Reducing Rare-Earth Magnet Reliance in Modern Traction Electric Machines
Abstract
1. Introduction

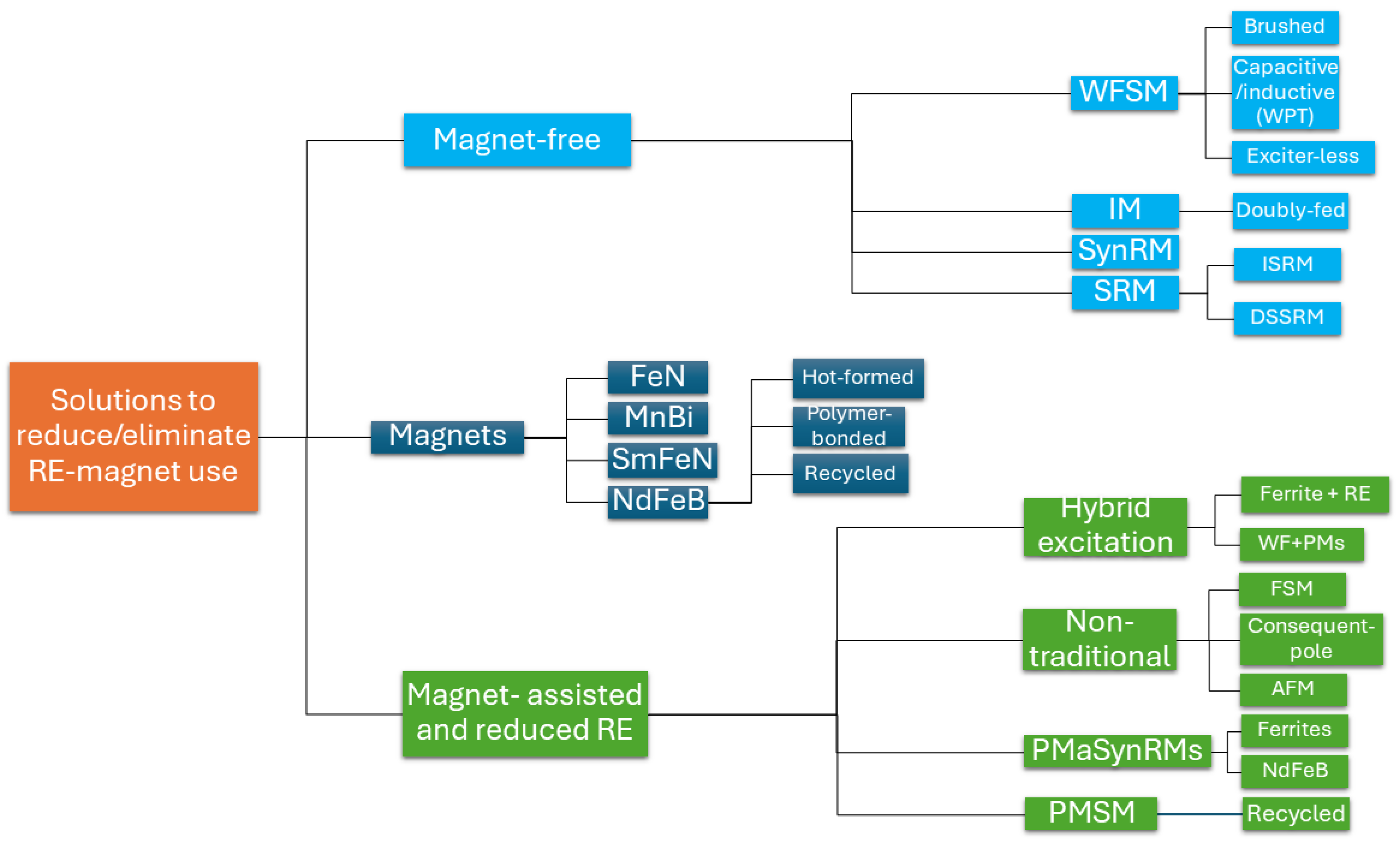
2. Review of Potential Magnetic Materials and Topological Solutions
2.1. Material Substitution Strategies
2.2. Topological Substitution Strategies
3. Materials and Methods
Methods for Data Collection
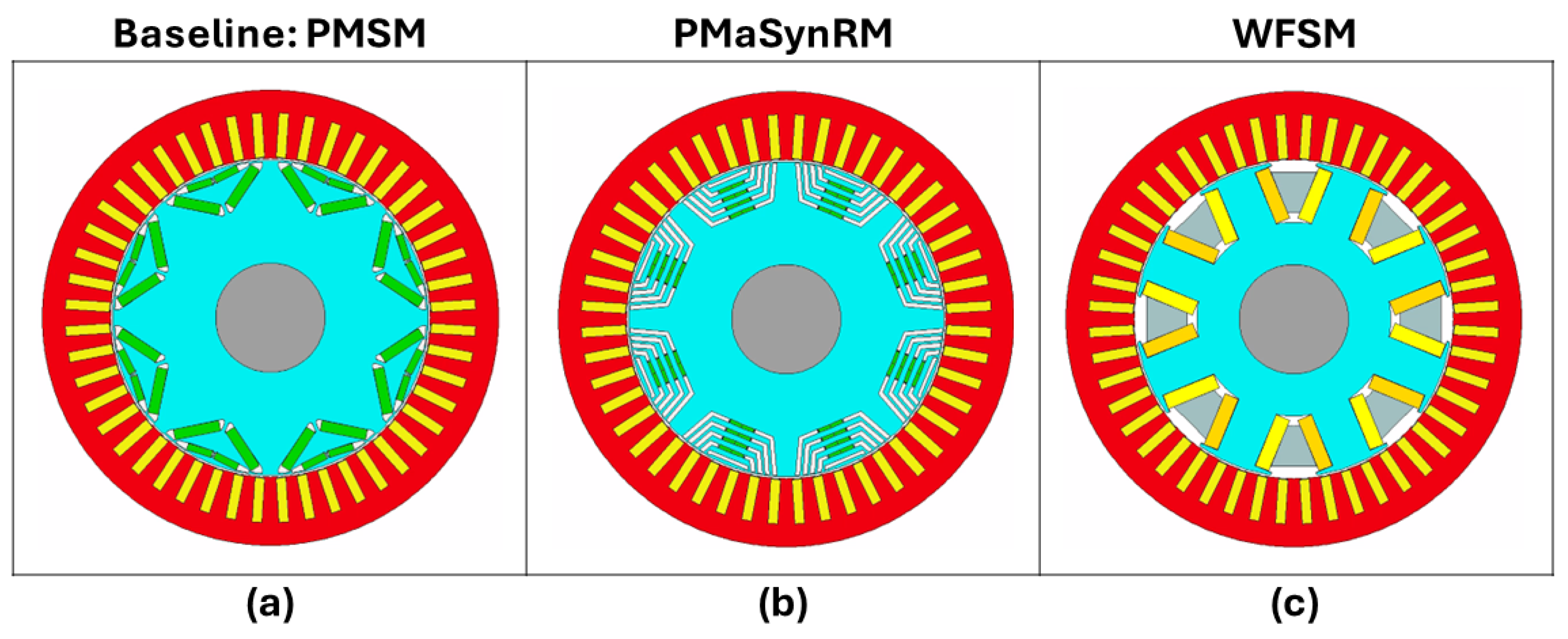
4. Simulation Results
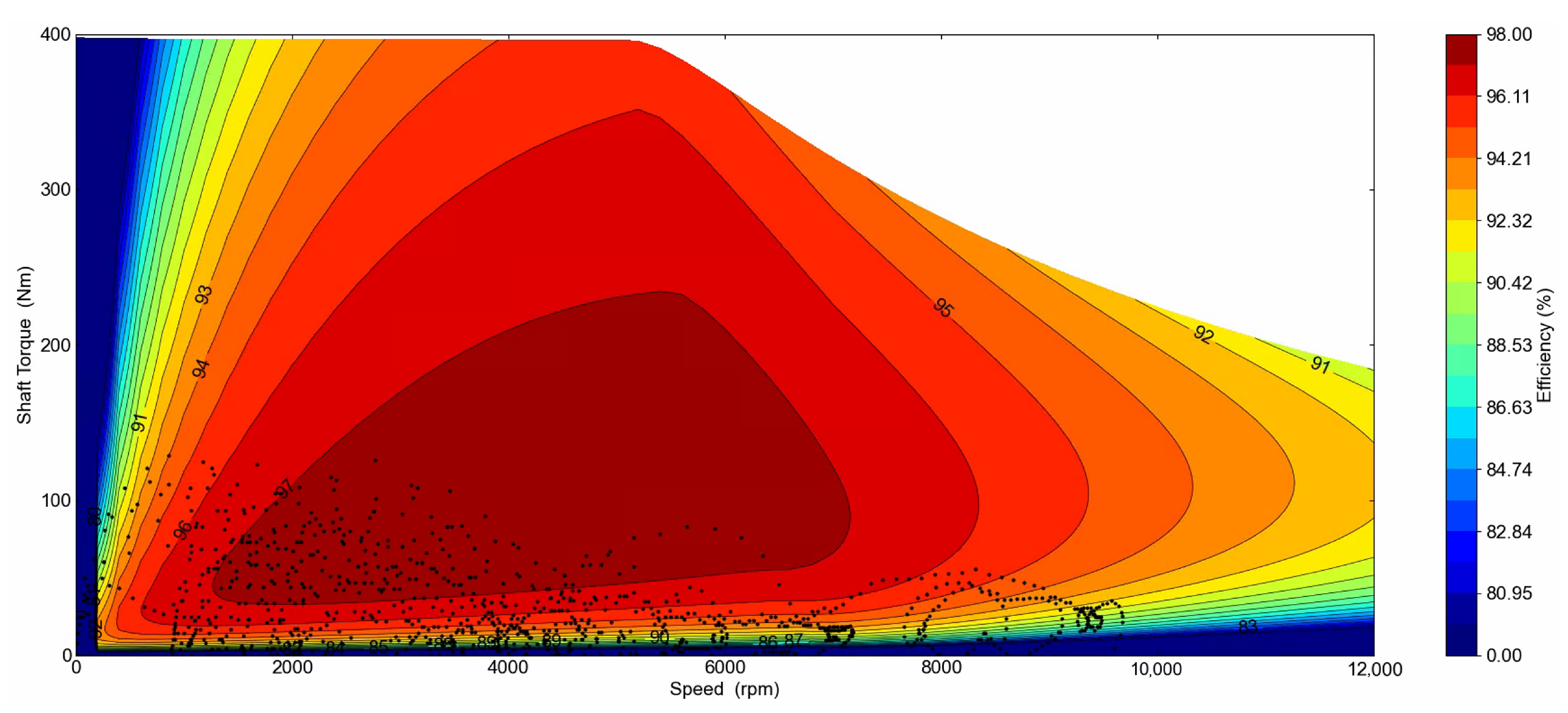
4.1. Peak Performance Envelopes
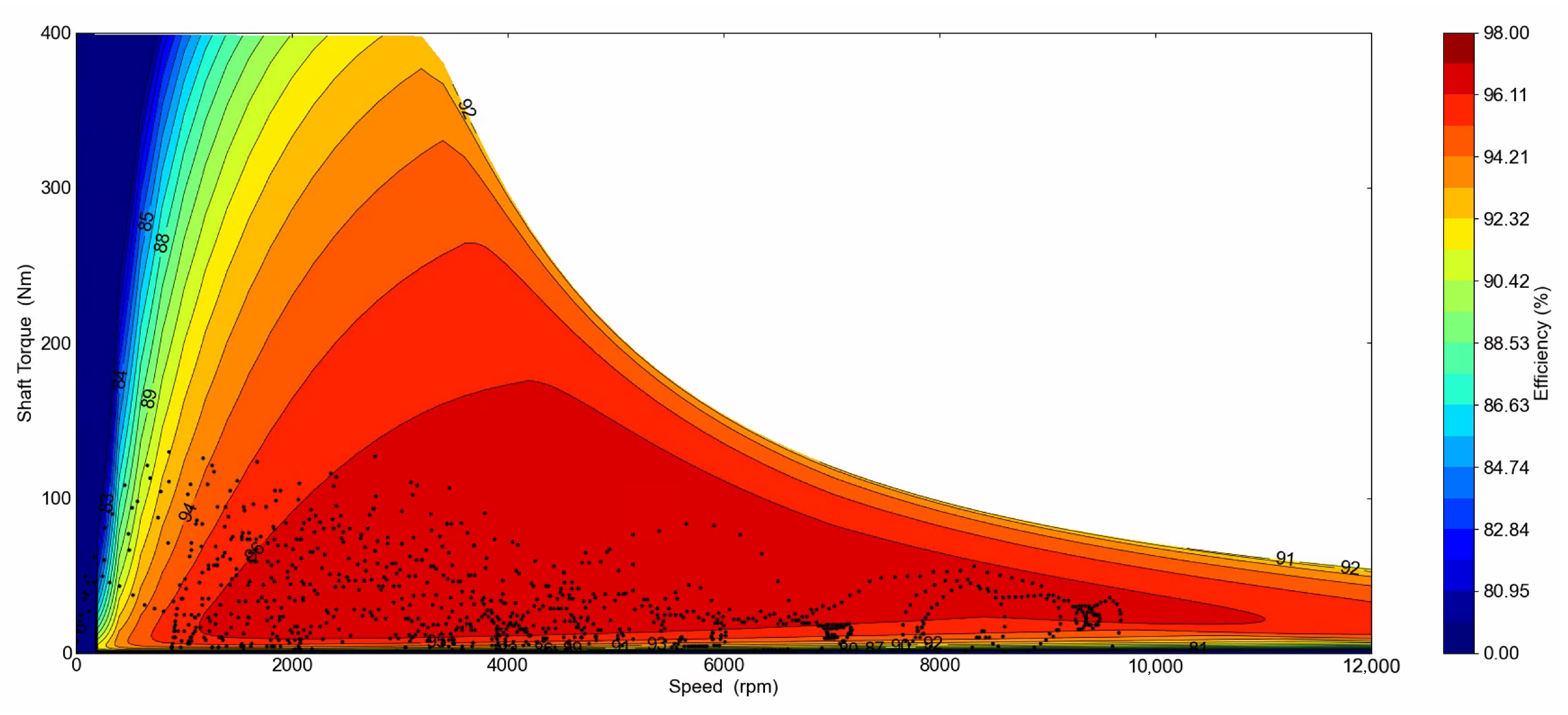
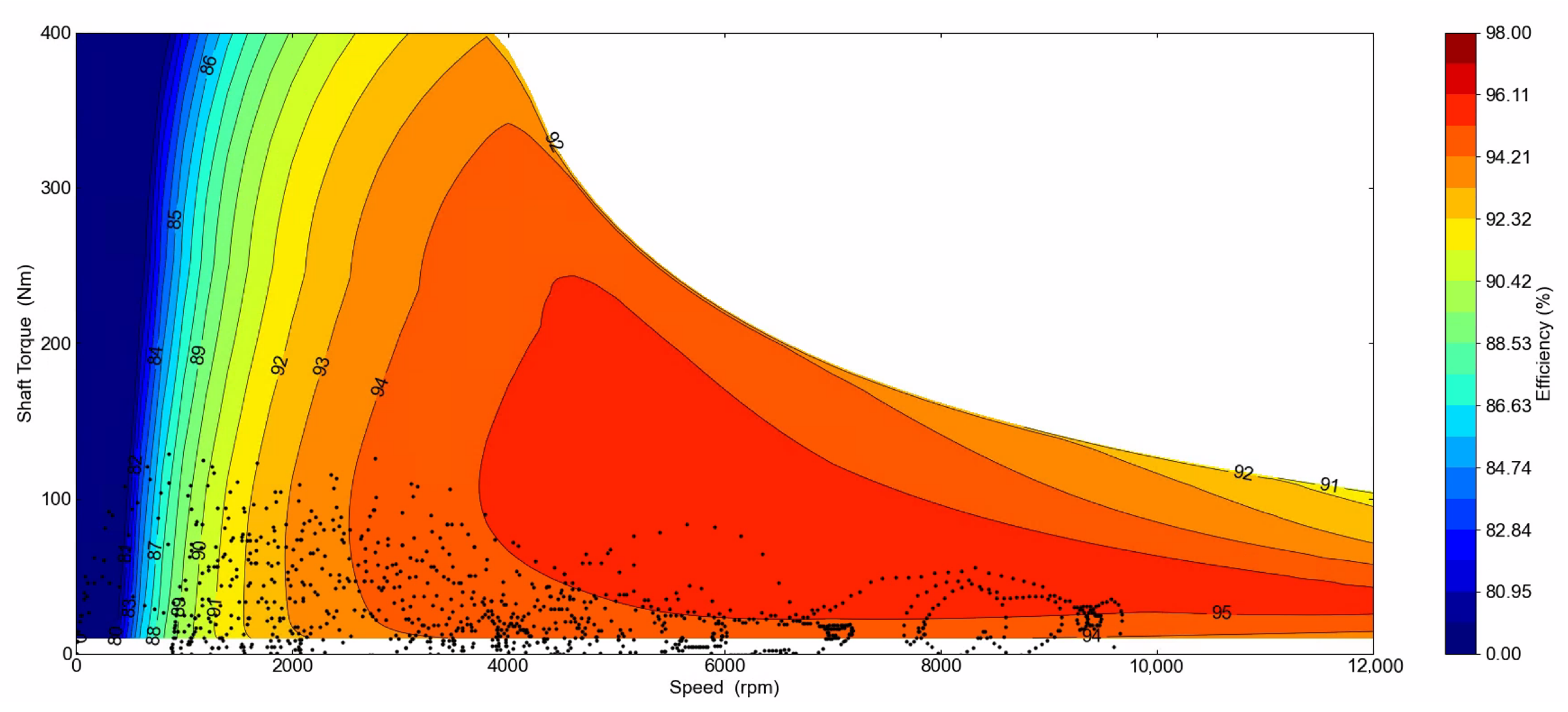
4.2. Efficiency Performance Envelopes
4.3. Continuous Performance
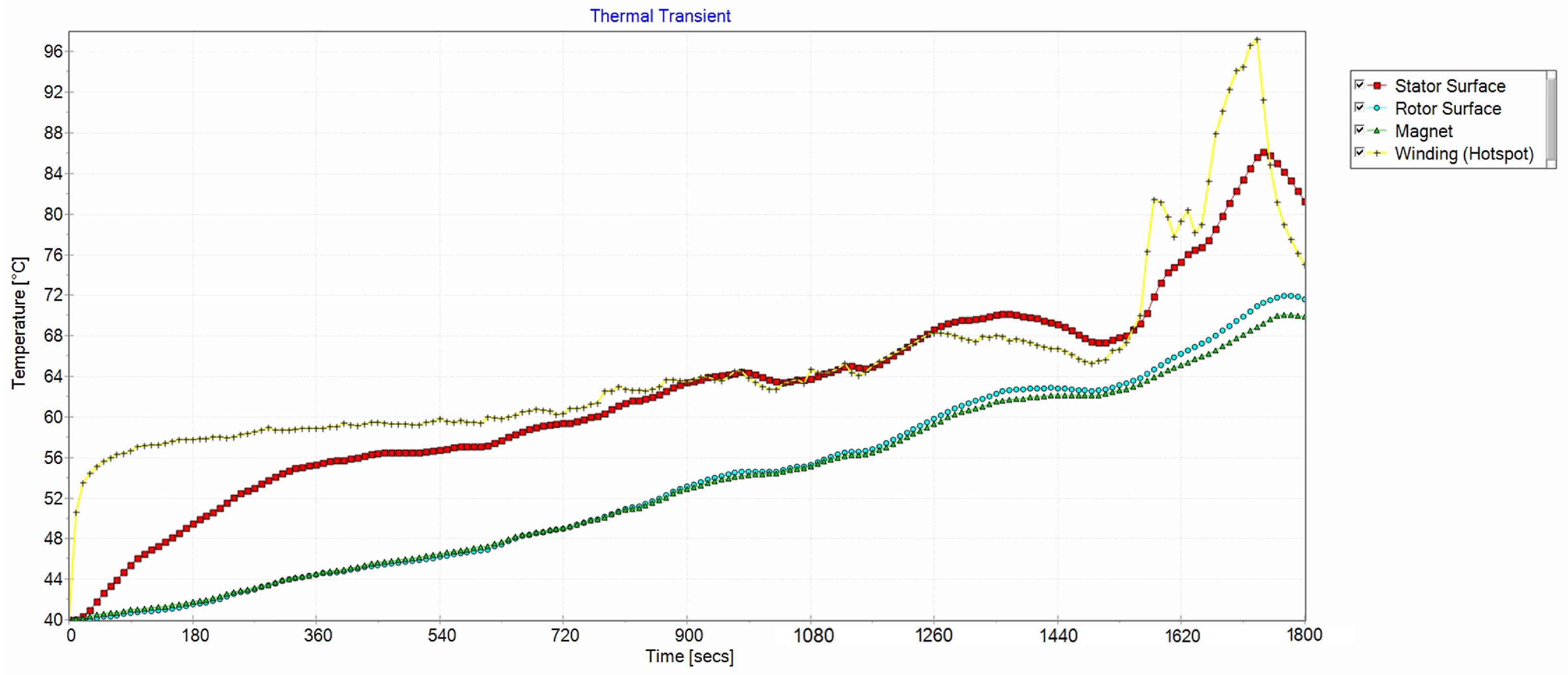
4.4. Thermal Performance
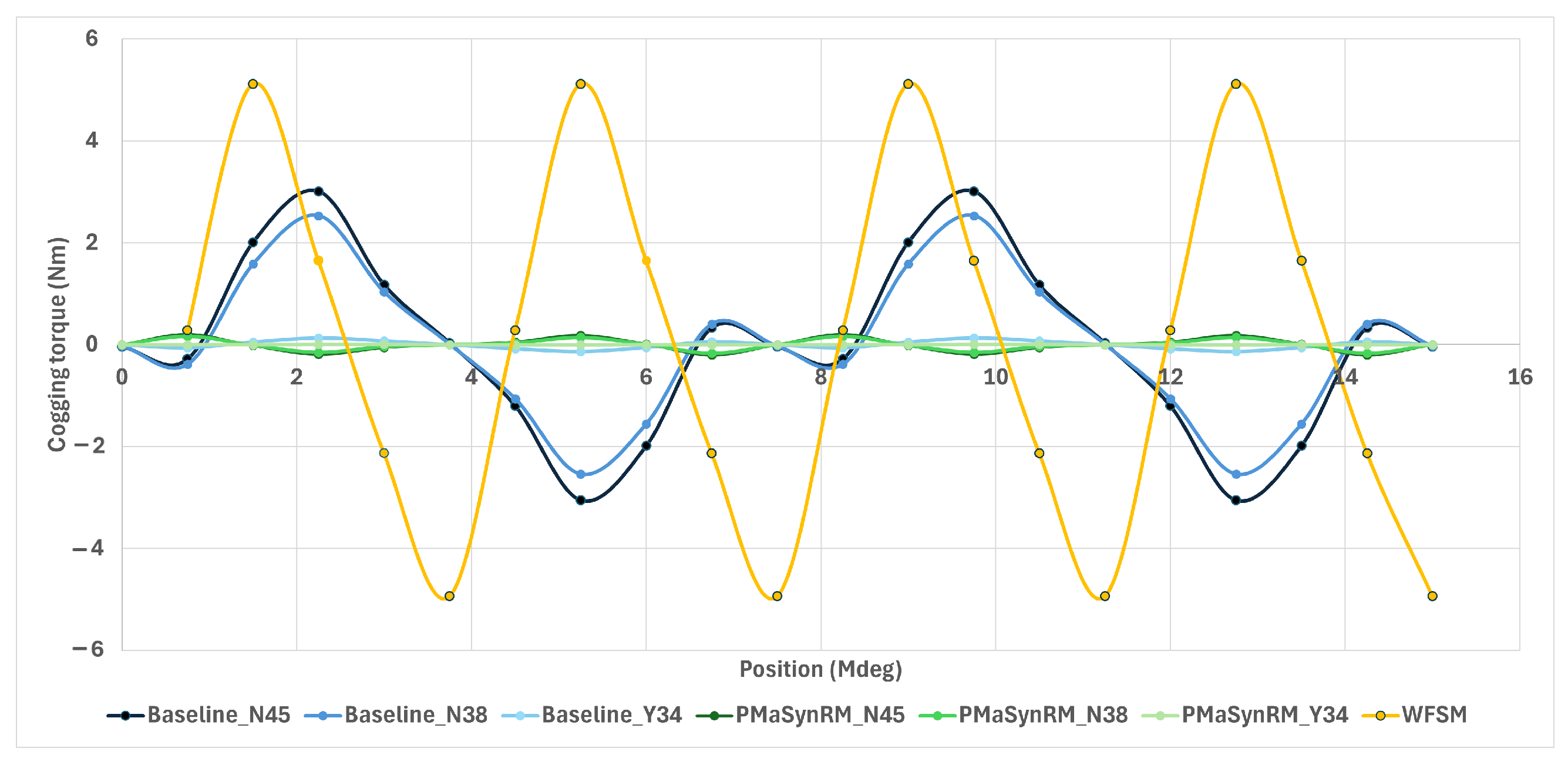
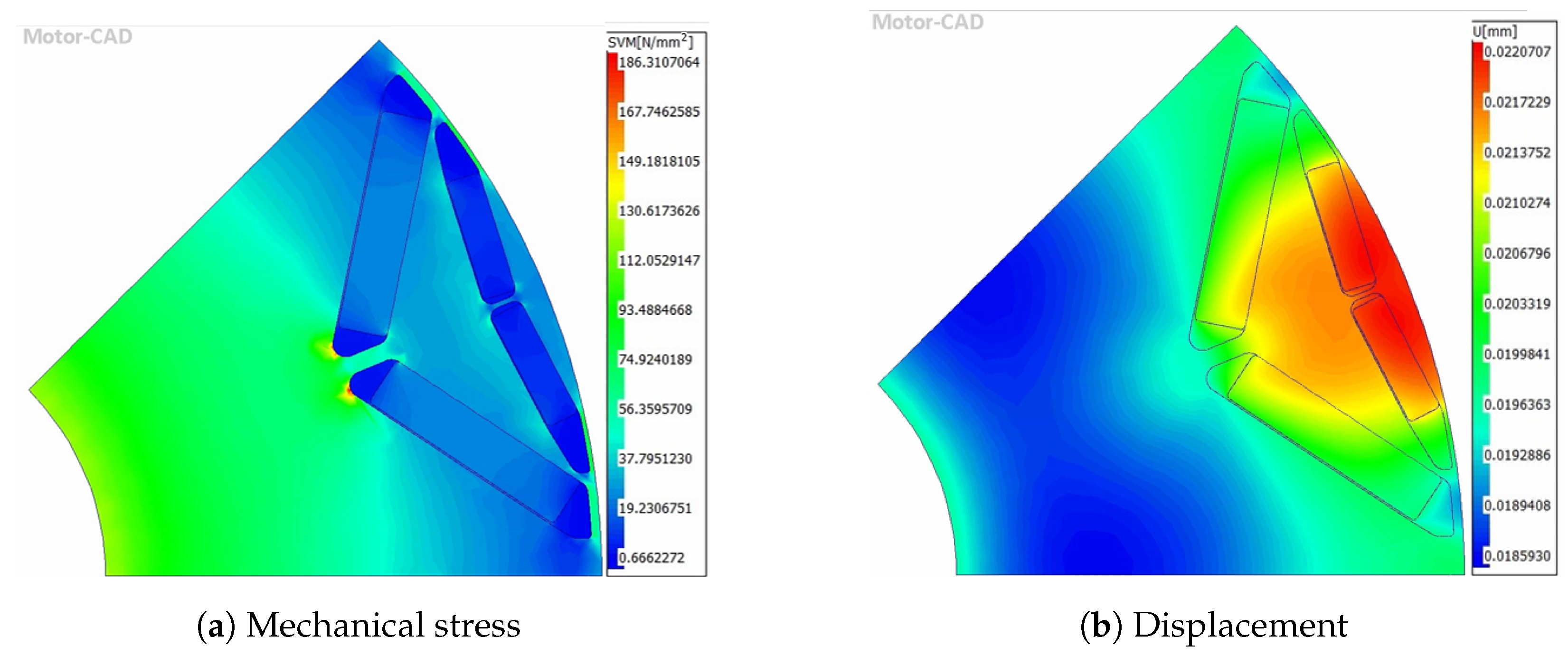
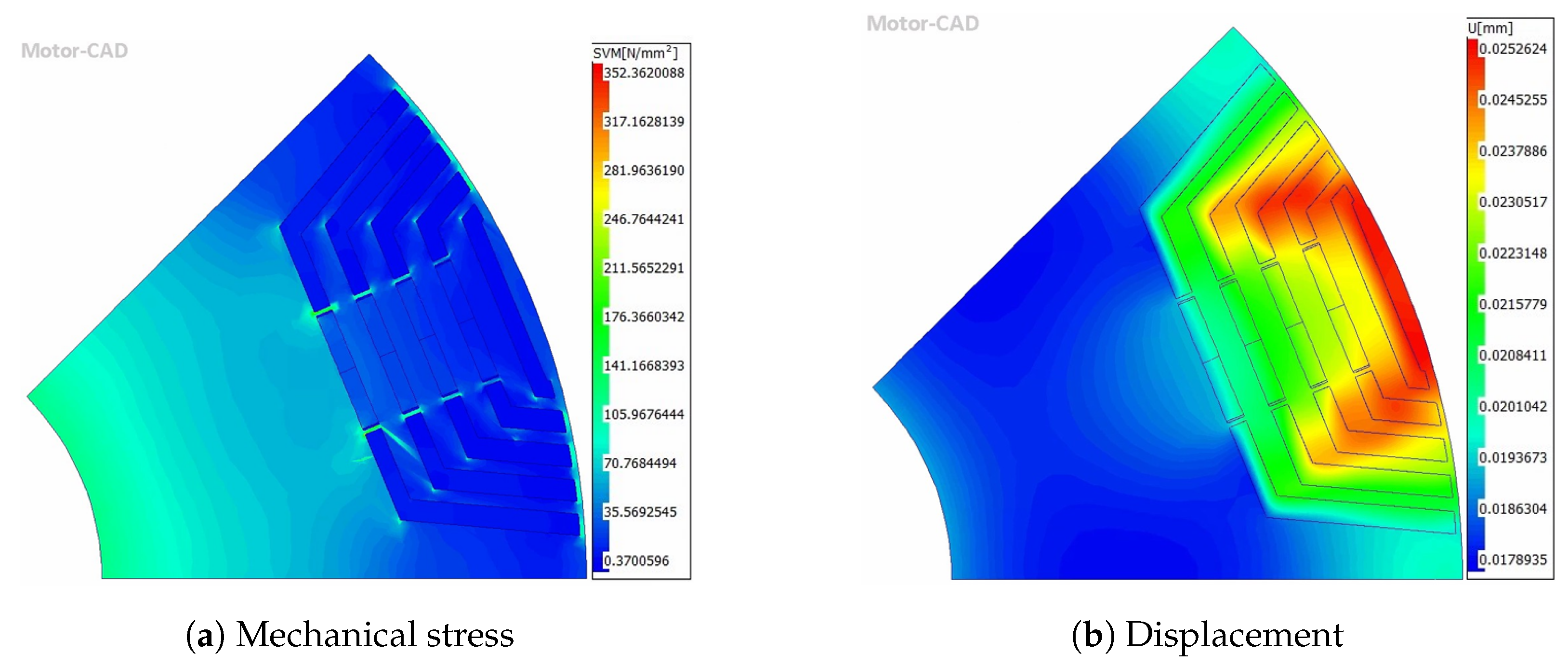
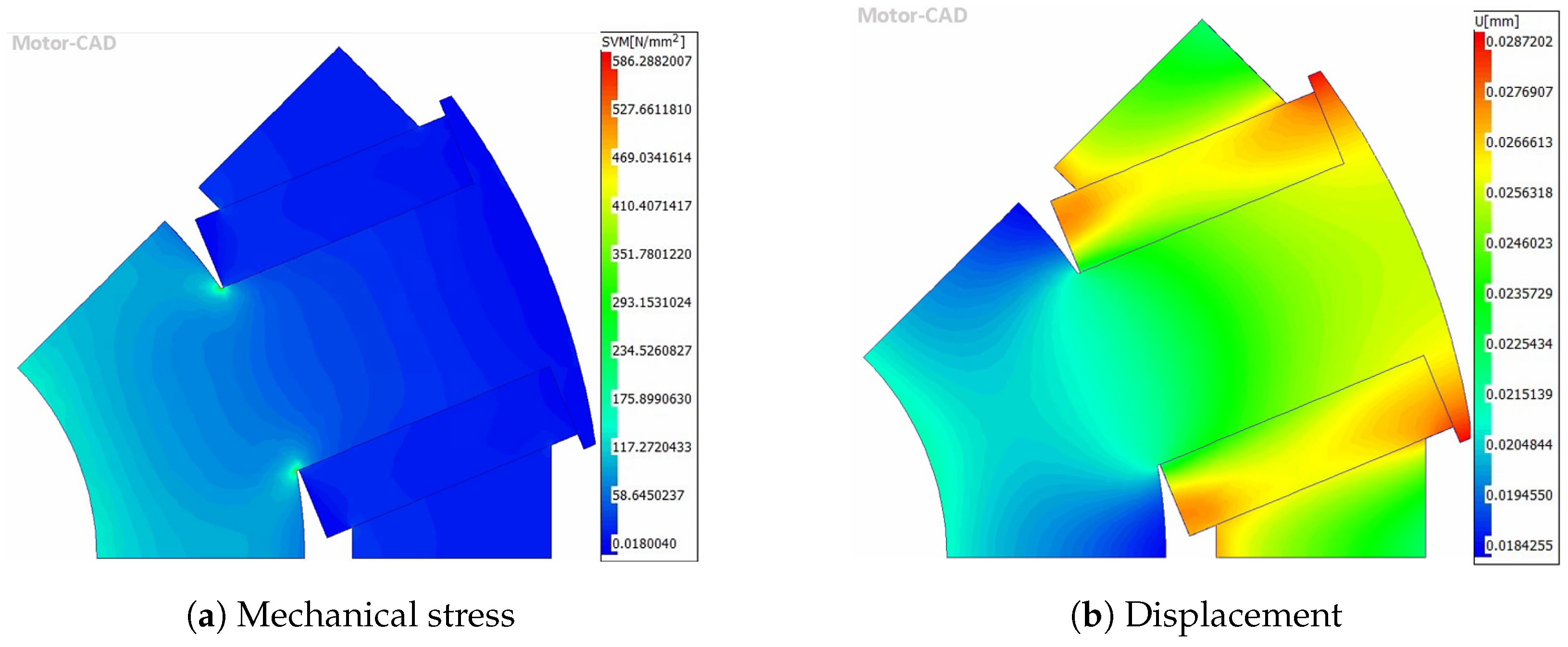
4.5. Mechanical and NVH Performance
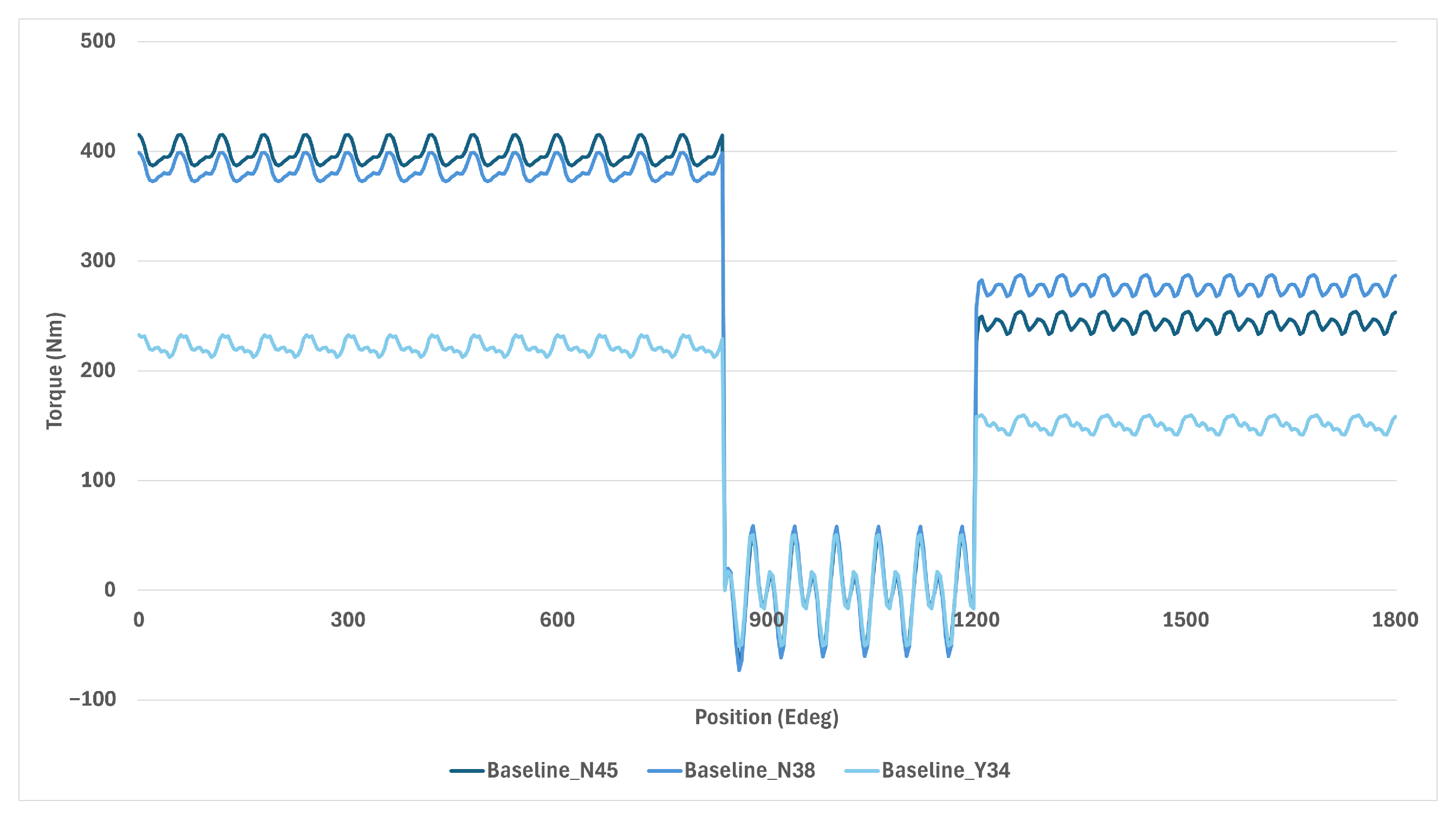
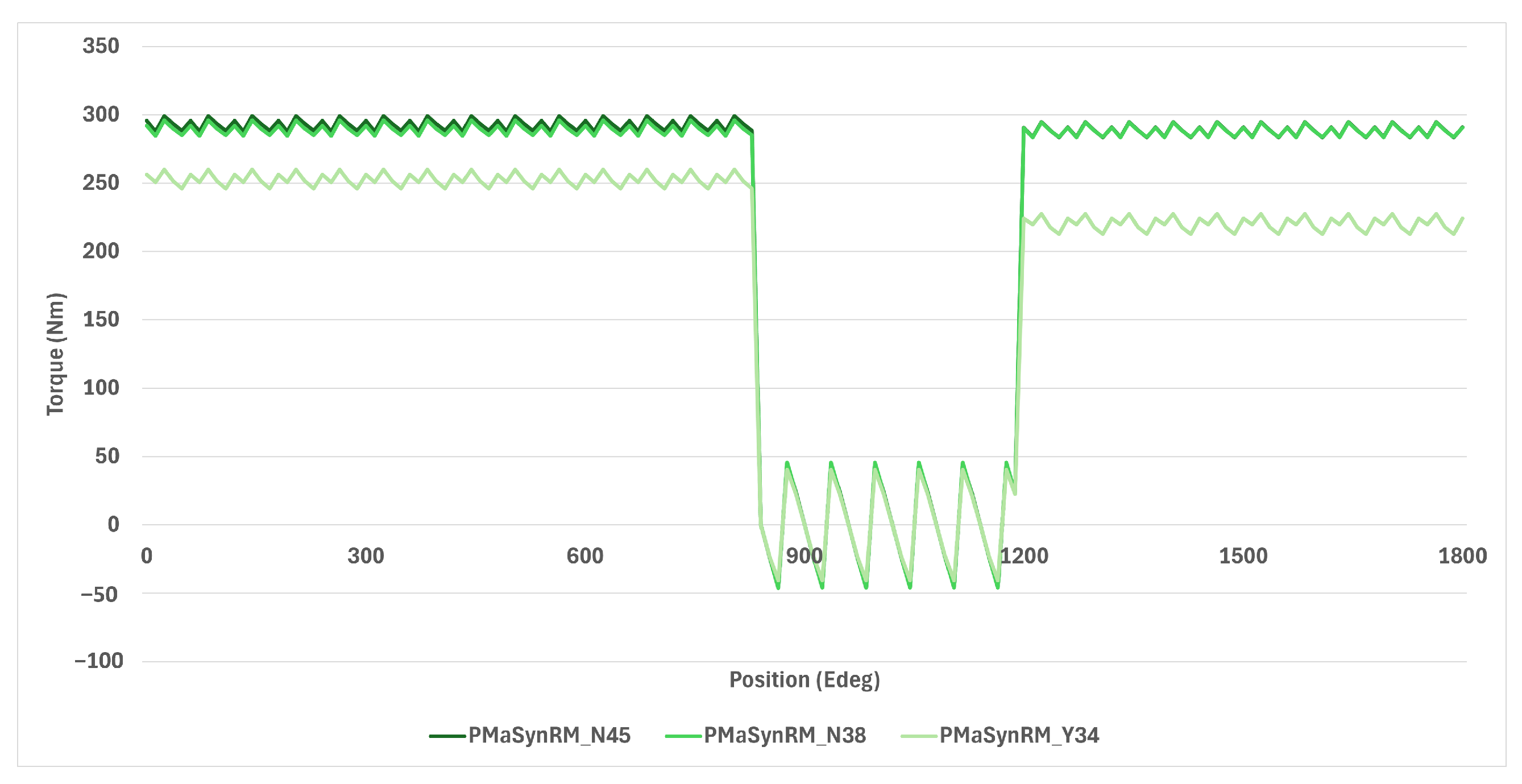
4.6. Demagnetisation Resilience
5. Discussion
5.1. Cost Analysis
5.2. Research Credibility
5.3. Recommendations for Practice
5.4. Limitations to Research
5.5. Suggestions for Future Research
6. Conclusions
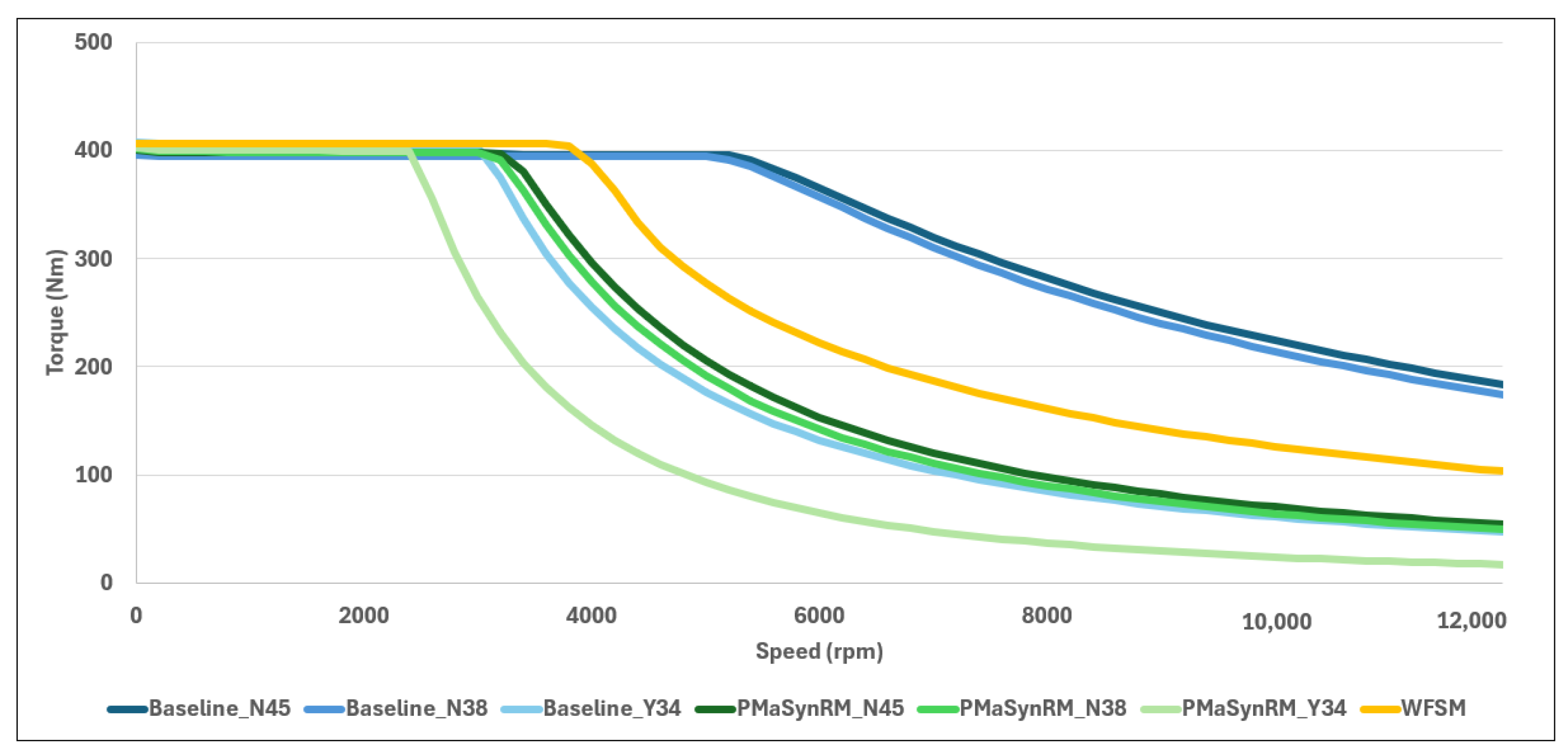
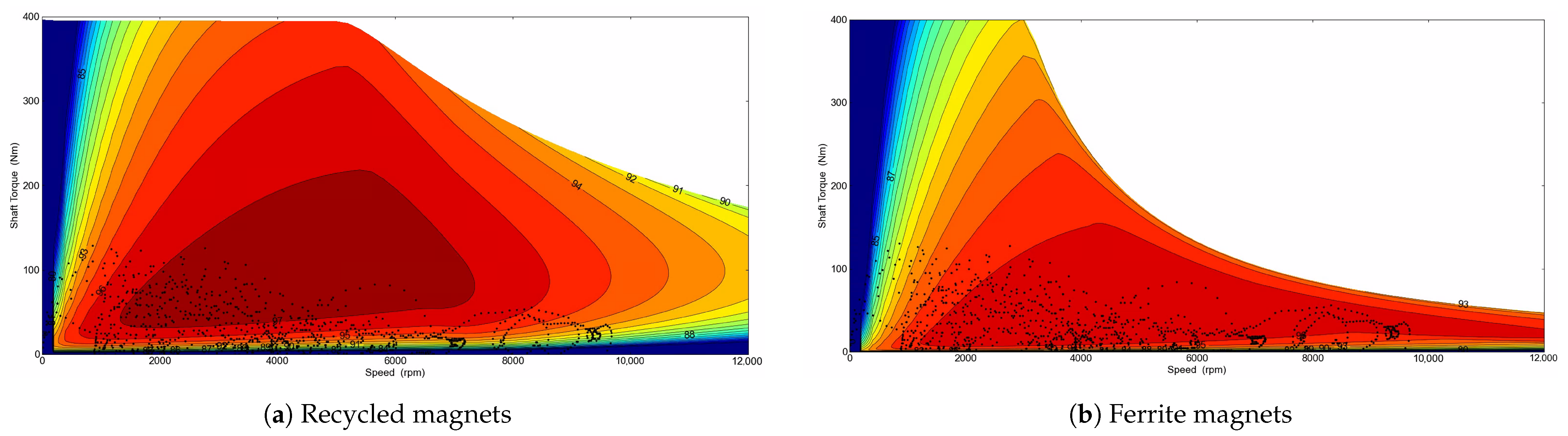
- The simulation results revealed that recycled NdFeB magnets were a cost-effective and sustainable alternative, offering performance comparable to primary NdFeB magnets with minimal volume increases of 3.5% for the PMSM and 2.9% for the PMaSynRM to achieve equivalent peak torque. In contrast, ferrite magnets required substantial volume increases—82% for PMSM and 31% for PMaSynRM—leading to lower torque density and higher torque ripple.
- The reference PMSM with virgin magnets achieved the highest gravimetric torque density at 11.5 Nm/kg, while the PMaSynRM with ferrites had the lowest at 6.5 Nm/kg.
- The PMSM with recycled magnets demonstrated superior high-speed and high-temperature performance compared to primary magnets.
- The use of ferrites exhibited increased torque ripple and reduced performance over the torque–speed curve. During demagnetisation, the recycled magnets showed a 27% torque decrease compared to 39% for primary NdFeB and 21% for ferrites, with PMaSynRM experiencing minimal demagnetisation impacts. The PMaSynRMs also had the lowest torque ripple.
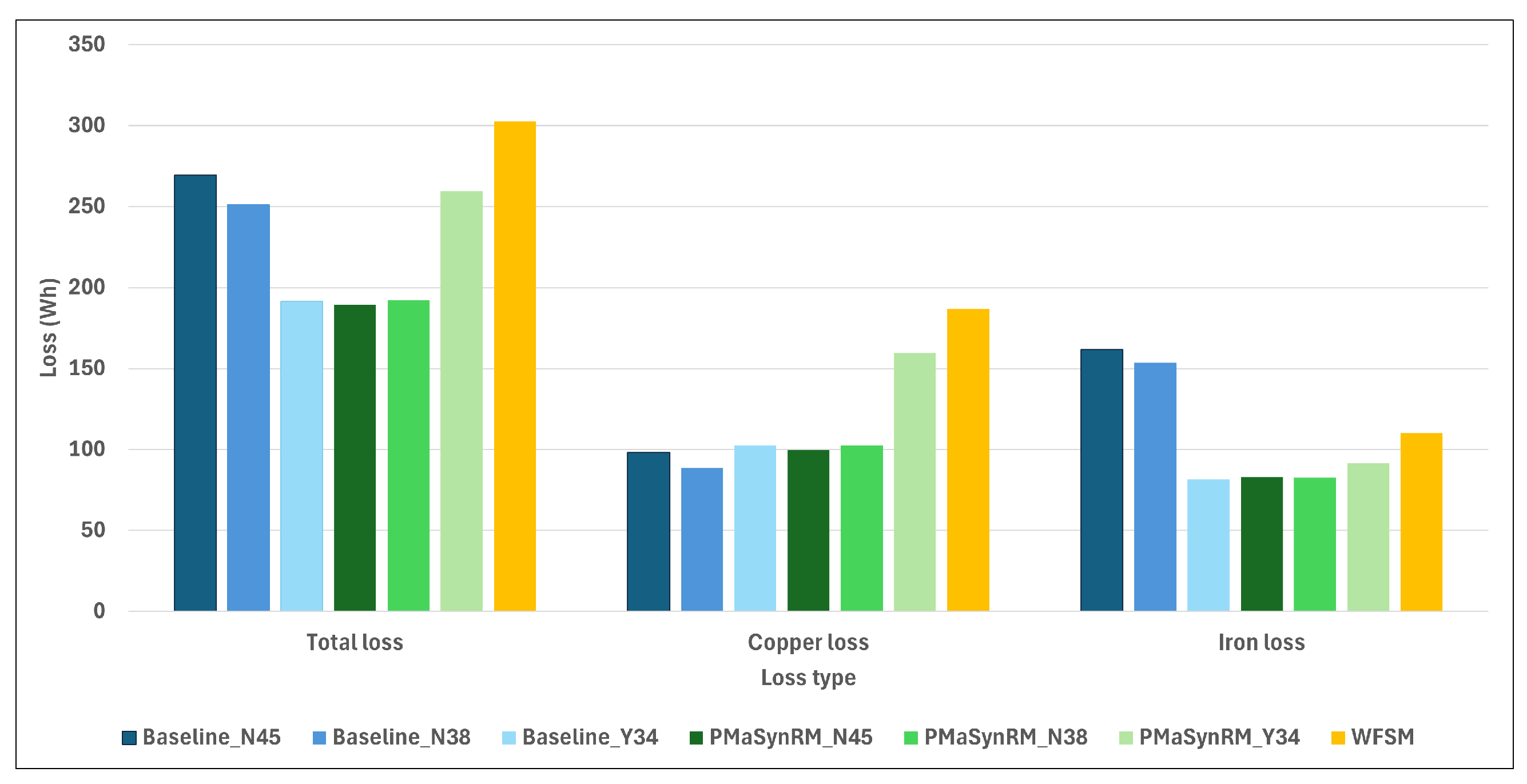
- During the WLTP Class 3 drive cycle, the WFSM incurred the highest losses at 302 Wh, but over the drive cycle, the baseline machine with N45UH magnets was inferior. NdFeB-based PMSMs had the highest iron loss but the lowest copper loss. The PMaSynRM with N45UH magnets and the reference PMSM with ferrites achieved the highest energy efficiency at 96.3% and 96.2%, respectively, with overall drive cycle efficiencies of 94.3% and 93.9%.
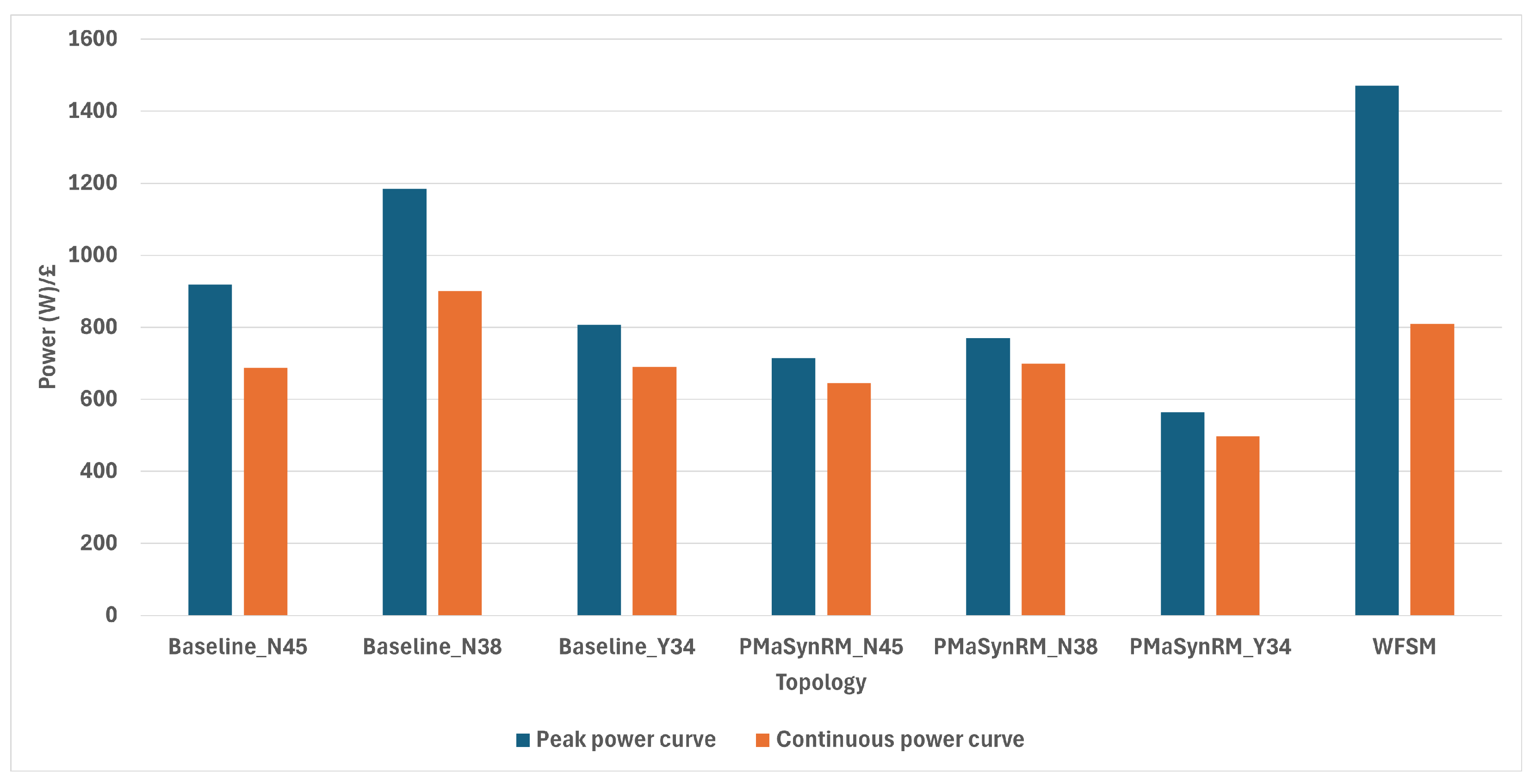
- The cost analysis revealed that the PMSM with N45UH magnets was the most expensive at GBP 447, the PMaSynRM at GBP 368, and the WFSM at GBP 220. The WFSM also offered the best peak performance value-for-money at ∑ 1.47 MW/GBP, while the reference PMSM had the highest continuous performance efficiency at ∑ 0.90 MW/GBP, compared to the lowest values for the PMaSynRM at ∑ 0.56 MW/GBP and ∑ 0.50 MW/GBP.
- The Pugh matrix analysis highlighted that, despite ongoing issues, the WFSM emerged as the most favourable overall solution for the machine variations simulated due to its cost-effectiveness and high-speed performance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PMSM | Permanent magnet synchronous machine |
| WFSM | Wound-field synchronous machine |
| AFM | Axial flux machine |
| SRM | Switched reluctance machines |
| RE | Rare-earth |
| HEV | Hybrid electric vehicle |
| EM | Electric machine |
| WPT | Wireless power transfer |
| GHG | Greenhouse gas |
| EV | Electric vehicle |
| ICE | Internal combustion engine |
| CPM | Consequent pole machine |
| CPSR | Constant power speed range |
| P | Power |
| Torque | |
| MGOe | Megagauss-Oersteds |
| NdFeB | Neodymium-iron-boron |
| Magnetic remanence | |
| MnBi | Manganese-bismuth |
| SmCo | Samarium-cobalt |
| Maximum energy product | |
| SmFeN | Samarium-iron-nitride |
| FeN | Iron-nitride |
| AlNiCo | Aluminum-Nickel-Cobalt |
| EOL | End-of-life |
| HD | Hydrogen decrepitation |
| OEM | Original equipment manufacturer |
| IPM | Interior permanent magnet |
| B-N45 | Baseline machine with N45UH neodymium magnets |
| B-N38 | Baseline machine with recycled (N45UH) neodymium magnets |
| B-Y34 | Baseline machine with Y34 ferrite magnets |
| P-N45 | Permanent magnet-assisted synchronous reluctance machine with N45UH neodymium magnets |
| P-N38 | Permanent magnet-assisted synchronous reluctance machine with recycled (N45UH) neodymium magnets |
| P-Y34 | Permanent magnet-assisted synchronous reluctance machine with Y34 ferrite magnets |
| CPC | Capacitive power coupler |
| ATF | Automatic transmission fluid |
| Torque | |
| SPM | Surface permanent magnet |
| PMaSynRM | Permanent magnet-assisted synchronous reluctance machine |
| PM | Permanent magnet |
Appendix A. Simulation Settings
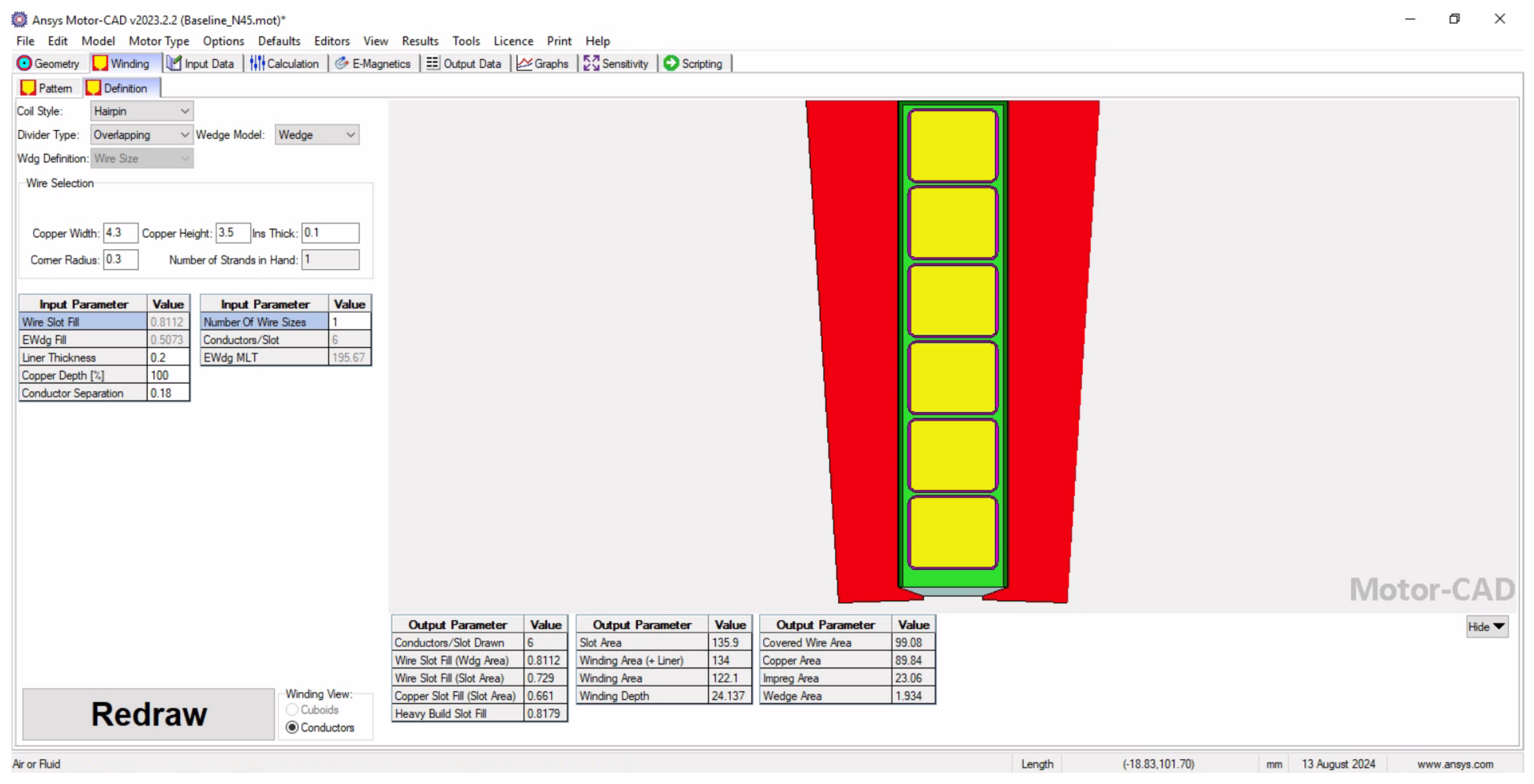
Appendix A.1. Hairpin Winding Setup


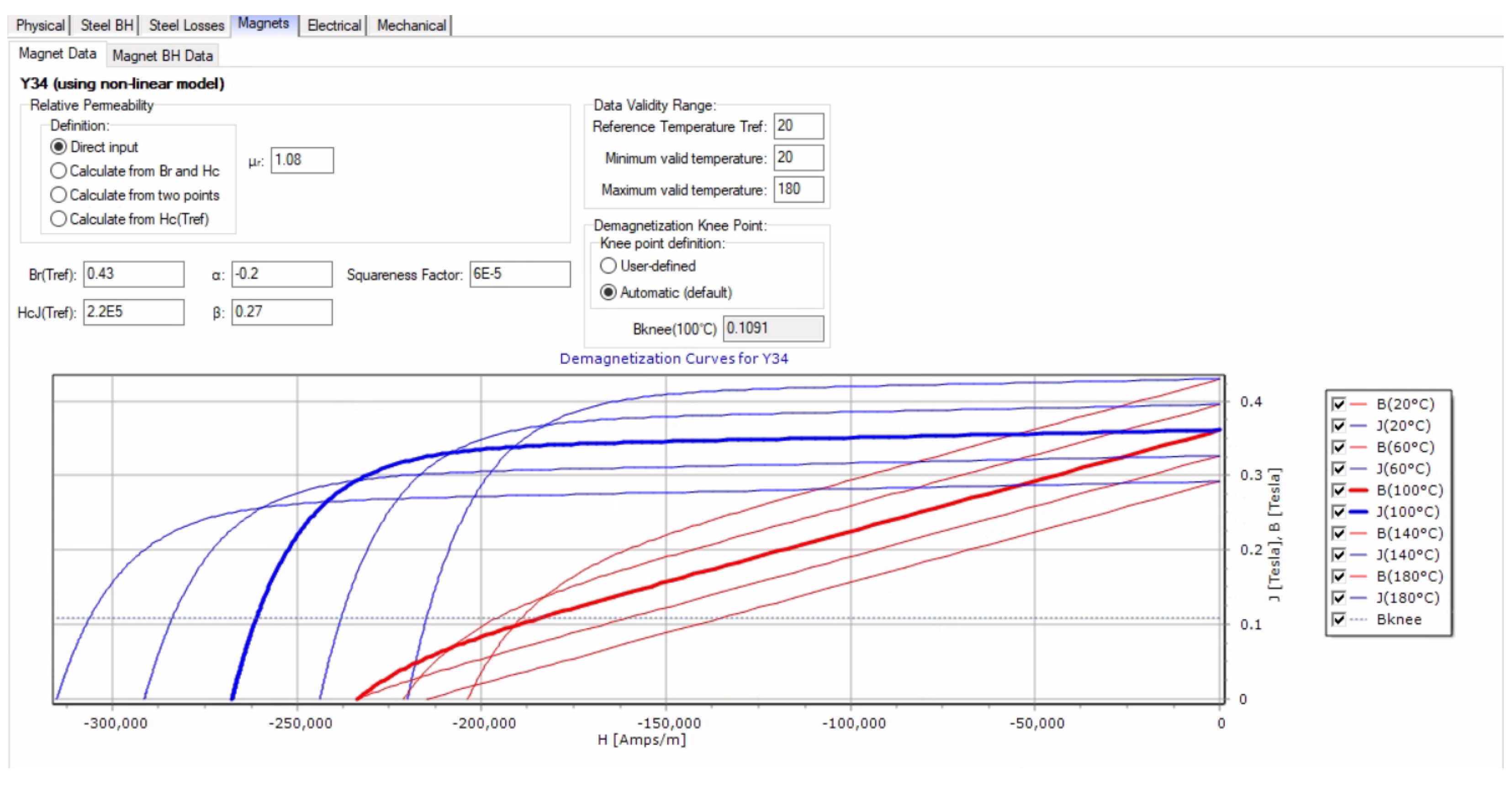
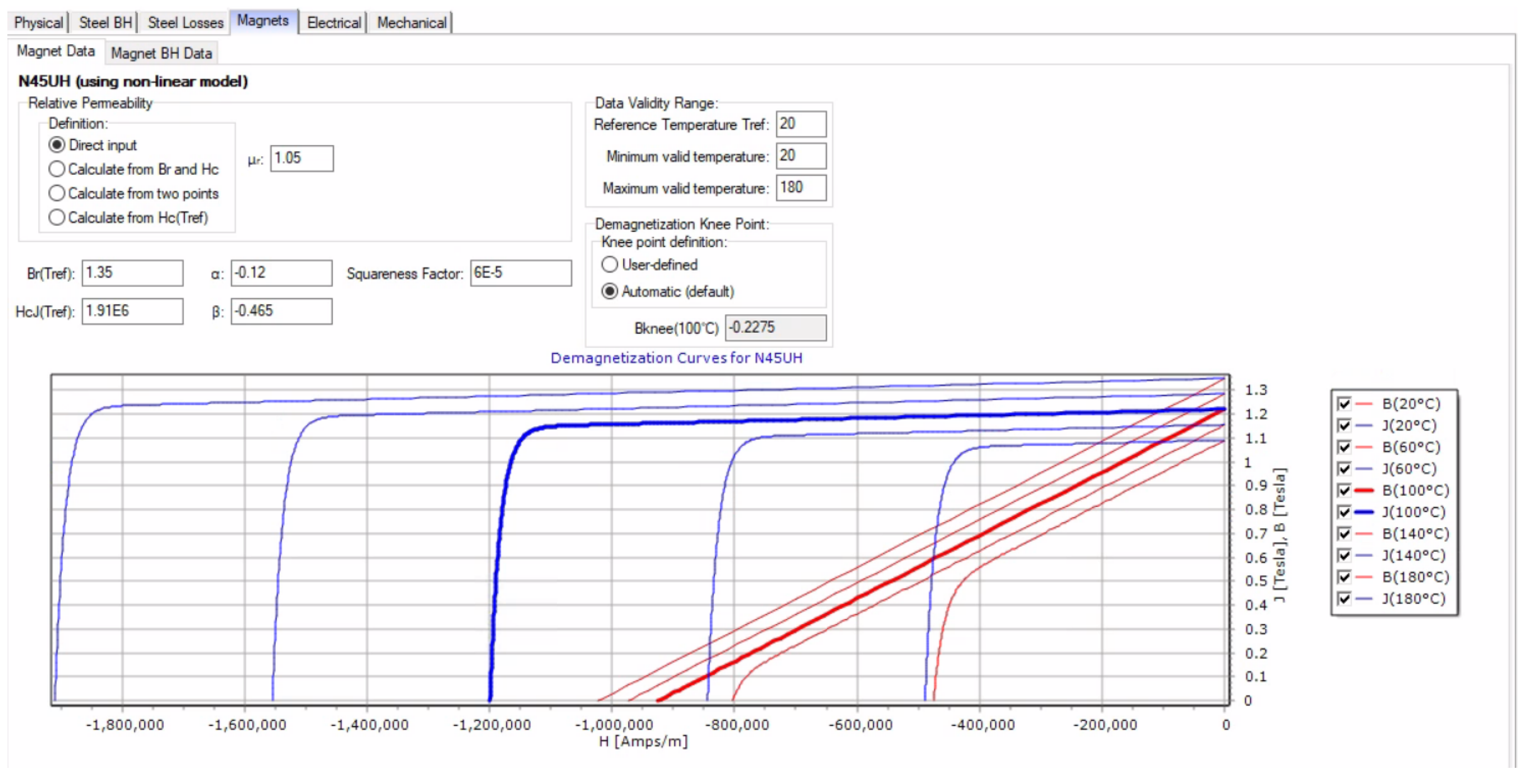
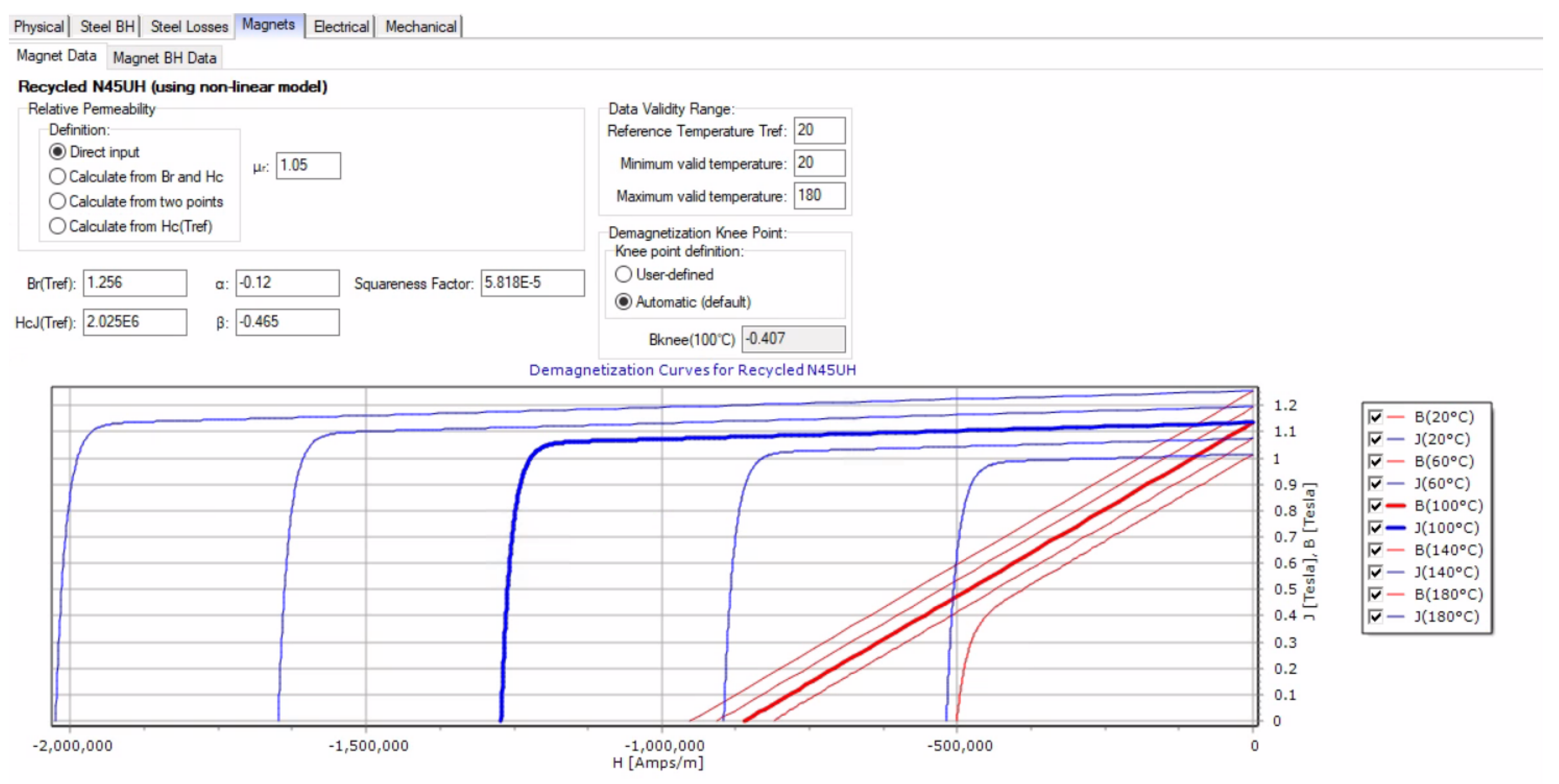
Appendix A.2. Magnet Data
References
- Poudel, B.; Amiri, E.; Rastgoufard, P.; Mirafzal, B. Toward Less Rare-Earth Permanent Magnet in Electric Machines: A Review. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 900119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Walton, A.; Sheridan, R.; Güth, K.; Gauß, R.; Gutfleisch, O.; Buchert, M.; Steenari, B.M.; Van Gerven, T.; Jones, P.T.; et al. REE recovery from end-of-life NdFeB permanent magnet scrap: A critical review. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 122–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. Distribution of Carbon Dioxide Emissions Worldwide in 2023, by Sector. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1129656/global-share-of-co2-emissions-from-fossil-fuel-and-cement/ (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- European Commision. Air. Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/air_en (accessed on 9 July 2024).
- Statista. Change in Average Temperature by Decade Worldwide from 1910 to 2019, by Region (in Degrees Celsius)*. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1062474/difference-temperature-decade-worldwide/ (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- SDM Magnets. PrNd Price Trend. Available online: https://www.magnet-sdm.com/prnd-price-trend/ (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- Statista. Breakdown of New Car Sales in the European Union in 2023, by Segment (in Million Vehicles). Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1413689/european-union-car-sales-distribution-by-segment/ (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Hioki, K. Development of High-Performance Hot-Deformed Neodymium–Iron–Boron Magnets without Heavy Rare-Earth Elements. Materials 2023, 16, 6581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IDTechEx. Electric Motors for Electric Vehicles 2024–2034. Available online: https://www.idtechex.com/en/research-report/electric-motors-for-electric-vehicles-2024-2034/941 (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- Bailey, G.; Mancheri, N.; Van Acker, K. Sustainability of permanent rare earth magnet motors in (H) EV industry. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 611–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advanced Propulsion Centre UK. Electric Machines. Available online: https://www.apcuk.co.uk/knowledge-base/resource/electric-machines-roadmap/ (accessed on 3 July 2024).
- Prosperi, D.; Bevan, A.; Ugalde, G.; Tudor, C.; Furlan, G.; Dove, S.; Lucia, P.; Zakotnik, M. Performance comparison of motors fitted with magnet-to-magnet recycled or conventionally manufactured sintered NdFeB. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 460, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimiabeigi, M.; Sheridan, R.S.; Widmer, J.D.; Walton, A.; Farr, M.; Scholes, B.; Harris, I.R. Production and Application of HPMS Recycled Bonded Permanent Magnets for a Traction Motor Application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 3795–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, G.; Nuzzo, S.; Zou, T.; Barater, D.; Franceschini, G.; Gerada, C. Review and future developments of wound field synchronous motors in automotive. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Electrical Systems for Aircraft, Railway, Ship Propulsion and Road Vehicles & International Transportation Electrification Conference (ESARS-ITEC), Venice, Italy, 29–31 March 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, W.; Kwon, J.W.; Kwon, B.I. Analytical Design of a Hybrid-Excited Wound Field Synchronous Machine for the Improvement of Torque Characteristics. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 87414–87421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.K.; Grainger, B.; McElhinny, S.; Brody, R.; Cui, J.; Sherman, A.; Ohodnicki, P. Multiphysics Design and Optimization of a Rare-Earth Free, Manganese Bismuth Based, Surface Mounted Permanent Magnet Machine. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference & Expo (ITEC), Detroit, MI, USA, 21–23 June 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rom, C.L.; Smaha, R.W.; O’Donnell, S.; Dugu, S.; Bauers, S.R. Emerging magnetic materials for electric vehicle drive motors. MRS Bull. 2024, 49, 738–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qarni, A.; El-Refaie, A. Optimum Rotor Design for Rare-Earth Free High Performance Traction Applications Interior Permanent Magnet Motors Enabled by Iron Nitride Permanent Magnet. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–18 May 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Nishio-Hamane, D. Production of Rare-Earth-Free Iron Nitride Magnets (a-Fe16N2). Metals 2024, 14, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keszler, M.; Grosswendt, F.; Assmann, A.C.; Krengel, M.; Maccari, F.; Gutfleisch, O.; Sebold, D.; Guillon, O.; Weber, S.; Bram, M. Direct Recycling of Hot-Deformed Nd–Fe–B Magnet Scrap by Field-Assisted Sintering Technology. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2024, 5, 2300184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J. Perspective and Prospects for Rare Earth Permanent Magnets. Engineering 2020, 6, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakelly, N.; Pérez-Cardona, J.R.; Pan, C.; Cui, J.; Sutherland, J.W. Techno-Economic Assessment of a Novel Continuous Hot-Roll Process for Manufacturing Nanograin NdFeB Magnets. Procedia CIRP 2024, 122, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnet Motion. HOT FORMED NdFeB MAGNETS (MQ3). Available online: https://magnetemotion.com/technology-mq3-ndfeb-extrusion.html (accessed on 5 July 2024).
- Sprecher, B.; Kleijn, R.; Kramer, G.J. Recycling potential of neodymium: The case of computer hard disk drives. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9506–9513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakotnik, M.; Harris, I.; Williams, A. Multiple recycling of NdFeB-type sintered magnets. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 469, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönfeldt, M.; Rohrmann, U.; Schreyer, P.; Hasan, M.; Opelt, K.; Gassmann, J.; Weidenkaff, A.; Gutfleisch, O. Magnetic and structural properties of multiple recycled and sustainable sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 939, 168709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, O.; Schönfeldt, M.; Brouwer, E.; Dirks, A.; Rachut, K.; Gassmann, J.; Güth, K.; Buckow, A.; Gauß, R.; Stauber, R.; et al. Towards an alloy recycling of Nd–Fe–B permanent magnets in a circular economy. J. Sustain. Metall. 2018, 4, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.; Drury, B. Electric Motors and Drives: Fundamentals, Types and Applications; Newnes: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Mahmoudi, A.; Kahourzade, S.; Soong, W.L. An Overview of Electric Motors for Electric Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2021 31st Australasian Universities Power Engineering Conference (AUPEC), Perth, Australia, 26–30 September 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agamloh, E.; von Jouanne, A.; Yokochi, A. An Overview of Electric Machine Trends in Modern Electric Vehicles. Machines 2020, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krings, A.; Monissen, C. Review and Trends in Electric Traction Motors for Battery Electric and Hybrid Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Gothenburg, Sweden, 23–26 August 2020; Volume 1, pp. 1807–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Husson, H.; Garbuio, L.; Gerbaud, L. Comparative study of the Tesla Model S and Audi e-Tron Induction Motors. In Proceedings of the 2021 17th Conference on Electrical Machines, Drives and Power Systems (ELMA), Sofia, Bulgaria, 1–4 July 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Credo, A.; Fabri, G.; Villani, M.; Popescu, M. Adopting the Topology Optimization in the Design of High-Speed Synchronous Reluctance Motors for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 5429–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Benomar, Y.; Deepak, K.; Aksoz, A.; Baghdadi, M.E.; Bostanci, E.; Hegazy, O. Switched Reluctance Motors and Drive Systems for Electric Vehicle Powertrains: State of the Art Analysis and Future Trends. Energies 2021, 14, 2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, A.; Kiyota, K.; Hoshi, N.; Takemoto, M.; Ogasawara, S. Development of a Rare-Earth-Free SR Motor with High Torque Density for Hybrid Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogusz, P.; Korkosz, M.; Prokop, J.; Daraż, M. Analysis Performance of SRM Based on the Novel Dependent Torque Control Method. Energies 2021, 14, 8203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Frikha, M.A.; Croonen, J.; Benômar, Y.; El Baghdadi, M.; Hegazy, O. Design Optimization of a Switched Reluctance Machine with an Improved Segmental Rotor for Electric Vehicle Applications. Energies 2022, 15, 5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, T.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, D.H.; Ahn, J.W. A Review on Segmented Switched Reluctance Motors. Energies 2022, 15, 9212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasian, M.; Moallem, M.; Fahimi, B. Double-stator switched reluctance machines (DSSRM): Fundamentals and magnetic force analysis. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazi, M.A.; Abbasian, M.; Gerling, D. Preliminary Evaluation of Induction Switched Reluctance Machine (ISRM) for Electric Vehicle Application. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 26693–26701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J. Investigation and Development of the Brushless and Magnetless Wound Field Synchronous Motor Drive System for Electric Vehicle Application. World Electr. Veh. J. 2023, 14, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tang, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, B.; Boscaglia, L. Electromagnetic Performance Investigation of A Brushless Electrically-Excited Synchronous Machine for Long-Distance Heavy-Duty Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 11, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancu, C.; Ward, T.; Rahman, K.M.; Dawsey, R.; Savagian, P. Separately Excited Synchronous Motor With Rotary Transformer for Hybrid Vehicle Application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludois, D.C.; Reed, J.K.; Hanson, K. Capacitive Power Transfer for Rotor Field Current in Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 4638–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raminosoa, T.; Wiles, R. Contactless Rotor Excitation for Traction Motors. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Portland, OR, USA, 23–27 September 2018; pp. 6448–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallows, D.; Nuzzo, S.; Galea, M. Exciterless Wound-Field Medium-Power Synchronous Machines: Their History and Future. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2022, 16, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, G.; Vagati, A.; Boazzo, B.; Guglielmi, P. Comparison of Induction and PM Synchronous Motor Drives for EV Application Including Design Examples. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 2322–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.A.; Hsieh, M.F. Comparative Study of PM-Assisted SynRM and IPMSM on Constant Power Speed Range for EV Applications. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 8211006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artetxe, G.; Caballero, D.; Prieto, B.; Martinez-Iturralde, M.; Elosegui, I. Eliminating rare earth permanent magnets on low-speed high-torque machines: A performance and cost comparison of synchronous reluctance machines, ferrite permanent magnet-synchronous reluctance machines and permanent magnet synchronous machines for a direct-drive elevator system. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2021, 15, 370–378. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Zhu, X.; Xiang, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Lee, C.H. Technology trends, challenges, and opportunities of reduced-rare-earth PM motor for modern electric vehicles. Green Energy Intell. Transp. 2022, 1, 100012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajini, V.; Nagarajan, V.; Bharath Kumar, S.; Barathkumar, M.; Balaji, R.; Manojshyaam, C. Comparative analysis of Synchronous Reluctance Motor with different Permanent Magnet materials. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Ouyang, X.; Chen, W. Characteristic analysis of conventional pole and consequent pole IPMSM for electric vehicle application. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Yan, L.; Jewell, G.W.; Gan, C.; Ren, Y.; Brockway, S.; Hilton, C. Effect of Pole Shaping on Torque Characteristics of Consequent Pole PM Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 3511–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Song, Z.; Zhao, H.; Liu, C. Overview of Axial-Flux Machines and Modeling Methods. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 8, 2118–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, D.J.; Colton, J.L.; Mularcik, B.; Kennedy, B.J.; Camilleri, S.; Rohoza, R. A comparison of radial and axial flux structures in electrical machines. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference, Miami, FL, USA, 3–6 May 2009; pp. 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Li, Q.; Sun, L.; Li, L. Development and Investigation of Novel Axial-Field Dual-Rotor Segmented Switched Reluctance Machine. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, T.; Zhu, X.; Fan, D.; Wang, Q. Analysis and Design of a New Type of Less-Rare-Earth Hybrid-Magnet Motor with Different Rotor Topologies. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2020, 30, 5200406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.; von Lindenfels, J.; Mayr, A.; Franke, J. Manufacturing Imperfections in Electric Motor Production with Focus on Halbach Array Permanent Magnet Rotor Assembly. In Proceedings of the 2018 8th International Electric Drives Production Conference (EDPC), Schweinfurt, Germany, 4–5 December 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graffeo, F.; Stiscia, O.; Vaschetto, S.; Cavagnino, A.; Tenconi, A. Doubly Excitated Synchronous Machines for Traction Applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 30th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Kyoto, Japan, 20–23 June 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, J.; Maktobian, M. Performance Enhancement of Flux Switching Motor for Electric Vehicle Applications: An Overview. IET Electr. Syst. Transp. 2024, 2024, 9071667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coteț, F.A.; Văscan, I.; Szabó, L. On the usefulness of employing ANSYS Motor-CAD software in designing permanent magnet synchronous machines. Designs 2023, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansys Motor-CAD. Integrated Multiphysics Analysis Software for Electric Motor Design. Available online: https://www.ansys.com/content/dam/product/electronics/motor-cad/ansys-motor-cad-brochure.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Park, H.J.; Lim, M.S. Design of High Power Density and High Efficiency Wound-Field Synchronous Motor for Electric Vehicle Traction. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 46677–46685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimiabeigi, M.; Widmer, J.D.; Long, R.; Gao, Y.; Goss, J.; Martin, R.; Lisle, T.; Soler Vizan, J.M.; Michaelides, A.; Mecrow, B. High-Performance Low-Cost Electric Motor for Electric Vehicles Using Ferrite Magnets. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold Magnet Technologies. N45UH. Sintered Neodymium-Iron-Boron Magnets. Available online: https://www.arnoldmagnetics.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/N45UH-151021.pdf (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- Arnold Magnet Technologies. N38UH. Sintered Neodymium-Iron-Boron Magnets. Available online: https://www.arnoldmagnetics.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/N38UH-151021.pdf (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, W.; McLoone, S.; Morrow, J. Design and Flux-Weakening Control of an Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Jia, Y.; Soong, W.L. Comparison of Five Topologies for an Interior Permanent-Magnet Machine for a Hybrid Electric Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 3606–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Zhang, M. The Loss and Efficiency Analysis and Research of Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors for Traction Applications. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 5538–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, A.; Brown, I.P.; Nie, Y.; Knippel, R.; Ludois, D.C.; Dai, J.; Hagen, S.; Alteheld, C. Design and Demonstration of a Wound Field Synchronous Machine for Electric Vehicle Traction With Brushless Capacitive Field Excitation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 1390–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, J. Performance Analysis of Electric Motor Technologies for an Electric Vehicle Powertrain; White Paper; Motor Design Ltd.: Wrexham, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Zhou, L.; Soulard, J.; Silvester, B.; Davis, C. Quantitative characterisation and modelling of the effect of cut edge damage on the magnetic properties in NGO electrical steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 551, 169185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.R.; Kim, D.M.; Jung, Y.H.; Lim, M.S. High energy efficiency oriented-control and design of WFSM based on driving condition of electric vehicle. Mechatronics 2022, 81, 102696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Soulard, J. Design procedure of 48v in-wheel outer rotor spms for fully electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives (PEMD 2020), Online Conference, 5–17 December 2020; IET: London, UK, 2020; Volume 2020, pp. 128–133. [Google Scholar]
- Sumega, M.; Zoššák, S.; Varecha, P.; Rafajdus, P. Sources of torque ripple and their influence in BLDC motor drives. Transp. Res. Procedia 2019, 40, 519–526, TRANSCOM 2019 13th International Scientific Conference on Sustainable, Modern and Safe Transport. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trading Economics. Steel. Available online: https://tradingeconomics.com/commodity/steel (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Ma, X.Y.; Soulard, J.; Slater, C.; Davis, C. Influence of Electrical Steel Grade on Different Types of Traction Motors. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Valencia, Spain, 5–8 September 2022; pp. 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trading Economics. Copper. Available online: https://tradingeconomics.com/commodity/copper (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Ma, Q.; El-Refaie, A.; Lequesne, B. Low-Cost Interior Permanent Magnet Machine with Multiple Magnet Types. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 1452–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakht, V.; Dmitrievskii, V.; Kazakbaev, V.; Ibrahim, M.N. Comparison between rare-earth and ferrite permanent magnet flux-switching generators for gearless wind turbines. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1365–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, M.S.; Ocak, C.; Dalcalı, A. Permanent Magnet Wind Generators: Neodymium vs. Ferrite Magnets. In Proceedings of the 2021 3rd International Congress on Human-Computer Interaction, Optimization and Robotic Applications (HORA), Ankara, Turkey, 11–13 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.Q.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Chen, J.T. Simplified Analytical Optimization and Comparison of Torque Densities Between Electrically Excited and Permanent-Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 5000–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-ani, M.; Walker, A.; Vakil, G.; Gerada, D.; Gerada, C.; Paciura, K. Modifications to PM-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machine to Achieve Rare-Earth Free Heavy-Duty Traction. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2023, 11, 2029–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Yuzawa, N. Effect of coercive force and characteristics of a pole changing permanent magnet motor for variable-speed drive. In Proceedings of the 2014 16th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Lappeenranta, Finland, 26–28 August 2014; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perigo, E.A.; Takiishi, H.; Motta, C.C.; Faria, R.N. On the Squareness Factor Behavior of RE-FeB (RE = Nd or Pr) Magnets Above Room Temperature. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 4431–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Zhang, G.; Li, H.; Hu, C. Comprehensive Comparative Study on Permanent-Magnet-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Motors and Other Types of Motor. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafaq, M.S.; Midgley, W.; Steffen, T. A Review of the State of the Art of Torque Ripple Minimization Techniques for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönfeldt, M.; Opelt, K.; Hasan, M.; Gröninger, M.; Jahnke, D.; Gassmann, J.; Gutfleisch, O. Functional Recycling and Reuse of Nd–Fe–B Permanent Magnets from Various Waste Streams for a more Sustainable and Resilient Electromobility. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2025, 27, 2402815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.A.; Hsieh, M.F.; Shih, K.J.; Kuo, H.F. An Investigation Into the Effect of PM Arrangements on PMa-SynRM Performance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 5856–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonova, O.; Malygin, I.; Plastun, A. Electromagnetic calculation for induction motors of various designs by ANSYS maxwell. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Industrial Engineering, Applications and Manufacturing (ICIEAM), St. Petersburg, Russia, 16–19 May 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- München, D.D.; Veit, H.M. Neodymium as the main feature of permanent magnets from hard disk drives (HDDs). Waste Manag. 2017, 61, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.C.; Chien, C.L.; Chen, M.C.; Liu, C.S.; Lee, C.P. Effect of Magnetic Alignment and Magnetic Field Molding on Magnetic Properties of C-Shape Anisotropic Sr-Hexaferrites Permanent Magnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2024, 60, 2100108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, S.; Silva, M.D. Comparison of Simulation Methods for Angular Dependency When Modeling Demagnetization. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Magnetic Conference (INTERMAG), Sendai, Japan, 15–19 May 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Tavernini, D.; Hartavi Karci, A.E.; Sorniotti, A. Design and optimisation of energy-efficient PM-assisted synchronous reluctance machines for electric vehicles. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2023, 17, 788–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z. Multi-physics and multi-objective optimisation design of interior permanent magnet synchronous motor for electric vehicles. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2020, 14, 2243–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Magnet Material | Material Properties | Practical Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Recycled NdFeB | + Higher Coercivity | + Propensity to be cheaper |
| − Small reduction in , , and squareness factor | − High-volume recycling methods unproven | |
| Polymer-bonded NdFeB | + Less brittle and isotropic | + Complex net-shapes possible |
| − Sizeable drop in , and lowered coercivity | − Less mainstream option means costlier | |
| Hot-formed NdFeB | + Less Brittle, better corrosion resistance and similar | + No heavy-RE additions |
| − Small drop in energy product | − Less mainstream option means costlier | |
| Iron nitride (FeN) | + Much higher theoretical and | + Abundant non-RE materials |
| − Lower coercivity and phase instability | − Synthesis challenges = lower (actual) energy product | |
| Manganese Bismuth (MnBi) | + Coercivity increases with temperature | + RE-free |
| − Low and moderate | − Poor oxidative stability and still experimental | |
| Samarium Iron Nitride (SmFeN) | + Better demagnetisation resilience at (very) high temperatures, better corrosion resistance | + Abundant and lower demand |
| − Moderate | − Thermal instability during manufacture and contains Samarium (RE) |
| Machine Topology | Machine Performance | Practical Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| PMaSynRM | + Less susceptible to demagnetisation | + Less RE-magnet usage and cost |
| − Lower power/torque density, | − Heavier and weaker mechanical robustness | |
| IM | + Self-starting and reliable | + Low maintenance, cost-effective and no PMs |
| − Lower efficiency and torque/power density | − Complex control methods | |
| WFSM | + Wide CPSR, fault tolerance, good power/torque density | + No PMs and cost-effective |
| − Poor efficiency at low-medium speeds | − Exciter complexity and maintenance | |
| SynRM | + High reluctance torque, low torque ripple | + Low cost |
| − Poor power/torque density and narrow CPSR | − Weak mechanical robustness | |
| Novel SRMs 1 | + High efficiency and torque density | + Prototypes demonstrate feasibility |
| − Torque ripple at low torque demands (ISRM) | − Complex manufacturing and scalability unclear | |
| Hybrid Excitation 2 | + High torque density and potential for wide CPSR | + Reduced PM usage |
| − Moderate efficiency | − Complex magnetic circuit and manufacturing | |
| FSMs | + High efficiency, torque density and wide CPSR | + Simple rotor design |
| − Lower power factor | − High stator complexity and limited research status | |
| CPMs | + Nearly equivalent torque production to PMSm | + Lowered PM usage |
| − Weak induced poles | − Limited research status | |
| AFMs | + Very high torque/power density and high efficiency | + Flat, compact structure |
| − High cogging torque | − Propensity for PM reduction unclear and complex manufacturing |
| Property | N45UH | Effect (Applied %) | Recycled N45UH | N38UH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy product (MGOe) | 45 | −14.9 | 38.3 | 38.0 |
| Density (kg/m3) | 7600 | −2.9 | 7380 | 7600 |
| Magnetic remanence (T) | 1.35 | −6.5 | 1.26 | 1.26 |
| Intrinsic coercivity (kA/m) | 1910 | +6.2 | 2028 | 1990 |
| Squareness factor | −3.0 |
| Attribute | B-N45 | B-N38 | B-Y34 | P-N45 | P-N38 | P-Y34 | WFSM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass (kg) | 34.8 | 36.1 | 57.4 | 49.3 | 50.5 | 62.1 | 41.8 |
| Volume (m3) | |||||||
| Grav. density (Nm/kg) | 11.5 | 11.1 | 7.0 | 8.1 | 7.9 | 6.4 | 9.6 |
| Vol. density (Nm/L) | 94.5 | 91.4 | 52.0 | 59.4 | 57.8 | 45.5 | 70.3 |
| Attribute | B-N45 | B-N38 | B-Y34 | P-N45 | P-N38 | P-Y34 | WFSM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak stress (MPa) | 186 | 185 | 173 | 352 | 351 | 329 | 570 |
| Average stress (MPa) | 43.9 | 43.5 | 39.5 | 27.1 | 27.0 | 26.3 | 68.6 |
| Peak displacement (mm) | 0.022 | 0.022 | 0.020 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.024 | 0.029 |
| Average displacement (mm) | 0.020 | 0.020 | 0.019 | 0.022 | 0.022 | 0.022 | 0.022 |
| Safety factor | 2.39 | 2.40 | 2.57 | 1.26 | 1.27 | 1.35 | 0.76 |
| Attribute | B-N45 | B-N38 | B-Y34 | P-N45 | P-N38 | P-Y34 | WFSM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-torque (Nm) | 399 | 383 | 222 | 293 | 289 | 253 | - |
| Post-Torque (Nm) | 244 | 277 | 151 | 288 | 288 | 217 | - |
| Change (%) | −39 | −28 | −32 | −1.7 | −0.3 | −14.2 | 0 |
| Machine Component | Material | Cost (GBP/kg) | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotor | N018-1160 | 2.50 | [74,76] |
| Stator | N018-1160 | 2.50 | [74,76] |
| Electrical steel scrap | N018-1160 | 0.25 | [74] |
| Winding | Copper (Pure) | 12.30 | [74,78] |
| Shaft | Stahl 37 | 1.21 | [74,76] |
| Magnets | N45UH, recycled N45UH, ferrites | 130, 75, 8 | [6,27,74,79,80,81] |
| Parameter | B-N45 | B-N38 | B-Y34 | P-N45 | P-N38 | P-Y34 | WFSM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stack Length (mm) | 86.2 | 89.2 | 156.7 | 137.1 | 141.1 | 179.2 | 115.9 |
| Base speed (rpm) | 5200 | 5200 | 3000 | 3200 | 3000 | 2400 | 3800 |
| Grav. density (Nm/kg) | 11.5 | 11.1 | 7.0 | 8.1 | 7.9 | 6.4 | 9.6 |
| Vol. density (Nm/L) | 94.5 | 91.4 | 52.0 | 59.4 | 57.8 | 45.5 | 70.3 |
| Torque ripple (%) | 7.7 | 7.4 | 9.4 | 4.6 | 4.8 | 7.7 | 5.5 |
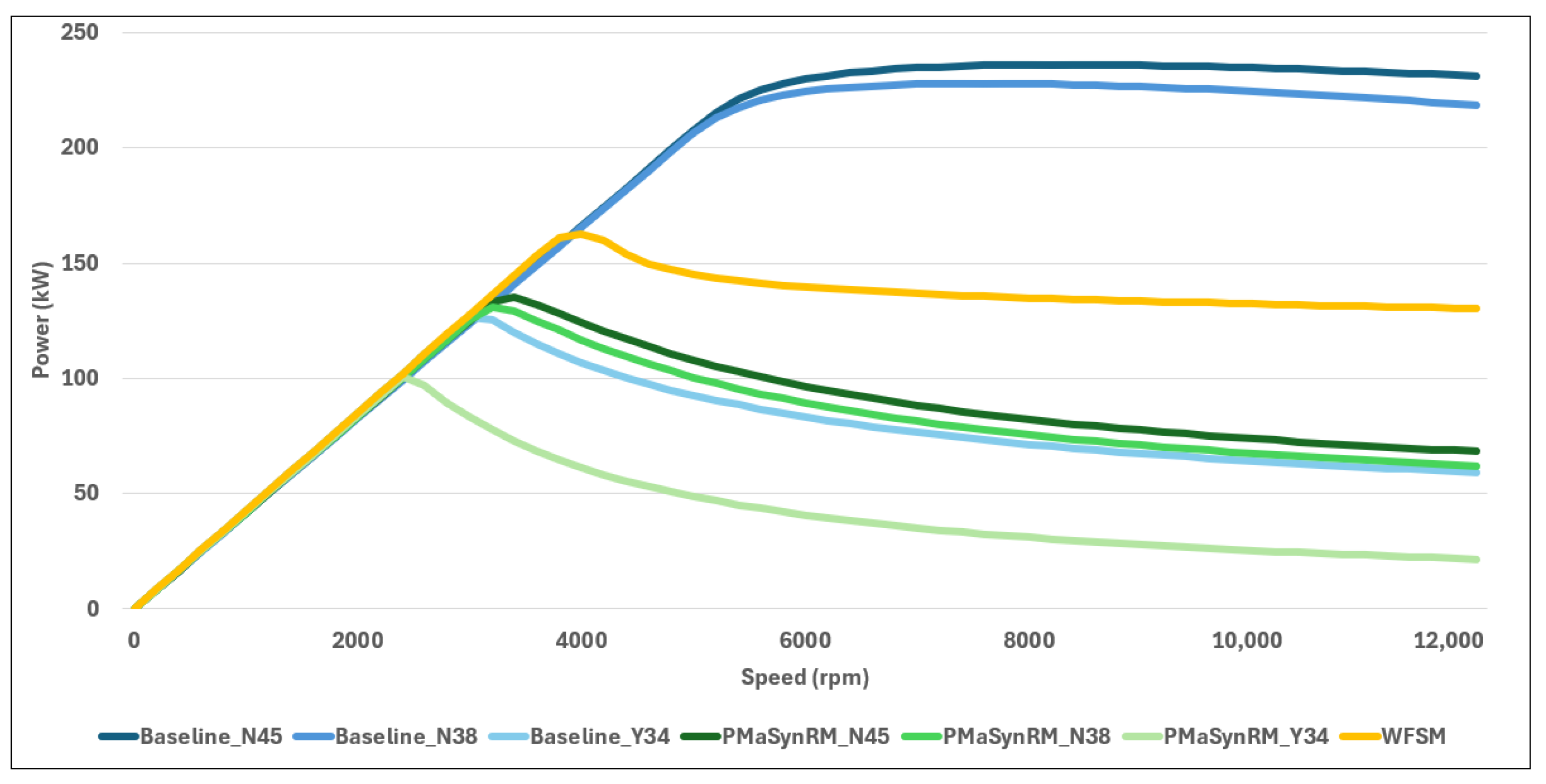
| Peak power (kW) | 236 | 228 | 126 | 135 | 131 | 102 | 162 |
| ∑ peak curve (MW) | 410 | 403 | 248 | 263 | 254 | 183 | 323 |
| ∑ cont. curve (MW) | 307 | 306 | 212 | 238 | 230 | 162 | 178 |
| Reluctance torque (Nm) | 180 | 187 | 250 | 307 | 313 | 348 | 0 |
| Efficiency (% use) | 91.73 | 95.08 | 96.24 | 96.27 | 96.21 | 94.80 | 93.36 |
| Efficiency (% drive) | 91.26 | 91.60 | 94.33 | 93.94 | 93.93 | 93.21 | 91.54 |
| Peak advance angle | 45° | 45° | 40° | 50° | 50° | 45° | 0° |
| Peak stress (MPa) | 186 | 185 | 173 | 352 | 351 | 329 | 570 |
| Peak displacement (mm) | 0.022 | 0.022 | 0.020 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.024 | 0.029 |
| Demagnetisation (%) | −39 | −28 | −32 | −1.7 | −0.3 | −14.2 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, O.M.; Abbasian, M. Reducing Rare-Earth Magnet Reliance in Modern Traction Electric Machines. Energies 2025, 18, 2274. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092274
Lee OM, Abbasian M. Reducing Rare-Earth Magnet Reliance in Modern Traction Electric Machines. Energies. 2025; 18(9):2274. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092274
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Oliver Mitchell, and Mohammadali Abbasian. 2025. "Reducing Rare-Earth Magnet Reliance in Modern Traction Electric Machines" Energies 18, no. 9: 2274. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092274
APA StyleLee, O. M., & Abbasian, M. (2025). Reducing Rare-Earth Magnet Reliance in Modern Traction Electric Machines. Energies, 18(9), 2274. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092274







