Mitigating Asphaltene Deposition in CO2 Flooding with Carbon Quantum Dots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. The Core Flooding Experiment
2.2.2. Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots
2.2.3. Extraction of Asphaltene
2.2.4. Inhibition of Asphaltene Precipitation by Carbon Quantum Dots
3. Results and Discussion
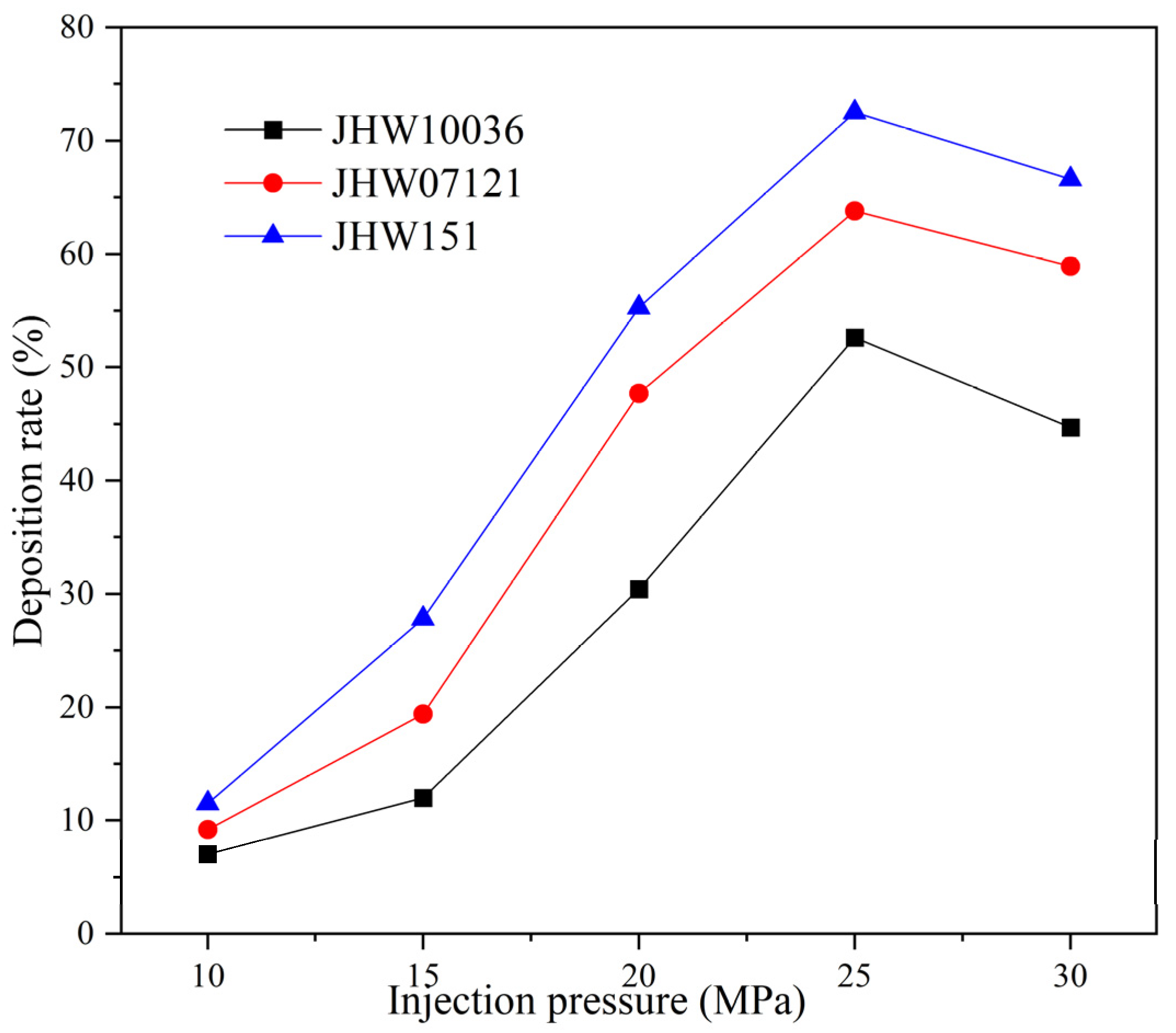
3.1. Influence of Injection Pressure on Asphaltene Deposition
3.2. Influence of CO2 Injection Ratio on Asphaltene Deposition
3.3. Influence of Temperature on Asphaltene Deposition
3.4. Influence of CQDs on the Asphaltene Deposition Onset Point
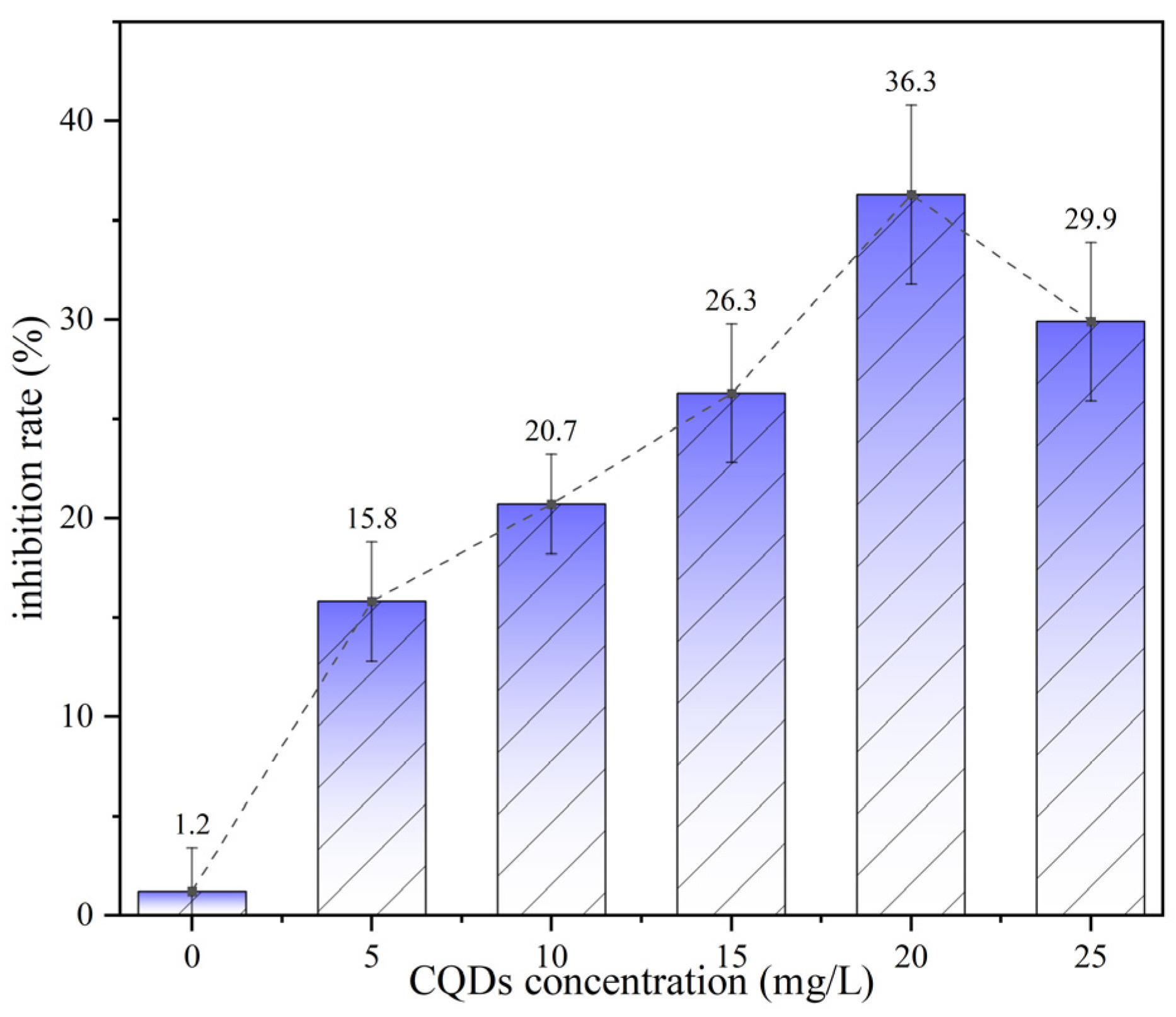
3.5. Influence of CQDs on the Inhibition Rate of Asphaltene Deposition
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEA. CO2 Emissions in 2022; IEA: Paris, France, 2023.
- Hepburn, C.; Adlen, E.; Beddington, J.; Carter, E.A.; Fuss, S.; Mac Dowell, N.; Minx, J.C.; Smith, P.; Williams, C.K. The technological and economic prospects for CO2 utilization and removal. Nature 2019, 575, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Pan, S.-Y.; Li, H.; Cai, J.; Olabi, A.G.; Anthony, E.J.; Manovic, V. Recent advances in carbon dioxide utilization. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 125, 109799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, C. Developing High-Capacity Solid “Molecular Basket” Sorbents for Selective CO2 Capture and Separation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2023, 56, 3358–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuov, Y.; Serik, G.; Lee, W. Techno-Economic Assessment and Life Cycle Assessment of CO2-EOR. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 8571–8580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakher, S.; Imqam, A. Asphaltene precipitation and deposition during CO2 injection in nano shale pore structure and its impact on oil recovery. Fuel 2019, 237, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.; Vargas, V.; Piscitelli, V.; Ordoñez, L.; Rojas, H. Study of asphaltene adsorption onto raw surfaces and iron nanoparticles by AFM force spectroscopy. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 151, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemzadeh, Y.; Sourani, S.; Doryani, H.; Reyhani, M.; Shabani, A.; Fallah, H. Recovery of asphaltenic oil during nano fluid injection. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2015, 33, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Shen, P.; Jia, Y.; Ye, J.; Li, S.; Bie, A. Prediction of asphaltene precipitation during CO2 injection. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2010, 37, 349–353. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, M.; Gu, Y. Oil recovery mechanisms and asphaltene precipitation phenomenon in immiscible and miscible CO2 flooding processes. Fuel 2013, 109, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanganeh, P.; Ayatollahi, S.; Alamdari, A.; Zolghadr, A.; Dashti, H.; Kord, S. Asphaltene deposition during CO2 injection and pressure depletion: A visual study. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chi, P.; Guo, X.; Sun, Q. CO2-induced asphaltene deposition and wettability alteration on a pore interior surface. Fuel 2019, 254, 115595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee Nezhad, E.; Heidarizadeh, F.; Sajjadifar, S.; Abbasi, Z. Dispersing of petroleum asphaltenes by acidic ionic liquid and determination by UV-visible spectroscopy. J. Petrol. Eng. 2013, 2013, 203036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhi, M.; Kharrat, R.; Hamoule, T. Screening of inhibitors for remediation of asphaltene deposits: Experimental and modeling study. Petroleum 2018, 4, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campen, S.; Moorhouse, S.J.; Wong, J.S. Mechanism of an asphaltene inhibitor in different depositing environments: Influence of colloid stability. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 184, 106502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horeh, N.B.; Hosseinpour, N.; Bahramian, A. Asphaltene inhibitor performance as a function of the asphaltene molecular/aggregate characteristics: Evaluation by interfacial rheology measurement and bulk methods. Fuel 2023, 339, 127420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehaghani, A.H.S.; Badizad, M.H. Inhibiting asphaltene precipitation from Iranian crude oil using various dispersants: Experimental investigation through viscometry and thermodynamic modelling. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2017, 442, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nagar, R.A.; Nessim, M.I.; Ismail, D.A.; Mohamed, M.G.; Ghanem, A. Investigation the effect of different ionic liquids based-aryl imidazole on the onset precipitation of asphaltene. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, N.N.; Hassan, A.; Pereira-Almao, P. Comparative oxidation of adsorbed asphaltenes onto transition metal oxide nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 384, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, S.; Malayeri, M.; Riazi, M. Utilization of Co3O4 nanoparticles for reducing precipitation of asphaltene during CO2 injection. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 31, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.; Gadikota, G. The role of calcite and silica interfaces on the aggregation and transport of asphaltenes in confinement. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 274, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Dadvar, M.; Dabir, B. Application of response surface methodology for optimization of the stability of asphaltene particles in crude oil by TiO2/SiO2 nanofluids under static and dynamic conditions. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2018, 39, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Dadvar, M.; Dabir, B. TiO2/SiO2 nanofluids as novel inhibitors for the stability of asphaltene particles in crude oil: Mechanistic understanding, screening, modeling, and optimization. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 238, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Sui, H.; Liu, X.; He, L.; Li, X.; Thormann, E. Effects of the N, O, and S heteroatoms on the adsorption and desorption of asphaltenes on silica surface: A molecular dynamics simulation. Fuel 2019, 240, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Meziani, M.J.; Sahu, S.; Sun, Y.-P. Photoluminescence properties of graphene versus other carbon nanomaterials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Xiang, C.; Lin, J.; Peng, Z.; Huang, K.; Yan, Z.; Cook, N.P.; Samuel, E.L.G.; Hwang, C.-C.; Ruan, G.; et al. Coal as an abundant source of graphene quantum dots. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, A. Carbon quantum dots: Synthesis, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 6921–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Wei, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Miao, Y. Synthesis of Triphenylmethyl Modified Oil-soluble Carbon Quantum Dots and Their Applications inLight-emitting Devices. Chin. J. Lumin. 2021, 42, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaati, F.; Riazi, M.; Mousavi, S.H.; Derikvand, Z. Experimental investigation of the inhibitory behavior of metal oxides nanoparticles on asphaltene precipitation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 531, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, S.; Jalilian, M.; Dolati, S. Review and perspectives on CO2 induced asphaltene instability: Fundamentals and implications for phase behaviour, flow assurance, and formation damage in oil reservoirs. Fuel 2024, 368, 131574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; Liu, B.; Shen, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, J. Study on the asphaltene precipitation in CO2 flooding: A perspective from molecular dynamics simulation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y. Investigation of the effect of CO2 on asphaltene deposition and flow mechanism under nano-confined environment. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 396, 124092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, K.G.; Moghadasi, J. Experimental investigating of the effect of CO2 injection parameters on asphaltene precipitation and formation damage in live oil. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2024, 14, 238–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Li, Z.; Du, L. Enhancing foam stability and addressing asphaltene deposition for improved oil recovery in CCUS applications using aerogel nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Oil Sample | Asphaltenes m% | Resins m% | Saturates m% | Aromatics m% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JHW10036 | 9.57 | 25.14 | 14.84 | 50.46 |
| JHW07121 | 15.58 | 20.58 | 16.47 | 47.37 |
| JHW151 | 21.11 | 22.32 | 16.26 | 40.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, H.; Liao, H.; Dai, Q.; Tiong, M.; Xian, C.; Luo, D. Mitigating Asphaltene Deposition in CO2 Flooding with Carbon Quantum Dots. Energies 2024, 17, 2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17112758
Liu Q, Zhu Y, Ye H, Liao H, Dai Q, Tiong M, Xian C, Luo D. Mitigating Asphaltene Deposition in CO2 Flooding with Carbon Quantum Dots. Energies. 2024; 17(11):2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17112758
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qi, Yangwen Zhu, Hang Ye, Haiying Liao, Quanqi Dai, Michelle Tiong, Chenggang Xian, and Dan Luo. 2024. "Mitigating Asphaltene Deposition in CO2 Flooding with Carbon Quantum Dots" Energies 17, no. 11: 2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17112758
APA StyleLiu, Q., Zhu, Y., Ye, H., Liao, H., Dai, Q., Tiong, M., Xian, C., & Luo, D. (2024). Mitigating Asphaltene Deposition in CO2 Flooding with Carbon Quantum Dots. Energies, 17(11), 2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17112758








