Partial Discharge (PD) Signal Detection and Isolation on High Voltage Equipment Using Improved Complete EEMD Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Partial Discharge (PD) Measurement
2.1. Conventional Method
2.2. Non-Conventionalconventional Method
3. Materials and Methods
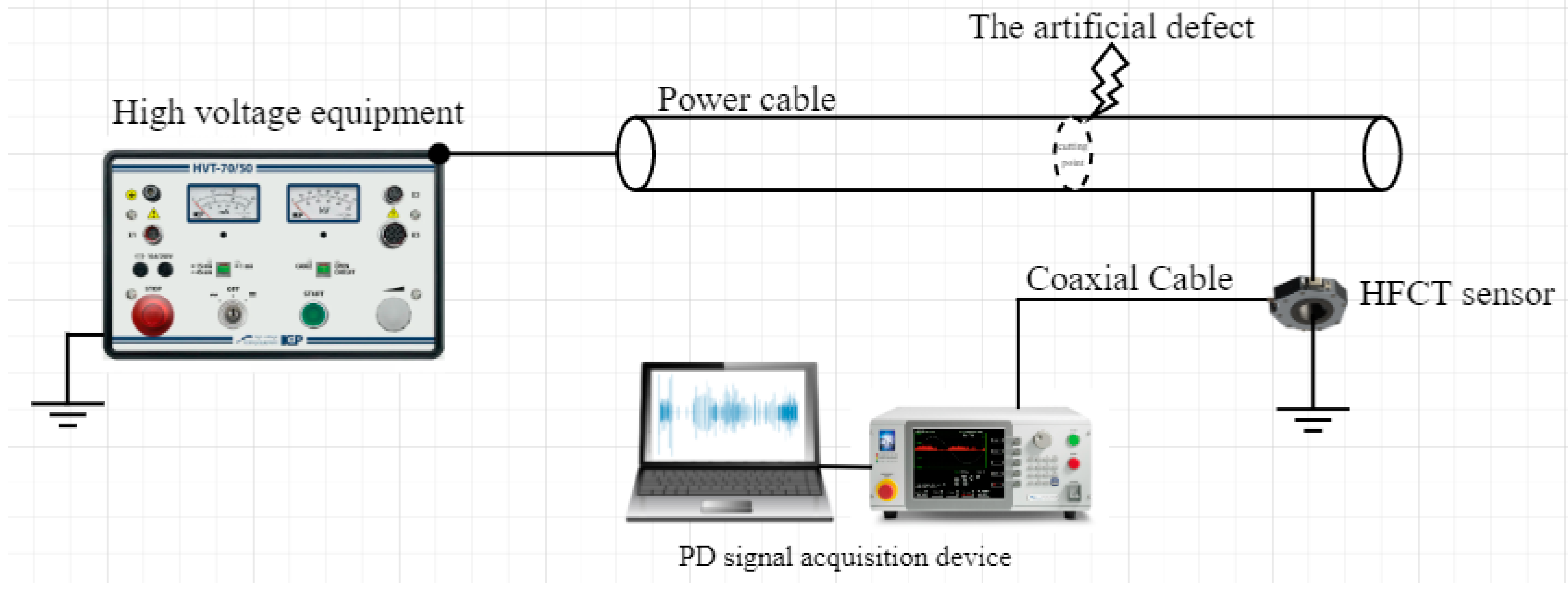
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
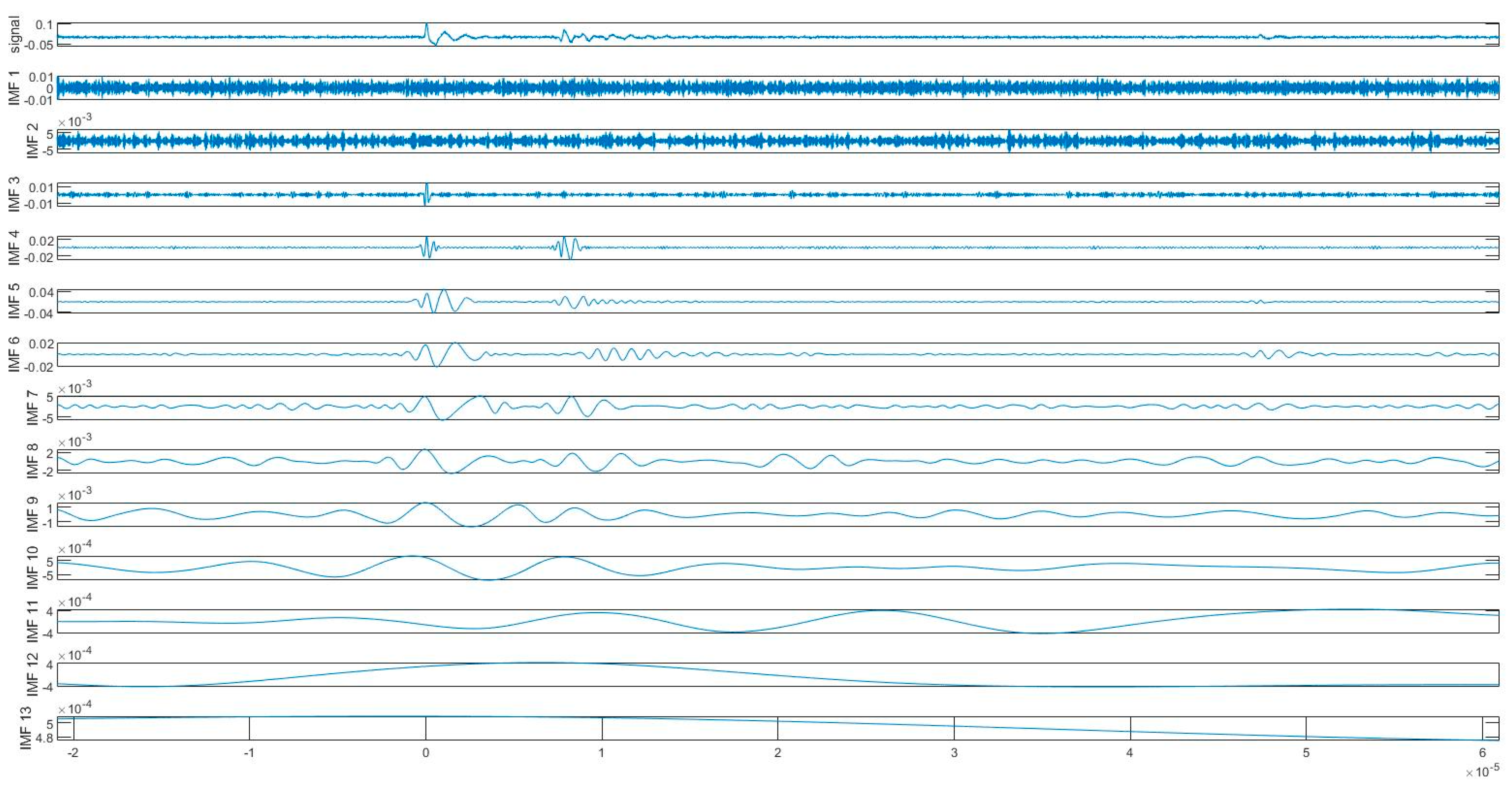
3.2.1. Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD)
- Step 1.
- Set k = 0 and find all extrema of ro = x.
- Step 2.
- Interpolate between minima (maxima) of rk to obtain the lower (upper) envelope emin (emax).
- Step 3.
- Compute the mean envelope m = (emin + emax)/2.
- Step 4.
- Compute the IMF candidate dk+1 = rk − m.IMF candidate is the result of the first sifting process
- Step 5.
- Is dk+1 an IMF?An IMF is an IMF candidate that satisfy two conditions of an IMF.Yes. Save dk+1, compute the residue rk+1 = x − , do k = k + 1, and treat rk as input data in step 2.No. Treat dk+1 as input data in step 2.
- Step 6.
- Continue until the final residue rk satisfies the predefined stopping criterion.
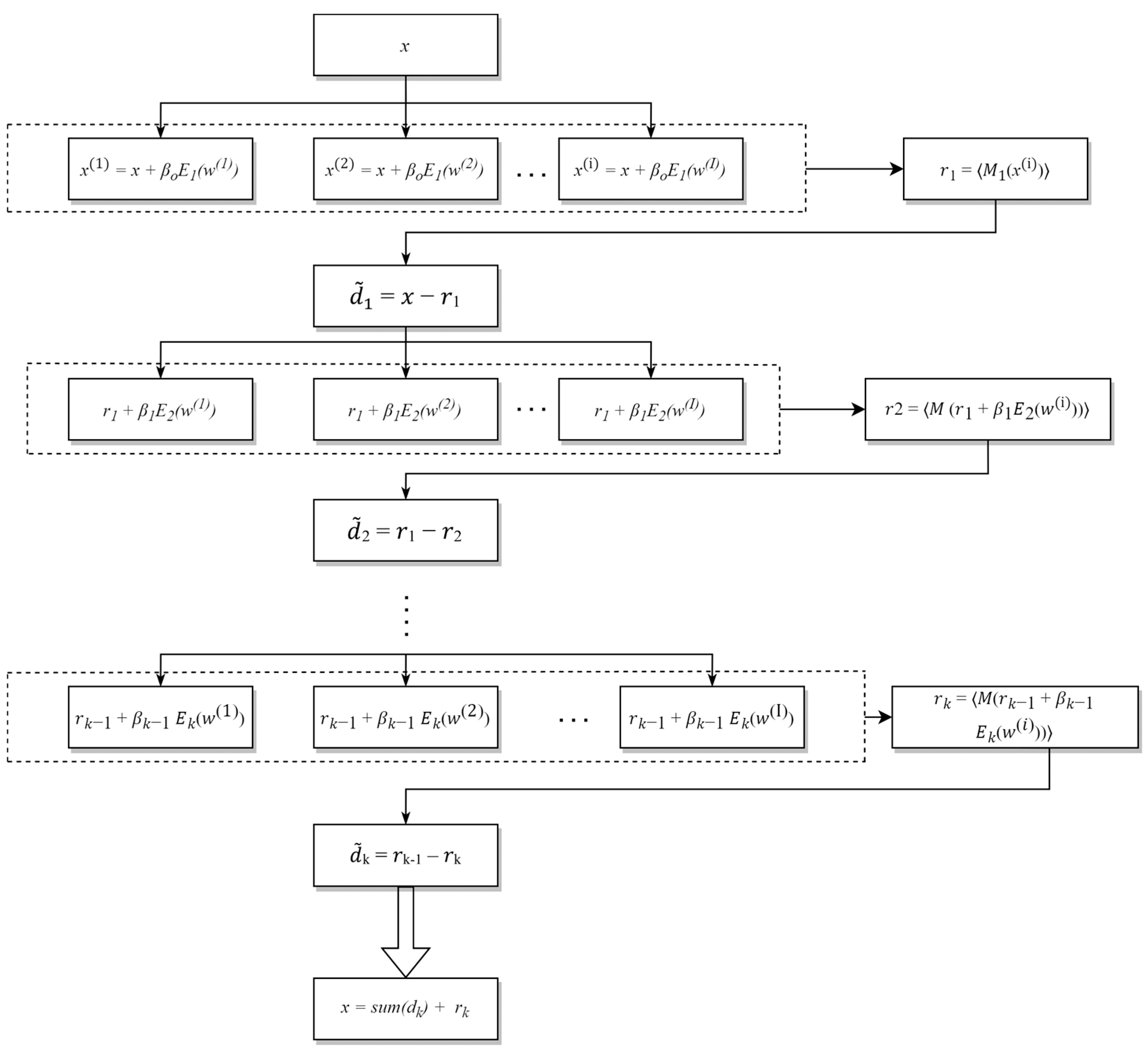
3.2.2. Improved CEEMDAN (ICEEMDAN)
- Step 1.
- Determine the local means of I realization using EMD x(i) = x + βoE1(w(i)) to get the first residual r1 = 〈M1(w(1))〉, where I is the number of realization in the ensemble and the magnitude of additional noise β > 0.
- Step 2.
- In the first phase (k = 1) compute the first mode: 1 = x − r1.
- Step 3.
- Estimate the second residue as the average of local means of the realizations r1 + β1E2(w(i)) and define the second mode: 2 = r1 − r2 = r1 − 〈M (r1 + β1E2(w(i)))〉.
- Step 4.
- For k = 3, …, K calculate the kth residue rk = 〈M(rk−1 + βk−1 Ek(w(i)))〉.
- Step 5.
- Compute the kth mode k = rk−1 − rk
- Step 6.
- Go to step 4 for next k.
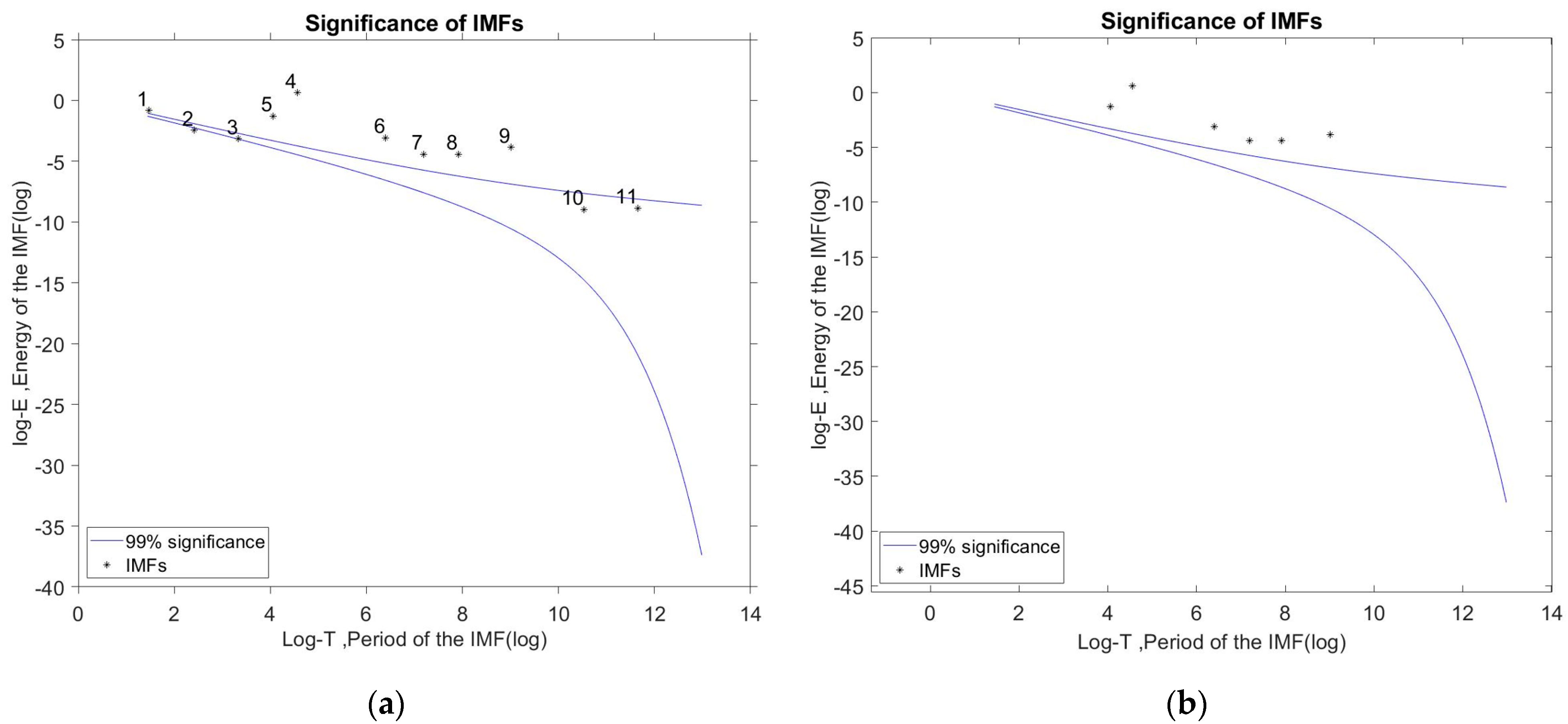
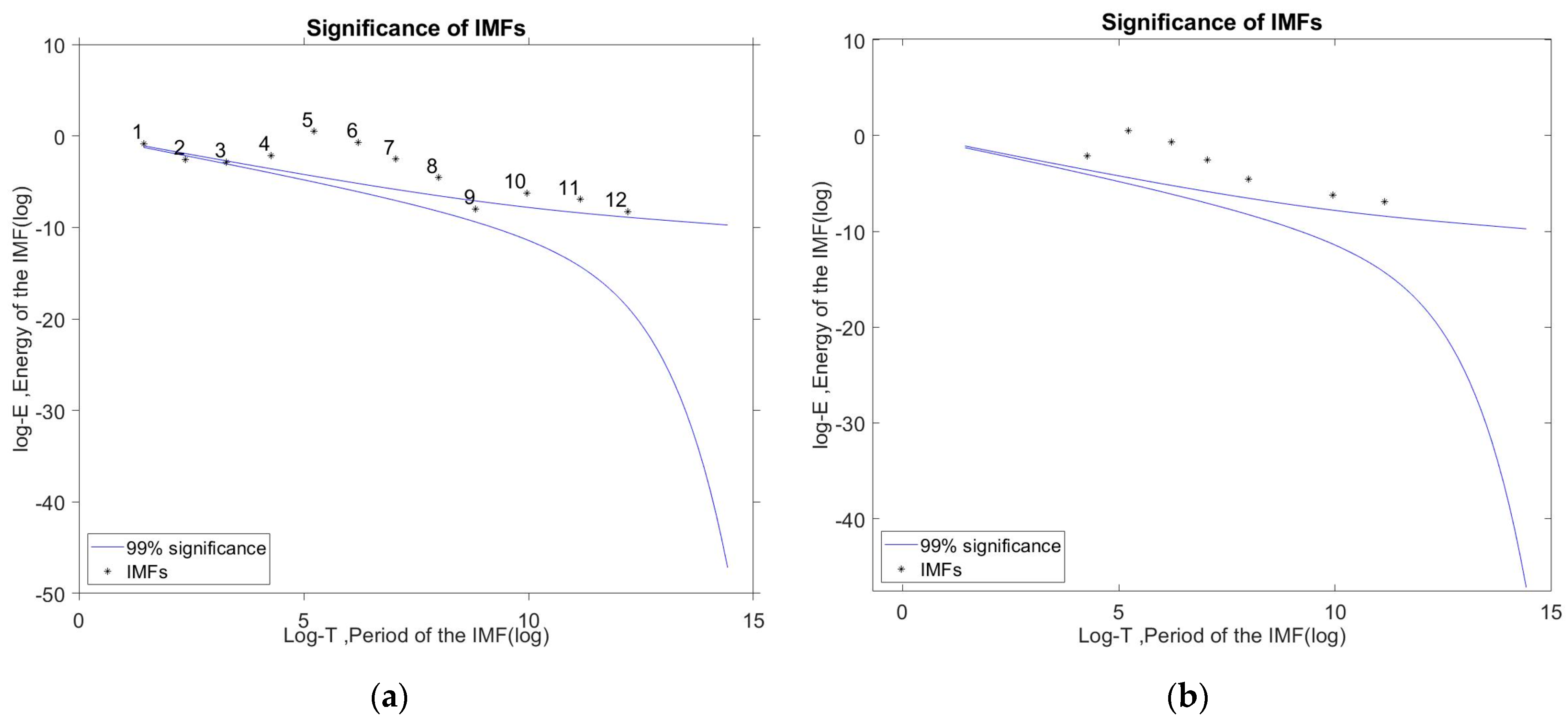
3.2.3. Statistical Significance Test (SST)
4. Results
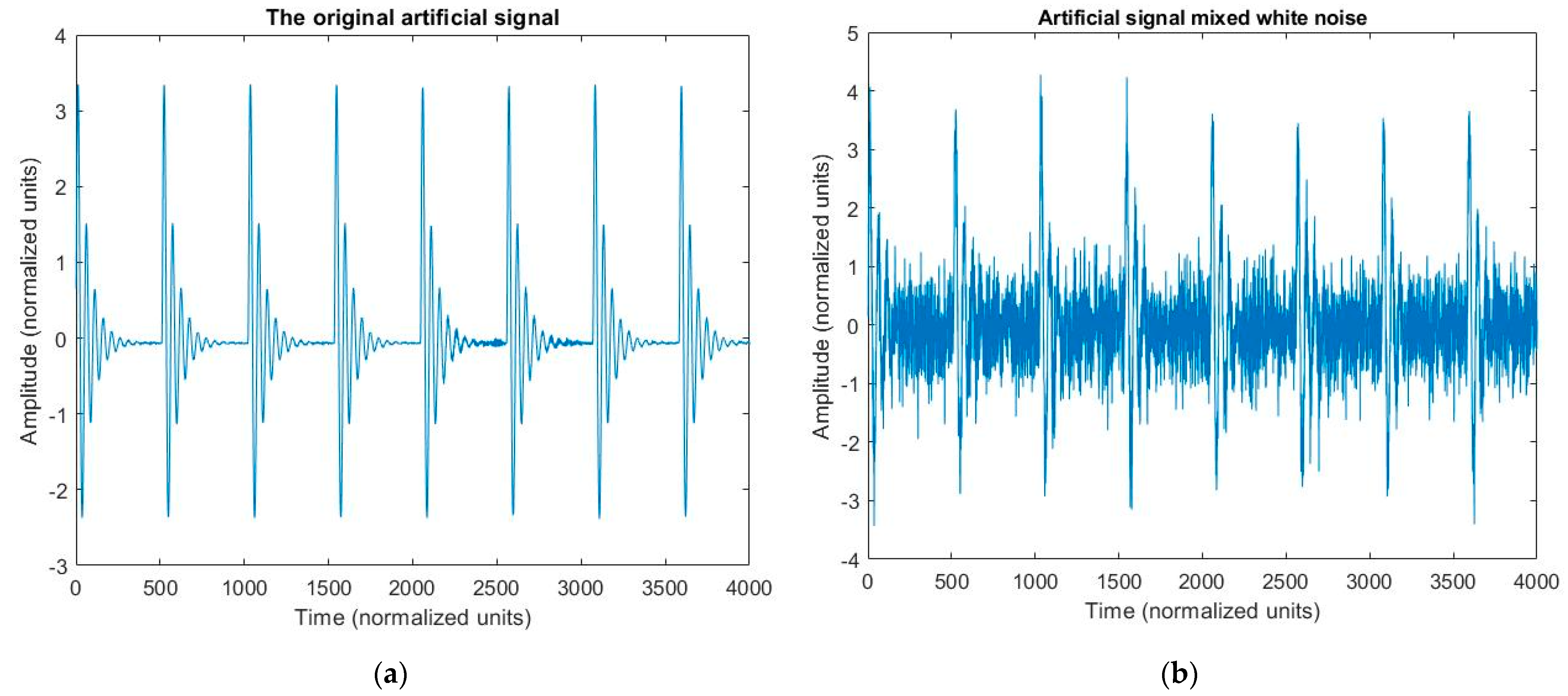
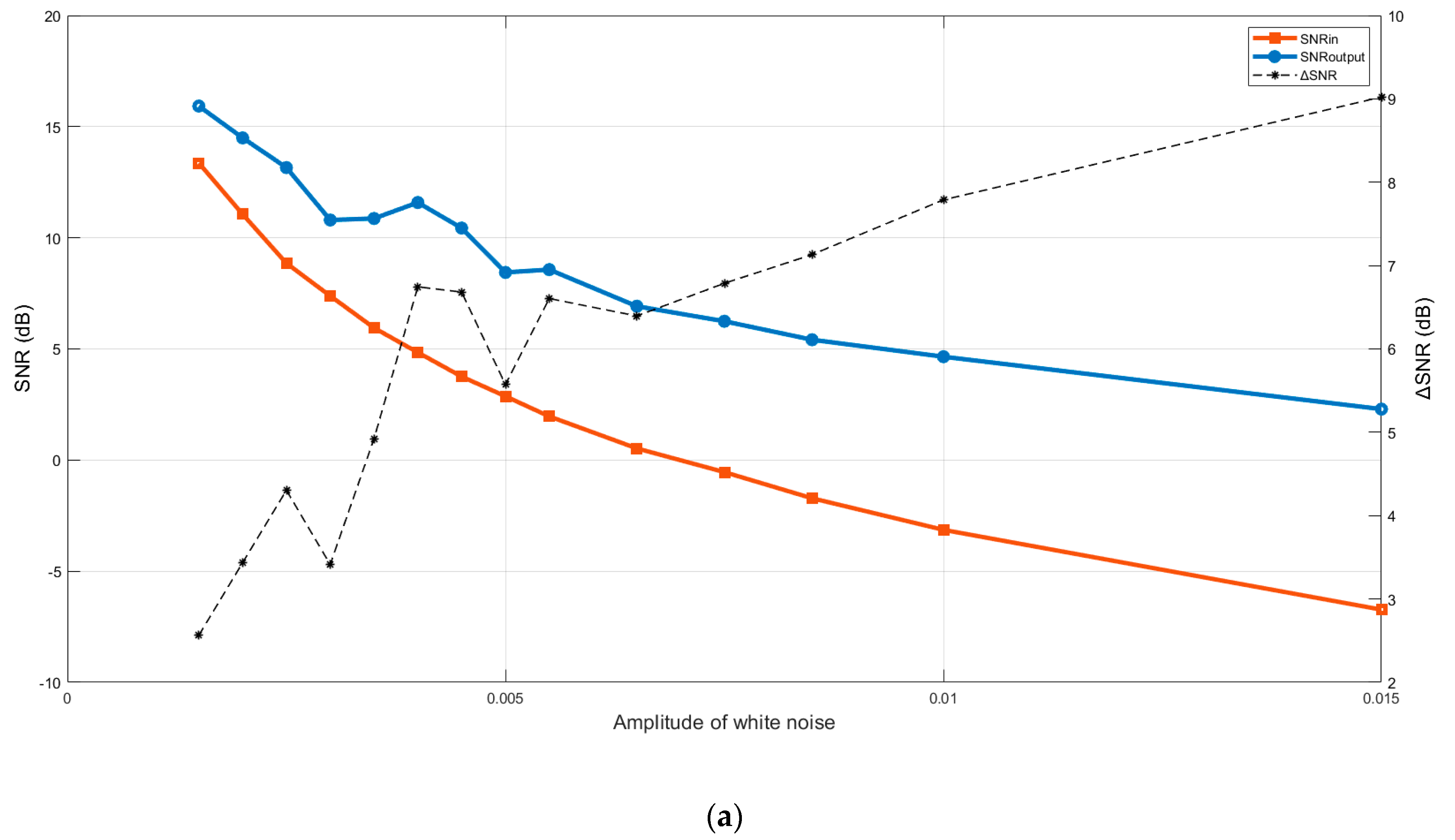
4.1. Artificial Signal
- The SNR of the input and output were determined using (1) and (2). The difference of SNR values was also computed using (3).
- 2.
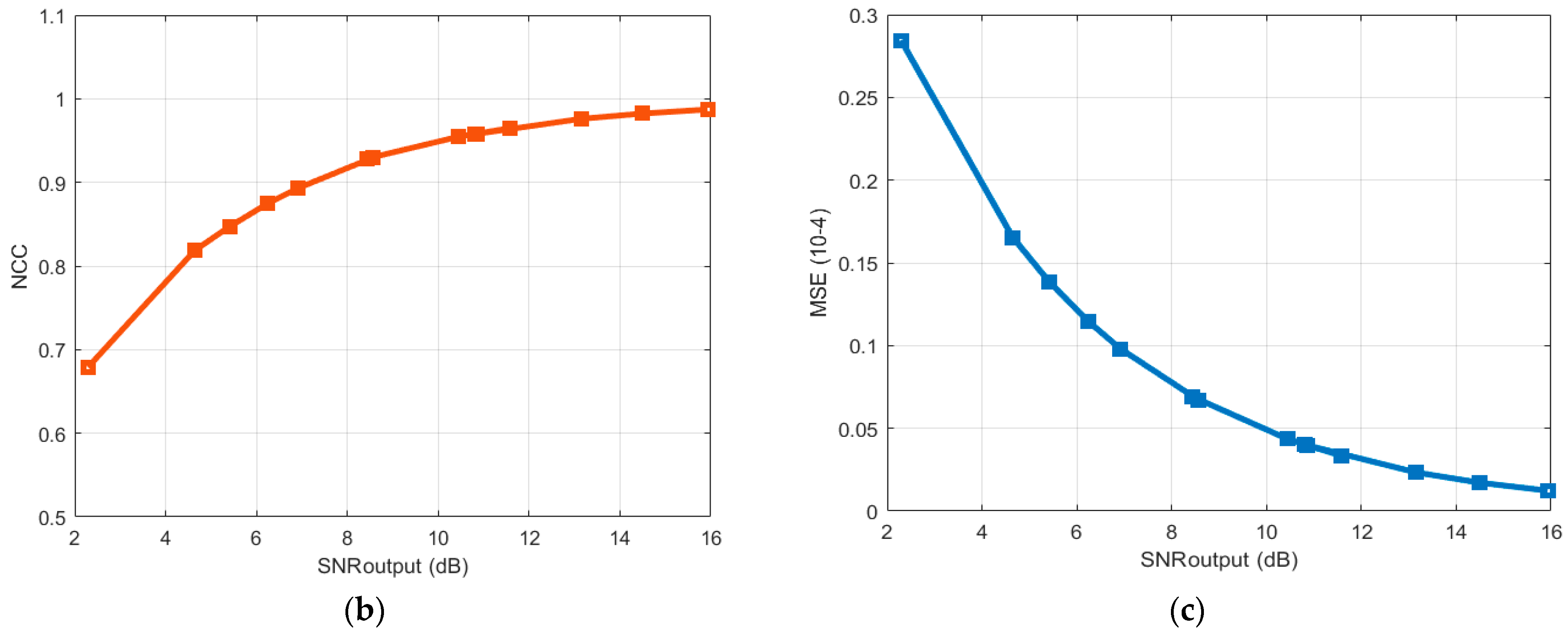
- Mean square error (MSE) is applied to compare the consistency between the original signal and the de-noised signal. The lower the MSE, the closer the original and the de-noised signals are;
- 3.
- Normalized correlation coefficient (NCC) is a widely used criteria for determining signal similarity, having a value range of 0 to 1. The higher the NCC number, the more similar the two signals are;
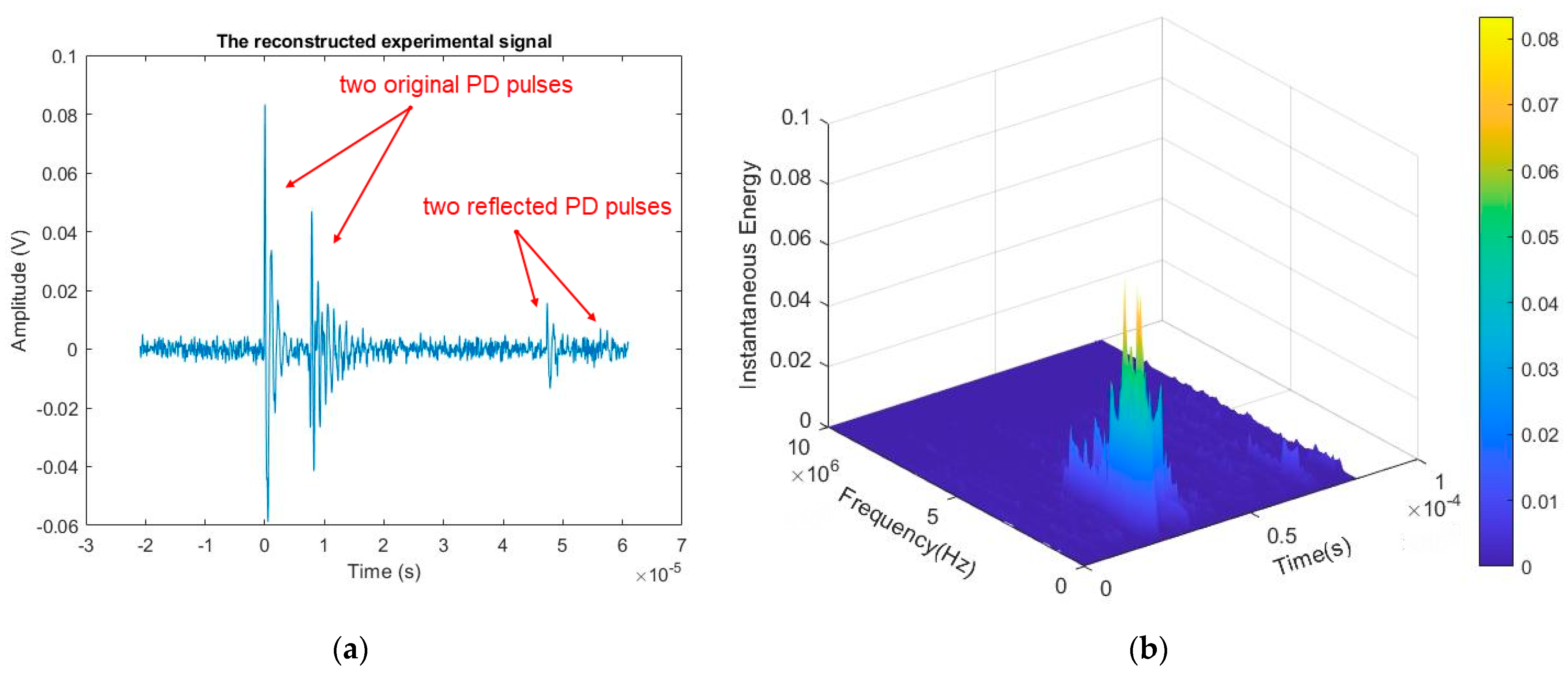
4.2. Experimental Signal
5. Conclusions
- The proposed method effectively removes white noise while keeping and isolating the characteristics of the PD signal.
- The ICEEMDAN algorithm, in conjunction with the statistically significant test approach, reduces the difficulty of picking significant IMFs and discarding insignificant IMFs.
- The high SNR, delta SNR, and NCC parameters show that this method is very effective even when the signal amplitude is very low and the SNRinput is negative.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
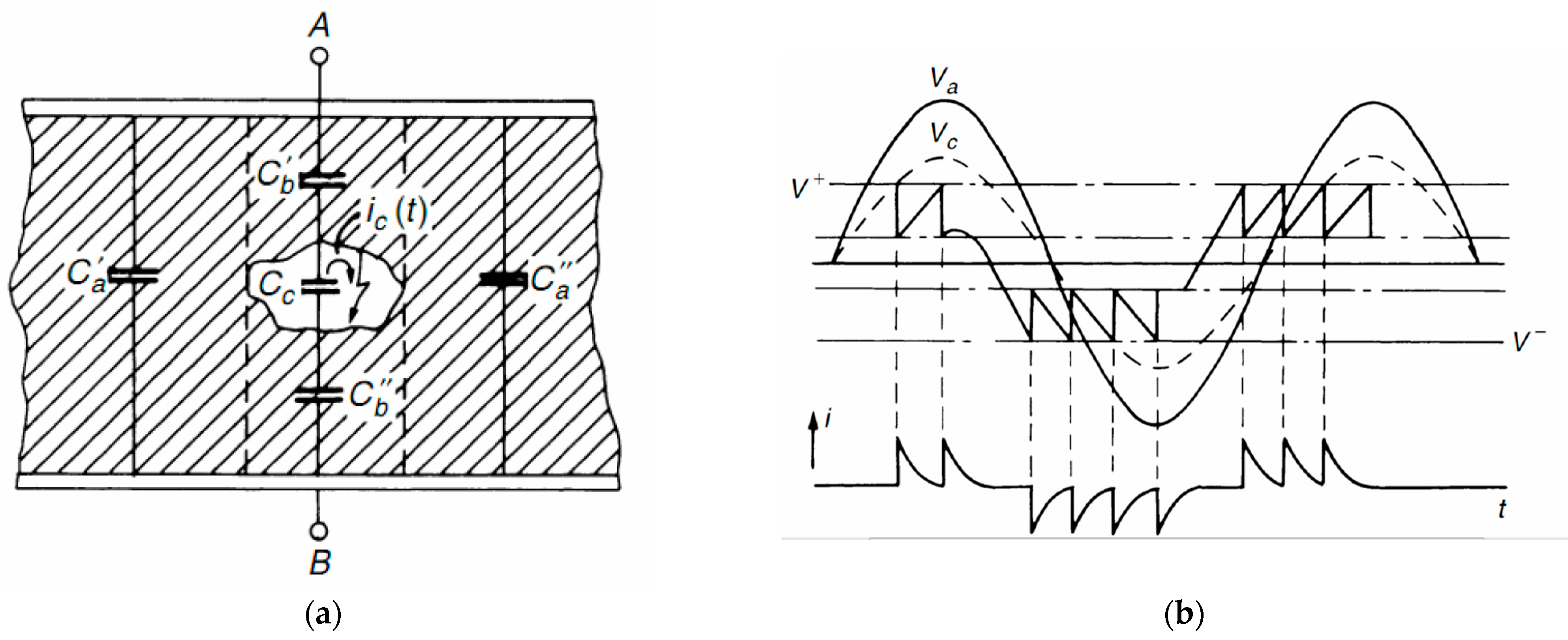
Appendix A.1. Partial Discharge Mechanism
Appendix A.2. Spread of Energy

Appendix A.3. Experimental PD Signal Diagram;
References
- Singh, J.; Singh, S. Transformer Failure Analysis: Reasons and Methods. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2016, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cigre 761. Condition Assessment of Power Transformer, WG A2.49, no. March. 2019.
- Chan, J.C.; Ma, H.; Saha, T.K.; Ekanayake, C. Stochastic noise removal on partial discharge measurement for transformer insulation diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE PES General Meeting| Conference & Exposition, National Harbor, MD, USA, 27–31 July 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulski, E. Digital analysis of partial discharges. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 1995, 2, 822–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 60270. High-Voltage Test Techniques—Partial Discharge Measurement, 3rd ed.; IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- IEC TS 62478. High Voltage Test Techniques—Measurement of Partial Discharges by Electromagnetic and Acoustic Methods, 1st ed.; IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kopf, U.; Feser, K. Rejection of narrow-band noise and repetitive pulses in on-site PD measurements [corrected version]. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 1995, 2, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.Z.; Deheng, Z.; Xianhe, J.; Kexiong, T. A new adaptive technique for on-line partial discharge monitoring. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 1995, 2, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruth, B.; Florkowski, M.; Gross, D. Partial discharge signal generation, transmission and acquisition. In Proceedings of the 1993 International Conference on Partial Discharge, Canterbury, UK, 28–30 September 1993; pp. 27–28. [Google Scholar]
- Sumarwoto, T.; Basuki, A.; Khayam, U.; Hozumi, N. Partial Discharge Signal Denoising by Discrete Wavelet Transformation. EPI Int. J. Eng. 2018, 1, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; He, J.; Sun, Y. Research on Noise Recognition and Suppression of Partial Discharge On-line Monitoring in Transformer. IEEJ Trans. Fundam. Mater. 2007, 127, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Li, Q.; Mohamed, M.A. A Novel Adaptive EEMD Method for Switchgear Partial Discharge Signal Denoising. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 58139–58147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, C.; Kemp, I. An improved methodology for application of wavelet transform to partial discharge measurement denoising. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2005, 12, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, N.A.; Isa, M.; Hamid, H.A.; Adzman, M.R. Denoising technique for partial discharge signal: AAA comparison performance between artificial neural network, fast fourier transform and discrete wavelet transform. In Proceedings of the PECON 2016—2016 IEEE 6th International Conference on Power and Energy, Melaka, Malaysia, 28–29 November 2017; pp. 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachan, S.M.; Rudd, S.; McArthur, S.D.; Judd, M.D.; Meijer, S.; Gulski, E. Knowledge-based diagnosis of partial discharges in power transformers. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2008, 15, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraetge, A.; Rethmeier, K.; Kruger, M.; Winter, P. Synchronous multi-channel PD measurements and the benefits for PD analyses. In Proceedings of the IEEE PES Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exposition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–22 April 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, M.; Kraetge, A.; Koch, M.; Rethmeier, K.; Pütter, M.; Hulka, L.; Summereder, C. New Diagnostic Tools for High Voltage Bushings; ISH: South Africa, 2009; p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Mazroua, A.A.; Bartnikas, R.; Salama, M.M.A. Discrimination between PD pulse shapes using different neural network paradigms. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 1994, 1, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Kexiong, T. Partial discharge recognition based on pulse waveform using time domain data compression method. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Properties and Applications of Dielectric Materials, Xi′an, China, 21–26 June 2000; Volume 1, pp. 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satish, L.; Nazneen, B. Buried in Excessive Noise and Interference. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2003, 10, 354–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhou, S.; Pan, C. A Denoising Algorithm for Partial Discharge Measurement Based on the Combination of Wavelet Threshold and Total Variation Theory. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 69, 3428–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunicki, M.; Wotzka, D. A Classification Method for Select Defects in Power Transformers Based on the Acoustic Signals. Sensors 2019, 19, 5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.-Y.; Tai, C.-C.; Tang, Y.-W.; Su, C.-C. Partial discharge signal extracting using the empirical mode decomposition with wavelet transform. In Proceedings of the 2011 7th Asia-Pacific International Conference on Lightning, Chengdu, China, 1–4 November 2011; pp. 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Bi, X.; Shu, Q.; Chen, M.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, D. Partial Discharge Signal Denoising Based on Singular Value Decomposition and Empirical Wavelet Transform. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 8866–8873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, D.; Li, M. Improved CEEMDAN–wavelet transform de-noising method and its application in well logging noise reduction. J. Geophys. Eng. 2017, 15, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Wu, Y.; Jia, D. Research on PD signals denoising based on EMD method. Prz. Elektrotechniczny 2012, 88, 137–140. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S. Improvement of Decomposing Results of Empirical Mode Decomposition and its Variations for Sea-level Records Analysis. J. Coast. Res. 2018, 85, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flandrin, P.; Torres, E.; Colominas, M.A. A Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition; Laboratorio de Senales y Dinamicas no Lineales, Universidad Nacional de Entre R; Laboratoire de Physique (UMR CNRS 5672), Ecole Normale Superieure de Lyon: Entre Ríos, Argentina; Lyon, France,, 2011; pp. 4144–4147. [Google Scholar]
- Colominas, M.A.; Schlotthauer, G.; Torres, M.E. Improved complete ensemble EMD: A suitable tool for biomedical signal processing. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2014, 14, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Cho, S.; Kwon, S.; Cho, S.-B. Fault Diagnosis Using Improved Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise and Power-Based Intrinsic Mode Function Selection Algorithm. Electronics 2018, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Z.; Yang, F.; Wu, J.; Li, T. Application of ICEEMDAN Energy Entropy and AFSA-SVM for Fault Diagnosis of Hoist Sheave Bearing. Entropy 2020, 22, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Búa-Núñez, I.; Roman, J.E.P.; Rubio-Serrano, J.; Garcia, J.A. Instrumentation System for Location of Partial Discharges Using Acoustic Detection with Piezoelectric Transducers and Optical Fiber Sensors. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2013, 63, 1002–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, D.; Punekar, G.S. Noniterative Method for Combined Acoustic-Electrical Partial Discharge Source Localization. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2017, 33, 1679–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-B.; Chang, D.-G.; Fan, Y.-H.; Zhang, G.-J.; Zhan, J.-Y.; Shao, X.-J.; He, W.-L. Acoustic localization of partial discharge sources in power transformers using a particle-swarm-optimization-route-searching algorithm. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2017, 24, 3647–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G. Transient Earth Voltage (TEV) Based Partial Discharge Detection and Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Lu, H.; Ning, W.; Jia, S.; Wu, J. Experimental investigation of transient earth voltage and acoustic emission measurements of partial discharge signals in medium-voltage switchgears. In Proceedings of the 2013 2nd International Conference on Electric Power Equipment-Switching Technology (ICEPE-ST), Matsue, Japan, 20–23 October 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhou, C.; Kemp, I. Automated wavelet selection and thresholding for PD detection. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2002, 18, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roepstorff, G. Fourier Decomposition. In Path Integral Approach to Quantum Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heilderberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 150–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, Y.; Singh, B. A comparative study of EMD and EEMD approaches for identifying chatter frequency in CNC turning. Eur. J. Mech. 2019, 73, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.W. Noise Reduction for LSTM using Wavelet Transform and Singular Spectrum Analysis; Leland Stanford Junior University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Chen, G.; Yu, H.; Chen, H.; An, F. Theoretical Analysis of Empirical Mode Decomposition. Symmetry 2018, 10, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Qi, B.; Yin, J. A Novel Hybrid Approach for Partial Discharge Signal Detection Based on Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise and Approximate Entropy. Entropy 2020, 22, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, M.A.; Anis, H.I.; El-Shahat, M. Denoising of Heavily Contaminated Partial Discharge Signals in High-Voltage Cables Using Maximal Overlap Discrete Wavelet Transform. Energies 2021, 14, 6540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, G.; Shafiq, M.; Martinez-Tarifa, J.M. Multiple Partial Discharge Source Localization in Power Cables Through Power Spectral Separation and Time-Domain Reflectometry. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 4703–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Zhang, H.; Qi, H.; Dai, Y. Comparison of EMD and EEMD in rolling bearing fault signal analysis. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Houston, TX, USA, 14–17 May 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, B.A.; dos Santos, V.V.; Lucas, G.B.; Ardila-Rey, J.A.; Riehl, R.R.; Andreoli, A.L. A Comparative Analysis Applied to the Partial Discharges Identification in Dry-Type Transformers by Hall and Acoustic Emission Sensors. Sensors 2022, 22, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inestigation of long term Ageing in Solid Insulatingmaterial by Studying the Effect of Variation of Parameters and Wavelettransform Analsis on Real Timed Data on Partial Discharge. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10603/34689 (accessed on 30 July 2022).
- Morshuis, P.; Smit, J. Partial discharges at dc voltage: Their mechanism, detection and analysis. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2005, 12, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gockenbach, E. High Voltage Engineering; Springer Handbooks: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 131–182. [Google Scholar]
- Landon, V.D. A Study of the Characteristics of Noise. Proc. IRE 1936, 24, 1514–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thuc, V.C.; Lee, H.S. Partial Discharge (PD) Signal Detection and Isolation on High Voltage Equipment Using Improved Complete EEMD Method. Energies 2022, 15, 5819. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15165819
Thuc VC, Lee HS. Partial Discharge (PD) Signal Detection and Isolation on High Voltage Equipment Using Improved Complete EEMD Method. Energies. 2022; 15(16):5819. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15165819
Chicago/Turabian StyleThuc, Vu Cong, and Han Soo Lee. 2022. "Partial Discharge (PD) Signal Detection and Isolation on High Voltage Equipment Using Improved Complete EEMD Method" Energies 15, no. 16: 5819. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15165819
APA StyleThuc, V. C., & Lee, H. S. (2022). Partial Discharge (PD) Signal Detection and Isolation on High Voltage Equipment Using Improved Complete EEMD Method. Energies, 15(16), 5819. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15165819