Hydrochemical Characteristics of Thermal Water Reservoir in Lądek-Zdrój in Light of Research into the Borehole LZT-1—The Deepest Borehole in the Sudetes (SW Poland)
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Previous Research into the Chemistry of Lądek Waters
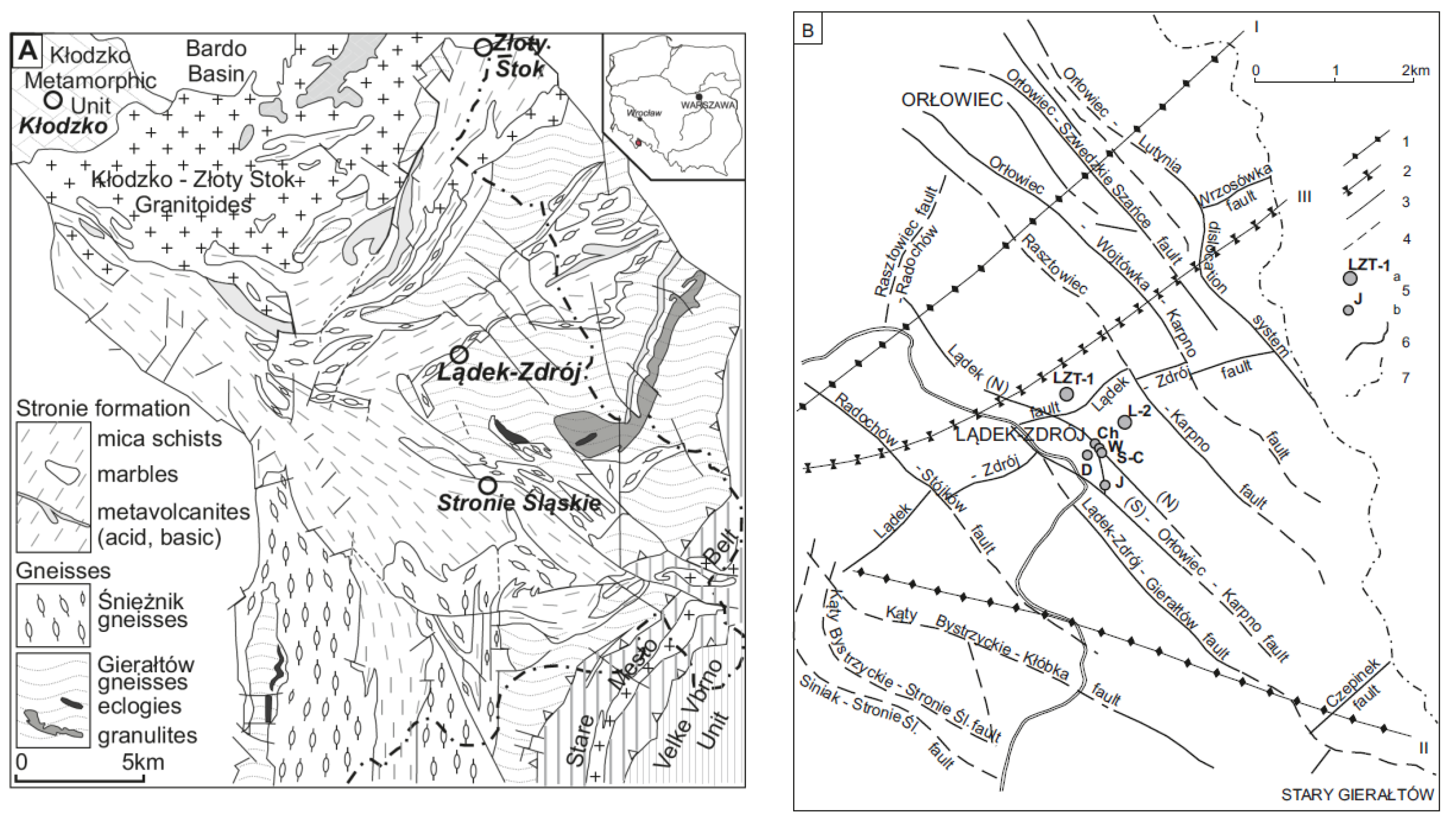
1.2. Geological Structure of the Study Area
- –
- schists of the so-called Stronie series (mica schists with paragneiss, quartzite, marble, erlan and amphibolite insertions),
- –
- Gierałtów gneisses (with amphibolite, eclogite, and granulite insertions),
- –
- Śnieżnik gneisses.
- –
- the Radochów anticlinorium (built of Gierałtów gneisses),
- –
- the Lądek synclinorium (formed within mica schists of the Stronie series),
- –
- the Gierałtów anticlinorium (formed by Gierałtów gneisses).
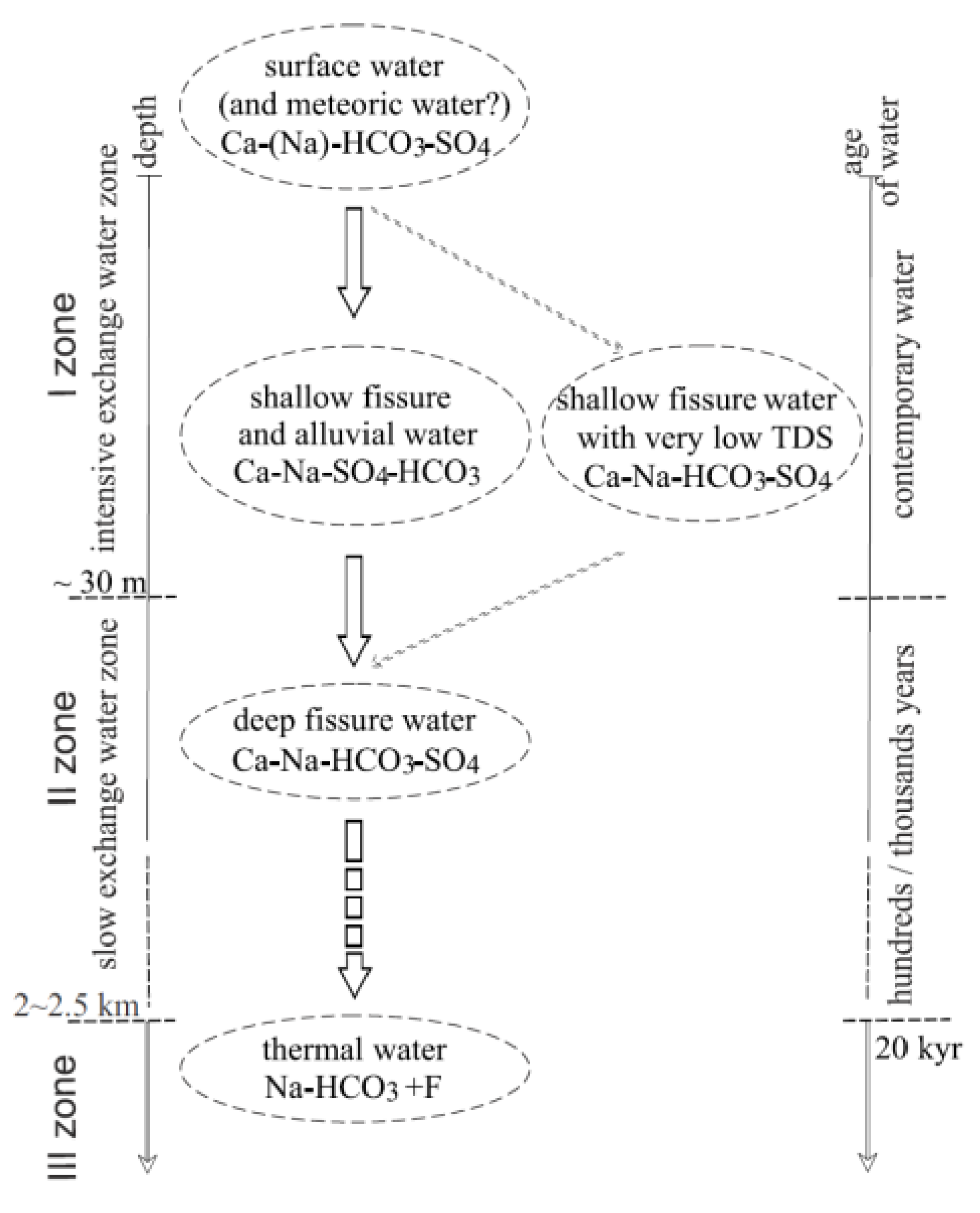
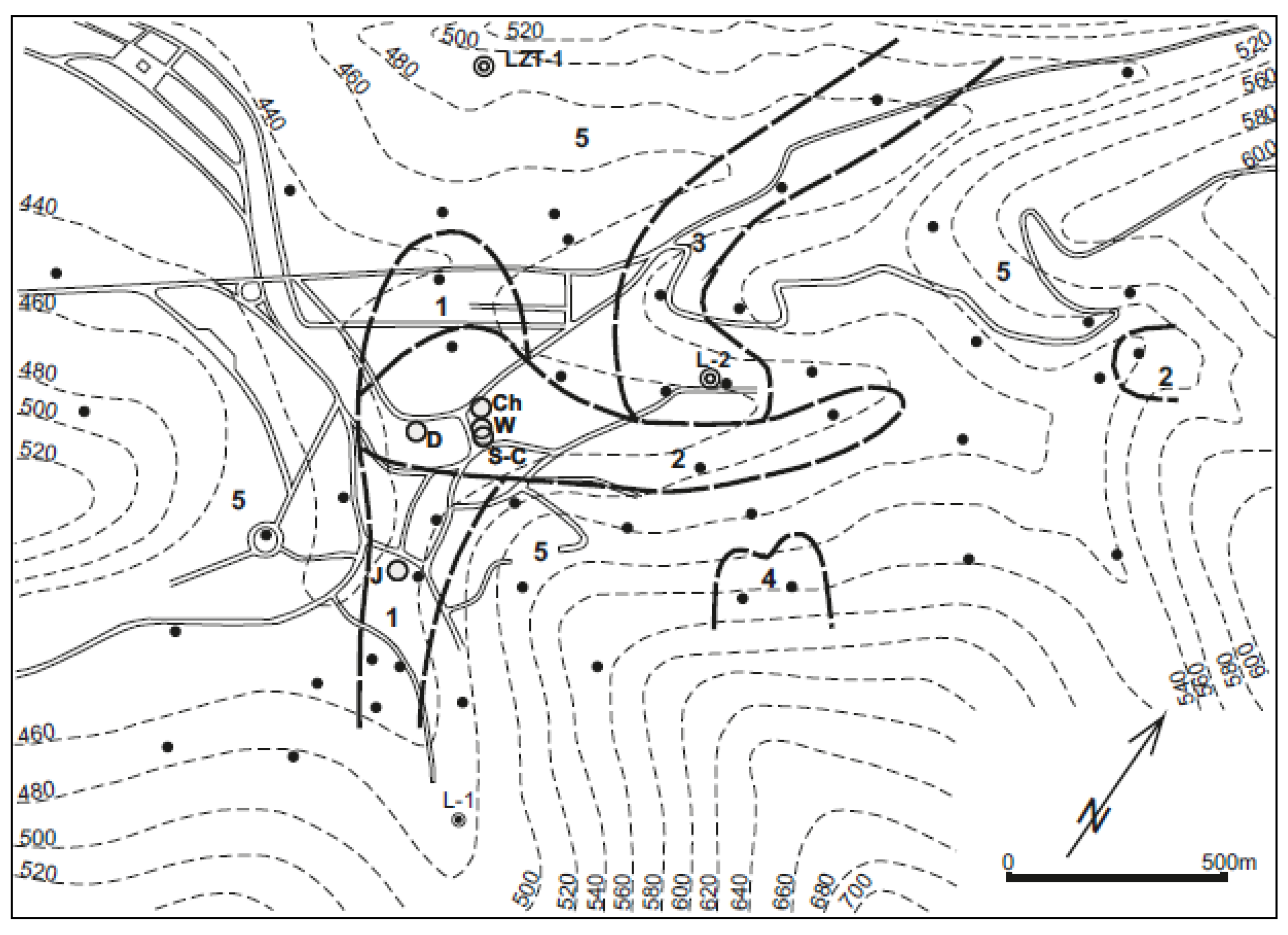
1.3. Conditions of Groundwater Occurrence
2. Materials and Methods
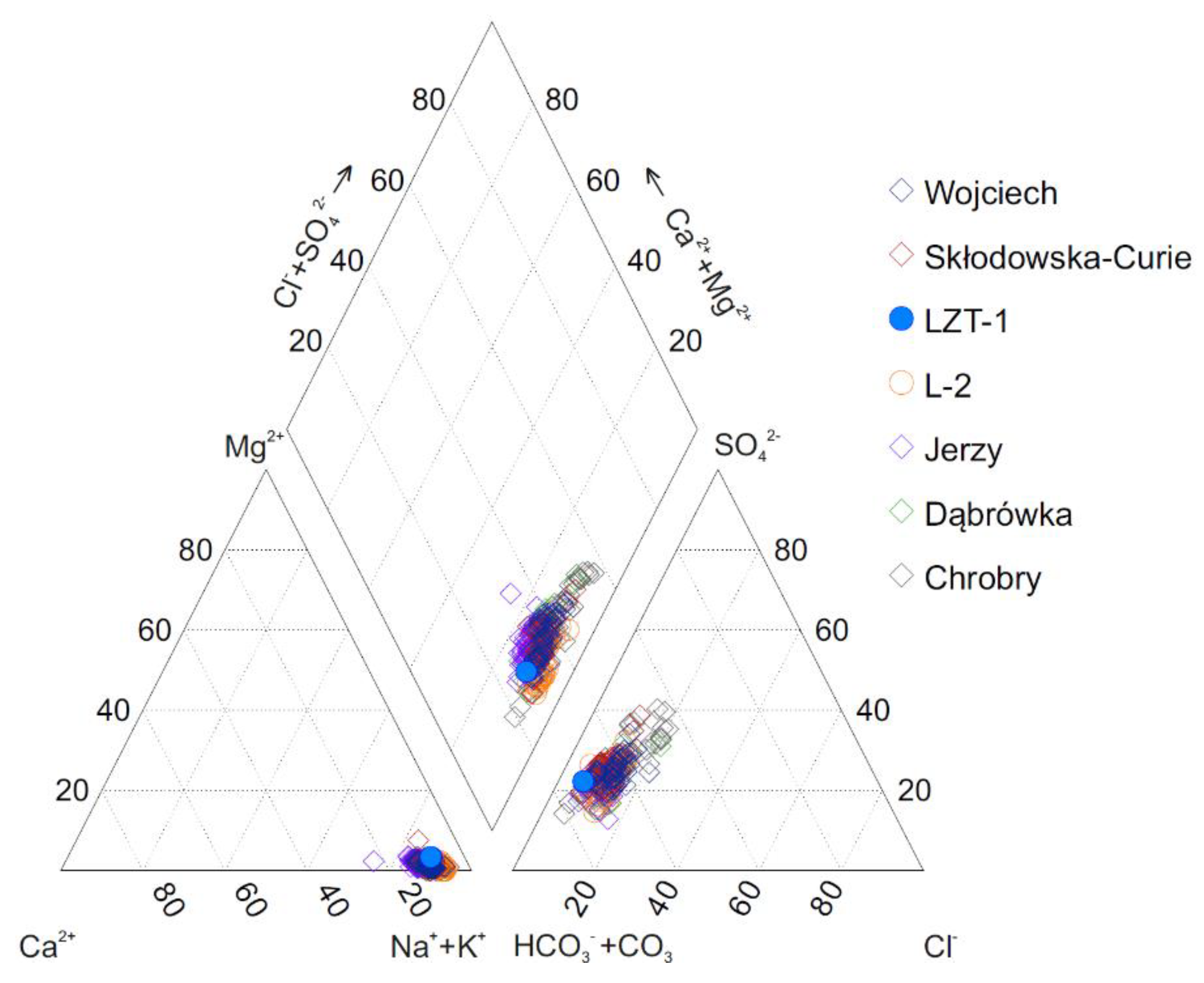
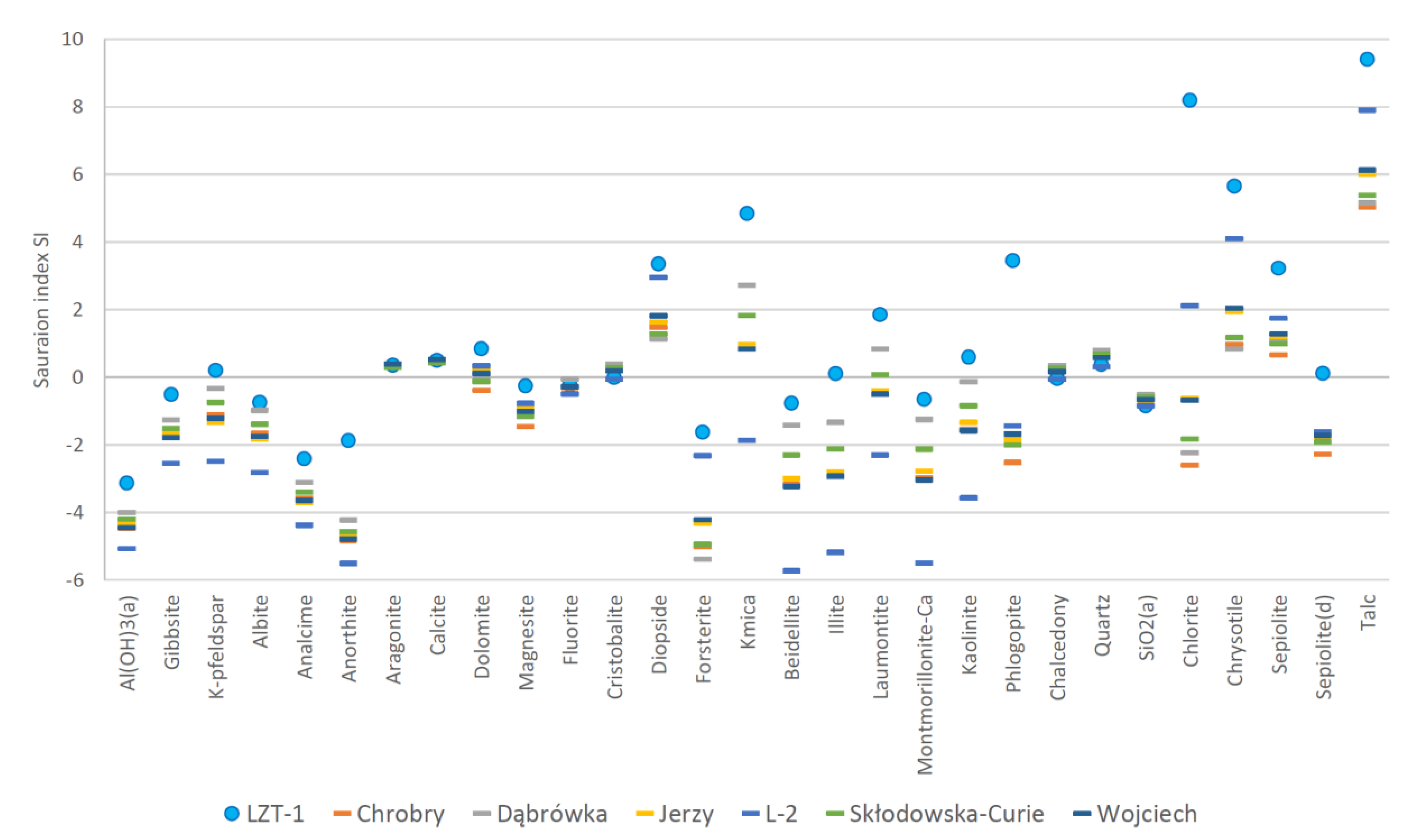
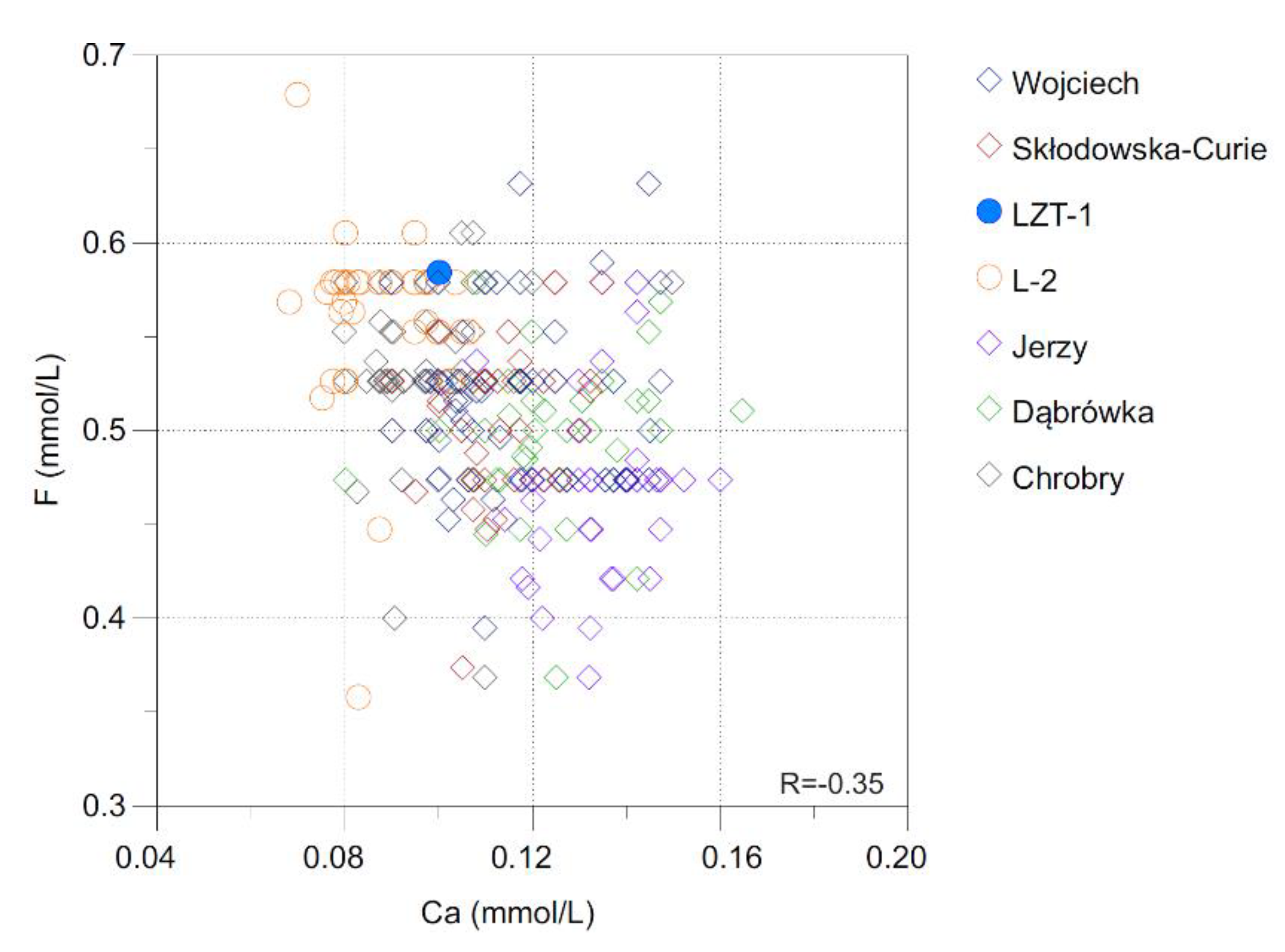
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Reults of the New LZT-1 Drilling
3.2. Estimation of Reservoir Temperature
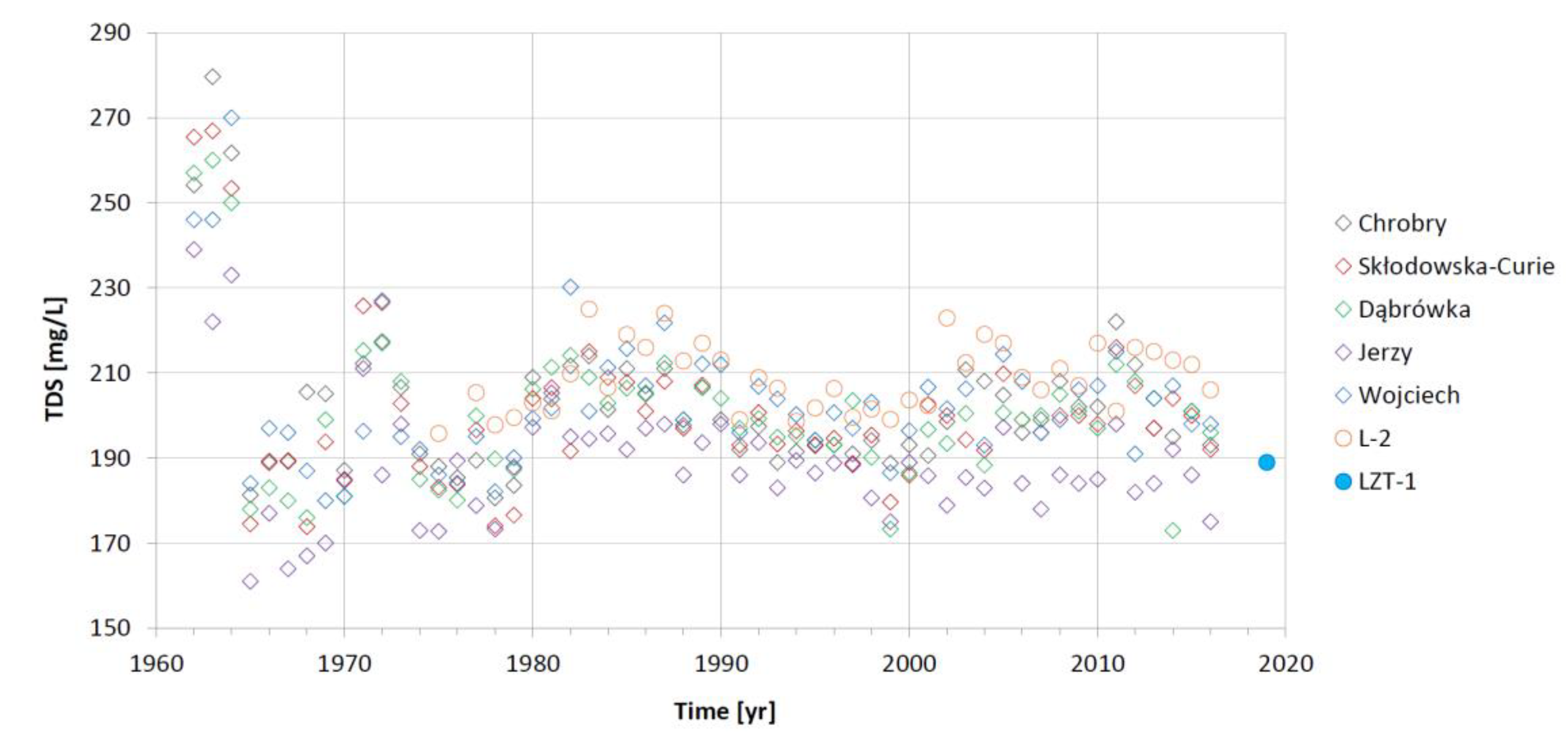
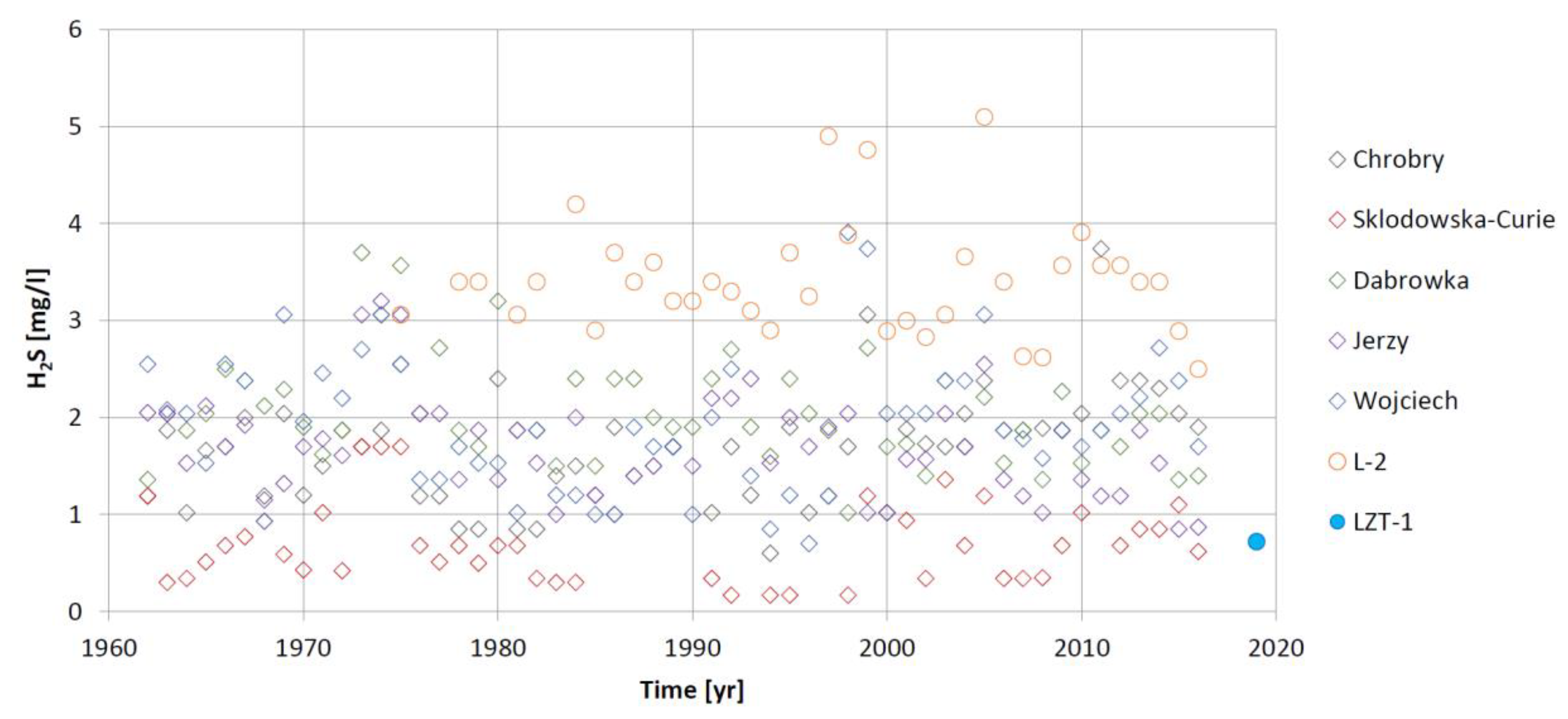
3.3. Variation in the Physicochemical Parameters of Lądek Waters in Longstanding Operation Conditions
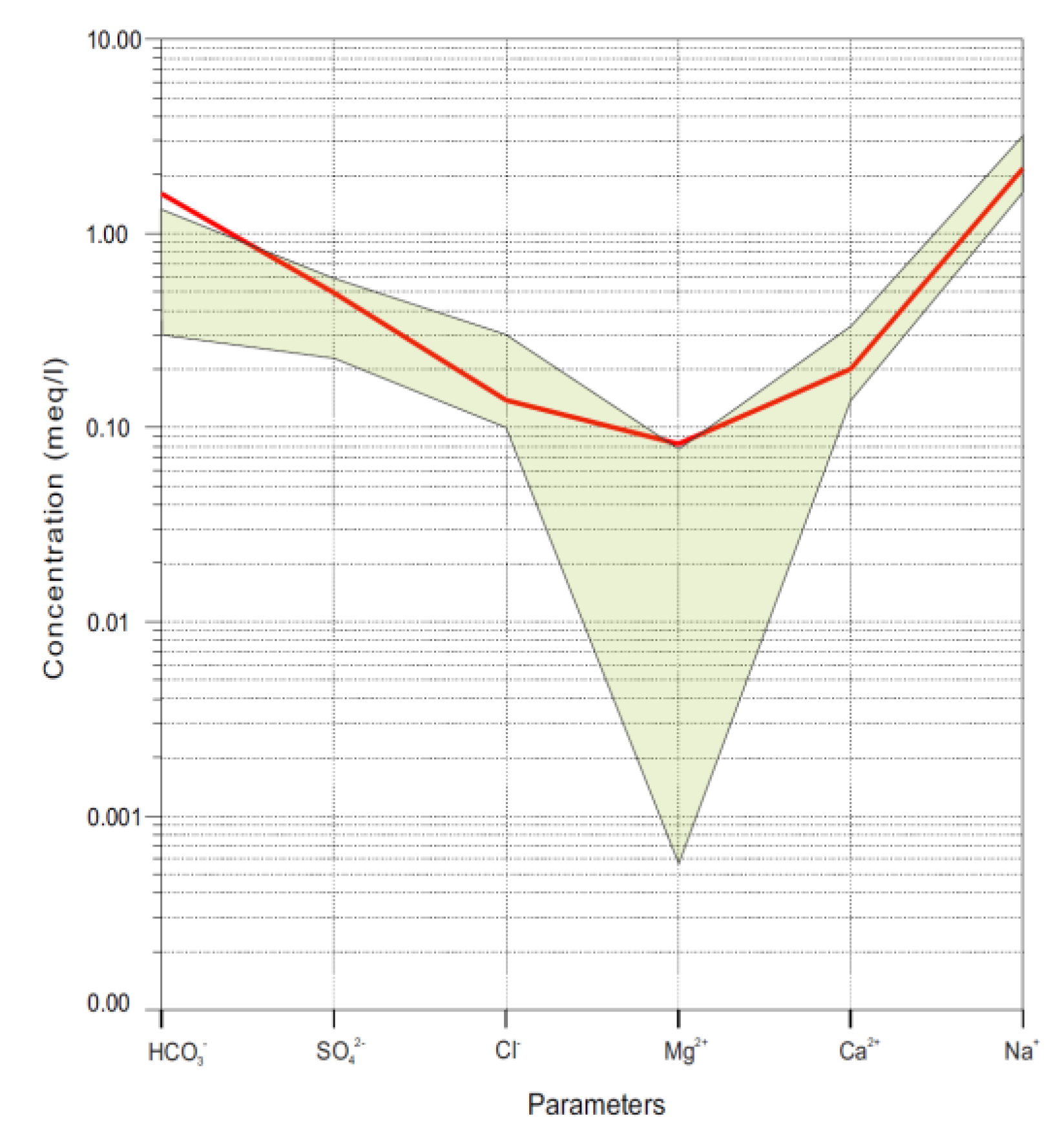
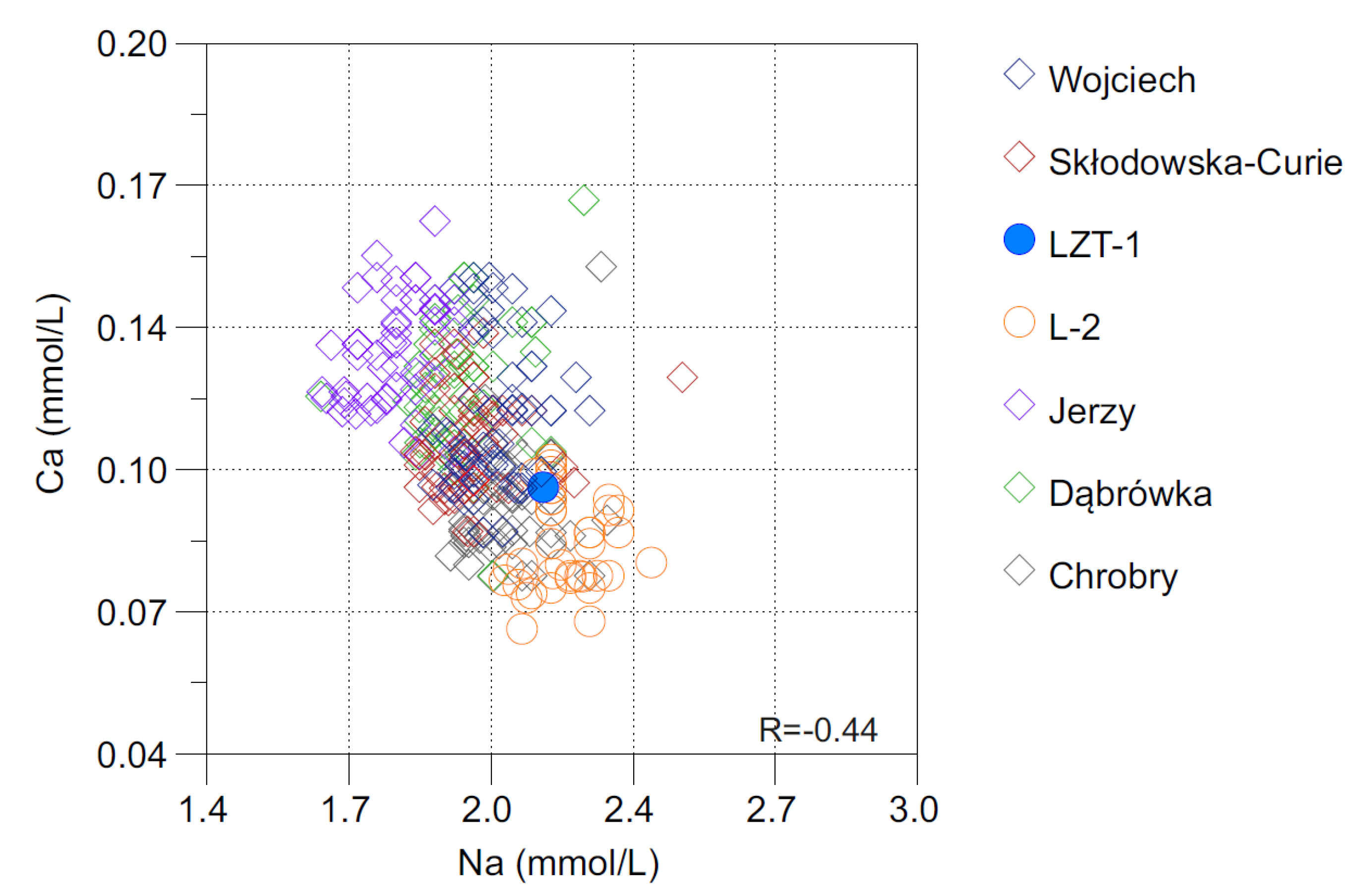
3.4. Formation of the Chemical Composition of Waters
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franko, O.; Kolářová, M.; Mateovič, L. Catalogue of Documental Points to the Map of Mineral Waters in Czechoslovakia, 1:500,000, 1st ed.; Dionýz Štúr Institute of Geology—Central Institute of Geology: Praha, Czech Republic, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Janoška, M. Minerální prameny v Čechách, na Moravě a ve Slezsku, 1st ed.; Academia: Praha, Czech Republic, 2011; p. 495. [Google Scholar]
- Franko, O.; Kolářová, M. Explanations to the Map of Mineral Waters in Czechoslovakia, 1:500,000, 1st ed.; Dionýz Štúr Institute of Geology—Central Institute of Geology: Bratislava, Praha, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Dowgiałło, J. Wody termalne Sudetów. Acta Geol. Pol. 1976, 26, 617–643. [Google Scholar]
- Ciężkowski, W. Studium Hydrogeochemii wód Leczniczych Sudetów Polskich; Pr. Nauk. Instyt. Geotech. PWr.; Wydawnictwo Politechniki Wroclawskiej: Warszawa, Poland, 1990; pp. 1–130. [Google Scholar]
- Albu, M.; Banks, D.; Nash, H. Hydrogeochemistry and origin of mineral waters. In Mineral and Thermal Groundwater Resources, 1st ed.; Albu, M., Banks, D., Nash, H., Eds.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1997; pp. 48–100. [Google Scholar]
- Papič, P. Mineral and Thermal Waters of Southeastern Europe, 1st ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2016; p. 171. [Google Scholar]
- Balderer, W.; Porowski, A.; LaMoreaux, J.W. Thermal and Mineral Waters. Origin, Properties and Applications, 1st ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; p. 135. [Google Scholar]
- Bundschuh, J.; Tomaszewska, B. Geothermal Water Management, 1st ed.; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2018; p. 462. [Google Scholar]
- Arnórsson, S.; Gunnlaugsson, E.; Svavarsson, H. The chemistry of geothermal waters in Iceland. III. Chemical geothermometry in geothermal investigations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1983, 47, 547–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, R. Application of water geochemistry to geothermal exploration and reservoir engineering. In Geothermal Systems: Principles and Case Histories, 1st ed.; Rybach, L., Muffler, L.P., Eds.; John Willey & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 1981; pp. 109–143. [Google Scholar]
- Pačes, T. Chemical characteristics and equilibration in natural water-felsic rock-CO2 system. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1972, 36, 217–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stober, I.; Bucher, K. 2005, The upper continental crust, an aquifer and its fluid: Hydraulic and chemical data from 4 km depth in fractured crystalline basement rocks at the KTB test site. Geofluids 2005, 5, 8–19. [Google Scholar]
- Shvartsev, S.L.; Zamana, L.V.; Plyusnin, A.M.; Tokarenko, O.G. Equilibrium of nitrogen-rich spring waters of the Baikal Rift Zone with host rock minerals as a basis for determining mechanisms of their formation. Geochem. Inter. 2015, 53, 720–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvartsev, S.L.; Sun, Z.; Borzenko, B.; Gao, B.; Tokarenko, O.G.; Zippa, E.V. Geochemistry of the thermal waters in Jiangxi Province. Chin. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 96, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucher, K.; Stober, I. Fluids in the upper continental crust. Geofluids 2010, 10, 241–253. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, R.O.; Truesdell, A.H. An empirical Na-K-Ca geothermometer for natural waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1973, 37, 1255–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, R.O. Chemical geothermometers and mixing models for geothermal systems. Geothermics 1977, 5, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnórsson, S. Chemical equilibria in Icelandic geothermal systems—implication for chemical geothermometry investigations. Geothermics 1983, 12, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnórsson, S. The quartz- and Na/K geothermometers. II Results and application for monitoring studies. In Proceedings of the World Geothermal Congress, Tohoku, Japan, 28 May–10 June 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Giggenbach, W.F. Geothermal solute equilibria. Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindycators. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 2749–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cave, L.; Clarke, S. A Feasibility Study on the Use of Chemical Geothermometers for Tracing Deep Groundwater Flow; Report to the Water Research Commision No. 1331/1/03; Division of Water, Environment and Forestry Technology: Pretoria, South Africa, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer, L.; Wanner, C.; Spycher, N.; Sonnenthal, E.L.; Kennedy, B.M.; Iovenitti, J. Optimized multicomponent vs. classical geothermometry: Insights from modelling studies at the Dixie Valley geothermal area. Geothermics 2014, 51, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.H.; Red, M.H. Theoretical chemical thermometry on geothermal waters: Problems and methods. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetel, J.; Rybařová, L. Minerální vody Východočeského kraje, 1st ed.; Ústřední ústav geologický: Praha, Czech Republic, 1979; p. 228. [Google Scholar]
- Kačura, G. Minerální vody Severočeského Kraje, 1st ed.; Ústřední ústav geologický: Praha, Czech Republic, 1980; p. 178. [Google Scholar]
- Zötl, J.; Goldbrunner, J.E. Die Mineral und Heilwässer Österreichs, 1st ed.; Springer: Wien, Austria, 1993; p. 329. [Google Scholar]
- Sonney, R. Groundwater Flow, Heat and Mass Transport in Geothermal Systems of a Central Alpine Massif. The cases of Lavey-les-Bains, Saint-Gervais-les-Bains and Val d’Illiez. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Neuchâtel, Neuchâtel, Switzerland, 2010. Available online: https://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-00923368/file/These-Sonney-2010 (accessed on 28 December 2020).
- Ricour, J.; Pomerol, C.h. Terroirs et Thermalisme en France Les eaux Minérales Françaises, 1st ed.; Éditions du BRGM: Orleans, France, 1992; p. 288. [Google Scholar]
- Baskov, E.A.; Surikov, S.N. Gidrotermi Zemli, 1st ed.; Nedra: Leningrad, Russia, 1989; p. 244. [Google Scholar]
- Das, P.; Maya, K.; Padmalal, D. Hydrochemistry, geothermometry and origin of the low temperature thermal springs of South Konkan region India. Geothermics 2021, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaguchi, M.; Muramatsu, Y.; Chiba, H.; Okumura, F.; Ohba, T.; Yamamuro, M. Hydrochemistry and isotopic characteristics of non-volcanic hot springs around the Miocene Kofu granitic complex surrounding the Kofu Basin in the South Fossa Magna region, central Honshu. Jpn. Geochem. J. 2000, 48, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominikiewicz, M. Wody Mineralne Polski, 1st ed.; Państwowy Zakład Wydawnictw Lekarskich: Warszawa, Poland, 1951; p. 620. [Google Scholar]
- Goebel, S. Analizy Chemiczne wód Mineralnych Polski, 1st ed.; Wyd. Geol.: Warszawa, Poland, 1963; p. 590. [Google Scholar]
- Jarocka, A. Analizy fizyko-chemiczne wód leczniczych z polskich uzdrowisk wykonane w 1968 r. Lądek. Probl. Uzdr. 1970, 1, 191–201. [Google Scholar]
- Gierwielaniec, J. Lądek-Zdrój i jego wody mineralne. Kwart. Geol. 1968, 12, 680–692. [Google Scholar]
- Gierwielaniec, J. Lądek Zdrój i jego wody mineralne w świetle dotychczasowych badań. Pr. Nauk. Inst. Geotech. PWr. 1970, 5, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Fistek, J. Wody mineralne Lądka Zdroju. In Przewodnik XXX Zjazdu Polskiego Towarzystwa Geologicznego; Polish Geological Society: Duszniki Zdrój, Poland, 1957; pp. 171–172. [Google Scholar]
- Fistek, J.; Szarszewska, Z. Nowe ujęcie wody termalnej w Lądku Zdroju. In Przewodnik XLVII Zjazdu Polskiego Towarzystwa Geologicznego; Polish Geological Society: Świdnica, Poland, 1975; pp. 259–262. [Google Scholar]
- Ciężkowski, M.; Ciężkowski, W. Źródła Lądka Zdroju—historia i badania. Balneol. Pol. 1983, 27, 5–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ciężkowski, W. Hydrochemical types of fissure waters from Lądek Zdroj. In Proceedings of the Conference Hydrogeochemistry of Mineralized Waters, Cieplice Spa, Poland, 31 May–3 June 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Ciężkowski, W. Wody termalne Lądka Zdroju. In Proceedings of the II Ogólnopolskie Sympozjum Współczesne Problemy Hydrogeologii Regionalnej, Lądek-Zdrój, Poland, 13–16 October 1982; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Wrocławskiego: Wrocław, Poland, 1983; pp. 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ciężkowski, W. Hydrogeologia i hydrochemia wód termalnych Lądka-Zdroju. Probl. Uzdr. 1980, 4, 125–193. [Google Scholar]
- Kiełczawa, B. Charakterystyka hydrochemiczna wód termalnych Lądka-Zdroju. Tech. Posz. Geol. Geoterm. Zrównoważony Rozwój 2013, 2, 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zuber, A.; Weise, S.M.; Osenbrück, K.; Grabczak, J.; Ciężkowski, W. Age and recharge area of thermal waters in Lądek Spa (Sudeten, Poland) deduced from environmental isotope and noble gas data. J. Hydrogeol. 1995, 167, 327–349. [Google Scholar]
- Ciężkowski, W.; Doktór, S.; Graniczny, M.; Kabat, T.; Kozłowski, J.; Liber, E.; Przylibski, T.; Teisseyre, B.; Wiśniewska, M.; Zuber, A. Próba Określenia Obszarów Zasilania wód Leczniczych Pochodzenia Infiltracyjnego w Polsce na Podstawie Badań Izotopowych; Zał. 20; Złoże wód leczniczych Lądka-Zdroju; Zakład Badawczo-Usługowy: Wrocław, Poland, 1996; Unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Dowgiałło, J.; Hałas, S.; Porowski, A. Isotope temperature indicators of thermal waters in South-Western Poland. In Proceedings of the World Geothermal Congress, Anatalya, Turkey, 24–29 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Porowski, A. Sens i znaczenie badań geotermometrycznych w poszukiwaniach wód termalnych o niskiej entalpii. Tech. Posz. Geol. Geoterm. Zrównoważony Rozwój 2007, 46, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Porowski, A.; Dowgiałło, J. Application of selected geothermometers to exploration of low-enthalpy thermal water: The Sudetic Geothermal Region in Poland. Environ. Geol. 2009, 58, 1629–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leśniak, P. Some ionic equlibria of Sudetic thermal waters. In Proceedings of the Conference Hydrogeochemistry of mineralized waters, Cieplice Spa, Poland, 1–3 October 1978; pp. 389–394. [Google Scholar]
- Leśniak, P.; Nowak, D. Water-rock interaction in some mineral waters in the Sudetes, Poland: Implications for chemical geothermometry. Ann. Soc. Geol. Pol. 1993, 63, 101–118. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrzyński, D.; Leśniak, P. Two contrasting geothermal systems—towards the identification of geochemical reaction pattern and groundwater temperature, the Sudetes, Poland. In Proceedings of the Extendend abstracts of 38th IAH Congress, Kraków, Poland, 12–17 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ciężkowski, W.; Solecki, A.; Śliwiński, W. Results of the long term monitoring of radon content in mineral springs of the Spa of Lądek Zdrój, southwestern Poland. In Gas Geochemistry; Dubois, C., Ed.; University of Franche-Comté: Besançon, France, 1995; pp. 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Przylibski, T.A.; Żebrowski, A. Origin of radon in medicinal waters of Lądek Zdrój (Sudety Mountains, SW Poland). J. Environ. Radioact. 1999, 46, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Przylibski, T.A. 222Rn concentration changes in medicinal groundwaters of Lądek Zdrój (Sudety Mountains, SW Poland). J. Env. Radioac. 2000, 48, 327–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przylibski, T.A. Radon. Składnik Swoisty wód Leczniczych Sudetów, 1st ed.; Oficyna Wydawnicza Politechniki Wrocławskiej: Wrocław, Poland, 2005; p. 329. [Google Scholar]
- Żelaźniewicz, A. Dzieje Ziemi. Przeszłość geologiczna. In Przyroda Dolnego Śląska, 1st ed.; Fabiszewski, J., Ed.; PAN Oddział we Wrocławiu: Wrocław–Warszawa, Poland, 2005; pp. 61–134. [Google Scholar]
- Gierwielaniec, J. Z geologii Lądka-Zdroju. Pr. Nauk. Inst. Geotech. PWr. 1970, 5, 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Don, J. Góry Złote i Krowiarki jako elementy składowe metamorfiku Śnieżnika. Geol. Sudet. 1964, 1, 117. [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmajer, K.; Pecskay, Z.; Grabowski, J.; Lorenc, M.W.; Zagożdżon, P.P. Radiometric dating of the Tertiary volcanics in Lower Silesia, Poland. II. K-Ar dating and paleomagnetic data from Neogene basanites near Lądek-Zdrój, Sudetes Mts. Ann. Soc. Geol. Polon. 2002, 72, 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- Jastrzębski, M. The tectonometamorphic evolution of the marbles in the Lądek-Śnieżnik metamorphic unit, West Sudetes. Geol. Sudet. 2005, 37, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Fistek, J.; Iwanowski, S.; Iciek, A.; Jagodziński, A. Metody badawcze w poszukiwaniu i rozpoznaniu złóż wód termalnych w sudeckim regionie geotermalnym. Biul. Inform. Geofizyka 1975, 1, 5–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ciężkowski, W. Hydrogeologia i Hydrochemia wód Termalnych Lądka Zdroju. Ph.D. Thesis, Wrocław University of Science and Technology, Wrocław, Poland, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Staśko, S.; Tarka, R. Zasilanie i drenaż wód podziemnych w obszarach górskich na podstawie badań w Masywie Śnieżnika. Acta Univ. Wratisl. 2002, 2528, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Ciężkowski, W.; Liber-Makowska, E.; Ciekot, B.; Ogórek, A. Charakterystyka warunków występowania i eksploatacji wód termalnych Lądka-Zdroju. Tech. Posz. Geol. Geoterm. Zrównoważony Rozwój 2011, 50, 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Liber-Makowska, E. Dynamiczne oddziaływanie pomiędzy ujęciami wód termalnych Lądka-Zdroju. Tech. Posz. Geol. Geoterm. Zrównoważony Rozwój 2011, 1, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Liber-Madziarz, E. Charakterystyka wydajności ujęć wód termalnych Lądka Zdroju. In Proceedings of the VIII Ogólnopolskie Sympozjum Hydrogeologiczne, Współczesne Problemy Hydrogeologii, Kiekrz/Poznań, Poland, 4–6 September 1997; Wyd. WIND: Poznań, Poland, 1997; pp. 357–360. [Google Scholar]
- Liber, E. Zmienność Wydajności ujęć wód Leczniczych Eksploatowanych Samoczynnie ze Złóż Sudeckich. Ph.D. Thesis, Wrocław University of Science and Technology, Wrocław, Poland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Liber, E. Charakterystyka opróżniania zbiornika wód szczelinowych głębokiego krążenia na przykładzie złoża wód termalnych Lądka-Zdroju. Biul. PIG 2009, 436, 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- Květ, R.; Kačura, G. Minerální vody Severomoravského kraje, 1st ed.; Ústřední Ústav Geologický: Praha, Czech Republic, 1978; p. 173. [Google Scholar]
- Sajner, J.; Křížek, V. Lázně Velké Losiny, Dějiny, Přitomnost, Přírodní Zdroje, 1st ed.; Avicenum: Praha, Czech Republic, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Rasała, M.; Ciężkowski, W.; Wąsik, M.; Kiełczawa, B. Dokumentacja geologiczna z wykonania prac geologicznych niekończących się udokumentowaniem zasobów złoża kopaliny w związku z wykonaniem otworu poszukiwawczego za wodami termalnymi LZT-1 w Lądku-Zdroju. Unpublished.
- Macioszczyk, A. Metody przedstawiania składu chemicznego wód podziemnych. In Hydrogeochemia, 1st ed.; Macioszczyk, A., Ed.; Wyd. Geol.: Warszawa, Poland, 1987; pp. 314–359. [Google Scholar]
- Dz.U. Poz. 1064: Obwieszczenie Marszałka Sejmu Rzeczpospolitej Polskiej z dnia 26 Marca 2020 r. w Sprawie Ogłoszenia Jednolitego Tekstu Ustawy; Prawo Geologiczne i Górnicze: Warszawa, Poland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Porowski, A. Mineral and Thermal Waters. In Encyclopedia of Sustainability Science and Technology, 1st ed.; Meyers, R., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, M.; Auqué, L.F.; Gimeno, M.J. Application of different geothermometrical techniques to a low enthalpy thermal system. Proc. Earth Planetary Sci. 2017, 17, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, R. Lectures on Geochemical Interpretation of Hydrothermal Waters, UNU-Geothermal Training Programme; Report 10; The United Nations University: Reykjavik, Iceland, 1989; p. 731. Available online: http://orkusofnu.is/gogn/unu-gtp-report/UNU-GTP-1898–10 (accessed on 28 December 2020).
- Besser, H.; Mokadem, N.; Redhaounia, B.; Hadji, R.; Hamad, A.; Hamed, Y. Groundwater mixing and geochemical assessment of low-enthalpy resources in the geothermal field of southwestern Tunisia. Eur. Mediter. J. Environ. Integ. 2018, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiełczawa, B.; Liber-Makowska, E.; Blachowski, J. Lądek-Zdrój study case. In Geothermal Energy—A Basis for Low-Emission Space Heating, Improving Living Conditions and Sustainable Development Preliminary Studies for Selected Areas in Poland, 1st ed.; Kępińska, B., Barbacki, A.P., Eds.; Study Visits’ Report; IGSMiE, PAN: Kraków, Poland, 2017; pp. 224–261. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, R.O.; Potter, R.W. A Magnesium Correction for the Na-K-Ca Chemical Geothermometer; Report 78–986; U.S. Geological Survey: Menlo Park, California, CA, USA, 1979. Available online: http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/1978/098/report (accessed on 12 November 2020).
- Dowgiałło, J. The Sudetic geothermal region of Poland. Geothermics 2002, 31, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.H.; Spycher, N. Calculation of pH and mineral equilibria in hydrothermal waters with application to geothermometry and studies of boiling and dilution. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 1479–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y. Estiamtion of reservoir temperature using silica and cationic solute geothermometers:a case study in the Tengchong geothermal area. Chin. J. Geochem. 2015, 34, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbacki, A.P.; Bujakowski, W.; Hajto, M.; Kępińska, B.; Kiełczawa, B.; Liber-Makowska, E.; Sapińska-Śliwa, A.; Sowiżdżał, A.; Stefaniuk, M.; Śliwa, T. Energia Geotermalna—Możliwości dla Niskoemisyjnego Ciepłownictwa, Poprawy Warunków Życia i Zrównoważonego Rozwoju w Wybranych Obszarach Polski, 1st ed.; Wydawnictwa AGH: Kraków, Poland, 2017; pp. 5–74. [Google Scholar]
- Szczepański, J. Proweniencja i Ewolucja Tektonometamorficzna Serii Suprakrustalnej w Krystaliniku Gór Bytrzyckich, 1st ed.; Wrocławska Drukarnia Naukowa PAN: Wrocław, Poland, 2010; p. 166. [Google Scholar]
- Redlińska-Marczyńska, A. Gierałtów versus Śnieżnik gneisses—what is the real difference? Geologos 2011, 17, 71–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, M.; Smedley, P. Fluoride in natural waters. In Essentials of Medical Geology, Impacts of the Natural Environment on Public Health, 1st ed.; Sellinus, O., Alloway, B.J., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 301–329. [Google Scholar]
- Polański, A.; Smulikowski, K. Geochemia, 1st ed.; Wydawnictwo Geologiczne: Warszawa, Poland, 1969; p. 662. [Google Scholar]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry Groundwater and Pollution, 2nd ed.; Balcema Publisher: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 119–132. [Google Scholar]
- Gierwielaniec, J.; Szarszewska, Z. Lądek-Zdrój (Lądek springs). In Proceedings of the Conference Hydrogeochemistry of Mineralized Waters, Cieplice Spa, Poland, 31 May–3 June 1978; pp. 371–373. [Google Scholar]
- Wise, W.S. Zeolites. In Encyclopedia of Geology, 1st ed.; Selley, R.C., Cocks, L.R.M., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2005; Volume 3, pp. 591–600. [Google Scholar]
- Dowgiałło, J. Stan rozpoznania zasobów wód termalnych Region Sudeckiego i perspektywy ich wykorzystania. Tech. Posz. Geol. Geoterm. Zrównoważony Rozwój 2007, 46, 29–34. [Google Scholar]

| Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | Concentration of Specific Components (Name of Medicinal Water) | TDS—Total Dissolved Solids (g/L) |
| ≥20 (thermal water) | 10 mg Fe(II) mg/L (ferruginous water) | ≥1 (mineral water) |
| 2 mg F− mg/L (fluoride water) | ||
| 1 mg I− mg/L (iodide water) | ||
| 1 mg S(II) mg/L (sulphide wat) | ||
| <20 (cold water) | 70 mg H2SiO3 mg/L (silica water) | <1 (lightly mineralized water) |
| 74 Bq Rn/L (radon water) | ||
| 250 mg free CO2 mg/L (carbonated water) | ||
| 1000 mg free CO2 mg/L (CO2-rich water, carbonated water) | ||
| Geothermometer | Equation | References |
|---|---|---|
| Q | [18] | |
| Ch1 | [18] | |
| Ch2 | [10] | |
| Na-K | [10] | |
| Na-K-Ca | [17] |
| pH | Na+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | Fe2+ | NH4 | HCO3− | F− | Cl− | SO42 | Ba | SiO2 | TDS | EC | Rn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | (mg/L) | (mS/cm) | (Bq/L) | ||||||||||||
| 9.6 | 49.6 | 2.51 | <1.2 | 4.01 | 0.148 | 0.117 | 97.6 | 11.1 | <5 | 20 | 0.041 | 35.7 | 189 | 0.305 | 93.9 ± 4.1 |
| Q (°C) | Ch1 (°C) | Ch2 (°C) | Na-K (°C) | Na-K-Ca (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Porowski and Dowgiałło, [49]) | |||||
| springs | 79.6–86.1 | 48.3–55.1 | 51.0–57.4 | 68.4–89.5 | 29.6–51.3 |
| L-2 | 78.9 | 47.5 | 50.3 | 76.8 | 36.7 |
| current research | |||||
| LZT-1 | 86.7 | 55.8 | 58.1 | 97.2 | 96.8 * |
| Intake (N) | Kurlov’s Formula |
|---|---|
| Chrobry (54) | |
| Dąbrówka (54) | |
| Jerzy (54) | |
| Skłodowska-Curie (54) | |
| Wojciech (54) | |
| L-2 (39) | |
| LZT-1 (1) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiełczawa, B.; Ciężkowski, W.; Wąsik, M.; Rasała, M. Hydrochemical Characteristics of Thermal Water Reservoir in Lądek-Zdrój in Light of Research into the Borehole LZT-1—The Deepest Borehole in the Sudetes (SW Poland). Energies 2021, 14, 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14041009
Kiełczawa B, Ciężkowski W, Wąsik M, Rasała M. Hydrochemical Characteristics of Thermal Water Reservoir in Lądek-Zdrój in Light of Research into the Borehole LZT-1—The Deepest Borehole in the Sudetes (SW Poland). Energies. 2021; 14(4):1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14041009
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiełczawa, Barbara, Wojciech Ciężkowski, Mirosław Wąsik, and Marek Rasała. 2021. "Hydrochemical Characteristics of Thermal Water Reservoir in Lądek-Zdrój in Light of Research into the Borehole LZT-1—The Deepest Borehole in the Sudetes (SW Poland)" Energies 14, no. 4: 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14041009
APA StyleKiełczawa, B., Ciężkowski, W., Wąsik, M., & Rasała, M. (2021). Hydrochemical Characteristics of Thermal Water Reservoir in Lądek-Zdrój in Light of Research into the Borehole LZT-1—The Deepest Borehole in the Sudetes (SW Poland). Energies, 14(4), 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14041009





