Nexus between Energy Consumption, Foreign Direct Investment, Oil Prices, Economic Growth, and Carbon Emissions in Italy: Fresh Evidence from Autoregressive Distributed Lag and Wavelet Coherence Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature
2.1. GDP and CO2 Emissions
2.2. Energy Consumption and CO2 Emissions
2.3. Foreign Direct Investment and CO2 Emissions
2.4. Exports and CO2 Emissions
2.5. Oil Price and CO2 Emissions
3. Data and Methodology
3.1. Data and Variables
3.2. Autoregressive Distributed Lag Model (ARDL)
3.3. Wavelet Coherence Approach
4. Empirical Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
4.2. Unit Root Test Results
4.3. ARDL Results
4.4. Robustness Check
4.5. Diagnostics Tests Results
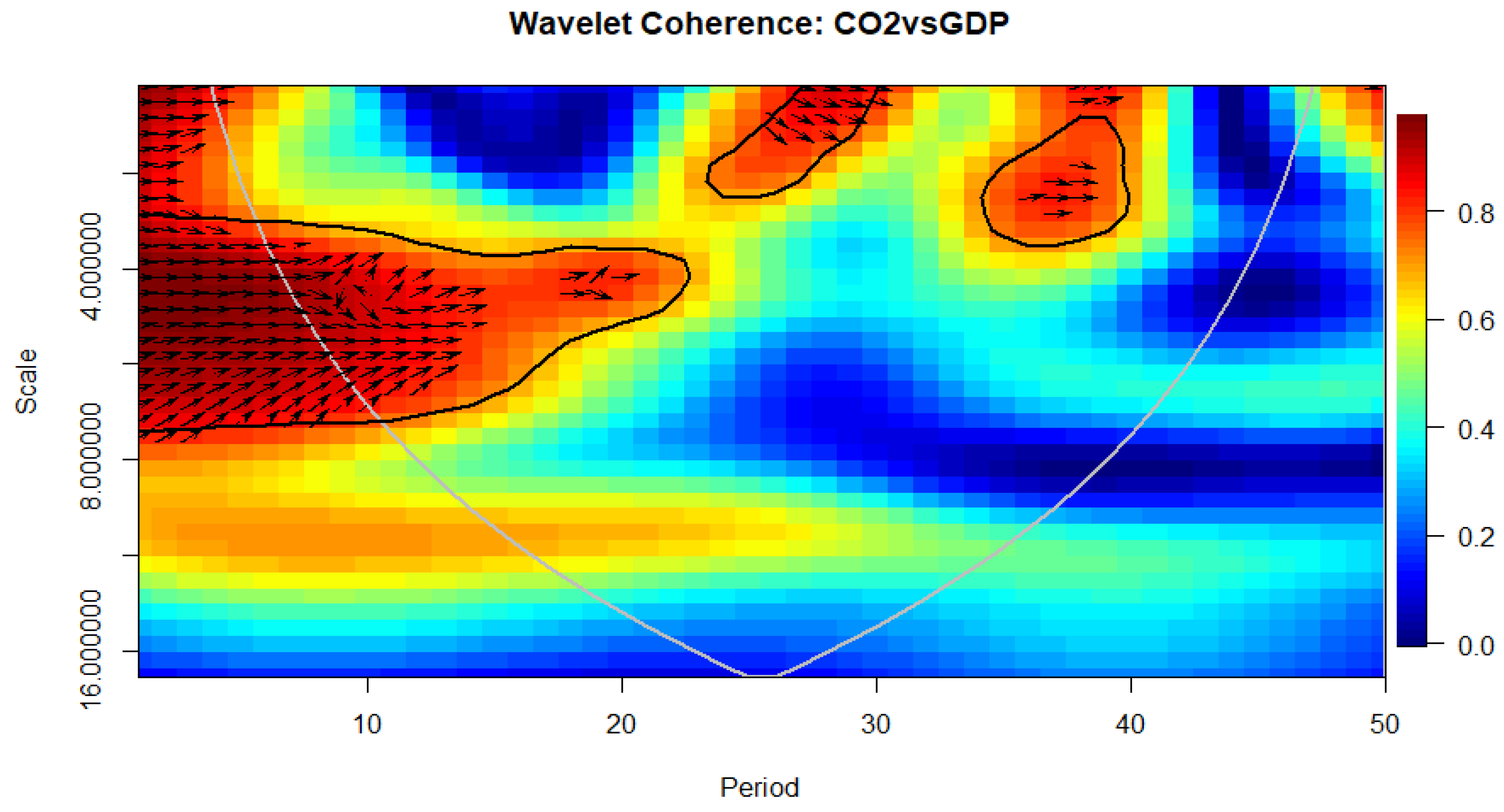
4.6. Wavelet Coherence Approach
5. Conclusions and Policy Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karimi, M.S.; Ahmad, S.; Karamelikli, H.; Dinç, D.T.; Khan, Y.A.; Sabzehei, M.T.; Abbas, S.Z. Dynamic linkages between renewable energy, carbon emissions and economic growth through nonlinear ARDL approach: Evidence from Iran. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadaoui, H. The impact of financial development on renewable energy development in the MENA region: The role of institutional and political factors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 39461–39472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Altarhouni, A.; Danju, D.; Samour, A. Insurance market development, energy consumption, and Turkey’s CO2 emissions. New Perspectives from a Bootstrap ARDL Test. Energies 2021, 14, 7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish; Wang, Z. Dynamic relationship between tourism, economic growth, and environmental quality. J. Sustain. Tour. 2018, 26, 1928–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.Z.; Chien, F.; Sadiq, M. A gateway towards a sustainable environment in emerging countries: The nexus between green energy and human Capital. Econ. Res. -Ekon. Istraživanja 2022, 35, 4159–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Shahzad, S.J.H.; Mahalik, M.K. Is globalization detrimental to CO2 emissions in Japan? New threshold analysis. Environ. Model. Assess. 2018, 23, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.W.; Sinha, A.; Ahmed, Z.; Qin, Q.; Zaidi, S.A.H. Effects of biomass energy consumption on environmental quality: The role of education and technology in Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation countries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 142, 110868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A.B. Environmental Impacts of a North American Free Trade Agreement; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, A.R.; Viswanathan, K.K.; Hassan, S. The Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) and the environmental problem of the day. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznet, S. Economic growth and income inequality. Am. Econ. Rev. 1955, 45, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Balsalobre-Lorente, D.; Shahbaz, M.; Roubaud, D.; Farhani, S. How economic growth, renewable electricity and natural resources contribute to CO2 emissions? Energy Policy 2018, 113, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheikh, N.B.; Zaied, Y.B.; Chevallier, J. On the nonlinear relationship between energy use and CO2 emissions within an EKC framework: Evidence from panel smooth transition regression in the MENA region. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2021, 55, 101331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lean, H.H.; Smyth, R. CO2 emissions, electricity consumption and output in ASEAN. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 1858–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selden, T.M.; Song, D. Environmental quality and development: Is there a Kuznets curve for air pollution emissions? J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 1994, 27, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, D.I. The rise and fall of the environmental Kuznets curve. World Dev. 2004, 32, 1419–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nižetić, S.; Djilali, N.; Papadopoulos, A.; Rodrigues, J.J. Smart technologies for promotion of energy efficiency, utilization of sustainable resources and waste management. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 231, 565–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, S.; Qayyum, U.; Majeed, T. FDI and environmental degradation: The role of political institutions in South Asian countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 32544–32553. [Google Scholar]
- Abdouli, M.; Kamoun, O.; Hamdi, B. The impact of economic growth, population density, and FDI inflows on CO2 emissions in BRICTS countries: Does the Kuznets curve exist? Empir. Econ. 2018, 54, 1717–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku, E.E.O.; Boachie, M.K. The environmental impact of industrialization and foreign direct investment. Energy Policy 2020, 137, 111178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujtaba, A.; Jena, P.K.; Joshi, D.P.P. Growth and determinants of CO2 emissions: Evidence from selected Asian emerging economies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 39357–39369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, M.Y.; Latif, K.; Khan, Z.; Butt, H.D.; Hussain, M.; Nadeem, M.A. Symmetric and asymmetric impact of oil price, FDI and economic growth on carbon emission in Pakistan: Evidence from A RDL and non-linear ARDL approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138421. [Google Scholar]
- Salman, M.; Long, X.; Dauda, L.; Mensah, C.N.; Muhammad, S. Different impacts of export and import on carbon emissions across 7 ASEAN countries: A panel quantile regression approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarin, S.A.; Al-Mulali, U.; Ozturk, I. Validating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in India and China: The role of hydroelectricity consumption. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 1578–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pata, U.K. Renewable energy consumption, urbanization, financial development, income and CO2 emissions in Turkey: Testing EKC hypothesis with structural breaks. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J. Do nuclear and renewable energy improve the environment? Empirical evidence from the United States. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destek, M.A.; Sarkodie, S.A. Investigation of environmental Kuznets curve for ecological footprint: The role of energy and financial development. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2483–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçak, E.; Şarkgüneşi, A. The impact of foreign direct investment on CO2 emissions in Turkey: New evidence from cointegration and bootstrap causality analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 790–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliru, A.M.; Loganathan, N.; Hassan, A.A.G.; Mardani, A.; Kamyab, H. Re-examining the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in the Economic Community of West African States: A panel quantile regression approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124247. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.F.; Tan, B.W. The impact of energy consumption, income and foreign direct investment on carbon dioxide emissions in Vietnam. Energy 2015, 79, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pao, H.T.; Tsai, C.M. Multivariate Granger causality between CO2 emissions, energy consumption, FDI (foreign direct investment) and GDP (gross domestic product): Evidence from a panel of BRIC (Brazil, Russian Federation, India, and China) countries. Energy 2011, 36, 685–693. [Google Scholar]
- Nasir, M.; Rehman, F.U. Environmental Kuznets curve for carbon emissions in Pakistan: An empirical investigation. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Zhou, D.Q.; Zhou, P.; Wang, Q.W. CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in China: A panel data analysis. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 4870–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozatac, N.; Gokmenoglu, K.K.; Taspinar, N. Testing the EKC hypothesis by considering trade openness, urbanization, and financial development: The case of Turkey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16690–16701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haseeb, A.; Xia, E.; Baloch, M.A.; Abbas, K. Financial development, globalization, and CO2 emission in the presence of EKC: Evidence from BRICS countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 31283–31296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesagan, E.P.; Nwachukwu, M.I. Determinants of environmental quality in Nigeria: Assessing the role of financial development. Econom. Res. Financ. 2018, 3, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, S.; Bulus, G.C. Testing validity of the EKC hypothesis in South Korea: Role of renewable energy and trade openness. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 29043–29054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Hye, Q.M.A.; Tiwari, A.K.; Leitão, N.C. Economic growth, energy consumption, financial development, international trade and CO2 emissions in Indonesia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 25, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Shahbaz, M.; Hye, Q.M.A. The environmental Kuznets curve and the role of coal consumption in India: Cointegration and causality analysis in an open economy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 18, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bölük, G.; Mert, M. The renewable energy, growth and environmental Kuznets curve in Turkey: An ARDL approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acaravci, A.; Ozturk, I. On the relationship between energy consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth in Europe. Energy 2010, 35, 5412–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, M.; Ecevit, E.; Yucel, A.G. The impact of economic growth, energy consumption, trade openness, and financial development on carbon emissions: Empirical evidence from Turkey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 36589–36603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, E.; Inglesi-Lotz, R. The impact of economic structure to the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis: Evidence from European countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12717–12724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekun, F.V.; Agboola, M.O.; Joshua, U. Fresh insight into the EKC hypothesis in Nigeria: Accounting for total natural resources rent. In Econometrics of Green Energy Handbook; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 221–243. [Google Scholar]
- Khattak, S.I.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, Z.U.; Khan, A. Exploring the impact of innovation, renewable energy consumption, and income on CO2 emissions: New evidence from the BRICS economies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 13866–13881. [Google Scholar]
- Zmami, M.; Ben-Salha, O. An empirical analysis of the determinants of CO2 emissions in GCC countries. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2020, 27, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Lai, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xia, H. Exploring the effects of economic growth, and renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on China’s CO2 emissions: Evidence from a regional panel analysis. Renew. Energy 2019, 140, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, S.; Okumus, I.; Guzel, A.E. Revisiting the Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis in OECD countries: The role of renewable, non-renewable energy, and oil prices. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 23655–23663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, N.; Elfaki, K.E. Examining the Relationship between Energy Consumption, Economic Growth, and Environmental Degradation in Indonesia: Do Capital and Trade Openness Matter? Int. J. Renew. Energy Dev. 2021, 10, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.A.H.; Hou, F.; Mirza, F.M. The role of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption in CO2 emissions: A disaggregate analysis of Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 31616–31629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogan, E.; Ozturk, I. The influence of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and real income on CO2 emissions in the USA: Evidence from structural break tests. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 10846–10854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agboola, P.O.; Hossain, M.; Gyamfi, B.A.; Bekun, F.V. Environmental consequences of foreign direct investment influx and conventional energy consumption: Evidence from dynamic ARDL simulation for Turkey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 53584–53597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Kashem, M.A. Carbon emissions, energy consumption and industrial growth in Bangladesh: Empirical evidence from ARDL cointegration and Granger causality analysis. Energy Policy 2017, 110, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehry, A.S.; Belloumi, M. Energy consumption, carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth: The case of Saudi Arabia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, T.S. Dynamic relationship between oil price and inflation in oil exporting economy: Empirical evidence from wavelet coherence technique. Energy Econ. Lett. 2020, 7, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Adebayo, T.S.; Akinsola, G.D. Investigating the Causal Linkage among Economic Growth, Energy Consumption and CO2 Emissions in Thailand: An Application of the Wavelet Coherence Approach. Int. J. Renew. Energy Dev. 2021, 10, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Shahbaz, M.; Nasreen, S.; Abbas, F.; Anis, O. Does foreign direct investment impede environmental quality in high-, middle-, and low-income countries? Energy Econ. 2015, 51, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarin, S.A.; Al-Mulali, U. Influence of foreign direct investment on indicators of environmental degradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 24845–24859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, M.A.; Zhang, J.; Iqbal, K.; Iqbal, Z. The effect of financial development on ecological footprint in BRI countries: Evidence from panel data estimation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 6199–6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F.; Su, H.; Li, Y.; Qian, W.; Xiao, J.; Guo, S. The Impact of Foreign Direct Investment on China’s Carbon Emissions. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jijian, Z.; Twum, A.K.; Agyemang, A.O.; Edziah, B.K.; Ayamba, E.C. Empirical study on the impact of international trade and foreign direct investment on carbon emission for belt and road countries. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 7591–7600. [Google Scholar]
- Rahaman, M.A.; Hossain, M.A.; Chen, S. The impact of foreign direct investment, tourism, electricity consumption, and economic development on CO2 emissions in Bangladesh. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 37344–37358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Hossain, M.E.; Khan, M.A.; Rana, M.J.; Ema, N.S.; Bekun, F.V. Heading towards sustainable environment: Exploring the dynamic linkage among selected macroeconomic variables and ecological footprint using a novel dynamic ARDL simulations approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 22260–22279. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhsh, K.; Rose, S.; Ali, M.F.; Ahmad, N.; Shahbaz, M. Economic growth, CO2 emissions, renewable waste and FDI relation in Pakistan: New evidences from 3SLS. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 196, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramati, S.R.; Ummalla, M.; Apergis, N. The effect of foreign direct investment and stock market growth on clean energy use across a panel of emerging market economies. Energy Econ. 2016, 56, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Khattak, S.I.; Khan, A.; Rahman, Z.U. Innovation, foreign direct investment (FDI), and the energy–pollution–growth nexus in OECD region: A simultaneous equation modeling approach. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 2020, 27, 203–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.; Umar, Z. The asymmetric relationship between foreign direct investment, oil prices and carbon emissions: Evidence from Gulf Cooperative Council economies. Cogent Econ. Financ. 2022, 10, 2080316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udemba, E.N. Mediation of foreign direct investment and agriculture towards ecological footprint: A shift from single perspective to a more inclusive perspective for India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 26817–26834. [Google Scholar]
- Hanif, I.; Raza SM, F.; Gago-de-Santos, P.; Abbas, Q. Fossil fuels, foreign direct investment, and economic growth have triggered CO2 emissions in emerging Asian economies: Some empirical evidence. Energy 2019, 171, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosupeng, M. The effect of exports on carbon dioxide emissions: Policy implications. Int. J. Manag. Econ. 2016, 51, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schmalensee, R.; Stoker, T.M.; Judson, R.A. World carbon dioxide emissions: 1950–2050. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1998, 80, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.P.; Wen, J.; Dong, M.; Hao, Y. Does government ideology affect environmental pollutions? New evidence from instrumental variable quantile regression estimations. Energy Policy 2018, 113, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antweiler, W.; Copeland, B.R.; Taylor, M.S. Is free trade good for the environment? Am. Econ. Rev. 2001, 91, 877–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Ren, X.; Wang, Z.; Yan, C. Heterogeneous impacts of renewable energy and environmental patents on CO2 emission-Evidence from the BRIICS. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 1328–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Nepal, R.; Alam, K. Impacts of human capital, exports, economic growth and energy consumption on CO2 emissions of a cross-sectionally dependent panel: Evidence from the newly industrialized countries (NICs). Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 121, 24–36. [Google Scholar]
- Haug, A.A.; Ucal, M. The role of trade and FDI for CO2 emissions in Turkey: Nonlinear relationships. Energy Econ. 2019, 81, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halicioglu, F. An econometric study of CO2 emissions, energy consumption, income and foreign trade in Turkey. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mulali, U.; Sheau-Ting, L. Econometric analysis of trade, exports, imports, energy consumption and CO2 emission in six regions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M. Do population density, economic growth, energy use and exports adversely affect environmental quality in Asian populous countries? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 77, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.L.; Chia, W.M.; Chang, Y. Energy consumption and energy R&D in OECD: Perspectives from oil prices and economic growth. Energy Policy 2013, 62, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar]
- Mensah, I.A.; Sun, M.; Gao, C.; Omari-Sasu, A.Y.; Zhu, D.; Ampimah, B.C.; Quarcoo, A. Analysis on the nexus of economic growth, fossil fuel energy consumption, CO2 emissions and oil price in Africa based on a PMG panel ARDL approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shang, W.; Wang, S. Text-based crude oil price forecasting: A deep learning approach. Int. J. Forecast. 2019, 35, 1548–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.A.; Warner, K.J. The 21st century population-energy-climate nexus. Energy Policy 2016, 93, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M.; Ji, X.; Mirza, N.; Rahat, B. The impact of resource curse on banking efficiency: Evidence from twelve oil producing countries. Resour. Policy 2021, 72, 102080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troster, V.; Shahbaz, M.; Uddin, G.S. Renewable energy, oil prices, and economic activity: A Granger-causality in quantiles analysis. Energy Econ. 2018, 70, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katircioglu, S. Investigating the role of oil prices in the conventional EKC model: Evidence from Turkey. Asian Econ. Financ. Rev. 2017, 7, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X. VECM Model Analysis of Carbon Emissions, GDP, and International Crude Oil Prices. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2018, 2018, 5350308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, M.Q.; Haseeb, A.; Adebayo, T.S.; Ahmed, Z.; Ahmad, M. The long-run relationship between energy consumption, oil prices, and carbon dioxide emissions in European countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 24234–24247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujtaba, A.; Jena, P.K. Analyzing asymmetric impact of economic growth, energy use, FDI inflows, and oil prices on CO2 emissions through NARDL approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 30873–30886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamued, E.A.; Ahmed, M.; Pypłacz, P.; Liczmańska-Kopcewicz, K.; Khan, M.A. Global oil price and innovation for sustainability: The impact of R&D spending, oil price and oil price volatility on GHG emissions. Energies 2021, 14, 1757. [Google Scholar]
- Royal, S.; Singh, K.; Chander, R. A nexus between renewable energy, FDI, oil prices, oil rent and CO2 emission: Panel data evidence from G7 economies. OPEC Energy Rev. 2022, 46, 208–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Ren, X.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y. The impacts of non-fossil energy, economic growth, energy consumption, and oil price on carbon intensity: Evidence from a panel quantile regression analysis of EU 28. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, R.F.; Granger, C.W. Co-integration and error correction: Representation, estimation, and testing. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1987, 55, 251–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, P.C.; Hansen, B.E. Statistical inference in instrumental variables regression with I(1) processes. Rev. Econ. Stud. 1990, 57, 99–125. [Google Scholar]
- Johansen, S. Statistical analysis of cointegration vectors. J. Econ. Dyn. Control. 1988, 12, 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, S.; Juselius, K. Maximum likelihood estimation and inference on cointegration—With applications to the demand for money. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 1990, 52, 169–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, M.H.; Smith, R. Estimating long-run relationships from dynamic heterogeneous panels. J. Econom. 1995, 68, 79–113. [Google Scholar]
- Pesaran, M.H.; Shin, Y.; Smith, R.J. Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J. Appl. Econom. 2001, 16, 289–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivot, E.; Andrews, D.W.K. Further evidence on the great crash, the oil-price shock, and the unit-root hypothesis. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 2002, 20, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goupillaud, P.; Grossmann, A.; Morlet, J. Cycle-octave and related transforms in seismic signal analysis. Geoexploration 1984, 23, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.; Mitra, S.K. Time-frequency contained co-movement of crude oil and world food prices: A wavelet-based analysis. Energy Econ. 2017, 62, 230–239. [Google Scholar]
- Adebayo, T.S.; Odugbesan, J.A. Modeling CO2 emissions in South Africa: Empirical evidence from ARDL based bounds and wavelet coherence techniques. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9377–9389. [Google Scholar]
- Kalmaz, D.B.; Kirikkaleli, D. Modeling CO2 emissions in an emerging market: Empirical finding from ARDL-based bounds and wavelet coherence approaches. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 5210–5220. [Google Scholar]
- Kirikkaleli, D. The effect of domestic and foreign risks on an emerging stock market: A time series analysis. North Am. J. Econ. Financ. 2020, 51, 100876. [Google Scholar]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, A.; Fuinhas, J.A.; Rapposelli, A. Asymmetric Nexus between Green Technology Innovations, Economic Policy Uncertainty, and Environmental Sustainability: Evidence from Italy. Energies 2023, 16, 3557. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.; Zhao, Z.Y. Empirics on linkages among industrialization, urbanization, energy consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth: A heterogeneous panel study of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 30617–30632. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, A.; Rapposelli, A.; Khan, F.; Javed, A. The impact of green technology innovation, environmental taxes, and renewable energy consumption on ecological footprint in Italy: Fresh evidence from novel dynamic ARDL simulations. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 191, 122534. [Google Scholar]
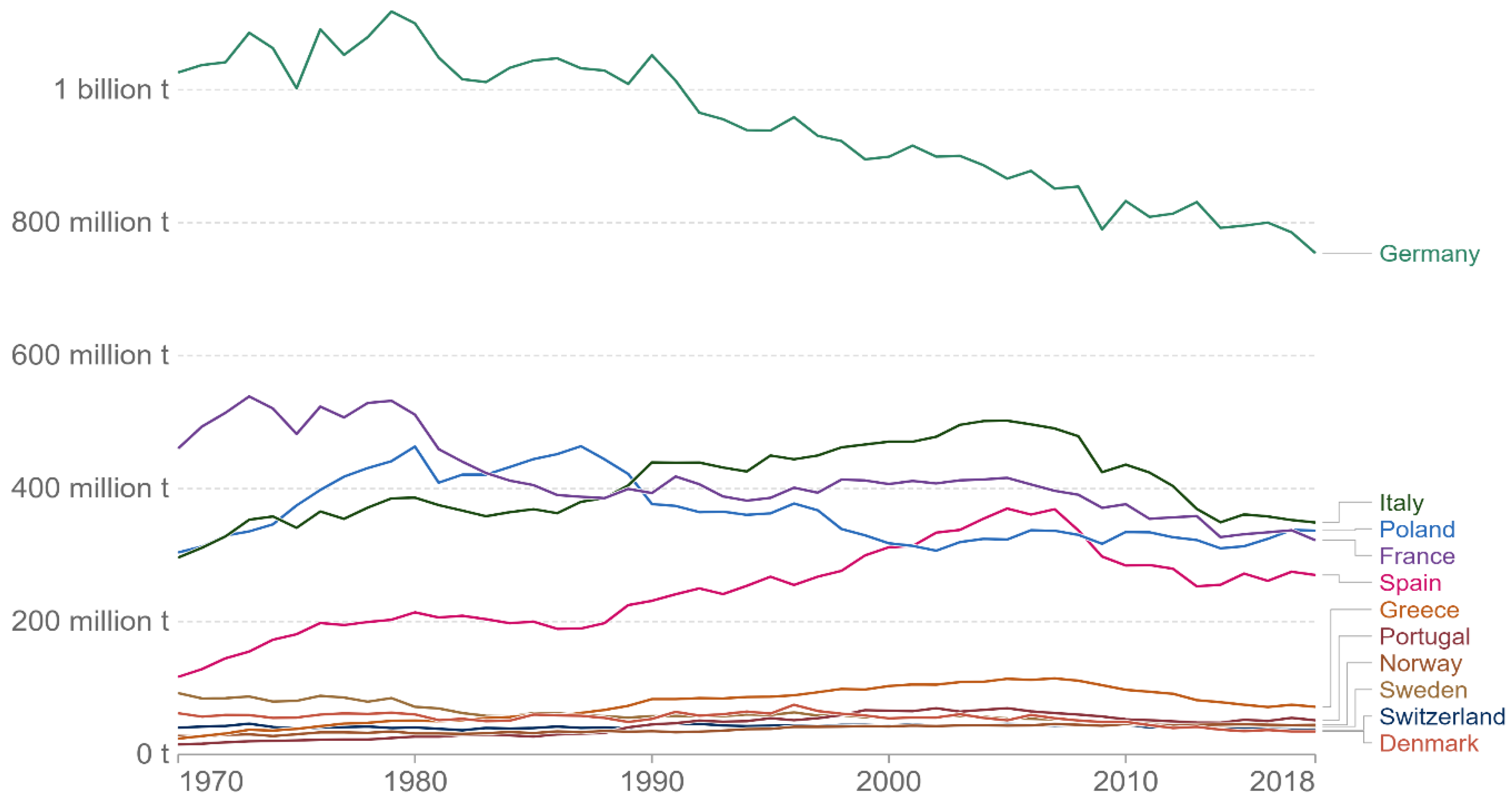
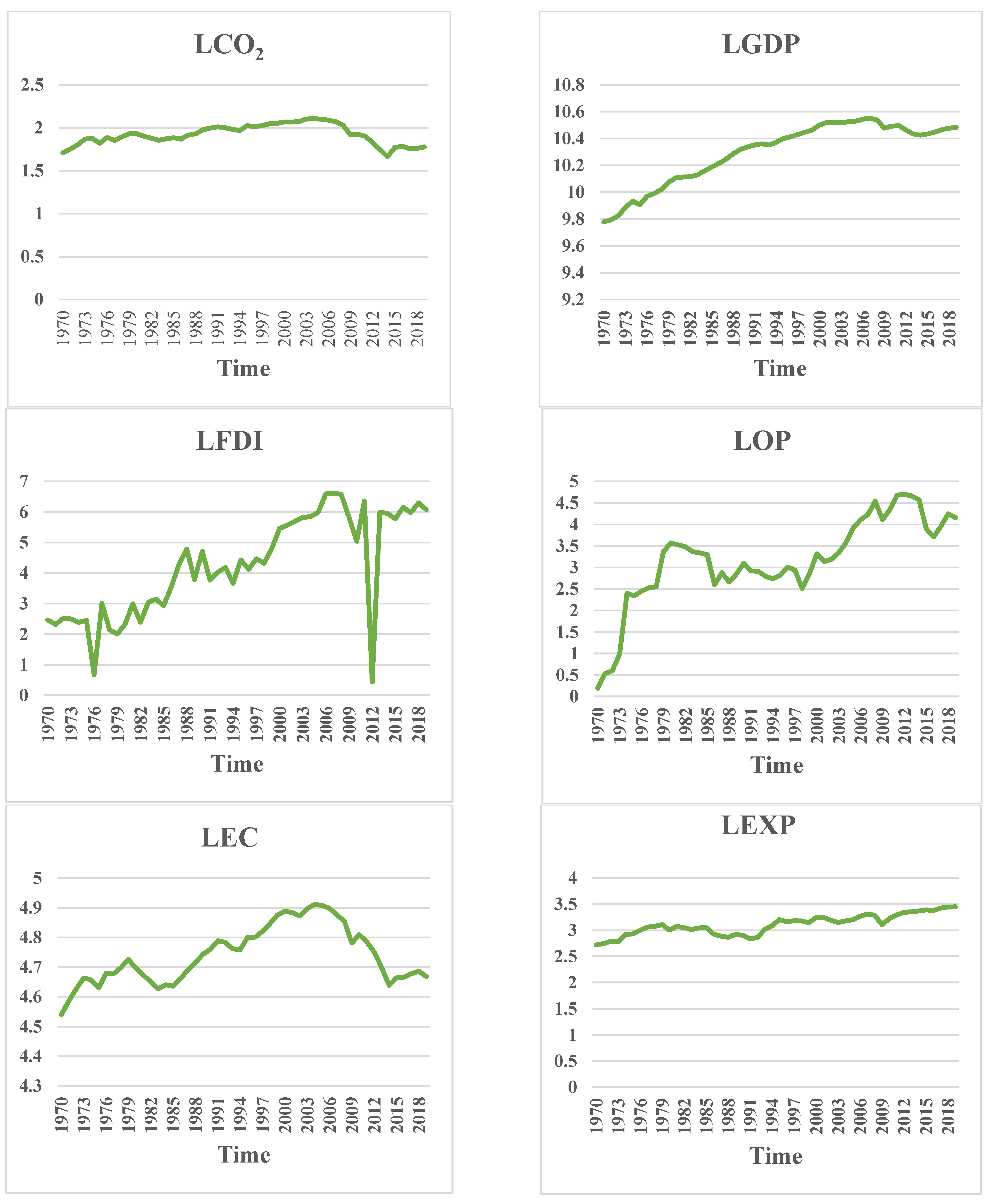
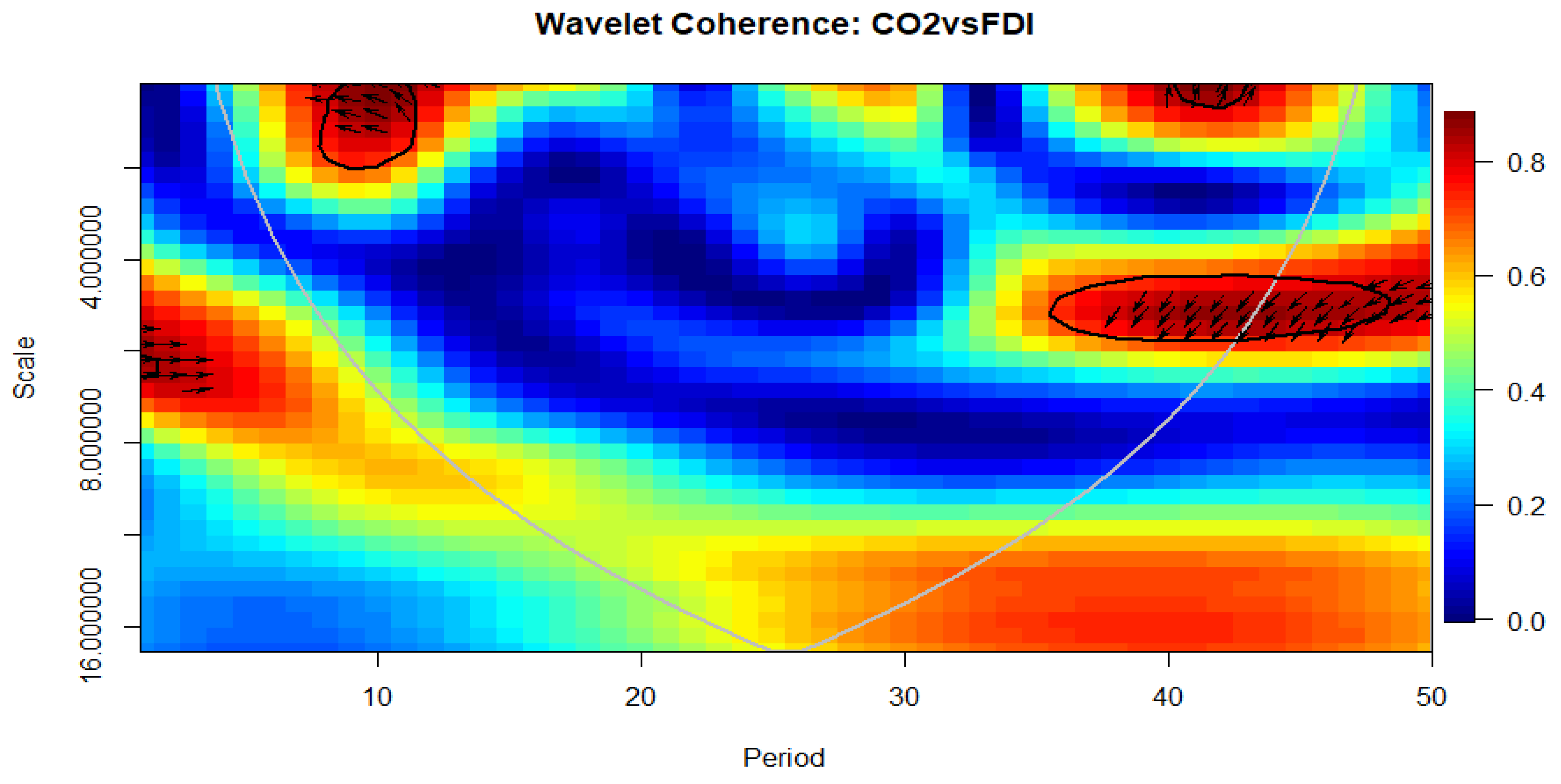
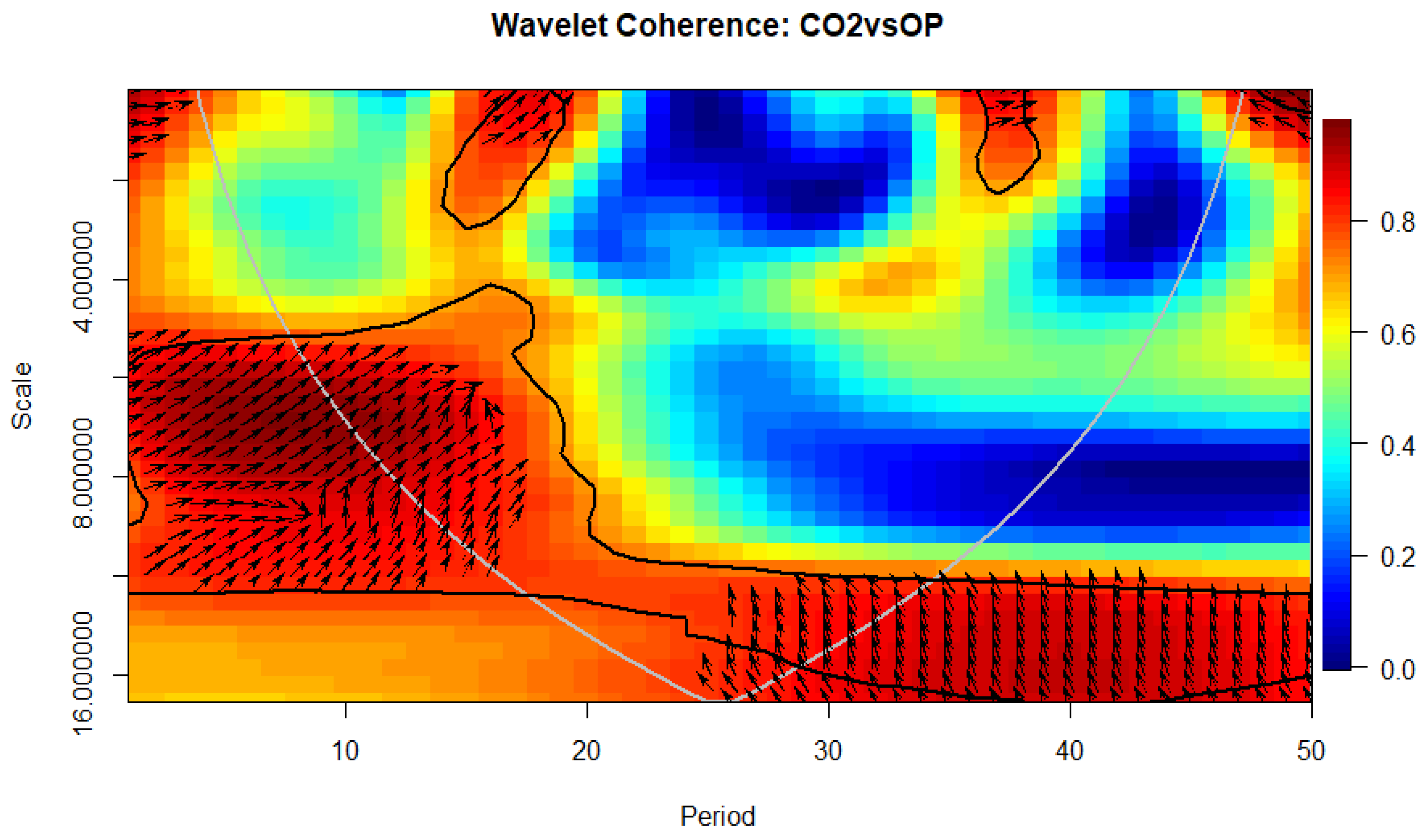
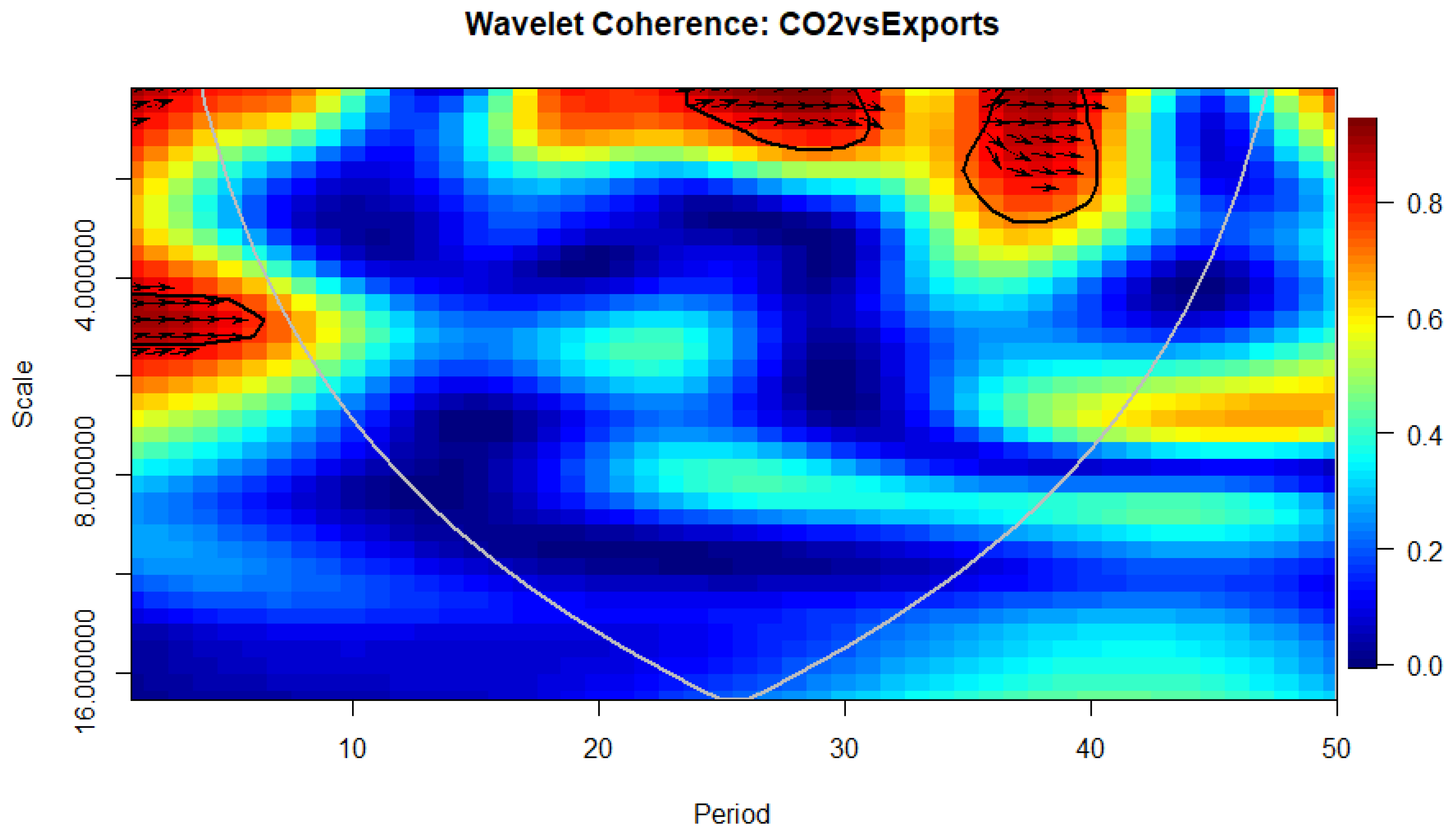
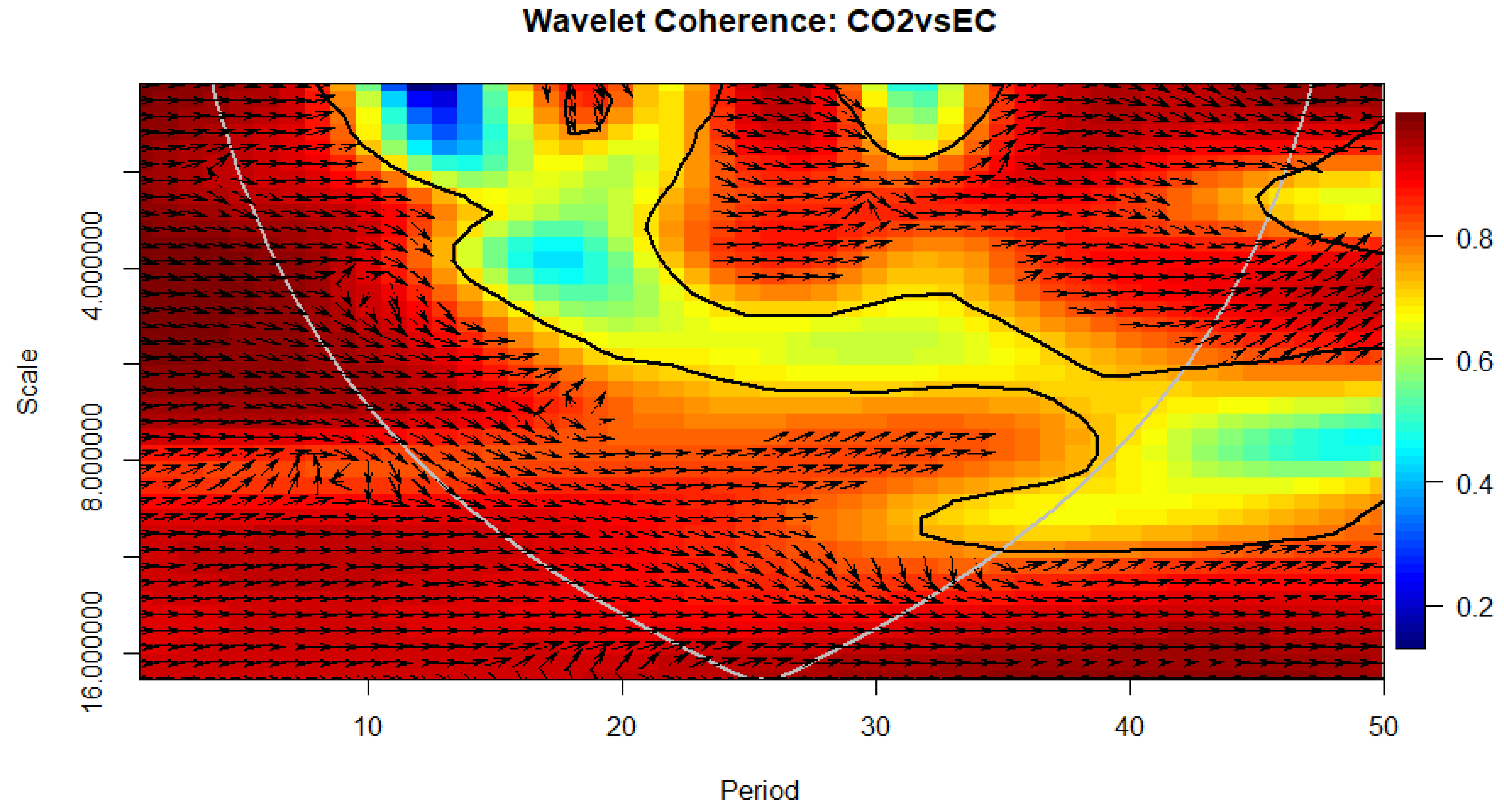
| Author(s) | Sample | Time Period | Methods | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [40] | Turkey | 1961–2010 | ARDL | EKC |
| [22] | Pakistan | 1971–2014 | ARDL, NARDL | EKC |
| [26] | USA | 1960–2010 | ARDL | EKC |
| [25] | Turkey | 1971–2014 | ARDL | EKC |
| [41] | Europe | 1960–2005 | ARDL, VECM | EKC for Italy and Denmark |
| [42] | Turkey | 1960–2013 | ARDL, VECM | EKC |
| [43] | European countries | 1980–2014 | Panel OLS, FMOLS, FE | No EKC |
| [44] | Nigeria | 1971–2015 | ARDL | EKC |
| [45] | BRICS | 1980–2016 | CCEMG technique | EKC |
| [46] | GCC countries | 1980–2017 | STIRPAT model, PMG | EKC |
| Variables | Symbol | Measurement | Sources | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon emission | CO2 | Metric tons per capita | World Bank | [31] |
| Gross domestic product | GDP | Constant 2010 US$ per capita | World Bank | [45] |
| Foreign direct investment | FDI | Per capita inflow of FDI | UNCTAD | [22] |
| Oil price | OP | Per barrel | Statista | [22] |
| Energy consumption | EC | Per capita (million tons oil equivalent) | British Petroleum Statistical Review | [52] |
| Exports | EXP | Per capita constant 2010 US$ | World Bank | [23] |
| LCO2 | LGDP | LFDI | LOP | LEC | LEXP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 1.920 | 10.296 | 4.212 | 3.171 | 4.740 | 3.108 |
| Median | 1.915 | 10.386 | 4.308 | 3.245 | 4.720 | 3.108 |
| Max. | 2.106 | 10.552 | 6.615 | 4.695 | 4.912 | 3.450 |
| Min. | 1.662 | 9.780 | 0.435 | 0.191 | 4.541 | 2.719 |
| Std. dev. | 0.116 | 0.230 | 1.646 | 1.026 | 0.097 | 0.195 |
| Skewness | −0.170 | −0.828 | −0.315 | −0.975 | 0.259 | −0.108 |
| Kurtosis | 2.104 | 2.407 | 2.088 | 4.260 | 2.050 | 2.146 |
| Jarque-Bera | 1.915 | 6.450 | 2.455 | 11.230 | 2.339 | 1.617 |
| Probability | 0.039 | 0.293 | 0.004 | 0.274 | 0.262 | 0.446 |
| Obs | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| LCO2 | LGDP | LFDI | LOP | LEC | LEXP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCO2 | 1.000 | |||||
| LGDP | 0.464 | 1.000 | ||||
| LFDI | 0.247 | 0.794 | 1.000 | |||
| LOP | 0.091 | 0.754 | 0.540 | 1.000 | ||
| LEC | 0.888 | 0.742 | 0.521 | 0.361 | 1.000 | |
| LEXP | −0.017 | 0.739 | 0.617 | 0.803 | 0.341 | 1.000 |
| ADF | PP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Level | First Difference | Level | First Difference |
| LCO2 | −1.409 | −6.189 *** | −1.471 | −6.187 *** |
| LGDP | −1.144 | −6.180 *** | −0.754 | −6.185 *** |
| LGDP-SQ | −1.082 | −6.080 *** | −0.683 | −6.086 *** |
| LFDI | −3.150 | −3.423 * | −6.152 | −34.610 *** |
| LOP | −2.922 | −6.476 *** | −2.937 | −6.465 *** |
| LEC | −0.939 | −5.448 *** | −1.123 | −5.429 *** |
| LEXP | −2.492 | −6.688 *** | −2.492 | −6.693 *** |
| Variables | Level | First Difference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test Statistic | Break Year | Test Statistic | Break Year | |
| LCO2 | −0.319 | 2007 | −5.145 *** | 2007 |
| LGDP | −3.506 | 1999 | −5.881 *** | 1980 |
| LGDP-SQ | −3.596 | 1999 | −5.145 *** | 1991 |
| LFDI | −0.655 | 1983 | −21.817 *** | 2012 |
| LOP | −1.437 | 1981 | −6.933 *** | 1980 |
| LEC | −1.806 | 2006 | −5.998 *** | 2014 |
| LEXP | −2.807 | 1978 | −7.675 *** | 2009 |
| F-Statistics | H0: No Level Relationship | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Significance | I(0) | I(1) | ||
| Optimal lag-length F-statistics | (3, 3, 3, 2, 3, 3, 2) | |||
| 12.791 *** | 10% | 1.99 | 2.94 | |
| K | 6 | 5% | 2.27 | 3.28 |
| 2.50% | 2.55 | 3.61 | ||
| 1% | 2.88 | 3.99 | ||
| Dependent Variable | Regressors | Coefficients | Std. Error | t-Statistics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCO2 | LGDP | 14.891 | 3.879 | 3.839 *** |
| LGDP-SQ | −0.740 | 0.192 | −3.852 *** | |
| LFDI | 0.039 | 0.007 | 5.271 ** | |
| LOP | −0.027 | 0.008 | −3.289 *** | |
| LEC | 0.525 | 0.170 | 3.085 ** | |
| LEXP | 0.081 | 0.038 | 2.138 ** |
| Dependent Variable | Regressors | Coefficients | Std. Error | t-Statistics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCO2 | LGDP | 35.528 | 4.012 | 8.855 *** |
| LGDP-SQ | −1.713 | 0.198 | −8.638 *** | |
| LFDI | 0.010 | 0.001 | 6.915 ** | |
| LOP | −0.041 | 0.006 | −7.075 *** | |
| LEC | 0.663 | 0.078 | 8.458 *** | |
| LEXP | 0.071 | 0.026 | 2.768 ** | |
| Coint. Eq. (−1) | −0.361 | 0.318 | −11.351 *** |
| Variables | Coeff. | Std. Error | t-Stat | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LGDP | 100.232 *** | 15.881 | 6.311 | 0.024 |
| LGDP-SQ | −5.002 ** | 0.789 | −6.339 | 0.024 |
| LFDI | 0.235 ** | 0.040 | 5.806 | 0.028 |
| LOP | −0.153 ** | 0.030 | −5.035 | 0.037 |
| LEC | 1.754 *** | 0.96 | 18.248 | 0.003 |
| LEXP | 0.888 ** | 0.126 | 7.064 | 0.019 |
| Variables | Coefficients | Std. Error | t-Statistic | Probability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LGDP | 32.969 *** | 1.243 | 26.534 | 0.000 |
| LGDP-SQ | −1.644 *** | 0.061 | −26.768 | 0.000 |
| LFDI | 0.072 *** | 0.002 | 34.993 | 0.000 |
| LOP | −0.079 *** | 0.003 | −20.239 | 0.000 |
| LEC | 1.603 *** | 0.037 | 42.712 | 0.000 |
| LEXP | 0.039 * | 0.020 | 1.926 | 0.061 |
| Diagnostics Tests | X2 | p-Value | Decision |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breusch-Godfrey LM | 0.986 | 0.473 | No issue with serial correlation |
| Breusch-Pagan-Godfrey | 0.703 | 0.776 | No issue with Heteroscedasticity |
| ARCH test | 0.019 | 0.889 | No issue with Heteroscedasticity |
| Normality | 3.708 | 0.157 | Estimated residuals are normal |
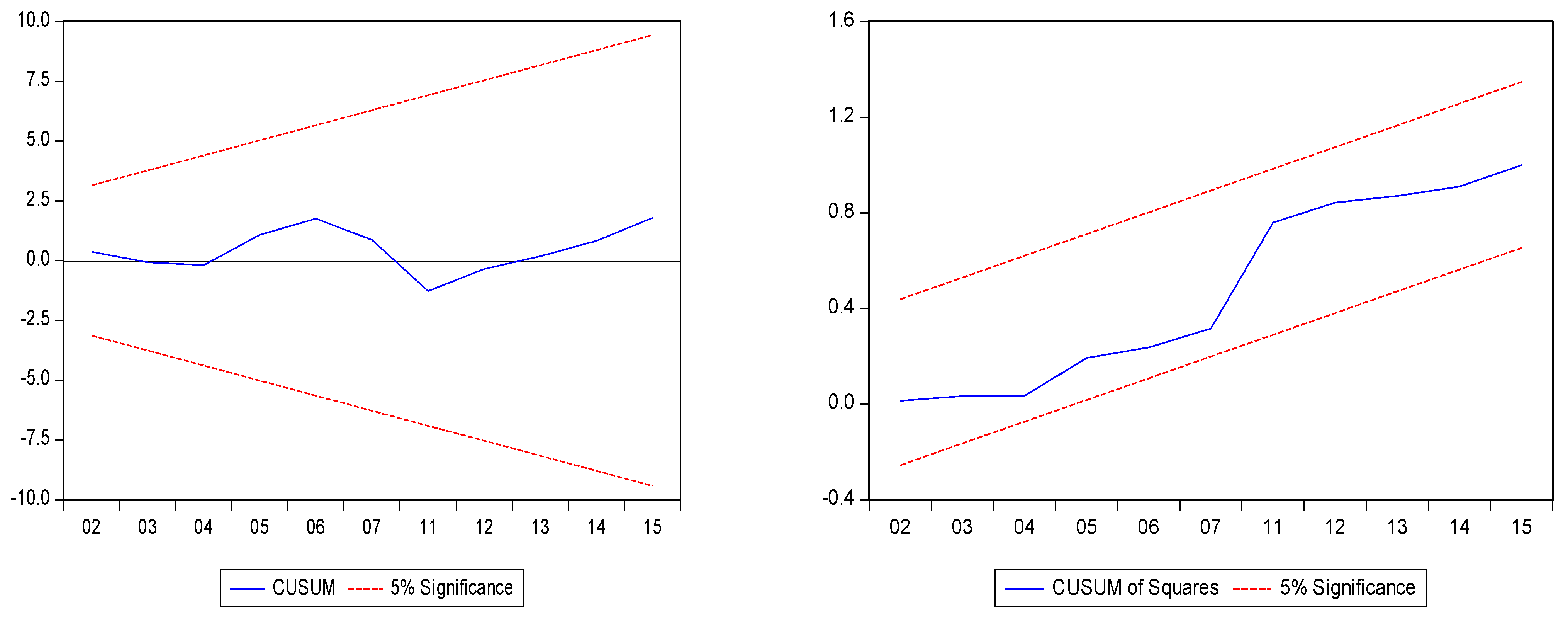
| CUSUM and CUSUM-SQ | Stable |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Javed, A.; Rapposelli, A.; Shah, M.; Javed, A. Nexus between Energy Consumption, Foreign Direct Investment, Oil Prices, Economic Growth, and Carbon Emissions in Italy: Fresh Evidence from Autoregressive Distributed Lag and Wavelet Coherence Approach. Energies 2023, 16, 5885. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165885
Javed A, Rapposelli A, Shah M, Javed A. Nexus between Energy Consumption, Foreign Direct Investment, Oil Prices, Economic Growth, and Carbon Emissions in Italy: Fresh Evidence from Autoregressive Distributed Lag and Wavelet Coherence Approach. Energies. 2023; 16(16):5885. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165885
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaved, Aamir, Agnese Rapposelli, Mohsin Shah, and Asif Javed. 2023. "Nexus between Energy Consumption, Foreign Direct Investment, Oil Prices, Economic Growth, and Carbon Emissions in Italy: Fresh Evidence from Autoregressive Distributed Lag and Wavelet Coherence Approach" Energies 16, no. 16: 5885. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165885
APA StyleJaved, A., Rapposelli, A., Shah, M., & Javed, A. (2023). Nexus between Energy Consumption, Foreign Direct Investment, Oil Prices, Economic Growth, and Carbon Emissions in Italy: Fresh Evidence from Autoregressive Distributed Lag and Wavelet Coherence Approach. Energies, 16(16), 5885. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165885







