Abstract
Energy production from biomass represents a strategic solution for the achievement of global sustainability goals. In addition, the use of biofuels offers both significant environmental advantages and several socio-economic benefits. In this study, the environmental life cycle impacts associated with the use of woodchips from forest residues for combined heat and power generation in Italy were analyzed. Moreover, the use of woodchips was compared to the use of conventional fossil fuels in similar applications, and different biomass supply scenarios were evaluated to understand their effect on the overall impact related to 1 kWh of electricity. The impacts on “Climate Change” (2.94 × 10−2 kgCO2eq/kWh) and “Resources” (4.28 × 10−1 MJ primary) were revealed to be minimal compared to fossil fuels (reduction of about 95–97%) and forest woodchips emerged as a sustainable alternative for electricity generation. Moreover, impacts regarding “Human health” (3.04 × 10−7 DALY) and “Ecosystem quality” (3.58 × 10−1 PDF·m2·yr) were revealed to be relevant and identified as a research area to be further explored. The findings of this study also highlighted the key role played by the supply mode/distance of the woodchips on the overall life cycle impacts, with the use of “local” biomass representing the best reduction option. Lastly, another aspect to be further investigated is the optimization of the biomass supply.
1. Introduction
The increasing energy demand and need for decarbonization of energy production are key challenges associated with sustainable energy transition. The supply of clean and affordable energy can bring clear environmental advantages, but also several socio-economic benefits supporting the achievement of various Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) [1]. Bioenergy can be considered one of the most relevant resources in this regard, due to its wide availability, potential use for different energy purposes and contribution to lowering carbon emissions and improving energy security.
Modern bioenergy accounts for 55% of renewable energy and more than 6% of the global energy supply and represents the largest source of renewable energy globally. The global supply of biomass (56.9 EJ in 2019 [2]) derives about 85% from solid biomass sources including woodchips, wood pellets, and other conventional biomass sources. Solid biofuel primary energy consumption in the EU27 increased by +8.1% in 2021 reaching a value of 104.2 Mtoe due, among various reasons, to the hike in fossil energy prices that characterized the second half of the year and made biomass fuels more competitive [3].
Although the heating sector remains the largest source of bioenergy use, in recent years bioenergy for electricity and transport biofuels have been growing rapidly, due to higher levels of policy support [4].
In this context, with a production of 7590 Mtoe and a primary energy gross domestic consumption equal to 8874 Mtoe, Italy is one of the main bioenergy users [3]. Solid biomass represents about two-thirds of bioenergy use, and is mostly used for heating in residential applications [5]. In recent years, the role of renewables in the Italian electricity mix has seen consistent growth in addition to bioenergy and waste which experienced an appreciable increase, reaching 7.5% of total generation in 2021 (compared to 3.9% in 2010) [6], with gross electricity production from solid biofuels estimated to be 4529 TWh [3].
Italy’s energy policy is manly guided by the 2023 National Energy and Climate Plan (NECP) [7]—an update to the 2019 version following the “fit for 55” package of the European Commission and the new global energy context consequent to recent events (COVID-19 pandemic, Russia’s war on Ukraine, dramatic increase in energy prices)—the 2022 Plan for the Ecological Transition [8] and the 2021 Long-Term National Strategy (LTS) on Reducing Greenhouse Gases (GHG) Emissions [9]. These strategic documents outline the national electricity policy and, among the other potential actions, clearly identify the increase in the share of renewable electricity, the phase out of coal-fired generation, and the reduction in the use of fossil fuels, as key strategies.
Solid biomass is still mainly considered concerning the production of thermal energy, strongly encouraging the use of sustainable and circular (valorisation of residues) biomass from short supply chains in efficient and low-emission plants. In line with these policy recommendations, previous studies (such as [10]) investigated specific aspects regarding decision-making in these applications. Anyway, also the potential use of solid biomass as a fuel for other industrial applications (see, for instance, [11]) and for electricity generation represents a relevant research area. Moreover, its potential use in fuelling electricity and heat production in combined heat and power plants (CHP) is of notable significance. Among the various renewable energy sources, in fact, it is among those that guarantee regular and continuous plant operation, with a constant and programmable production that is not dependent on climatic and environmental factors. It is moreover evident that this aspect becomes more strategic when the used biomass is a residual one.
Previous literature studies investigated the state of the art in energy generation from solid biomass in Italy, focussing on specific regions and conversion technologies, such as thermochemical conversion [12] and direct electricity production by means of combustion and gasification [13]. These studies highlighted that solid biomass from forests and agriculture represents a largely underexploited energy source, with noteworthy advantages related to a more extensive and integrated management. In addition, they showed that producing power from residual biomass, especially in small agricultural communities, significantly reduced their environmental impacts while improving the economic feasibility of their waste management practices. Similarly, the use of residual solid biomass in CHP plants was analysed in other studies, such as [14], supporting the idea that forest residues would be an interesting and potential feedstock for bio-energy purposes, although optimization biomass supply distances should be investigated in further specific research.
Focussing on the environmental impact evaluation of solid biomass, several LCA-based studies are available in the literature and most of them (for instance [15,16,17,18,19,20,21]) investigated woodchips (of different typologies and for different applications) focussing on the supply chain, but not including the energy conversion. These studies showed the fuel production and transportation as relevant phases of the life cycle and identified chipping and forest operations (e.g., fertilization, harvesting, and extraction) as environmental hotspots within it. On the other hand, the literature on wood-to-energy chains emphasised the environmental suitability of using biomass (woodchips from forest/residues are included in the investigated fuels in some cases) both for heat (in different applications [22,23]) and power generation, also showing the relevance of the plant size and combustion characteristics ([24,25,26]).
More specifically, Balcioglu et al. [27] performed an LCA of the energy conversion of two different types of forest residues (chips and pellets) through various technologies, suggesting that the combustion of woodchips for heat and power cogeneration is, among the other options, associated with the lowest environmental impacts (and costs). Klavina et al. [28], instead, compared the use of woodchips in pyrolysis and heat and power production and showed again the convenience of woodchip use in a CHP plant in terms of environmental impact. Similarly, Sgarbossa et al. [29] carried out a comparative LCA of bioenergy production from different wood pellet supply chains, including also logging residues as wood feedstock option and showing their good performance in terms of Global Warming Potential (GWP) compared to the other ones. Xu et al. [30] also focussed their study on GHG emissions (evaluated through a cradle-to-grave LCA) of forest biomass suggesting logging residues as an intermediate option in terms of environmental impact.
Moreover, although the literature has shown a certain (more or less recent) level of development, it seems that a dedicated assessment of woodchip energy deployment in a CHP plant based on an Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) with a life cycle approach is still partly missing, and can thus be considered an interesting topic of exploration.
Therefore, in this study we assessed the environmental life cycle impacts associated with the use of woodchips from forest residues in a CHP plant for combined heat and power generation in Italy, in order to characterize the specific use of circular biomass from an environmental perspective. In detail, we analysed the production of heat and electricity in a plant where an ORC cogeneration unit is coupled with a biomass boiler, representing one of the most widely adopted arrangements in these applications, and also investigated using LCA by [31].
We then compared the use of woodchips to the use of conventional fossil fuels in similar applications, still from a life cycle approach, so to clearly highlight the potential environmental benefits/impact modifications. Finally, different biomass supply scenarios were defined and evaluated to understand the effect of this relevant aspect of the life cycle on the overall impact related to the generation of 1 kWh of electricity.
The impact assessment was performed using a combined midpoint/damage method that considers 15 different impact categories and links them to 4 damage categories related to human health, ecosystem quality, climate change and resources depletion. In this way, the study presents a clear and comprehensive characterization of the impacts related to the production of electricity from woodchips at a national level, also identifying the effect of relevant internal variables of the biomass-to-energy chain. This can be considered of interest in the Italian context since, despite according to the national policy documents, the share of energy from solid biomass in the country’s future electricity mix is expected to increase less compared to other renewable sources (such as solar and wind energy), it will remain particularly relevant for its role and its specific impacts in certain fields [32,33]. In general terms, the results of this study could be useful to support optimization strategies in the woodchips-to-energy chains and a proper source of information and communication concerning this type of renewable and circular fuel.
According to the results of this Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) study, woodchips from forest residues can be considered a valid and sustainable alternative to fossil fuel for electricity generation, with the greatest environmental benefits regarding the “Climate change” and “Resources” impacts. Further, other impacts regarding “Human health” and “Ecosystem quality” emerged as relevant, also comparing the use of forest woodchips to conventional fossil fuels and their assessment represent research areas to be further explored. The study also highlighted the key role of woodchips supply mode/distance on the overall life cycle impact associated with the generation of 1 kWh electricity, suggesting that the use of “local” biomass represents the best solution for the reduction of impacts.
The remainder of the manuscript is organized as follows: Section 2 describes the material and methods, including all details regarding the specific woodchips production case study, the LCA analysis and the alternative scenarios considered (a sensitivity analysis is also presented); Section 3 shows the main results of the study; Section 4 discusses implications and limitations, and links and compares the current research with previous literature; and Section 5 provides summarized conclusions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Forest Woodchips Production Case Study
A specific case study in Italy, analyzed in the framework of the ARCADIA project (“Life cycle approach in public contracts and Italian LCA database for the efficient use of resources”) [34] financed by the 2014–2020 National Operational Programme on Governance and Institutional Capacity [35], was considered to model the production of the forest woodchips.
The case study is related to the production of forest woodchips in the North-East of Italy (Friuli Venezia Giulia region) and can be considered representative, both from a geographical and technological point of view, of other Italian (and not only) regions where the production of woody biomass occurs mainly in a mountain (or similar) environment. The source of forest biomass consists of a mix of silver fir and spruce wood obtained from mature stands managed within a management scheme promoting the natural regeneration of tree species (cutting of trees at a typical age of 30–40 years).
The studied product is a by-product of the production process of good quality forest woodchips, i.e., woodchips obtained from the chipping of branches, tops and other residual parts of such process (Figure 1). According to the specifications of the ISO 17225-4 standard [36] the product is representative of “class B” woodchips, that include wood from gardens and plantation, short rotation coppice from contaminated soil, but also chemically treated/untreated industrial byproducts/residues and chemically untreated used wood.

Figure 1.
Case study for the production of the forest woodchips (colored icons and arrows identify the reference production chain).
2.2. Life Cycle Assessment
The LCA study was performed in compliance with ISO 14040 [37] and 14044 [38] standards, and also following the specific Product Category Rule (PCR) available for “Electricity, steam and hot/cold water generation and distribution” (even if currently being updated) [39].
According to the above a “cradle-to-gate” approach was adopted, and therefore all the upstream (fuel extraction, processing, preparation, transportation and storage) and core (energy conversion process at the power plant) processes were included, while the downstream module that comprise all the processes after the power plant transforming process to the customer meter was excluded (Figure 2). According to the specific PCR [39], the use stage of electricity fulfils various functions in different contexts and is therefore excluded from the downstream module as well as the end-of-life of the product. Transmission/distribution losses associated with the transmission and distribution of electricity to a customer (defined with respect to connection voltage) should instead be included in the study, and representative average national transmission and distribution losses in the power networks could be used in this regard. Anyway, since these losses are independent from the used fuel, to assess 1 kWh fed into the grid, they were excluded from the system boundaries.
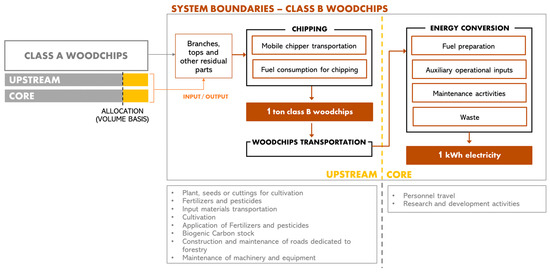
Figure 2.
LCA study system boundaries (grey phases/processes are out of the system boundaries).
Regarding the forest woodchips production phase, based on the abovementioned PCR all the processes in conjunction with forestry shall be included in the study when biomass fuel is made from primary forest products (such as logs). Moreover, the production and maintenance of the machinery and equipment used for forestry activities were excluded from the system boundaries, following the recommendations of other methodological documents related to forest products available in the literature [40,41] and also considering the negligible impact related to these processes that could be attributed to the single forestry worksite. Also, road construction and maintenance activities were excluded from the study, since no primary data and no information for a detailed modelling based on secondary data were available. In fact, the forest worksite related to the specific case study was already set and no new infrastructure was built to give access to the forest, and no solid secondary data could be gathered from the literature for this specific processes (forest roads are generally excluded from the system boundaries of LCA studies and, moreover, due to overall complexity and high differences characterizing road construction and maintenance reliable data should be very detailed and gathered from a higher level [41]). The travel of personnel (business travel and travel to and from work) is beyond the scope of the study (and can also be considered similar for different fuels production), and the land-use transformation and occupation can be reasonably considered as having occurred more than 20 years before harvesting and, therefore, irrelevant according to [40]. Moreover, since forest management activities can be assumed to have similar contributions in terms of emissions and removal of biogenic carbon dioxide to and from the forest carbon stocks, the net biogenic carbon dioxide emissions associated with forest woodchips production were assumed to be zero. Primary data regarding forest operations (i.e., fossil fuels consumption in the machinery and related emissions) were directly collected as referred to the total volume of wood processed for the production of class A woodchips (main product of the process) and class B woodchips (by-product of the process). Therefore, to estimate the quantity of inputs (and related environmental loads) associated with the class B woodchips an allocation procedure was adopted. In particular, these data were allocated on a volume basis referring to primary data available in the ARCADIA project (also in line with literature and specific documents [42,43,44,45]), which showed that branches, tops and residual parts represent 8% in volume of the total wood intended for felling. The inputs to the system were then calculated considering the specific values of the sawlogs-to-woodchips conversion factor and the bulk density, and the woodchips required to generate 1 kWh electricity. The transportation of forest woodchips was modelled based on data regarding distances within the fuel production chain and distances to the energy conversion plant, as well as the type of vehicles used, according to [46].
With regard to the CORE phase, forest woodchips are supposed to be used in a CHP plant for the generation of high voltage electricity. According to the specific PCR [39] recommendations, business travel of personnel, travel to and from work by personnel and research and development activities were not included in the system boundaries. CORE infrastructures were instead considered in the LCA and modelled through background data (dataset of the ecoinvent 3.9 database [47]), as well as other auxiliary operational inputs, fuel preparation processes at plant, maintenance activities and core waste management. According to the ecoinvent dataset, the CHP plant is equipped with a woodchips furnace with silo (5000 kW), an ORC heat and power co-generation unit (1000 kW electrical) and an electrostatic precipitator for particulate matter emission reduction.
The selected Functional Unit (FU) for the LCA study is 1 kWh net of electricity generated and, as detailed above, Life Cycle Inventory (LCI) data were both primary and secondary (Table 1).

Table 1.
Life cycle inventory data (FU = 1 kWh net electricity).
The study was performed in SimaPro (v. 9.5) [48], which represents one of the commonly used software tools widely accepted as reliable for LCA [49], offering the possibility to choose between several different databases and having a wide range of different environmental impact assessment methodologies. The Life Cycle Impact Assessment (LCIA) was performed using the Impact 2002+ method (v2.15) [50], which has demonstrated validity in assessing and highlighting the environmental burdens best representing the investigated system both at the midpoint and endpoint levels. The method, in fact, implements a combined midpoint/damage approach linking all types of LCI results (elementary flows and other interventions) to 4 damage categories via 15 different impact categories (in SimPro “Human Toxicity” is split up in “Carcinogens” and “Non-carcinogens”) [50]. The “normalization” and “weighting” phases were included in the assessment as part of the endpoint approach and, therefore, overall results are shown in the form of “points” to create a scale of the overall environmental profile and identify the most relevant categories and life cycle phases. Anyway, the impact assessment was also extended to the midpoint level, analyzing the damage categories with their specific unit of measure, with the aim of describing the environmental compartments being damaged by the system in its life cycle. The results of the characterization step concerning all the 15 impact categories included in the method are given in the Supplementary Materials.
2.3. Comparison with Conventional Fossil Fuels
With the aim of understanding, from a life cycle perspective, the potential environmental benefits and/or environmental impact modifications associated with the use of woodchips compared to the use of conventional fossil fuels in electricity generation, the following alternatives were considered:
- A1: electricity production in a conventional natural gas CHP plant,
- A2: electricity production in a conventional oil CHP plant,
The life cycle of alternative A1 was modelled using background data and, in particular, the ecoinvent 3.9 dataset “Electricity, high voltage {IT}| heat and power co-generation, natural gas, conventional power plant, 400MW electrical”. Similarly, the life cycle of alternative A2 was modelled using the ecoinvent 3.9 dataset “Electricity, high voltage {IT}| heat and power co-generation, oil”.
2.4. Woodchips Supply Scenarios
In total, two different biomass supply scenarios were defined to understand the effect of this relevant phase of the life cycle on the overall impact related to the generation of electricity from woodchips. In particular, assuming based on [51] that 90% of the required biomass is of Italian origin while the remaining is partly supplied from Europe (8%) and partly from USA and Canada (2%), the following were considered:
- S1: woodchips from Italy supplied by road for a distance of 350 km—considering that forestry are widespread in various geographic area in the Country and, therefore, an indicative mean distance for their availability [14]—woodchips from Europe supplied by road for a distance of 543 km and woodchips from USA and Canada shipped for a distance of 7458 km [51];
- S2: woodchips from Italy supplied by road for a distance of 70 km—according to the definition of “biomass from short supply chains” given in [52]—woodchips from Europe supplied by road for a distance of 543 km and woodchips from USA and Canada shipped for a distance of 7458 km [51].
Road transport was modelled using the ecoinvent 3.9 dataset “Transport, freight, lorry >32 metric ton, euro4 {RER}”, while sea transport referring to the ecoinvent 3.9 dataset “Transport freight, sea, container ship {GLO}”.
2.5. Sensitivity Analysis
Since the environmental impact related to energy production is strictly dependent on the conversion process performance, a sensitivity analysis was performed to assess how the efficiency of the CHP plant affects the results of the study. Specifically, compared to the baseline for which the overall electrical efficiency (the ratio of electric power output to the thermal power input to the system) was equal to 22.6%, an alternative scenario with a hypothetical efficiency increase was analysed. In detail, an overall electrical efficiency of the system equal to 27.8% was adopted (consequent to an increase in thermal efficiency equal to +10%).
3. Results
As shown in Figure 3, the most relevant categories are “Human health” and “Ecosystem quality”, respectively, with about 57% (4.29 × 10−5 Pt) and 35% (2.62 × 10−6 Pt) of the overall impact, while the share of “Climate change” (2.97 × 10−6 Pt) and “Resources” (2.82 × 10−6 Pt) is both about 4%. It is also clearly evident that the CORE phase is the most significant, being the main factor responsible for the impact related to “Human health” and “Ecosystem quality” (about 97% in both cases), mainly because of the direct impacts related to the energy conversion process (emissions and waste). On the other hand, the UPSTREAM phase is particularly relevant for the categories “Climate change” and “Resources”, with a contribution to their impact values, respectively, equal to 74% and 93%.
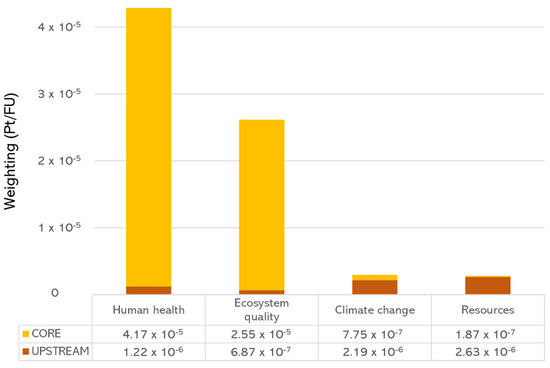
Figure 3.
LCA results per damage category and life cycle phase (weighting).
Results of the impact assessment at the midpoint level are instead summarized in Table 2, showing again the great relevance of the CORE phase for the categories “Human health” and “Ecosystem quality” and the significance of the UPSTREAM phase for the categories “Climate change” and “Resources”.

Table 2.
LCA results per damage category and life cycle phase (damage assessment).
The endpoint assessment also focused on the inventory flows analysis, in order to identify the output streams contributing most to the damage value associated with the related damage category, i.e., the most burdening emissions in the various environmental compartments for “Human health”, “Ecosystem quality” and “Climate Change”, and the primary-energy and natural resources exploited affecting the damage category “Resources” (Table 3). It is worth noting that the emissions of both nitrogen oxides (in air) and zinc (in air and soil) represent the most relevant output flows for “Human health” and “Ecosystem quality”, together with Particulates <2.5 μm. Carbon dioxide, fossil and Dinitrogen monoxide are instead the most contributing flows for the category “Climate Change”, while Oil, crude and Gas, natural represent the most impacting outputs on “Resources”. Each of these relevant substances was also addressed in terms of output–inventory amount and damage assessment values, in order to quantify the real output flow and the related consequent impact on the damage category, and thus a comprehensive environmental profile of the investigated system (Table 4).

Table 3.
Most environmentally damaging emitted substances and resources consumed (weighting).

Table 4.
Most environmentally damaging substances and resources consumed: output inventory analysis and damages assessment.
In comparing the case study to conventional fossil fuels at the endpoint level, it is evident that the overall impact is significantly lower than the natural gas (A1) and oil (A2) cases. In particular, with 7.48 × 10−5 Pt/kWh, the electricity generation by forest woodchips has an impact 34% less than its generation by natural gas and 72% less than its generation by oil. It is also clearly evident that the use of forest woodchips is characterized by a negligible impact in the categories “Climate change” and “Resources” compared to natural gas and oil (Figure 4). These categories, in fact, represent together about 8% of the overall impact in terms of damage points in the case study, while they account respectively for about 42% and 51% in the natural gas case and about 34% and 29% in the oil case. Focusing on the latter it is also worth noting the relevance of “Human health”, with a contribution of about 36% of the total damage points.
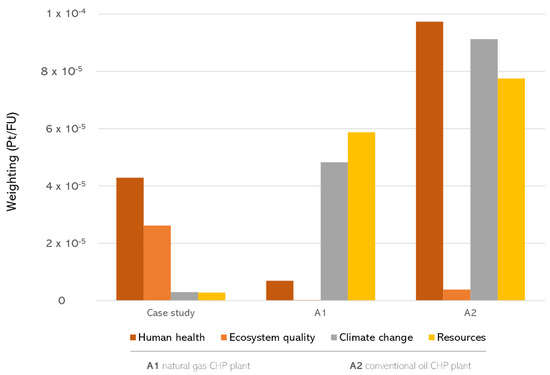
Figure 4.
Comparison with electricity generation by natural gas (A1) and oil (A2) (weighting).
According to the above, in terms of midpoint indicators, while the electricity generated by the use of forest woodchips is characterized by a value of 2.94 × 10−2 kg CO2 eq/kWh and a value of 4.28 × 10−1 MJ primary, electricity from natural gas has impacts respectively equal to 4.78 × 10−1 kg CO2 eq/kWh and 8.93 MJ primary, and electricity from oil values of 9.03 × 10−1 kg CO2 eq/kWh and 1.18 × 10 MJ primary.
The analysis of woodchips supply scenarios showed a significant impact increase (about +11%) in S1 and also an appreciable impact increase (about +2%) in S2 compared to the case study (Figure 5). Given that in both these scenarios an 8% of woodchips is supplied from Europe (by road for 543 km) and a 2% from USA and Canada (by ship for 7458 km), this evidence clearly reflects the effect of the characteristics of these “foreign” woodchips and the effect of the transportation of the 90% of woodchips that is supplied by road from Italy. In particular, it is evident that for a transportation distance (350 km) greater than the one considered in the case study, there is a slight increase in the impact of the categories “Human health” and “Ecosystem quality” (respectively about +5% and +10%), while the impact related to the categories “Climate change” and “Resources” notably changes, with an increase respectively of about +61% and +69%. On the other hand, for a transportation distance (70 km) lower than the one of the reference case study, given a similar slight impact increase for the categories “Human health” and “Ecosystem quality” (respectively about +1% and +5%), a reduction in the impact related to “Climate change” (about −7%) and “Resources” (about −11%) was observed.
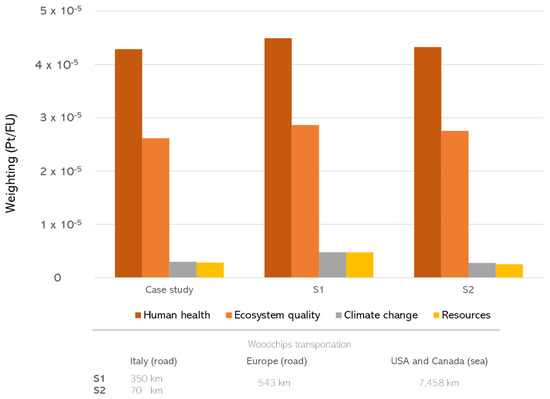
Figure 5.
Analysis of woodchips supply scenarios (weighting).
According to the above, in terms of midpoint indicators, scenario S1 is characterized by an impact equal to 4.72 × 10−2 kg CO2 eq/kWh and 7.23 × 10−1 MJ primary, while scenario S2 has an impact of 2.74 × 10−2 kg CO2 eq/kWh and 3.80 × 10−1 MJ primary (compared to the 2.94 × 10−2 kg CO2 eq/kWh and 4.28 × 10−1 MJ primary of the case study).
The sensitivity analysis showed an appreciable impact decrease for all the considered damage categories associated with an increase of the overall electrical efficiency of the system. As shown in Table 5, in particular, the greatest reduction is observed for the impact on the “Ecosystem quality” (−18.4%), followed by the reduction of impact on “Human health” (−17.0%). The reduction of impacts on “Climate change” and “Resources” are instead less relevant and equal to −7.2% and −8.5%, respectively.

Table 5.
Results of the sensitivity analysis per damage category.
4. Discussion
The results of the environmental LCA performed in this study clearly showed that woodchips from forest residues represent a valid and sustainable alternative to fossil fuel for electricity generation. The overall impact associated with the use of this circular biofuel, in fact, is significantly lower than those related to conventional energy sources such as natural gas (−34%) and oil (−72%). The greatest environmental benefits concern the categories “Climate change” and “Resources”, for which a 95–97% impact reduction is observed, while the evidence regarding the other studied categories is multifaceted. In detail, the use of forest woodchips also showed a significant advantage in terms of “Human health” when compared to oil, with an impact reduction of about 66%, but is characterized by a one order of magnitude impact increase in this category compared to natural gas. The same applies for the category “Ecosystem quality”, for which an increase of one (or two) order of magnitude in the impact is observed in comparison to fossil fuels.
The detailed analysis of the impact related to the use of forest woodchips allowed us to identify the energy conversion process in the CORE phase and, in particular its direct emissions and waste, as the main factors responsible for the impact related to “Human health” and “Ecosystem quality”. Moreover, an assessment focused on the inventory flows, both in terms of outputs amount and endpoint/midpoint indicators, showed the most relevant output streams contributing to these categories, i.e., Nitrogen oxides and Particulates <2.5 μm emissions (in air) and Zinc emissions (in air and soil).
The comparison of different scenarios regarding woodchips supply and, in particular, considering the supply of woodchips for a 10% from abroad (8% Europe, 2% USA and Canada) and for a 90% from Italy, from a distance respectively of 350 km in S1 and 70 km in S2, highlighted a general small increase in the impact on “Human health” and “Ecosystem quality” (respectively, about +5% and +10% in S1, and about +1% and +5% in S2). It was therefore evident that the nature/characteristics of the used woodchips and the transportation mode/distance can play a not negligible role in determining the overall impact affecting these two relevant categories. At the same time, it was even more evident the role of transportation in terms of “Climate change” and “Resources” impacts, with an increase, respectively, of about +61% and +69% in S1 and a reduction of about −7% and −11% in S2.
It has to be highlighted that the UPSTREAM phase processes were modelled based on primary data from a specific Italian supply chain that is reasonably representative of the production of woodchips in a mountain (or similar) environment. On the other hand, the energy conversion process and the related ORC based CHP plant were modelled using specific ecoinvent datasets and, therefore, the CORE phase modelling rely on secondary data. This LCA study and the obtained results are therefore affected by the potential limitations and uncertainties related to these specific assumptions. Moreover, although a comparison with other studies is quite complex—due to the geographic reference area, the production/conversion system (forest residues, short rotation, plant efficiency, …), the wood species considered, and the LCA study characteristics (functional unit, modelling choices, …)—the outcomes of this research can be considered in line with previous literature.
As shown in Table 6, focusing on the Climate Change impact category, since it represents one of the most used to evaluate and communicate the environmental impact of products to different audiences, the results of this study are quite similar to others concerning analogous applications of forest woodchips for energy purposes. Major differences can be observed considering the production of electricity, with an impact of our case study that is about 27% to 40% lower compared to other studies ([27] and [30], respectively), with a maximum deviation of about −65% compared to [31]. As stated before, such appreciable variations can be considered mainly related to the differences in the characteristics of the study, its geographic representativeness, and the specifics of the power plant, with particular regard to the electric efficiency. Focusing on the generation of thermal energy or on the production of woodchips our results are instead more aligned with the previous literature, with differences in the order of about −20% and +2% respectively compared to [21] and [29].

Table 6.
Comparison with other relevant literature studies.
5. Conclusions
The present study analyzed the environmental life cycle impacts associated with the use of woodchips from forest residues for combined heat and power generation in Italy. Moreover, a comparison between the use of woodchips to conventional fossil fuels in similar applications was presented, and different biomass supply scenarios were investigated to understand the effect of this relevant aspect of the life cycle on the overall impact related to 1 kWh of electricity.
Since the Organic Rankine Cycle represents a consolidated technology with good efficiency and high reliability in the energy sector, in this study we analysed a plant where an ORC cogeneration unit is coupled with a biomass boiler to produce heat and electricity.
The climate change impact was equal to 2.94 × 10−2 kgCO2eq/kWh, while the impact in terms of resources deployment was calculated in 4.28 × 10−1 MJ primary. On the other hand, the effects on human health and ecosystem quality were evaluated to be, respectively, 3.04 × 10−7 Disability Adjusted Life Years (DALY) and 3.58 × 10−1 Potentially Disappeared Fraction of species (PDF) per m2 per year.
These results confirm the overall environmental convenience of electricity generation from solid biomass, showing very low impacts in terms of “Climate change” and “Resources” and significant reductions in these impact categories (about 95–97%) compared to fossil fuels. At the same time, it brings attention to the relevance of this renewable source in terms of “Human health” and “Ecosystem quality”, for which greater impacts were observed compared to conventional fossil fuels, giving evidence to the relevance of improving the understanding of such generally unstudied aspects.
According to these main findings, the use of biomass boilers coupled with ORC can therefore be considered a viable option for the cogeneration of electricity and heat, although additional research should be addressed to study the direct effects in greater detail—and also the potential improvement options—of solid biomass energy conversion process in terms of “Human health” and “Ecosystem quality”. These impact categories, in fact, emerged as particularly relevant and are generally less investigated and debated. Moreover, future researchers can investigate a more reliable modelling of the ORC-based CHP plant considered in this study (e.g., collecting data regarding in-operation commercial plants based on the same ORC unit) and also at evaluating how different management strategies can affect the overall impact of the plant.
The study also confirms the key role that woodchips supply mode/distance can play on the overall life cycle impact associated with the generation of 1 kWh electricity, as well as the great relevance of these aspects in decision-making strategies, supporting the idea that the use of “local” biomass represents the desirable choice. Therefore, the optimization of biomass supply distances also represents a crucial aspect that should be investigated in further specific research.
Finally, research concerning the environmental aspects in addition to the social and economic factors is recommended to provide a comprehensive sustainability overview regarding this interesting circular biofuel.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/en17010105/s1, Table S1. Primary data collected within the ARCADIA project (referred to 1 m3 wood processed). Table S2. Carachterization—Case study. Table S3. Carachterization—Sensitivity analysis. Figure S1. Mass and energy flows for the studied system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.S.; methodology, F.S.; software, F.S.; writing—original draft preparation, F.S.; writing—review and editing, F.S., G.B., L.C. and C.R.; supervision, G.B., L.C. and C.R.; project administration, L.C. and C.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work here presented is based on the LCA activities carried out in the framework of the ARCADIA project (“Life cycle approach in public contracts and Italian LCA database for the efficient use of resources”), financed by the 2014–2020 National Operational Programme on Governance and Institutional Capacity.
Data Availability Statement
Data used in this study are from Scrucca et al. (2021) [46]. All the data are available under request to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Nomenclature
| CHP | Combined Heat and Power |
| DALY | Disability Adjusted Life Years |
| FU | Functional Unit |
| GHG | Greenhouse Gases |
| LCA | Life Cycle Assessment |
| LCI | Life Cycle Inventory |
| LCIA | Life Cycle Impact Assessment |
| LTS | Long-Term National Strategy |
| NECP | National Energy and Climate Plan |
| ORC | Organic Rankine Cycle |
| PCR | Product Category Rule |
| Potentially Disappeared Fraction of species | |
| SDGs | Sustainable Development Goals |
References
- United Nations. Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- World Bioenergy Association. Global Bioenergy Statistics 2021. Available online: https://www.worldbioenergy.org/news/640/47/Global-Bioenergy-Statistics-2021/ (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- EUROBSERV’ER. Solid Biofuels Barometer 2022. Available online: https://www.eurobserv-er.org/solid-biomass-barometer-2022/ (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- International Energy Agency. Bioenergy. Available online: https://www.iea.org/fuels-and-technologies/bioenergy (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- IEA Bioenergy 2021 Country Reports. Implementation of Bioenergy in Italy. 2021. Available online: https://www.ieabioenergy.com/blog/publications/2021-country-reports/ (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- International Energy Agency. Italy 2023 Energy Policy Review. Available online: https://iea.blob.core.windows.net/assets/71b328b3-3e5b-4c04-8a22-3ead575b3a9a/Italy_2023_EnergyPolicyReview.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Italian Ministry of the Environment and Energetic Safety. National Energy and Climate Plan. Available online: https://www.mase.gov.it/sites/default/files/PNIEC_2023.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Italian Ministry of the Environment and Energetic Safety. Plan for the Ecological Transition. Available online: https://www.mase.gov.it/sites/default/files/archivio/allegati/PTE/PTE-definitivo.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Italian Ministry of the Environment and Energetic Safety. Long-Term National Strategy on Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Available online: https://www.mase.gov.it/sites/default/files/lts_gennaio_2021.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Scrucca, F.; Barberio, G.; Cutaia, L.; Rinaldi, C. A simplified methodology for estimating the Carbon Footprint of heat generation by forest woodchips as a support tool for sustainability assessment in decision-making. Clean. Environ. Syst. 2023, 9, 100126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbano, D.G.; Aquino, A.; Scrucca, F. Energy Performance, Environmental Impacts and Costs of a Drying System: Life Cycle Analysis of Conventional and Heat Recovery Scenarios. Energies 2023, 16, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moliner, C.; Arato, E.; Marchelli, F. Current Status of Energy Production from Solid Biomass in Southern Italy. Energies 2021, 14, 2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Scalia, G.; Adelfio, L.; La Fata, C.M.; Micale, R. Economic and Environmental Assessment of Biomass Power Plants in Southern Italy. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, S.; Bacenetti, J. Exploring the production of bio-energy from wood biomass. Italian case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, F.; Devlin, G.; McDonnell, K. Forest biomass supply chains in Ireland: A life cycle assessment of GHG emissions and primary energy balances. Appl. Energy 2014, 116, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, T.; Athanassiadis, D.; González-García, S.; Nordfjell, T. Cradle-togate life cycle assessment of forest supply chains: Comparison of Canadian and Swedish case studies. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 866–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyrens, J.P.; Therasme, O.; Germain, R.H. Quantifying the life cycle greenhouse gas emissions of a mechanized shelterwood harvest producing both sawtimber and woodchips. Forests 2022, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laina, R.; Herrero, S.J.; Corona, B.; Tolosana, E.; De La Fuente, T.; San Miguel, G. Economic and environmental assessment of a multifunctional poplar plantation for roundwood and wood chip production in Spain. For. Syst. 2022, 31, e002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perić, M.; Antonijević, D.; Komatina, M.; Bugarski, B.; Rakin, M. Life cycle assessment of wood chips supply chain in Serbia. Renew. Energy 2020, 155, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.V.; Viana, H.; Esteves, B.; Cruz Lopes, L.P.; Domingos, I. Life cycle assessment of residual forestry biomass chips at a power plant: A Portuguese case study. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2014, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincione, R.; Longo, S.; Cellura, M.; Guarino, F.; Brunetti, A. Life Cycle Assessment of Wood Chips from Residual Biomass: A Case Study. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2023, 18, 2253–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, E.; Cespi, D.; Setti, L.; Gombi, E.; Bernardi, E.; Vassura, I.; Passarini, F. Biomass residues to renewable energy: A life cycle perspective applied at a local scale. Energies 2016, 9, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, C.; Rogaume, Y.; Dieckhoff, L.; Bardeau, G.; Pons, M.N.; Dufour, A. Effect of combustion technology and biogenic CO2 impact factor on global warming potential of wood-to-heat chains. Appl. Energy 2019, 235, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Canter, C.E.; Kumar, A. Life-cycle energy and emission analysis of power generation from forest biomass. Appl. Energy 2014, 128, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliaferri, C.; Evangelisti, S.; Clift, R.; Lettieri, P. Life cycle assessment of a biomass CHP plant in UK: The Heathrow energy centre case. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 133, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, B.; Shen, L.; Sommersacher, P.; Junginger, M. Consequential Life Cycle Assessment of energy generation from waste wood and forest residues: The effect of resource-efficient additives. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcioglu, G.; Jeswani, H.K.; Azapagic, A. Energy from forest residues in Turkey: An environmental and economic life cycle assessment of different technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klavina, K.; Romagnoli, F.; Blumberga, D. Comparative life cycle assessment of woodchip uses in pyrolysis and combined heat and power production in Latvia. Energy Procedia 2017, 113, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgarbossa, A.; Boschiero, M.; Pierobon, F.; Cavalli, R.; Zanetti, M. Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of Bioenergy Production from Different Wood Pellet Supply Chains. Forests 2020, 11, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Latta, G.; Lee, U.; Lewandrowski, J.; Wang, M. Regionalized Life Cycle Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Forest Biomass Use for Electricity Generation in the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 14806–14816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoppato, A.; Benato, A. Life Cycle Assessment of a Commercially Available Organic Rankine Cycle Unit Coupled with a Biomass Boiler. Energies 2020, 13, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargiulo, A.; Carvalho, M.L.; Girardi, P. Life Cycle Assessment of Italian Electricity Scenarios to 2030. Energies 2020, 13, 3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, J.; Prina, M.G.; Garcia, R. Life-cycle assessment of current and future electricity supply addressing average and marginal hourly demand: An application to Italy. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 399, 136563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENEA. ARCADIA Project. Available online: https://www.arcadia.enea.it/ (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Available online: http://www.pongovernance1420.gov.it/it/progetto/arcadia-approccio-ciclo-di-vita-nei-contratti-pubblici-e-banca-dati-italiana-lca-per-luso-efficiente-delle-risorse/ (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- ISO 17225-4; Solid Biofuels—Fuel Specifications and Classes—Part 4: Graded Wood Chips. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- ISO 14040; Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Principles and Framework. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- ISO 14044; Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Requirements and Guidelines. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- EPD® System. Product Category Rules: Electricity, Steam and Hot/Cold Water Generation and Distribution. Available online: https://www.environdec.com/product-category-rules-pcr/find-your-pcr (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- EPD® System. Product Category Rules: Basic Products from Forestry. Available online: https://www.environdec.com/product-category-rules-pcr/find-your-pcr (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- SCS Global. Product Category Rule Module for Roundwood. Available online: https://cdn.scsglobalservices.com/files/program_documents/pcr_final_wood-products_101816.pdf (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Đuka, A.; Vusić, D.; Horvat, D.; Šušnjar, M.; Pandur, Z.; Papa, I. LCA studies in forestry—Stagnation or progress? Croat. J. For. Eng. 2017, 38, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Piano di Gestione Forestale Della Proprietà Silvo-Pastorale del Consorzio Boschi Carnici—Validità 2012–2023. Available online: https://www.consorzioboschicarnici.it/il-piano-di-gestione-forestale/ (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Brun, F.; Giau, B.; Magnani, C. Appunti per la Stesura Della Stima del Prezzo di Macchiatico. Università degli Studi di Torino. 2003. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/301884697.pdf (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Fonti, P.; Giudici, F. Quantitative and Qualitative Recording of Wood Volume from an Over-Aged Chestnut Coppice Forest. Schweiz. Z. Forstwes. 2001, 152, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Scrucca, F.; Rinaldi, C.; Morara, E.; Argnani, A. Studio di Filiera Cippato Forestale. ARCADIA Project Report. 2021. Available online: https://www.arcadia.enea.it/component/jdownloads/?task=download.send&id=12&catid=16&Itemid=101 (accessed on 27 September 2023).[Green Version]
- Wernet, G.; Bauer, C.; Steubing, B.; Reinhard, J.; Moreno-Ruiz, E.; Weidema, B. The ecoinvent database version 3 (part I): Overview and methodology. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 21, 1218–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PRé Sustainability. SimaPro Software. Available online: https://simapro.com/ (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Giama, E.; Kyriaki, E.; Papaevaggelou, A.; Papadopoulos, A. Energy and Environmental Analysis of Renewable Energy Systems Focused on Biomass Technologies for Residential Applications: The Life Cycle Energy Analysis Approach. Energies 2023, 16, 4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SimaPro Database Manual—Methods Library. Available online: https://simapro.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/DatabaseManualMethods.pdf (accessed on 4 October 2023).
- Fiorentino, G.; Ansanelli, G.; Cerbone, A.; Giocoli, A.; Motola, V.; Zucaro, A. La Filiera delle Biomasse Solide per la Produzione di Energia Elettrica in Italia. ARCADIA Project Report. 2023. Available online: https://www.arcadia.enea.it/component/jdownloads/?task=download.send&id=41&catid=12&Itemid=101 (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Italian Decree “D.M. 2 marzo 2010” on the Traceability of Biomass for the Production of Electricity. Available online: https://www.politicheagricole.it/flex/cm/pages/ServeBLOB.php/L/IT/IDPagina/13563 (accessed on 4 October 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).