting Electricity Consumption in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Energies 2023, 16, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Ma, J.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Pang, M. Decomposition-Based Dynamic Adaptive Combination Forecasting for Monthly Electricity Demand. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksawang, P.; Suphachan, S.; Kaewnuch, K. Electricity Consumption Forecasting in Thailand Using Hybrid Model SARIMA and Gaussian Process with Combine Kernel Function Technique. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 2018, 8, 98–109. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, S.E.; Tay, K.G.; Huong, A.; Tiong, W.K. Forecasting Electricity Consumption Using SARIMA Method in IBM SPSS Software. Univers. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2019, 6, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansor, R.; Zaini, B.J.; Yee, C.S. Forecasting of Electricity Consumption and Supply for Campus University Using Time Series Models. Int. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2019, 8, 467–472. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, J. Panel Quantile Regression Neural Network for Electricity Consumption Forecasting in China: A New Framework. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2021, 16, 420–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Gao, Y.; Yao, W.; Yu, N. A Robust Segmented Mixed Effect Regression Model for Baseline Electricity Consumption Forecasting. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2022, 10, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekhade, R.; Sakhare, D.K. Forecasting Sector-Wise Electricity Consumption for India Using Various Regression Models. Curr. Sci. 2021, 121, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ran, M.; Zhuang, C. Prediction of Building Electricity Consumption Based on Joinpoint−Multiple Linear Regression. Energies 2022, 15, 8543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavaklioglu, K. Principal Components Based Robust Vector Autoregression Prediction of Turkey’s Electricity Consumption. Energy Syst. 2019, 10, 889–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, F.R.; Csala, D. A Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average with Exogenous Factors (SARIMAX) Forecasting Model-Based Time Series Approach. Inventions 2022, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abulibdeh, A.; Zaidan, E.; Jabbar, R. The Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Electricity Consumption and Electricity Demand Forecasting Accuracy: Empirical Evidence from the State of Qatar. Energy Strategy Rev. 2022, 44, 100980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, S.; Gao, M. A Discrete Time-Varying Grey Fourier Model with Fractional Order Terms for Electricity Consumption Forecast. Energy 2024, 296, 131065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Dang, Y.; Gong, Y. Novel Grey Prediction Model with Nonlinear Optimized Time Response Method for Forecasting of Electricity Consumption in China. Energy 2017, 118, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wu, W.-Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, J. Forecasting Annual Electricity Consumption in China by Employing a Conformable Fractional Grey Model in Opposite Direction. Energy 2020, 202, 117682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Wu, D.; Yan, Y. Prediction of Electricity Consumption Based on GM(1,Nr) Model in Jiangsu Province, China. Energy 2023, 262, 125439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Liu, C.; Wu, W.-Z. A Novel Discrete GM(2,1) Model with a Polynomial Term for Forecasting Electricity Consumption. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 214, 108926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yang, Y.; Ning, T.; Zhu, J. A Novel Grey Power-Markov Model for the Prediction of China’s Electricity Consumption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 21717–21738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Jiang, R.; Ding, S.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Tao, H. A Novel Grey Prediction Model for Seasonal Time Series. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 229, 107363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. A Novel Multivariate Grey Model for Forecasting Periodic Oscillation Time Series. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 211, 118556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z. A Novel Rolling and Fractional-Ordered Grey System Model and Its Application for Predicting Industrial Electricity Consumption. J. Syst. Sci. Syst. Eng. 2024, 33, 207–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Guo, J.; Sun, S.; Wang, S.; Wu, J. A Novel Two-Stage Seasonal Grey Model for Residential Electricity Consumption Forecasting. Energy 2022, 258, 124664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-X.; Li, Q.; Pei, L.-L. A Seasonal GM(1,1) Model for Forecasting the Electricity Consumption of the Primary Economic Sectors. Energy 2018, 154, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Du, P.; Lu, H.; Yang, W.; Niu, T. An Improved Grey Model Optimized by Multi-Objective Ant Lion Optimization Algorithm for Annual Electricity Consumption Forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 72, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayvaz, B.; Kusakci, A.O. Electricity Consumption Forecasting for Turkey with Nonhomogeneous Discrete Grey Model. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2017, 12, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-C. Electricity Consumption Prediction Using a Neural-Network-Based Grey Forecasting Approach. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2017, 68, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A. Empowering Tomorrow: Innovative Forecasting for UAE’s Electricity Consumption. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Sci. 2024, 35, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Hipel, K.W.; Dang, Y. Forecasting China’s Electricity Consumption Using a New Grey Prediction Model. Energy 2018, 149, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Tao, H.; Chang, J.; Jiang, H.; Chen, L. Forecasting Chinese Electricity Consumption Based on Grey Seasonal Model with New Information Priority. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, T. Forecasting Electricity Consumption Using an Improved Grey Prediction Model. Information 2018, 9, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Tan, Y.; Xu, H.; Quan, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X. Forecasting the Electricity Consumption of Commercial Sector in Hong Kong Using a Novel Grey Dynamic Prediction Model. J. Grey Syst. 2018, 30, 159–174. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, T.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, H.; Nie, J.; Xiong, Z.; Wu, X.; Feng, W. GM(1,1) Based Improved Seasonal Index Model for Monthly Electricity Consumption Forecasting. Energy 2022, 252, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-N.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Tran, T.-T. Integrated DEA Models and Grey System Theory to Evaluate Past-to-Future Performance: A Case of Indian Electricity Industry. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 638710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-Z.; Pang, H.; Zheng, C.; Xie, W.; Liu, C. Predictive Analysis of Quarterly Electricity Consumption via a Novel Seasonal Fractional Nonhomogeneous Discrete Grey Model: A Case of Hubei in China. Energy 2021, 229, 120714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, C.; Gou, X.; Ren, Y.; Zeng, B.; Khalid, J.; Ma, Y. Seasonal Electricity Consumption Forecasting: An Approach with Novel Weakening Buffer Operator and Fractional Order Accumulation Grey Model. Grey Syst. 2024, 14, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, B.; Nan, F.; Zhu, N.; Yuan, Y.; Xie, W. UFNGBM (1,1): A Novel Unbiased Fractional Grey Bernoulli Model with Whale Optimization Algorithm and Its Application to Electricity Consumption Forecasting in China. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 7405–7423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Gao, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X. Using a Novel Multi-Variable Grey Model to Forecast the Electricity Consumption of Shandong Province in China. Energy 2018, 157, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Dang, Y.; Ding, S. Using a Self-Adaptive Grey Fractional Weighted Model to Forecast Jiangsu’s Electricity Consumption in China. Energy 2020, 190, 116417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Shen, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, J. Using Fractional Discrete Verhulst Model to Forecast Fujian’s Electricity Consumption in China. Energy 2022, 255, 124484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhao, H.; Guo, S. Using GM (1,1) Optimized by MFO with Rolling Mechanism to Forecast the Electricity Consumption of Inner Mongolia. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Wu, L. Support Vector Regression with Fruit Fly Optimization Algorithm for Seasonal Electricity Consumption Forecasting. Energy 2016, 115, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, C.; Bozkurt, A. An Advanced Framework for Net Electricity Consumption Prediction: Incorporating Novel Machine Learning Models and Optimization Algorithms. Energy 2024, 296, 131259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almuhaini, S.H.; Sultana, N. Forecasting Long-Term Electricity Consumption in Saudi Arabia Based on Statistical and Machine Learning Algorithms to Enhance Electric Power Supply Management. Energies 2023, 16, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shine, P.; Scully, T.; Upton, J.; Murphy, M.D. Annual Electricity Consumption Prediction and Future Expansion Analysis on Dairy Farms Using a Support Vector Machine. Appl. Energy 2019, 250, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.-F.; Zhang, R.-T.; Cao, C.-C.; Yeh, Y.-H.; Hong, W.-C. Applications of Empirical Wavelet Decomposition, Statistical Feature Extraction, and Antlion Algorithm with Support Vector Regression for Resident Electricity Consumption Forecasting. NONLINEAR Dyn. 2023, 111, 20139–20163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-León, J.; Rubio-Cienfuegos, J.; Vidal-Silva, C.; Cárdenas-Cobo, J.; Duarte, V. Applying Fuzzy Time Series for Developing Forecasting Electricity Demand Models. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Luan, C.; Liu, L.; Liu, W.; Zhu, Y. Data-Driven Random Forest Forecasting Method of Monthly Electricity Consumption. Electr. Eng. 2022, 104, 2045–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Lin, Y.; Pan, N.; Fu, Q.; Chen, L.; Yang, J. Demand-Side Electricity Load Forecasting Based on Time-Series Decomposition Combined with Kernel Extreme Learning Machine Improved by Sparrow Algorithm. Energies 2023, 16, 7714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurinec, P.; Loderer, M.; Lucka, M.; Rozinajova, V. Density-Based Unsupervised Ensemble Learning Methods for Time Series Forecasting of Aggregated or Clustered Electricity Consumption. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2019, 53, 219–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, R.R.; Garg, R.D. Design of Electricity Tariff Plans Using Gap Statistic for K-Means Clustering Based on Consumers Monthly Electricity Consumption Data. Int. J. Energy Sect. Manag. 2017, 11, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paikaray, B.K.; Jena, S.P.; Mondal, J.; Van Thuan, N.; Tung, N.T.; Mallick, C. Electricity Consumption Classification Using Various Machine Learning Models. EAI Endorsed Trans. Energy Web 2024, 11, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, K.G.; Muwafaq, H.; Ismail, S.B.; Ong, P. Electricity Consumption Forecasting Using Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS). Univers. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2019, 6, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, L.; Ditschuneit, K.; Schambach, M.; Kaymakci, C.; Wollmann, T.; Sauer, A. Explainability and Interpretability in Electric Load Forecasting Using Machine Learning Techniques—A Review. Energy AI 2024, 16, 100358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Suh, D.; Otto, M.-O. Forecasting Electricity Consumption in Commercial Buildings Using a Machine Learning Approach. Energies 2020, 13, 5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, D.; Tunc, K.M.M.; Gunay, M.E. Forecasting Electricity Consumption of OECD Countries: A Global Machine Learning Modeling Approach. Util. Policy 2021, 70, 101222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, S.; Nebot, À.; Mugica, F.; Avellana, N. Hybrid Methodologies for Electricity Load Forecasting: Entropy-Based Feature Selection with Machine Learning and Soft Computing Techniques. Energy 2015, 86, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Omella, M.; Esnaola-Gonzalez, I.; Ferreiro, S.; Sierra, B. K-Nearest Patterns for Electrical Demand Forecasting in Residential and Small Commercial Buildings. Energy Build. 2021, 253, 111396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrini, F.C.; Souza, R.C.; Cyrino Oliveira, F.L.; Moreira Pessanha, J.F. Long Term Electricity Consumption Forecast in Brazil: A Fuzzy Logic Approach. Socioecon. Plann. Sci. 2016, 54, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkamel, M.; Schleider, L.; Pasiliao, E.L.; Diabat, A.; Zheng, Q.P. Long-Term Electricity Demand Prediction via Socioeconomic Factors-a Machine Learning Approach with Florida as a Case Study. Energies 2020, 13, 3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Fard, R.H. Machine Learning Algorithms for Predicting Electricity Consumption of Buildings. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 121, 3329–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Metrik, M.A.; Musleh, D.A. Machine Learning Empowered Electricity Consumption Prediction. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 72, 1427–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, P.C.; Cajueiro, D.O.; Rossi, M.D.C. Machine Learning Models for Forecasting Power Electricity Consumption Using a High Dimensional Dataset. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 187, 115917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-T.; Sun, E.W.; Lin, Y.-B. Machine Predicting Sectoral Electricity Consumption Based e Learning with Parallel Neural Networks for Analyzing and Forecasting Electricity Demand. Comput. Econ. 2020, 56, 569–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zini, M.; Carcasci, C. Machine Learning-Based Monitoring Method for the Electricity Consumption of a Healthcare Facility in Italy. Energy 2023, 262, 125576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charfeddine, L.; Zaidan, E.; Alban, A.Q.; Bennasr, H.; Abulibdeh, A. Modeling and Forecasting Electricity Consumption amid the COVID-19 Pandemic: Machine Learning vs. Nonlinear Econometric Time Series Models. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 98, 104860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, R.; Das, P.; Ray, S.; Biswas, A. Prediction of Electrical Energy Consumption Based on Machine Learning Technique. Electr. Eng. 2021, 103, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Guo, R.; Li, H.; Wu, J.; Sun, X. T-LGBKS: An Interpretable Machine Learning Framework for Electricity Consumption Forecasting. Energies 2023, 16, 4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, F.; Mor, G.; Cipriano, J.; Gabaldon, E.; Grillone, B.; Chemisana, D.; Solsona, F. User Behaviour Models to Forecast Electricity Consumption of Residential Customers Based on Smart Metering Data. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 3680–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neo, H.Y.R.; Wong, N.H.; Ignatius, M.; Cao, K. A Hybrid Machine Learning Approach for Forecasting Residential Electricity Consumption: A Case Study in Singapore. Energy Environ. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.F.; Martinez-Alvarez, F.; Troncoso, A. A Deep LSTM Network for the Spanish Electricity Consumption Forecasting. NEURAL Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 10533–10545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Chiroma, H.; Imran, M.; Khan, A.; Bangash, J.I.; Asim, M.; Hamza, M.F.; Aljuaid, H. Forecasting Electricity Consumption Based on Machine Learning to Improve Performance: A Case Study for the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC). Comput. Electr. Eng. 2020, 86, 106737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, F.L.C.; da Costa, K.; Rodrigues, P.C.; Salas, R.; López-Gonzales, J.L. Statistical and Artificial Neural Networks Models for Electricity Consumption Forecasting in the Brazilian Industrial Sector. Energies 2022, 15, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J. Annual Electricity and Energy Consumption Forecasting for the UK Based on Back Propagation Neural Network, Multiple Linear Regression, and Least Square Support Vector Machine. Processes 2023, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, D.; Faria, P.; Gomes, L.; Vale, Z. A Contextual Reinforcement Learning Approach for Electricity Consumption Forecasting in Buildings. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 61366–61374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, A.J.; Harish Ram, D.S.; Nair, B.B. A Deep Learning Approach to Electric Energy Consumption Modeling. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 36, 4049–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atik, I. A New CNN-Based Method for Short-Term Forecasting of Electrical Energy Consumption in the Covid-19 Period: The Case of Turkey. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 22586–22598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.-W.; Alattas, K.; El-Sousy, F.; Alanazi, A.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Tavoosi, J.; Mobayen, S.; Skruch, P. A New Short Term Electrical Load Forecasting by Type-2 Fuzzy Neural Networks. Energies 2022, 15, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Kim, C.-S.; Sontakke, P. Accurate Forecasting Energy Demand Using Conditional Random Deep Model for Electricity Consumption Forecasting Using Multi-Channel and Multi-Scale Feature Fusion CNN-LSTM. Energies 2020, 13, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Jang, B. Accurate Prediction of Electricity Consumption Using a Hybrid CNN-LSTM Model Based on Multivariable Data. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0278071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedinec, A.; Filiposka, S.; Dedinec, A.; Kocarev, L. Deep Belief Network Based Electricity Load Forecasting: An Analysis of Macedonian Case. Energy 2016, 115, 1688–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, J.; Toshniwal, D. Deep Learning Framework to Forecast Electricity Demand. Appl. Energy 2019, 238, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, M.; Arbab, M.A.; Rehman, S. ur Deep Learning-Based Forecasting of Electricity Consumption. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oprea, S.-V.; Pirjan, A.; Carutasu, G.; Petrosanu, D.-M.; Bara, A.; Stanica, J.-L.; Coculescu, C. Developing a Mixed Neural Network Approach to Forecast the Residential Electricity Consumption Based on Sensor Recorded Data. Sensors 2018, 18, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, E.; Pinto, T.; Guedes, V.; Morais, H. Electrical Load Demand Forecasting Using Feed-Forward Neural Networks. Energies 2021, 14, 7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroșanu, D.-M.; Pîrjan, A. Electricity Consumption Forecasting Based on a Bidirectional Long-Short-Term Memory Artificial Neural Network. Sustainability 2021, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, K.G.; Muwafaq, H.; Ismail, S.B.; Ong, P. Electricity Consumption Forecasting Using Nonlinear Autoregressive with External (Exogeneous) Input Neural Network. Univers. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2019, 6, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deina, C.; dos Santos, J.L.F.; Biuk, L.H.; Lizot, M.; Converti, A.; Siqueira, H.V.; Trojan, F. Forecasting Electricity Demand by Neural Networks and Definition of Inputs by Multi-Criteria Analysis. Energies 2023, 16, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavel, A.; Govindaraj, V. Forecasting Energy Demand Using Conditional Random Field and Convolution Neural Network. Elektron. Ir Elektrotechnika 2022, 28, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiprijanovska, I.; Stankoski, S.; Ilievski, I.; Jovanovski, S.; Gams, M.; Gjoreski, H. HousEEC: Day-Ahead Household Electrical Energy Consumption Forecasting Using Deep Learning. Energies 2020, 13, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, D.; Faria, P.; Vale, Z.; Mourinho, J.; Correia, R. Industrial Facility Electricity Consumption Forecast Using Artificial Neural Networks and Incremental Learning. Energies 2020, 13, 4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Sarkar, B.D.; Hossain, M.E.; Rej, S.; Mallick, M.A. Modelling and Forecasting India’s Electricity Consumption Using Artificial Neural Networks. OPEC Energy Rev. 2024, 48, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, K.; Wang, F.; Xuan, Z.; Mi, Z.; Li, W.; Dehghanian, P.; Fotuhi-Firuzabad, M. Monthly Electricity Consumption Forecasting: A Step-Reduction Strategy and Autoencoder Neural Network. IEEE Ind. Appl. Mag. 2021, 27, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouktif, S.; Fiaz, A.; Ouni, A.; Serhani, M.A. Optimal Deep Learning LSTM Model for Electric Load Forecasting Using Feature Selection and Genetic Algorithm: Comparison with Machine Learning Approaches. Energies 2018, 11, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Lin, J. Panel Semiparametric Quantile Regression Neural Network for Electricity Consumption Forecasting. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 67, 101489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Srikumar, V.; Smith, A.D. Predicting Electricity Consumption for Commercial and Residential Buildings Using Deep Recurrent Neural Networks. Appl. Energy 2018, 212, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, L.; Tian, Y. Predicting Sectoral Electricity Consumption Based on Complex Network Analysis. Appl. Energy 2019, 255, 113790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, C.; Liu, Y.; Kusiak, A. Probabilistic Load Forecasting with a Non-Crossing Sparse-Group Lasso-Quantile Regression Deep Neural Network. Energy 2022, 242, 122955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, D. Research on Electricity Consumption Forecasting Model Based on Wavelet Transform and Multi-Layer LSTM Model. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Chi, H.; Shao, X. Forecasting Residential Electricity Consumption Using a Hybrid Machine Learning Model with Online Search Data. Appl. Energy 2021, 300, 117393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaytez, F. A Hybrid Approach Based on Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average and Least-Square Support Vector Machine for Long-Term Forecasting of Net Electricity Consumption. Energy 2020, 197, 117200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çağlayan-Akay, E.; Topal, K.H. Forecasting Turkish Electricity Consumption: A Critical Analysis of Single and Hybrid Models. Energy 2024, 305, 132115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Chang, J. A Hybrid Prediction Model Based on Improved Multivariable Grey Model for Long-Term Electricity Consumption. Electr. Eng. 2021, 103, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Grandón, T.; Schwenzer, J.; Steens, T.; Breuing, J. Electricity Demand Forecasting with Hybrid Classical Statistical and Machine Learning Algorithms: Case Study of Ukraine. Appl. Energy 2024, 355, 122249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Qi, Q. A Novel Hybrid Grey System Forecasting Model Based on Seasonal Fluctuation Characteristics for Electricity Consumption in Primary Industry. Energy 2024, 287, 129585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, M.; Sahabi, B. A Hybrid Approach to Model and Forecast the Electricity Consumption by NeuroWavelet and ARIMAX-GARCH Models. Energy Effic. 2019, 12, 2099–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Ahuja, S. A Hybrid Arima and Discrete Wavelet Transform Model for Predicting the Electricity Consumption of Punjab. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2019, 8, 1915–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Liu, F.; Song, Y. A Hybrid Forecasting Model Based on Date-Framework Strategy and Improved Feature Selection Technology for Short-Term Load Forecasting. Energy 2017, 119, 694–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, B.; Zhang, C.; Li, F. A Hybrid Prediction Model for Residential Electricity Consumption Using Holt-Winters and Extreme Learning Machine. Appl. Energy 2020, 275, 115383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Fu, Y.; Shi, H.; Wang, X. A Small-Sample Adaptive Hybrid Model for Annual Electricity Consumption Forecasting. Math. Probl. Eng. 2017, 2017, 7427131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, M.; Chakrabarty, T.K. A Wavelet Based Hybrid SARIMA-ETS Model to Forecast Electricity Consumption. Electron. J. Appl. Stat. Anal. 2017, 10, 408–430. [Google Scholar]
- Oladipo, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Amole, A.O. Analysis of the Impact of Clustering Techniques and Parameters on Evolutionary-Based Hybrid Models for Forecasting Electricity Consumption. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 82838–82856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ding, Z.; Yi, J.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, G. Deep Belief Network Based Hybrid Model for Building Energy Consumption Prediction. Energies 2018, 11, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.-F.; Wei, X.; Li, Y.-T.; Hong, W.-C. Forecasting Electricity Consumption Using a Novel Hybrid Model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 61, 102320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.-F.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, W.-J.; Peng, L.-L.; Yeh, Y.-H.; Hong, W.-C. Forecasting Residential Electricity Consumption Using the Novel Hybrid Model. Energy Build. 2023, 290, 113085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, C.; Dahiya, R. Robust Framework Based on Hybrid Deep Learning Approach for Short Term Load Forecasting of Building Electricity Demand. Energy 2023, 268, 126660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranj, A.; Zolfaghari, M. The Electricity Consumption Forecast: Adopting a Hybrid Approach by Deep Learning and ARIMAX-GARCH Models. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 7657–7679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Lu, Q.-Y.; Wang, S.-Y.; Lai, K.K. Analysis of Road Transportation Energy Consumption Demand in China. Transp. Res. Part Transp. Environ. 2016, 48, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M.; Osińska, M. Comparing Forecasting Accuracy of Selected Grey and Time Series Models Based on Energy Consumption in Brazil and India. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 212, 118840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.-B. Using Grey Models for Forecasting China’s Growth Trends in Renewable Energy Consumption. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2016, 18, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgil, H. Department of Mathematics, Aksaray University, Aksaray 68100, Turkey New Grey Forecasting Model with Its Application and Computer Code. AIMS Math. 2021, 6, 1497–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abellan-Nebot, J.V.; Romero Subirón, F. A Review of Machining Monitoring Systems Based on Artificial Intelligence Process Models. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 47, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademujimi, T.T.; Brundage, M.P.; Prabhu, V.V. A Review of Current Machine Learning Techniques Used in Manufacturing Diagnosis. In Advances in Production Management Systems. The Path to Intelligent, Collaborative and Sustainable Manufacturing; Lödding, H., Riedel, R., Thoben, K.-D., Von Cieminski, G., Kiritsis, D., Eds.; IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 513, pp. 407–415. ISBN 978-3-319-66922-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Alam, M.S.B.; Hassan, M.; Rozbu, M.R.; Ishtiak, T.; Rafa, N.; Mofijur, M.; Shawkat Ali, A.B.M.; Gandomi, A.H. Deep Learning Modelling Techniques: Current Progress, Applications, Advantages, and Challenges. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 13521–13617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sina, L.B.; Secco, C.A.; Blazevic, M.; Nazemi, K. Hybrid Forecasting Methods—A Systematic Review. Electronics 2023, 12, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, S.; Deo, R.; Shojafar, M.; Conti, M.; Shamshirband, S. Computational Intelligence Approaches for Energy Load Forecasting in Smart Energy Management Grids: State of the Art, Future Challenges, and Research Directions. Energies 2018, 11, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, H.; Silva, E.S. The Role of ChatGPT in Data Science: How AI-Assisted Conversational Interfaces Are Revolutionizing the Field. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2023, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, H.; Silva, E.S. Predictions from Generative Artificial Intelligence Models: Towards a New Benchmark in Forecasting Practice. Information 2024, 15, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, F.; Apiletti, D.; Assimakopoulos, V.; Babai, M.Z.; Barrow, D.K.; Ben Taieb, S.; Bergmeir, C.; Bessa, R.J.; Bijak, J.; Boylan, J.E.; et al. Forecasting: Theory and Practice. Int. J. Forecast. 2022, 38, 705–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. Bibliometrix: An R-Tool for Comprehensive Science Mapping Analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wu, X.; Gong, Y.; Yu, W.; Zhong, X. Holt–Winters Smoothing Enhanced by Fruit Fly Optimization Algorithm to Forecast Monthly Electricity Consumption. Energy 2020, 193, 116779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
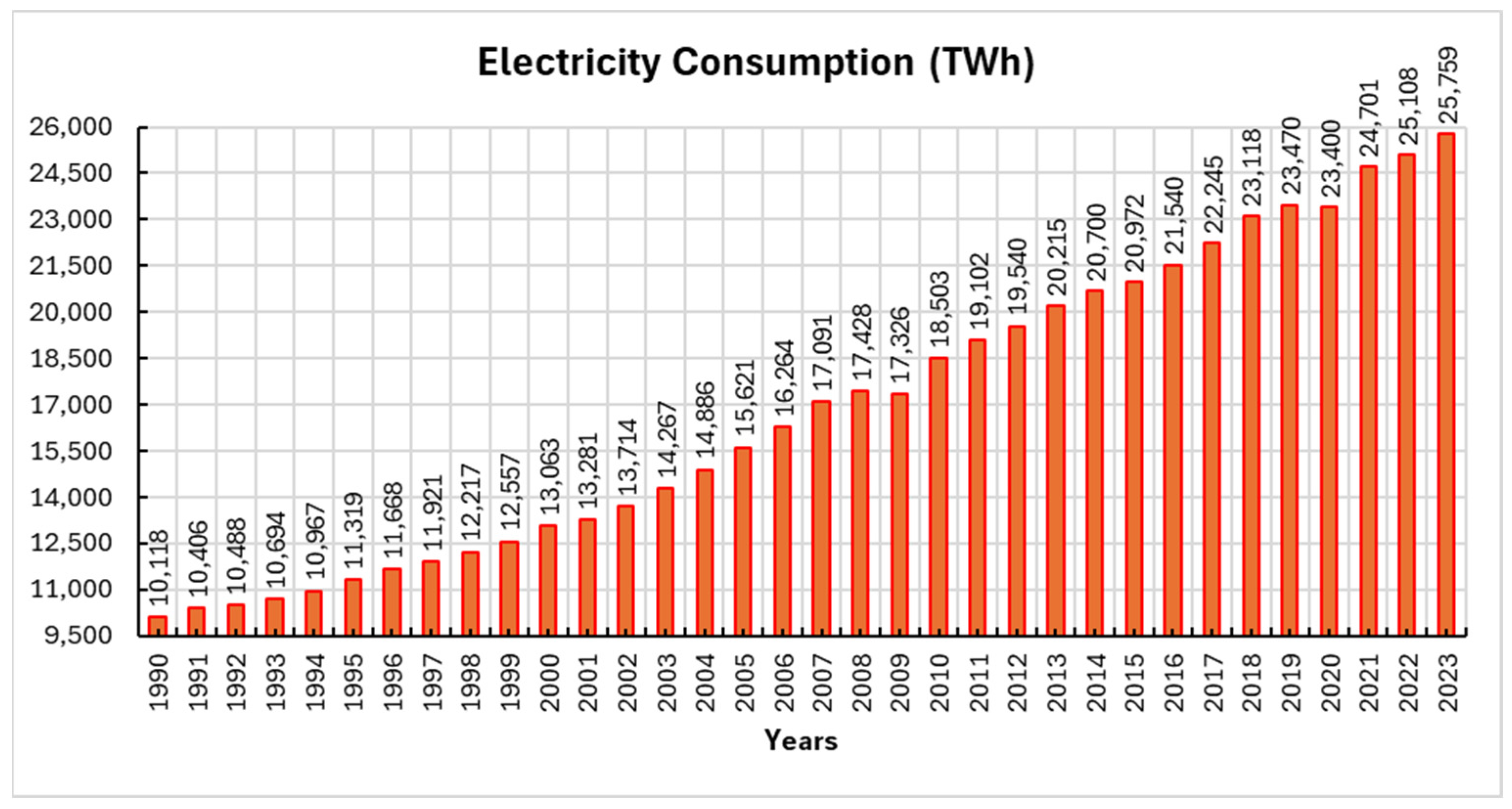
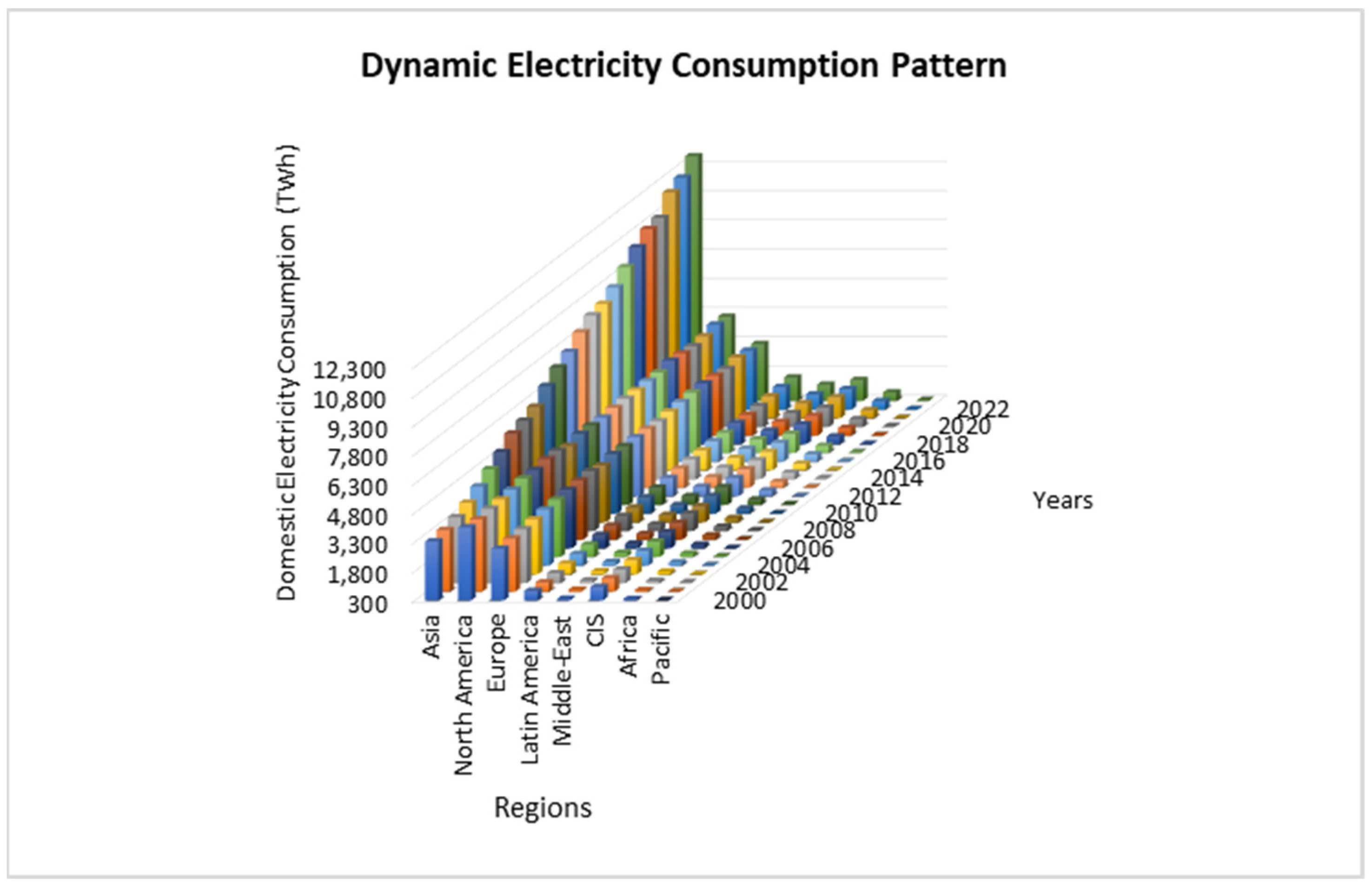
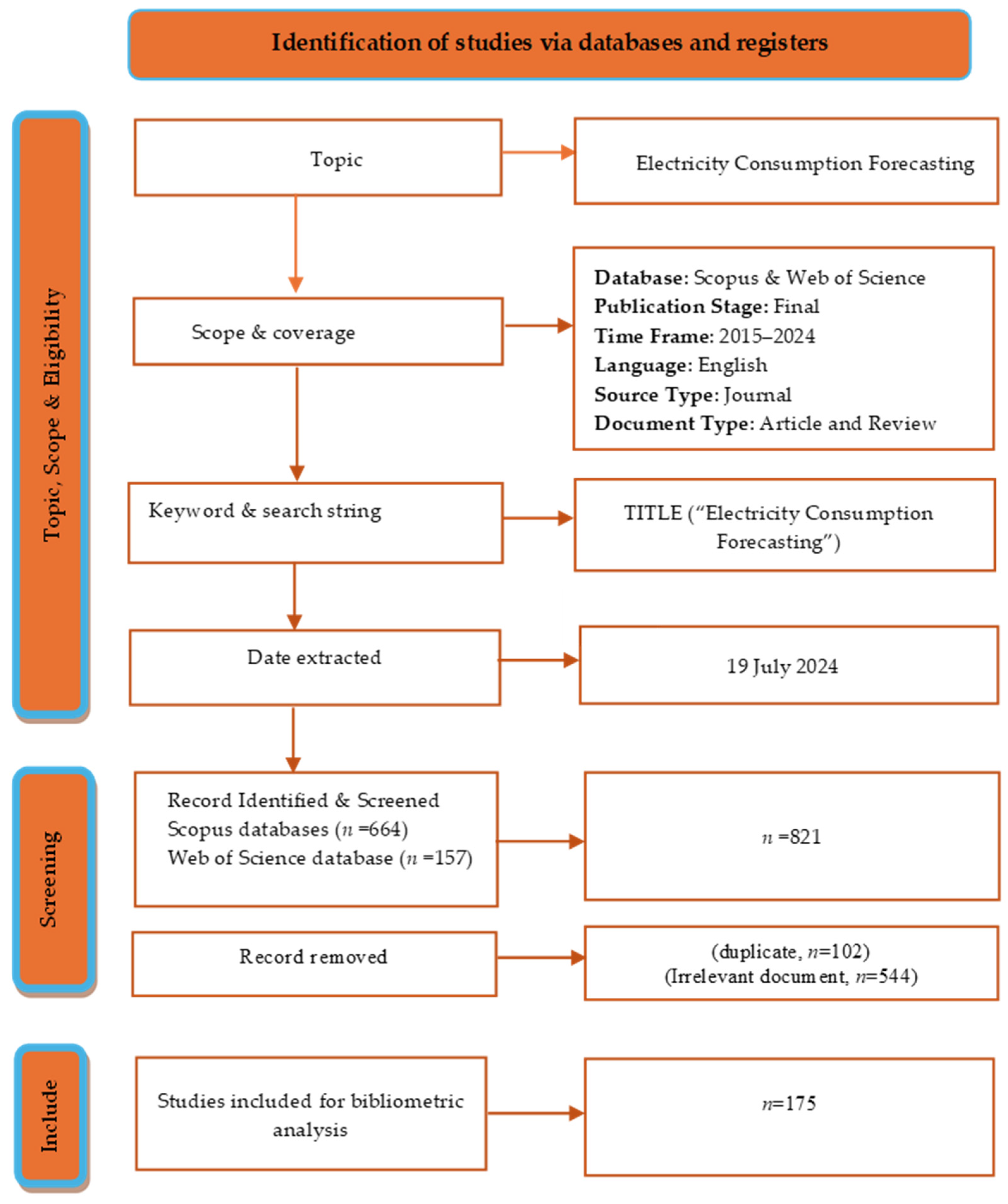
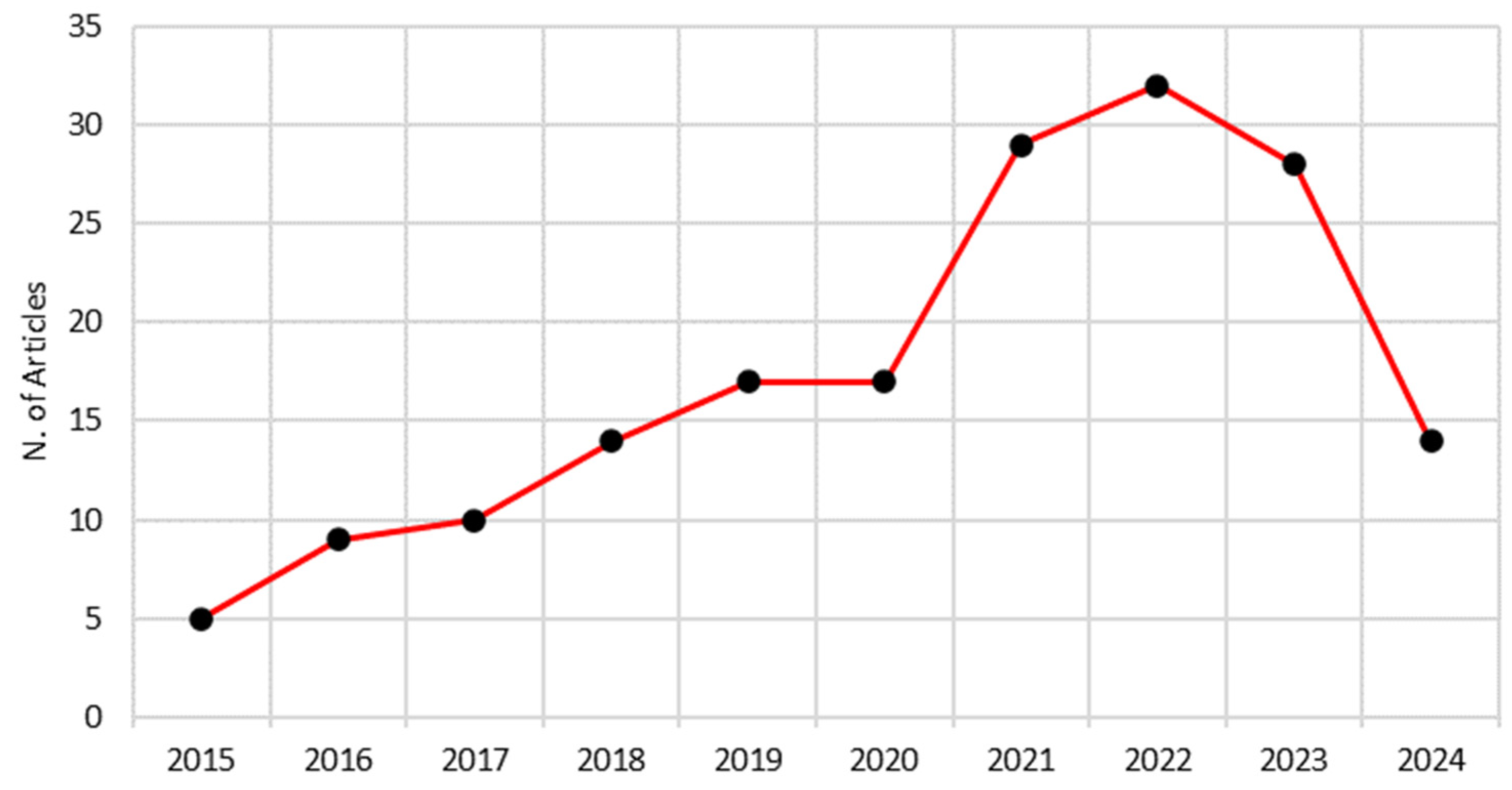
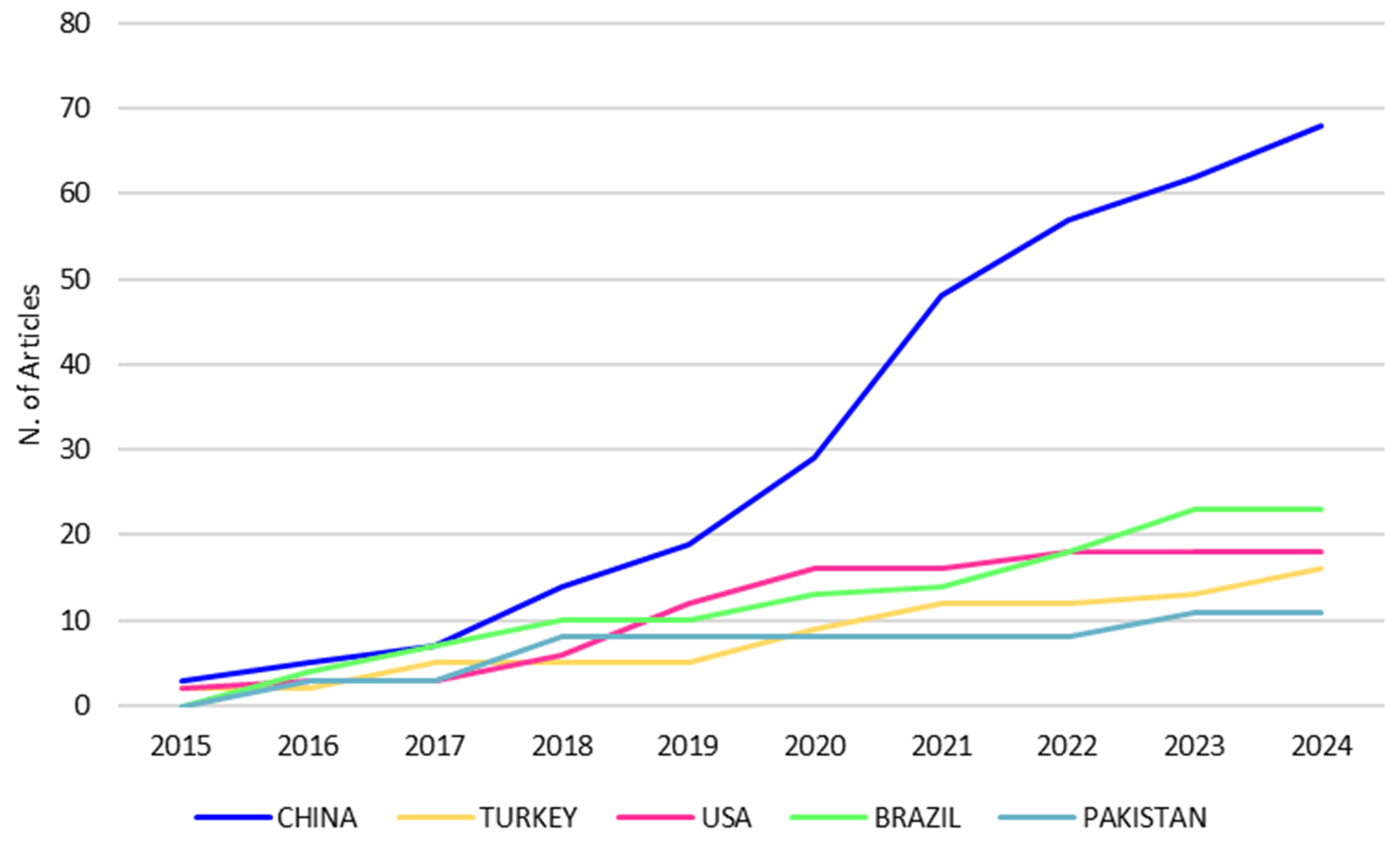

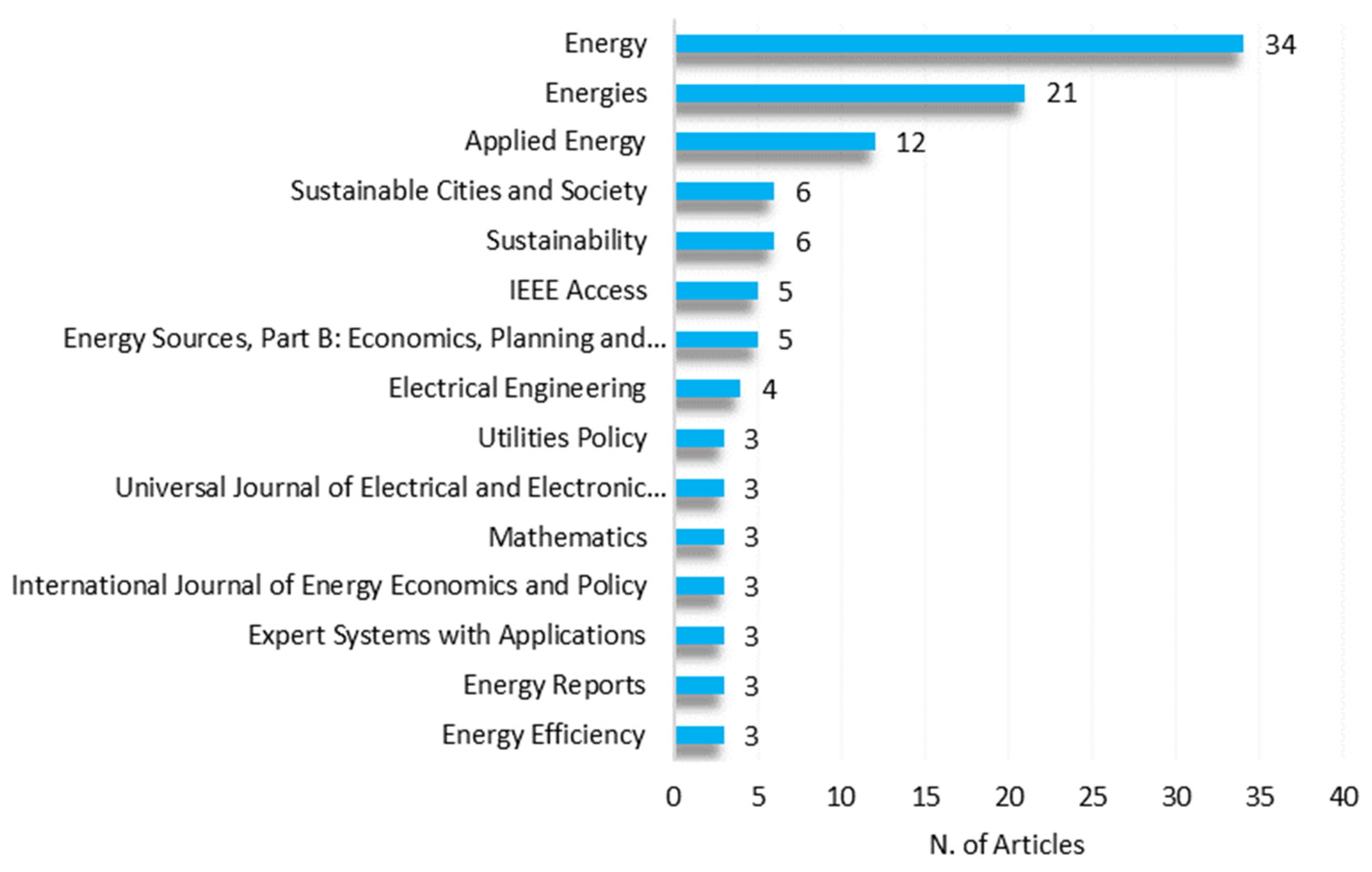

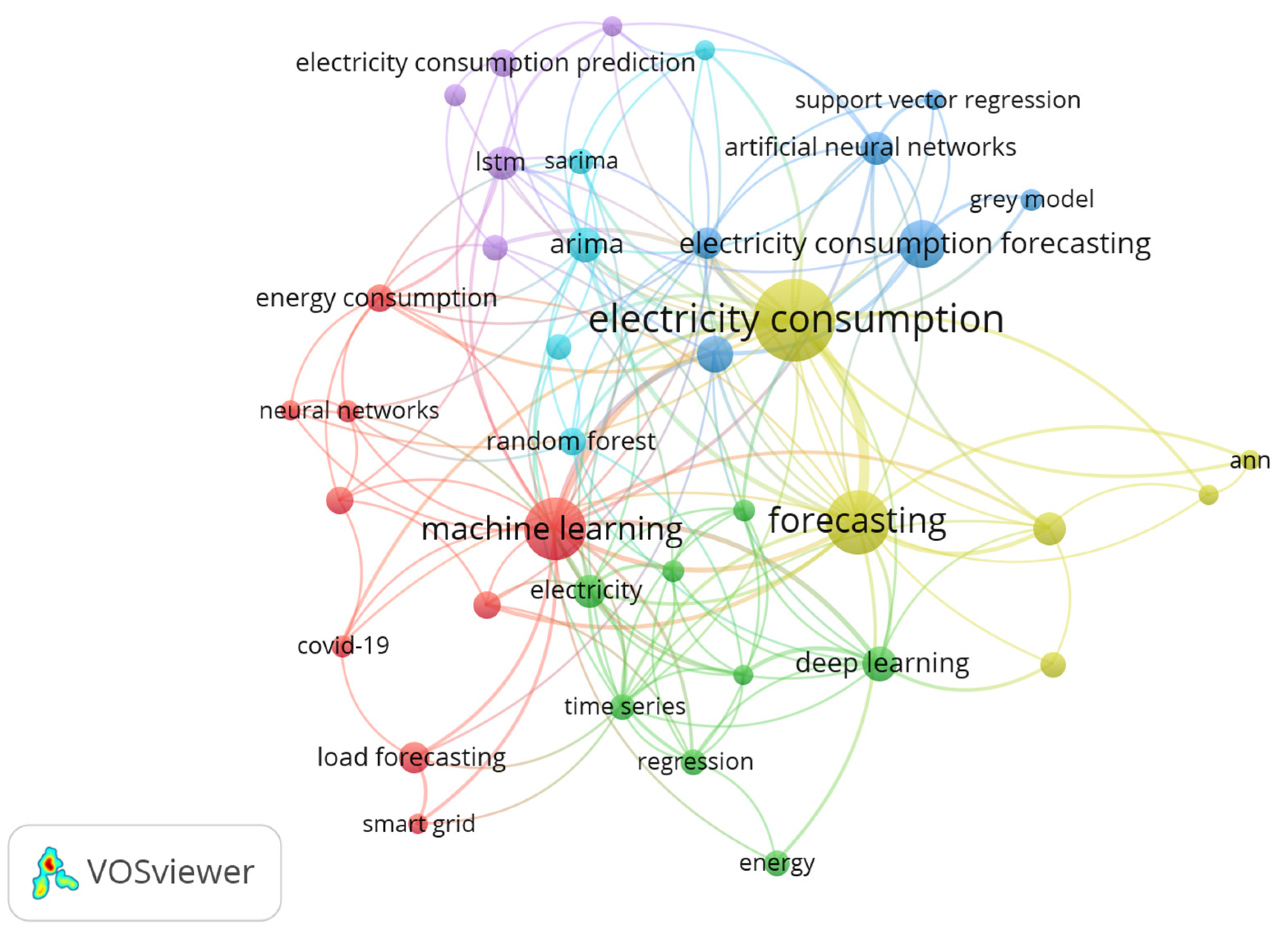
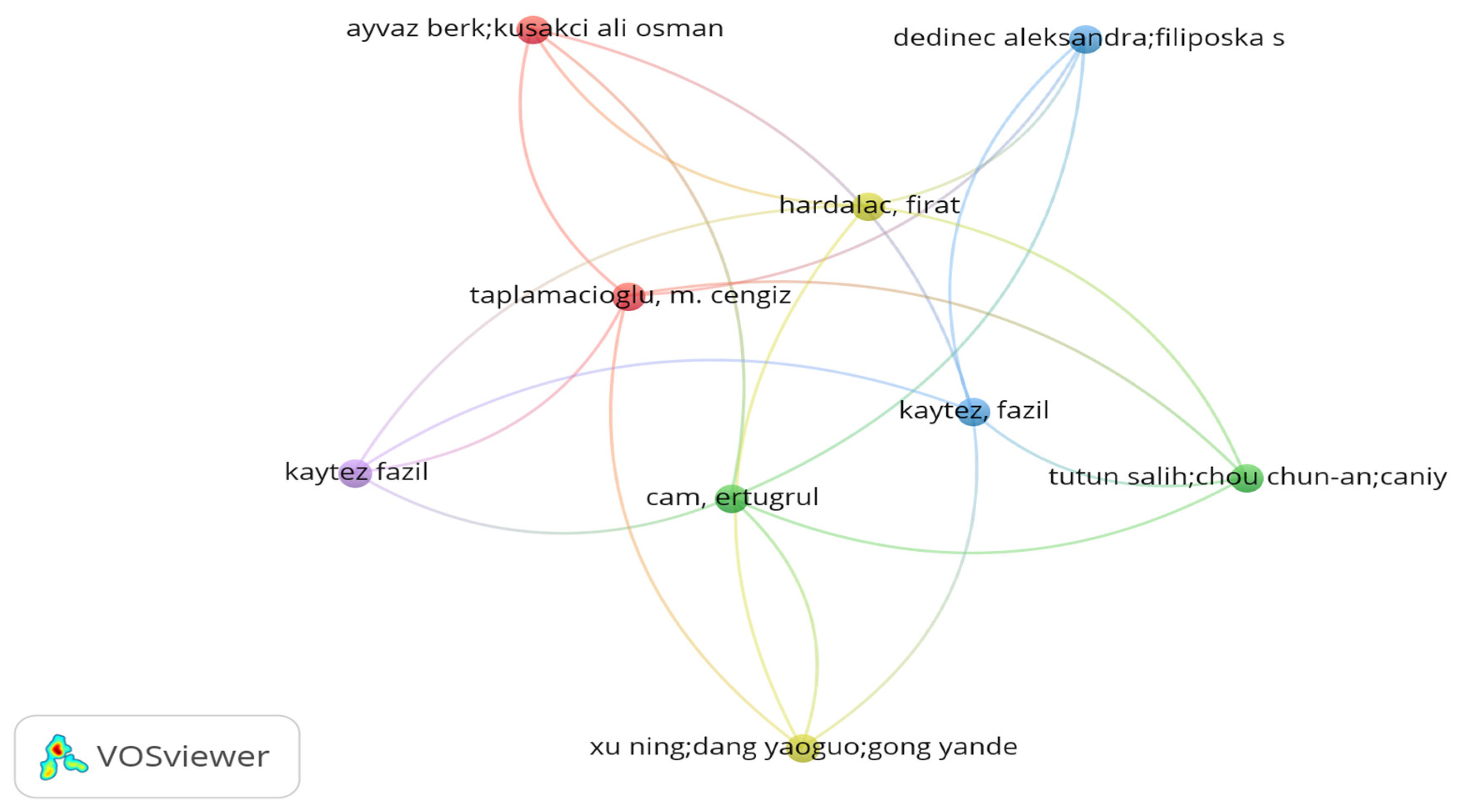
| Author’s Name | Affiliation | Country | P | h | g | m | C | C/P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dang, Y. | College of Economics and Management, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing | China | 4 | 4 | 4 | 0.50 | 502 | 125.5 |
| Liu, C. | College of Sciences, Northeastern University, Shenyang | China | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0.60 | 186 | 62.0 |
| Wu, L. | School of Economics and Business Administration, Central China Normal University, Wuhan | China | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0.33 | 344 | 114.7 |
| Yang, L. | Big Data Research Center, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China | China | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0.50 | 22 | 7.3 |
| Almuhaini, S. | Department of Computer Science, Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University | Saudi Arabia | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0.67 | 26 | 13.0 |
| Chen, L. | Faculty of Civil Aviation and Aeronautics, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming | China | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1.00 | 6 | 3.0 |
| Ddeinec, A. | Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering, Ss. Cyril and Methodius University, Skopje | North Macedonia | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0.22 | 488 | 244.0 |
| Ding, S. | College of Economics and Management, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics | China | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0.29 | 352 | 176.0 |
| Fan, G. | School of Mathematics & Statistics, Pingdingshan University, Pingdingshan | China | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0.40 | 169 | 84.5 |
| Gao, F. | Institutes of Science and Development, Chinese Academy of Sciences | China | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0.20 | 65 | 32.5 |
| S. NO | Author(s) | Sample(s) | Time/Frequency | Country(s) | Target Variable(s) | Methodology | Empirical Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [5] | 2007 m1–2016 m12 | 2016 m1–2016 m12 (SR&LR) | 7 countries | EC | ANN, ANFIS, LSSVM, FTS | The FTS model performed well. |
| 2 | [6] | January 1975–December 2021 | January 2022–December 2031 | Turkie | EC | SARIMA, LSTM | The LSTM model generally outperformed the SARIMA model, with the lowest MAPE (2.42%) values and the most excellent R2 (0.9992). |
| 3 | [7] | 1970–2009 | 2010–2011 | Turkey | EC | SVM; LSSVM; ANN | The proposed LSSVM model is an accurate prediction method. |
| 4 | [8] | Daily 2009–2018 (3652 obs) | January 2018–December 2018 (SR) | Thailand | EC | ANN, MLR, SVM, hybrid models (NFL theorem) | The forecasting performance of ANNs and MLR is the best. |
| 5 | [9] | January 1990–December 2010 | January 2011–December 2020 | Turkey | EC | SARIMA, NARANN, LADES, RADES | LADES and RADES are more robust and reliable forecasts. |
| 6 | [10] | January 1999–December 2019 | 2009–2019 (annual data) 2018–2019 (daily data) 1 January 2009–31 December 2014 1 January 2021–31 December 2025 | Brazil | ED | RS, ES, ARIMA, RS-ES, AFT, AWT, ANN | AWT performs better with a 3% average percent error in most cases. |
| 7 | [62] | 2000–2019 | 2020–2026 | Rwanda | EC | ARIMA, MLR | ARIMA (1,1,1) was the best model to forecast EC. |
| 8 | [71] | January 2000–January 2014 | January 2012–December 2014 | China | EC | SAS-SVECM, X-12-ARIMA | The results verify that SAS-SVECM achieves better forecasting. |
| 9 | [72] | January 2003–December 2013 | July 2013–December 2013 | Brazil | REC | ARIMA, ARIMAspa | ARIMASp shows better predictive performance than ARIMA. |
| 10 | [73] | January 2002–December 2020 January 2002–December 2014 January 2002–December 2019 January 2002–December 2014 January 2002–December 2015 January 2002–December 2014 January 2010–December 2020 January 2010–December 2014 January 2009–December 2019 January 2009–December 2014 | January 2021–December 2025 January 2015–December 2019 January 2020–December 2025 January 2015–December 2019 January 2016–December 2025 January 2015–December 2019 January 2021–December 2025 January 2015–December 2019 January 2020–December 2025 January 2015–December 2019 | Brazilian Regions | ED | RS, ES, ARIMA, RS + ES + ARIMA, ARIMA + RS, RS + ES | RS, RS + ES has the best forecasting performance. |
| 11 | [82] | January 2005–December 2015 | January 2016–December 2025 | Thailand | EC | SARIMA-ANNs and SARIMA-GP (with combined Kernel Functions) | SARIMA-GP with the combined Kernel Function technique outperformed the SARIMA-ANN model with a MAPE of 4.7072 × 10−9 and 4.8623, respectively. |
| 12 | [85] | 1999–2017 | 2018–2022 | China | EC | PQRNN, BPNN, GRNN, ELM, SVM | PQRNN has advantages over both CQR and ANN. |
| 13 | [90] | 1990–2018 | 2021–2050 | Saudia Arabia | EC | SARIMAX | SARIMAX has the best performance. |
| 14 | [92] | 1 January 2017–31 December 2020 1 January 2010–31 December 2021 | 2022 | Qatar | EC | XGBoost, RF, SVM | The XGBoost algorithm’s performance is the best. |
| 15 | [92] | January 2015–December 2022 | January 2022–December 2022 | China | REC | ARIMA, DNN, GM (1,1), DGM (1,1), SGM (1,1), GMP (1,1,1), GFM (1,1,n), DTFGM(1,1,N) | The proposed model performs better than benchmark grey and non-grey prediction models. |
| 16 | [93] | 2003–2013 | 2014–2020 | China | EC | GM, NP-GM, OICGM, IRGM | The forecasting performance of the IRGM (1,1) model is the best. |
| 17 | [94] | 1999–2018 | 2019–2023 | China | EC | GM, DGM, CFGM, CFGOM | CFGOM shows the best forecasting performance with a minimum MAPE of 1.54% and 0.65% for Fujian and Shandong, respectively. |
| 18 | [95] | 2010–2020 | 2021–2030 | China (Jiangsu) | EC | GM, FDGM, HES | GM (1,Nr) is the best performer. |
| 19 | [120] | January 2010–December 2015 January 1994–December 2014 | January 2014–December 2014 January 2015–December 2015 | China | EC | SARIMA, BPNN, SVR, PSOSVR, FOASVR, SPSOSVR, SFOASVR | The SFOASVR hybrid model has a better forecasting performance. |
| 20 | [121] | January 1990–December 2010 | – | Türkiye | EC | XGBoost-Based hybrid models (XGBoost-GWO, XGBoost-PPSO, XGBoost-SSA), CatBoost-Based hybrid models (CatBoost-GWO, CatBoost-PPSO, CatBoost-SSA) | The XGBoost-SSA model has superior forecasting performance with a MAPE of 0.00229. |
| 21 | [122] | 2005–2020 | 2021–2024 | Saudi Arabia | EC; weather parameters, demographics, and economic variables | ARIMA AIM, MLR | ARIMA:APE = 3.8%, MAE = 0.1308; AIM: APE = 8.1%, MAE = 0.1308; MLR: APE = 5.6%, MAE = 0.2264. |
| 22 | [149] | January 2007–June 2016 | next 4 h | Spain | EC | LSTM, CVOA | The LSTM network obtains the smallest errors. |
| 23 | [150] | 1980–2012 | 2013–2015 2013–2018 2013–2021 2013–2025 | OPEC | EC | ANN, PSO, ABCA, GA, CSA | The cuckoo search neural network is effective, efficient, robust, consistent, and reliable. |
| 24 | [151] | January 1979–December 2020 | next 24 h | Brazil | IEC | HW, SARIMA, DLM, TBATS, ARMA, ANN, ARNN, MLP | The MLP model obtains the best forecasting performance. |
| 25 | [152] | 1993–2019 | 2020 | UK | EC | BPNN, MLR, LSSVM | The LS-SVM model has the best forecasting performance. |
| 26 | [172] | January 2008–December 2016 | 2 weeks Between 2 and 4 weeks Between 2 and 3 months Between 3 and 4 months | France | ELC | GA, LSTM, GA-LSTM, LSTM-RNN | The LSTM-RNN-based forecasting method has lower forecast errors with 339 (RMSE for 2 weeks). |
| 27 | [178] | 2000–2009 | – | China | REC | BPNN, SVM, ELM, Jaya-ELM, SARIMA | The forecasting performance of Jaya-ELM is better than that of BPNN, SVM, ELM, and SARIMA. |
| 28 | [179] | 1970–2017 | 2019 –2022 | Turkey | EC | ARIMA, MLR, ARIMA-LSSVM | The hybrid-based ARIMA-LSSVM can generate more realistic and reliable forecasts. |
| 29 | [180] | June 2013 –March 2020 | – | Turkey | EC | SARIMA, ANNs, MLPs, SARIMA-ANNs, SARIMA-MLPs | The hybrid models are more accurate than single time series/machine learning models. |
| 30 | [181] | 1999–2018 | 2019–2020 | China | EC | IMGM, SFOGM, GMC, FOAGRNN, MGM | The forecasting performance of IMGM, SFOGM, GMC, and FOAGRNN is better than that of the MGM model. |
| 31 | [182] | 2013–2020 (Hourly) | 2019–2020 (17,520 h) | Ukraine | ED | MLR, MLR-ARIMA, MLR-LSTM, MLR-ARIMA-LSTM | The ARIMA-LSTM hybrid model has the best forecasting performance. |
| 32 | [183] | 2010 Q1–2016 Q4 | – | China | EC | GM, SGM, DSGM, RSGM, FDSGM | FDSGM has better forecasting performance with MAPE values of 0.2% and 6.02% for training and testing data, respectively. |
| 33 | [209] | January 2010–December 2018 | – | China | EC | SI, MHW-default, FOASVR, GASVR GA-MHW, FOA-MHW | The FOA-MHW hybrid model has the best forecasting performance, with a MAPE of 3.58% and only 3 years of training data. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, A.M.; Wyrwa, A. A Survey of Quantitative Techniques in Electricity Consumption—A Global Perspective. Energies 2024, 17, 4910. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17194910
Khan AM, Wyrwa A. A Survey of Quantitative Techniques in Electricity Consumption—A Global Perspective. Energies. 2024; 17(19):4910. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17194910
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Atif Maqbool, and Artur Wyrwa. 2024. "A Survey of Quantitative Techniques in Electricity Consumption—A Global Perspective" Energies 17, no. 19: 4910. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17194910
APA StyleKhan, A. M., & Wyrwa, A. (2024). A Survey of Quantitative Techniques in Electricity Consumption—A Global Perspective. Energies, 17(19), 4910. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17194910









