The Feasibility of Heat Extraction Using CO2 in the Carbonate Reservoir in Shandong Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
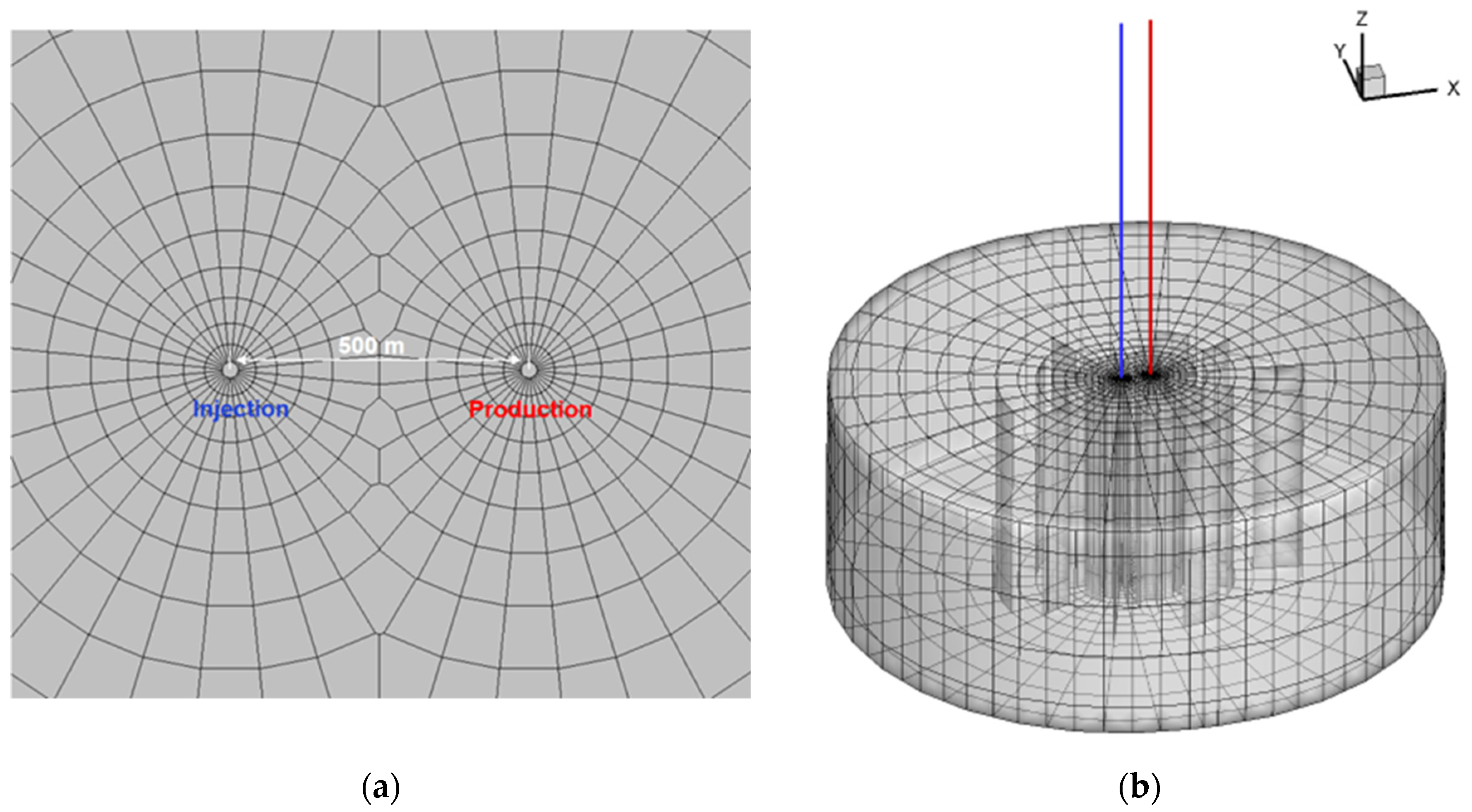
2. Model Setup
2.1. Geological Setting
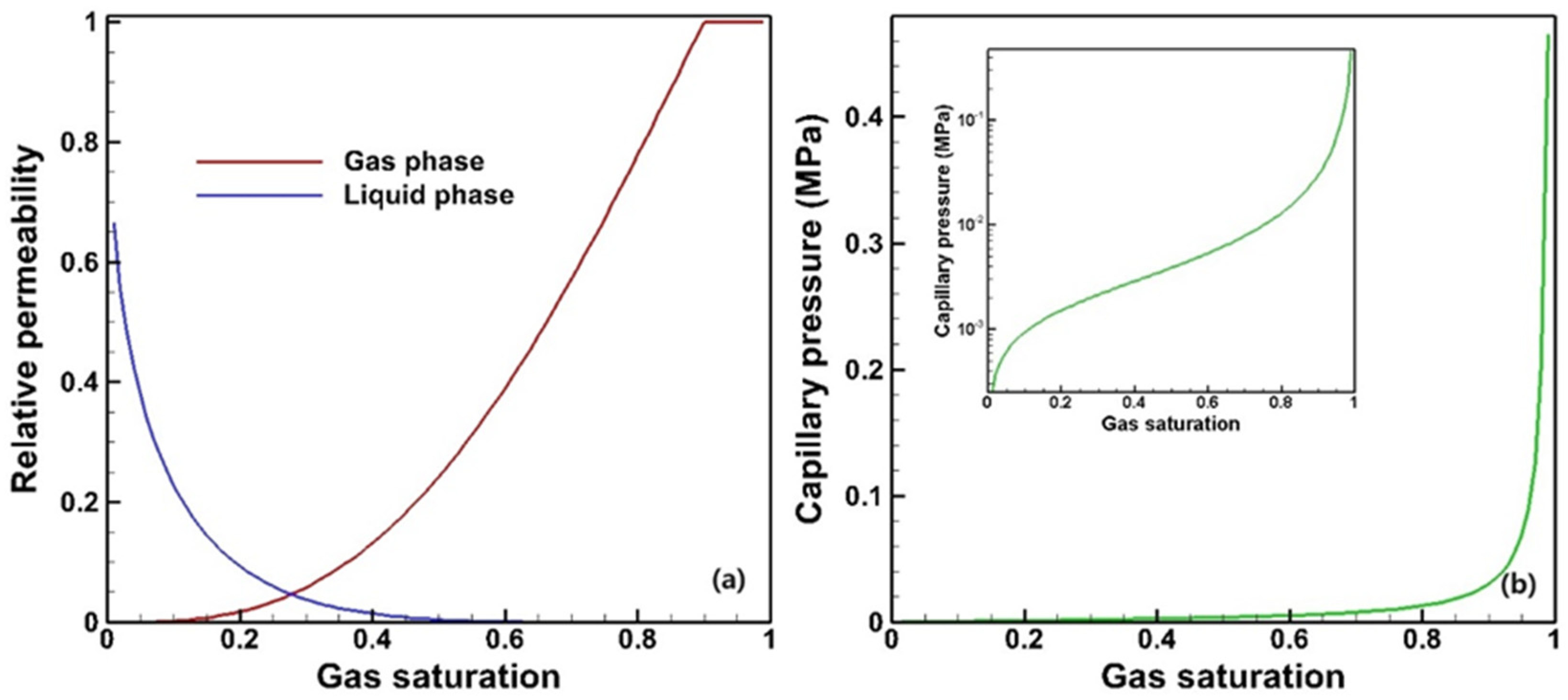
2.2. Parameters Configuration
2.3. Simulation Approach
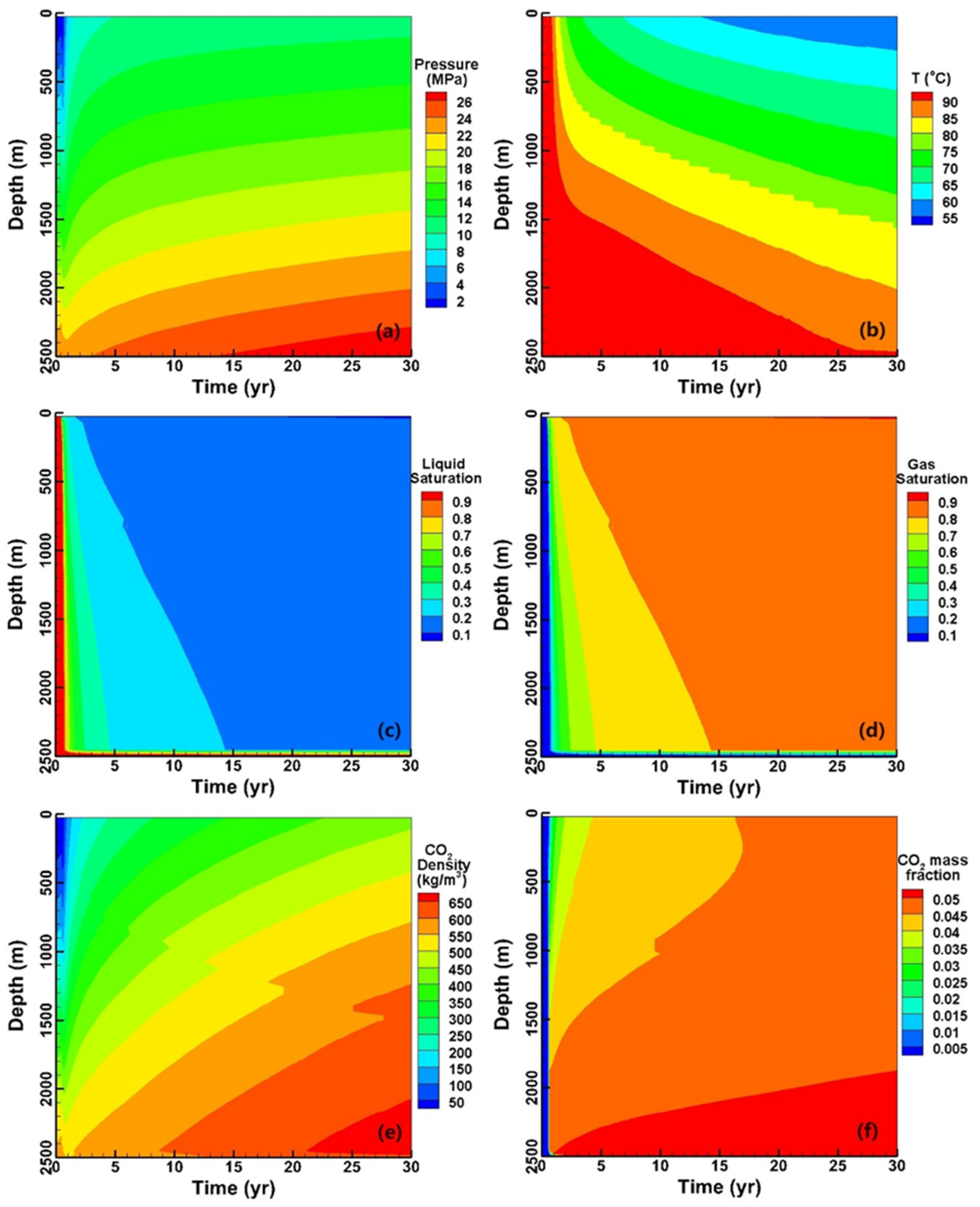
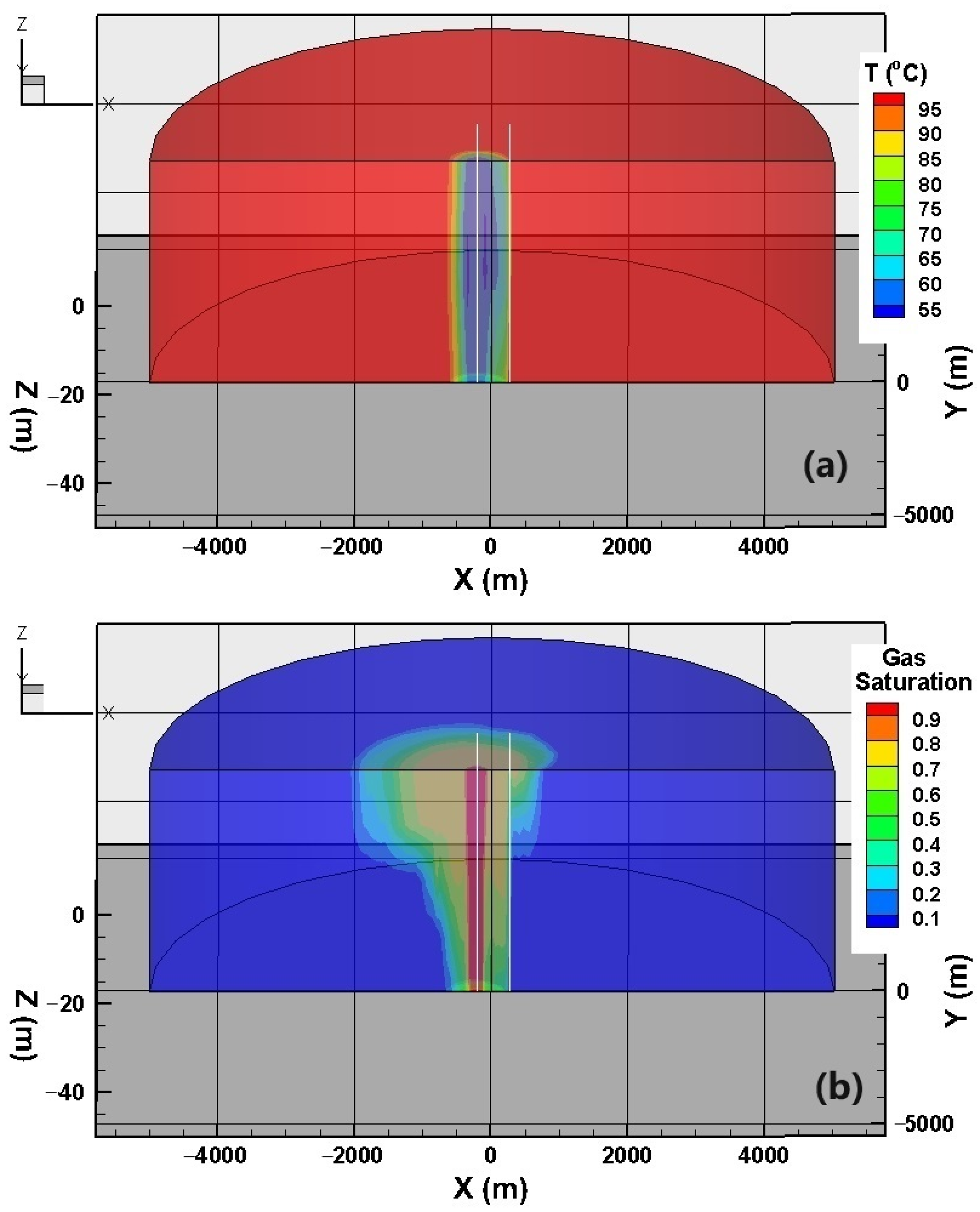
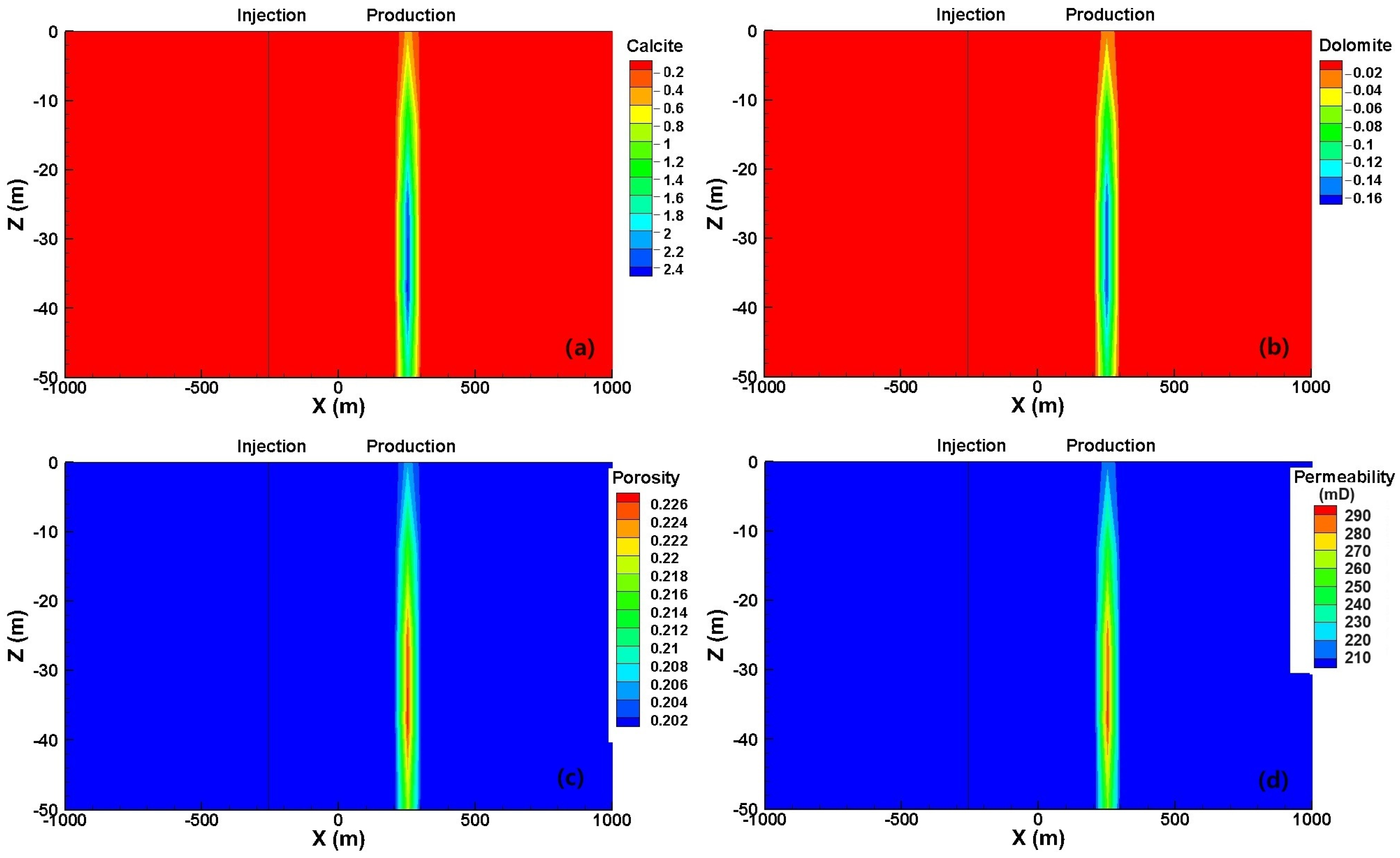
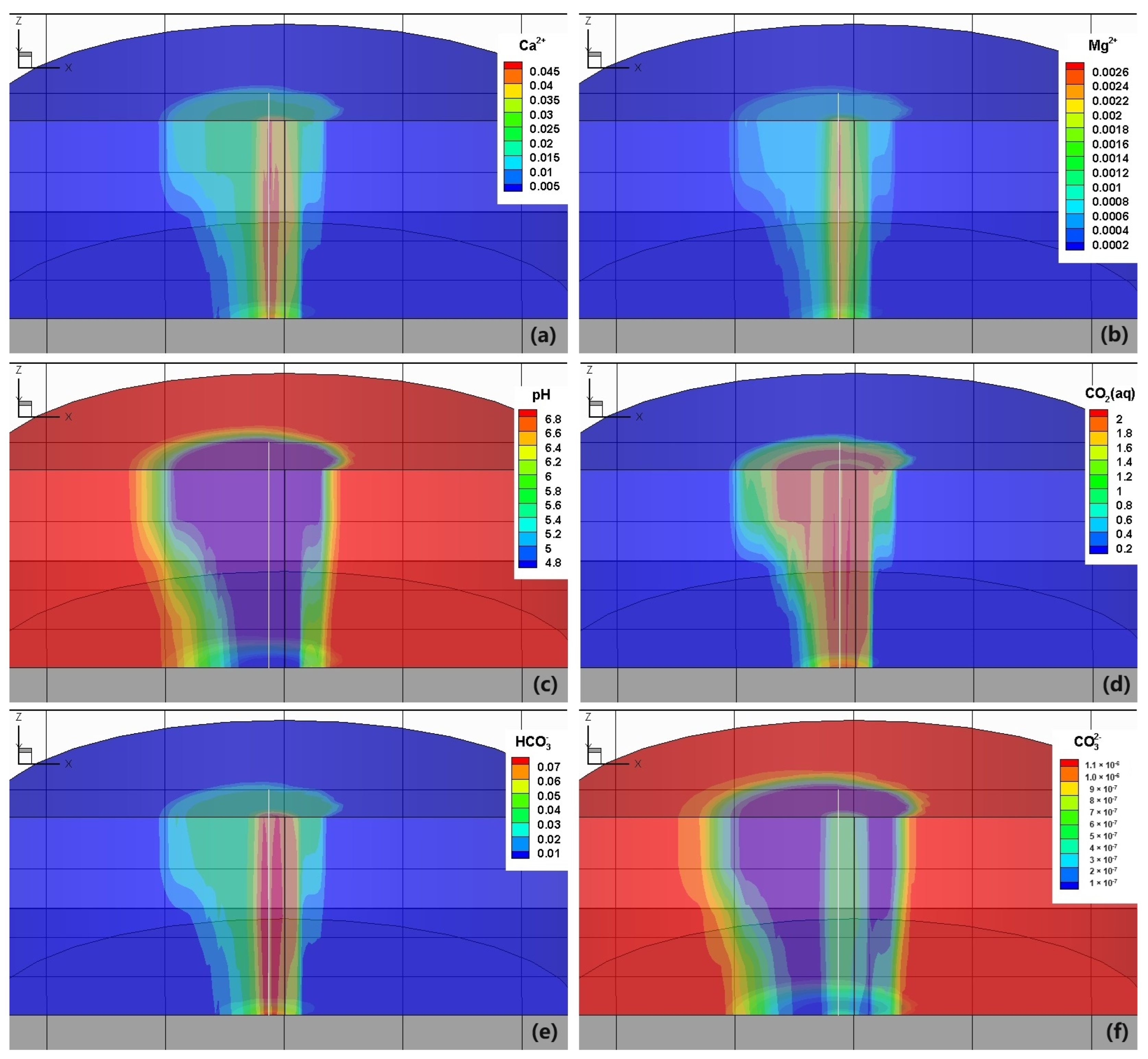
3. Results and Discussion
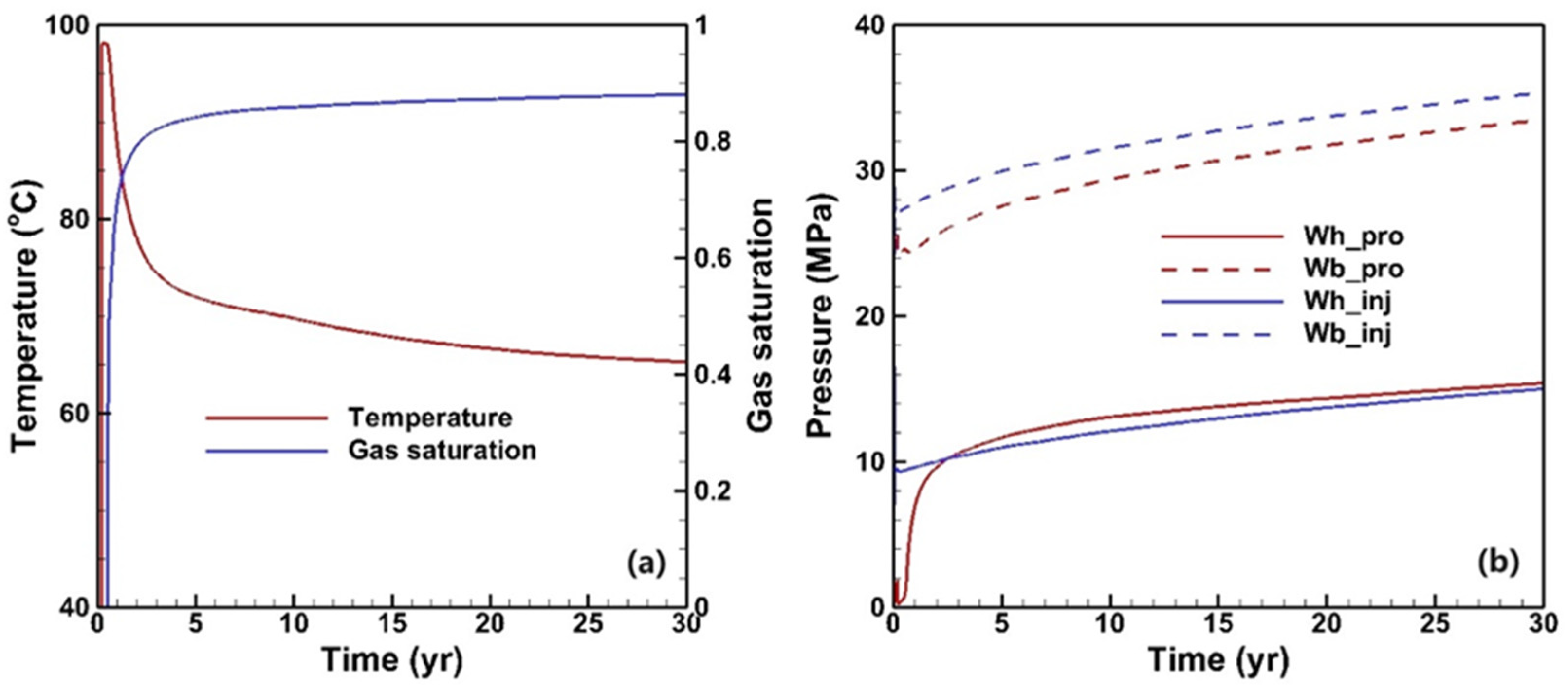
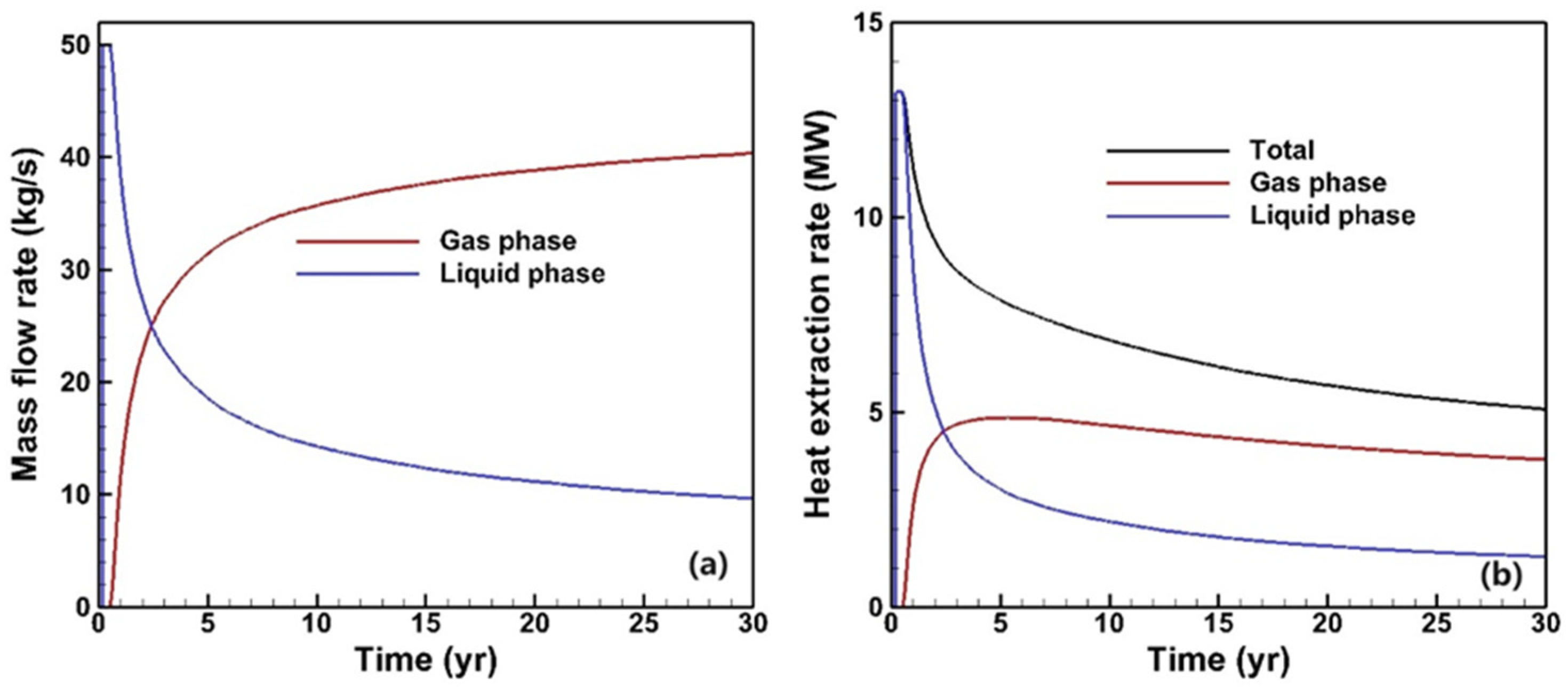
3.1. Fluid and Heat Flow
3.2. Reactive Transport Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, D. A Hot Dry Rock Geothermal Energy Concept Utilizing Supercritical CO2 Instead of Water. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 24–26 January 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pruess, K. Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) using CO2 as working fluid—A novel approach for generating renewable energy with simultaneous sequestration of carbon. Geothermics 2006, 35, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruess, K. On production behavior of enhanced geothermal systems with CO2 as working fluid. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Xu, R.-N.; Jiang, P.-X. Numerical investigation of fluid flow and heat transfer in a doublet enhanced geothermal system with CO2 as the working fluid (CO2–EGS). Energy 2014, 64, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Zhang, L.; Ren, B.; Enechukwu, C.; Liu, Y.; Ren, S. Geothermal exploitation from depleted high temperature gas reservoirs via recycling supercritical CO2: Heat mining rate and salt precipitation effects. Appl. Energy 2016, 183, 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Ren, S.; Rui, Z.; Ezekiel, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H. The influence of complicated fluid-rock interactions on the geothermal exploitation in the CO2 plume geothermal system. Appl. Energy 2018, 227, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, B.M.; Kuehn, T.H.; Bielicki, J.M.; Randolph, J.B.; Saar, M.O. On the importance of the thermosiphon effect in CPG (CO2 plume geothermal) power systems. Energy 2014, 69, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrens, A.D.; Gurgenci, H.; Rudolph, V. CO2 thermosiphon for competitive geothermal power generation. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrens, A.D.; Gurgenci, H.; Rudolph, V. Electricity generation using a carbon-dioxide thermosiphon. Geothermics 2010, 39, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrens, A.D.; Gurgenci, H.; Rudolph, V. Economic Optimization of a CO2-Based EGS Power Plant. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 3765–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majer, E.L.; Baria, R.; Stark, M.; Oates, S.; Bommer, J.; Smith, B.; Asanuma, H. Induced seismicity associated with Enhanced Geothermal Systems. Geothermics 2007, 36, 185–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, A.; Oye, V.; Jousset, P.; Deichmann, N.; Gritto, R.; McGarr, A.; Majer, E.; Bruhn, D. Analysis of induced seismicity in geothermal reservoirs—An overview. Geothermics 2014, 52, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, J.B.; Saar, M.O.; Bielicki, J. Geothermal Energy Production at Geologic CO2 Sequestration sites: Impact of Thermal Drawdown on Reservoir Pressure. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 6625–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schifflechner, C.; Wieland, C.; Spliethoff, H. CO2 Plume Geothermal (CPG) Systems for Combined Heat and Power Production: An Evaluation of Various Plant Configurations. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 31, 1266–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Zhang, L.; Tan, C.; Ren, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Enechukwu, C. Injection of supercritical CO2 for geothermal exploitation from sandstone and carbonate reservoirs: CO2–water–rock interactions and their effects. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 20, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Frost, R.R.; Harvey, R.D. Thermal conductivity of carbonate rocks. Eng. Geol. 1973, 7, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Feng, G.; Hou, Z.; Tian, H.; Shi, Y.; Lei, H. Wellbore–reservoir coupled simulation to study thermal and fluid processes in a CO2-based geothermal system: Identifying favorable and unfavorable conditions in comparison with water. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 6797–6813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, L.; Audigane, P.; Azaroual, M.; Menjoz, A. Numerical modeling of fluid–rock chemical interactions at the supercritical CO2–liquid interface during CO2 injection into a carbonate reservoir, the Dogger aquifer (Paris Basin, France). Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 1782–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, A.; Kato, K.; Ohsumi, T.; Yajima, T.; Ito, H.; Kaieda, H.; Metcalfe, R.; Takase, H. Experimental studies of CO2-rock interaction at elevated temperatures under hydrothermal conditions. Geochem. J. 2005, 39, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Feng, G.; Shi, Y. On fluid–rock chemical interaction in CO2-based geothermal systems. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 144, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinsome, P.; Westerveld, J. A simple method for predicting cap and base rock heat losses in thermal reservoir simulators. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 1980, 19, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils 1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolery, T. EQ3/6, a Software Package for Geochemical Modeling of Aqueous Systems: Package Overview and Installation Guide, Version 7.0; Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory: Livermore, CA, USA, 1992.
- Johnson, J.W.; Oelkers, E.H.; Helgeson, H.C. SUPCRT92: A software package for calculating the standard molal thermodynamic properties of minerals, gases, aqueous species, and reactions from 1 to 5000 bar and 0 to 1000 °C. Comput. Geosci. 1992, 18, 899–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Spycher, N.; Sonnenthal, E.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, L.; Pruess, K. TOUGHREACT Version 2.0: A simulator for subsurface reactive transport under non-isothermal multiphase flow conditions. Comput. Geosci. 2011, 37, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Sonnenthal, E.; Spycher, N.; Pruess, K. TOUGHREACT—A simulation program for non-isothermal multiphase reactive geochemical transport in variably saturated geologic media: Applications to geothermal injectivity and CO2 geological sequestration. Comput. Geosci. 2006, 32, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruess, K.; Oldenburg, C.; Moridis, G. TOUGH2 User’s Guide, Version 2.0; Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1999.
- Pruess, K. ECO2N: A TOUGH2 Fluid Property Module for Mixtures of Water, NaCl and CO2; Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.; Oldenburg, C.M.; Wu, Y.-S.; Pruess, K. T2Well/ECO2N Version 1.0: Multiphase and Non-Isonthermal Model for Coupled Wellbore-Reservoir Flow of Carbon Dioxide and Variable Salinity Water; Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.; Oldenburg, C.M. T2Well—An integrated wellbore–reservoir simulator. Comput. Geosci. 2014, 65, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Holmes, J.A.; Durlofsky, L.J.; Aziz, K.; Diaz Teran Ortegon, L.R.; Alkaya, B.; Oddie, G. Drift-flux modeling of two-phase flow in wellbores. SPE J. 2005, 10, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Formation | |
|---|---|
| Depth | 2500 m |
| Thickness | 50 m |
| Porosity | 0.2 |
| Permeability | 2.0 × 10−13 m2 |
| Rock grain density | 2650 kg/m3 |
| Rock specific heat | 920 J/kg/°C |
| Rock thermal conductivity | 2.51 W/m/°C |
| Well spacing | 500 m |
| Reservoir temperature | 100 °C |
| Reservoir pressure | 24.6 MPa |
| Wellbores | |
| Diameter | 0.18 m |
| Roughness | 0.046 mm |
| Heat conductivity | 2.51 W/m/°C |
| The inclination of wells | Vertical |
| Production/Injection | |
| Injection temperature | 33 °C |
| Mass flow rate | 50 kg/s |
| Parameter for Relative Permeability (van Genuchten’s Model for Liquid and Corey’s Model for Gas) | |
| Residual liquid saturation | 0.10 |
| Residual gas saturation | 0.01 |
| Saturated liquid saturation | 1.00 |
| λ | 0.457 |
| Parameter for capillary pressure (van Genuchten’s model) | |
| Residual liquid saturation | 0.00 |
| Saturated liquid saturation | 1.00 |
| λ | 0.457 |
| Gas entry pressure | 2000 Pa |
| Maximum capillary pressure | 1.0 MPa |
| Mineral | Calcite | Dolomite | Quartz | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial volume of solid (%) | 85 | 10 | 5 | ||
| A (cm2/g) | 9.8 | 9.8 | 9.8 | ||
| Parameters for kinetic rate law | Neutral mechanism | k25 (mol/m2/s) | 1.55 × 10−6 | 2.95 × 10−8 | 1.02 × 10−14 |
| Ea (kJ/mol) | 23.5 | 52.2 | 87.7 | ||
| Acid mechanism | k25 (mol/m2/s) | 0.501 | 6.46 × 10−4 | - | |
| Ea (kJ/mol) | 14.4 | 36.1 | - | ||
| n (H+) | 1.0 | 1.0 | - | ||
| Parameters for equilibrium constants | a | 142.62643 | 298.77008 | −23.56122 | |
| b | −904.76695 | 1899.4949 | 154.45001 | ||
| c | −0.14454508 | −0.29974401 | 0.017816442 | ||
| d | 50,724.016 | 106,828.32 | −10,900.331 | ||
| e | 2,936,998.1 | −6,150,330.1 | 648,509.8 | ||
| Chemical Species | Concentration (mol/L) |
|---|---|
| H+ | 1.279 × 10−7 |
| OH− | 4.854 × 10−6 |
| Ca2+ | 6.788 × 10−4 |
| Mg2+ | 2.389 × 10−5 |
| HCO3− | 1.406 × 10−3 |
| CO32− | 1.140 × 10−6 |
| CO2(aq) | 3.929 × 10−4 |
| Ca(HCO3−)+ | 1.988 × 10−5 |
| Mg(HCO3−)+ | 7.263 × 10−7 |
| pH | 6.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Zhang, F.; Song, S.; Tan, X.; Feng, G. The Feasibility of Heat Extraction Using CO2 in the Carbonate Reservoir in Shandong Province, China. Energies 2024, 17, 2910. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17122910
Liu X, Zhang F, Song S, Tan X, Feng G. The Feasibility of Heat Extraction Using CO2 in the Carbonate Reservoir in Shandong Province, China. Energies. 2024; 17(12):2910. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17122910
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiao, Feng Zhang, Shuailiang Song, Xianfeng Tan, and Guanhong Feng. 2024. "The Feasibility of Heat Extraction Using CO2 in the Carbonate Reservoir in Shandong Province, China" Energies 17, no. 12: 2910. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17122910
APA StyleLiu, X., Zhang, F., Song, S., Tan, X., & Feng, G. (2024). The Feasibility of Heat Extraction Using CO2 in the Carbonate Reservoir in Shandong Province, China. Energies, 17(12), 2910. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17122910







