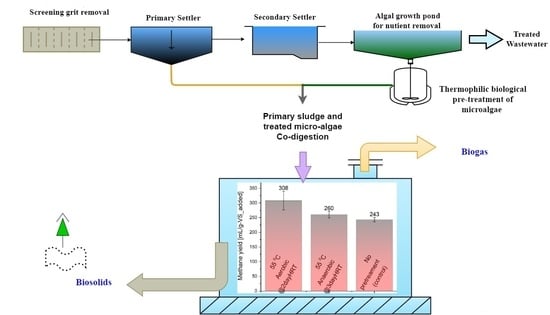
Synergistic Co-Digestion of Microalgae and Primary Sludge to Enhance Methane Yield from Temperature-Phased Anaerobic Digestion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Substrate and Inoculum
2.1.1. Algal Biomass Preparation
2.1.2. Primary Sludge, Inoculum and the Sampling Plant
2.2. Phase One (Thermophilic Pre-Treatment of Microalgae)
2.3. Phase Two (Mesophilic Digestion) BMP Tests
2.4. Analytical Procedures and Equipment
2.5. Modeling Kinetics of BMP Assay
3. Results and Discussion
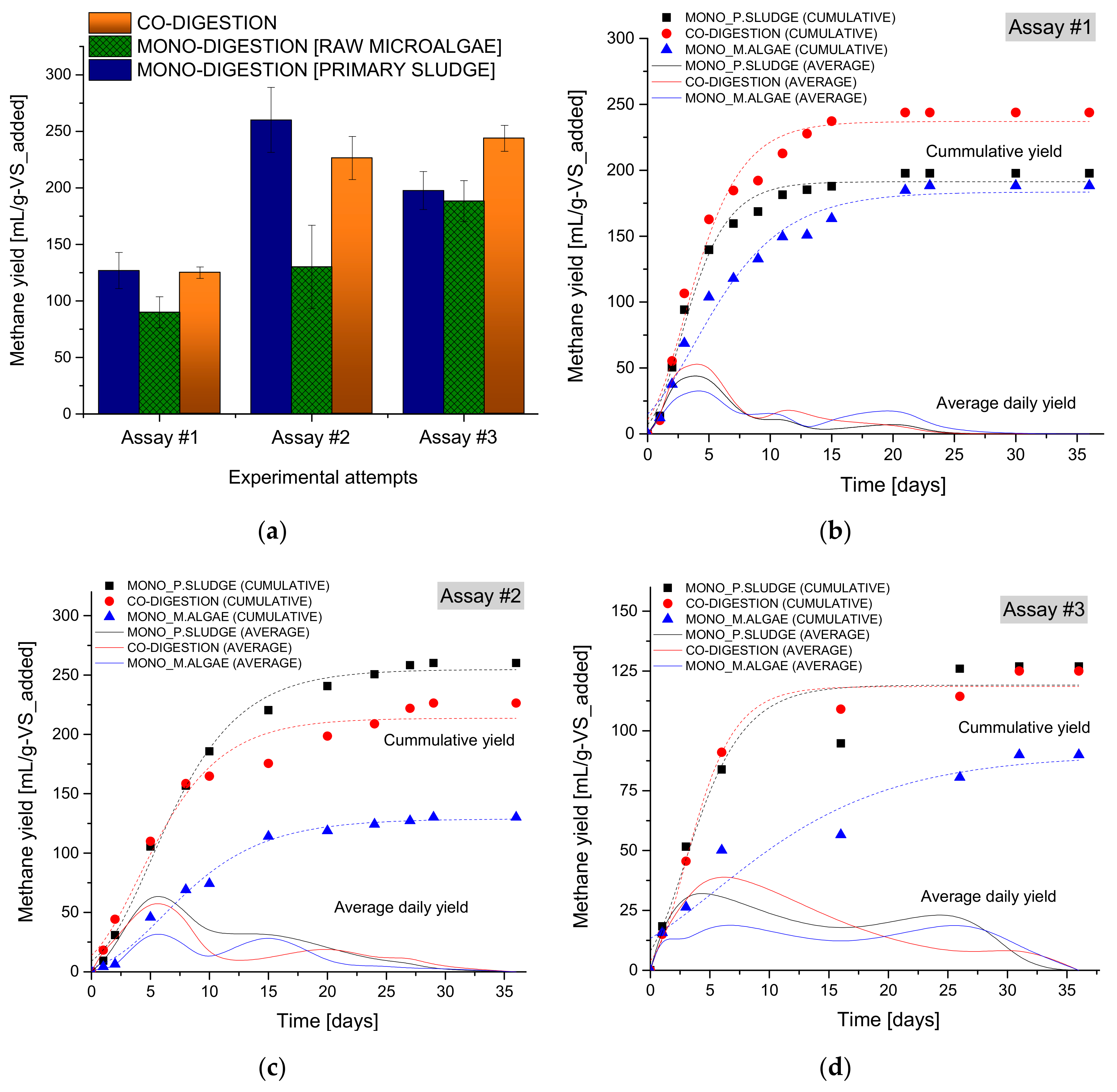
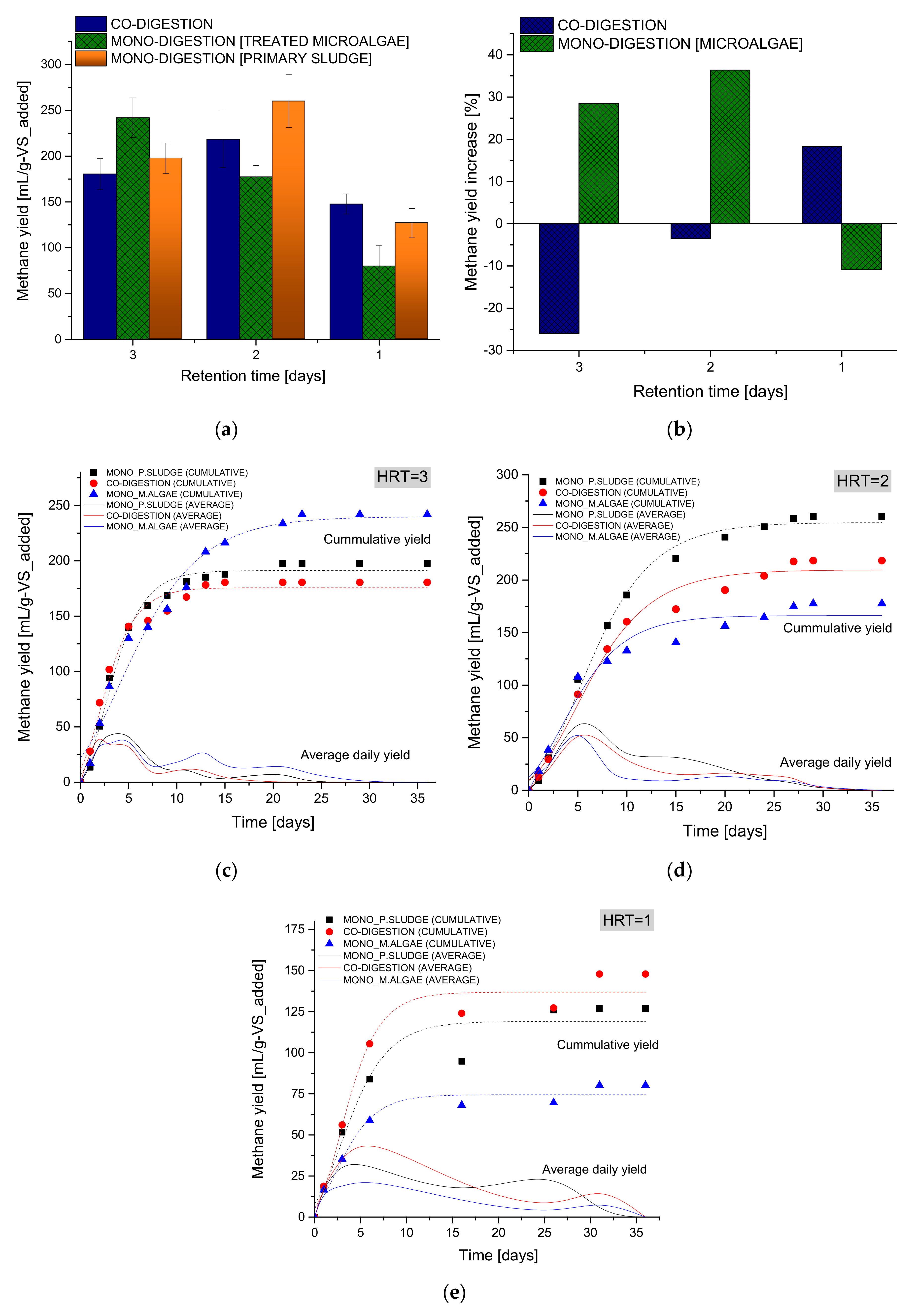
3.1. Effects of Co-Digestion on Methane Yield
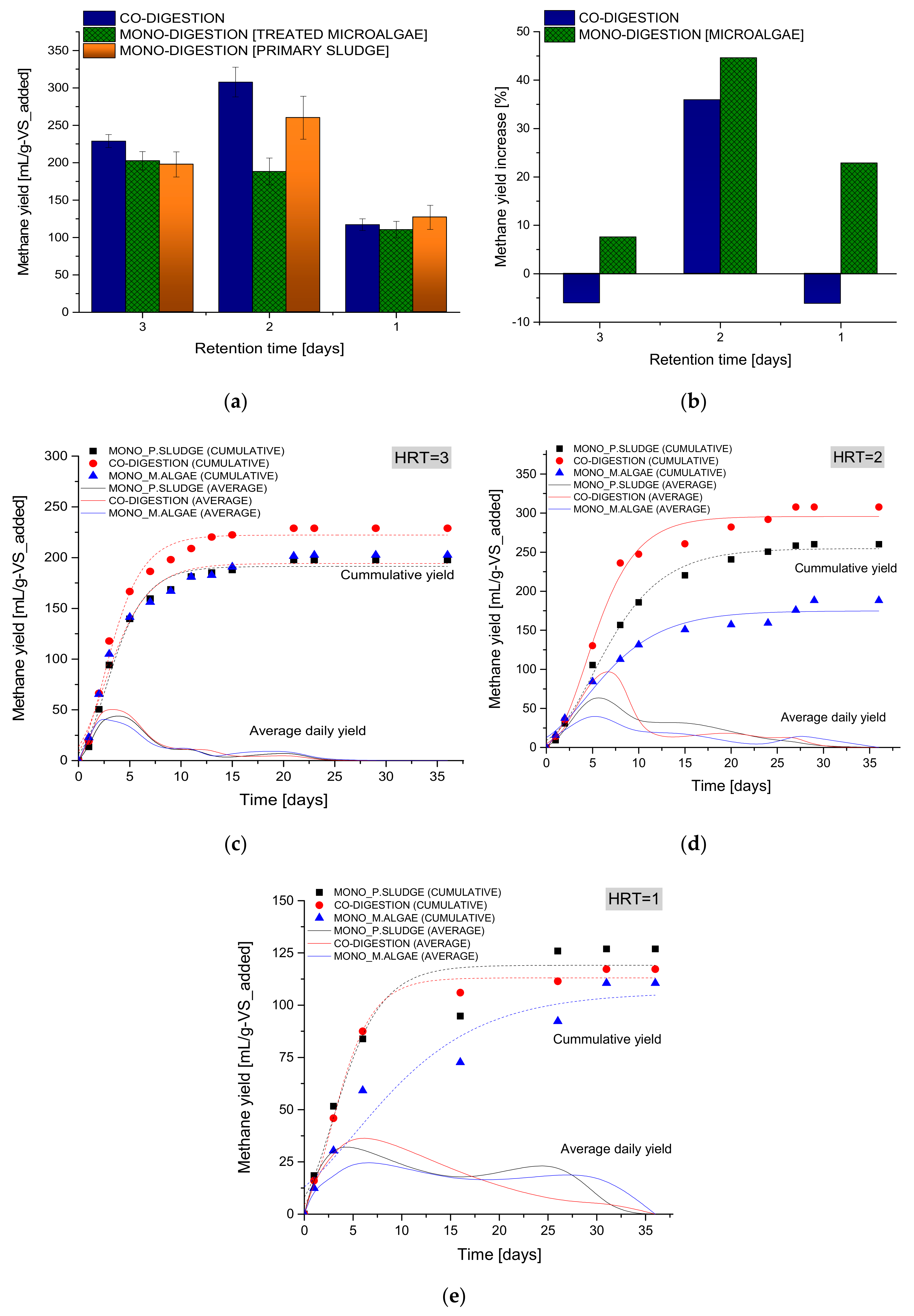
3.2. The Dual-Effect of Co-Digestion and Pretreatment
3.2.1. Co-Digestion after Aerobic Pretreatment
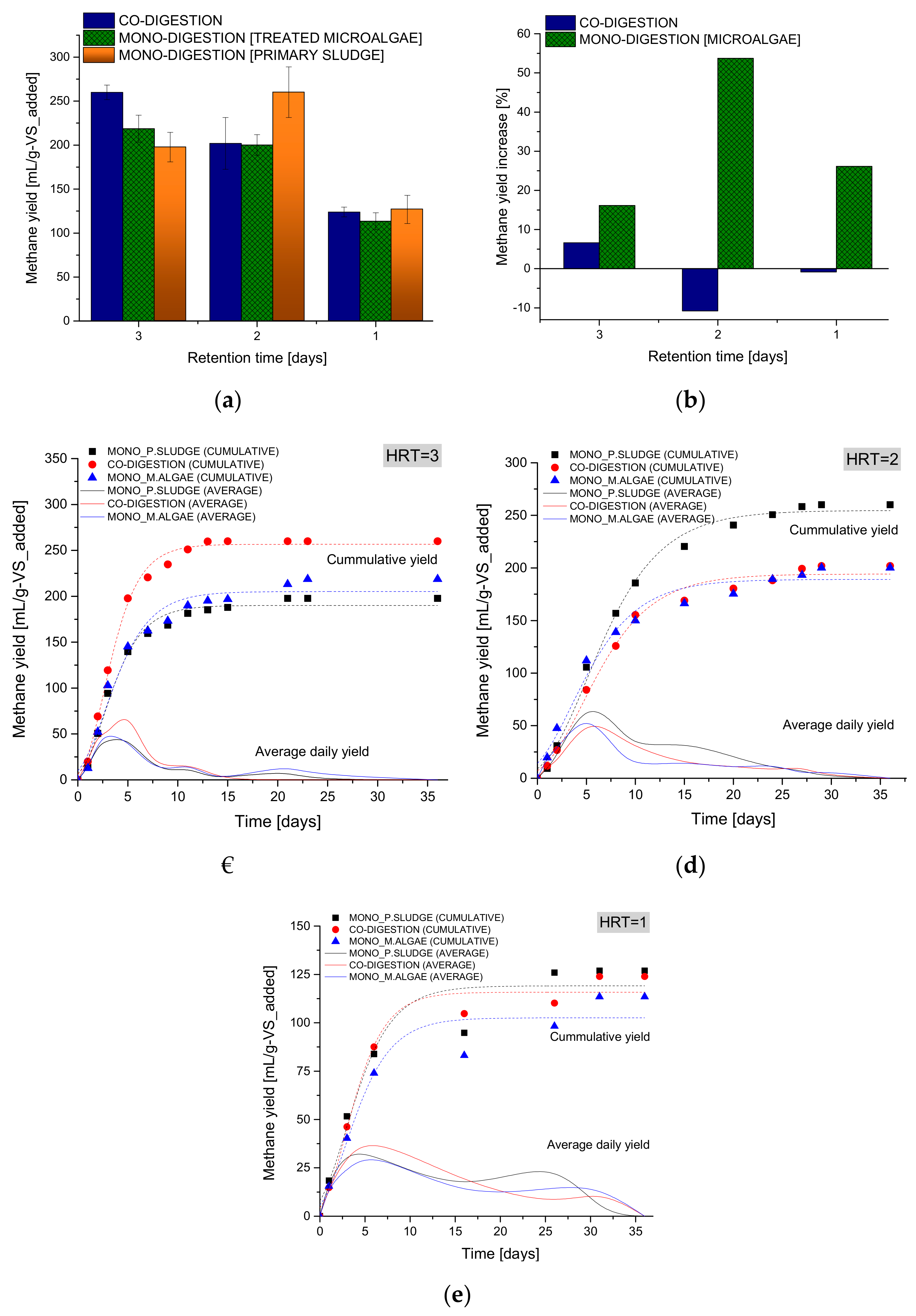
3.2.2. Co-Digestion after Anaerobic Pretreatment
3.2.3. Co-Digestion after 85 °C Anaerobic Pretreatment
3.3. Performance Comparison with Previous Works
3.4. Implications on the Circular Economy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghaffari, Y.; Gupta, N.K.; Bae, J.; Kim, K.S. One-step fabrication of Fe2O3/Mn2O3 nanocomposite for rapid photodegradation of organic dyes at neutral pH. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 113691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Damtie, M.M.; Yu, Z.M.; Liu, Y.; Jin, J.; Wu, K.; Deng, C.X.; Wei, W.; Wei, X.L.; Ni, B.-J. Green synthesis of Fe3O4@carbon filter media for simultaneous phosphate recovery and nitrogen removal from domestic wastewater in biological aerated filters. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 16698–16709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Yu, Z.M.; Damtie, M.M.; Wu, K.; Jin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, X.L.; Frost, R.L. Use of autoclaved aerated concrete particles for simultaneous removal of nitrogen and phosphorus as filter media from domestic wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, M.; Kumar, N.; Kumar, V.; Negi, S.; Banerjee, C. Microalgae: A way forward approach towards wastewater treatment and bio-fuel production. In Applied Microbiology and Bioengineering; Shukla, P., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 229–243. ISBN 9780128154076. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, A.J.; Lewis, D.M.; Green, F.B. Anaerobic digestion of algae biomass: A review. Algal Res. 2014, 5, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdy, A.; Mendez, L.; Ballesteros, M.; González-Fernández, C. Algaculture integration in conventional wastewater treatment plants: Anaerobic digestion comparison of primary and secondary sludge with microalgae biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 184, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé-Bundó, M.; Garfí, M.; Ferrer, I. Pretreatment and co-digestion of microalgae, sludge and fat oil and grease (FOG) from microalgae-based wastewater treatment plants. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Prasad, R.; Higgins, B.T. Aerobic bacterial pretreatment to overcome algal growth inhibition on high-strength anaerobic digestates. Water Res. 2019, 162, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohutskyi, P.; Phan, D.; Kopachevsky, A.M.; Chow, S.; Bouwer, E.J.; Betenbaugh, M.J. Synergistic co-digestion of wastewater grown algae-bacteria polyculture biomass and cellulose to optimize carbon-to-nitrogen ratio and application of kinetic models to predict anaerobic digestion energy balance. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 269, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Jensen, P.D.; Batstone, D.J. Pre-treatment mechanisms during thermophilic–mesophilic temperature phased anaerobic digestion of primary sludge. Water Res. 2010, 44, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atelge, M.R.; Atabani, A.E.; Banu, J.R.; Krisa, D.; Kaya, M.; Eskicioglu, C.; Kumar, G.; Lee, C.; Yildiz, Y.Ş.; Unalan, S.; et al. A critical review of pretreatment technologies to enhance anaerobic digestion and energy recovery. Fuel 2020, 270, 117494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Reyes, J.; Barragán-Trinidad, M.; Buitrón, G. Biological pretreatments of microalgal biomass for gaseous biofuel production and the potential use of rumen microorganisms: A review. Algal Res. 2016, 18, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Schanbacher, F.L.; Yu, Z. Putting microbes to work in sequence: Recent advances in temperature-phased anaerobic digestion processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 9409–9414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.M.; Cho, H.U.; Park, S.K.; Ha, J.H.; Park, J.M. Influence of thermophilic aerobic digestion as a sludge pre-treatment and solids retention time of mesophilic anaerobic digestion on the methane production, sludge digestion and microbial communities in a sequential digestion process. Water Res. 2014, 48, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mshandete, A.; Björnsson, L.; Kivaisi, A.K.; Rubindamayugi, S.T.; Mattiasson, B. Enhancement of anaerobic batch digestion of sisal pulp waste by mesophilic aerobic pre-treatment. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Sahu, A.K.; Rusten, B.; Park, C. Anaerobic co-digestion of microalgae Chlorella sp. and waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé-Bundó, M.; Eskicioglu, C.; Garfí, M.; Carrère, H.; Ferrer, I. Anaerobic co-digestion of microalgal biomass and wheat straw with and without thermo-alkaline pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 237, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, J.; Feng, X.M.; Ascue, J.; Gentili, F.G.; Shabiimam, M.A.; Nehrenheim, E.; Thorin, E. Co-digestion of cultivated microalgae and sewage sludge from municipal waste water treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jeon, J.H.; Shin, J.; Jang, H.M.; Kim, S.; Song, M.S.; Kim, Y.M. Quantitative and qualitative changes in antibiotic resistance genes after passing through treatment processes in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA/AWWA/WEF 2540 solids. In Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Filer, J.; Ding, H.H.; Chang, S. Biochemical methane potential (BMP) assay method for anaerobic digestion research. Water 2019, 11, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, W.; Sun, M.; Xu, X.; Zhang, B.; Sun, Y. Evaluation of biochemical methane potential and kinetics on the anaerobic digestion of vegetable crop residues. Energies 2019, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lee, E.; Dilbeck, M.P.; Liebelt, M.; Zhang, Q.; Ergas, S.J. Thermal pretreatment of microalgae for biomethane production: Experimental studies, kinetics and energy analysis. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damtie, M.M.; Choi, J.-S.; Shon, H.K. Fluoride Removal and Nitrogen Recovery from Wastewater by Membrane Distillation Process. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology (UST), Daejeon, Korea, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Damtie, M.M.; Choi, J.-S. Modeling and application of direct contact membrane distillation for fluoride removal from aqueous solutions. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 97, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Damtie, M.M.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Frost, R.L.; Yu, Z.M.; Jin, J.; Wu, K. Catalytic degradation of P-chlorophenol by muscovite-supported nano zero valent iron composite: Synthesis, characterization, and mechanism studies. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 195, 105735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Tan, W.; Zhao, X.; Dang, Q.; Song, Q.; Xi, B.; Zhang, X. Evaluation on the methane production potential of wood waste pretreated with NaOH and co-digested with pig manure. Catalysts 2019, 9, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Bauddh, K.; Bux, F. (Eds.) Algae and environmental sustainability. In Developments in Applied Phycology; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2015; ISBN 9788132226390. [Google Scholar]
- Mendez, L.; Mahdy, A.; Timmers, R.A.; Ballesteros, M.; González-Fernández, C. Enhancing methane production of Chlorella vulgaris via thermochemical pretreatments. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 149, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solé-Bundó, M.; Carrère, H.; Garfí, M.; Ferrer, I. Enhancement of microalgae anaerobic digestion by thermo-alkaline pretreatment with lime (CaO). Algal Res. 2017, 24, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, A.; Lyautey, E.; Montuelle, B.; Casper, P. Effects of increasing temperatures on methane concentrations and methanogenesis during experimental incubation of sediments from oligotrophic and mesotrophic lakes. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 1394–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwede, S.; Rehman, Z.-U.; Gerber, M.; Theiss, C.; Span, R. Effects of thermal pretreatment on anaerobic digestion of Nannochloropsis salina biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 143, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzonella, D.; Cavinato, C.; Fatone, F.; Pavan, P.; Cecchi, F. High rate mesophilic, thermophilic, and temperature phased anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge: A pilot scale study. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Jensen, P.D.; Batstone, D.J. Increased temperature in the thermophilic stage in temperature phased anaerobic digestion (TPAD) improves degradability of waste activated sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 187, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé-Bundó, M.; Salvadó, H.; Passos, F.; Garfí, M.; Ferrer, I. Strategies to optimize microalgae conversion to biogas: Co-digestion, pretreatment and hydraulic retention time. Molecules 2018, 23, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, X.; Wang, Z.; Kong, X.; Li, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, S.; Feng, S.; Luo, X.; Lv, P. Enhancement of the energy yield from microalgae via enzymatic pretreatment and anaerobic co-digestion. Energy 2018, 164, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Tao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, H. Stimulating methane production from microalgae by alkaline pretreatment and co-digestion with sludge. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 1546–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, G.; Lu, X.; Kobayashi, T.; Kumar, G.; Xu, K. Anaerobic co-digestion on improving methane production from mixed microalgae (Scenedesmus sp., Chlorella sp.) and food waste: Kinetic modeling and synergistic impact evaluation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 299, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamorano-López, N.; Borrás, L.; Seco, A.; Aguado, D. Unveiling microbial structures during raw microalgae digestion and co-digestion with primary sludge to produce biogas using semi-continuous AnMBR systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-García, R.; Zamorano-López, N.; Seco, A.; Bouzas, A. Co-digestion of harvested microalgae and primary sludge in a mesophilic anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR): Methane potential and microbial diversity. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé-Bundó, M.; Garfí, M.; Matamoros, V.; Ferrer, I. Co-digestion of microalgae and primary sludge: Effect on biogas production and microcontaminants removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadros-Blázquez, F.; González-González, A.; Sánchez-Sánchez, C.; Díaz-Rodríguez, V.; Cuadros-Salcedo, F. Waste valorization as an example of circular economy in extremadura (Spain). J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 181, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisser, J.; Wirth, M.; de Gusseme, B.; van Eekert, M.; Zeeman, G.; Schoenborn, A.; Vinnerås, B.; Finger, D.C.; Kolbl-Repinc, S.; Bulc, T.G.; et al. A review of nature-based solutions for resource recovery in cities. Blue Green Syst. 2020, 2, 138–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Microalgae | Primary Sludge | Inoculum |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.7 | 6.1 | 7.61 |
| Total solids, TS (g/L) | 114.3 ± 0.9> | 49.3 ± 7.2 | 27.77 ± 0.8 |
| Volatile solids, VS (g/L) | 108.3 ± 0.2 | 33.6 ± 4.8 | 17.30 ± 2.1 |
| Total chemical oxygen demand, tCOD (g/L) | 103.5 ± 0.2 | 87.0 ± 4.4 | 14.31 ± 0.3 |
| Soluble chemical oxygen demand, sCOD (g/L) | 5.4 ± 0.0 | 11.2 ± 0.9 | 4.25 |
| Soluble carbohydrate (g/L) | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.0 | - |
| Soluble protein (g/L) | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 2.7 ± 0.2 | 2.66 ± 0.4 |
| Model * Para Meters | ** Assay#1 | Assay#2 | Assay#3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mono-p.sludge | Mono-m.algae | Co-Digestion | Mono-p.sludge | Mono-m.algae | Co-Digestion | Mono-p.sludge | Mono-m.algae | Co-Digestion | |
| Go | 191.28 | 183.51 | 236.96 | 254.68 | 128.76 | 213.63 | 119.10 | 90.06 | 118.53 |
| λ | 0.44 | 0.34 | 0.33 | 0.85 | 1.32 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 2.95 | 0.52 |
| Rmax | 32.25 | 16.45 | 33.24 | 22.43 | 9.97 | 20.05 | 15.30 | 3.96 | 18.49 |
| R2 | 0.987 | 0.973 | 0.978 | 0.994 | 0.990 | 0.973 | 0.937 | 0.907 | 0.984 |
| * Model Para Meters | HRT = 3 | HRT = 2 | HRT = 1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mono-p.sludge | Mono-m.algae | Co-Digestion | Mono-p.sludge | Mono-m.algae | Co-Digestion | Mono-p.sludge | Mono-m.algae | Co-Digestion | |
| Go | 191.27 | 194.24 | 222.2 | 254.68 | 174.86 | 295.68 | 119.10 | 106.17 | 113.06 |
| λ | 0.44 | 0.06 | 0.34 | 0.85 | 0.17 | 1.26 | 0.03 | 1.84 | 0.41 |
| Rmax | 32.25 | 29.17 | 38.8 | 22.43 | 14.33 | 35.86 | 15.30 | 5.49 | 17.67 |
| R2 | 0.987 | 0.975 | 0.985 | 0.99 | 0.973 | 0.99 | 0.937 | 0.917 | 0.99 |
| Model Parameters | HRT = 3 | HRT = 2 | HRT = 1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mono-p.sludge | Mono-m.algae | Co-Digestion | Mono-p.sludge | Mono-m.algae | Co-Digestion | Mono-p.sludge | Mono-m.algae | Co-Digestion | |
| Go | 190.02 | 205.15 | 256.66 | 254.68 | 189.11 | 194.19 | 119.10 | 102.56 | 115.82 |
| λ | 0.47 | 0.27 | 0.63 | 0.85 | 0.18 | 0.74 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.44 |
| Rmax | 32.79 | 30.71 | 48.38 | 22.43 | 18.85 | 18.34 | 15.31 | 13.59 | 17.63 |
| R2 | 0.987 | 0.972 | 0.998 | 0.993 | 0.974 | 0.989 | 0.937 | 0.933 | 0.975 |
| Model Parameters | HRT = 3 | HRT = 2 | HRT = 1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mono-p.sludge | Mono-m.algae | Co-Digestion | Mono-p.sludge | Mono-m.algae | Co-Digestion | Mono-p.sludge | Mono-m.algae | Co-Digestion | |
| Go | 191.28 | 239.93 | 175.72 | 254.69 | 166.21 | 209.61 | 119.10 | 74.48 | 136.85 |
| λ | 0.44 | 0.60 | 0.03 | 0.85 | 0.15 | 0.50 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.40 |
| Rmax | 32.24 | 18.94 | 31.46 | 22.43 | 17.35 | 18.13 | 15.31 | 11.40 | 21.28 |
| R2 | 0.987 | 0.973 | 0.977 | 0.994 | 0.96 | 0.983 | 0.9367 | 0.964 | 0.969 |
| SN | Type of Process | Type of Substrate | Experimental Conditions | Methane Yield | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Thermal pretreatment and co-digestion | Microalgae, primary sludge and FOG | Thermal pretreatment (75 °C for 10 h), BMP Temp = 35 °C VS-based microalgae to sludge ratio = 50–50% | 237 ± 1, 298 ± 12, and 334 ± 1 mL CH4/gVS for FOG = 0%, FOG = 10%, and FOG = 20% resp. | [7] |
| 2 | Thermal pretreatment and co-digestion | Microalgae and primary sludge | Thermal pretreatment (120 °C for 40 min), BMP Temp = 35 °C, Microalgae and sludge ratio = varying | 261.7, 282.8 and 293.4 mL CH4/COD for ratio = 75%/25%, 50%/50% and 25%/75% resp. | [6] |
| 3 | Thermal pretreatment and co-digestion | Microalgae and Secondary sludge | Thermal pretreatment (120 °C for 40 min), BMP Temp = 35 °C, Microalgae and secondary sludge ratio = varying | ~150, 136 and 102 mL CH4/COD for ratio = 75%/25%, 50%/50% and 25%/75% resp. | |
| 4 | Thermo-alkaline pretreatment and co-digestion | Microalgal biomass and wheat straw | Thermo-alkaline pretreatment (72 °C for 24 h), HRT = 20 days, Total operation = 106 days, OLR = 1.5 g VS/L·day, BMP Temp = 37 ± 1 °C, microalgae to straw ratio (50–50%) | 0.24 L CH4/g vs. | [17] |
| 5 | Thermal pretreatment and co-digestion | Microalgae and primary sludge | Thermal pretreatment (75 °C for 10 h), HRT = 20/30 days, Microalgae/sludge ratio = 25%/75%, BMP Temp = 37 ± 1 °C, OLR = 1.17 (g VS/L·day) | 0.46 ± 0.27L CH4/g VS) | [35] |
| 6 | Enzymatic pretreatment and co-digestion | algal residues and Pennisetum hybrid energy grass | Mixed enzyme (Cellulase, Xynalase, Pectinase) algal to grass ratio = 1:3 (VS-based), BMP Temp = 35 °C | 207.35 ± 15.66 mLCH4/gVS | [36] |
| 7 | Alkaline pretreatment and co-digestion | Microalgae and mixed primary secondary sludge | Alkaline treatment (0.1 mol/L NaOH for 12 h), Microalgae to sludge ratio 2:1, BMP Temp = 35 ± 1°C, one month experiment | 298 mLCH4/gVS | [37] |
| 8 | Temperature phased Anaerobic co-digestion | Activated sludge | Pretreatment HRT=2 days pH=7, Temp = varying, BMP Temp = 37 °C | 160 mL/gVS and 300 mL/gVS for 50 °C and 65 °C resp. | [34] |
| 9 | Temperature phased co-digestion | Microalgae with primary sludge | Thermophilic Aerobic (HRT = 2 days) and anaerobic (HRT = 3 days) pretreatment at 55 °C, Sludge/algae ratio = 9 & ISR = 2, BMP Temp = 35 °C | 308 mL/g-VS and 260 mL/g-VS | This study |
| 10 | Only co-digestion | mixed microalgae and food waste | BMP Temp = 35 °C, microalgae to food waste ratio = 0.2:0.8, reaction day = 40 days | 639.8 ± 1.3 mL/g VS_added | [38] |
| 11 | Only co-digestion | Microalgae and primary sludge | AnMBR, SRT = 100 days, HRT = 30 days, OLR = 0.5 gVS/L d, Sludge to microalgae ratio = 62%:38%, BMP Temp = 35 °C | 228 ± 3 and 241 ± 18 mLCH4/gCOD for Vulgaris and Scenedesmus resp. | [39,40] |
| 12 | Only co-digestion | Microalgae and primary sludge | Microalgae to sludge ratio (25%/75% vs.-based) HRT = 20 days, BMP Temp = 37 ± 1 °C, OLR = 1.89 ± 0.26 kg VS/m3·day | 0.33 ± 0.05 m3 CH4/kg VS | [41] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Damtie, M.M.; Shin, J.; Jang, H.M.; Kim, Y.M. Synergistic Co-Digestion of Microalgae and Primary Sludge to Enhance Methane Yield from Temperature-Phased Anaerobic Digestion. Energies 2020, 13, 4547. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13174547
Damtie MM, Shin J, Jang HM, Kim YM. Synergistic Co-Digestion of Microalgae and Primary Sludge to Enhance Methane Yield from Temperature-Phased Anaerobic Digestion. Energies. 2020; 13(17):4547. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13174547
Chicago/Turabian StyleDamtie, Mekdimu Mezemir, Jingyeong Shin, Hyun Min Jang, and Young Mo Kim. 2020. "Synergistic Co-Digestion of Microalgae and Primary Sludge to Enhance Methane Yield from Temperature-Phased Anaerobic Digestion" Energies 13, no. 17: 4547. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13174547
APA StyleDamtie, M. M., Shin, J., Jang, H. M., & Kim, Y. M. (2020). Synergistic Co-Digestion of Microalgae and Primary Sludge to Enhance Methane Yield from Temperature-Phased Anaerobic Digestion. Energies, 13(17), 4547. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13174547