Selective Catalytic Removal of High Concentrations of NOx at Low Temperature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- The standard SCR reaction: 4NH3 + 4NO + O2 = 4N2 + 6H2O;
- (2)
- The NO2-SCR reaction: 4NH3 + 2NO2 + O2 = 3N2 + 6H2O;
- (3)
- The fast SCR reaction: 4NH3 + 2NO + 2NO2 = 4N2 + 6H2O.
2. Experiment
2.1. Catalysts’ Preparation
2.2. Catalysts’ Characterization
2.3. Activity Test
3. Results and Discussion
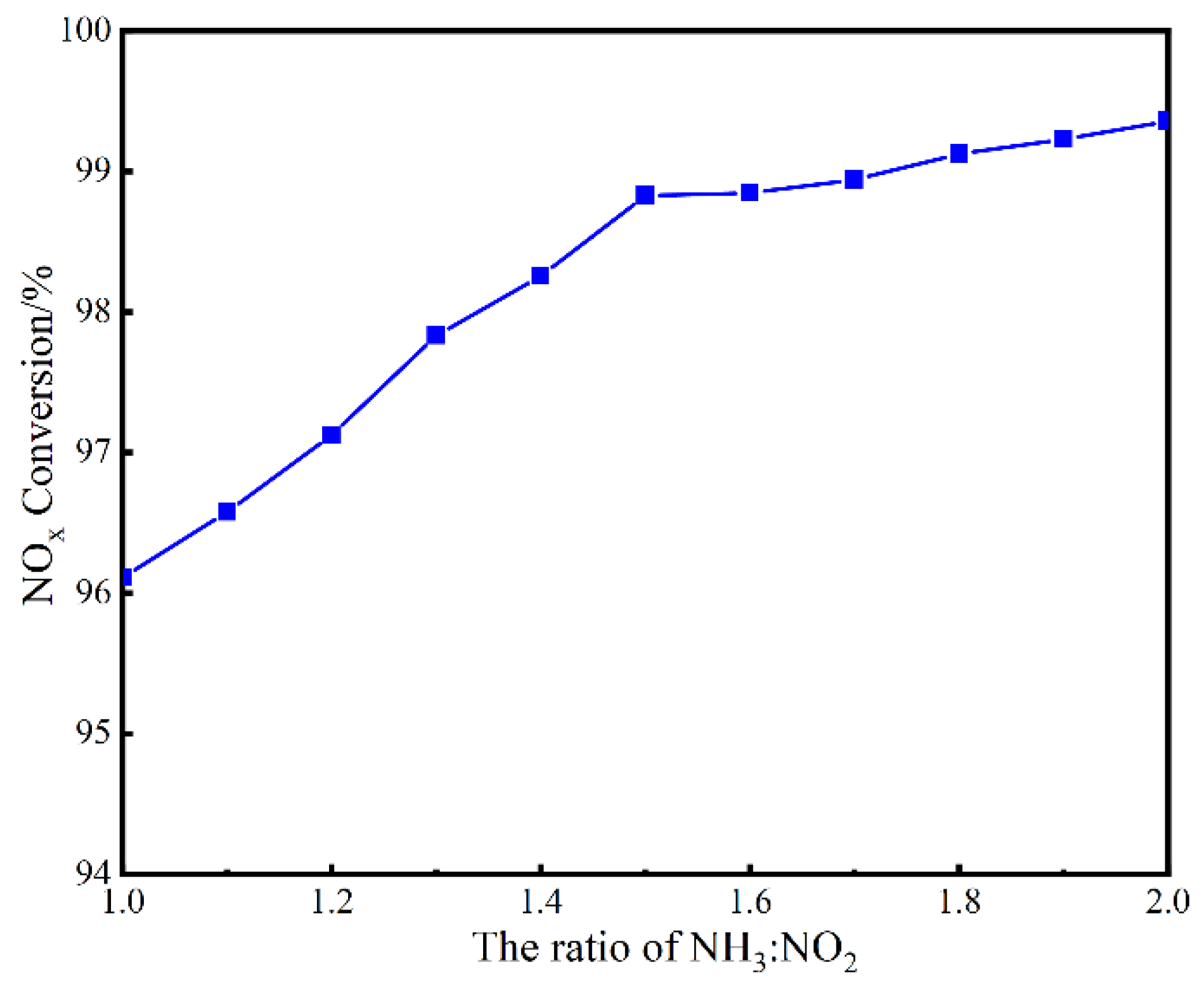
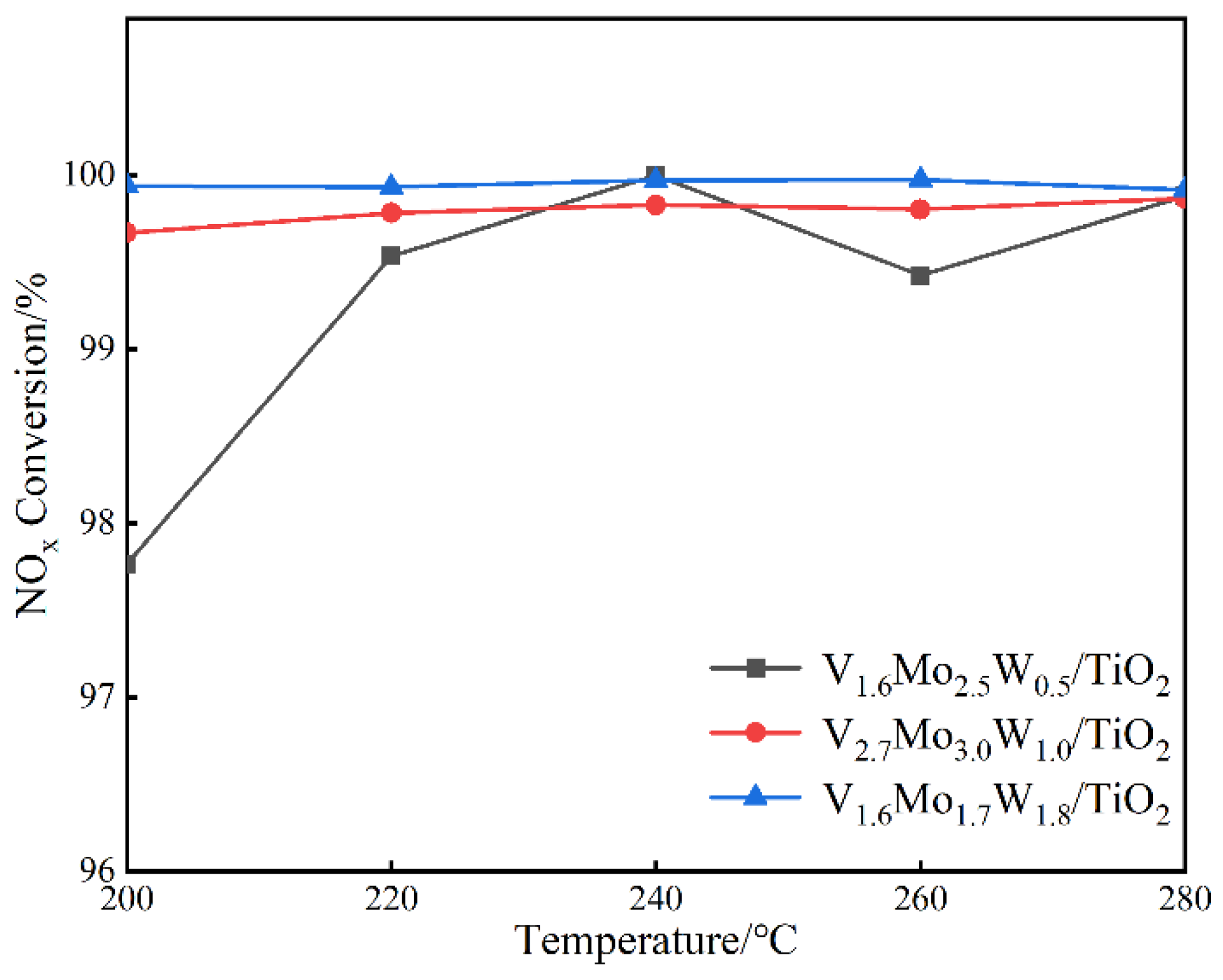
3.1. Catalytic Activity Evaluation
3.2. Characterization of the Catalysts
3.2.1. BET
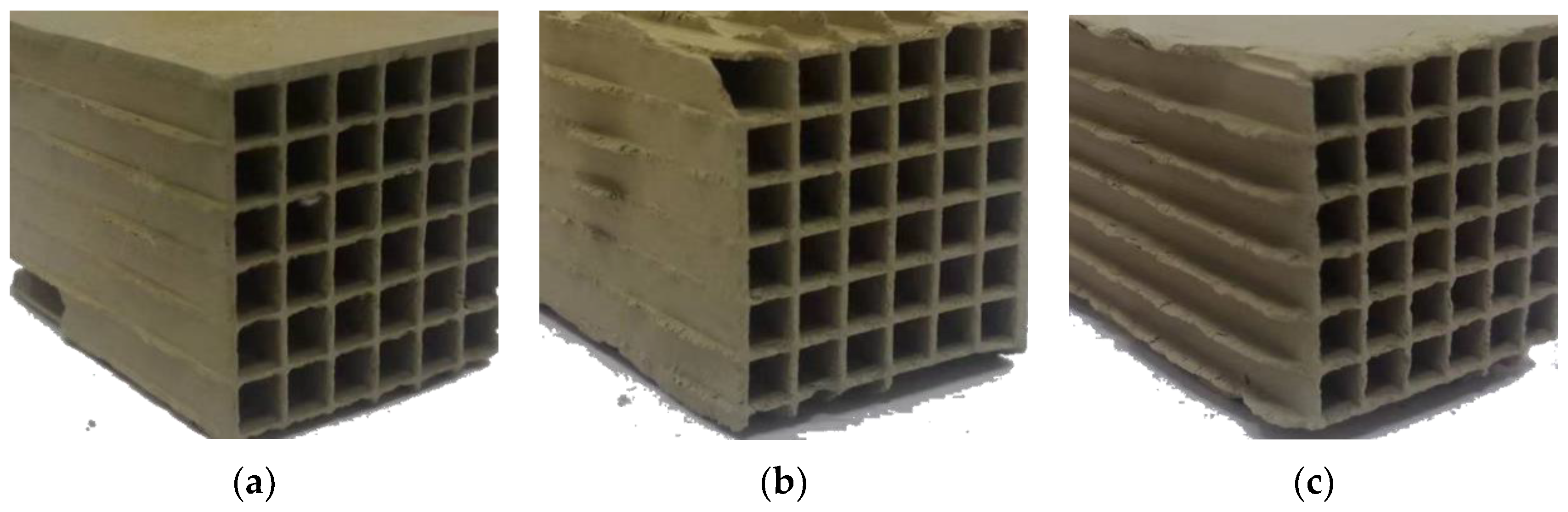
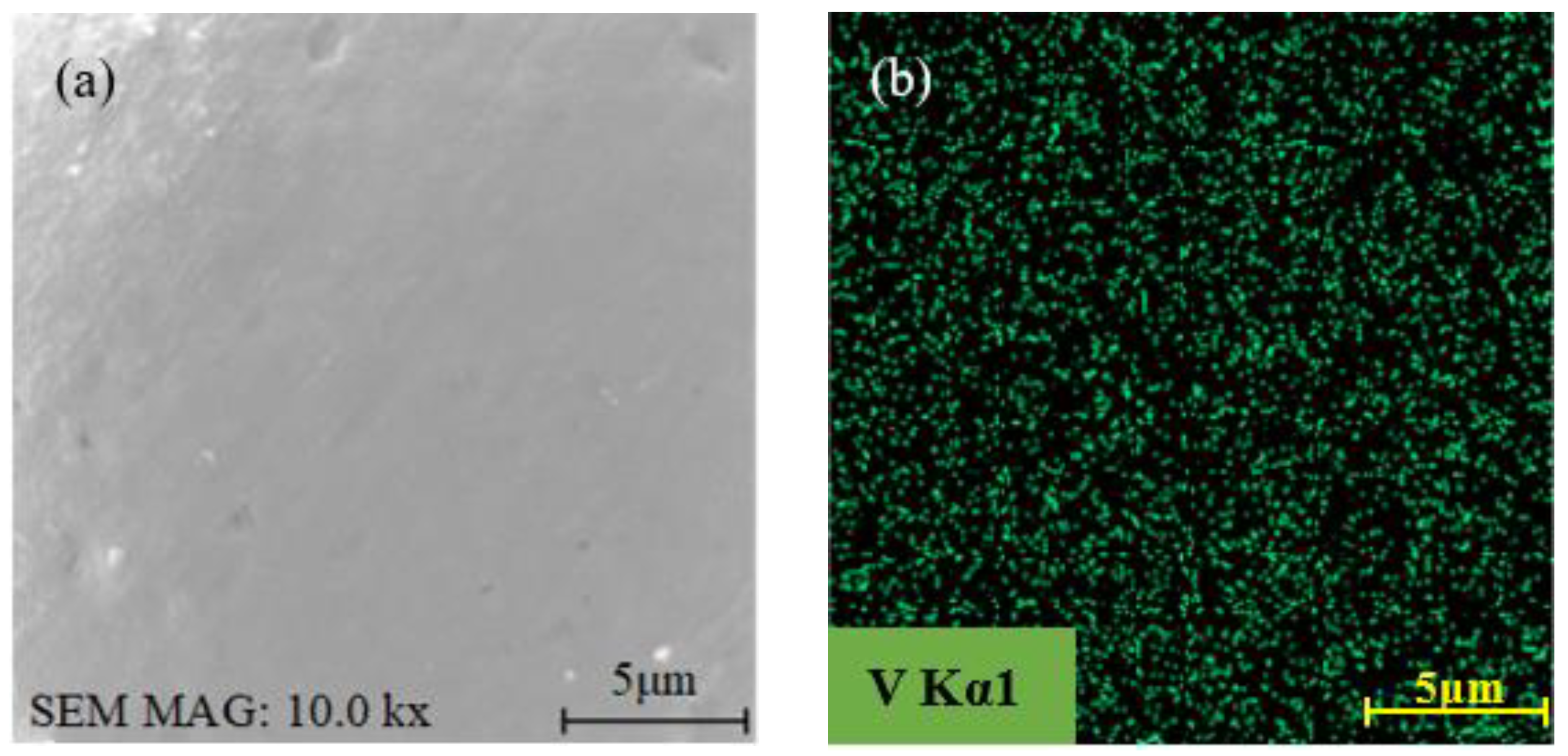
3.2.2. Morphology Evolution
3.2.3. XRD
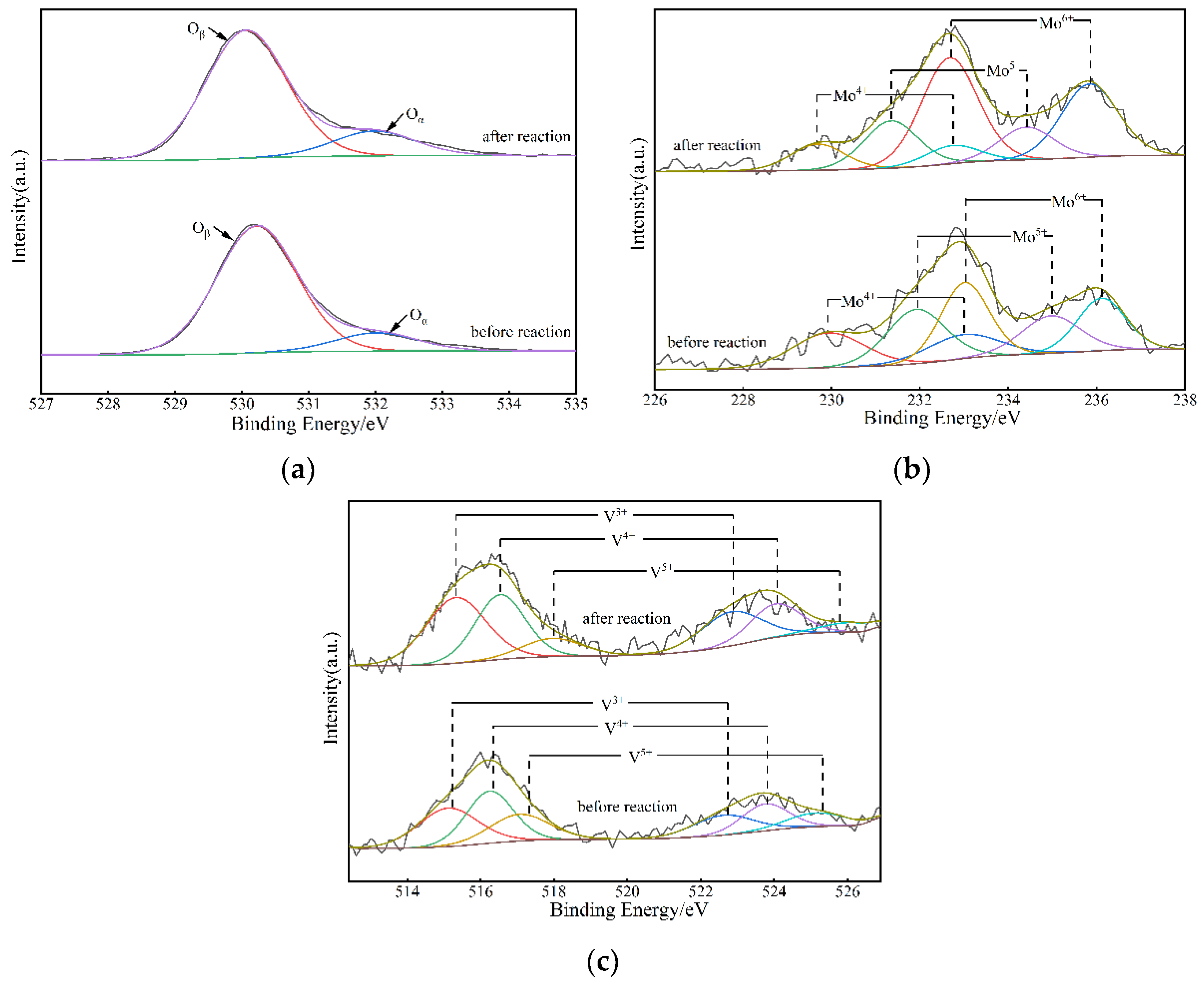
3.2.4. XPS
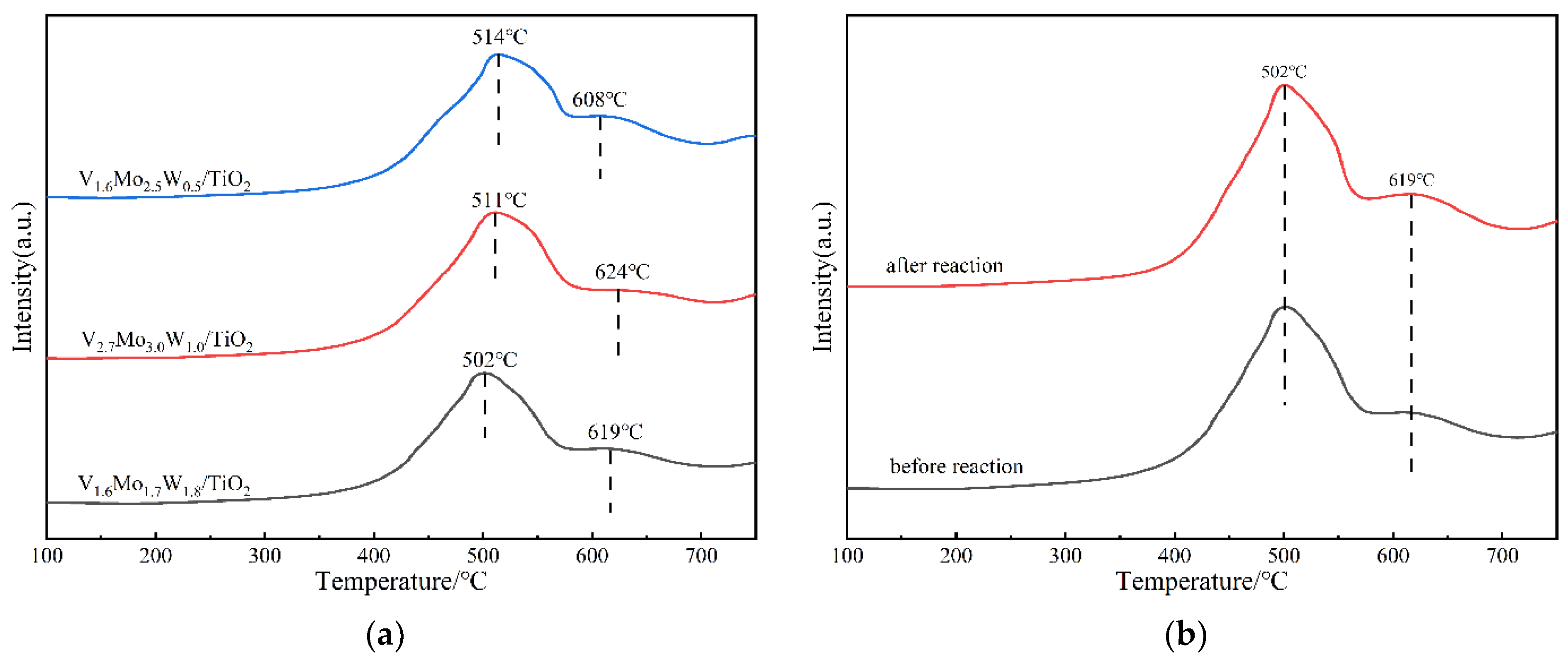
3.2.5. H2-TPR
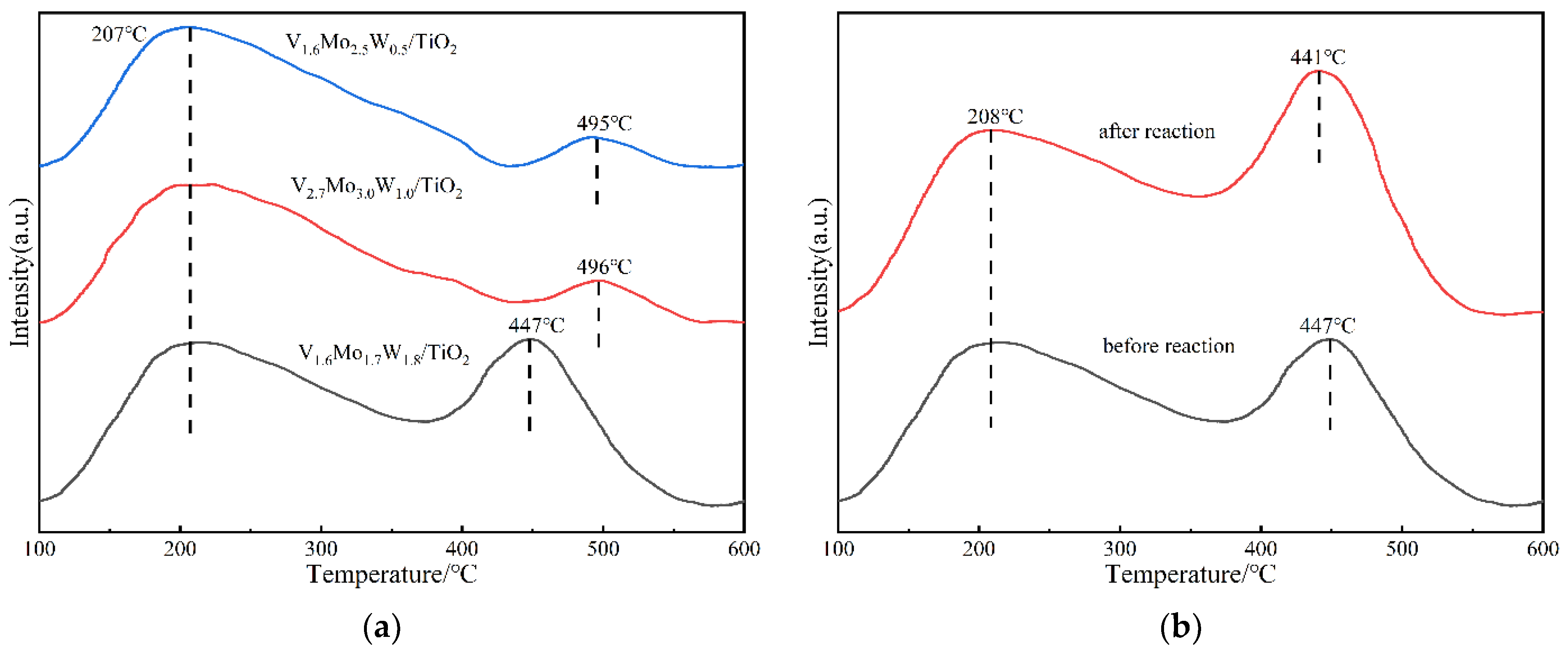
3.2.6. NH3-TPD
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Under high concentration NOx and 4%H2O, the three vanadium-based catalysts all showed excellent de-NOx activity, and the NOx conversion reached more than 97% at 200–280 °C.
- (2)
- After the NH3-SCR reaction, the valence changes in the V and Mo atoms and thermal sintering may lead to changes in the microstructure of the catalyst and thus reduce its lifetime.
- (3)
- The higher content of V4+ and V3+ and active oxygen on the surface of the catalysts were beneficial to the fast SCR reaction, which improved the low-temperature activity of the catalyst.
- (4)
- After the NH3-SCR reaction, neither the microstructure of the catalyst intensely changed nor the acid content or the intensity of the reduction peak changed, which indicated that the V1.6Mo1.7W1.8/TiO2 had strong stability.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gunnarsson, F.; Granlund, M.Z.; Englund, M.; Dawody, J.; Pettersson, L.J.; Härelind, H. Combining HC-SCR over Ag/Al2O3 and hydrogen generation over Rh/CeO2-ZrO2 using biofuels: An integrated system approach for real applications. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 162, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.B.; Nguyen, V.T.; Heo, I.J.; Mok, Y.S. Removal of NOx by selective catalytic reduction coupled with plasma under temperature fluctuation condition. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 72, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kapteijn, F.; Makkee, M. NOx reduction in the Di-Air system over noble metal promoted Ceria. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 231, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.A.; Jeong, Y.E.; Ha, H.P. Low temperature NH3-SCR activity enhancement of antimony promoted vanadia-ceria catalyst. Catal. Today 2017, 293–294, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourkhalil, M.; Izadi, N.; Rashidi, A.; Mohammad-Taheri, M. Synthesis of CeOx/γ-Al2O3 catalyst for the NH3-SCR of NOx. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 97, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.B.; Kwon, D.W.; Hong, S.C. DRIFT study on promotion effects of tungsten-modified Mn/Ce/Ti catalysts for the SCR reaction at low-temperature. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 542, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.M.; Grange, P. Characterization and reactivity of V2O5-WO3 supported on TiO2-SO42− catalyst for the SCR reaction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2001, 32, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, H.J.; Nam, I.S.; Ham, S.; Hong, S.B. Characteristics of vanadia on the surface of V2O5/Ti-PILC catalyst for the reduction of NOx by NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2004, 53, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, G.; Lietti, L.; Ramis, G.; Berti, F. Chemical and mechanistic aspects of the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by ammonia over oxide catalysts: A review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 1998, 18, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Shan, W.; Shi, X.; He, H. Vanadium-Based Catalysts for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3. Prog. Chem. 2012, 24, 445–455. [Google Scholar]
- Nova, I.; dall’Acqua, L.; Lietti, L.; Giamello, E.; Forzatti, P. Study of thermal deactivation of a de-NOx commercial catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2001, 35, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madia, G.; Elsener, M.; Koebel, M.; Raimondi, F.; Wokaun, A. Thermal stability of vanadia-tungsta-titania catalysts in the SCR process. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2002, 39, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forzatti, P. Present status and perspectives in de-NOx SCR catalysis. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 222, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Geng, Y.; Xiong, S.; Huang, X.; Kong, L.; Yang, S.; Peng, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, J. The promotion effect of ceria on high vanadia loading NH3-SCR catalysts. Catal. Commun. 2019, 121, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, W.; Ehrman, S.H.; Jurng, J. CeO2 added V2O5/TiO2 catalyst prepared by chemical vapor condensation (CVC) and impregnation method for enhanced NH3-SCR of NOx at low temperature. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Zhu, J.; Ma, L. Novel V2O5–CeO2/TiO2 catalyst with low vanadium loading for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 158–159, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Lian, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, K.; Shi, X.; Yan, Z.; Shan, W.; He, H. Polymeric vanadyl species determine the low-temperature activity of V-based catalysts for the SCR of NOx with NH3. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, 4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, G.J.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, Y. Effect of the pH value of precursor solution on the catalytic performance of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 in the low temperature NH3-SCR of NOx. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2014, 42, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjkhanlou, Y.; Janssens, T.V.; Vennestrøm, P.N.; Mino, L.; Paganini, M.C.; Signorile, M.; Bordiga, S.; Berlier, G. Location and activity of VOx species on TiO2 particles for NH3-SCR catalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 278, 119337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapkowski, M.; Siudyga, T.; Bartczak, P.; Zubko, M.; Sitko, R.; Szade, J.; Balin, K.; Witkowski, B.S.; Ożga, M.; Pietruszka, R.; et al. Catalytic Removal of NOx on Ceramic Foam-Supported ZnO and TiO2 Nanorods Ornamented with W and V Oxides. Energies 2022, 15, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djerad, S.; Tifouti, L.; Crocoll, M.; Weisweiler, W. Effect of vanadia and tungsten loadings on the physical and chemical characteristics of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2004, 208, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, L.; Tong, W.; Yang, J.; Ren, S.; Li, J.; Tian, Y. K+ deactivation of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst during selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: Effect of vanadium content. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 370, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Gao, S.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Wu, Z. Enhanced dual resistance to alkali metal and phosphate poisoning: Mo modifying vanadium-titanate nanotubes SCR catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 561, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lietti, L.; Nova, I.; Ramis, G.; Dall’Acqua, L.; Busca, G.; Giamello, E.; Forzatti, P.; Bregani, F. Characterization and Reactivity of V2O5–MoO3/TiO2 De-NOx SCR Catalysts. J. Catal. 1999, 187, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.K.; Wachs, I.E. A Perspective on the Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) of NO with NH3 by Supported V2O5–WO3/TiO2 Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 6537–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xia, Y.; Fang, R.; Huang, H.; Gan, Y.; Liang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X. The effects of tungsten and hydrothermal aging in promoting NH3-SCR activity on V2O5/WO3-TiO2 catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 459, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhong, Q.; Cai, W.; Li, H. Promotional effect of Si-doped V2O5/TiO2 for selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 1703–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Kuma, R.; Masaki, S.; Sugishima, N. TiO2-SiO2 and V2O5/TiO2-SiO2 catalyst: Physico-chemical characteristics and catalytic behavior in selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2005, 60, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.L.; Ji, L.M.; Liu, Z.K.; Hu, Y.T. Study on the Production of Uranium Oxide by Thermal Denitration of Uranyl Nitrate. Cotemporary Chem. Ind. 2019, 48, 1036–1038+1064. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, W.; Liu, X.; Tian, D.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, B. A Mixing Process of SCR Honeycomb Denitration Catalyst. CN104888805B, 8 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.K.; He, C.; Chen, J.S.; Meng, X.R. Deactivation mechanism of de-NOx catalyst (V2O5-WO3/TiO2) used in coal fired power plant. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2012, 40, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Xie, S.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, D. Solvothermal of Sr2+ doped and nonstoichiometric LaFeO3 and their photocatalytic activity. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2016, 33, 1755–1761. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Shen, B.; Chi, G.; Zhang, X. Low-temperature SCR of NO over Fe and Co co-doped Mn-Ce /TiO2 catalyst. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2017, 11, 3633–3639. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Liu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Che, Y.; Jing, C. Photocatalytic Property of Eu/BiVO4 Photocatalyst by Citric Acid Sol-Gel Method. J. Inorg. Mater. 2013, 28, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar Romero, M.; Camposeco, R.; Castillo, S.; Marín, J.; Rodríguez González, V.; García Serrano, L.A.; Mejía Centeno, I. Acidity, surface species, and catalytic activity study on V2O5-WO3/TiO2 nanotube catalysts for selective NO reduction by NH3. Fuel 2017, 198, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Shen, B.; Tian, L.; Li, G.; He, C. Enhancement of SCR activity and mechanical stability on cordierite supported V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst by substrate acid pretreatment and addition of silica. Powder Technol. 2016, 297, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nova, I.; Ciardelli, C.; Tronconi, E.; Chatterjee, D.; Bandl Konrad, B. NH3–NO/NO2 chemistry over V-based catalysts and its role in the mechanism of the Fast SCR reaction. Catal. Today 2006, 114, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, H.; Zong, Y.; Chang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X. Influence of yttrium on denitrification performance of V2O5-MoO3/TiO2 catalyst. Mod. Chem. Ind. 2020, 40, 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, J. New insight into the promotion effect of Cu doped V2O5/WO3–TiO2 for low temperature NH3-SCR performance. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 35155–35165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Xu, T.; Wang, D.; Si, Z.; Ran, R. Effects of silica additive on the SCR activity and thermal stability of a V2O5/WO3-TiO2 catalyst. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murkute, A.D.; Vanderwiel, D. Active Sites Evaluation of Vanadia Based Powdered and Extruded SCR Catalysts Prepared on Commercial Titania. Catal. Lett. 2015, 145, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, S.; Chang, H.; Peng, Y.; Li, J. Dispersion of tungsten oxide on SCR performance of V2O5WO3/TiO2: Acidity, surface species and catalytic activity. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


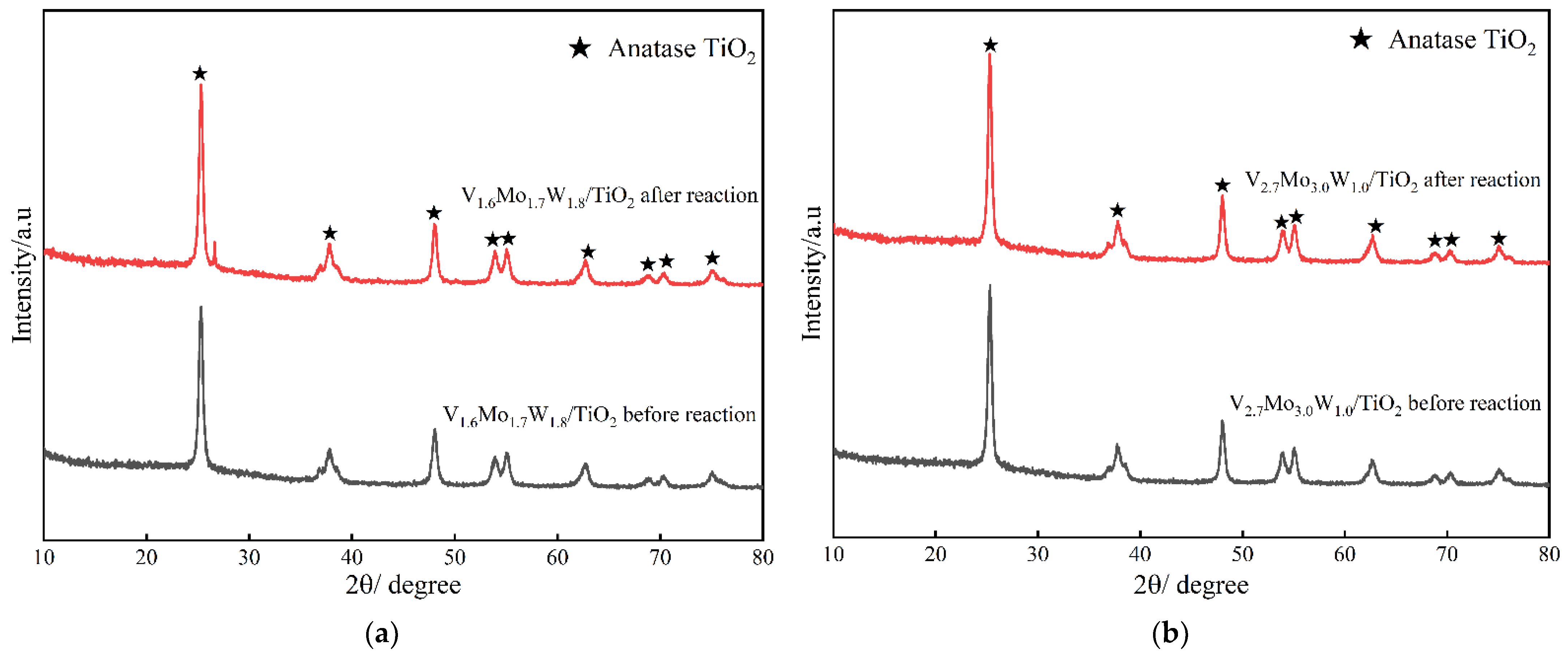
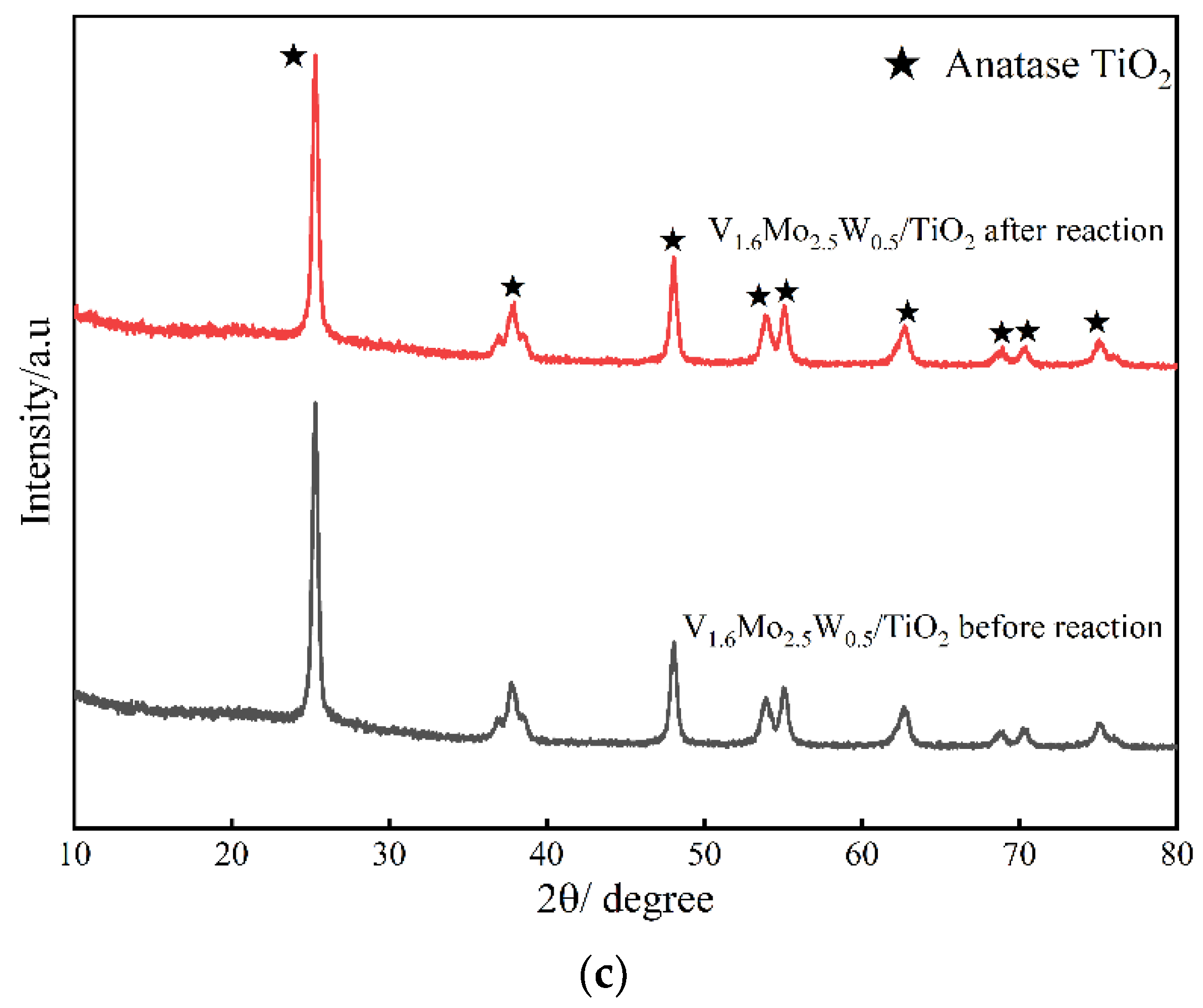
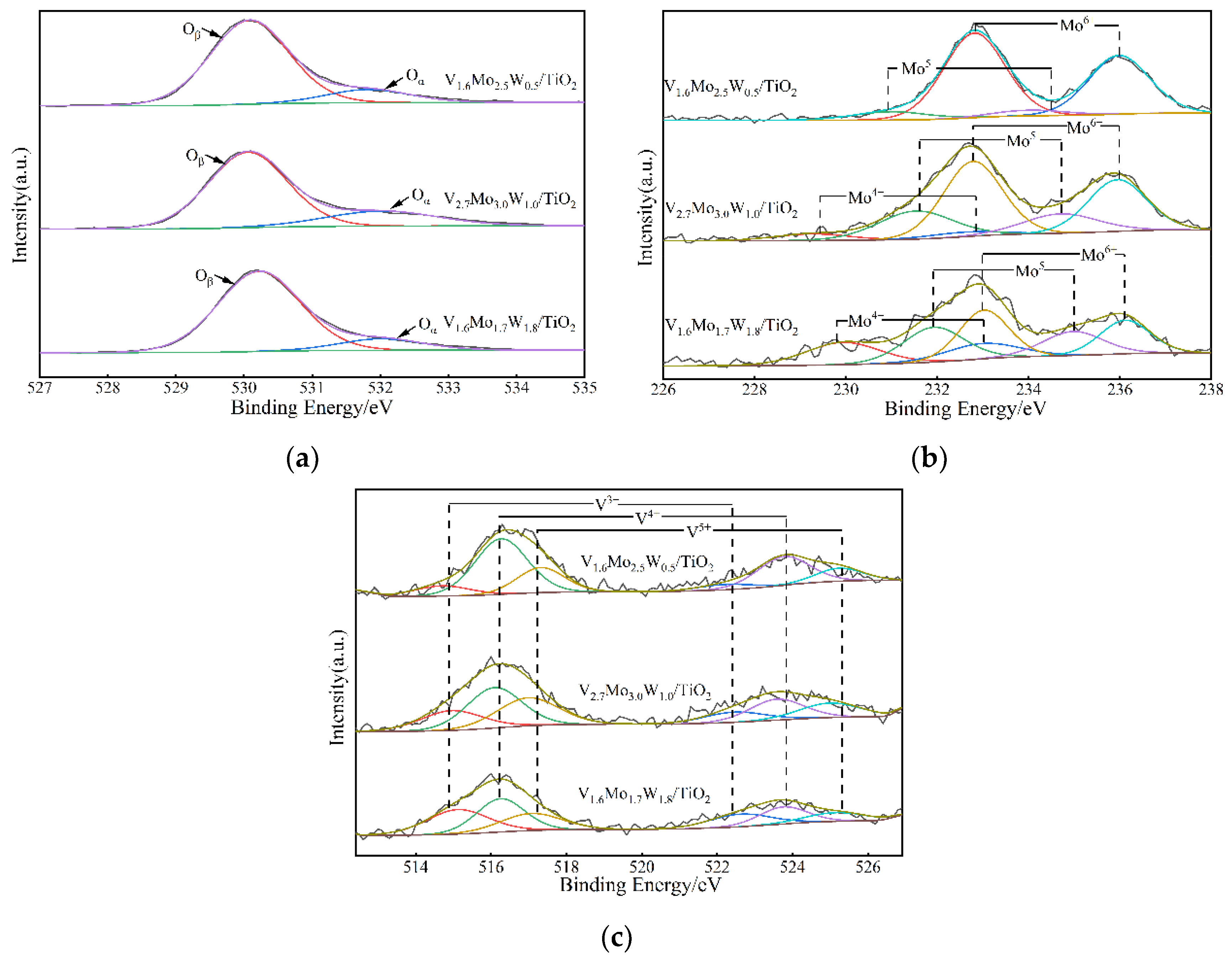
| Catalyst | Surface Area (m2/g) | Surface Area Reduction Percentage (%) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1.6Mo1.7W1.8/TiO2 | before reaction | 75.23 | 5.69 | 0.267 | 11.54 |
| after reaction | 70.95 | 0.250 | 11.64 | ||
| V2.7Mo3.0W1.0/TiO2 | before reaction | 70.90 | 5.98 | 0.284 | 13.32 |
| after reaction | 66.66 | 0.297 | 12.88 | ||
| V1.6Mo2.5W0.5/TiO2 | before reaction | 83.14 | 23.09 | 0.303 | 12.59 |
| after reaction | 63.94 | 0.251 | 12.39 |
| Catalyst | Oβ (%) | Oα (%) | Oα/(Oα + Oβ) (%) | (V3+ + V4+)/V5+ (%) | Mo6+/(Mo6+ + Mo5+ + Mo4+) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1.6Mo1.7W1.8/TiO2 before reaction | 87.3% | 12.7% | 0.127 | 2.967 | 0.392 |
| V1.6Mo1.7W1.8/TiO2 after reaction | 83.6% | 16.4% | 0.164 | 6.541 | 0.600 |
| V2.7Mo3.0W1.0/TiO2 | 78.1% | 21.9% | 0.220 | 1.985 | 0.627 |
| V1.6Mo2.5W0.5/TiO2 | 85.7% | 14.3% | 0.143 | 2.901 | 0.894 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, B.; Liu, Q.; Yang, H.; Li, Q.; Lu, H.; Yang, L.; Liu, F. Selective Catalytic Removal of High Concentrations of NOx at Low Temperature. Energies 2022, 15, 5433. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155433
Yu B, Liu Q, Yang H, Li Q, Lu H, Yang L, Liu F. Selective Catalytic Removal of High Concentrations of NOx at Low Temperature. Energies. 2022; 15(15):5433. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155433
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Bo, Qing Liu, Heng Yang, Qichao Li, Hanjun Lu, Li Yang, and Fang Liu. 2022. "Selective Catalytic Removal of High Concentrations of NOx at Low Temperature" Energies 15, no. 15: 5433. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155433
APA StyleYu, B., Liu, Q., Yang, H., Li, Q., Lu, H., Yang, L., & Liu, F. (2022). Selective Catalytic Removal of High Concentrations of NOx at Low Temperature. Energies, 15(15), 5433. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155433






