Effect of Scale and Structure Changes of China’s High-Carbon Industries on Regional Carbon Emissions
Abstract
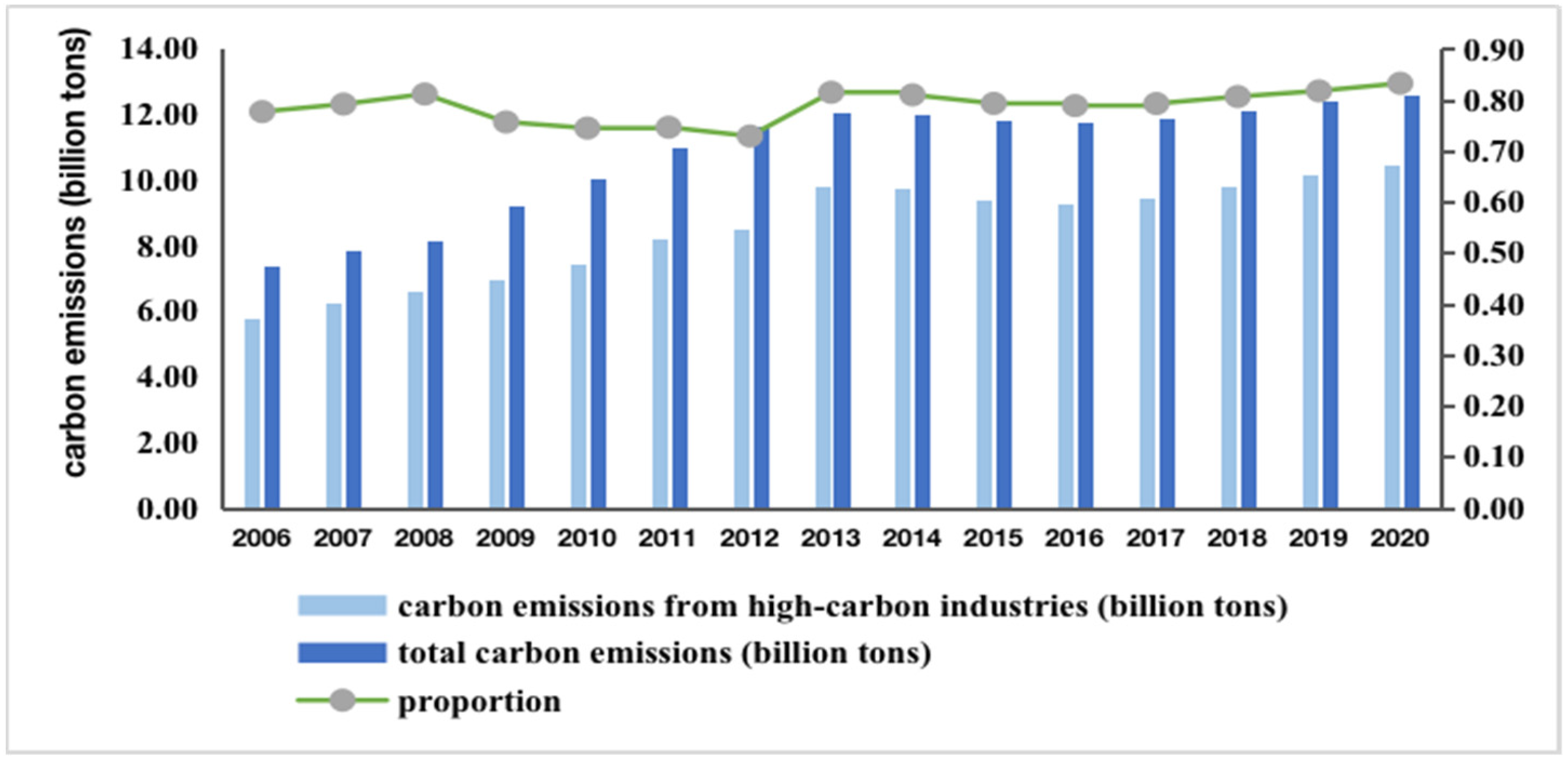
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Mechanism and Research Hypothesis
2.1. Structural Effects
2.2. Resource Utilization Effect
2.3. Policy Effect
3. Study Design
3.1. Model Construction
3.2. Variable Selection and Data Description
3.2.1. Interpreted Variables
3.2.2. Core Explanatory Variables
3.2.3. Control Variables
4. Empirical Analysis
4.1. Unit Root Inspection
4.2. Multiple Collinearity Test
4.3. Hausman-Test
4.4. Empirical Results Analysis Based on a Fixed-Effects Model
4.5. Heterogeneity Analysis
4.6. Empirical Results Analysis Based on Double Difference Model
4.7. Robustness Test
5. Study Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, T. Which policy is more effective, carbon reduction in all industries or in high energy-consuming Industries?—From dual perspectives of welfare effects and economic effects. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 216, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; Fan, J.; Zeng, Y.X.; Guo, R. Space and temporal differences of carbon emission intensity of China’s energy-consuming industries and its influencing factors. J. Ecol. 2019, 39, 8357–8369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.J.; Qin, Y.C.; Zhang, J.F. The spatial and temporal evolution of carbon emissions in China’s high carbon manufacturing industry. Resour. Sci. 2020, 42, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. Research on the influencing factors of living energy consumption and carbon emissions based on spatiotemporal model. J. Comb. Optim. 2022, 45, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Yi, J.Z.; Chen, A.B.; Zhou, G. Application of PVAR model in the study of influencing factors of carbon emissions. Math. Biosci. Eng. MBE 2022, 19, 13227–13251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.L.; Han, Y. Influencing factors and decoupling analysis of carbon emissions in China’s manufacturing industry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 64719–64738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Sun, Z.Y. Analysis of Influencing Factors of Land Use Carbon Emission based on STIRTAP Model: A Case Study of Duolun County, Inner Mongolia. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2021, 2, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.H.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.J. Study on Influencing Factors of Carbon Emission of Civil Buildings Based on Regional Differences. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 647, 012194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, C.J.; Cheng, X.J.; Yu, S.S.; Ye, X. Analysis on the influencing factors of carbon emission in China’s logistics industry based on LMDI method. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 138473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Xu, P.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Liu, C. Influencing mechanisms and decoupling effects of embodied carbon emissions: An analysis based on China’s industrial sector. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2023, 41, 320–333. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, J.; Jiang, H. An Analysis of the Influencing Factors of Carbon Dioxide Emissions—Base on the Consumption Choice. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1578, 012223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Chen, S.; Gao, Q.; Xu, L. Analysis of the influencing factors of energy-related carbon emissions in Kazakhstan at different stages. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 36630–36638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cifuentes-Faura, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, L. Government environmental attention and carbon emissions governance: Firm-level evidence from China. Econ. Anal. Policy 2023, 80, 121–142. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Qiu, F.; Li, H.; Zeng, M.; Sun, C. Influencing Factors Model of Carbon Emissions from a Global Perspectives. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 514, 032037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.; Tang, Z.; Wang, W.; Liang, Y. Evaluation and influencing factors of the tourism industry efficiency under carbon emission constraints in China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1093. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, P. Short-term carbon emission prediction method of green building based on IPAT model. Int. J. Glob. Energy Issues 2023, 45, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Tan, H.; Wang, F.; You, X. Analysis of the impact factors on carbon emission in Fujian province. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 170, 032025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, B.; Zheng, H.B. Study on influencing factors of carbon emissions for industrial energy consumption in Dalian based on LMDI model. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 64, 012043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.C. Enterprise Innovation, Executive Experience and Internationalization Strategy: Evidence from High-Carbon Industrial Enterprises versus Low-Carbon Industrial Enterprises in China. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 9, 821269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.M.; Liu, C.J.; Yang, M. The effects of environmental regulation on China’s total factor productivity: An empirical study of carbon-intensive industries. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 179, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.L.; Fang, L. Empirical study on the impact of environmental regulation on enterprise competitiveness in pollution-intensive industries in China. China’s Popul. Resour. Environ. 2012, 22, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Sun, F.L. Research on the transformation of development mode of high energy consumption industry in China from the perspective of low carbon economy. Econ. Forum 2016, 7, 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.E.; Guan, Y.J.; Duan, H.Y. The interest game of setting up low-carbon trade barriers and China’s export trade countermeasures. Bus. Econ. Res. 2016, 12, 142–143. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, S.; Arshed, N.; Anwar, A.; Iqbal, M.; Sattar, N. Renewable Energy Consumption and Carbon Emissions—Testing Nonlinearity for Highly Carbon Emitting Countries. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Research on the dynamic relationship between China’s renewable energy consumption and carbon emissions based on ARDL model. Resour. Policy 2022, 77, 102764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, J.J.; Shi, D. The impact of emissions trading system on corporate energy efficiency: Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Energy 2021, 233, 121129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Yu, M.; Sun, C.; Han, Z. Green innovation effect of emission trading policy on pilot areas and neighboring areas: An analysis based on the spatial econometric model. Energy Policy 2021, 156, 112431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Duan, M.S.; Zhang, P. Analysis of the Impact of China’s Emissions Trading Scheme on Reducing Carbon Emissions. Energy Procedia 2019, 158, 3596–3601. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Shi, B.; Ji, H. How to decouple income growth from household carbon emissions: A perspective based on urban-rural differences in China. Energy Econ. 2023, 125, 106816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Luo, Y.; Zou, H.; Huang, J. Understanding the driving factors and finding the pathway to mitigating carbon emissions in China’s Yangtze River Delta region. Energy 2023, 278, 127897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. The impact of environmental regulation and carbon emissions on green technology innovation from the perspective of spatial interaction: Empirical evidence from urban agglomeration in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoyan, L. Local government decision-making competition and regional carbon emissions: Experience evidence and emission reduction measures. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 50, 101800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, Y.; Guo, L. Environmental Regulation Strength and Production Technology Progress. Econ. Res. 2012, 22, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Feng, X.; Liu, P.; Wang, N. Impact of Intelligence on the Carbon Emissions of Ener Consumption in the Mining Industry Based on the Expanded STIRPAT Model. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 159, 105504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fan, D. Carbon emission quota allocation of high energy consumption industries in undeveloped areas–A case study of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Xiong, Y.; Du, C. Does carbon emission trading policy promote the corporate technological innovation? Empirical evidence from China’s high-carbon industries. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 411, 137286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y. Dynamic evaluation of low-carbon development in China’s power industry and the impact of carbon market policies. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.M.; Huo, C.J. Impact of Green Innovation Efficiency on Carbon Emission Reduction in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao GBA. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hong, X.; Peng, K. A spatial panel analysis of carbon emissions, economic growth and high-technology industry in China. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2019, 49, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, G.; Guo, X. Long-Term and Short-Term Effects of Carbon Emissions on Regional Healthy Development in Shanxi Province, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Observations | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE | 450 | 386.96 | 282.62 | 19.79 | 1541.12 |
| S | 450 | 0.3829 | 0.3676 | 0.0305 | 1.7522 |
| V | 450 | 8837.39 | 8310.66 | 239.58 | 44,905.82 |
| Urban | 450 | 0.5577 | 0.1373 | 0.2745 | 0.8958 |
| Ei | 450 | 0.997 | 0.655 | 0.170 | 4.099 |
| Open | 450 | 0.2959 | 0.3552 | 0.0076 | 1.7991 |
| Er | 450 | 0.0041 | 0.0037 | 0.0001 | 0.0310 |
| Fdi | 450 | 0.0215 | 0.0198 | 0.0001 | 0.1210 |
| Variable | LLC Test | First-Order Differential LLC Test |
|---|---|---|
| lnCE | 0.0003 *** | 0.0000 *** |
| lnS | 0.0000 *** | 0.0000 *** |
| InV | 0.0000 *** | 0.0000 *** |
| lnUrban | 0.0000 *** | 0.0000 *** |
| lnEi | 0.0026 *** | 0.0000 *** |
| lnOpen | 0.0000 *** | 0.0000 *** |
| lnEr | 0.0377 ** | 0.0000 *** |
| lnFdi | 0.0000 *** | 0.0000 *** |
| Variable | VIF | 1/VIF |
|---|---|---|
| lnS | 1.25 | 0.798574 |
| lnV | 1.31 | 0.765428 |
| lnUrban | 1.86 | 0.537268 |
| lnEi | 2.31 | 0.433342 |
| lnOpen | 1.83 | 0.547277 |
| lnEr | 1.72 | 0.582415 |
| lnFdi | 1.16 | 0.862921 |
| Mean VIF | 1.63 |
| Test | p | The Results Indicate That |
|---|---|---|
| F-test | 0.0000 | The fixed effect was better than the mixed effects. |
| LM-test | 0.0000 | Random effects outperformed mixed effects. |
| Hausman-test | 0.0000 | The fixed effect was better than the random effects. |
| Explanatory Variable | Explained Variable lnCEs | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
| lnS | 0.0775 *** (4.46) | 0.0888 *** (5.70) | 0.166 *** (7.86) |
| lnV | 0.395 *** (29.84) | 0.407 *** (18.98) | 0.424 *** (20.13) |
| lnS × lnV | −0.0361 *** (−5.23) | ||
| lnUrban | 0.833 *** (9.27) | 0.773 *** (8.79) | |
| lnEi | 0.298 *** (9.86) | 0.295 *** (10.09) | |
| lnOpen | −0.0458 * (−2.39) | −0.0393 * (−2.12) | |
| lnEr | 0.00575 (0.64) | 0.00303 (0.35) | |
| lnFdi | −0.0200 (−1.87) | −0.0257 * (−2.46) | |
| _cons | 2.364 *** (20.72) | 2.712 *** (11.88) | 2.725 *** (12.31) |
| Division Basis | Region |
|---|---|
| Rich in high-carbon energy industries | Shandong, Shanxi, Liaoning, Inner Mongolia, Shaanxi, Guangdong, Hebei, Henan |
| Rich in high-carbon non-energy industries | Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Hubei, Sichuan, Fujian, Hunan, Anhui, Tianjin, Shanghai, Jiangxi, Guangxi, Guizhou, Yunnan, Xinjiang |
| Sparse in high-carbon industries | Hainan, Qinghai, Ningxia, Chongqing, Gansu, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Beijing |
| Explanatory Variable | Explained Variable lnCEs | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| lnS | 0.439 *** (8.74) | 0.300 *** (8.28) | 0.0703 * (2.47) |
| lnV | 0.444 *** (15.08) | 0.372 *** (13.18) | 0.487 *** (13.87) |
| lnS × lnV | −0.0764 *** (−8.24) | −0.154 *** (−9.86) | 0.0017 (0.18) |
| lnUrban | 0.778 *** (5.55) | 0.206 (1.66) | 1.556 *** (10.43) |
| lnEi | 0.216 *** (3.42) | 0.0909 * (2.50) | 0.483 *** (8.78) |
| lnOpen | −0.0477 (−1.55) | −0.0577 (−1.93) | 0.0170 (0.69) |
| lnEr | −0.00053 (−0.04) | 0.00862 (0.64) | −0.00452 (−0.40) |
| lnFdi | −0.0743 *** (−4.83) | 0.0285 (1.46) | 0.0368 ** (2.67) |
| _cons | 3.205 *** (10.70) | 3.459 *** (10.44) | 2.314 *** (6.62) |
| Explanatory Variable | Explained Variable lnCEs | |
|---|---|---|
| (7) | (8) | |
| treat × time | −0.245 *** (−3.10) | −0.079 * (−1.87) |
| lnS | 0.151 ** (2.61) | |
| lnV | 0.426 *** (8.78) | |
| lnS × lnV | −0.033 * (−1.89) | |
| lnUrban | 0.630 ** (2.17) | |
| lnEi | 0.272 ** (2.40) | |
| lnOpen | −0.042 (−1.13) | |
| lnEr | −0.0017 (−0.16) | |
| lnFdi | −0.026 (−1.52) | |
| _cons | 5.563 *** (290.32) | 2.547 *** (4.92) |
| Area fixation effect | Yes | Yes |
| Time fixed effect | Yes | Yes |
| R-sq | 0.3736 | 0.7820 |
| Explanatory Variable | Explained Variable lnPCEs | Explained Variable lnCI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coef. | t | Coef. | t | |
| lnS | 0.191 *** | 8.51 | 0.277 *** | 10.24 |
| lnV | 0.368 *** | 16.45 | 0.042 * | 1.55 |
| lnS × lnV | −0.0354 *** | −4.82 | −0.0365 *** | −4.12 |
| lnUrban | 0.865 *** | 9.25 | −0.599 *** | −5.31 |
| lnEi | 0.313 *** | 10.05 | 0.646 *** | 17.19 |
| lnOpen | 0.0066 | 0.33 | 0.0780 ** | 3.27 |
| lnEr | 0.0061 | 0.66 | 0.0166 | 1.49 |
| lnFdi | −0.0252 * | −2.27 | 0.0165 | 1.23 |
| _cons | −4.787 *** | −20.33 | −3.607 *** | −12.68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, J.; Pan, L. Effect of Scale and Structure Changes of China’s High-Carbon Industries on Regional Carbon Emissions. Energies 2023, 16, 6676. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16186676
Liang J, Pan L. Effect of Scale and Structure Changes of China’s High-Carbon Industries on Regional Carbon Emissions. Energies. 2023; 16(18):6676. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16186676
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Jing, and Lingying Pan. 2023. "Effect of Scale and Structure Changes of China’s High-Carbon Industries on Regional Carbon Emissions" Energies 16, no. 18: 6676. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16186676
APA StyleLiang, J., & Pan, L. (2023). Effect of Scale and Structure Changes of China’s High-Carbon Industries on Regional Carbon Emissions. Energies, 16(18), 6676. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16186676





