The Effect of Salty Environments on the Degradation Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Nafion Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Membrane Pretreatment
2.2.2. Accelerated Degradation via Fenton’s Test
2.2.3. Degradation Analysis and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
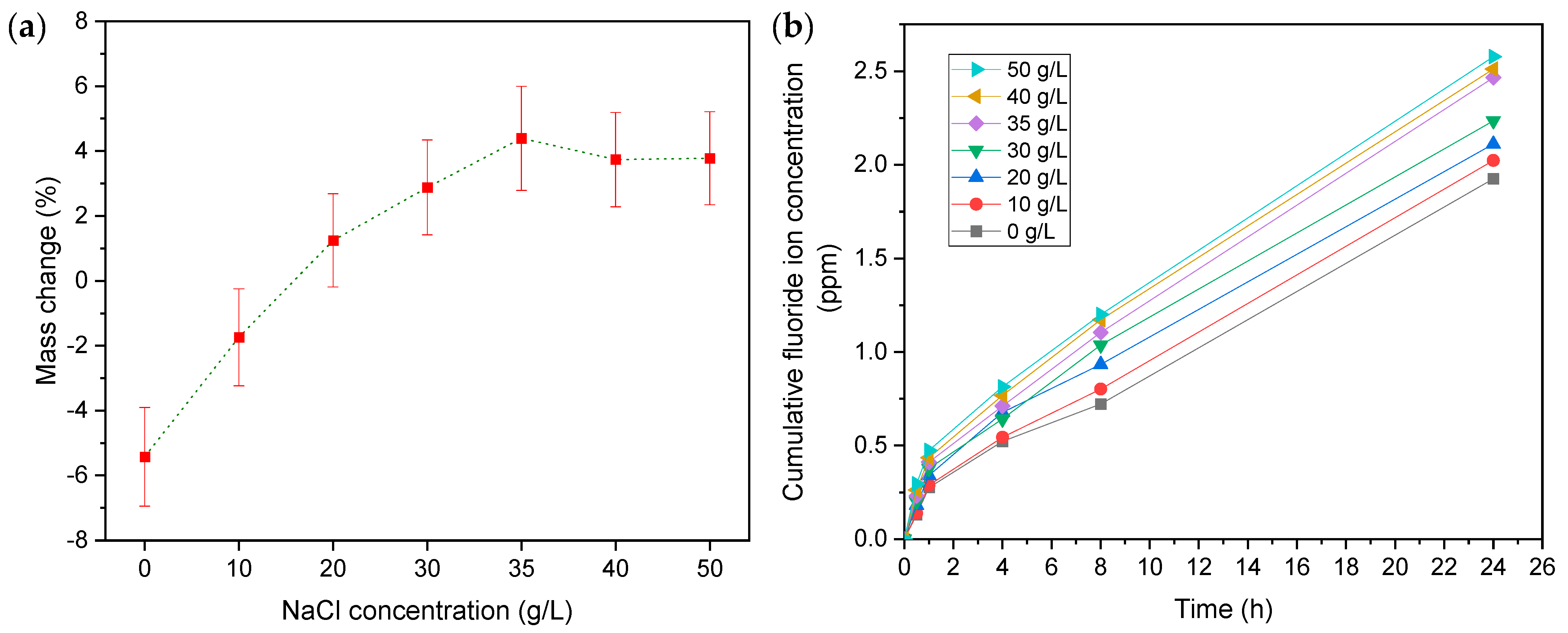
3.1. Effect of NaCl Concentration
3.1.1. Mass Change and Fluoride Emissions
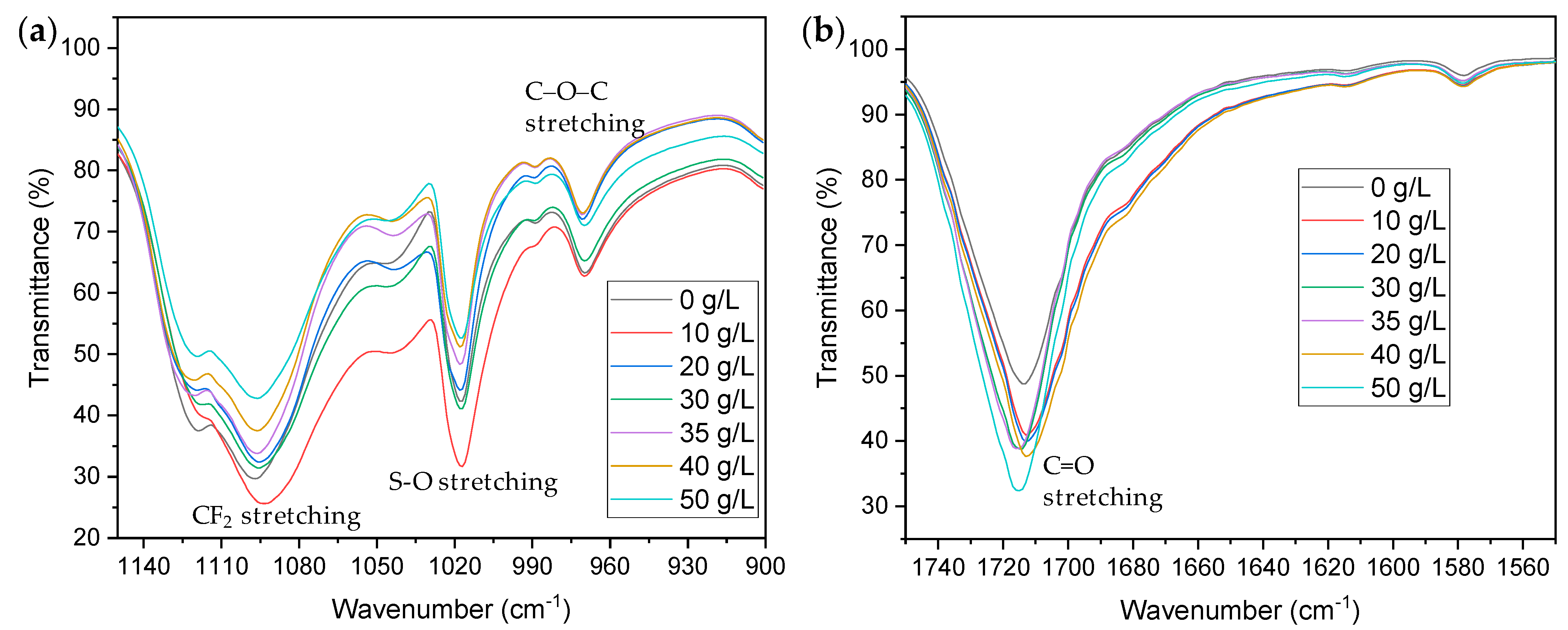
3.1.2. Changes in Chemical Properties
3.1.3. Changes in Mechanical Properties
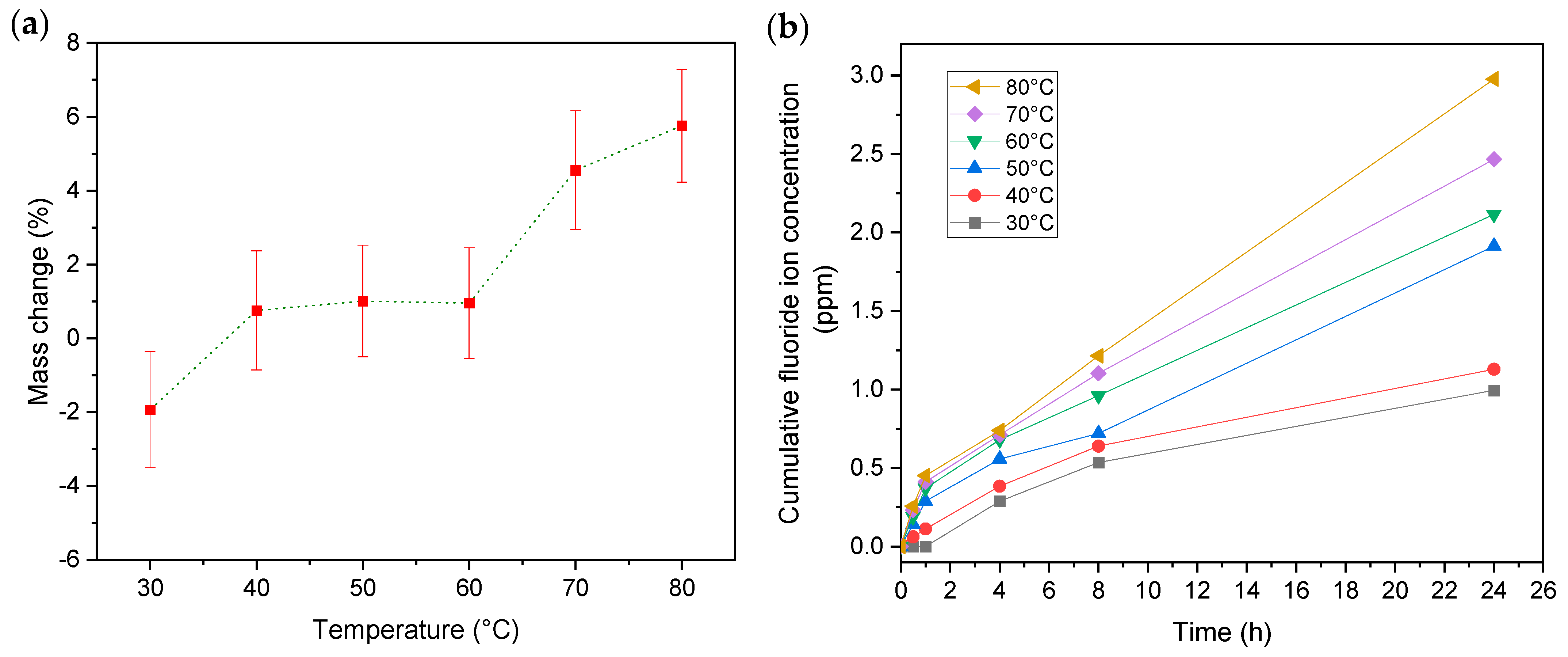
3.2. Effect of Test Temperature
3.2.1. Mass Change and Fluoride Emissions
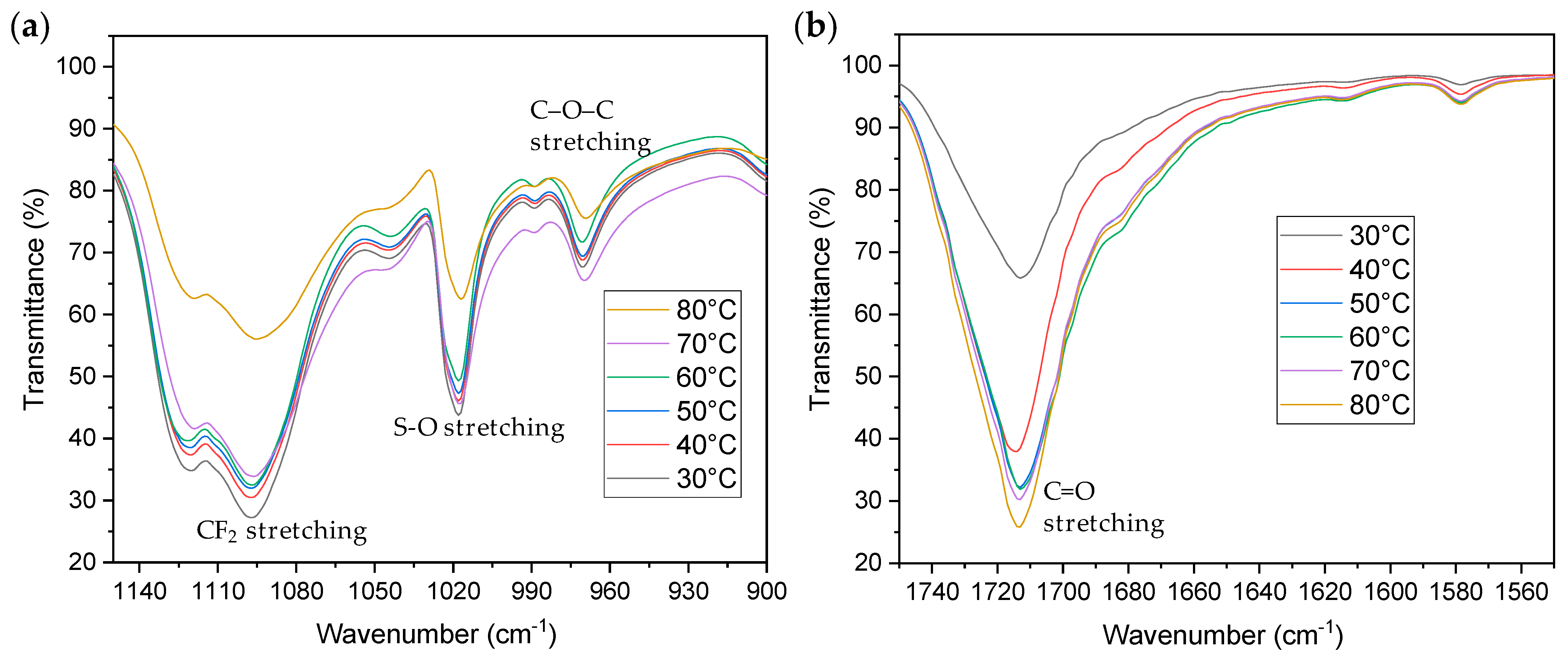
3.2.2. Changes in Chemical Properties
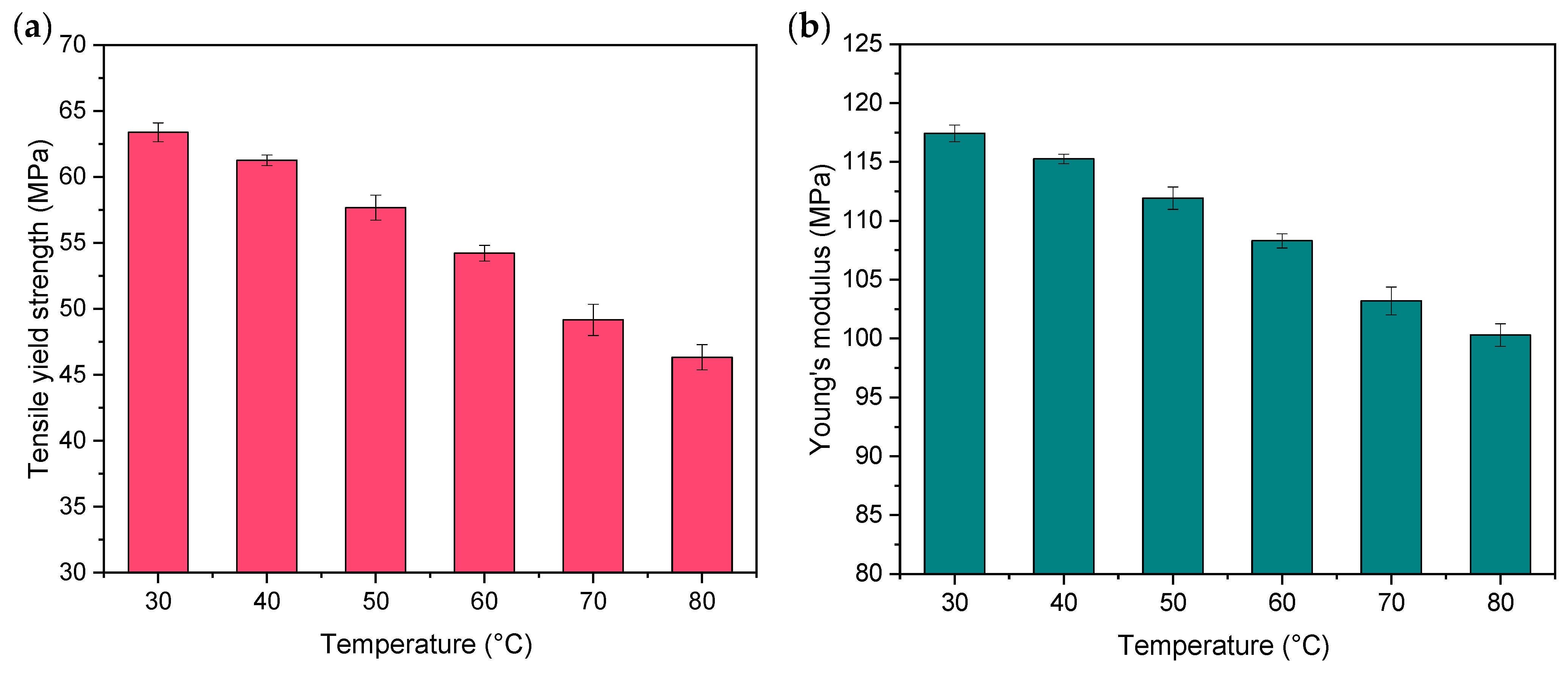
3.2.3. Changes in Mechanical Properties
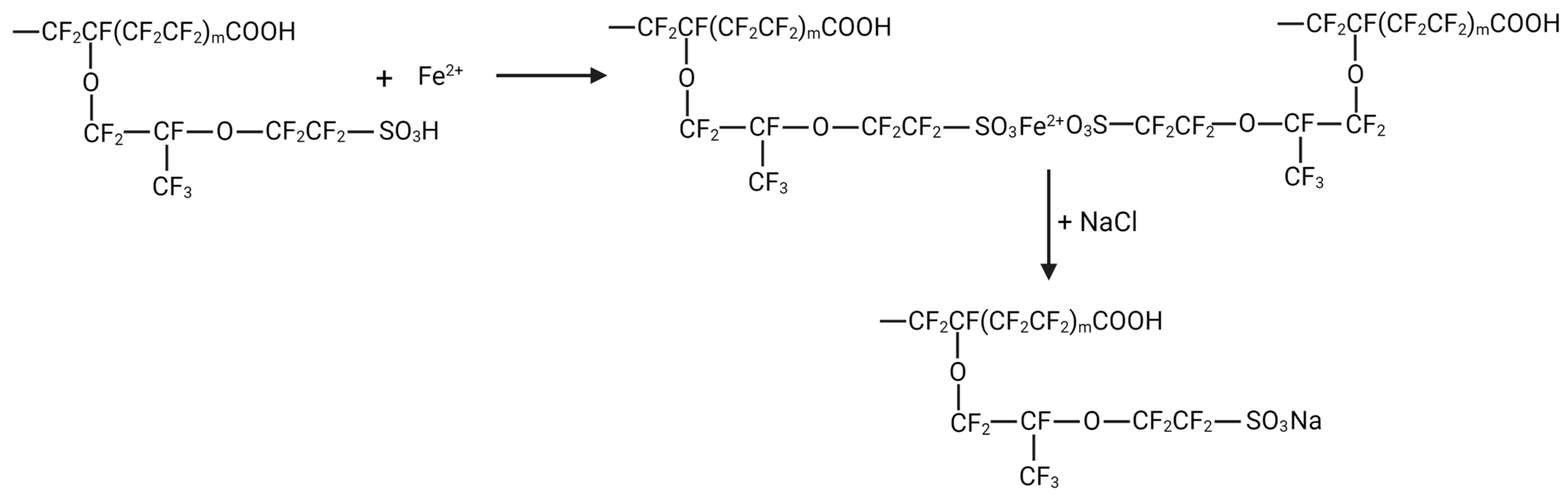
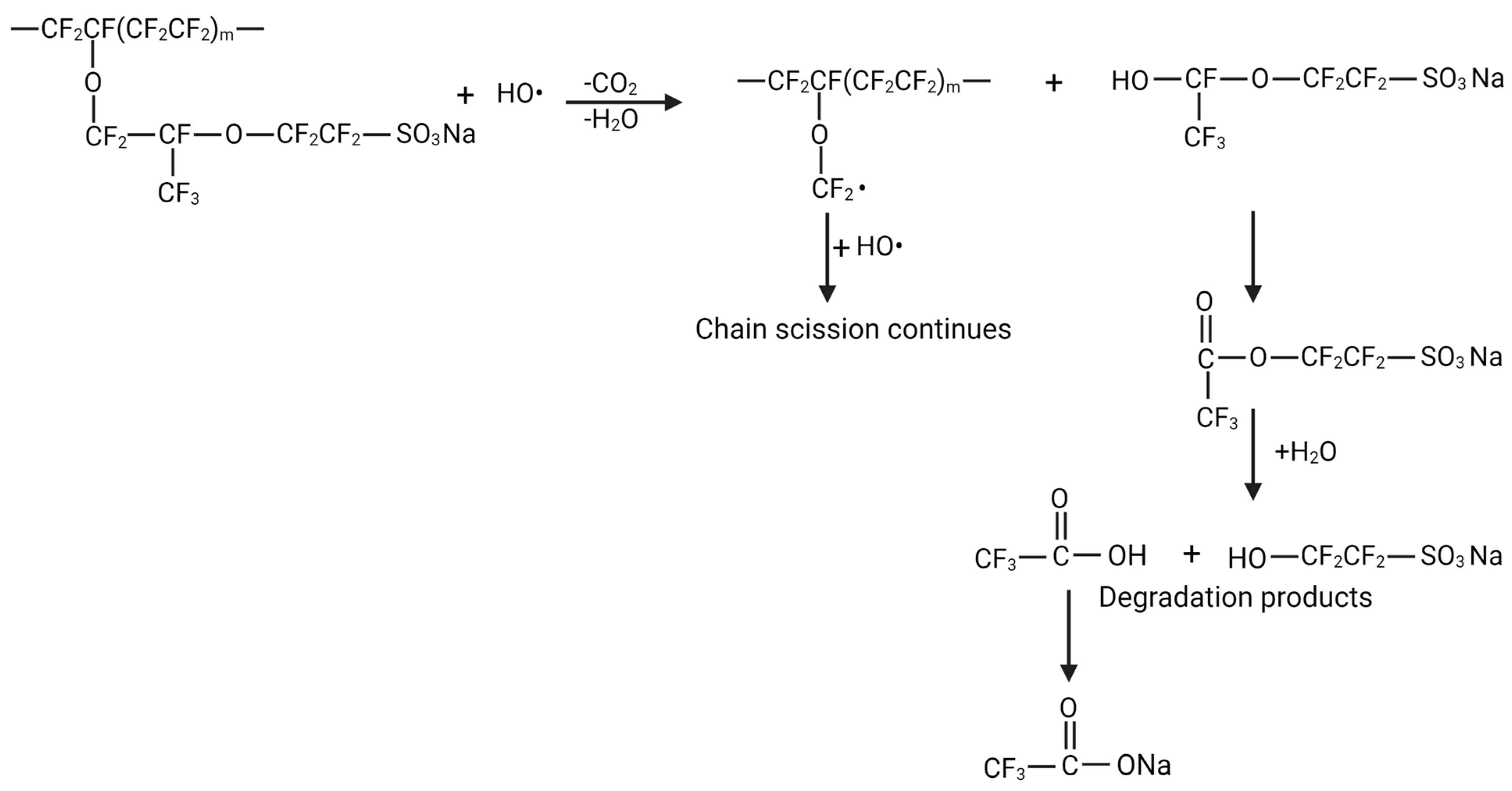
4. Mechanism of Degradation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rivarolo, M.; Rattazzi, D.; Lamberti, T.; Magistri, L. Clean Energy Production by PEM Fuel Cells on Tourist Ships: A Time-Dependent Analysis. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 25747–25757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaraftis, H.N.; Kontovas, C.A. Decarbonization of Maritime Transport: Is There Light at the End of the Tunnel? Sustainability 2021, 13, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yang, G.; Li, S.; Shen, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Liao, J.; Zhang, H. Molecular Dynamics Study on the Impacts of Cations in Sea Salt Aerosol on Transport Performance of Nafion Membranes for PEMFCs in Marine Application. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 27139–27149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marine Application of a New Fuel Cell Powertrain Validated in Demanding Arctic Conditions. Available online: https://projectsites.vtt.fi/sites/maranda/ (accessed on 6 January 2023).
- Elkafas, A.G.; Rivarolo, M.; Gadducci, E.; Magistri, L.; Massardo, A.F. Fuel Cell Systems for Maritime: A Review of Research Development, Commercial Products, Applications, and Perspectives. Processes 2023, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- First Fuel Cell Passenger Ship Unveiled in Hamburg. Fuel Cells Bull. 2008, 2008, 4–5. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Tan, J.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Z.; Hou, Q. Effects of Mg2+ Contamination on the Performance of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell. Energy 2019, 189, 116135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Wang, X.; Ozdemir, M.O.; Uddin, M.A.; Bonville, L.; Pasaogullari, U.; Molter, T. Effect of Cationic Contaminants on Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell Performance. J. Power Sources 2015, 286, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qi, J.; Ozdemir, O.; Uddin, A.; Pasaogullari, U.; Bonville, L.J.; Molter, T. Ca2+ as an Air Impurity in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, F1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yang, G.; Shen, Q.; Li, S.; Li, Z.; Liao, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Ye, W. Study on the Transport Performance Degradation of Nafion Membrane Due to the Presence of Na+ and Ca2+ Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Power Sources 2022, 542, 231740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongsirikarn, K.; Goodwin, J.G.; Greenway, S.; Creager, S. Effect of Cations (Na+, Ca2+, Fe3+) on the Conductivity of a Nafion Membrane. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 7213–7220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasank, B.V.; Rajalakshmi, N.; Dhathathreyan, K.S. Performance Analysis of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cell Stack Operated under Marine Environmental Conditions. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2016, 21, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkola, M.S.; Rockward, T.; Uribe, F.A.; Pivovar, B.S. The Effect of NaCl in the Cathode Air Stream on PEMFC Performance. Fuel Cells 2007, 7, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinumoto, T.; Inaba, M.; Nakayama, Y.; Ogata, K.; Umebayashi, R.; Tasaka, A.; Iriyama, Y.; Abe, T.; Ogumi, Z. Durability of Perfluorinated Ionomer Membrane against Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Power Sources 2006, 158, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passalacqua, E.; Pedicini, R.; Carbone, A.; Gatto, I.; Matera, F.; Patti, A.; Saccà, A. Effects of the Chemical Treatment on the Physical-Chemical and Electrochemical Properties of the Commercial NafionTM NR212 Membrane. Materials 2020, 13, 5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriarte, D.; Andrada, H.; Maldonado Ochoa, S.A.; Silva, O.F.; Vaca Chávez, F.; Carreras, A. Effect of Acid Treatment on the Physico-Chemical Properties of Nafion 117 Membrane. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 21253–21260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Simon, L.C.; Fowler, M.W. Comparison of Two Accelerated NafionTM Degradation Experiments. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millero, F.J.; Feistel, R.; Wright, D.G.; McDougall, T.J. The Composition of Standard Seawater and the Definition of the Reference-Composition Salinity Scale. Deep Sea Res. Part Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2008, 55, 50–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilczuk, M.; Bosnjakovic, A.; Kadirov, M.K.; Schlick, S. Direct ESR and Spin Trapping Methods for the Detection and Identification of Radical Fragments in Nafion Membranes and Model Compounds Exposed to Oxygen Radicals. J. Power Sources 2007, 172, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, A.H.; Joerissen, L. Accelerated Degradation of Perfluorinated Sulfonic Acid Membranes. ECS Trans. 2009, 25, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, M.; El Kaddouri, A.; Perrin, J.-C.; Raya, J.; Lottin, O. Time-Resolved Monitoring of Composite NafionTM XL Membrane Degradation Induced by Fenton’s Reaction. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 621, 118977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.S.; Rashmi, K.R.; Manjunatha, D.V.; Jayarama, A.; Pinto, R. Role of UV Irradiation of Nafion Membranes on Ionic Groups Responsible for Proton Conduction and Mechanical Strength: A FTIR Spectroscopic Analysis. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.S.; Rashmi, K.R.; Manjunatha, D.V.; Jayarama, A.; Prabhu, S.; Pinto, R. Pore Size Tuning of Nafion Membranes by UV Irradiation for Enhanced Proton Conductivity for Fuel Cell Applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 23762–23774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauritz, K.A.; Moore, R.B. State of Understanding of Nafion. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4535–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.R.; De Haseth, J.A. Chemical analysis. In Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-471-19404-0. [Google Scholar]
- Okonkwo, P.C.; Ben Belgacem, I.; Emori, W.; Uzoma, P.C. Nafion Degradation Mechanisms in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) System: A Review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 27956–27973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Fuller, T.F. The Effect of Humidity on the Degradation of Nafion® Membrane. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 1436–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, Y.; Wang, Y.; Palmer, R.A.; Aubuchon, S.R. Stress-Strain Curves of Nafion Membranes in Acid and Salt Forms. Polímeros 2002, 12, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Simon, L.C.; Fowler, M.; Grot, S. Mechanical Properties of NafionTM Electrolyte Membranes under Hydrated Conditions. Polymer 2005, 46, 11707–11715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, D.E.; Lousenberg, R.D.; Henry, T.J.; Tangeman, P.C.; Tisack, M.E. Advanced Materials for Improved PEMFC Performance and Life. J. Power Sources 2004, 131, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, T.; Kawashima, N.; Murakami, T.N. Kinetic Study of Nafion Degradation by Fenton Reaction. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 2615–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühwirt, P.; Kregar, A.; Törring, J.T.; Katrašnik, T.; Gescheidt, G. Holistic Approach to Chemical Degradation of Nafion Membranes in Fuel Cells: Modelling and Predictions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 5647–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madhav, D.; Shao, C.; Mus, J.; Buysschaert, F.; Vandeginste, V. The Effect of Salty Environments on the Degradation Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Nafion Membranes. Energies 2023, 16, 2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16052256
Madhav D, Shao C, Mus J, Buysschaert F, Vandeginste V. The Effect of Salty Environments on the Degradation Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Nafion Membranes. Energies. 2023; 16(5):2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16052256
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadhav, Dharmjeet, Changyuan Shao, Jorben Mus, Frank Buysschaert, and Veerle Vandeginste. 2023. "The Effect of Salty Environments on the Degradation Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Nafion Membranes" Energies 16, no. 5: 2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16052256
APA StyleMadhav, D., Shao, C., Mus, J., Buysschaert, F., & Vandeginste, V. (2023). The Effect of Salty Environments on the Degradation Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Nafion Membranes. Energies, 16(5), 2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16052256







