A Novel Hybrid Model for Cu–Al2O3/H2O Nanofluid Flow and Heat Transfer in Convergent/Divergent Channels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
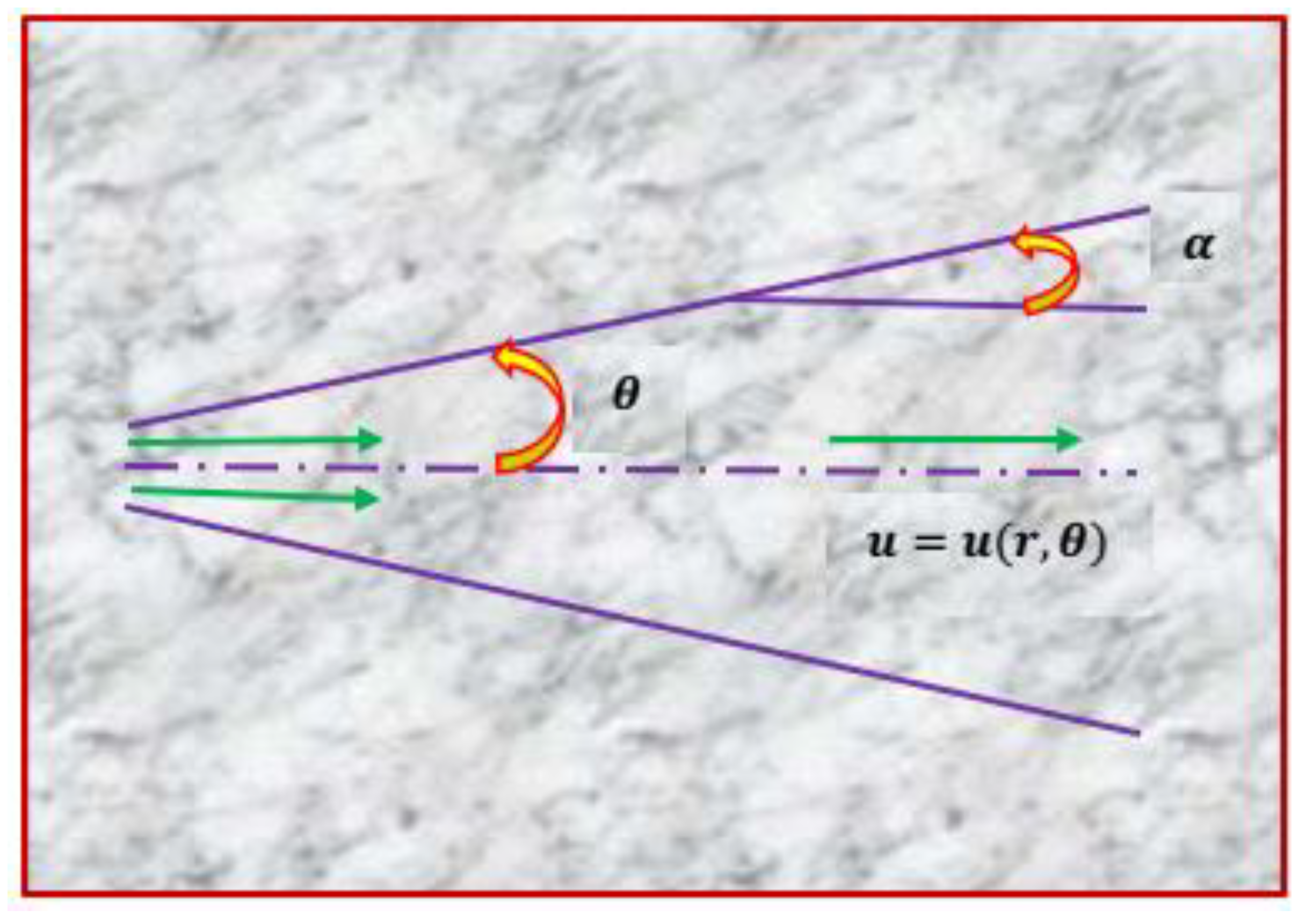
2.1. Model Formulation
2.2. Solution of the Problem
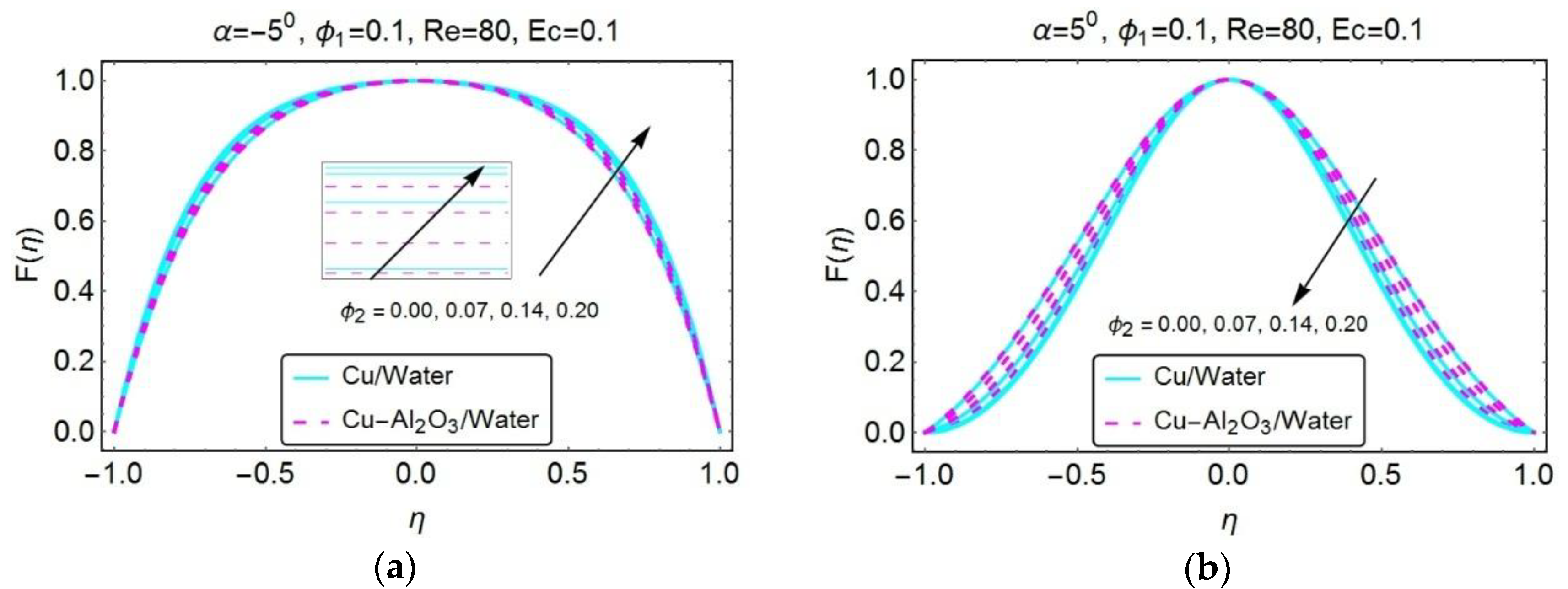
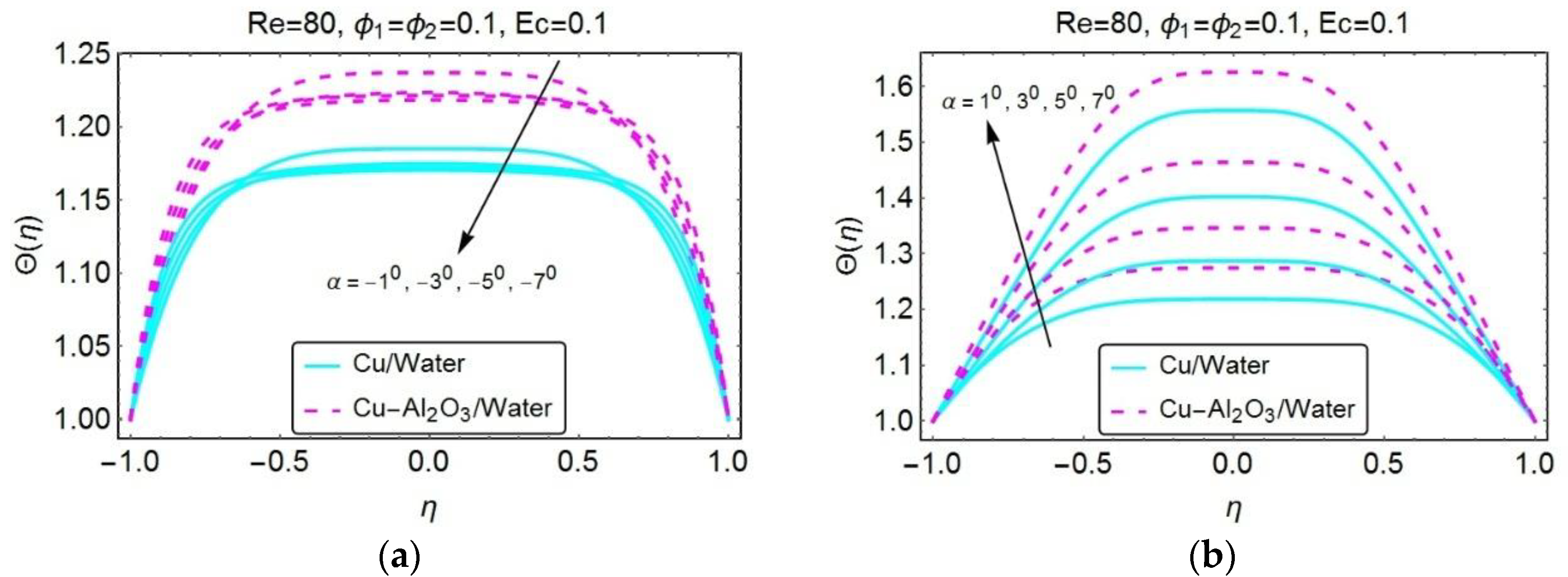
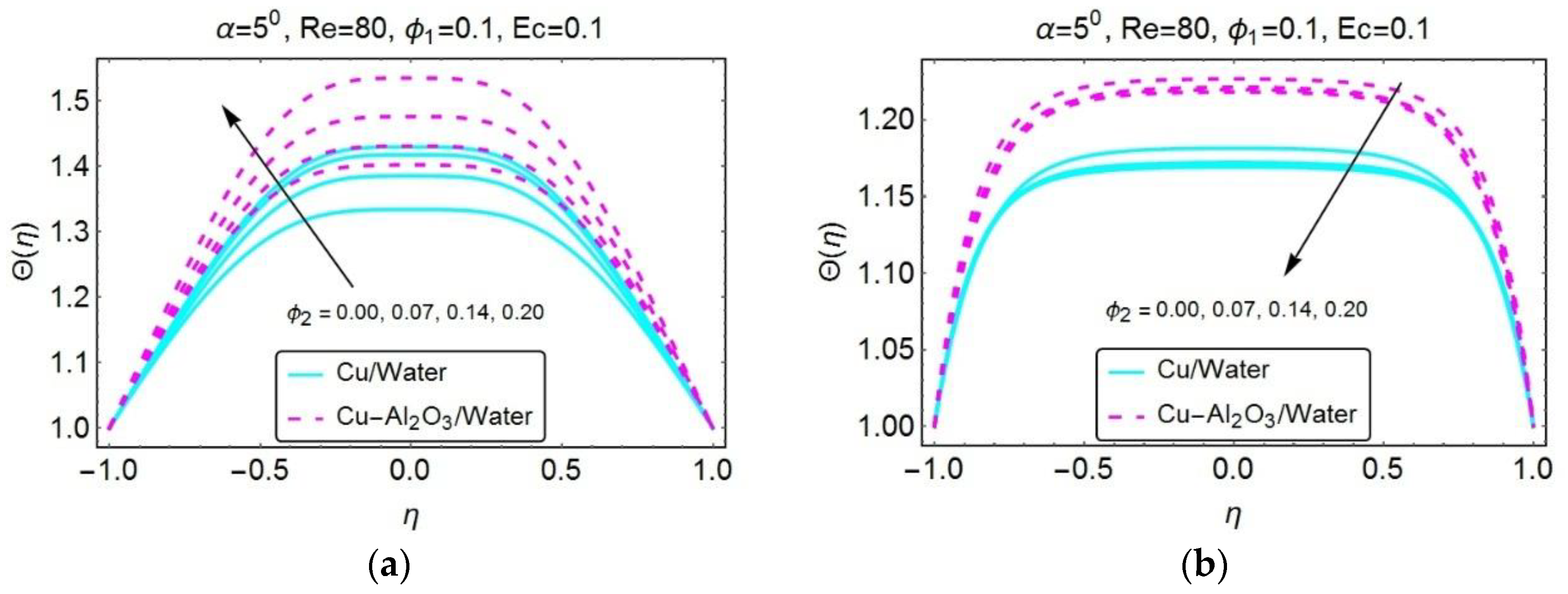
3. Graphical Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, S. Enhancing Thermal Conductivity of Fluids with Nanoparticles in Developments and Applications of Non-Newtonians Flows. ASME J. Heat Trans. 1995, 66, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Q.; Mujumdar, A.S. A Review on Nanofluids Part-I: Theoretical and Numerical Investigations. Bra. J. Chem. Eng. 2008, 25, 613–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, G.B. The two-dimensional steady motion of a viscous fluid. Phil. Mag. Ser. 1915, 29, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, G. Spiralformige Bewgungen zaher Flussigkeiten. Jahresber. Deutsch. Math.-Ver. 1916, 25, 34–60. [Google Scholar]
- Adnan; Asadullah, M.; Khan, U.; Ahmed, N.; Mohyud-Din, S.T. Analytical and numerical investigation of thermal radiation effects on flow of viscous incompressible fluid with stretchable convergent/divergent channels. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 224, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan; Khan, U.; Ahmed, N.; Mohyud-Din, S.T. Thermo-diffusion and diffusion-thermo effects on flow of second grade fluid between two inclined plane walls. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 224, 1074–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohyud-Din, S.T.; Khan, U.; Ahmed, N.; Hassan, S.M. Magnetohydrodynamic Flow and Heat Transfer of Nanofluids in Stretchable Convergent/Divergent Channels. Appl. Sci. 2015, 5, 1639–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, N.F.M.; Abbasbandy, S.; Hashim, I. Heat and mass transfer of thermophoretic MHD flow over an inclined radiate isothermal permeable surface in the presence of heat source/sink. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 2122–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.; Adnan; Asadullah, M.; Ahmed, N.; Mohyud-Din, S.T. Influence of Joule Heating and Viscous Dissipation on MHD Flow and Heat Transfer of Viscous Fluid in Converging/Diverging Stretchable Channels. J. Nanofluids 2017, 6, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Shehzad, S.A. A revised model for Darcy-Forchheimer three-dimensional flow of nanofluid subject to convective boundary condition. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 2791–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Muhammad, T.; Mustafa, M.; Alsaedi, A. An optimal study for three-dimensional flow of Maxwell nanofluid subject to rotating frame. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 229, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Ahmed, S.; Muhammad, T.; Alsaedi, A. Modern aspects of homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions and variable thickness in nanofluids through carbon nanotubes. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2017, 94, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M.M.; Abbas, M.A.; Rashidi, M.M. A robust numerical method for solving stagnation point flow over a permeable shrinking sheet under the influence of MHD. Appl. Math. Comput. 2018, 316, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M.M.; Rashidi, M.M.; Abbas, M.A. Analytic Study of Drug Delivery in Peristaltically Induced Motion of Non-Newtonian Nanofluid. J. Nanofluids 2016, 5, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, M.M.; Abbas, M.A. Effect of Slip Conditions and Entropy Generation Analysis with an Effective Prandtl Number Model on a Nanofluid Flow through a Stretching Sheet. Entropy 2017, 19, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Sadoughi, M. Simulation of CuO-water nanofluid heat transfer enhancement in presence of melting surface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 116, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Rokni, H.B. Simulation of nanofluid heat transfer in presence of magnetic field: A review. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 115, 1203–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M. Influence of magnetic field on nanofluid free convection in an open porous cavity by means of Lattice Boltzmann method. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 234, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Rashidi, M.M. Non-uniform magnetic field effect on nanofluid hydrothermal treatment considering Brownian motion and thermophoresis effects. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2015, 38, 1171–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, J.; Bhatti, M.M.; Abbas, M.A.; Rashidi, M.M.; Ali, M. Entropy Generation on MHD Casson Nanofluid Flow over a Porous Stretching/Shrinking Surface. Entropy 2016, 18, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabood, F.; Shateyi, S.; Rashidi, M.M.; Momoniat, E.; Freidoonimehr, N. MHD stagnation point flow heat and mass transfer of nanofluids in porous medium with radiation, viscous dissipation and chemical reaction. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M. Magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid forced convection in a porous lid driven cubic cavity using Lattice Boltzmann method. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 231, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M. CuO-water nanofluid free convection in a porous cavity considering Darcy law. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2017, 132, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, M.; Rashidi, M.M. Effect of Magnetic Field on Hydrodynamic Behavior. Available online: https://www.ukessays.com/essays/engineering/effect-magnetic-field-hydrodynamic-7437.php?vref=1 (accessed on 30 March 2020).
- Khalili, S.; Tamim, H.; Khalili, A.; Rashidi, M.M. Unsteady convective heat and mass transfer in pseudoplastic nanofluid over a stretching wall. Adv. Powder Tech. 2015, 26, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.; Adnan; Ahmed, N.; Mohyud-Din, S.T. 3D Squeezed Flow of γAl2O3–H2O and γAl2O3–C2H6O2 Nanofluids: A Numerical Study. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 24620–24633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Adnan; Khan, U.; Mohyud-Din, S.T. Unsteady radiative flow of chemically reacting fluid over a convectively heated stretchable surface with cross-diffusion gradients. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2017, 121, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.; Adnan; Ahmed, N.; Mohyud-Din, S.T. Heat Transfer Enhancement in Hydromagnetic Dissipative Flow Past a Moving Wedge suspended by H2O-Aluminum Alloy Nanoparticles in the Presence of Thermal Radiation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2017, 42, 24634–24644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Adnan; Khan, U.; Mohyud-Din, S.T. Influence of an Effective Prandtl number Model on Squeezed Flow of γAl2O3-H2O and γAl2O3-C2H6O2 Nanofluids. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 238, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeeva, E.V.; Routbort, J.L.; Singh, D. Particle shape effects on thermophysical properties of alumina nanofluids. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 14304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.; Ahmed, N.; Mohyud-Din, S.T. Heat transfer effects on carbon nanotubes suspended nanofluid flow in a channel with non-parallel walls under the effect of velocity slip boundary condition: A numerical study. Neural Comput. Appl. 2015, 28, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.S.U.; Devi, S.A. Numerical investigation of three-dimensional hybrid Cu–Al2O3/water nanofluid flow over a stretching sheet with effecting Lorentz force subject to Newtonian heating. Can. J. Phys. 2016, 94, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.; Ahmed, N.; Mohyud-Din, S.T. Thermo-diffusion, diffusion-thermo and chemical reaction effects on MHD flow of viscous fluid in divergent and convergent channels. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 141, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motsa, S.S.; Sibanda, P.; Marewo, G. On a new analytical method for flow between two inclined walls. Numer. Algorithms 2012, 61, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkyilmazoglu, M. Extending the traditional Jeffery-Hamel flow to stretchable convergent/divergent channels. Comput. Fluids 2014, 100, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




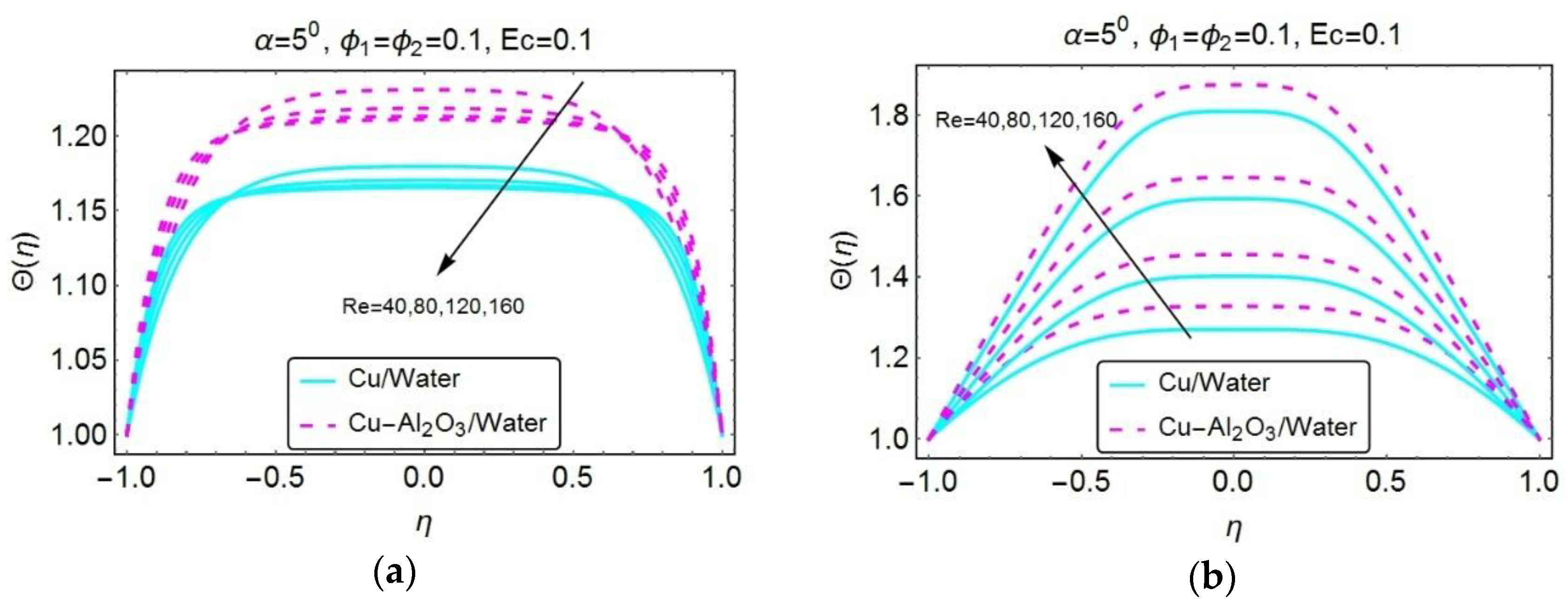
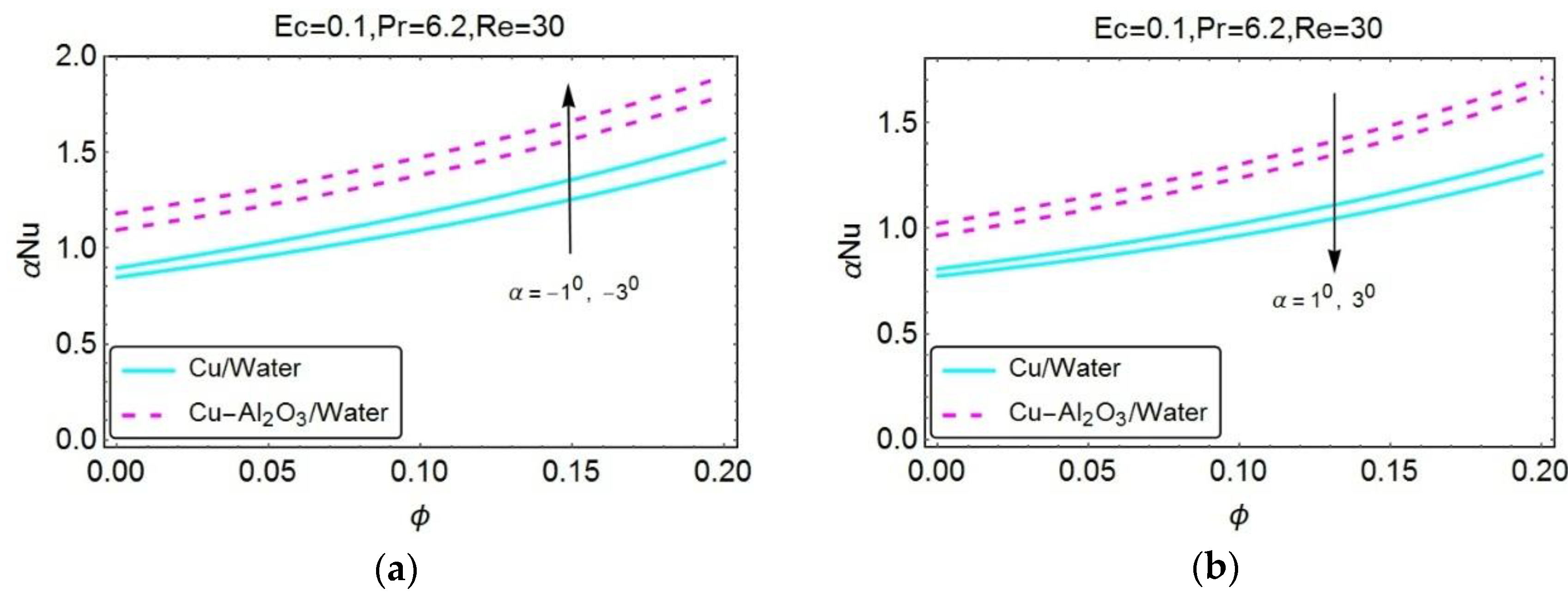
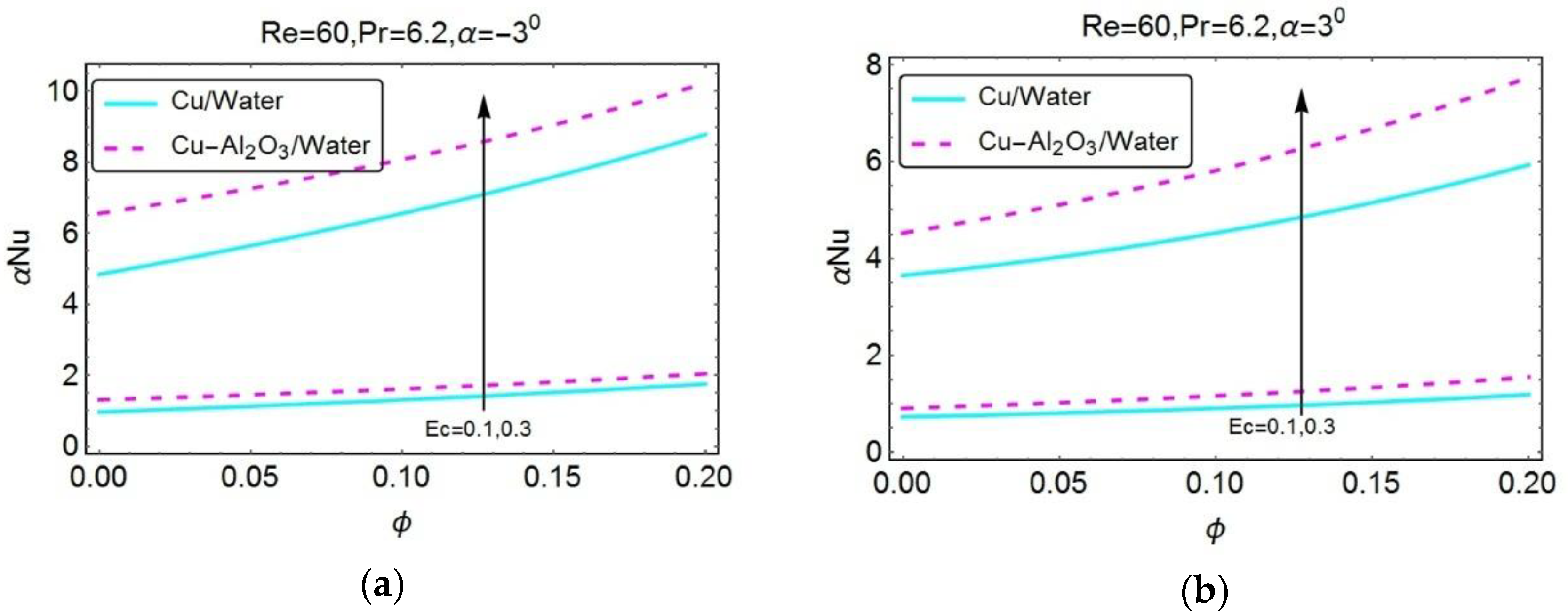

| Properties | Nanofluid | Hybrid Nanofluid |
|---|---|---|
| Density | ||
| Heat capacity | ||
| Viscosity | ||
| Thermal conductivity | here: |
| Characteristics | |||
|---|---|---|---|
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, U.; Adnan; Ahmed, N.; Mohyud-Din, S.T.; Baleanu, D.; Khan, I.; Nisar, K.S. A Novel Hybrid Model for Cu–Al2O3/H2O Nanofluid Flow and Heat Transfer in Convergent/Divergent Channels. Energies 2020, 13, 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071686
Khan U, Adnan, Ahmed N, Mohyud-Din ST, Baleanu D, Khan I, Nisar KS. A Novel Hybrid Model for Cu–Al2O3/H2O Nanofluid Flow and Heat Transfer in Convergent/Divergent Channels. Energies. 2020; 13(7):1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071686
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Umar, Adnan, Naveed Ahmed, Syed Tauseef Mohyud-Din, Dumitru Baleanu, Ilyas Khan, and Kottakkaran Sooppy Nisar. 2020. "A Novel Hybrid Model for Cu–Al2O3/H2O Nanofluid Flow and Heat Transfer in Convergent/Divergent Channels" Energies 13, no. 7: 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071686
APA StyleKhan, U., Adnan, Ahmed, N., Mohyud-Din, S. T., Baleanu, D., Khan, I., & Nisar, K. S. (2020). A Novel Hybrid Model for Cu–Al2O3/H2O Nanofluid Flow and Heat Transfer in Convergent/Divergent Channels. Energies, 13(7), 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071686








