Abstract
In order to solve the problem of pollution of acid mine drainage (AMD), such as low pH value and being rich in SO42−, Fe and Mn pollution ions, etc., immobilized particles were prepared by using sugar cane-refining waste (bagasse), a natural composite mineral (called medical stone in China) and sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) as substrate materials, based on microbial immobilization technology. Medical stone is a kind of composite mineral with absorbability, non-toxicity and biological activity. The adsorption capacity of medical stone is different according to its geographic origins. Two dynamic columns were constructed with Column 1 filled by Fuxin’s medical stone-enhanced SRB immobilized particles, and Column 2 filled by Dengfeng’s medical stone-enhanced SRB immobilized particles as fillers. The treatment effect on AMD with SRB-immobilized particles enhanced by medical stone from different areas was compared. Results showed that Column 2 had better treatment effect on AMD. The average effluent pH value of Column 2 was 6.98, the average oxidation reduction potential (ORP) value was −70.17 mV, the average removal percentages of SO42−, Fe2+ and Mn2+ were 70.13%, 83.82% and 59.43%, respectively, and the average chemical oxygen demand (COD) emission was 555.48 mg/L.
1. Introduction
As the main body of energy, coal resources are one of the main driving forces of rapid economic development [1]. Coal mining destroys groundwater resources, produces greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane [2], and produces large amounts of solid waste. Some associated minerals in coal mines will undergo oxidation reactions after contact with water and oxygen, and dissolve SO42− and a variety of metal ions to form acid mine drainage (AMD). AMD is characterized by extremely low pH value and elevated in SO42−, Fe2+, Mn2+ and other polluting ions [3]. The untreated AMD directly flows into surface water and groundwater, which will adversely impact water resources [4]. AMD has become a global environmental threat, seriously affecting the water resources and soil ecosystem around the coal-mining areas [5]. Therefore, the problem of repairing AMD pollution has been studied by some domestic scholars. The study found that heavy metals in acid mine water can be removed by adsorption, ion exchange, reverse osmosis and other methods, but there are some disadvantages such as saturation of adsorption, susceptible to external factors, and high maintenance costs [6,7]. In recent years, microbial methods represented by sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) have been considered as a promising alternative to traditional methods due to their high treatment efficiency, low operating cost and strong reproducibility [8,9]. However, SRB growth is inhibited by low pH and high concentration of metal ions [10], and continuous carbon source addition and other issues have limited the large-scale application of microbial method. Microbial immobilization technology can create a suitable microenvironment, improve biological activity and toxicity resistance, which has become one of the most effective measures to solve the above problems.
In order to improve the adaptability and long-term efficiency of microbial immobilization particles in the treatment of AMD, the structure and characteristics of the immobilized particles were improved by adding substrate materials in the immobilization process, which has become an important part of the study of the immobilization method of SRB. Bagasse, a sugar cane-refining waste, contains soluble carbon sources and easily decomposable substances. The study found that the growth and the metabolism activity of SRB using bagasse as the carbon source was better than that of corncob and peanut shell, and bagasse could provide SRB with a more durable carbon source [11]. Therefore, bagasse is an ideal cohesive carbon source material for microbial immobilized particles. The main nature of the original rock of medical stone is granite which is formed by long-term weathering and other geological effects [12]. Medical stone is a kind of composite mineral or medicinal rock with absorbability, non-toxicity and biological activity [13,14]. The main chemical composition of medical stone is aluminosilicate, including SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, FeO, MgO, CaO, K2O, Na2O, TiO2, P2O5, MnO, and etc., containing all the major elements required by biology. It has large surface area, more pores and strong cation exchange capacity, and has been widely used in wastewater treatment [15,16]. In addition, medical stone has a good bidirectional adjustment ability to the pH value in the aqueous solution, and it is capable of adsorbing and fixing metal ions [17,18]. Therefore, if medical stone is used as the filler of microbial immobilized particles, not only the activity of acid pH to SRB can be reduced, but also the metal ions in AMD can be removed by adsorption. However, to date few studies focus on the use of medical stone as microbial-immobilized particulate filler, and even fewer comparative studies focus on the characteristics of different kinds of medical stone as fillers to prepare bio-immobilized particles.
Therefore, the medical stone-enhanced sulfate-reducing bacteria-immobilized particles were prepared using medical stone, bagasse and SRB as substrate materials for this paper, based on microbial immobilization technology. The bagasse was used as the slow release carbon source to ensure normal metabolism of SRB in the particles. With the bidirectional pH regulation and adsorption characteristics, medical stone was used to reduce the toxic effect of acidic pH and high concentration metal ions on SRB. Two groups of dynamic columns was constructed by using medical stone from Fuxin and medical stone from Dengfeng as the substrate material of SRB-immobilized particles. By comparing and analyzing the changes of concentration of SO42−, Mn2+, and Fe2+, pH increase, oxidation reduction potential (ORP) value, chemical oxygen demand (COD) release and other indicators, the ability of the two particle systems to treat AMD was determined to optimize the substrate materials composition of the immobilized particles. Finally, the particles before and after the reaction would be analyzed by a scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with an energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) probe and X-ray diffractometer (XRD). The internal mechanism of pollutants removal by immobilization particles was studied further, the synergistic mechanism of different kinds of medical stone and SRB was revealed, and the difference and feasibility of removal of AMD pollution by different kinds of medical stone was studied. These studies provide a scientific theoretical basis and technical reference for the practical application of SRB immobilization particles enhanced by medical stone.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
Fuxin’s medical stone (1): The medical stone was taken from Fumeng County, Fuxin City, Liaoning Province. After drying and crushing, the medical stone with a particle size of 0.046–0.074 mm was sieved.
Dengfeng’s medical stone (2): The medical stone, 0.046–0.074 mm in size, was purchased from Gongyi Wanying Environmental Protection Material Company in Dengfeng City, Henan Province. According to Table 1a, the two kinds of medical stone contain similar macroelements. However, the content of SiO2 in the Dengfeng medical stone is significantly higher than that of Fuxin’s, while the content of Fe, Ti and P is slightly lower. According to Table 1b, the content of beneficial elements such as Fe, Zn, Na and Ni leached from Dengfeng’s medical stone is similar to that of Fuxin, while the leaching amount of Ca, Mg, P, Sr and other elements are obviously higher than that of Fuxin’s. In addition, the content of toxic elements leached from medical stone from Dengfeng is significantly lower than that of Fuxin’s.
Modified Starkey medium: 0.5 g Na2SO4, 1.0 g NH4Cl, 0.5 g K2HPO4, 0.1 g CaCl2·H2O, 2.0 g MgSO4·7H2O, 1.2 g (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2·6H2O, 0.1 g ascorbic acid, 4.0 mL sodium lactate, 1.0 g yeast extract, and 1L distilled water, with pH = 7.0, were sterilized at 121 °C for 30 min.
SRB sludge: The wet mud at the foot of the coal gangue pile in Fuxin was taken as seed mud. Then it was inoculated into sterilized modified Starkey medium for anaerobic culture. The SRB with strong activity was enriched and cultured.
Bagasse: The bagasse was taken from a sugar factory in Huizhou, Guangdong Province, and washed three times with deionized water. After drying and pulverizing, the bagasse particles with a size of about 0.149 mm were sieved.
AMD: The concentrations of Fe2+, Mg2+, Mn2+, Ca2+ and SO42− in the AMD simulated in laboratory were 14 mg/L, 50 mg/L, 6 mg/L, 100 mg/L and 816 mg/L respectively, and the pH value was 4.0.
2.2. Experimental Apparatus and Method
Preparation method of immobilized particle: Based on the preliminary results of the research group, the preparation method of immobilized particle is as follows [19]. The mass fraction of 9% of PVA and 0.5% of sodium alginate were dissolved in distilled water. After being sealed for 24 h at normal temperature, it was placed in a constant temperature water bath and stirred at 90 °C until no bubbles formed. The bagasse with a mass fraction of 4.5% and 15% of medical stone from Fuxin (or medical stone from Dengfeng) were slowly added to the gel, stirred well until it was evenly distributed, and cooled to room temperature. The culture solution containing the SRB sediment was centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 min and the supernatant was removed; 30 mg/L of the SRB-containing precipitate was added to the above gel mixture and stirred evenly. The gel mixture was dropped into 2% CaCl2 saturated boric acid solution with a specific syringe and the particles were removed after 4 h of cross-linking and stirring with a 100 rpm agitator. Finally, the particles were washed with 0.9% saline and activated in an anaerobic environment with a modified Starkey medium solution without organic inredients for 12 h before being used. According to the above method, Particle No.1 (medical stone-enhanced SRB-immobilized particles from Fuxin) and Particle No.2 (medical stone-enhanced SRB-immobilized particles from Dengfeng) were prepared separately.
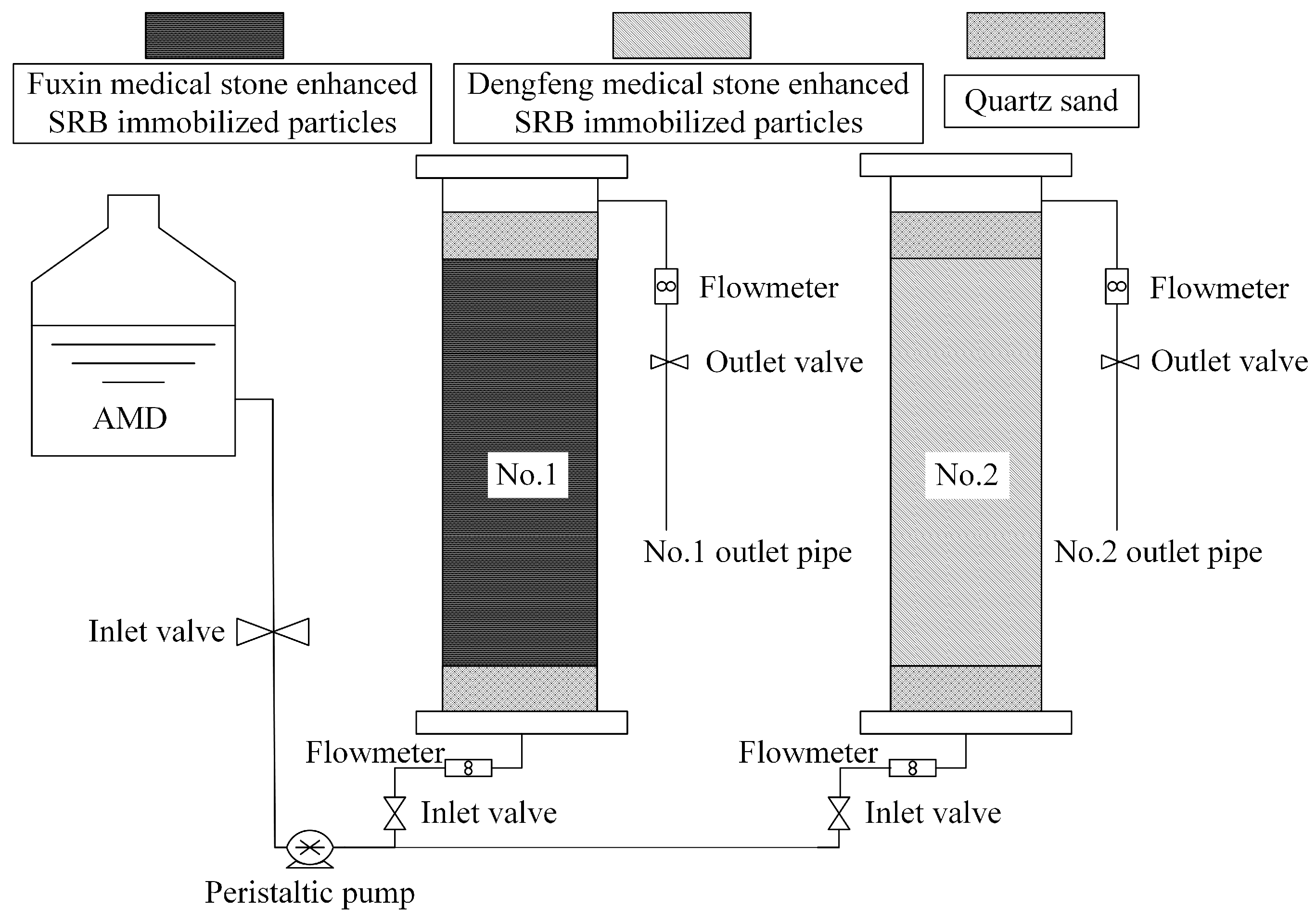
An organic glass tube with an inner diameter of 54 mm and height of 500 mm was used as the reaction vessel in the dynamic experiment, and the dynamic experimental apparatus is shown in Figure 1. Two dynamic columns with a height of 250 mm were constructed, including Column 1 filled with medical stone enhanced SRB immobilized particles from Fuxin and Column 2 filled with the particles from Dengfeng. The tubes were filled with 50 mm quartz sand of 3–5 mm in diameter on the top and bottom of immobilized particles, for fixed and protective purposes. The AMD flew in from the bottom and out from the top to ensure sufficient react between the immobilized particles and AMD in an anaerobic environment. The flow rate of the AMD was 0.26 mL/min controlled by a peristaltic pump. The test was carried out continuously and sampled once a day at 7:30 a.m. to check the pH values, ORP values and SO42−, Fe2+, Mn2+, and COD concentrations in the AMD influent water and the effluent water of the two dynamic columns. The removal percentages of SO42−, Fe2+ and Mn2+ ions in the AMD influent water by two dynamic columns were calculated.
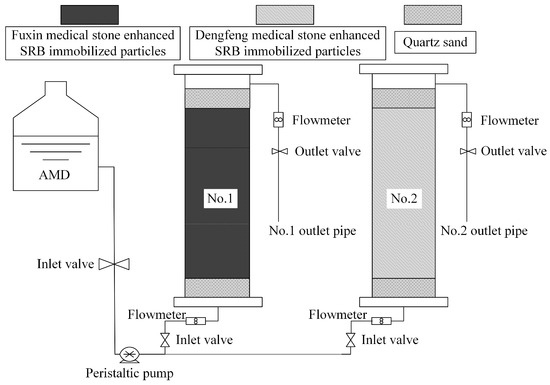
Figure 1.
System diagram of dynamic testing device.
Removal percentage = ((C0 − Ct)/C0) × 100% where, C0 is the initial ion concentration in AMD, mg/L. Ct is the residual ion concentration in the effluent water after dynamic experimental treatment, mg/L.
2.3. Water Quality Detection Methods
pH: glass electrode method; ORP: ORP detector; SO42−: barium chromate spectrophotometry (HJ/T 342-2007); Mn2+: potassium periodate spectrophotometry (GB 11906-89); Fe2+: phenanthroline spectrophotometry (HJ/T 345-2007); COD: potassium dichromate method (HJ/T 399-2007).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of the Change of pH and Oxidation Reduction Potential (ORP)
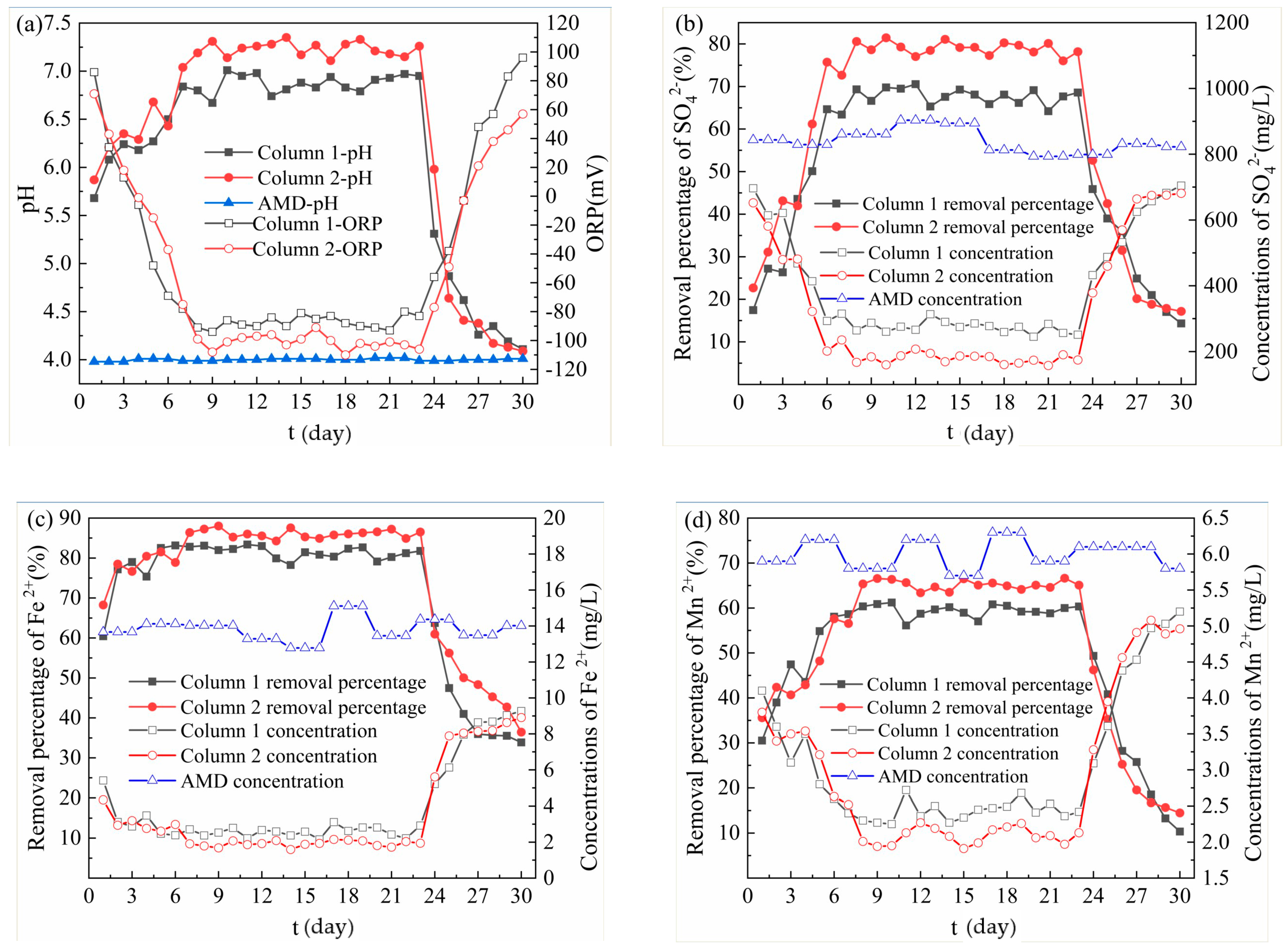
From Figure 2a, the effluent pH values were improved in the dynamic reaction process, and the average effluent pH values of Column 1 and Column 2 were 6.69 and 6.98, respectively. At the same time, the effluent ORP values of both Column 1 and Column 2 showed a trend of decreasing first and then increasing, and the average ORP values were −63.74 mV and −70.17 mV, respectively. On 1–7 days, the pH value increased rapidly, mainly due to the pH adjustment ability of medical stone [18] and the tight binding of ligands on the surface of bagasse to H3O+ [11]. The rapid decrease of effluent ORP value at this stage was due to the reaction between AMD and SRB in the particles. The study found that the quantity and activity of anaerobic bacteria such as SRB are important factors for changing the ORP value, and the reducing environment caused by the decrease of ORP value further promotes the growth and reproduction activities of anaerobes [20]. On 8–23 days, the strains gradually adapted to AMD environment, so the effluent pH value tended to be stable, ORP value decreased to negative value, and the filling layer began to blacken. Among them, the effluent pH value of Column 1 was stable between 6.67 and 7.01, and that of Column 2 was stable between 7.11 and 7.35. At this time, the pH regulation mainly depended on the SRB growth and metabolism to produce alkaline substances. The sugars produced by the hydrolysis of bagasse provided a sufficient carbon source for SRB, which increased the amount of sulfate reduction. Hao T. [21] found the sulfate reduction process is accompanied by organic carbon mineralization, bicarbonate production and, subsequently, an increase in pH and alkalinity. At the same time, bagasse and medical stone absorbed the free H+ by electrostatic adsorption, so the pH of the effluent was stable in the neutral range, which can provide favorable growth conditions for SRB [22] and promote the growth of SRB. Studies have shown that the composite minerals such as quartz and feldspar in the medical stone [23] have a strong regulatory effect on acidic pH. At this stage, the reason why the effluent pH of Column 2 was significantly higher than that of Column 1 is that the pH regulation effect of Dengfeng’s medical stone was better than that of Fuxin, and the promotion effect of Dengfeng’s medical stone on SRB growth was more obvious. The high-efficiency regulation of pH of medical stone from Dengfeng promoted the growth and metabolism of SRB, and the ORP value of the Column 2 effluent was optimal and slightly fluctuated. After 24 days, the effluent pH gradually decreased, while the effluent ORP value gradually increased. This indicated that the reduction of carbon source released by bagasse, low pH and high concentration of metal ions reduce the biological activity of SRB [24], resulting in a decrease in the ability of microbial metabolism to produce alkalinity and a decrease in the pH of the effluent. The proliferation and activity of SRB were inhibited, resulting in an increase in the effluent ORP value. Chang [25], Neufeld [26] and other studies found that SRB can grow normally under the condition that the ORP value is negative, and the SRB reduction activity decreases with the increase of ORP value. In addition, the adsorption of H+ of bagasse and medical stone in the particles being saturated gradually was another reason.
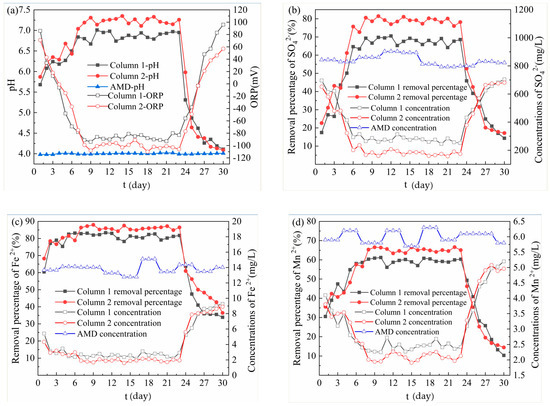
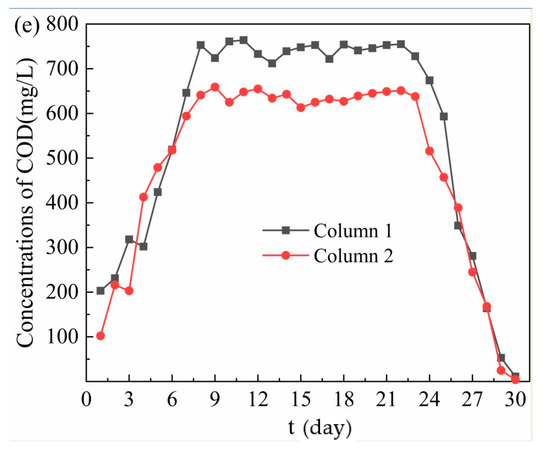
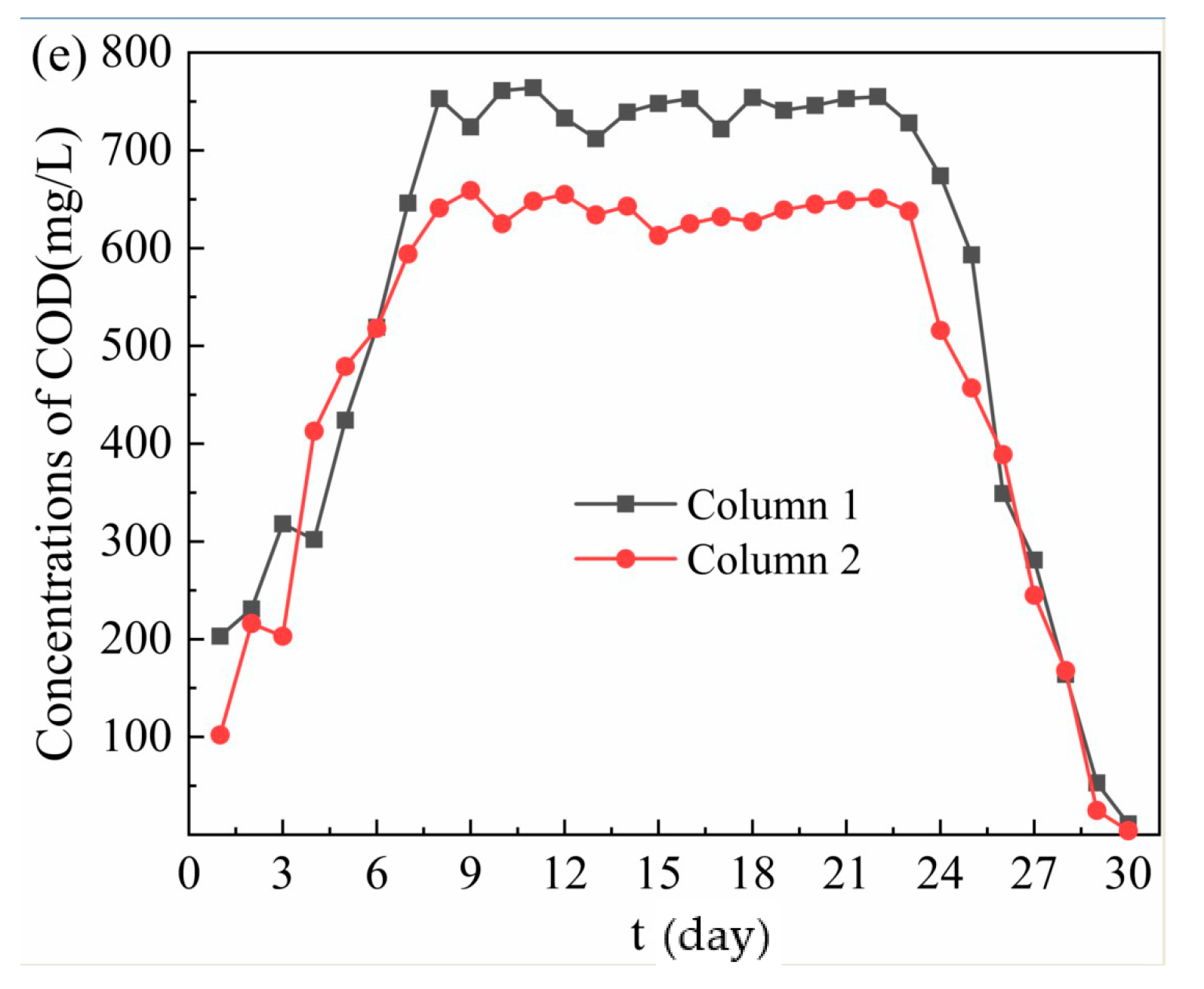
Figure 2.
Removal effect of acid mine drainage (AMD) by Column 1 and Column 2. (a) Changes of pH and oxidation reduction potential (ORP) values; (b) SO42− removal effect; (c) Fe2+ removal effect; (d) Mn2+ removal effect; (e) Release of chemical oxygen demand (COD).
3.2. Analysis of the Removal Effect of SO42−
From Figure 2b, in the dynamic reaction process, although both columns had the removal effect on the SO42− in the AMD influent, the removal effect of Column 2 was better than that of Column 1. The average removal percentages of SO42− by Column 1 and Column 2 were 59.93% and 70.13%, respectively. The highest removal percentages of SO42− by Column 1 and Column 2 were 70.55% and 81.44%, respectively, and the corresponding residual concentrations of SO42− were 266.1 mg/L and 159.8 mg/L respectively. On 0–6 days, the residual concentration of SO42− decreased rapidly, while the removal percentage of SO42− increased significantly. It was because the SRB in the particles gradually adapted to the new living environment at the initial reaction stage, and made SO42− become an electron acceptor with its own metabolic activity, and it was reduced to S2− [27]. In addition, the beneficial elements released by the medical stone and the organic matter produced by the hydrolysis of bagasse could provide trace elements for the growth and metabolism of SRB, which could enhance the biological activity of SRB, and accelerate the metabolism of SO42−. Therefore, the concentration of SO42− decreased rapidly. On 7–23 days, bagasse and medical stone provided sufficient carbon and trace elements for SRB. Therefore, the activity of SRB reached the highest level, with the strongest dissimilation and reduction ability to SO42−, and the highest removal percentage of SO42−. At this stage, the removal effect of Column 2 on SO42− was better than that of Column 1, because the alkaline materials and trace elements released by the medical stone from Dengfeng were more than that of the medical stone from Fuxin. The biological activity of SRB can be enhanced by alkaline and trace elements, which promoted the transformation of SO42−. After 24 days, the concentration of SO42− increased significantly, possibly due to insufficient hydrolysis of bagasse at a later stage, which could not provide enough nutrients for SRB. At the same time, since the precipitate produced in the previous reaction adhered to the surface of the particle, which blocked the internal channels of the particles, the matrix could not exchange ions with the outside. Therefore, the activity of SRB was low, and the removal percentage of SO42− decreased. In addition, studies have shown that the presence of sulfides and metal ions can interfere with the biological removal of sulfate by SRB [28,29].
3.3. Analysis of the Removal Effect of Fe2+
From Figure 2c, the average removal percentages of Fe2+ by Column 1 and Column 2 were 79.98% and 83.82%, respectively, which means Column 2 performed better than Column 1. The highest removal percentages of Fe2+ by Column 1 and Column 2 were 83.37% and 88.03%, respectively, and the residual concentrations of Fe2+ in the corresponding effluent were 2.21 mg/L and 1.68 mg/L respectively. On 1–7 days, the removal percentage of Fe2+ by Column 1 increased rapidly from 60.42% to 82.82%, and that by Column 2 increased rapidly from 68.25% to 86.39%. The reason was that the medical stone and bagasse in the initial reaction stage had a strong adsorption capacity for Fe. Z.U. Halim [30] found that bagasse has an adsorption capacity for Fe, and the adsorption of Fe conforms to the pseudo-secondary adsorption kinetics model. Medical stone has more pores and strong physical adsorption capacity for heavy metal elements [31,32]. On 8–23 days, the removal percentage of Fe2+ by Column 1 was 78.25–83.37%, and that by Column 2 was 87.56–86.00%. At this stage, the removal percentage of Fe2+ by the two dynamic columns was relatively high and stable, which resulted from the synergistic effect of bagasse, medical stone and SRB. On the one hand, Fe in AMD was adsorbed by bagasse and medical stone. On the other hand, medical stone released a large amount of trace elements and bagasse released a large amount of organic matter, which provided sufficient nutrition for growth and metabolism of SRB. The dissimilation reduction ability of SRB to SO42− was enhanced, and the reduction product S2− increased. Metal sulfide precipitate, formed by the combination of S2− and Fe, made the removal percentage of Fe2+ optimal and stable. At this stage, the removal effect of SO42− by Column 2 was better than that of Column 1, because the enhanced effect of Dengfeng’s medical stone was better than that of Fuxin. On 23–30 days, the removal percentage of Fe2+ by Column 1 decreased from 81.77% to 33.88%, and the removal percentage of Fe2+ by Column 2 decreased from 86.50% to 36.45%. The results were consistent with the removal effect of SO42−. This indicated that the sediments produced in the first two stages accumulated on the surface of the particles, and the organic matter released from the bagasse decreased, resulting in a decrease both in activity of SRB and in the ability to reduce SO42−. Therefore, the removal effect of Fe2+ was poor.
3.4. Analysis of the Removal Effect of Mn2+
From Figure 2d, the highest removal percentages of Mn2+ by Column 1 and Column 2 were 61.21% and 66.61%, respectively, and the residual concentrations of Mn2+ in the corresponding effluent were 2.25 mg/L and 1.97 mg/L. Among them, the average removal percentages of Mn2+ by Column 1 and Column 2 were 55.81% and 59.43%, respectively, which means Column 2 functioned better than Column 1. On 1–8 days, the removal percentage of Mn2+ by Column 1 increased from 30.51% to 60.34%, and Column 2 increased from 35.59% to 65.34%. On 9–23 days, the removal percentage of Mn2+ by Column 1 was 56.13–61.21%, and Column 2 was 63.39–66.61%. The removal mechanism of Mn from AMD by both columns was similar to that of Fe, but the average removal percentage of Fe2+ was slightly higher than that of Mn2+. Karathanasis [33] found that in the presence of other metal ions, the biological sulfide of Mn2+ is difficult to form, so Mn2+ is mainly removed by adsorption. Meanwhile, Soltan [34] proved that bagasse can adsorb metal ions in solution, and its adsorption effect on Fe is better than that on Mn. On 24–30 days, the removal percentage of Mn2+ by Column 1 in the effluent decreased from 49.34% to 10.34%, and that by Column 2 decreased from 46.23% to 14.48%. The decreasing trend of removal percentage of Mn2+ by Column 1 and Column 2 were consistent with SO42− and Fe2+. The adsorption of Mn2+ by bagasse and medical stone in the immobilized particles tended to be saturated. The SRB in the immobilized particles is poisoned and inhibited by Mn2+ and low acidity in the AMD influent [35], resulting in a significant decrease in the removal percentage of Mn2+ in the later reaction stage.
3.5. Analysis on Release of Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD)
From Figure 2e, in the dynamic reaction process, COD was released from the effluent of Column 1 and Column 2, and the average release of COD was 631.70 mg/L and 555.48 mg/L, respectively. When the release reached equilibrium, the COD release of effluent by Column 2 was lower than that of Column 1. The COD of effluent from the dynamic column was related to the organic matter released from bagasse and the leakage of SRB biometabolites in immobilized particles. Therefore, the biological activity of SRB in the immobilized particles of Column 2 was stronger, the ability of SRB to grow with the organic matter released by bagasse as a carbon source was stronger, and the leakage amount of hydrolyzed products of bagasse and SRB biometabolites in the particles was smaller. On 1–7 days, the release of COD in the effluent by Column 1 increased from 203 mg/L to 646 mg/L, and Column 2 increased from 102 mg/L to 594 mg/L. The rapid increase of COD release was due to the hydrolysis of bagasse on the surface of immobilized particles into sugar and other organic compounds. On 8–23 days, the COD release in the effluent of Column 1 and Column 2 were 712–764 mg/L and 613–659 mg/L respectively. At this stage, the bagasse inside the immobilized particles continued to hydrolyze, resulting in a significant increase in COD release. At the same time, the activity of SRB in the immobilized particles and the ability to utilize organic substances were gradually enhanced. Studies have shown that natural cellulose and lignin contained in bagasse can be decomposed by anaerobic fermentation microbial into small molecular substances, which can be used by SRB [36,37]. Therefore, When the amount of organic matter released from bagasse and the amount of organic matter utilized by SRB remain stable, the amount of COD released in the system basically remains stable. At this time, the COD value of Column 2 effluent was significantly lower than that of Column 1, mainly because the medical stone from Dengfeng in Column 2 had a better repair effect on AMD, enhanced the activity of SRB, and accelerated the metabolism of organic matter. On 24–30 days, most of the bagasse in the particles had been hydrolyzed, and the precipitate produced in the early stage blocked the internal channel, leading to the gradual decrease of organic matter content produced by bagasse and the significant decrease of COD release. At this time, with the continuous consumption of carbon source released from bagasse, the COD/SO42− ratio is lower than the optimum carbon–sulfur ratio of 0.67 for SRB growth [38]. As a result, the metabolic activity of SRB and the utilization rate of organic matter decreased, and the removal effects of SO42−, Fe2+ and Mn2+ in AMD also decreased accordingly.
3.6. Instrumental Analysis
3.6.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy/Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (SEM/EDS) Analysis
Particle No.1 and No.2 before and after treatment of AMD were dried at 60 °C for 24 h. The surface of the particles and the section structure were observed by Hitachi S-3400N field emission scanning electron microscope equipped with Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy probe (SEM/EDS), and the magnification was 200 times. The SEM/EDS microscopic scan results are shown in Figure 3.
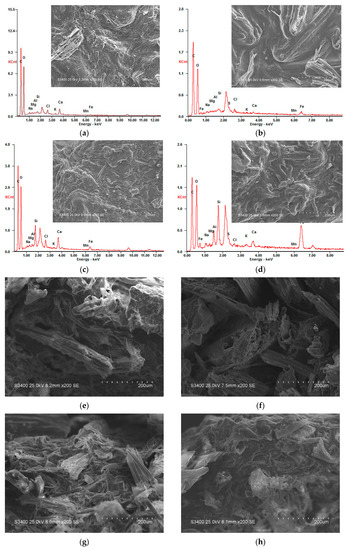
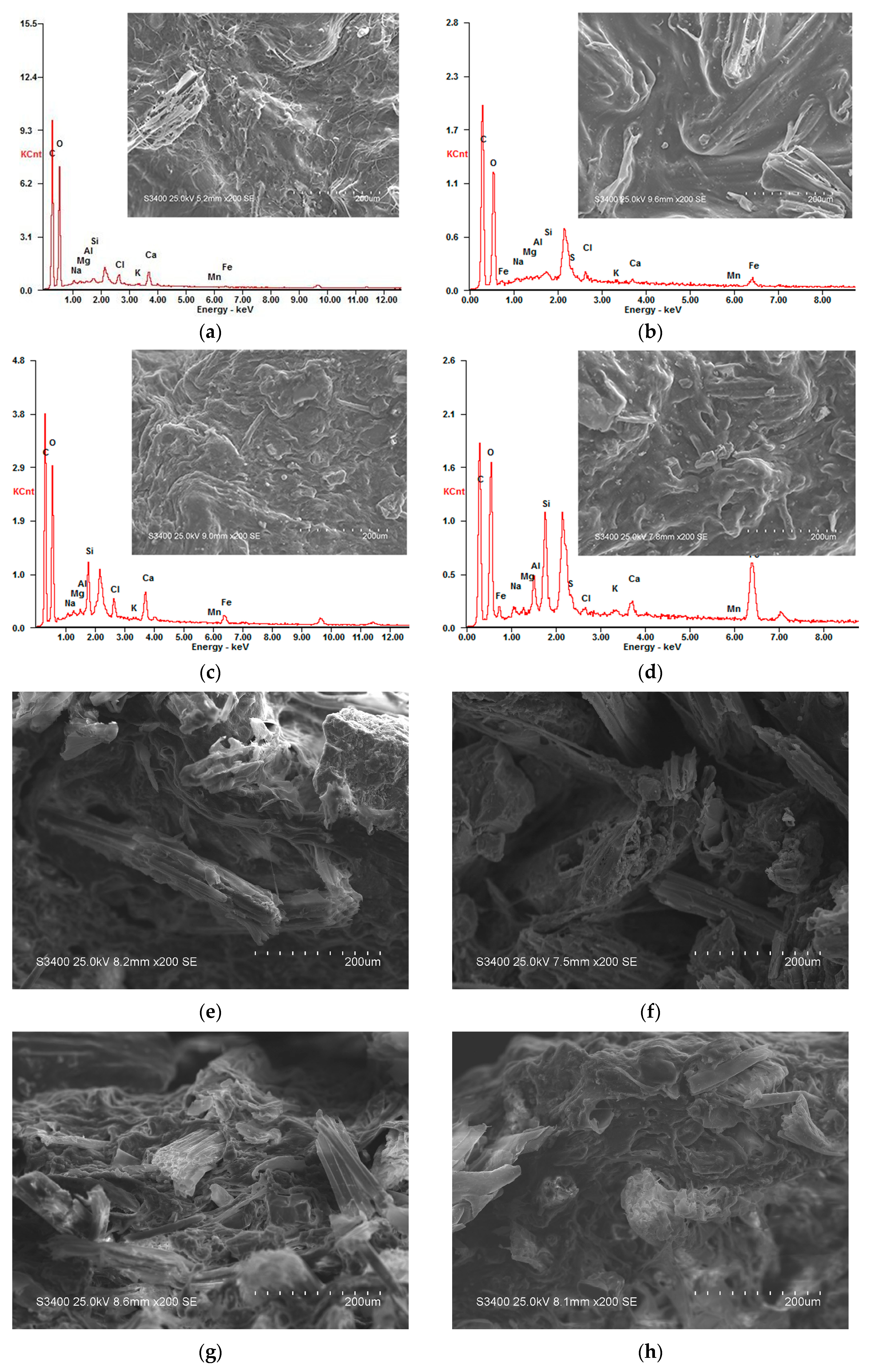
Figure 3.
Scanning electron microscopy/energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM/EDS) images of particle surface (section) before and after treating AMD. (a) Particle No.1 surface; (b) Particle No.1 surface after treating AMD; (c) Particle No.2 surface; (d) Particle No.2 surface after treating AMD; (e) Particle No.1 section; (f) Particle No.1 section after treating AMD; (g) Particle No.2 section; (h) Particle No.2 section after treating AMD.
From Figure 3a, before treatment of AMD with Particle No.1, there were many uneven pores and folds on the particles surface according to SEM. Meanwhile, EDS results show that Particle No.1 mainly contained C, O, Na, Mg, Al, Si, Cl, K, Ca, Mn and Fe, and the weight percentage of each element was 45.31%, 49.64%, 0.70%, 0.20%, 0.18%, 0.51%, 1.02%, 0.19%, 1.98%, 0.03% and 0.27%, respectively. From Figure 3b, after treatment of AMD with Particle No.1, a large number of particles deposited on the surface, the surface folds were significantly reduced, and no pore channels were observed according to SEM. Meanwhile, EDS results show that Particle No.1 mainly contained C, O, S, Mn, Fe and other elements, and the weight percentage of each element was 49.10%, 44.44%, 0.96%, 0.20% and 2.19%, respectively. From Figure 3c, before the treatment of AMD with Particle No.2, the surface texture of the particles was relatively flat and the pores were even from the SEM. Meanwhile, EDS results show that Particle No.2 mainly contained C, O, Na, Mg, Al, Si, Cl, K, Ca, Mn and Fe, and the weight percentage of each element was 45.11%, 42.32%, 0.66%, 0.17%, 0.98%, 3.72%, 1.27%, 0.34%, 3.74%, 0.04% and 1.53%, respectively. From Figure 3d, after treatment of AMD with Particle No.2, a lot of small particles deposited on the surface of the particles, and more pore channels were observed from the SEM. EDS results show that Particle No.2 mainly contained C, O, S, Mn, Fe and other elements, and the weight percentage of each element was 41.78%, 34.91%, 1.16%, 0.17% and 10.31%, respectively.
By comparing Figure 3a–d, after the immobilized particles were treated with AMD, a large amount of small particles were attached to the surface, and the contents of S, Mn and Fe on the surface increased significantly. It is caused by the joint repair of AMD with medical stone, bagasse and SRB in the particles. During the treatment of AMD, a series of complex physical adsorption, chemical replacement and biological metabolic reactions occurred, and the precipitate formed by the reaction accumulated on the surface of the particles. Among them, medical stone had strong pH value bidirectional adjustment ability and metal cation exchange performance, which could repair the acidity of AMD, adsorb metal ions in AMD, and reduce the toxic effect of low pH value and high concentration metal ions on SRB. Studies have found that medical stone has large surface area, many pores and strong cation exchange capacity, which can effectively fix metal ions [14,17]. Milani [39] found that bagasse can also adsorb and remove Fe and Mn ions from the solution. The bagasse not only adsorbed and removed Fe and Mn ions from the solution, but also released organic matter, which provide carbon source for the growth and metabolism of SRB. The SRB contained in the particles could reduce SO42− to S2−, and S2− formed precipitates with Fe and Mn ions. Therefore, the content of S, Mn and Fe in the particles increased significantly after reaction.
By comparing Figure 3b,d, the weight percentage of S and Fe elements on the surface of the particles after treating AMD with Particle No.2 increased significantly, and the increase rate was significantly higher than that of Particle No.1. This indicates that the adsorption effect on Fe in AMD solution by Dengfeng’s medical stone was better than that of Fuxin, and so was the promotion effect on SRB activity. Under the action of medical stone from Dengfeng, SRB activity in Particle No.2 was excellent, SO42− could be excellently reduced to HS− and OH−, then Fe and Mn ions formed precipitates with the reduction products in the solution. Therefore, after treatment of AMD with Particle No.2, the increase of S and Fe content on particle surface was higher than that of Particle No.1. This result is consistent with the AMD treatment effect in dynamic experiment.
From Figure 3e, before the dynamic reaction of Particle No.1, it is clear that a large number of uneven folds and uneven pore channels existed in the bagasse and medical stone inside the particles according to the SEM of the section. From Figure 3f, after treatment of AMD with Particle No.1, the section became smooth and a small amount of deposited particles appeared on the section. The reason for this phenomenon was that, during the process of AMD treatment, the particles exchanged ions with outside solution. Some ions entered the interior of the particle and reacted with the matrix, so the interior structure became relatively smooth, and a small amount of precipitation was formed and accumulated in the interior of the particle. From Figure 3g, before the dynamic reaction of Particle No.2, the SEM of the section showed that the bagasse and medical stone inside the particles had a large number of flat folds and even pore channels. From Figure 3h, after treatment of AMD with Particle No.2, a small amount of precipitate, many tiny pore channels and small raised folds appeared on the section. The reason for this phenomenon was that a series of physical, chemical and biological reactions had taken place during the treatment of AMD in the medical stone enhanced SRB immobilization system. These reactions made its polluted ions remain in the internal pores in the form of precipitation, making the internal structure relatively smooth while effectively inhibiting the diffusion of pollutants.
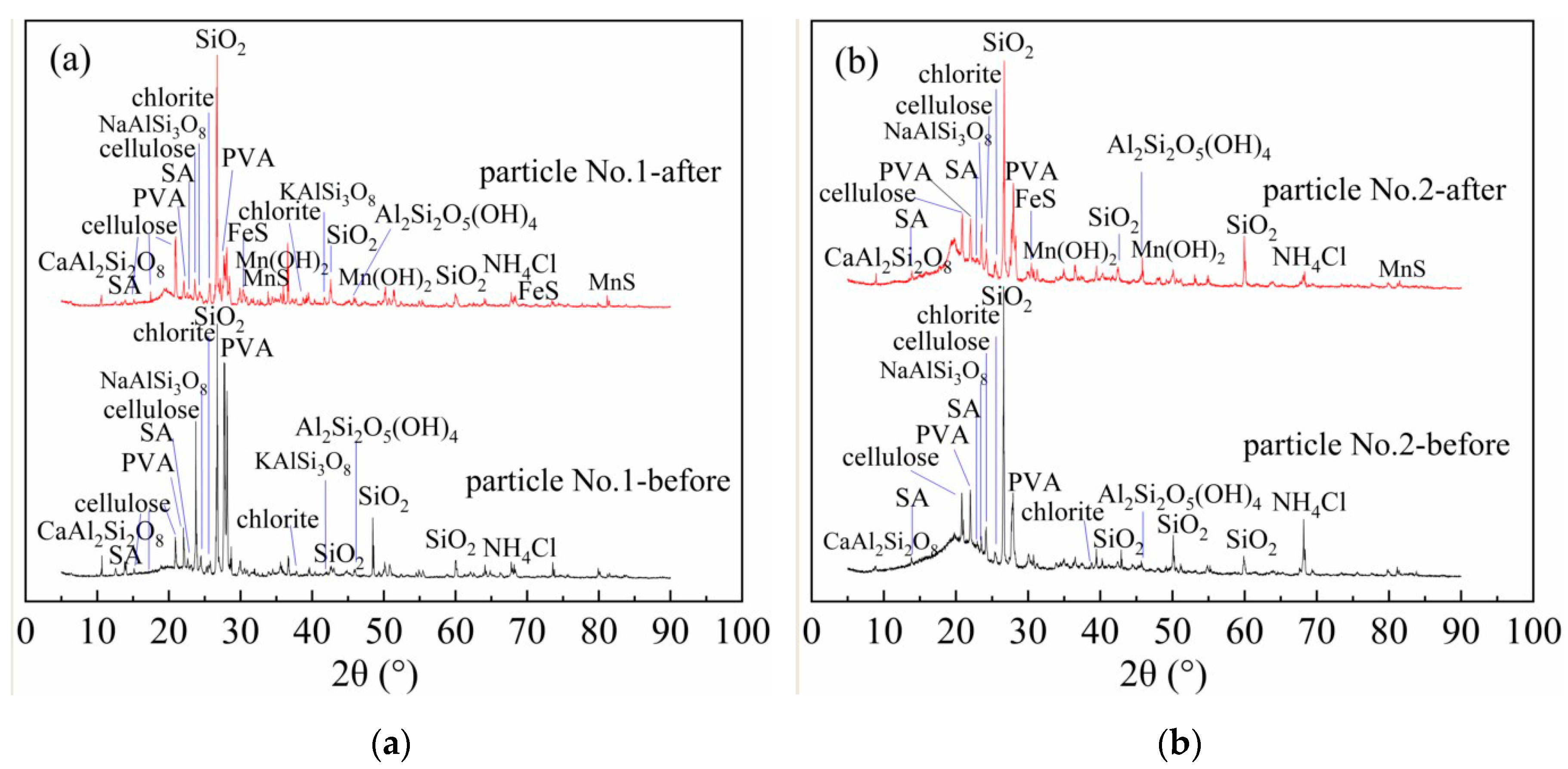
3.6.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
The immobilized particles before and after the dynamic experiment were dried at 60 °C and ground into 0.046 micron powder. The XRD-6100 X-ray diffractometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) was used to analyze the XRD phase of the particles. The results are shown in Figure 4.
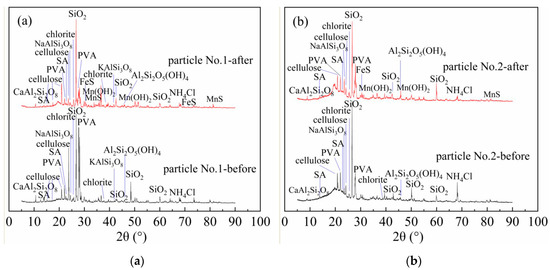
Figure 4.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of particles before and after treating AMD. (a) Particle No.1; (b) Particle No.2.
From Figure 4a, Particle No.1 mainly contained quartz, albite, potash feldspar, anorthite, kaolin, chlorite, polyvinyl alcohol, sodium alginate, NH4Cl, and cellulose. From Figure 4b, immobilized Particle No.2 mainly contained quartz, albite, anorthite, kaolin, chlorite, polyvinyl alcohol, sodium alginate, NH4Cl, and cellulose. Quartz, albite, potash feldspar, anorthite, kaolin and chlorite in the immobilized particles are all composite minerals in medical stone. This is consistent with the findings of Wen Ke et al. [23]. By comparing Figure 4a,b, the diffraction peak intensity of mineral components of medical stone from Dengfeng in Particle No.2 was stronger than that of No.1. Among them, the diffraction peaks of albite at 23.5° were 461 (No.1) and 867 (No.2), potash feldspar at 41.76° were 175 (No.1) and 304 (No.2), kaolin at 45.79° were 128 (No.1) and 406 (No.2), and chlorite at 25.2° and 38.58° were 255 (No.1), 443 (No.2) and 126 (No.1), 291 (No.2) respectively. Combined with the water quality test results, the mineral components such as albite, anorthite, kaolin, and chlorite in medical stone from Dengfeng contained in Particle No.2 had a strong regulating effect on acidity and heavy metals in AMD. The diffraction peaks of polyvinyl alcohol appeared at 22.3°and 27.4°of 2θ for both two immobilized particles. Hai T. A. P. et al. have shown that the diffraction peak of PVA at 2θ values of 22.31°, which corresponds to the (200) plane of the monoclinic unit cell [40]. The diffraction peak of sodium alginate appeared at 13.7° and 23.0° of 2θ, which is consistent with the results of Wang, Q. [41]. The diffraction peak of cellulose appears at 15°, 17°, 21°, and 23° of 2θ. Studies have shown that the chemical composition of bagasse is about 50% cellulose, 25% lignin, 25% hemicellulose and a small amount of extract [42,43]. XRD analysis shows that the immobilized particles contain cellulose. Flauzino [44] found that cellulose appeared at 15°, 17°, 21° and 23° of 2θ are cellulose I-type structure. From Figure 4a,b, after treatment of AMD with both immobilized particles, new phases of MnS, FeS and Mn(OH)2 appeared in the XRD patterns. This is due to the fact that the medical stone and bagasse in the immobilized particles promoted the reduction of SO42− to S2− and OH− by SRB, and the metal ions were removed as precipitates of metal sulfides and metal hydroxides. In addition, some Fe2+ and Mn2+ were removed by adsorption of bagasse. The results are consistent with SEM/EDS analysis and changes of AMD detection indexes.
4. Conclusions
(1) Dynamic Column 2 had a better repair effect on AMD than Column 1. Therefore, the optimal composition of the substrate material in immobilized particles was bagasse, SRB and medical stone from Dengfeng.
(2) The SEM/EDS analysis showed that the contents of S, Mn and Fe on the surface of the particles increased significantly after treatment of AMD. XRD analysis shows that FeS, MnS and Mn(OH)2 appeared after treatment of AMD. Medical stone, bagasse and SRB in immobilized particles worked together to remove AMD pollution through a series of complex biological, physical and chemical reactions.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed equally to this work. Y.D., J.D., X.W., L.X., Z.Y., X.G. and M.L. are the main authors of this work. Conceptualization, Y.D. and J.D.; methodology, Y.D. and L.X.; formal analysis, Y.D., J.D., X.W. and L.X.; investigation, Z.Y., X.G. and M.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.D., X.W., L.X. and M.L.; writing—review and editing, J.D., Z.Y. and X.G.; project administration, J.D. All authors have been involved in the manuscript preparation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41672247, 41102157), Liaoning Province’s “Program for Promoting Liaoning Talents” (XLYC1807159).
Acknowledgments
The author(s) would like to thank all editors and anonymous reviewers for their comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
References
- Betz, M.R.; Partridge, M.D.; Farren, M.; Lobao, L. Coal mining, economic development, and the natural resources curse. Energy Econ. 2015, 50, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Elsworth, D.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Luo, M.; Song, Y.; Zhang, H. Modelling and optimization of enhanced coalbed methane recovery using CO2/N2 mixtures. Fuel 2019, 253, 1114–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Han, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yang, C.; Chen, M.; Dang, Z.; Yi, X.; Lu, G. Isotope geochemistry, hydrochemistry, and mineralogy of a river affected by acid mine drainage in a mining area, South China. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 43310–43318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skousen, J.; Zipper, C.E.; Rose, A.; Ziemkiewicz, P.F.; Nairn, R.; McDonald, L.M.; Kleinmann, R.L. Review of Passive Systems for Acid Mine Drainage Treatment. Mine Water Environ. 2017, 36, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.K.; Jho, E.H. Heavy metal and sulfate removal from sulfate-rich synthetic mine drainages using sulfate reducing bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcil, A.; Koldas, S. Acid Mine Drainage (AMD): Causes, treatment and case studies. J. Clean. Prod. 2005, 14, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, T.; Li, P.; Xie, Q.; Zhan, X. Cu Removal from Acid Mine Drainage by Modified Pyrite: Batch and Column Experiments. Mine Water Environ. 2016, 36, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Sun, R.; Liang, Z.; Hong, Y.; Wu, D.; Wang, J. Research Progress on the Treatment of Acid Mine Drainage by Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria. J. South China Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2018, 50, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Di, J.; Wang, M.; Ren, Y. Experimental study on the treatment of acid mine drainage by modified corncob fixed SRB sludge particles. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 19016–19030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, H. Preparation of immobilized sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) granules for effective bioremediation of acid mine drainage and bacterial community analysis. Miner. Eng. 2016, 92, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.; Li, T.; Zhao, W. Treatment acid mine drainage by sulfate reducing bacteria using different biomass carbon sources. J. China Coal Soc. 2019, 44, 1915–1922. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, P.; Ma, Z.; Gao, Y. The Primary Research of Fuxin Maifan Stone Mineral Resources. China Non-Met. Min. Ind. Her. 2008, 2, 10–12, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Hou, C.; Du, S.; Ren, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, Q.; Hu, X. A sub-nanomole level electrochemical method for determination of prochloraz and its metabolites based on medical stone doped disposable electrode. Talanta 2010, 83, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Awasthi, S.K.; Li, R.; Zhao, J.; Ren, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z. Feasibility of medical stone amendment for sewage sludge co-composting and production of nutrient-rich compost. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 216, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Lei, Y.; Dong, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Chang, X.; Liu, T.; Yin, Y.; Ajayan, P.M. Synthesis of Nanocomposites of Silver Nanoparticles with Medical Stone and Carbon Nanotubes for Their Antibacterial Applications. Mater. Express 2012, 2, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J. Liquefaction of cotton seed in sub-critical water/ethanol with modified medical stone for bio-oil. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Awasthi, M.K.; Jiang, Y.; Li, R.; Ren, X.; Zhao, J.; Shen, F.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z. Evaluation of medical stone amendment for the reduction of nitrogen loss and bioavailability of heavy metals during pig manure composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Z. Experiment on the treatment of acid mine drainage with optimized biomedical stone particles by response surface methodology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 7978–7990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F. Bioremediation of Acid Mine Drainage using immobilized SRB sludge with inner cohesive corncob in a Permeable Reactive Barrier. Master’s Thesis, Liaoning Technical University, Fuxin, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Sheng, S.; Yang, Z.; Liu, H.; Jiao, X.; Wan, A. Analysis of Black-odor Factors of Lake Sediment and Elimination Strategies of Key Factor. Environ. Sci. Surv. 2019, 38, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, T.W.; Xiang, P.Y.; Mackey, H.R.; Chi, K.; Lu, H.; Chui, H.K.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.; Chen, G.H. A review of biological sulfate conversions in wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2014, 65, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.; Neculita, C.M.; Han, J.I. Biosulfides precipitation in weathered tailings amended with food waste-based compost and zeolite. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, K.; Liu, G.; Yin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhu, J. Process Mineralogical Study on the Maifan Stone in Qiqihar Nianzishan. J. Mineral. Petrol. 2016, 36, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kikot, P.; Viera, M.; Mignone, C.; Donati, E. Study of the effect of pH and dissolved heavy metals on the growth of sulfate-reducing bacteria by a fractional factorial design. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Chang, Y.; Hung, C.; Lee, J.; Liao, H.; Chou, H. Microbial community analysis of anaerobic bio-corrosion in different ORP profiles. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 95, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeld, R.D.; Ropelewski, L.; Acheson, M. Sewage as a Mixed Organic Substrate for Desulfurization Bacteria. Proc. Water Environ. Fed. 2012, 2012, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Han, X. Preparation of metal-resistant immobilized sulfate reducing bacteria beads for acid mine drainage treatment. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, L.P.; Costa, P.F.; Bertolino, S.M.; Silva, J.C.C.; Guerra-Sá, R.; Leão, V.A.; Teixeira, M.C. Nickel, manganese and copper removal by a mixed consortium of sulfate reducing bacteria at a high COD/sulfate ratio. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 2171–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijmans, M.F.; Dopson, M.; Peeters, T.W.; Lens, P.N.; Buisman, C.J. Sulfate reduction at pH 5 in a high-rate membrane bioreactor: Reactor performance and microbial community analyses. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 19, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, Z.; Cut, A.; Said, A. Removal and Kinetics Adsorption Fe (II) Ions in Ground Water using Sugarcane Bagasse of Various Treatments Adsorbent with Column Method. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 536, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Deng, L.; Fang, C.; Lei, Y.; He, C.; Gao, C.; Zhao, S.; Xiang, Y. Adsorption of Cr(VI) in Water by Maifanite Modified with Different LDHs Coatings. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 300–309. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, T.; Wang, W.; Wang, A. A pH-sensitive composite hydrogel based on sodium alginate and medical stone: Synthesis, swelling, and heavy metal ions adsorption properties. Macromol. Res. 2011, 19, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karathanasis, A.D.; Edwards, J.D.; Barton, C.D. Manganese and Sulfate Removal from a Synthetic Mine Drainage through Pilot Scale Bioreactor Batch Experiments. Mine Water Environ. 2010, 29, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltan, M.E.; Sirry, S.M.; Fawzy, E.M. Evaluation of the Sorptive Capacity of Sugarcane Bagasse and Its Coal for Heavy Metals in Solution. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2007, 54, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, K.; Sasaki, K.; Hiroyoshi, N.; Tsunekawa, M.; Hirajima, T. The Effect of Mn2+ Concentration on Mn Removal by a Sulfate Reducing Bacteria Bioreactor. Mater. Trans. 2004, 45, 2429–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jong, T.; Parry, D.L. Microbial sulfate reduction under sequentially acidic conditions in an upflow anaerobic packed bed bioreactor. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2561–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Xia, L.; Jin, S.; Wang, Y.; Ning, P. Treating synthetic mine leaching wastewater by sulfate-reducing bacteria with sugarcane bagasse as carbon source. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 10, 2355–2360. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Brand, T.P.H.; Roest, K.; Chen, G.; Brdjanovic, D.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Effects of Chemical Oxygen Demand, Nutrients and Salinity on Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2015, 32, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, P.A.; Debs, K.B.; Labuto, G.; Carrilho, E.N.V.M. Agricultural solid waste for sorption of metal ions: Part I—Characterization and use of lettuce roots and sugarcane bagasse for Cu(II), Fe(II), Zn(II), and Mn(II) sorption from aqueous medium. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 35895–35905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, T.A.P.; Sugimoto, R. Synthesis and characterization of poly(3-hexylthiophene)-grafted polyvinyl alcohol. Synth. Met. 2018, 240, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, N.; Hu, X.; Yang, J.; Du, Y. Alginate/polyethylene glycol blend fibers and their properties for drug controlled release. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 82, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, B.; Du, F.; Xian, X.; Huang, H.; Tang, P. Structure and combustion characteristics of lignin from black liquor of bagasse soda pulping. CIESC J. 2017, 68, 345–352. [Google Scholar]
- Ladeira, N.C.; Peixoto, V.J.; Penha, M.P.; Barros, E.B.D.P.; Leite, S.G.F. Optimization of 6-pentyl-alpha-pyrone production by solid state fermentation using sugarcane bagasse as residue. Bioresources 2010, 5, 2297–2306. [Google Scholar]
- Flauzino Neto, W.P.; Silvério, H.A.; Dantas, N.O.; Pasquini, D. Extraction and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from agro-industrial residue—Soy hulls. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 42, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).