Chemical Composition Variations of Altered and Unaffected Coals from the Huaibei Coalfield, China: Implications for Maturity
Abstract
Highlights
- Detailed comparative analyses of magma altered and unaffected coals were carried out.
- Hydrogen exhibits significantly difference between the magma altered and unaffected coals.
- Aromatization degree is closely related with maximum vitrinite reflectance.
- Mass fraction of coals varies greatly between 450–1000 °C with different heating rates.
1. Introduction
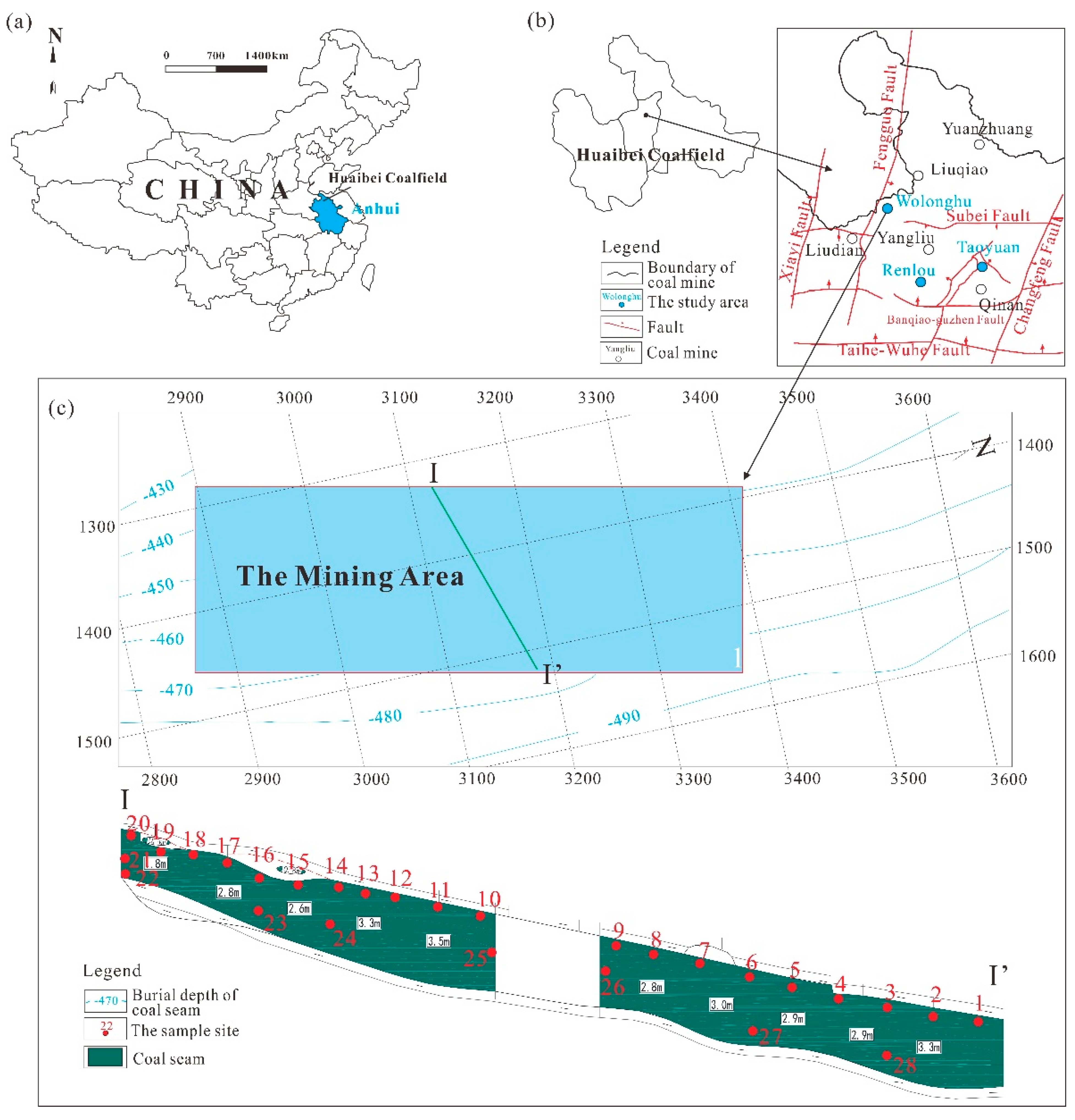
2. Geological Setting
3. Samples and Methods
3.1. Samples Collection
3.2. Ultimate Analysis
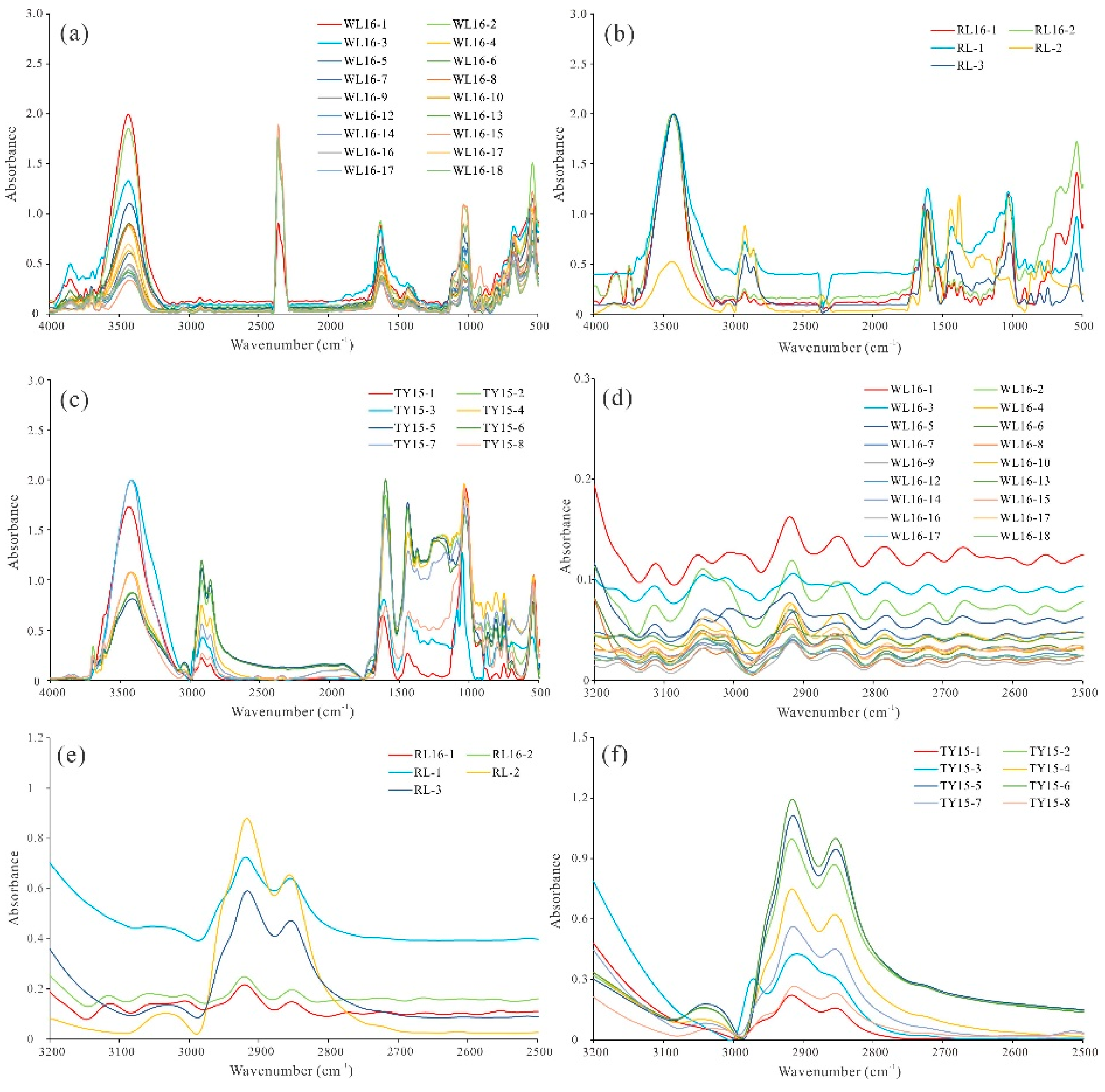
3.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
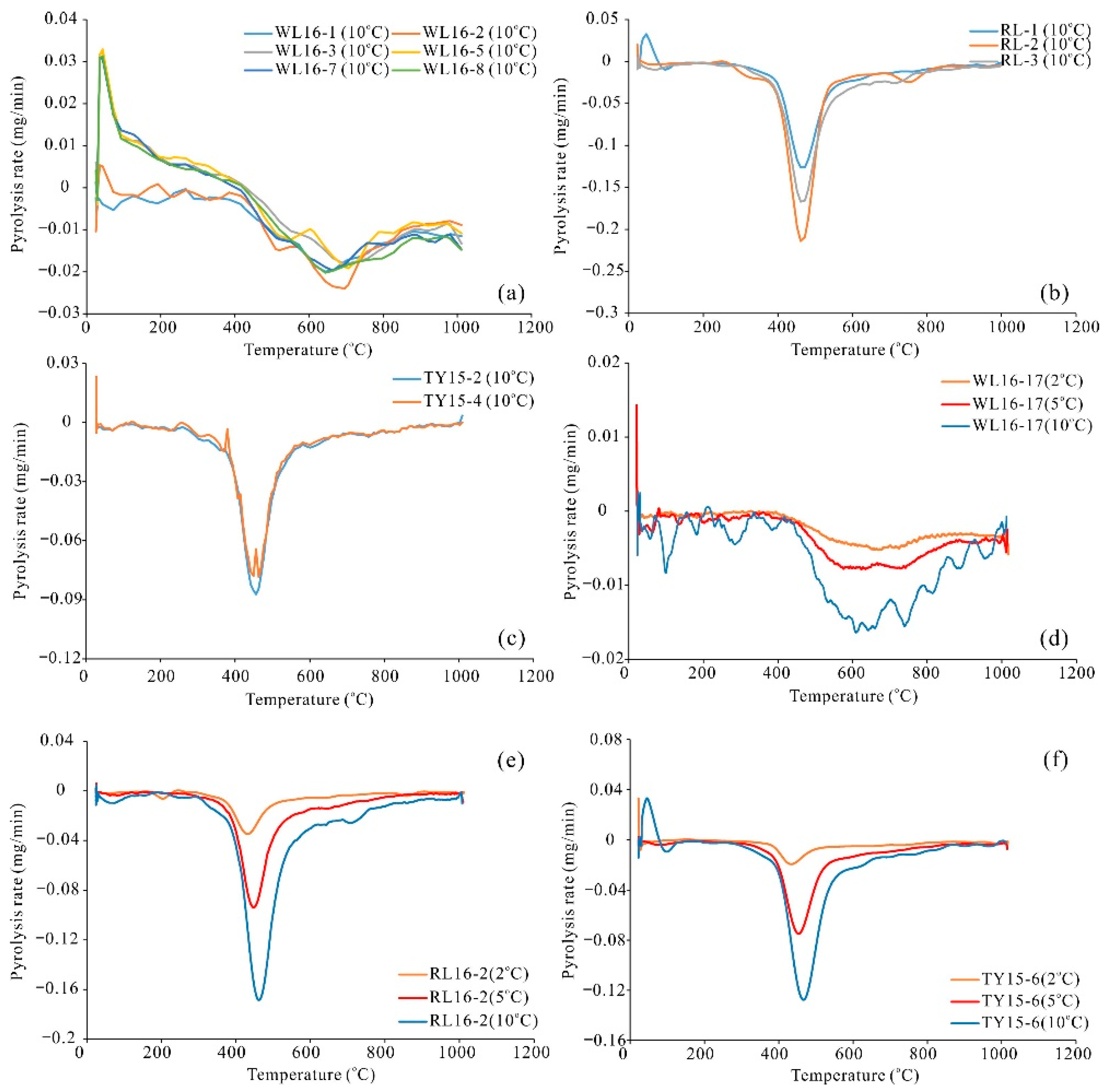
3.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Coal Rank and Basic Characteristics of Coals
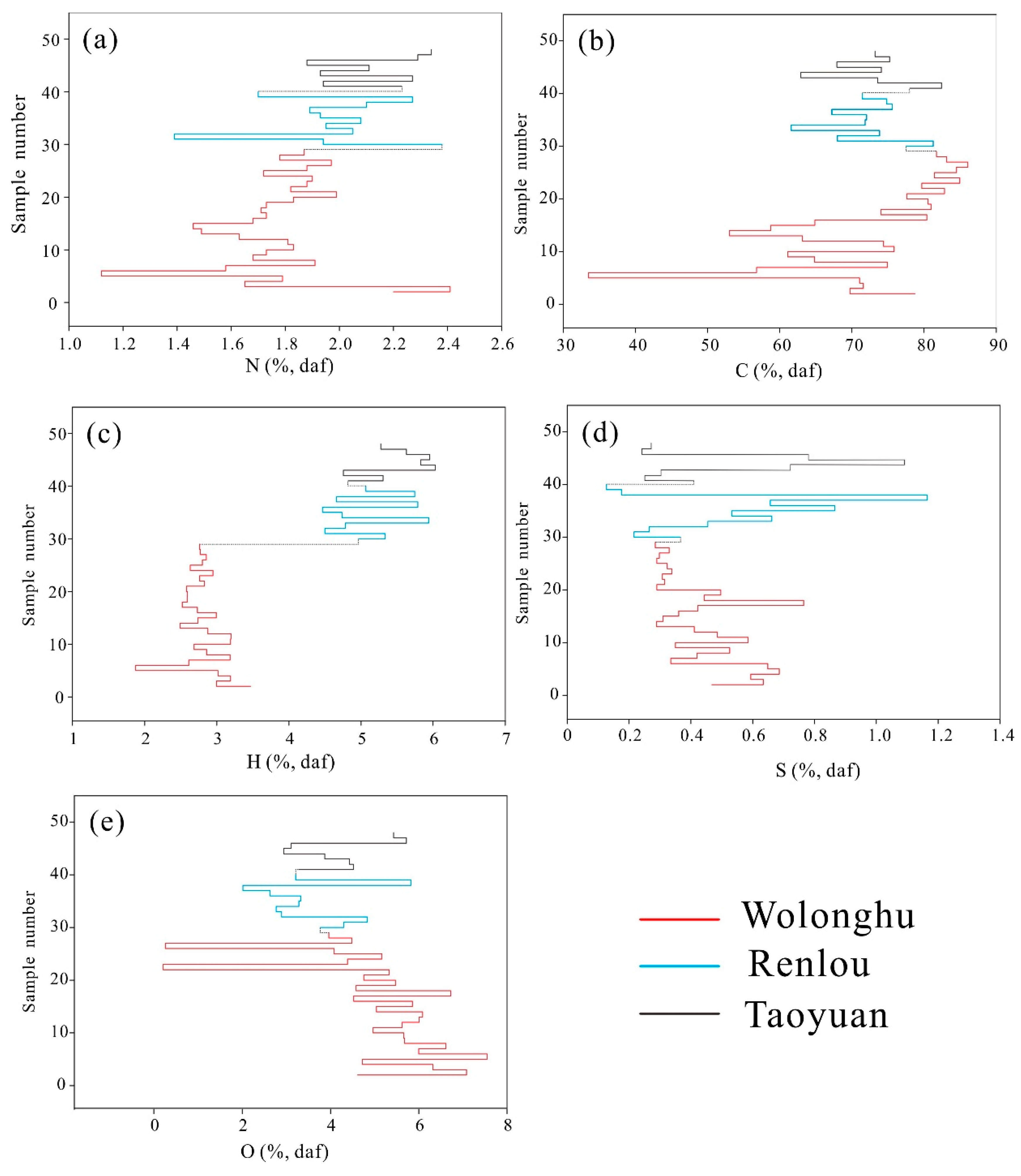
4.2. Element Contents of Coals
4.3. FTIR Characterisitics of Coals
4.4. Pyrolysis Characteristics of Coals
5. Discussion
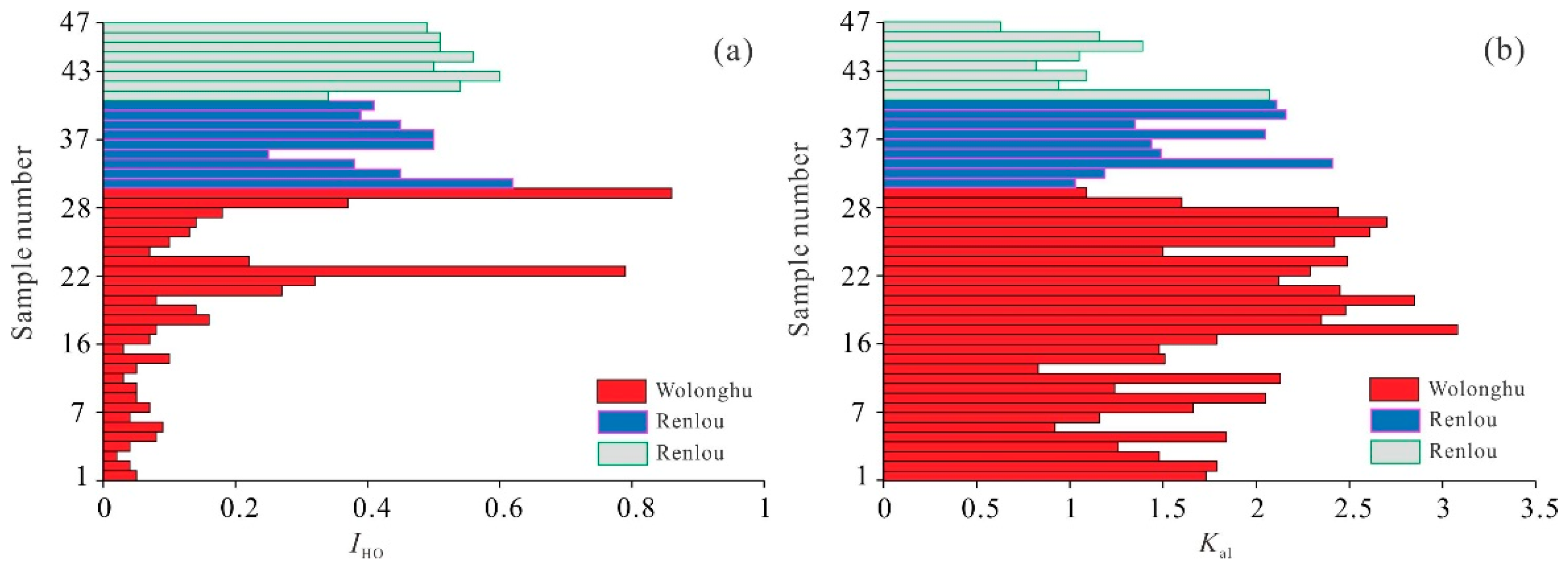
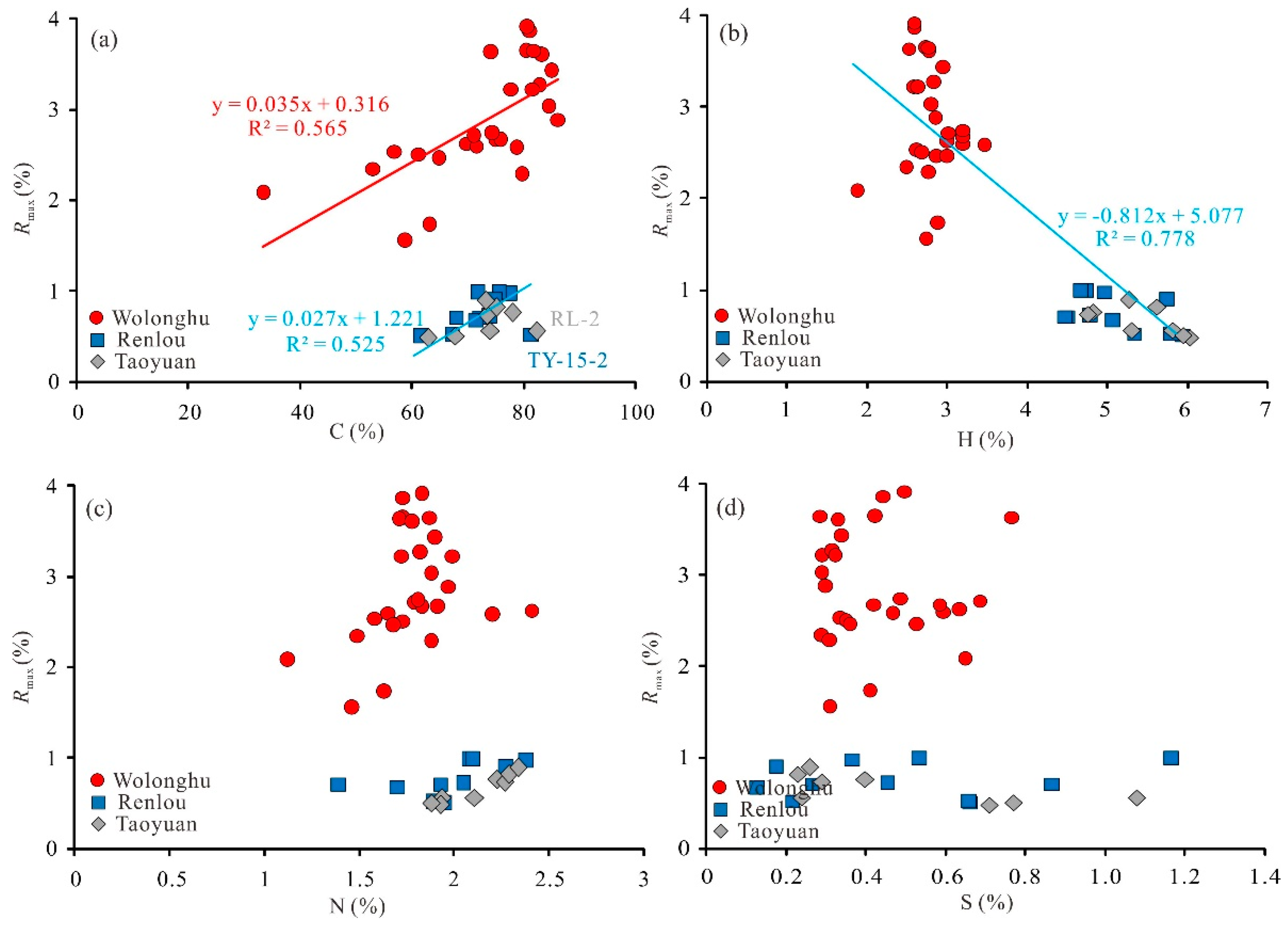
5.1. Influence of Maturity on the Basic Characteristics and Hydrogen Element Content of Coals
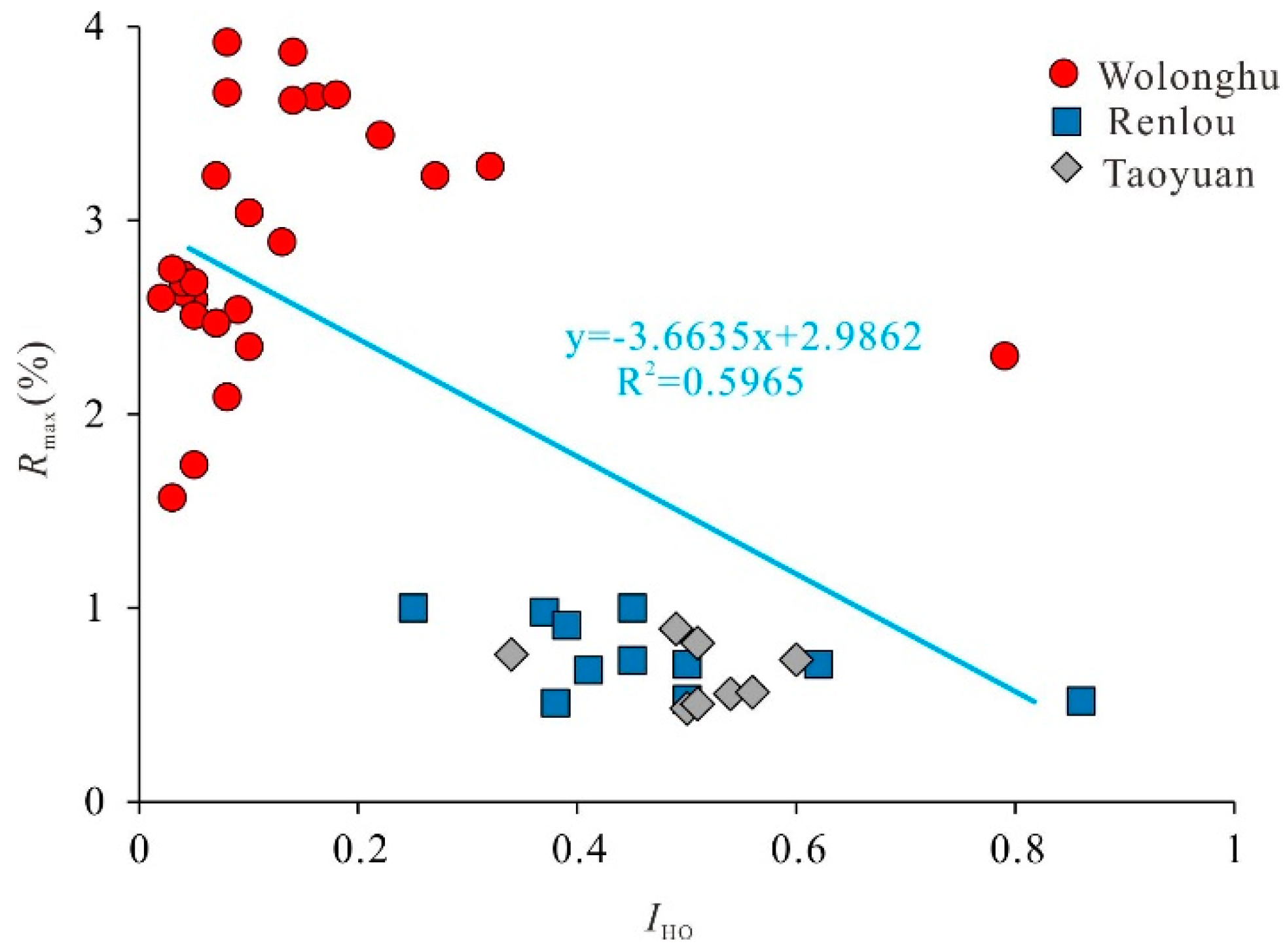
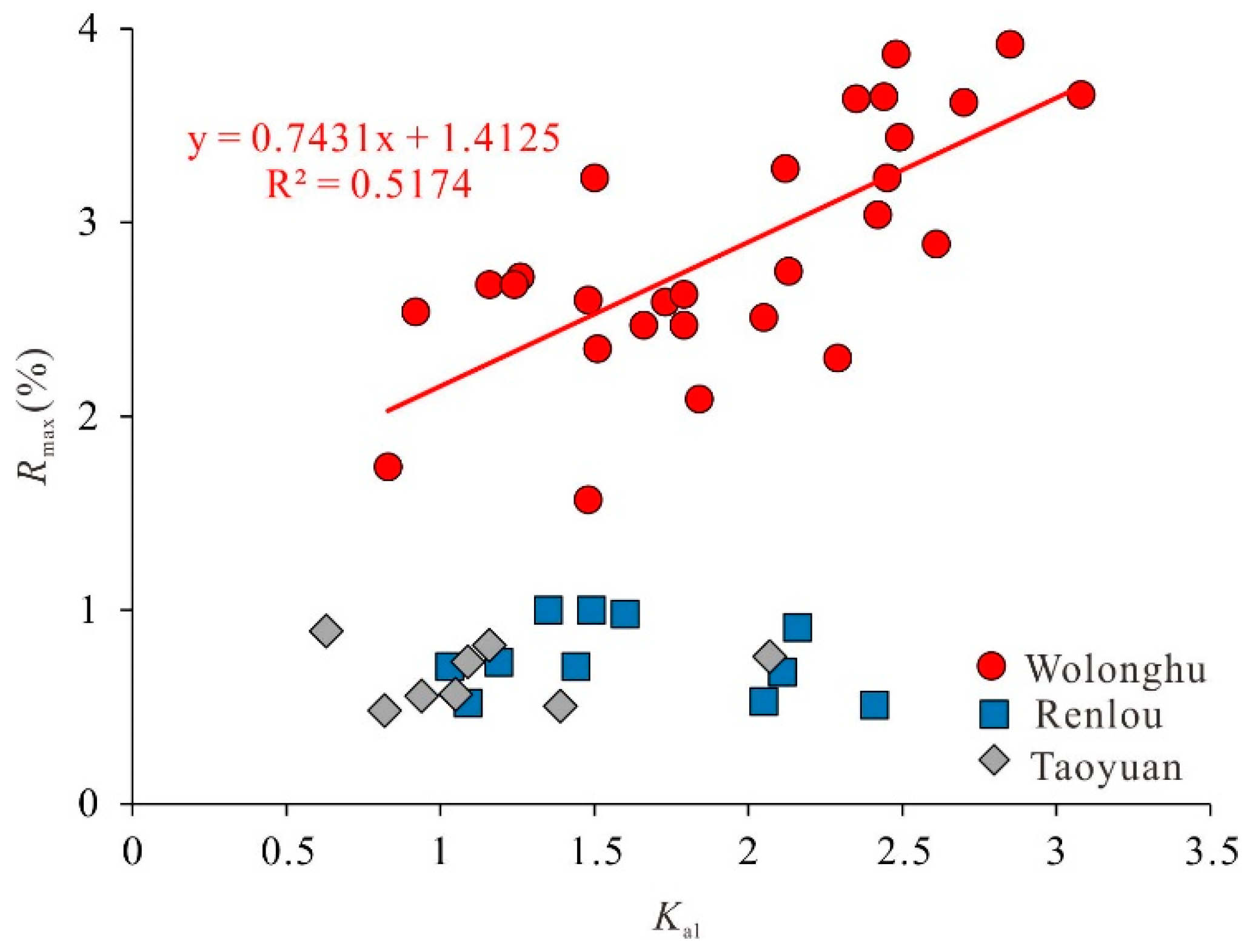
5.2. Influence of Maturity on the Structure of Organic Matters and Pyrolysis Characteristics of Coals
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, M.M.; Liu, G.J.; Wu, B.; Zheng, L.G. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in coal from magmatic intrusion area from Wolonghu coal mine. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. China 2012, 42, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.F.; Ward, C.R.; Graham, I.T.; French, D.; Hower, J.C.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.B. Altered volcanic ashes in coal and coal-bearing sequences: A review of their nature and significance. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 175, 44–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golab, A.N.; Hutton, A.C.; French, D. Petrography, carbonate mineralogy and geochemistry of thermally altered coal in Permian coal measures, Hunter Valley, Australia. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2007, 70, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.F.; Liu, L.L.; Wang, M.N.; Zheng, S.; Guo, Y.J.; Zhang, S.; Lai, C.K. Source and Enrichment of Toxic Element in coal seams around mafic intrusions: Constraints from Pyrites in the Yuandian coal mine in Anhui, eastern China. Minerals 2018, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Han, B.W.; Chen, S.D. Characteristics of REES in coals from the igneous intrusion area of the Zhuji Coal mine, Anhui. Bull. Miner. Petrol. Geochem. 2014, 33, 493–499. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.B.; Yu, L.; Che, Q.S.; Liu, M.Q. Transition metal element geochemical characteristic at Wolonghu coal mine of Anhui province. Coal Geol. China 2015, 27, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kuboušková, S.; Krmíček, L.; Coufalík, P.; Pokorný, R. Petrological and geochemical characteristics of Palaeogene of low-rank coal on the Faroe islands: Restricted effects of alteration by basaltic lava flow. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 165, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, X.B.; Jiang, Y.F.; Zhou, G.Q.; Wang, P.P.; Wang, R.X.; Zhao, L. Behavior of minerals and trace elements during natural coking: A case study of an intruded bituminous coal in the shuoli mine, Anhui Province, China. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 4013–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tang, D.Z.; Xu, H.; Li, S.; Pang, J.D.; Yao, C.H.; Li, J.J.; Yu, T.X. Magmatism effect on different transformation characteristics of coal reservoirs physical properties in Xishan Coalfield. J. China Coal Soc. 2015, 40, 1900–1910. [Google Scholar]
- Mastalerz, M.; Drobniak, A.; Schimmelmann, A. Changes in optical properties, chemistry, and micropore and mesopore characteristics of bituminous coal at the contact with dikes in the Illinois basin. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2009, 77, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, G.J.; Li, H.; Wu, B. Mineralogical and geochemical responses of coal to igneous intrusion in the Pansan Coal mine of the Huainan coalfield, Anhui, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 124, 11–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.W.; Rimmer, S.M. Effects of rapid thermal alteration on coal: Geochemical and petrographic signatures in the Springfield (NO.5) coal, illinois Basin. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 131, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presswood, S.M.; Rimmer, S.M.; Anderson, K.B.; Filiberto, J. Geochemical and petrographic alteration of rapidly heated coals from the herrin (No.6) coal seam, Illinois basin. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 165, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.D.; Liu, G.J.; Fu, B.; Yuan, Z.J.; Chen, B.Y. Influence of magmatic intrusions on organic nitrogen in coal: A case study from the Zhuji mine, the Huainan coalfield, China. Fuel 2018, 219, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.L.; Qin, B.T.; Liang, H.J.; Gao, Y.; Bao, Q. Effects of igneous intrusions on the structure and spontaneous combustion propensity of coal: A case study of bituminous coal in daxing mine, China. Fuel 2018, 216, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.F.; Chen, Y.X.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.Y.; Lai, C.K. New discovery of post-magmatic pyrite in natural coke at Yangliu coal mine, Northern China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2018, 92, 2436–2437. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Ward, C.R.; French, D.; Graham, I.T. Major and Trace Element Geochemistry of Coals and Intra-Seam Claystones from the Songzao Coalfield, SW China. Minerals 2015, 5, 870–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Y.P.; Nie, Z.; Wang, H.F.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J. Effect of an extremely thick igneous rock on gas occurrence and outburst disasters in a coal seam. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2011, 40, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.B.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Y.P.; Jin, K.; Zhao, W. Gas desorption index of drill cuttings affected by magmatic sills for predicting outbursts in coal seams. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 61, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.F.; Wang, M.N.; Liu, L.L.; Li, Y.F.; Cheng, J.; Liu, L. Microfabrics response of coal to magma among coal seam VIII in Yuandian Mine of Huaibei City, China. J. Coal Sci. Eng. 2017, 42, 2976–2980. [Google Scholar]
- Misz, M.; Fabiańska, M.J.; Ćmiel, S.R. Organic components in thermally altered coal waste: Preliminary petrographic and geochemical investigations. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2007, 71, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Cheng, Y.P.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.L.; Shao, Z.J. Study on magma intrusion affected to coal properties of Daxing Mine. Coal Sci. Technol. 2015, 43, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.Y.; Chen, Y.P.; Wang, H.F.; Zhou, H.X.; Jin, K. Effect of igneous intrusion on adsorption characteristics of coal to gas. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2012, 29, 118–123. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.Y.; Zheng, L.G.; Zhang, Q.W.; Hao, C.; Hao, C.; Yan, X.X.; Han, Y.Y. Distribution and models of occurrence of mercury in coal seams altered by magmatic hydrothermal from Wolonghu coal mine. Geol. J. China Univ. 2015, 21, 280–287. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, J.P.; Zheng, L.G.; Wei, X.P.; Liu, S.K.; Liu, L.Y.; Liu, M.; Huang, X.Y. Occurrence of antimony in magmatic intrusive coal seam: A case study from the Wonglonghu coal mine, Huaibei coalfield, China. Coal Geol. Explor. 2019, 47, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.Y.; Cheng, Y.P.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Wang, L. Petrographic and geochemical effects of sill intrusions on coal and their implications for gas outbursts in the Wolonghu Mine, Huaibei Coalfield, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2011, 88, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.L.; Li, W.; Li, B.Q. Pyrolysis of shenmu coal macerals and kinetics analysis. J. Chem. Ind. Eng. 2002, 53, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Sarana, S.; Kar, R. Effect of igneous intrusive on coal microconstituents: Study from an Indian Gondwana coalfield. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2011, 85, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmer, S.M.; Yoksoulian, L.E.; Hower, J.C. Anatomy of an intruded coal, I: Effect of contact metamorphism on whole-coal geochemistry, Springfield (No. 5) (Pennsylvanian) coal, Illinois Basin. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2009, 79, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.F.; Feng, S.B. Pyrolysis Characteristics of Different Maceral of Coal in Renlou Coal Mine of Huaibei Coalfield. J. Xichang Univ. 2019, 33, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zhang, Y.F.; Xie, K.C. Effect of the mineral matter on the pyrolysis reaction of Coal Macerals. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 1992, 20, 301–306. [Google Scholar]
- Ibarra, J.; Moliner, R.A.; Bonet, A.J. FT-IR investigation on char formation during the early stages of coal pyrolysis. Fuel 1994, 73, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.G.; Chen, J.P.; Hao, D.H. Micro-FTIR spectroscopy of macerals in coals from the Tarim basin. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pek. 2001, 37, 832–838. [Google Scholar]
- Kus, J. Impact of underground coal fire on coal petrographic properties of high volatile bituminous coals: A case study from coal fire zone No.3.2 in the Wuda Coalfield, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, North China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2017, 171, 185–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stach, P.; Natkaniec-Nowak, L.; Wagner, M.; Dumańska-Słowik, M.; Mroczkowska-Szerszén, M.; Wesełucha-Birczyńska, A.; Drzewicz, P.; George, C.; Garcia, E. A Study on the Formation Environment of the La Cumbre Amber Deposit, from Santiago Province, the Northwestern Part of the Dominican Republic. Minerals 2020, 10, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lyu, S.; Jiao, X.W. Experimental study on influence of included minerals on the char combustion characteristics. Coal Conver. 2009, 32, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.X. The influence of mineral on the coal reactivity. Coal Geol. China 1993, 5, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Song, Q.; Lyu, J.X.; Shu, Y.F.; Wang, Z.M.; Yan, J.; Zeng, M.; Shu, X.Q. Effect of additive ironore on pyrolysis characteristics of a low rank coal from Hami. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2016, 44, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Lin, J.Y.; Chang, L.P. The effect of mineral matter on the NH3 formation during Coal Pyrolysis and gasification. Environ. Chem. 2004, 23, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
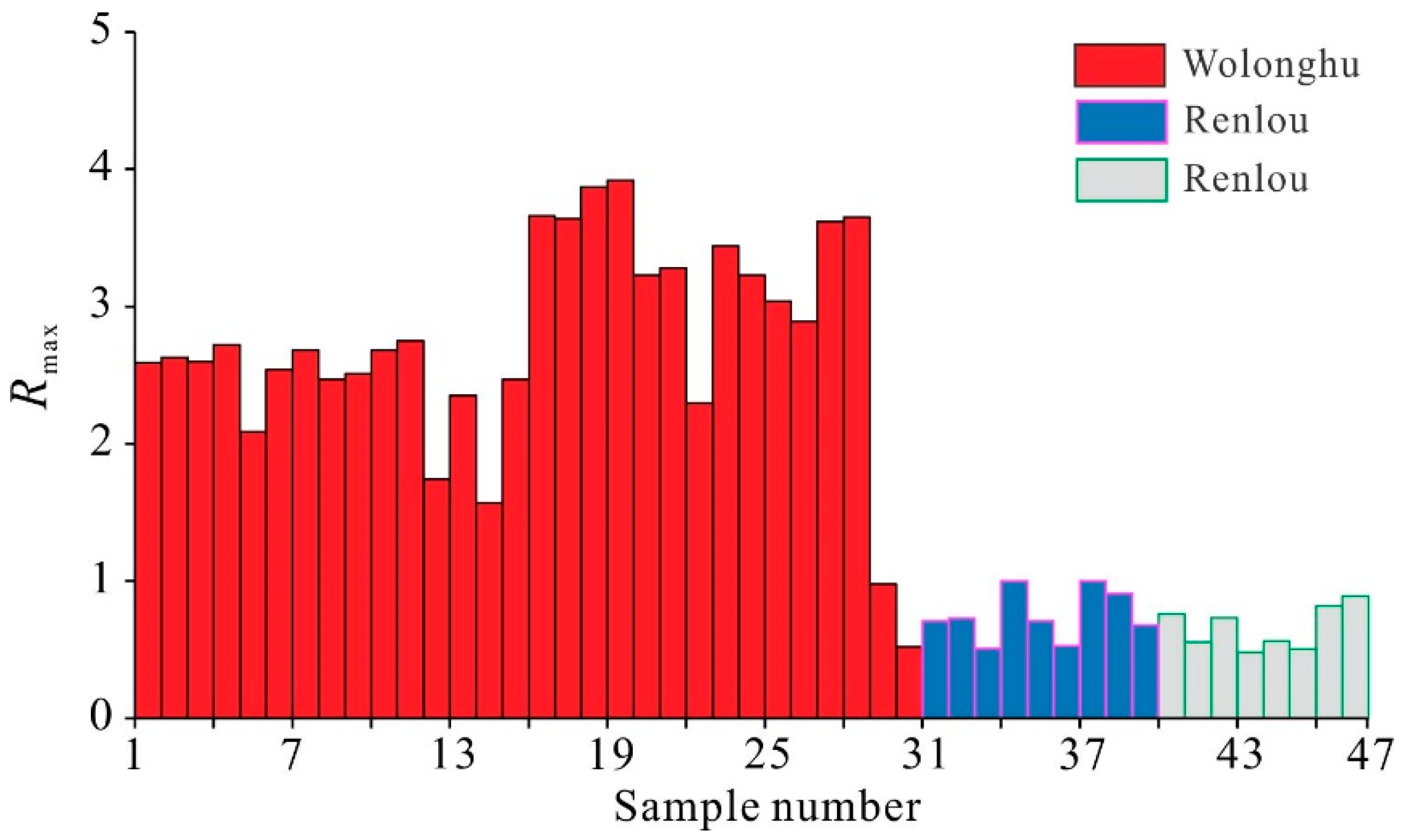
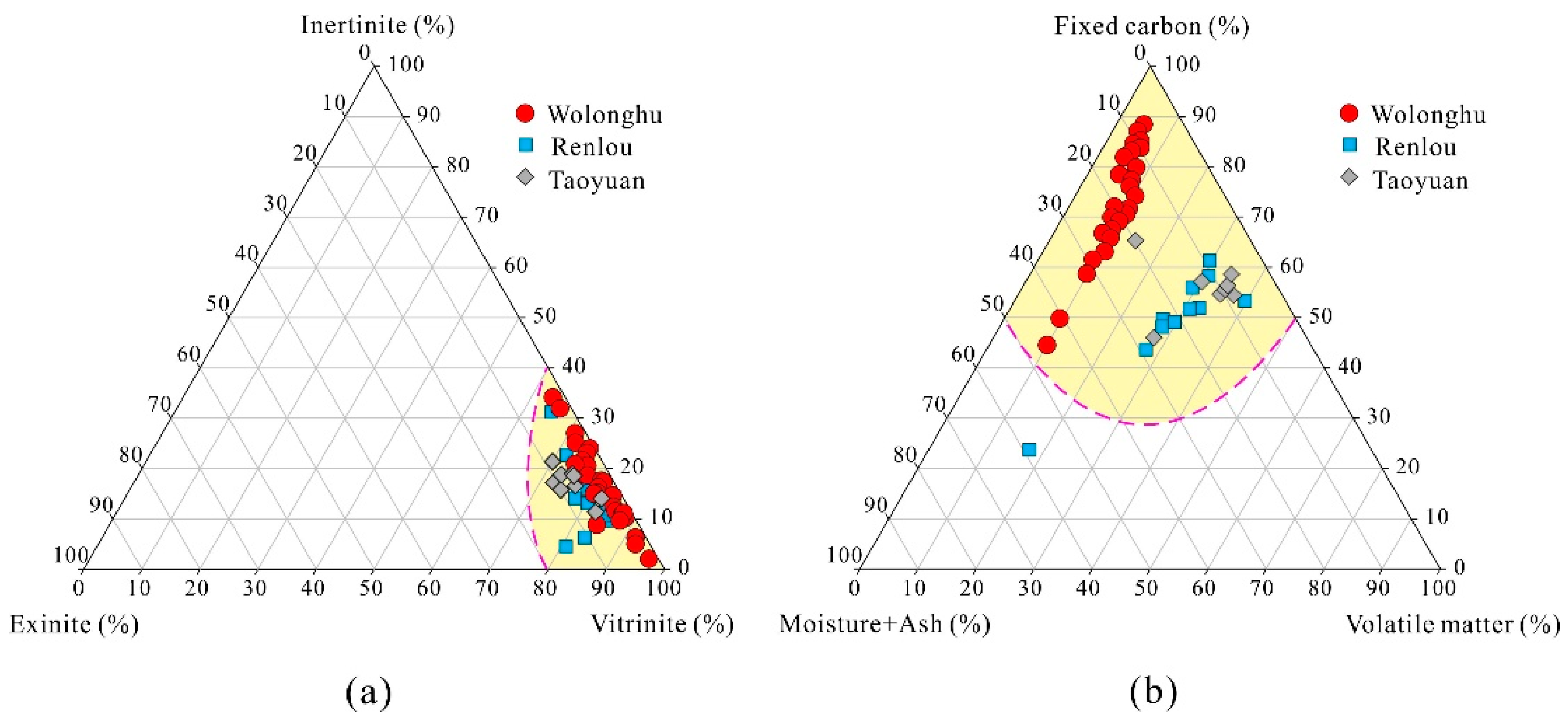

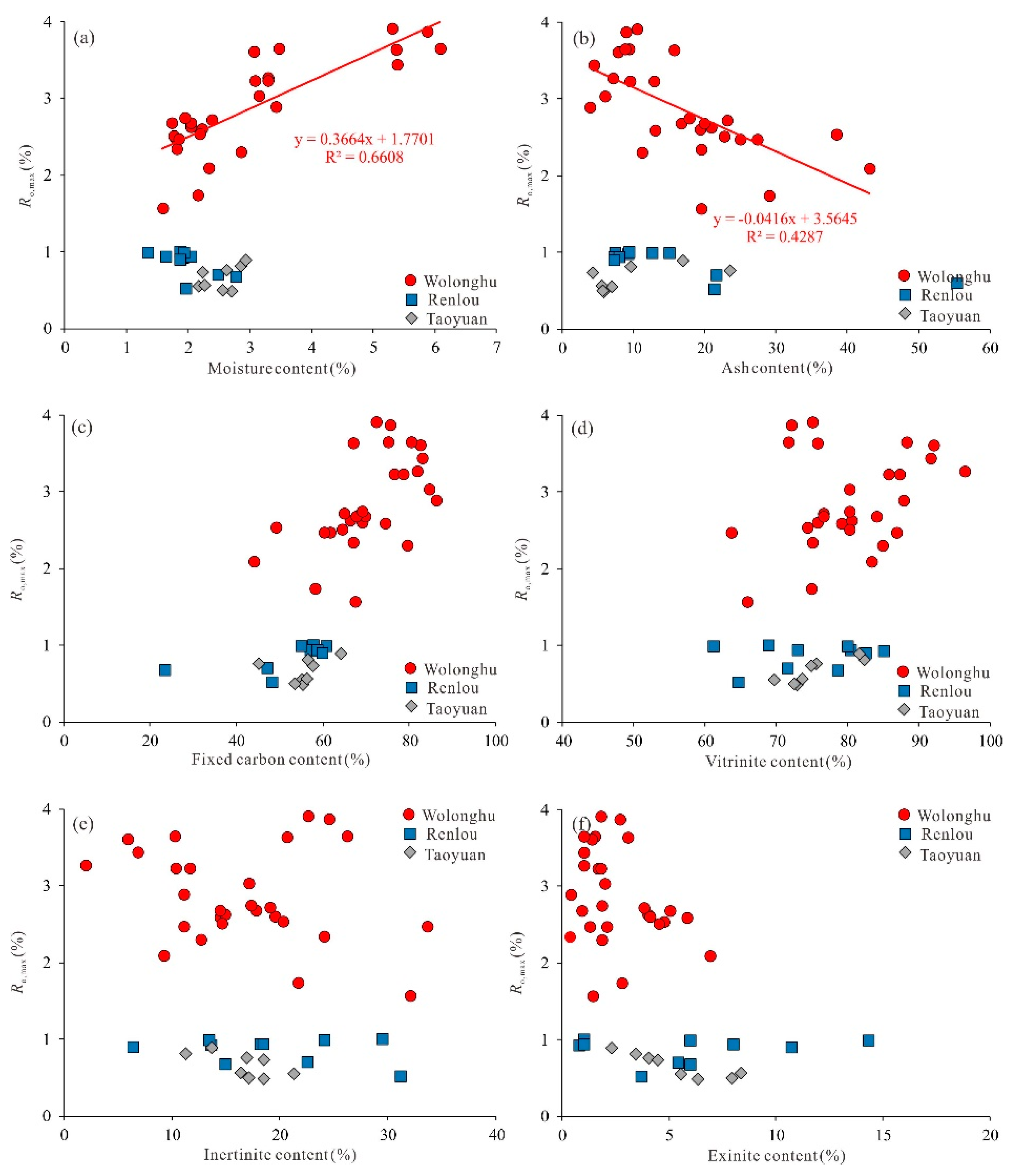
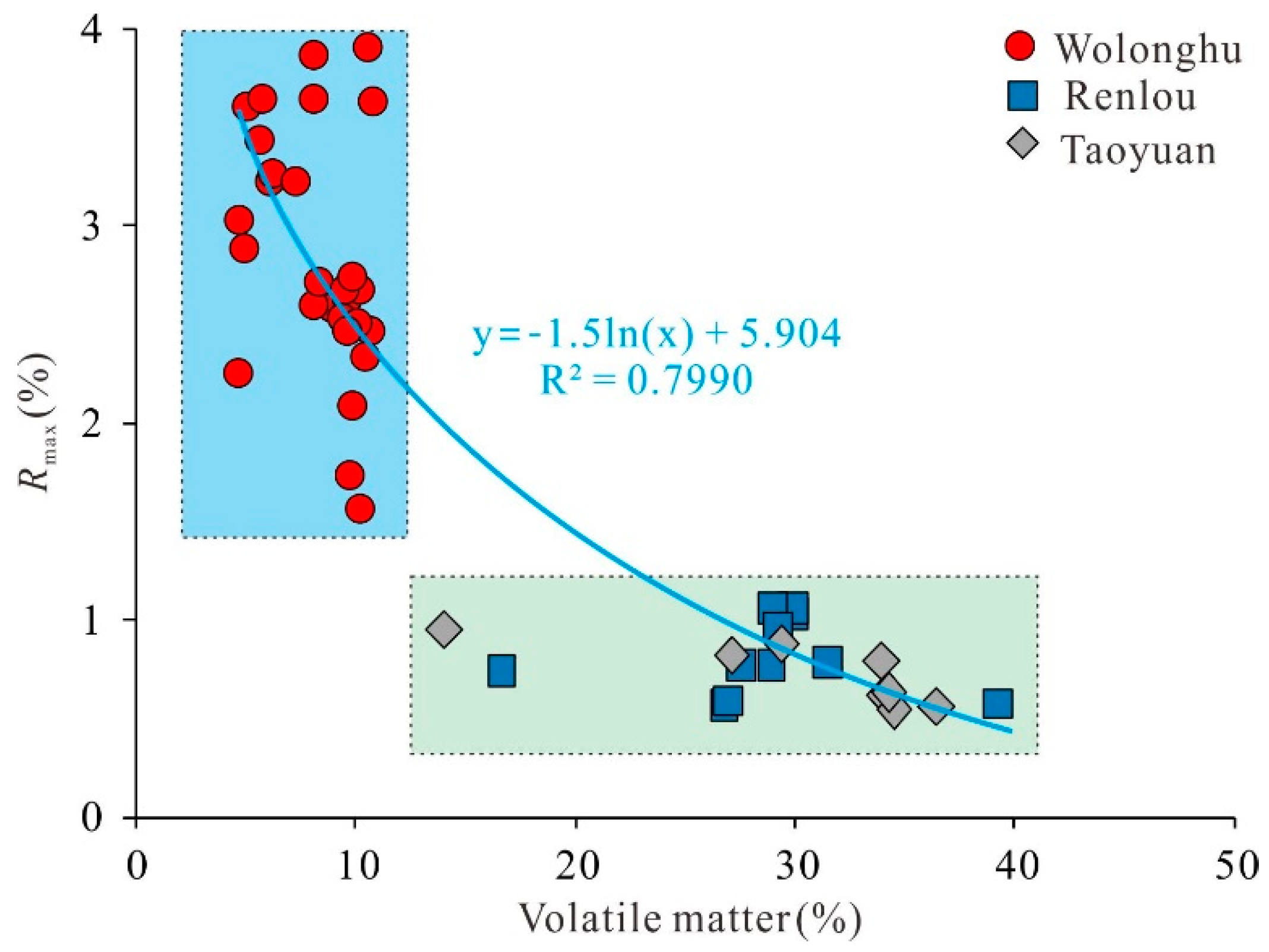
| Coal Mine | Proximate Analysis (wt. %) | Maceral Analysis (vol. %) | Rmax (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | Ash | Volatile | Fixed Carbon | Vitrinite | Inertinite | Exinite | ||
| Wolonghu | 1.6–6.1 3.0 | 3.9–38.4 16.9 | 4.9–10.7 8.3 | 50.1–87.8 71.9 | 66.2–97.0 80.6 | 2.0–34.0 16.8 | 0.4–6.9 2.54 | 1.6–3.9 2.9 |
| Renlou | 0.7–2.8 2.1 | 6.3–56.2 19.0 | 17.3–39.8 29.2 | 23.8–61.0 49.7 | 64.9–85.7 79.8 | 4.2–31.4 13.8 | 3.7–15.9 7.1 | 0.5–1.0 0.8 |
| Taoyuan | 2.2–2.9 2.5 | 5.5–23.6 9.8 | 14.7–37.1 31.1 | 46.1–65.4 56.6 | 70.1–82.9 75.8 | 11.4–21.5 16.9 | 2.3–8.4 5.3 | 0.5–0.9 0.7 |
| Coal Mine | Conventional Element Content (%, daf) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O | N | S | |
| Wolonghu | 53.3–86.1 72.5 | 1.9–3.5 2.8 | 0.2–7.6 5.1 | 1.1–2.4 1.8 | 0.3–0.8 0.4 |
| Renlou | 61.6–81.3 72.3 | 4.2–5.7 4.8 | 2.0–7.8 3.7 | 1.4–2.4 2.0 | 0.1–0.9 0.5 |
| Taoyuan | 73.2–82.4 73.4 | 4.8–6.0 5.5 | 2.9–5.7 4.2 | 1.9–2.3 2.1 | 0.4–1.1 0.5 |
| Coal Mine | IHO | Kal |
|---|---|---|
| Wolonghu | 0.0–0.8 0.1 | 0.8–3.1 1.9 |
| Renlou | 0.3–0.9 0.5 | 1.0–2.4 1.6 |
| Taoyuan | 0.3–0.6 0.5 | 1.1–2.1 1.14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, S.; Wei, Q.; Li, X. Chemical Composition Variations of Altered and Unaffected Coals from the Huaibei Coalfield, China: Implications for Maturity. Energies 2021, 14, 3028. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14113028
Feng S, Wei Q, Li X. Chemical Composition Variations of Altered and Unaffected Coals from the Huaibei Coalfield, China: Implications for Maturity. Energies. 2021; 14(11):3028. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14113028
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Songbao, Qiang Wei, and Xianqing Li. 2021. "Chemical Composition Variations of Altered and Unaffected Coals from the Huaibei Coalfield, China: Implications for Maturity" Energies 14, no. 11: 3028. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14113028
APA StyleFeng, S., Wei, Q., & Li, X. (2021). Chemical Composition Variations of Altered and Unaffected Coals from the Huaibei Coalfield, China: Implications for Maturity. Energies, 14(11), 3028. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14113028





