Control of Grid-Connected and Standalone Microhydraulic Turbine Using a Six-Phase Induction Generator
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- A squirrel cage six-phase induction generator for power generation.
- -
- A back-to-back converter linking the generator to the grid and/or local load to extract and inject power via DC link. Two three-phase voltage source inverters (VSIs) are employed to connect the six-phase induction generator, with the VSI on the grid-side connected to the load and/or grid via an LCL filter.
- -
- A lithium-ion battery connected to the DC link through a bidirectional DC-DC converter.
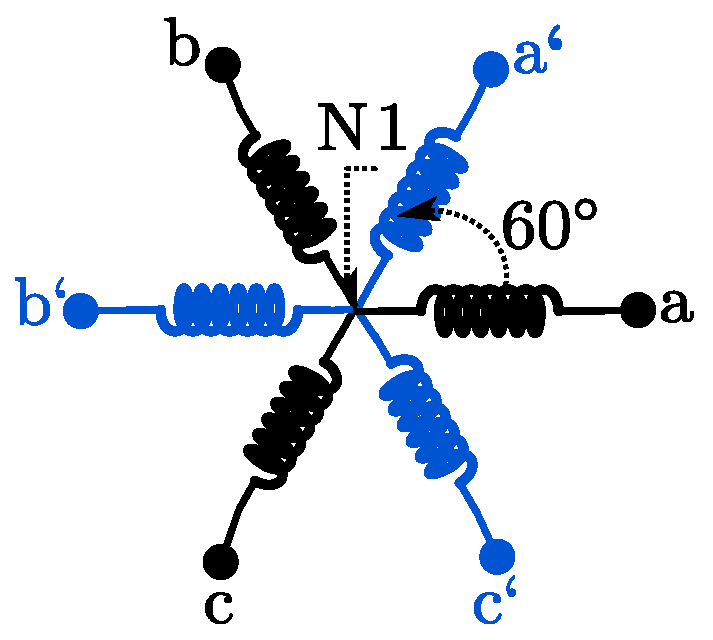
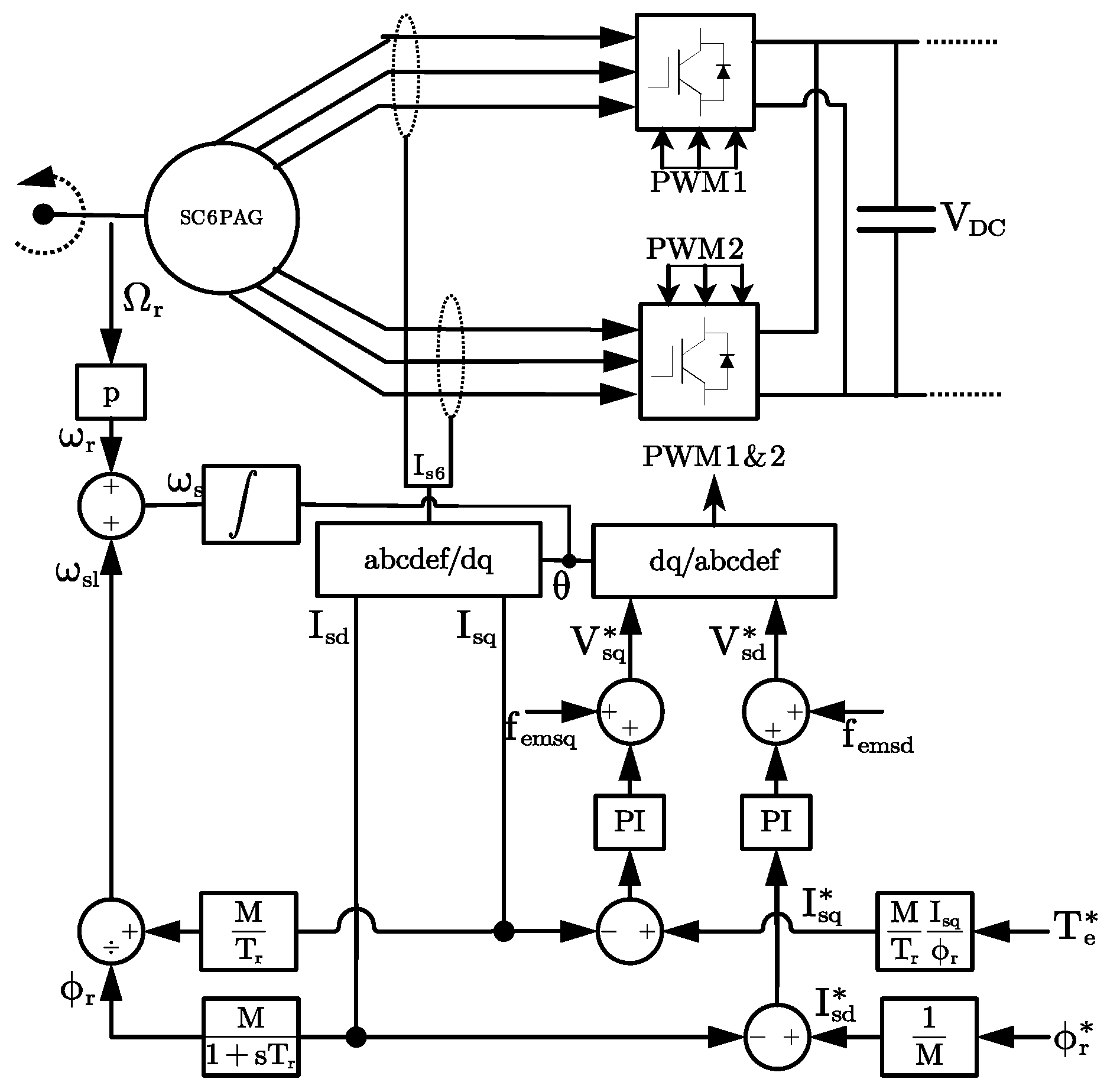
2. Modeling and Control of a Six-Phase Induction Generator
2.1. Modeling
2.2. Indirect Field-Oriented Control
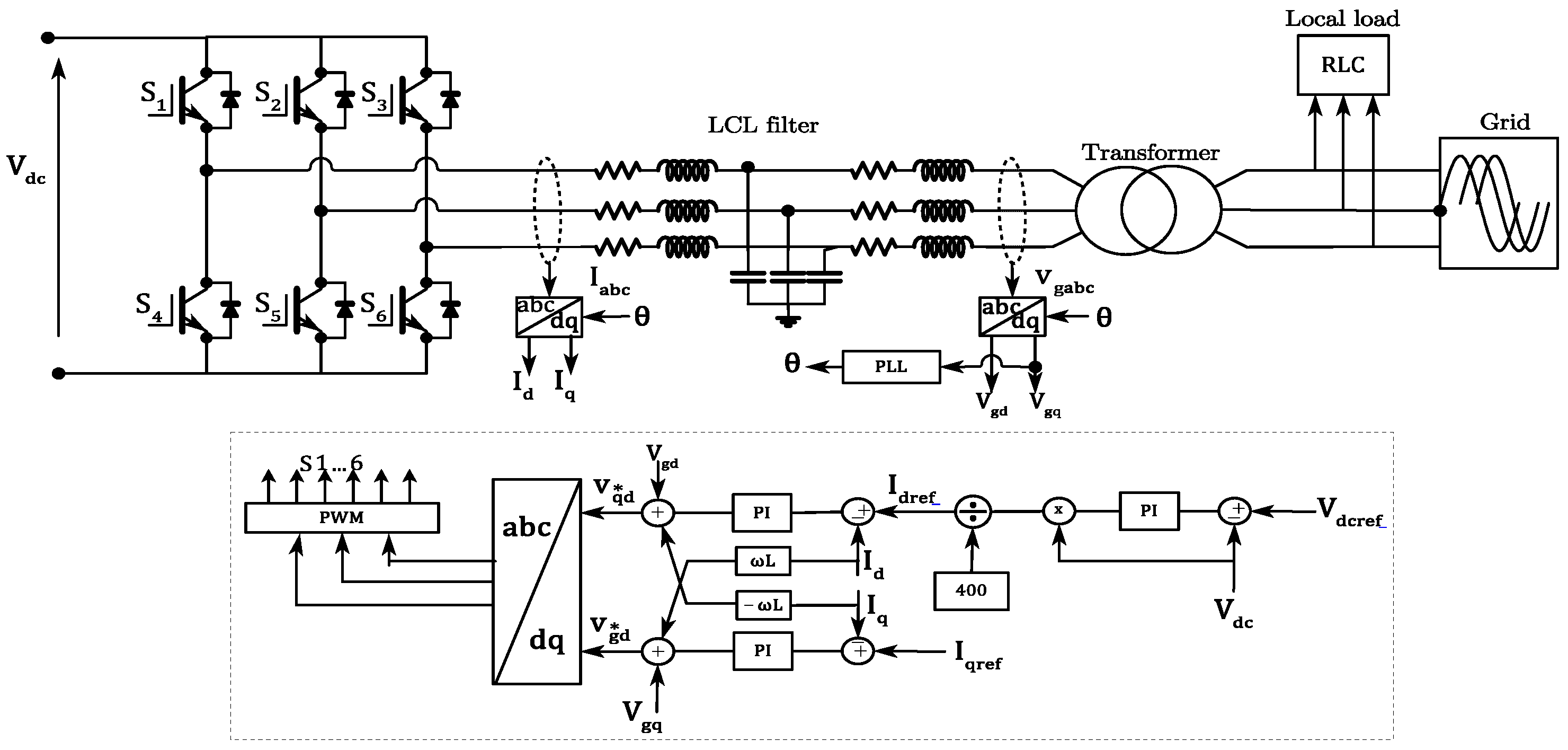
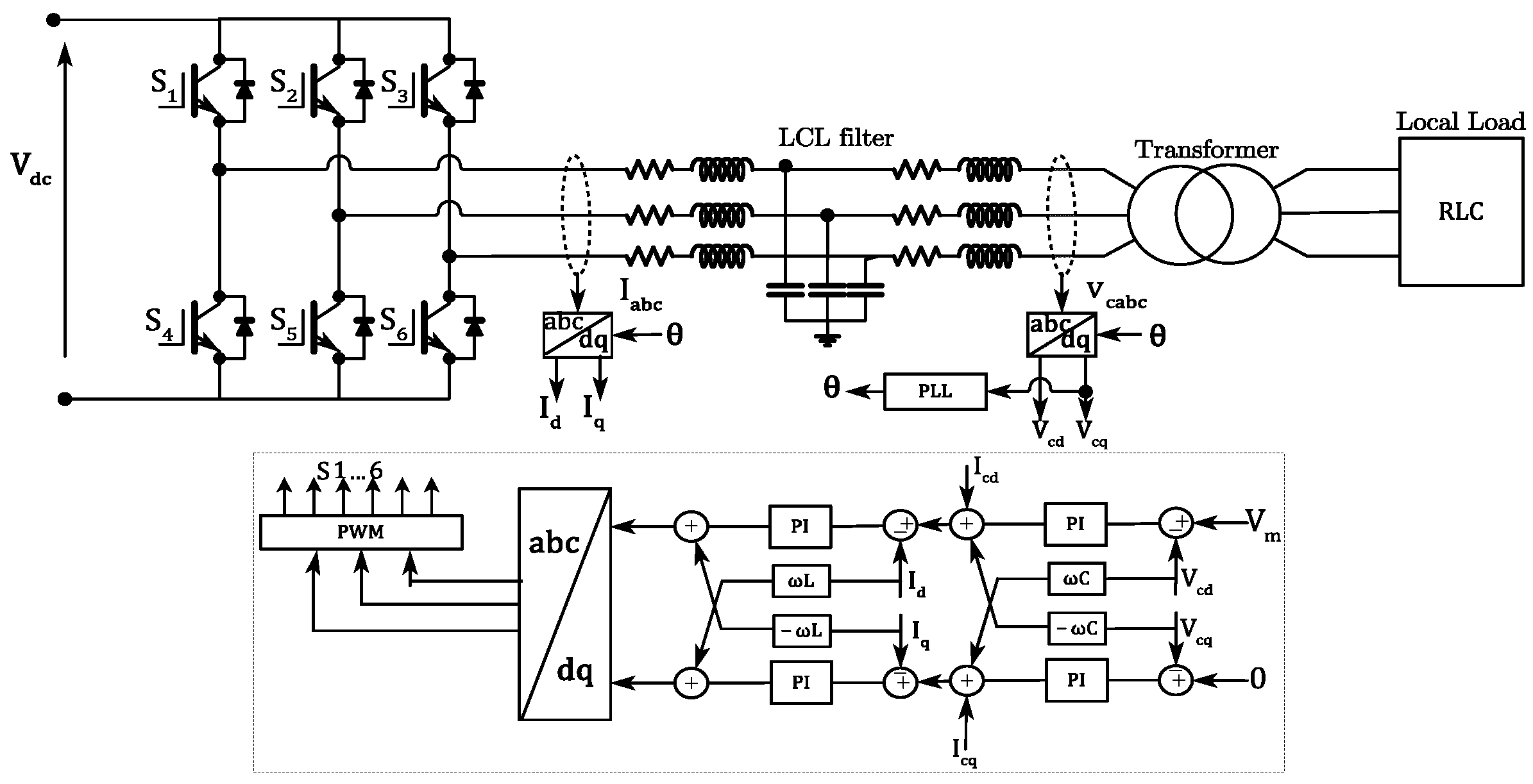
3. Grid-Connected Control Scheme
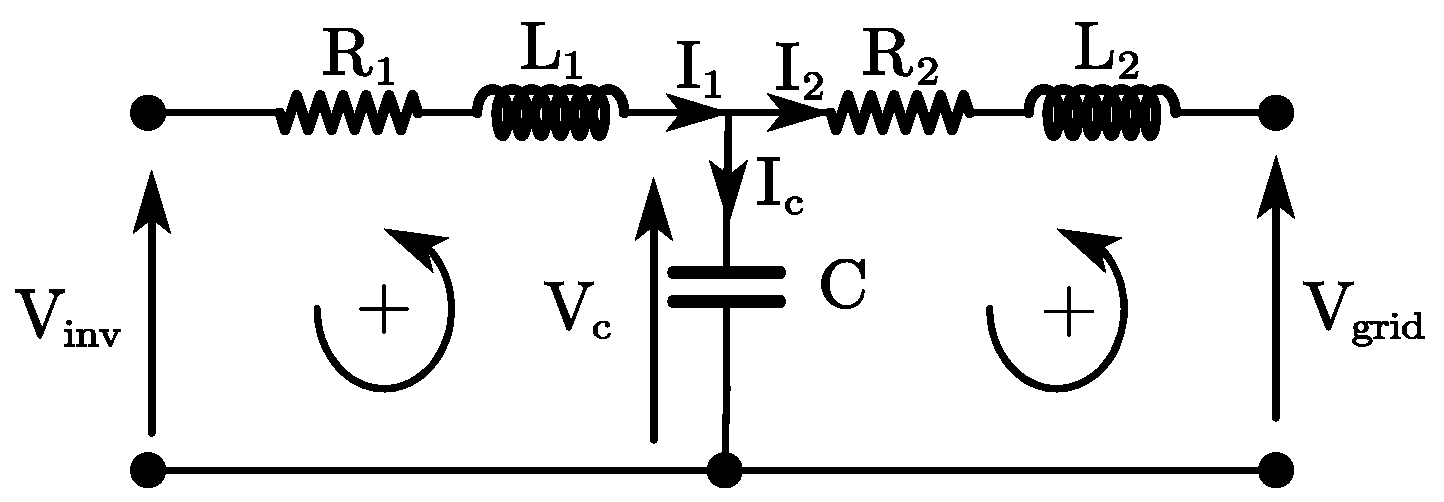
3.1. Voltage Source Inverter for Grid-Connected and Standalone Mode
3.2. DC Link Control
3.3. Grid Currents Control
3.4. Active and Reactive Power Control
3.5. Grid Synchronization
4. Control Scheme for Standalone Mode
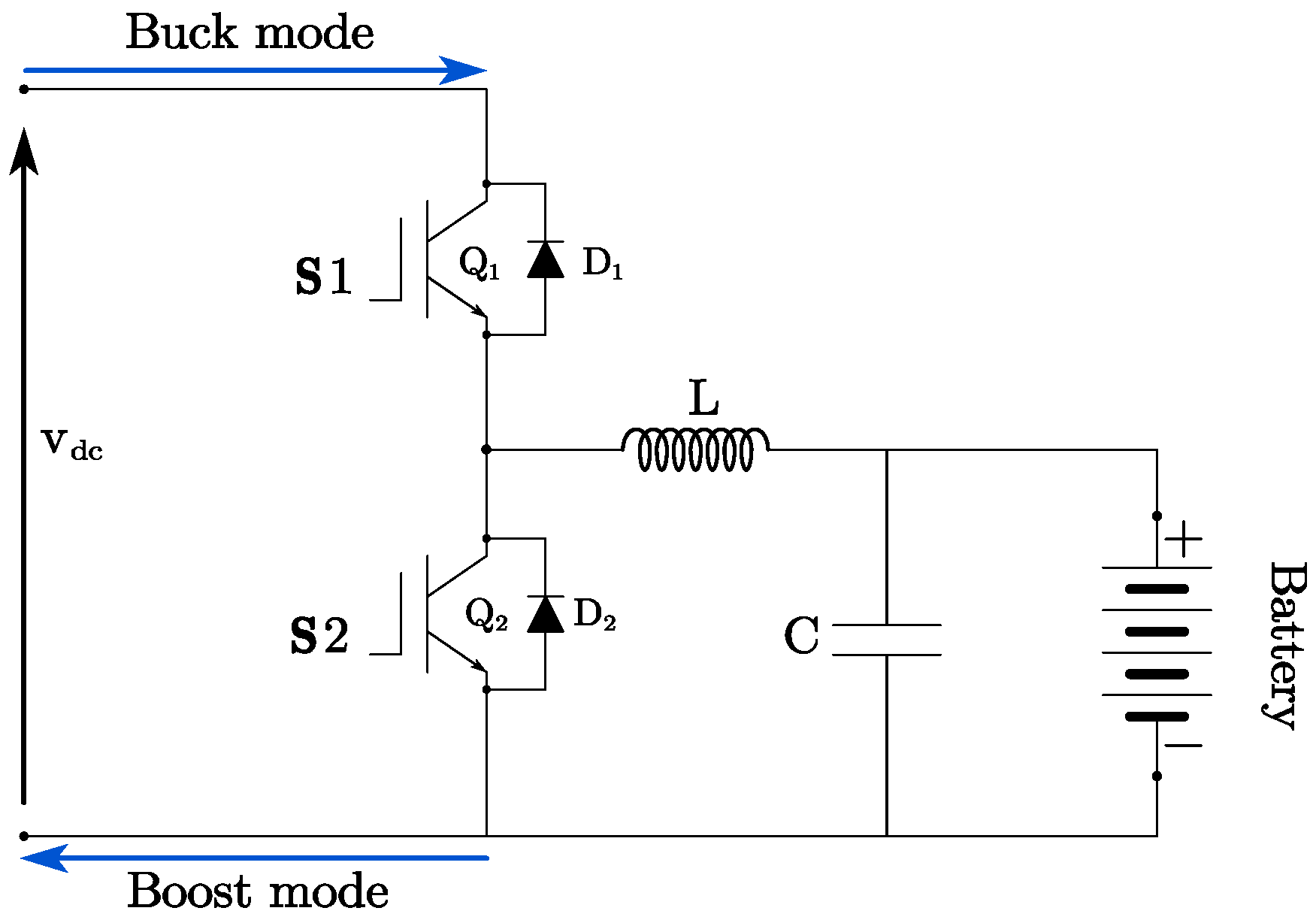
5. Energy Storage System
- (1)
- For isolated locations, it ensures autonomy by building up an energy reserve during periods of excess production and releasing it when production temporarily falls short or stops. It means that it ensures the balance of energy between the source and the local load [53].
- (2)
- For grid-connected systems, it maintains a real-time balance between production and consumption, improves the stability and reliability of the grid, and promotes a more efficient use of renewable energies, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and associated greenhouse gas emissions from electricity production using polluting energy sources.
Bidirectional DC/DC Converter Control
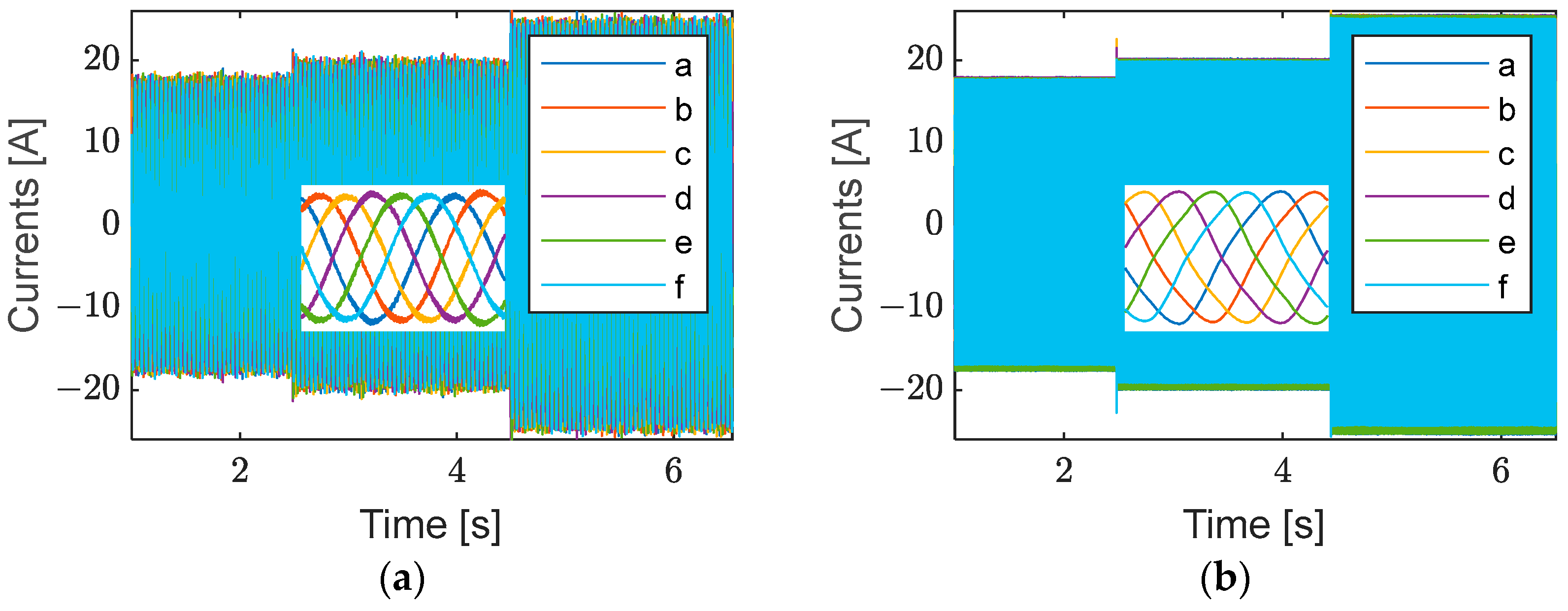
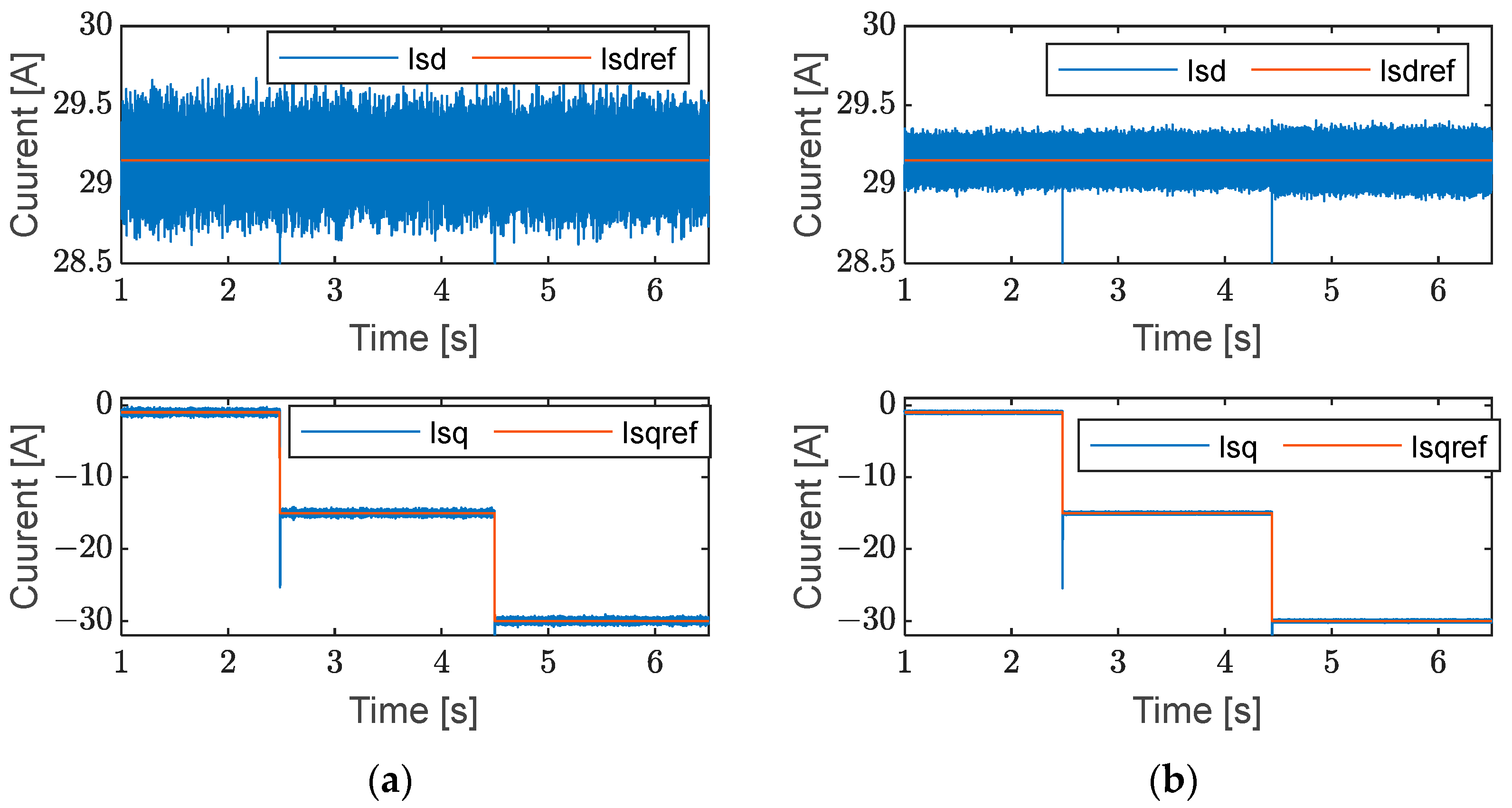
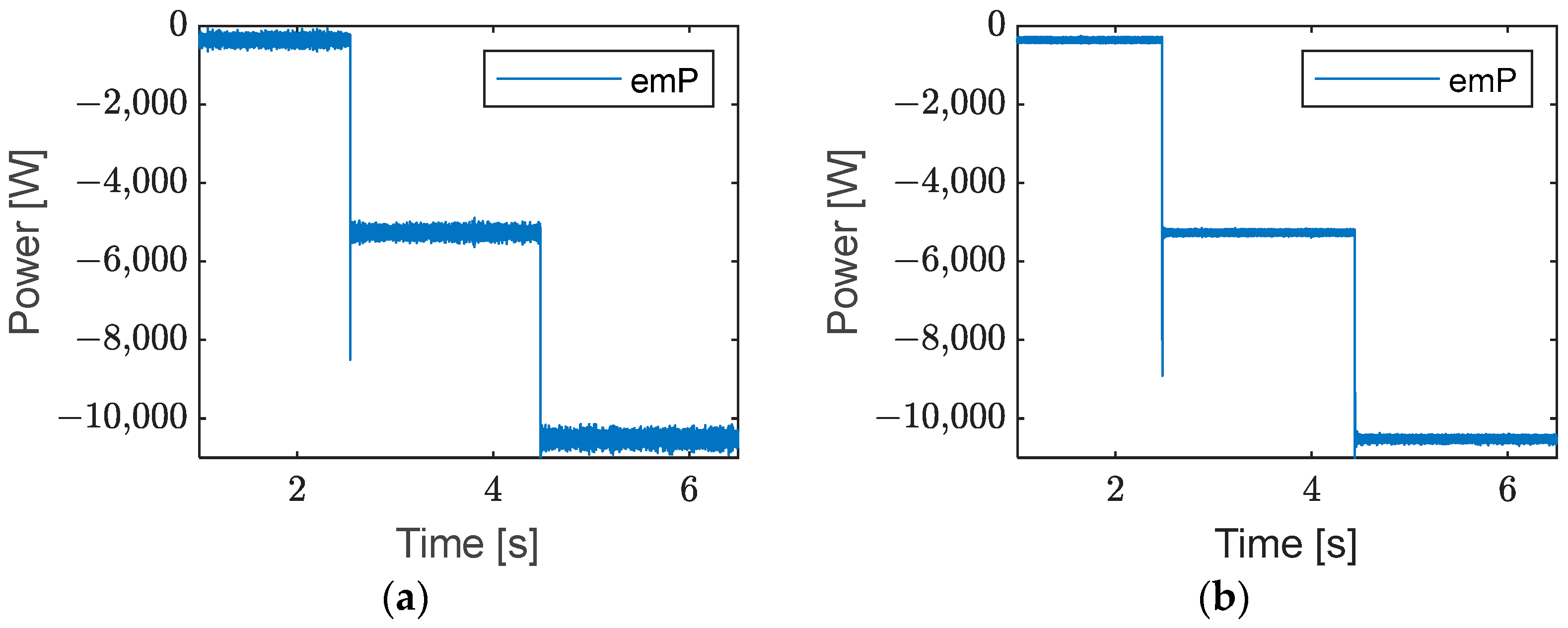
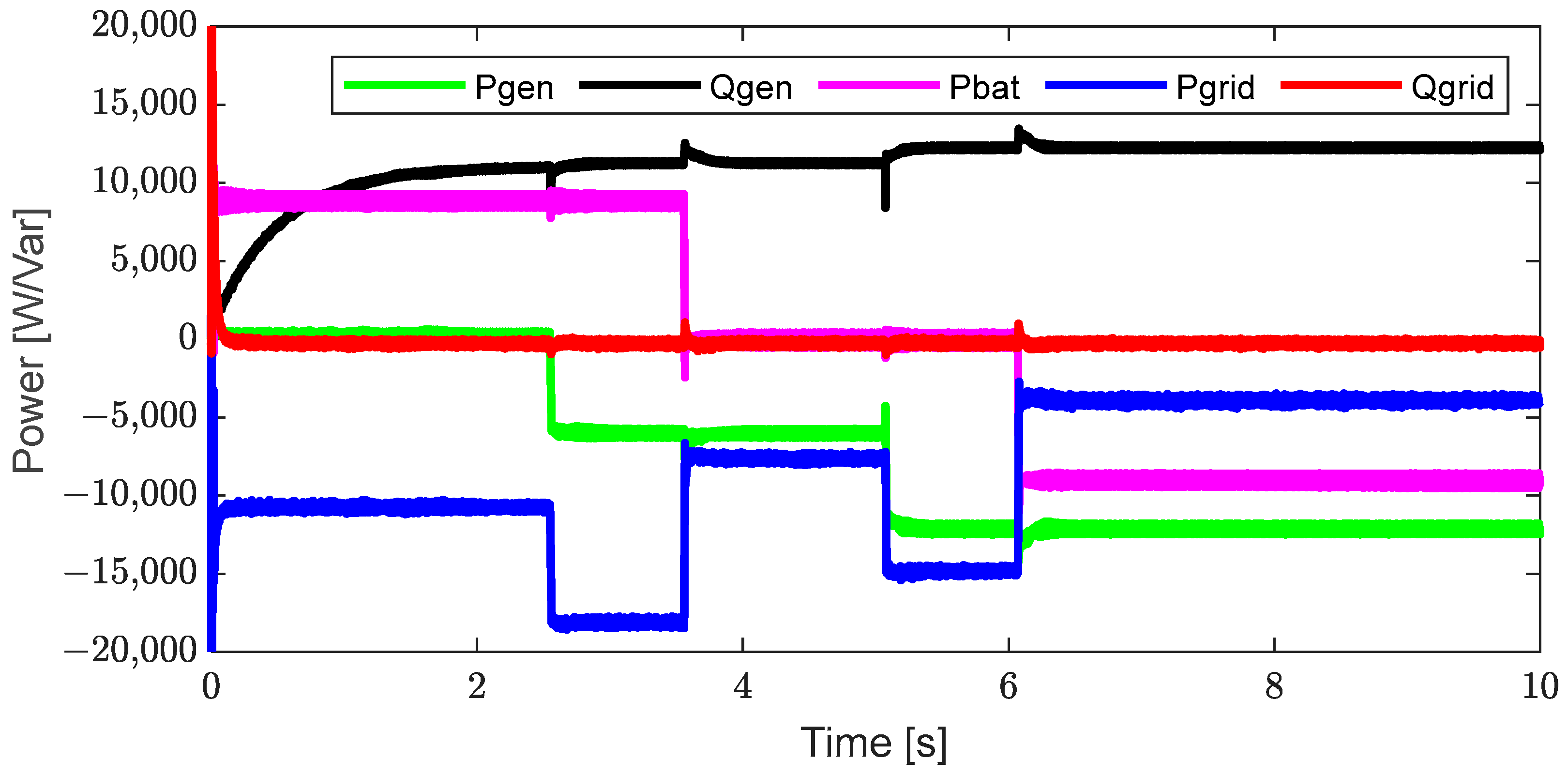
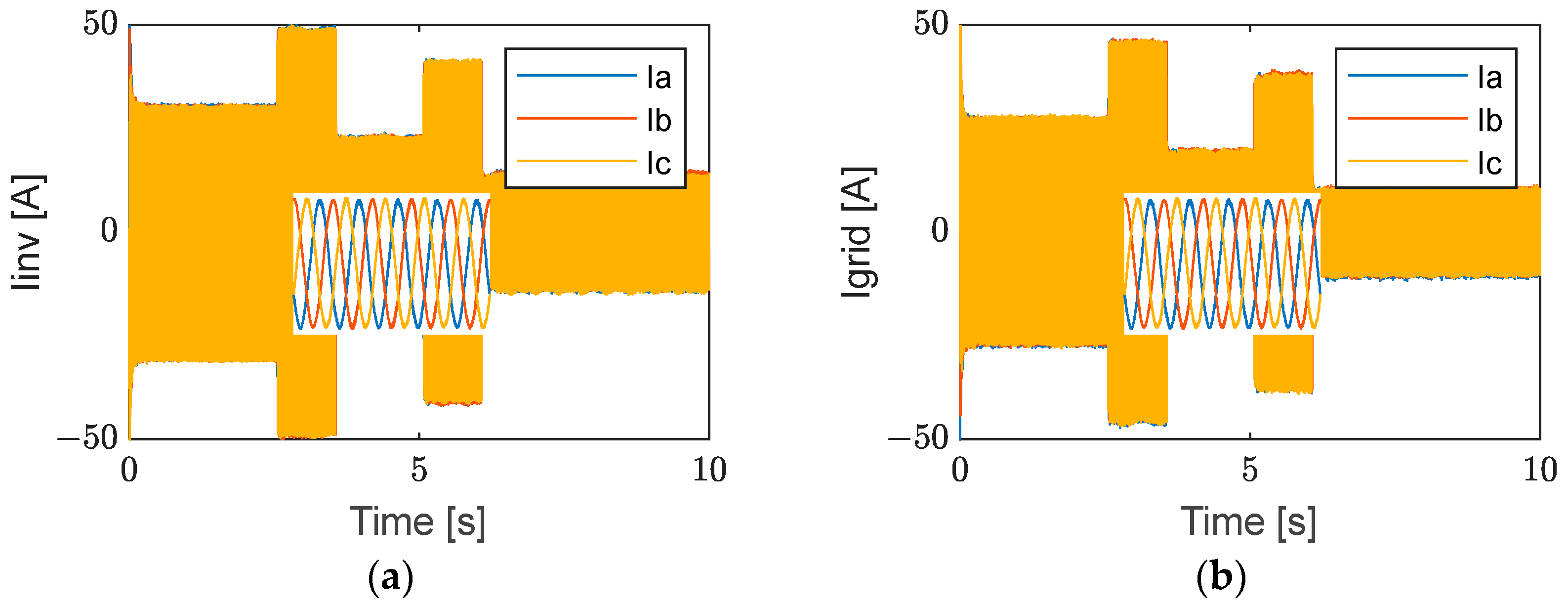
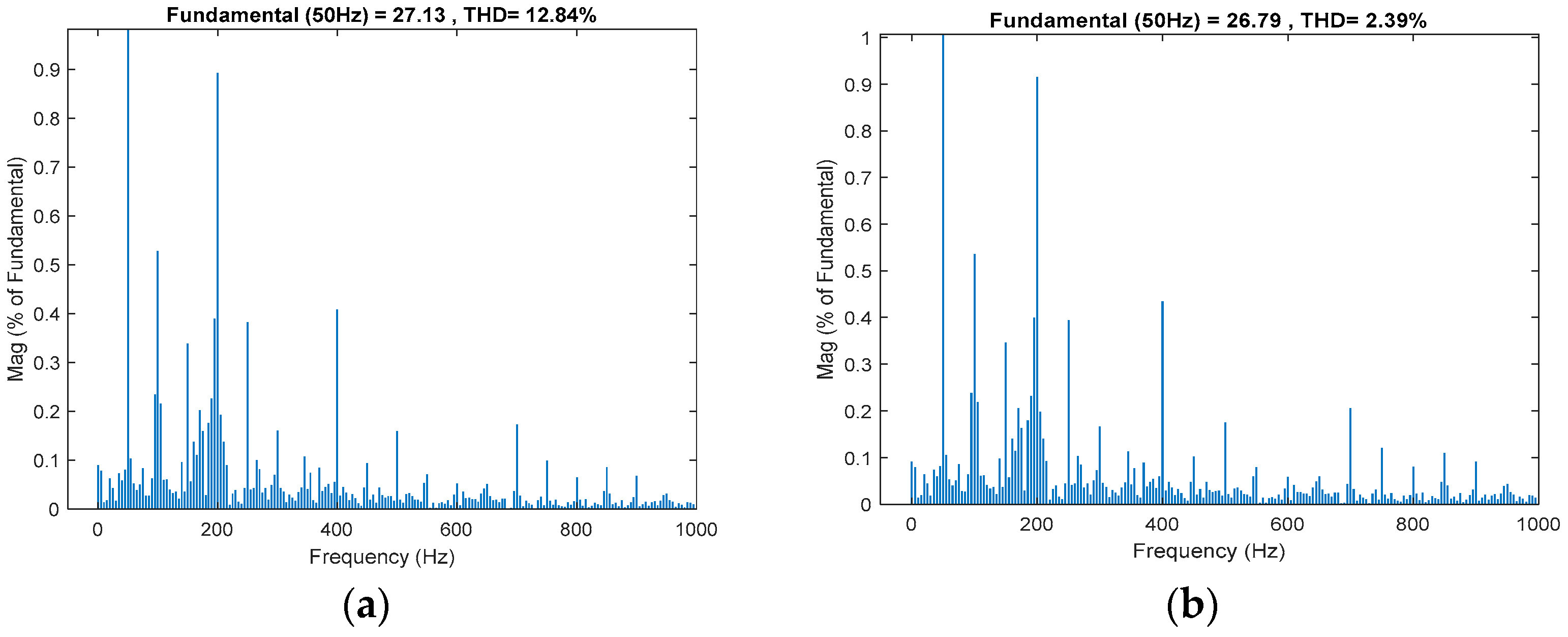
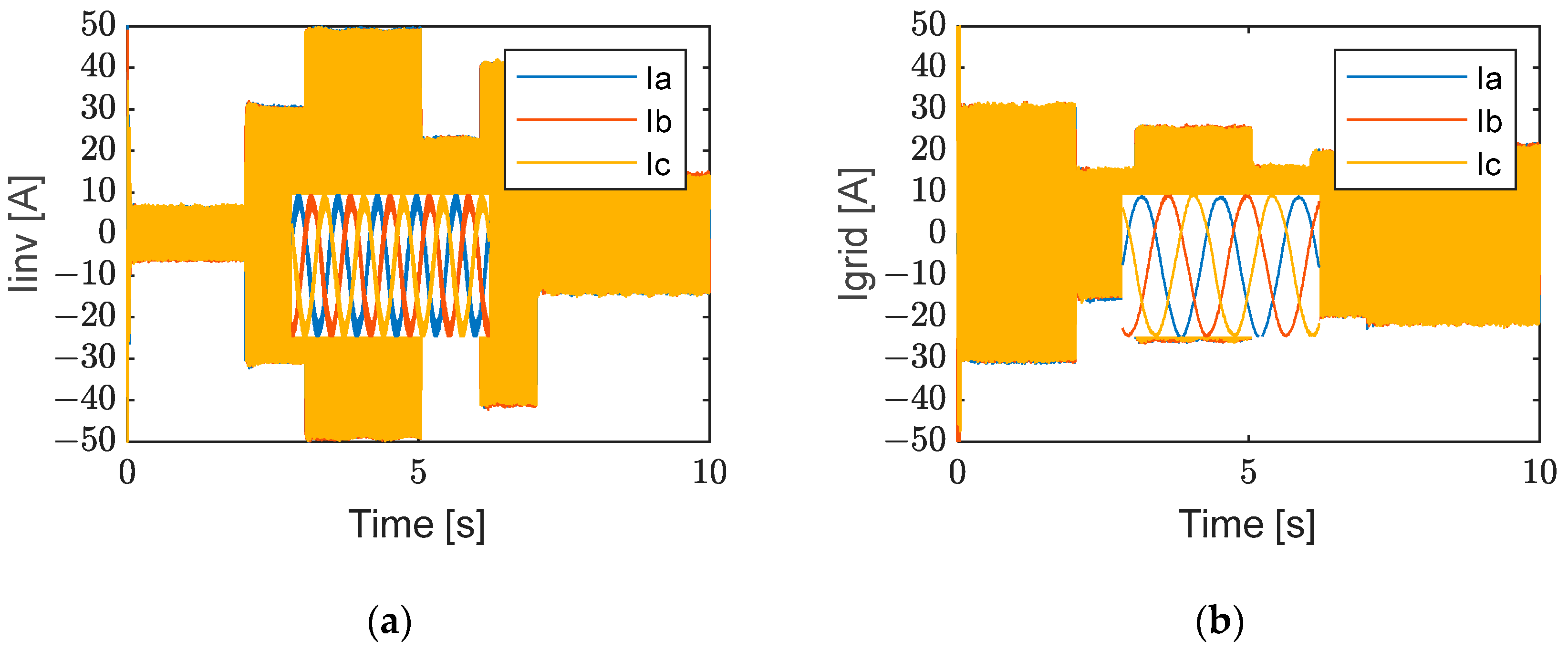
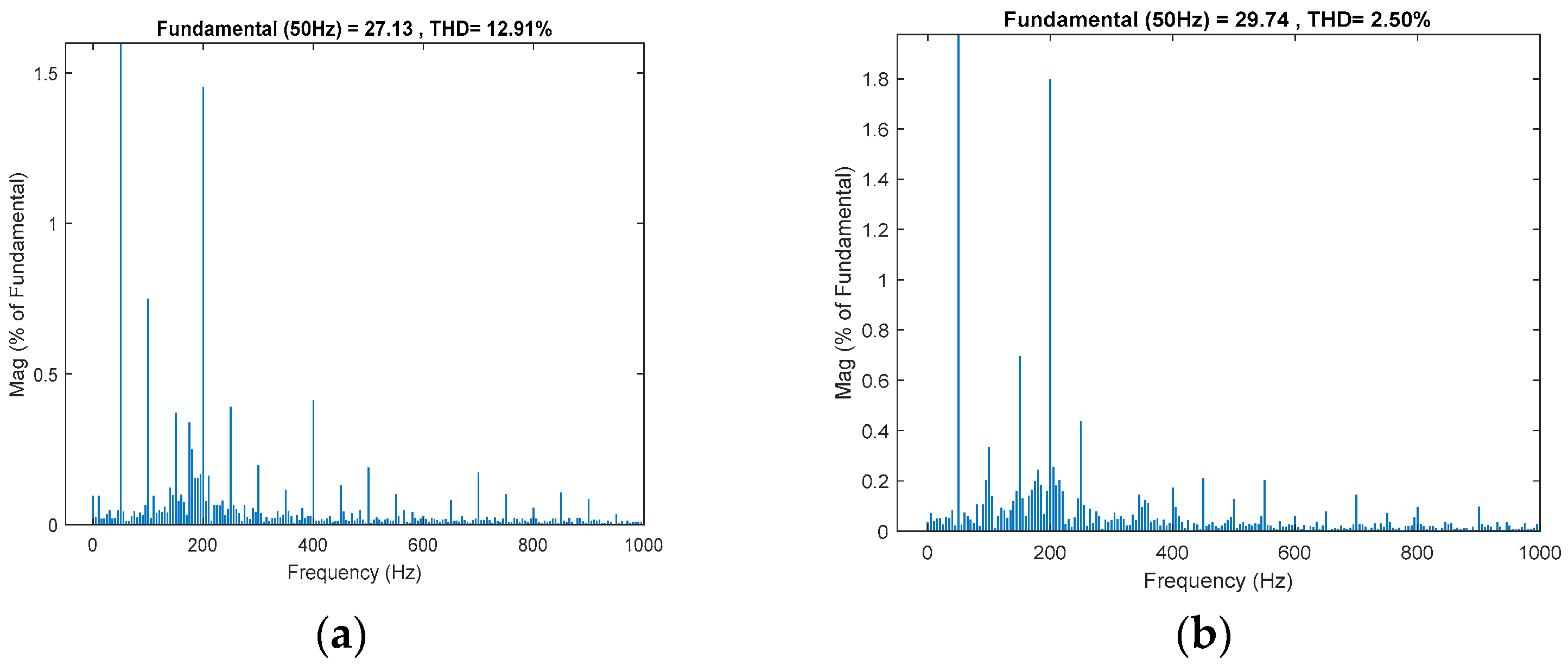
6. Results and Interpretation
6.1. Results in Grid-Connected Mode
6.1.1. Without Local Load
6.1.2. With Local Load
6.2. Standalone Mode Results
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| SC6PIG | Squirrel Cage Six-Phase Induction Generator |
| BDC | Bidirectional DC-DC converter |
| PLL | Phase locked loop |
| DG | Distributed generator |
| IGBT | Isolate gate bipolar transistor |
| FOC | Field-oriented control |
| VSI | Voltage source inverter |
| THD | Total harmonic distortion |
| PI | Proportional integral |
| FLC | Fuzzy logic controller |
Appendix B
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Rated Power | 24 | Kw |
| Rated Torque | 2350 | Nm |
| Rated Voltage | 230 | V |
| Rated Speed | 119 | Rpm |
| Rated Current | 32.3 | A |
| Frequency | 25 | Hz |
| Number of pole pairs | 12 | - |
| Stator Resistance Rs | 0.262 | Ω |
| Rotor Resistance Rr | 0.64 | Ω |
| Stator Inductance Ls | 0.0827 | H |
| Rotor Inductance Lr | 0.0813 | H |
| Mutual Inductance M | 0.0789 | H |
| Friction Coefficient | 21.39 | Nm/rad/s |
| Inertia Coefficient | 704 | Kg∙ |
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Total energy capacity | 9.8 kWh@25 °C (77 °F), 100% SOC | - |
| Battery capacity | 63 | Ah |
| Voltage range | Charge (468 to 550 Vdc) | V |
| Discharge (430 to 507 Vdc) | V | |
| Current range | Charge (10.7 A@467 V) | A |
| Discharge (11.7 A@427 V) | A |
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| DC bus voltage | 650 | V |
| Filter resistors (R1 & R2) | 0.2 | Ω |
| Filter inductance (L1 & L2) | 1500 & 750 | μH |
| Filter capacitors | 10 | μf |
| Grid voltage | 400 | V |
| Frequency | 50 | Hz |
Appendix C
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Proportional gain Ki | 1383 |
| Proportional gain kp | 5.5 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Proportional gain Ki () | 100 |
| Proportional gain kp () | 2.5 |
| Proportional gain Ki () | 5 |
| Proportional gain kp () | 0.5 |
| Proportional gain Ki () | 25 |
| Proportional gain kp () | 0.001 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Proportional gain Ki ( | 100 |
| Proportional gain kp () | 0.001 |
| Proportional gain Ki () | 0.1 |
| Proportional gain kp () | 10 |
| Proportional gain Ki () | 100 |
| Proportional gain kp () | 0.01 |
| Proportional gain Ki () | 25 |
| Proportional gain kp () | 0.01 |
References
- Li, L.; Lin, J.; Wu, N.; Xie, S.; Meng, C.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y. Review and outlook on the international renewable energy development. Energy Built Environ. 2022, 3, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoq, M.T.; Nawshad, U.; Islam, M.; Sina, I.; Syfullah, M.; Rahman, R. Micro Hydro Power: Promising Solution for Off-Grid Renewable Energy Source. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2011, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Nababan, S.; Muljadi, E.; Blaabjerg, F. An overview of power topologies for micro-hydro turbines. In Proceedings of the 2012 3rd IEEE International Symposium on Power Electronics for Distributed Generation Systems (PEDG), Aalborg, Denmark, 25–28 June 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worku, M. Recent Advances in Energy Storage Systems for Renewable Source Grid Integration: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micro Hydro Power (MHP)-Pros and Cons-Energypedia. Available online: https://energypedia.info/wiki/Micro_Hydro_Power_(MHP)_-_Pros_and_Cons (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- Youssef, K.H.; Wahba, M.A.; Yousef, H.A.; Omar, A.S. A new method for voltage and frequency control of stand-alone self-excited induction generator using PWM converter with variable DC link voltage. In Proceedings of the 2008 American Control Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 11–13 June 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 2486–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didik, H.; Bambang, P.N.; Asep, S.; Purwanto, Y.A. Sustainability Challenge of Micro Hydro Power Development in Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 147, 012031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Using Regulated Electrical Machines in Small Hydropower Plants Operating in a Power Network|Russian Electrical Engineering. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.3103/S1068371218050061 (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- Pantea, A.; Yazidi, A.; Betin, F.; Capolino, G.A.; Lanfranchi, V. Six-phase Axial Flux Permanent Magnet generator model: Simulation and experimental validation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 25th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Santa Clara, CA, USA, 8–10 June 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semail, E.; Meibody-Tabar, F.; Benkhoris, M.F.; Razik, H.; Pietrzak-David, M.; Monmasson, E.; Bouscayrol, A.; Davat, B.; Delarue, P.; Fornel, B.; et al. Machines polyphasées: De la modélisation multimachine à la commande. J3ea 2005, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Khalik, A.S.; Ahmed, S. Performance Evaluation of a Five-Phase Modular Winding Induction Machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 2654–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulandaivel, G.; Sundaram, E.; Gunasekaran, M.; Chenniappan, S. Five-phase induction motor drive-A comprehensive review. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1178169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazidi, A.; Pantea, A.; Betin, F.; Carriere, S.; Henao, H.; Capolino, G.-A. Six-phase induction machine model for simulation and control purposes. In Proceedings of the IECON 2014—40th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Dallas, TX, USA, 29 October 2014–1 November 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantea, A.; Yazidi, A.; Betin, F.; Taherzadeh, M.; Carriere, S.; Henao, H.; Capolino, G.-A. Six-Phase Induction Machine Model for Electrical Fault Simulation Using the Circuit-Oriented Method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandramohan, K.; Kalyanasundaram, R. Dynamic Modeling of Seven-Phase Induction Generator. Energy Procedia 2017, 117, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, T.S.; Bastos, R.R.; Cardoso Filho, B.J. Modeling and Control of a Nine-Phase Induction Machine with Open Phases. IEEE Trans. Ind. Applicat. 2018, 54, 6576–6585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, M.I.; Abdelkhalik, A.S. Performance Evaluation of Eleven-Phase Induction Machine with Different PWM Techniques. J. Eng. Res. TJER 2015, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantea, A. Modélisation, Simulation et Contrôle D’une Génératrice Multiphasée à Grand Nombre de Pôles Pour L’éolien. Available online: https://theses.hal.science/tel-03650568 (accessed on 23 June 2024).
- Pantea, A.; Yazidi, A.; Betin, F.; Carriere, S.; Capolino, G.-A. Simulation and experimental control of six-phase induction generator for wind turbines. In Proceedings of the 2016 XXII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Lausanne, Switzerland, 4–7 September 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alattar, M.; Alsammak, A. Speed Control of Asymmetrical Six Phase Induction Motor based Fuzzy Logic Controller. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. IRJET 2020, 7, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Pantea, A.; Yazidi, A.; Betin, F.; Carriere, S.; Sivert, A.; Capolino, G.-A. Fault tolerant control of six-phase induction generator for wind turbines. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference (IEMDC), Miami, FL, USA, 21–24 May 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Khalik, A.S.; Abdel-Majeed, M.S.; Ahmed, S. Effect of Winding Configuration on Six-Phase Induction Machine Parameters and Performance. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 223009–223020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantea, A.; Yazidi, A.; Betin, F.; Carriere, S.; Sivert, A.; Vacossin, B.; Henao, H.; Capolino, G.-A. Fault-Tolerant Control of a Low-Speed Six-Phase Induction Generator for Wind Turbines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantea, A.; Yazidi, A.; Betin, F.; Carriere, S.; Sivert, A.; Capolino, G.-A. Fault Tolerant Control of Six-Phase Induction Gene.Pdf. 2017. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stampPDF/getPDF.jsp?tp=&a-number=8002161&ref=aHR0cHM6Ly9pZWVleHBsb3JlLmllZWUub3JnL2Fic3RyYWN0L2RvY3VtZW50LzgwMDIxNjE= (accessed on 22 January 2024).
- Pantea, A.; Nurwati, T.; Yazidi, A.; Betin, F.; Carriere, S.; Capolino, G.-A. Fuzzy Logic Control of a Low Speed Six-Phase Induction Generator for Wind Turbines. In Proceedings of the IECON 2018-44th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Washington, DC, USA, 21–23 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 5813–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OBouyahia, O.; Yazidi, A.; Betin, F.; Capolino, G.-A. Fuzzy Variable Structure Control of a Six Phase Induction Generator. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–18 May 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyahia, O.; Betin, F.; Yazidi, A. Fault-tolerant Variable Structure Control of a Low Speed 6-Phase Induction Generator. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 13th International Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics and Drives (SDEMPED), Dallas, TX, USA, 22–25 August 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Xu, D.; Mian, M.; Ahmed, J. A micro hydro power plant for distributed generation using municipal water waste with archimedes screw. In Proceedings of the 2013 16th International Multi Topic Conference, INMIC 2013, Lahore, Pakistan, 19–20 December 2013; pp. 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analysis and Controller Design for Stand-Alone VSIs in Synchronous Reference Frame-Ramezani-2017-IET Power Electronics-Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://ietresearch.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1049/iet-pel.2016.0883 (accessed on 27 January 2024).
- Ünlü, M.; Çamur, S.; Beşer, E.; AriFoğlu, B. Sinusoidal current injection based on a line-commutated inverter for single-phase grid-connected renewable energy sources. Turk. J. Elec. Eng. Comp. Sci. 2016, 24, 4670–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y. A Unified Control Strategy for Three-Phase Inverter in Distributed Generation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 1176–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedo, J.; Kascak, S. Design of output LCL filter and control of single-phase inverter for grid-connected system. Electr. Eng. 2017, 99, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.; Liu, Z.; Cha, H. A New Design Method of LCL Filter for Single Phase Grid Connected Power Converter. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Symposium on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ISEE), Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam, 10–12 October 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liserre, M.; Blaabjerg, F.; Hansen, S. Design and Control of an LCL-Filter-Based Three-Phase Active Rectifier. IEEE Trans. Ind. Applicat. 2005, 41, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaneria, A.; Khambhadiya, H. Design of AC side filter for Grid Tied Solar Inverter. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference on Recent Trends on Electronics, Information, Communication & Technology (RTEICT), Bangalore, India, 17–18 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1375–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, N.; Kedjar, B.; Al-Haddad, K. D-Q frame optimal control of single phase grid connected inverter with LCL filter. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Electrical Power and Energy Conference (EPEC), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 12–14 October 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; He, Y.; Tang, T.; Blaabjerg, F. A New Design Method for the Passive Damped LCL and LLCL Filter-Based Single-Phase Grid-Tied Inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 4339–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.-F.; Wang, X.; Blaabjerg, F. Passivity-based LCL Filter Design of Grid-Connected VSCs with Converter Side Current Feedback. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Power Electronics Conference (IPEC-Niigata 2018-ECCE Asia), Niigata, Japan, 20–24 May 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1711–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Blaabjerg, F.; Loh, P.C. Passivity-Based Stability Analysis and Damping Injection for Multiparalleled VSCs with LCL Filters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 8922–8935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinmaya, K.A.; Singh, G.K. Modeling and experimental analysis of grid-connected six-phase induction generator for variable speed wind energy conversion system. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2019, 166, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.K. Modeling and experimental analysis of a self-excited six-phase induction generator for stand-alone renewable energy generation. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 1605–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurwati, T. Contribution to Fuzzy Logic Controller of Six-Phase Induction Generator for Wind Turbine Application. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Picardy Jules Verne, Amiens, France, 2019. Available online: https://www.theses.fr/2019AMIE0064 (accessed on 23 January 2024).
- Aroquiadassou, G.; Henao, H.; Capolino, G.A.; Boglietti, A.; Cavagnino, A. A simple circuit-oriented model for predicting six-phase induction machine performances. In Proceedings of the IECON 2006-32nd Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics, Paris, France, 6–10 November 2006; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renukadevi, G.; Rajambal, K. Generalized model of multi-phase induction motor drive using matlab/simulink. In ISGT2011-India; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghli, L. Modélisation et Commande de la Machine Asynchrone. 2020. Available online: https://www.baghli.com/dl/courscmde/cours_cmde_MAS.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2024).
- Bouyahia, O. Génération Électrique Tolérante Aux Défauts à Base de Structures Multiphasées: Comparaison, Choix D’une Technologie, Transfert Technologique. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Picardie Jules Verne, Amiens, France, 2022. Available online: https://theses.hal.science/tel-04073881 (accessed on 28 January 2024).
- Abdulelah, A.M.; Ouahid, B.; Youcef, S. Control of a Stand-Alone Variable Speed Wind Turbine with a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator. In Proceedings of the 2021 18th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices (SSD), Monastir, Tunisia, 22–25 March 2021; pp. 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguiba, I.; Houari, A.; Belloumi, H.; Kourda, F. Control of single-phase grid connected photovoltaic inverter. In Proceedings of the 2016 4th International Conference on Control Engineering & Information Technology (CEIT), Hammamet, Tunisia, 16–18 December 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Gupta, T.; Kumar, D.; Chaudhary, K. Modelling and analysis of grid-tied fuel cell system with synchronous reference frame control. In Proceedings of the 2017 4th International Conference on Power, Control & Embedded Systems (ICPCES), Allahabad, India, 9–11 March 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, J. Study on control method for the grid-connected inverter with LCL filter. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Workshop on Advanced Research and Technology in Industry Applications (WARTIA), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29–30 September 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1337–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrouni, N.; Jraidi, M.; Chérif, A. New method of current control for LCL-interfaced grid-connected three phase voltage source inverter. Rev. Des Energ. Renouvelables 2010, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagiraju, D.; Obulesu, Y.P.; Choppavarapu, S. Dynamic performance improvement of standalone battery integrated PMSG wind energy system using proportional resonant controller. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2017, 20, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.K.; Jena, S.; Babu, B.C. Power management and bus voltage control of a battery backup-based stand-alone PV system. Electr. Eng. 2022, 104, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidirectional DC-DC Converter in Solar PV System for Battery Charging Application|IEEE Conference Publication|IEEE Xplore. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8537391 (accessed on 24 January 2024).
- Wang, Y.-X.; Qin, F.-F.; Kim, Y.-B. Bidirectional DC-DC converter design and implementation for lithium-ion battery application. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE PES Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference (APPEEC), Hong Kong, China, 7–10 December 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.M.; Senjyu, T.; Orabi, M.; Wahab, M.A.A.; Hamada, M.M. Control of a Stand-Alone Variable Speed Wind Energy Supply System. Appl. Sci. 2013, 3, 437–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

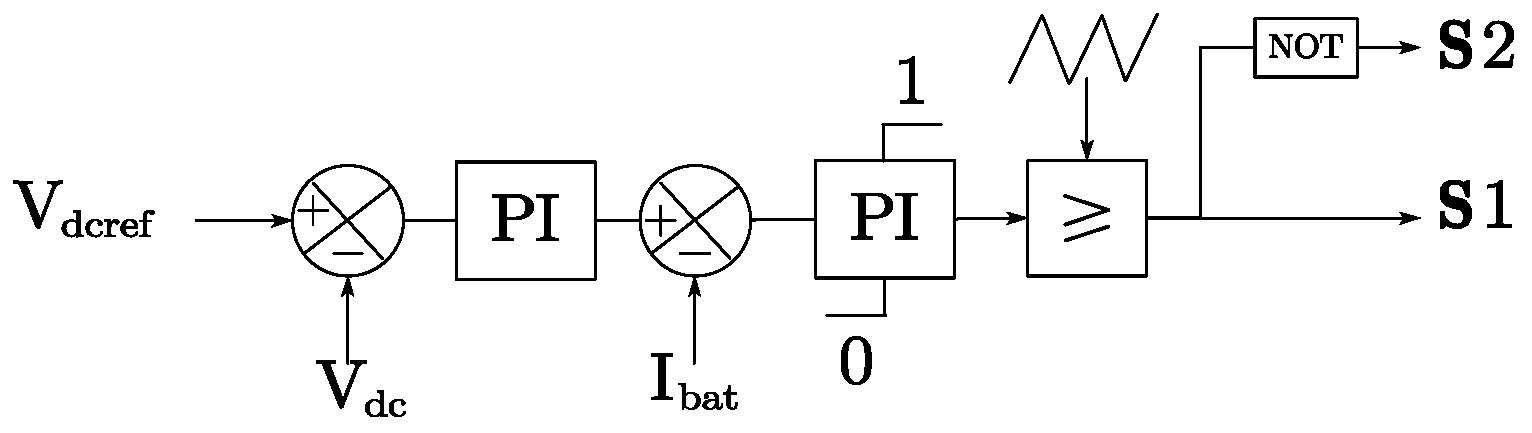



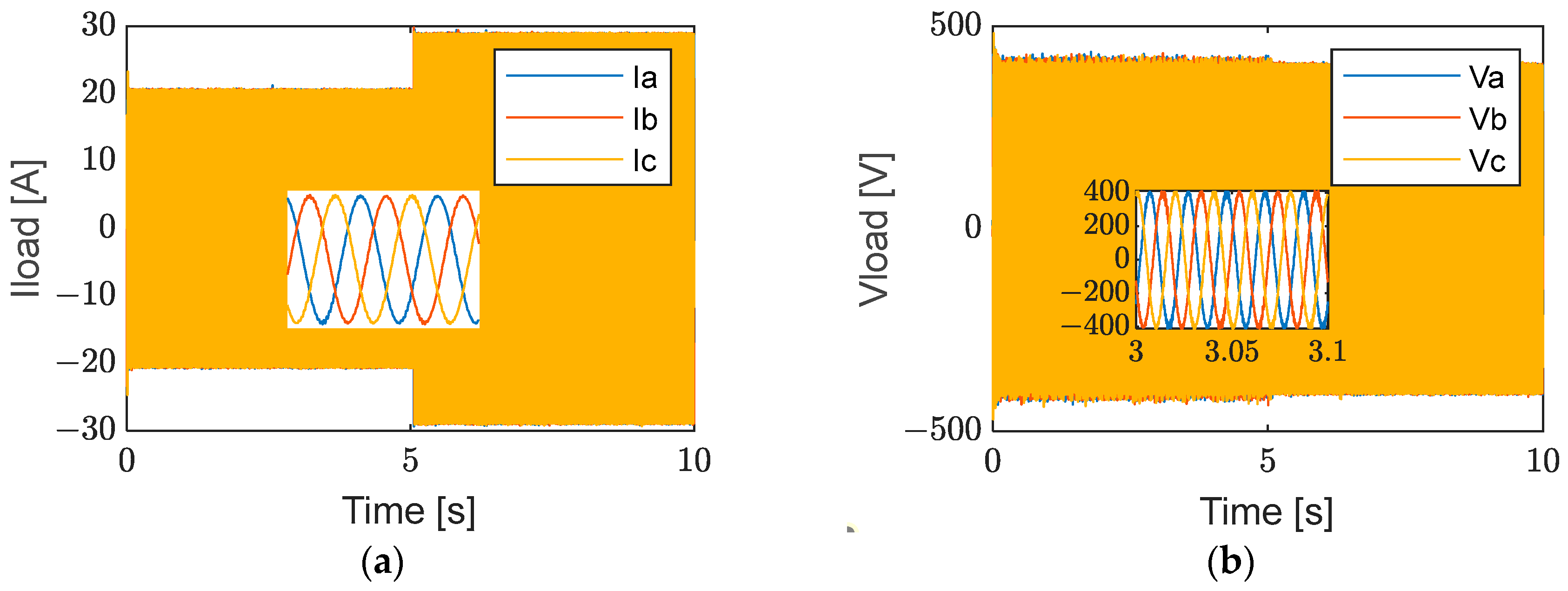
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouédraogo, M.; Yazidi, A.; Betin, F. Control of Grid-Connected and Standalone Microhydraulic Turbine Using a Six-Phase Induction Generator. Energies 2024, 17, 3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17143581
Ouédraogo M, Yazidi A, Betin F. Control of Grid-Connected and Standalone Microhydraulic Turbine Using a Six-Phase Induction Generator. Energies. 2024; 17(14):3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17143581
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuédraogo, Marius, Amine Yazidi, and Franck Betin. 2024. "Control of Grid-Connected and Standalone Microhydraulic Turbine Using a Six-Phase Induction Generator" Energies 17, no. 14: 3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17143581
APA StyleOuédraogo, M., Yazidi, A., & Betin, F. (2024). Control of Grid-Connected and Standalone Microhydraulic Turbine Using a Six-Phase Induction Generator. Energies, 17(14), 3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17143581








