Diagnostic and Performance Analysis of a Water Electrolyzer by Magnetic Field Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. 2-D Biot–Savart Model
2.1. Water Electrolyzer to Hydrogen Production
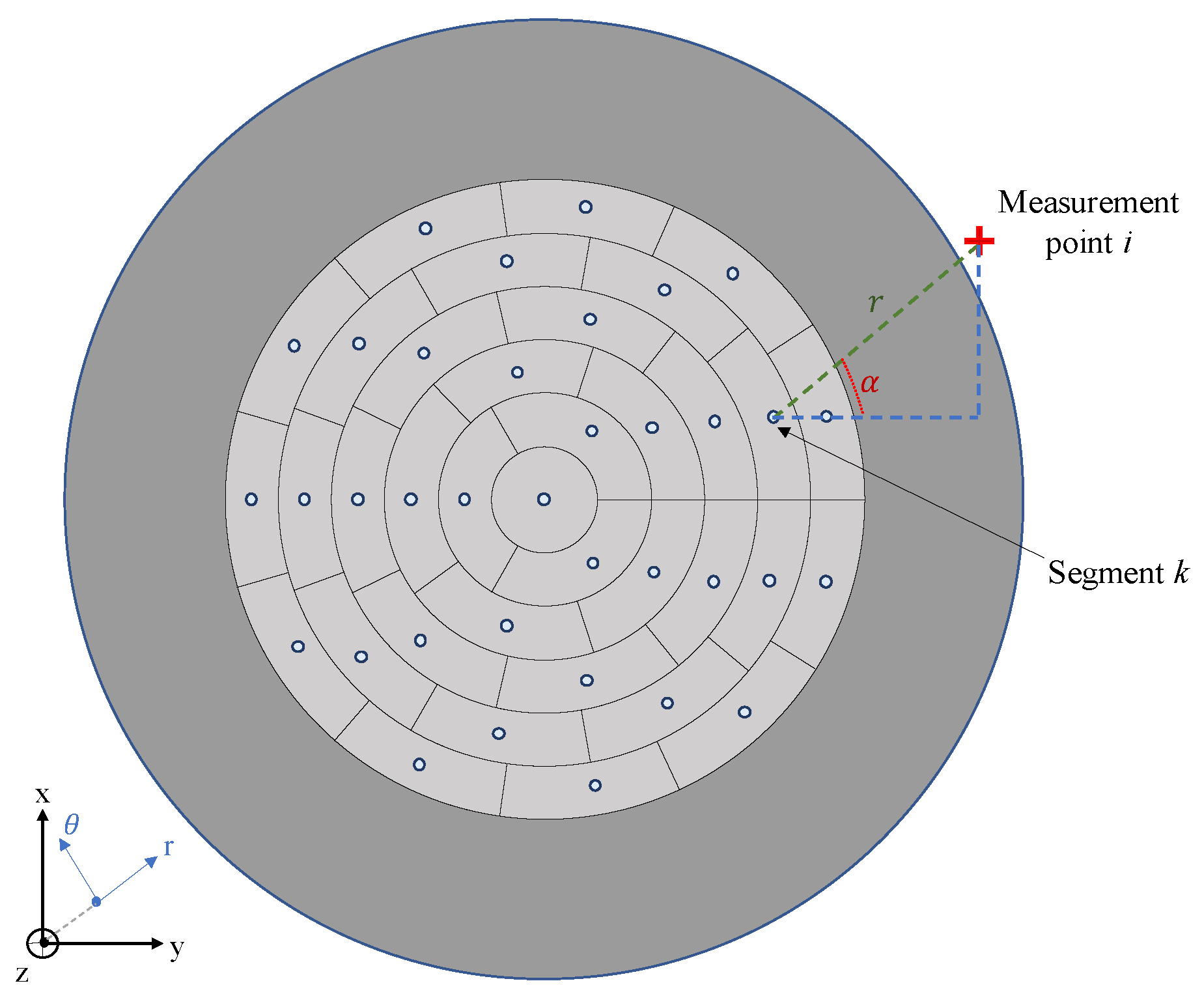
2.2. Considered Electrolyzer Stack Geometry
3. Experimental Validation
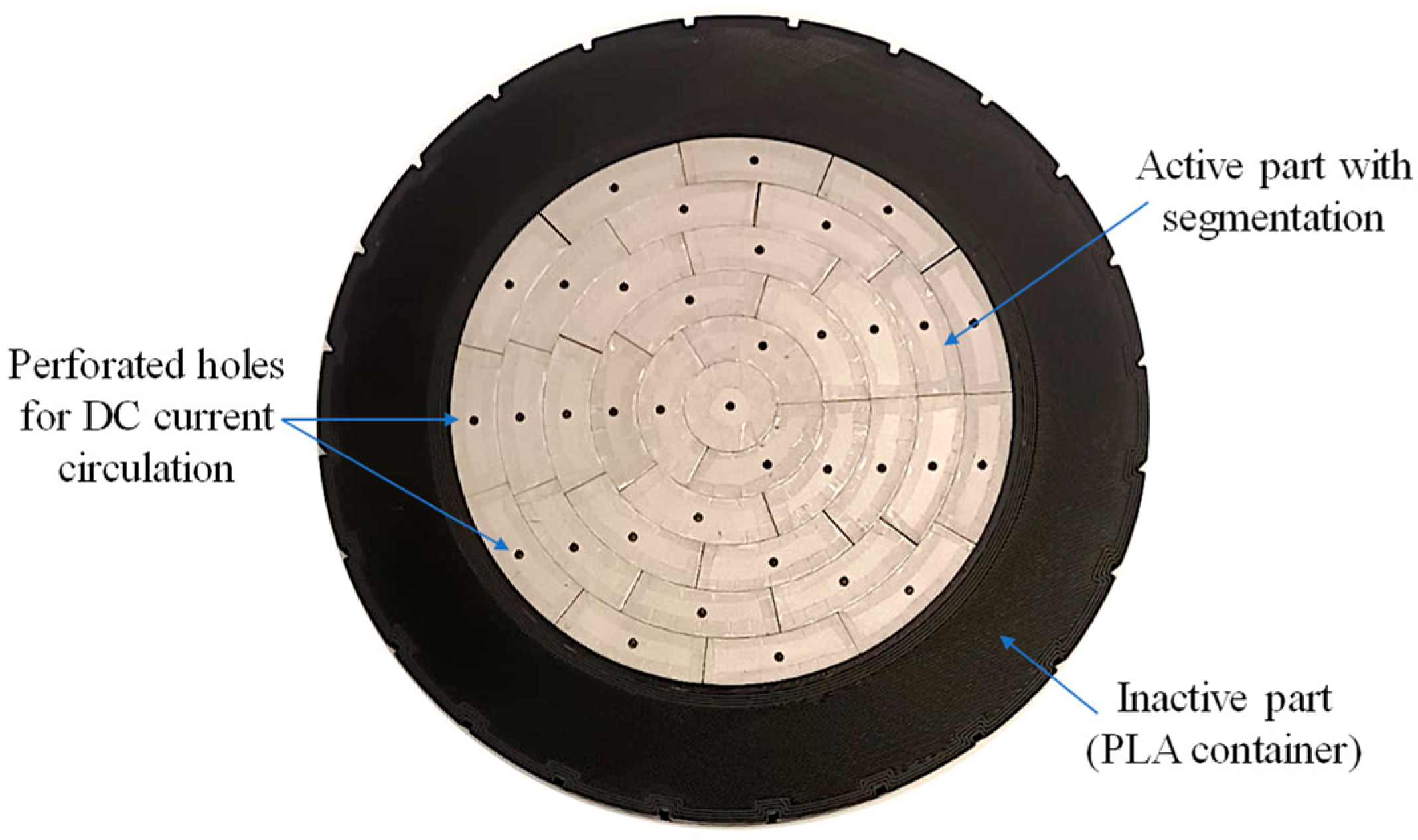
3.1. Electrolyzer Emulator
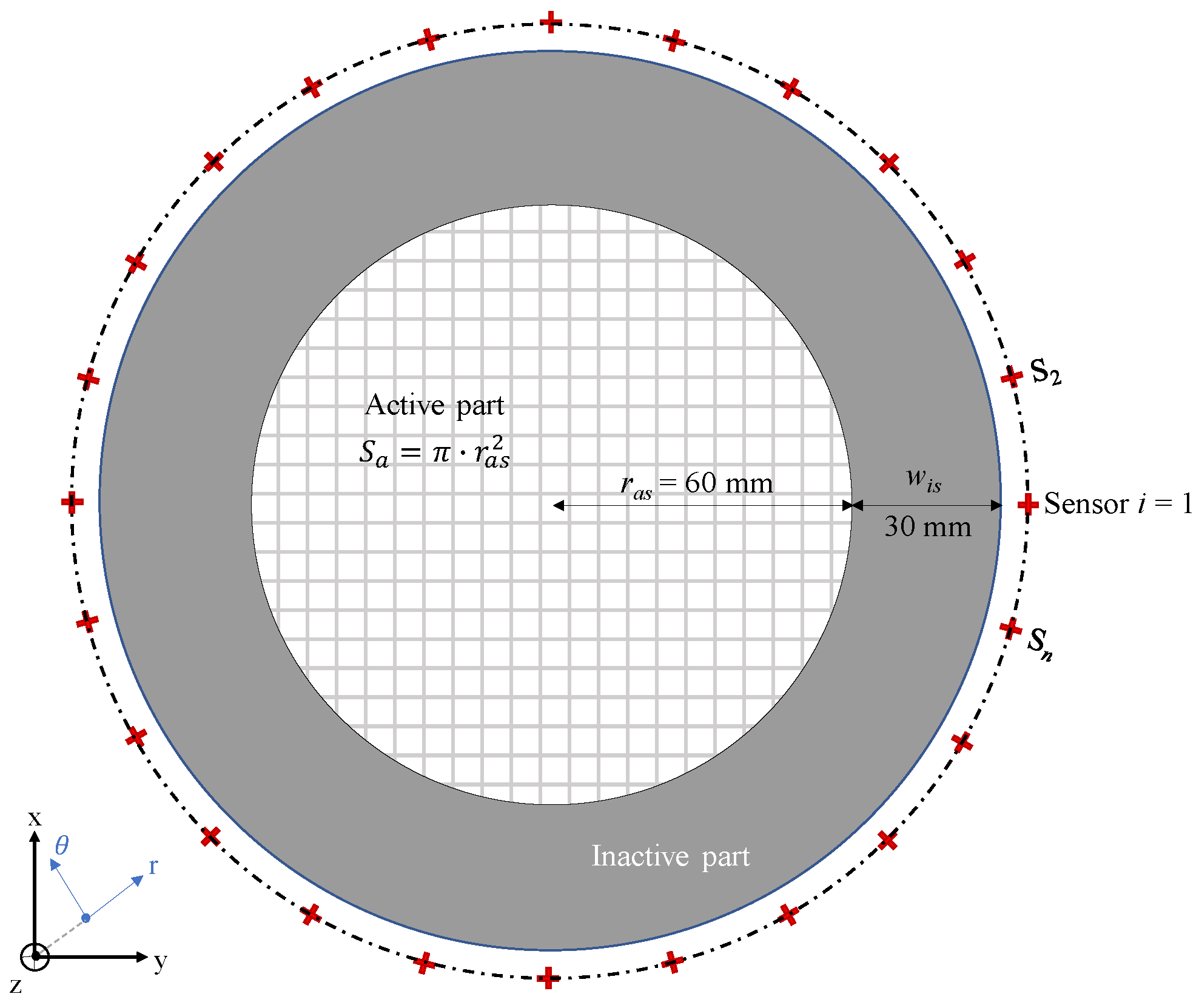
3.2. Magnetic Field Measurement Support
3.3. Experimental Measurements on Complete Emulator
4. Results, Validation and Discussion
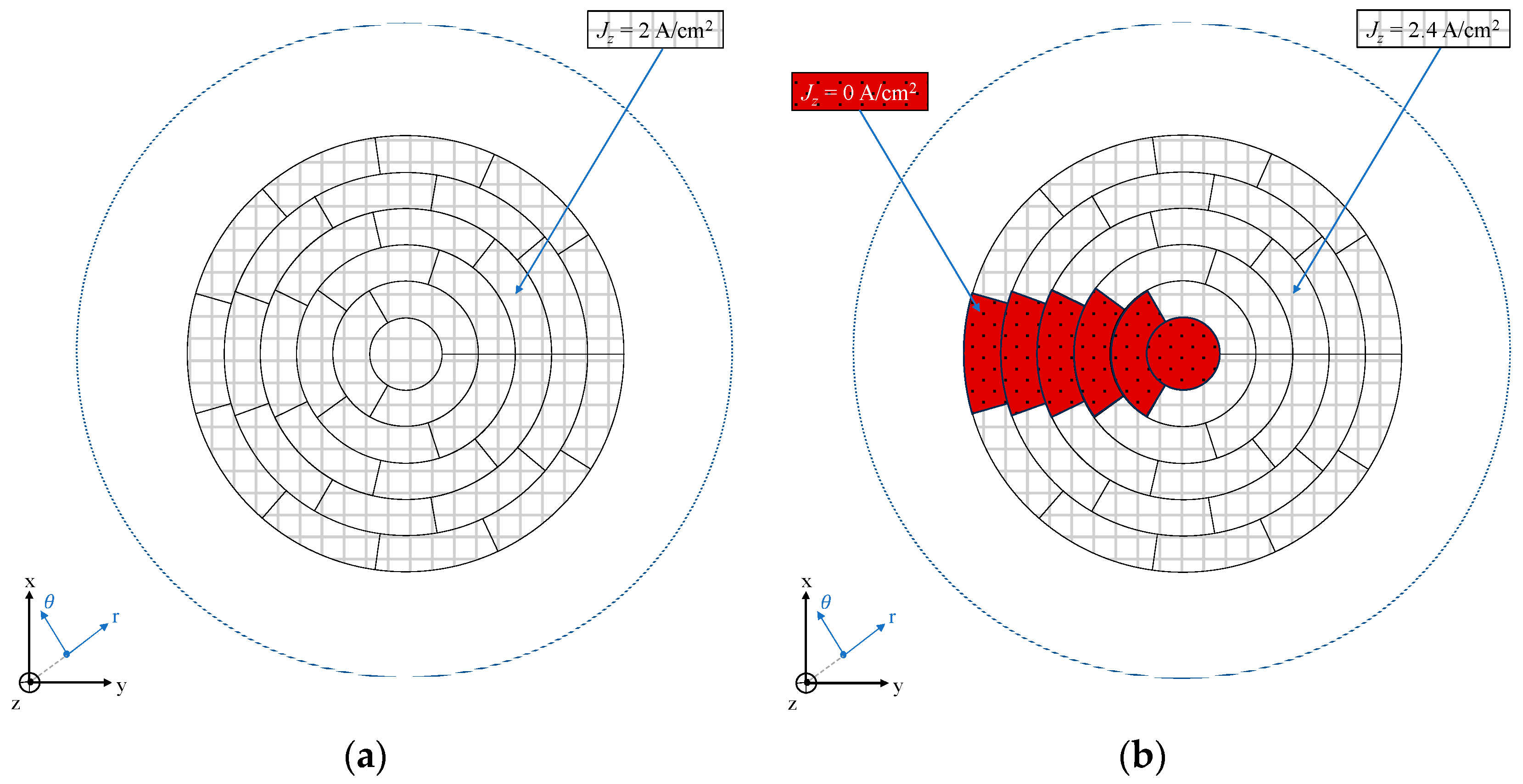
4.1. Magnetic Field Estimation Knowing Current Density Distribution
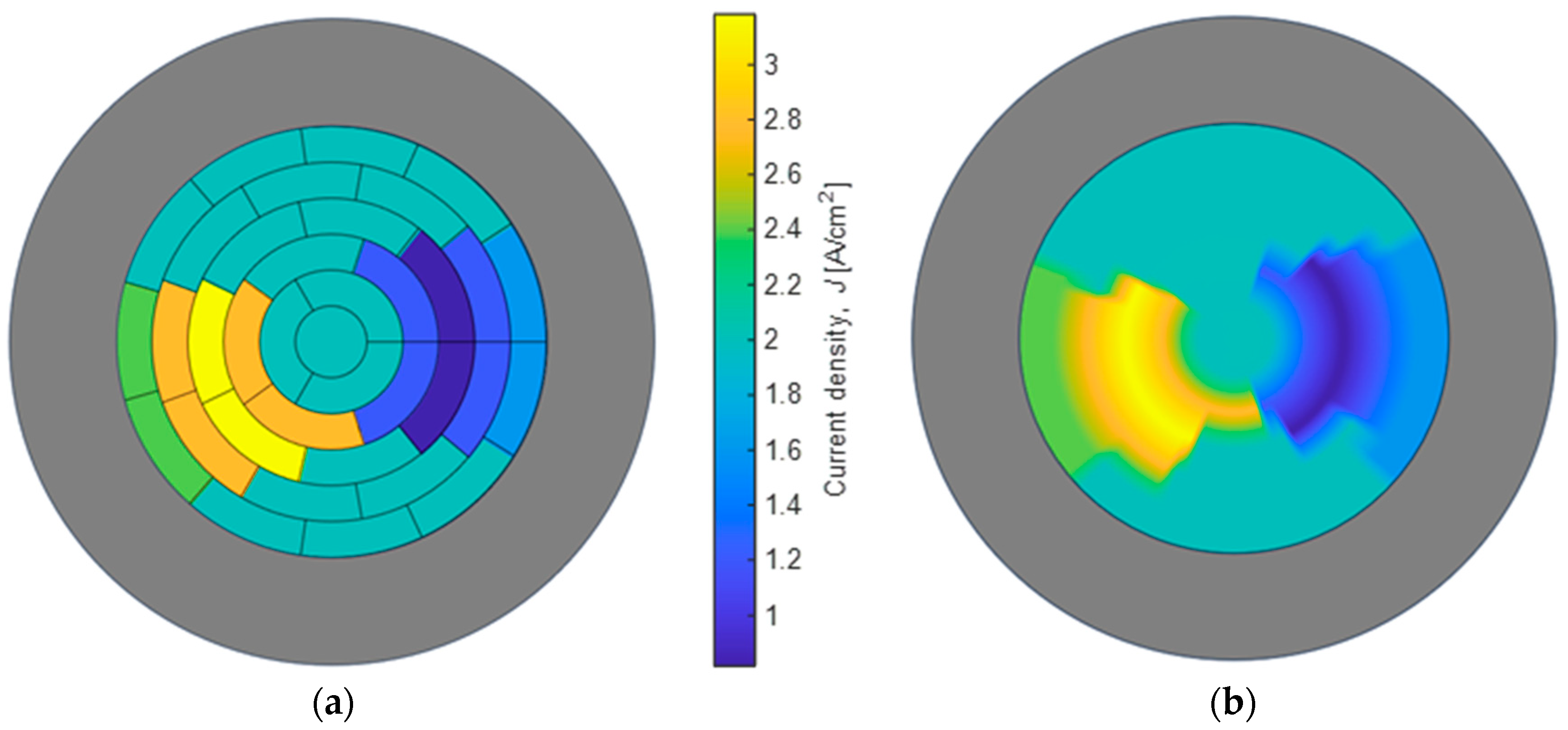
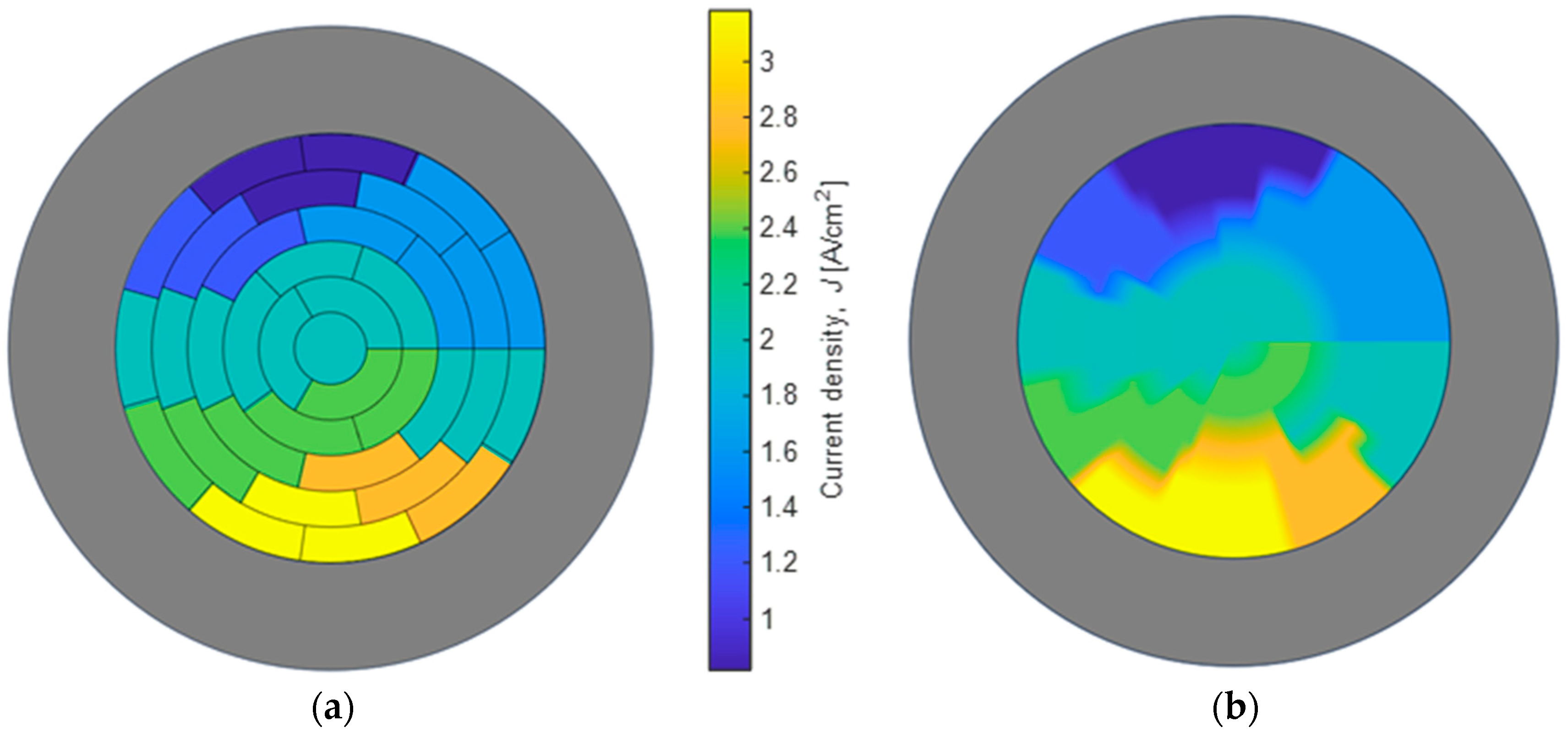
4.2. Current Density Distribution Estimation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, W.; Zuo, H.; Wang, J.; Xue, Q.; Ren, B.; Yang, F. The production and application of hydrogen in steel industry. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 10548–10569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.M.; Beswick, R.R.; Yan, Y. A green hydrogen economy for a renewable energy society. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2021, 33, 100701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Himabindu, V. Hydrogen production by PEM water electrolysis—A review. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2019, 2, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, D.; Pinto, A. A review on PEM electrolyzer modelling: Guidelines for beginners. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, P.; Bourasseau, C.; Bouamama, B. Dynamic and multiphysic PEM electrolysis system modelling: A bond graph approach. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 14872–14904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, A.; Haas, M.; Elliot, I.; Nazari, S. Control and control-oriented modeling of PEM water electrolyzers: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 30621–30641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Merwe, J.; Uren, K.; van Schoor, G.; Bessarabov, D. Characterisation tools development for PEM electrolysers. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 14212–14221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinson, C.; van Schoor, G.; Uren, K.; Bessarabov, D. Characterisation of a PEM electrolyser using the current interrupt method. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 20865–20878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Steen, S.M., III; Mo, J.; Zhang, F.Y. Electrochemical performance modeling of a proton exchange membrane electrolyzer cell for hydrogen energy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 7006–7016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Su, S.; Lin, G.; Chen, J. Efficiency Calculation and Configuration Design of a PEM Electrolyzer System for Hydrogen Production. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 4143–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selamet, F.; Becerikli, F.; Mat, M.D.; Kaplan, Y. Development and testing of a highly efficient proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolyzer stack. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 11480–11487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilbert, D.; Papakonstantinou, G. Modeling, Degradation Study, Failures Diagnosis and Faulty Operating Management of Electrolyzers. Membranes 2022, 12, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Immerz, C.; Schweins, M.; Trinke, P.; Bensmann, B.; Paidar, M.; Bystroň, T.; Bouzek, K.; Hanke-Rauschenbach, R. Experimental characterization of inhomogeneity in current density and temperature distribution along a single-channel PEM water electrolysis cell. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 260, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Lee, C.; Fahy, K.F.; Zhao, B.; LaManna, J.M.; Baltic, E.; Jacobson, D.L.; Hussey, D.S.; Bazylak, A. Critical Current Density as a Performance Indicator for Gas-Evolving Electrochemical Devices. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2020, 1, 100147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, M.; Smith, K.; Dodwell, J.; Hinds, G.; Shearing, P.; Brett, D. Mass transport in PEM water electrolysers: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 30–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedigama, I.; Angeli, P.; Ayers, K.; Robinson, J.; Shearing, P.; Tsaoulidis, D.; Brett, D. In situ diagnostic techniques for characterisation of polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolysers—Flow visualisation and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 4468–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomić, A.Z.; Pivac, I.; Barbir, F. A review of testing procedures for proton exchange membrane electrolyzer degradation. J. Power Sources 2023, 557, 232569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Du, B.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xie, C.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, L.; Song, J.; et al. Optimization of power allocation for wind-hydrogen system multi-stack PEM water electrolyzer considering degradation conditions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 5850–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauer, K.-H.; Potthast, R.; Wüster, T.; Stolten, D. Magnetotomography—A new method for analysing fuel cell performance and quality. J. Power Sources 2005, 143, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plait, A.; Dubas, F. A 2D Multi-Layer Model to Study the External Magnetic Field Generated by a Polymer Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustfeld, H.; Reißel, M.; Schmidt, U.; Steffen, B. Reconstruction of Electric Currents in a Fuel Cell by Magnetic Field Measurements. J. Fuel Cell Sci. Technol. 2009, 6, 021012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasu, T.; Matsushita, Y.; Okano, J.; Okajima, K. Study of Current Distribution in PEMFC Stack Using Magnetic Sensor Probe. J. Int. Counc. Electr. Eng. 2012, 2, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Ny, M.; Chadebec, O.; Cauffet, G.; Dedulle, J.-M.; Bultel, Y.; Rosini, S.; Fourneron, Y.; Kuo-Peng, P. Current Distribution Identification in Fuel Cell Stacks From External Magnetic Field Measurements. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 1925–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifrek, L.; Chadebec, O.; Rosini, S.; Cauffet, G.; Bultel, Y.; Bannwarth, B. Fault Identification on a Fuel Cell by 3-D Current Density Reconstruction From External Magnetic Field Measurements. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimoto, Y.; Shibata, M.; Tsuzuki, Y.; Okajima, K.; Suzuki, S.-N. In-situ on-board evaluation and control of proton exchange membrane fuel cells using magnetic sensors. Appl. Energy 2023, 351, 121873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katou, T.; Gotoh, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Izumi, M. Measurement technique of distribution of power generation current using static magnetic field around polymer electrolyte fuel cell by 3D inverse problem FEM. Mater. Trans. 2012, 53, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanashi, R.; Gotoh, Y.; Izumi, M.; Nara, T. Evaluation of generation current inside membrane electrode assembly in polymer electrolyte fuel cell using static magnetic field around fuel cell. ECS Trans. 2015, 65, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plait, A.; Dubas, F. Experimental validation of a purely analytical model dedicated to fuel cell diagnosis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 67, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plait, A.; Giurgea, S.; Hissel, D.; Espanet, C. New magnetic field analyzer device dedicated for polymer electrolyte fuel cells noninvasive diagnostic. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 14071–14082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plait, A.; Dubas, F. Improvement of fuel cell diagnosis by magneto-tomography with magnetic field concentration. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Computation in Electromagnetics (CEM2023), Cannes, France, 11–14 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Tikhonov, A.N. Solution of incorrectly formulated problems and the regularization method. Sov. Math. Dokl. 1963, 4, 1035–1038, English translation: Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 1963, 151, 501–504. [Google Scholar]
- Asensor Technology AB. Linear High Precision Analog Hall Sensors. Available online: https://www.asensor.eu (accessed on 8 November 2022).






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plait, A.; Dubas, F.; Bouquain, D.; Hissel, D. Diagnostic and Performance Analysis of a Water Electrolyzer by Magnetic Field Measurements. Energies 2024, 17, 4135. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17164135
Plait A, Dubas F, Bouquain D, Hissel D. Diagnostic and Performance Analysis of a Water Electrolyzer by Magnetic Field Measurements. Energies. 2024; 17(16):4135. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17164135
Chicago/Turabian StylePlait, Antony, Frédéric Dubas, David Bouquain, and Daniel Hissel. 2024. "Diagnostic and Performance Analysis of a Water Electrolyzer by Magnetic Field Measurements" Energies 17, no. 16: 4135. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17164135
APA StylePlait, A., Dubas, F., Bouquain, D., & Hissel, D. (2024). Diagnostic and Performance Analysis of a Water Electrolyzer by Magnetic Field Measurements. Energies, 17(16), 4135. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17164135








