A Review of the Power Converter Interfaces for Switched Reluctance Machines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Two-Level Converters
2.1. A—Bridge Topologies
- Asymmetrical half-bridge (classical one)
- Shared phase winding
- Shared switch (Miller converter)
- Full-bridge (H-bridge)
- Conventional Three-Phase Bridge
2.2. B—Capacitive Topologies
- C-Dump
- Sood
- Split DC
- Buck-Boost
2.3. C—Magnetic topologies
- Bifilar
- Auxiliary winding
2.4. D—Dissipative Topologies
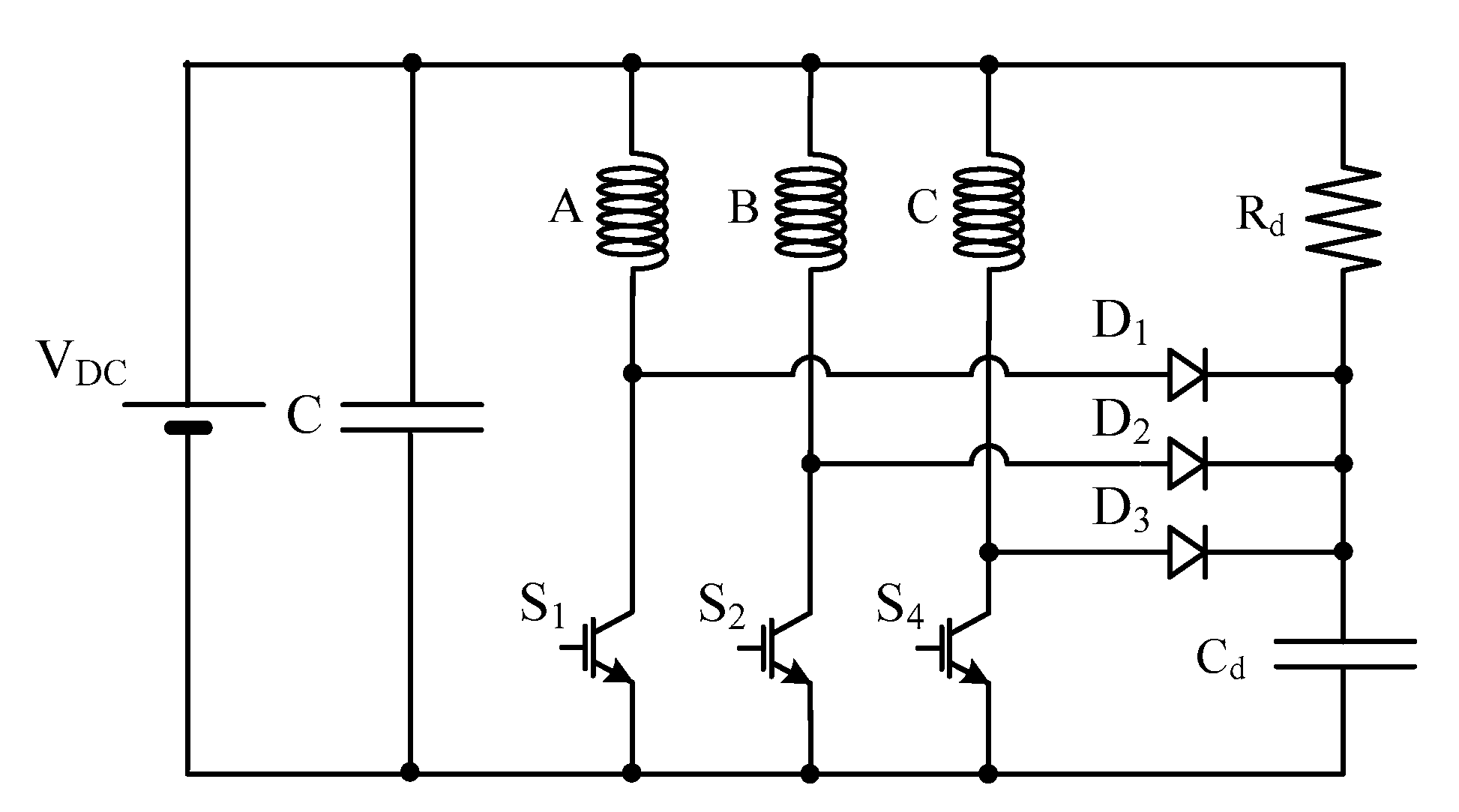
- R-Dump
3. Multilevel Converters
4. Converters Based on Impedance Source Network
5. Converters with Fault-Tolerant Capability
5.1. Power Converters with Controlled Power Semiconductors and Static (or Mechanical) Switches
5.2. Solutions Using Only Controlled Power Semiconductors
5.3. Solutions Combining Modified Converters and Modified SRMs
5.4. Comparative Summary of the Several Fault-Tolerant Topologies
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bostanci, E.; Moallem, M.; Parsapour, A.; Fahimi, B. Opportunities and challenges of switched reluctance motor drives for electric propulsion: A comparative study. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2017, 3, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seon, H.G.; Han, M.S.; Ahn, H.J.; Kim, J.; Lim, Y.C. Efficiency enhancement of a low-voltage automotive vacuum cleaner using a switched reluctance motor. Energies 2016, 9, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inderka, R.B.; Menne, M.; De Doncker, R.W. Control of switched reluctance drives for electric vehicle applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2002, 49, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezig, A.; Boudendouna, W.; Djerdir, A.; N’Diaye, A. Investigation of optimal control for vibration and noise reduction in-wheel switched reluctance motor used in electric vehicle. Math. Comput. Simul. 2020, 167, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlioglu, B.; Morris, C.T. More electric aircraft: Review, challenges, and opportunities for commercial transport aircraft. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2015, 1, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolo, J.B.; Degano, M.; Espina, J.; Gerada, C. Design and initial testing of a high-speed 45-kW switched reluctance drive for aerospace application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castano, S.M.; Yang, R.; Mak, C.; Bilgin, B.; Emadi, A. External-rotor switched reluctance motor for direct-drive home appliances. In Proceedings of the IECON 2018—44th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Washington, DC, USA, 21–23 October 2018; pp. 514–521. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, K.; Lee, D.; Ahn, J. Characteristic analysis of a novel single-phase hybrid SRM for blender application. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo, Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific), Bangkok, Thailand, 6–9 June 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas, R.; Pena, R.; Perez, M.; Clare, J.; Asher, G.; Wheeler, P. Power smoothing using a flywheel driven by a switched reluctance machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.; Wang, J.; Hu, K.; Liaw, C. Development and operation control of a switched-reluctance motor driven flywheel. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, J.; Andrade, R.; Rolim, L.; Ferreira, A.; Sotelo, G.; Suemitsu, W. Experimental validation of a dynamic model of a SRM used in superconducting bearing flywheel energy storage system. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Montreal, QC, Canada, 9–13 July 2006; pp. 2492–2497. [Google Scholar]
- Greenhough, P. Switched reluctance variable speed drives-a focus on applications. Min. Technol. 1996, 78, 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Elhomdy, E.; Li, G.; Liu, J.; Bukhari, S.A.; Cao, W.P. Design and experimental verification of a 72/48 switched reluctance motor for low-speed direct-drive mining applications. Energies 2018, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, Y. Development of a 2-degree-of-freedom rotational/linear switched reluctance motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2007, 43, 2564–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C. Topology analysis and performance evaluation of a high thrust force density linear switched reluctance machine for low cost conveyor applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 17th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Hangzhou, China, 22–25 October 2014; pp. 1283–1288. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Xiong, L. Performance analysis of a dual stator linear switch reluctance machine with rectangular segments considering force ripples for long stroke conveyor applications. In Proceedings of the 2015 18th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Pattaya, Thailand, 25–28 October 2015; pp. 295–298. [Google Scholar]
- Rafael, S.; Costa Branco, P.J.; Pires, A.J. Sliding mode angular position control for an 8/6 switched reluctance machine: Theoretical concept, design and experimental results. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2015, 129, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogusz, P.; Korkosz, M.; Prokop, J. Performance analysis of Switched Reluctance Motor with asymmetric stator. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Gdansk, Poland, 27–30 June 2011; pp. 661–666. [Google Scholar]
- Bogusz, P.; Korkosz, M.; Prokop, J. The study on the switched reluctance motor use in the food processor drive. Prz. Elektrotechniczny 2009, 85, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bogusz, P.; Korkosz, M.; Prokop, J. Chosen research results of switched reluctance motor with asymmetric stator magnetic circuit. In Proceedings of the 2015 Selected Problems of Electrical Engineering and Electronics (WZEE), Kielce, Poland, 17–19 September 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.Y.; Jung, Y.C.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, Y.W.; Min, J.C. High efficiency and low-cost switched reluctance motor for air-conditioner blower. In Proceedings of the Power Conversion Conference—Osaka 2002 (Cat. No.02TH8579), Osaka, Japan, 2–5 April 2002; Volume 3, pp. 1460–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Xu, G.; Jian, L.; Li, L. Electric air conditioner system with on-board charger for PHEV. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Shenzhen, China, 6–8 June 2011; pp. 421–426. [Google Scholar]
- Cordeiro, A.; Chaves, M.; Canacsinh, H.; Luis, R.; Pires, V.; Foito, D.; Pires, A.; Martins, J. Hybrid Sepic-Ćuk DC-DC converter associated to a SRM drive for a solar PV powered water pumping system. In Proceedings of the 2019 8th International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Applications (ICRERA), Brasov, Romania, 3–6 November 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Mishra, A.K.; Kumar, R. Solar powered water pumping system employing switched reluctance motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 3949–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, X.; Wu, N.; Xu, R.; Cui, M.; Jiang, Z.; Ni, K.; Alkahtani, M. Design and analysis of a novel converter topology for photovoltaic pumps based on switched reluctance motor. Energies 2019, 12, 2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardenas, R.; Pena, R.; Perez, M.; Clare, J.; Asher, G.; Wheeler, P. Control of a switched reluctance generator for variable-speed wind energy applications. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2005, 20, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos Barros, T.A.; dos Santos Neto, P.J.; Nascimento Filho, P.S.; Moreira, A.B.; Filho, E.R. An approach for switched reluctance generator in a wind generation system with a wide range of operation speed. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 8277–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato, P.; Dente, J.A.; Martins, J.F.; Pires, A.J. Scale models formulation of switched reluctance generators for low speed energy converters. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2015, 9, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellaban, O.; Abu-Rub, H. Switched reluctance motor converter topologies: A review. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (CIT), Busan, South Korea, 26 February–1 March 2014; pp. 840–846. [Google Scholar]
- Cabezuelo, D.; Andreu, J.; Kortabarria, I.; Ibarra, E.; Garate, I. SRM converter topologies for EV application: State of the technology. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 26th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Edinburgh, UK, 19–21 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, K.; Lee, C.; Kim, J.; Krishnan, R.; Oh, S. Design and development of low-cost and high-efficiency variable-speed drive system with switched reluctance motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2007, 43, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.; Pollock, C. Power electronic converters for switched reluctance drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1998, 13, 1100–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Farzan Moghaddam, A.; Hussein Mohamed, A.; Nabil Ibrahim, M.; Sergeant, P.; Van den Bossche, A. Controlling a switched reluctance motor with a conventional three-phase bridge instead of asymmetric H-bridges. Energies 2018, 11, 3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Moghaddam, A.F.; Sergeant, P.; den Bossche, A.V. A novel driving method for switched reluctance motor with standard full bridge inverter. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, G.; Chen, H.; Guan, G. Generalised fault diagnostic method for power transistors in asymmetric half-bridge power converter of SRM drive. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2019, 13, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, W.; Huang, B. Integrated Driving/Charging/Discharging Battery-Powered Four-Phase Switched Reluctance Motor Drive With Two Current Sensors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 5019–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabovcová, V.; Rafajdus, P.; Lipták, M.; Szabó, L. Performance of converters suitable for switched reluctance generator (SGR) operation. J. Electr. Eng. 2013, 64, 201–211. [Google Scholar]
- Marinkov, S.; de Jager, B. Four-quadrant control of 4/2 switched reluctance machines. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7393–7403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K. Electric Vehicle Machines and Drives: Design, Analysis and Application; Wiley: Singapore, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pittermann, M.; Fort, J.; Diesl, J.; Pavlicek, V. Converters for switched reluctance motor—Topology comparison. In Proceedings of the 2018 18th International Conference on Mechatronics—Mechatronika (ME), Brno, Czech Republic, 5–7 December 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Cheung, N.C.; Cheng, K.W.E.; Xue, X.D.; Lin, J.K.; Bao, Y.J. Analysis and design of a cost effective converter for switched reluctance motor drives using component sharing. In Proceedings of the 2011 4th International Conference on Power Electronics Systems and Applications, Hong Kong, China, 8–10 June 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pollock, C.; Williams, B.W. Power convertor circuits for switched reluctance motors with the minimum number of switches. IEE Proc. B Electr. Power Appl. 1990, 137, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.; Michaelides, A.M.; Pollock, C. The design and performance of a self-starting 2-phase switched reluctance drive. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Power Electronics and Variable Speed Drives, Nottingham, UK, 23–25 September 1996; pp. 419–423. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, J.W.; Liang, J.; Lee, D.H. Classification and analysis of switched reluctance converters. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2010, 5, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Hu, K.; Liaw, C. On a battery/supercapacitor powered SRM drive for EV with integrated on-board charger. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Seville, Spain, 17–19 March 2015; pp. 2667–2672. [Google Scholar]
- Kamalakannan, C.; Kamaraj, V.; Paramasivam, S.; Paranjothi, S.R. Switched reluctance machine in automotive applications—A technology status review. In Proceedings of the 2011 1st International Conference on Electrical Energy Systems (ICEES), Newport Beach, CA, USA, 3–5 January 2011; pp. 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- Mir, S.; Husain, I.; Elbuluk, M.E. Energy-efficient C-dump converters for switched reluctance motors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1997, 12, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczewski, K.; Wrobel, K. Improved C-dump converter for switched reluctance motor drives. IET Power Electron. 2014, 7, 2628–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Mishra, A.K. Performance analysis of a solar-powered water pumping using improved SIDO buck–boost converter. IET Power Electron. 2019, 12, 2904–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhumal, K.R.; Dhamse, S.S. Solar PV array based water pumping by using SRM drive: A review. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Computation of Power, Energy, Information and Communication (ICCPEIC), Chennai, India, 28–29 March 2018; pp. 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Elwakil, E.S.; Darwish, M.K. Critical review of converter topologies for switched reluctance motor drives. Int. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2007, 2, 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopal, S.; Dash, S.S. Implementation of low cost single switch based switched reluctance motor drive. In Power Electronics and Renewable Energy Systems; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2015; pp. 1077–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Kavitha, P.; Umamaheswari, B. R dump converter without DC link capacitor for an 8/6 SRM: Experimental investigation. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 393629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahmoud, S.M.; El-Sherif, M.Z.; Abdel-Aliem, E.S.; Nashed, M.N. Studying different types of power converters fed switched reluctance motor. Int. J. Electron. Electr. Eng. 2013, 1, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Materu, P.N. Analysis and design of a low-cost converter for switched reluctance motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1993, 29, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, C. PWM control of switched reluctance motor drive system at four quadrants. Int. J. Adv. Syst. Sci. Appl. 2000, 1, 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins, S.J.; Corda, J.; Zhang, L. Multilevel asymmetric power converters for switched reluctance machines. In Proceedings of the 2002 International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives, Sante Fe, NM, USA, 4–7 June 2002; pp. 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Borecki, J.; Orlik, B. Novel, multilevel converter topology for fault-tolerant operation of switched reluctance machines. In Proceedings of the 2017 11th IEEE International Conference on Compatibility, Power Electronics and Power Engineering (CPE-POWERENG), Cadiz, Spain, 4–6 April 2017; pp. 375–380. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, D.; Wang, S.; Gu, L. Multilevel converter topologies for high-power high-speed switched reluctance motor: Performance comparison. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, 20–24 March 2016; pp. 2889–2896. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, N.; Hoshi, N. Experimental verification on a switched reluctance motor driven by asymmetric flying capacitor multilevel h-bridge inverter. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 6th International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Applications, San Diego, CA, USA, 5–8 November 2017; pp. 971–976. [Google Scholar]
- Korkosz, M.; Pakla, B. Multilevel converter for high-voltage high-speed switched reluctance motor. In Proceedings of the 2018 Innovative Materials and Technologies in Electrical Engineering (i-MITEL), Sulecin, Poland, 18–20 April 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Velmurugan, V.R. Performance analysis of SRM drive using multi level inverter. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Recent Advancements in Electrical, Electronics and Control Engineering, Sivakasi, India, 15–17 December 2011; pp. 532–535. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, C.; Sun, Q.; Wu, J.; Kong, W.; Shi, C.; Hu, Y. MMC-based SRM drives with decentralized battery energy storage system for hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 2608–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azer, P.; Bauman, J. An asymmetric three-level T-type converter for switched reluctance motor drives in hybrid electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Detroit, MI, USA, 19–21 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.; Yuan, K.; Yang, Q.; Yang, S. Open-circuit fault-tolerant control strategy based on five-level power converter for SRM system. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2019, 3, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aziz, A.A.; Ahmed, K.H.; Wang, S.; Massoud, A.M.; Williams, B.W. A neutral-point diode-clamped converter with inherent voltage-boosting for a four-phase SRM drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 5313–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Gan, C.; Cao, W.; Li, C.; Finney, S.J. Split converter-fed SRM drive for flexible charging in EV/HEV applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 6085–6095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Yang, S.; Hu, Y. Performance improvement for segmented-stator hybrid-excitation SRM drives using an improved asymmetric half-bridge converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 898–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, V.F.; Foito, D.; Pires, A.J.; Cordeiro, A.; Martins, J.F.; Chen, H. Multilevel converter fed SRM drive for single stage PV array based water pumping. In Proceedings of the IECON 2019—45th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 October 2019; pp. 6361–6366. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Peng, C.; Guo, Z.; Ma, R.; Liu, W. Direct instantaneous torque control of switched reluctance machine based on modular multi-level power converter. In Proceedings of the 2019 22nd International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Harbin, China, 11–14 August 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Wang, H.; Ahn, J. An advanced multi-level converter for four-phase SRM drive. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Rhodes, Greece, 15–19 June 2008; pp. 2050–2056. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, V.F.; Cordeiro, A.; Pires, A.J.; Martins, J.F.; Chen, H. A multilevel topology based on the T-type converter for SRM drives. In Proceedings of the 2018 16th Biennial Baltic Electronics Conference (BEC), Tallinn, Estonia, 8–10 October 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ellabban, O.; Abu-Rub, H. An overview for the Z-source converter in motor drive applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 61, 537–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, M.H. SRM drives using Z-source inverter with the simplified fuzzy logic rule base. Int. Electr. Eng. J. 2014, 5, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, F.; Cai, W. A quasi-Z-source integrated multiport power converter as switched reluctance motor drives for capacitance reduction and wide-speed-range operation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 7661–7676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, F.; Cai, W. A quasi-Z-source integrated multi-port power converter with reduced capacitance for switched reluctance motor drives. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, 20–24 March 2016; pp. 1057–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, W.; Yi, F. An integrated multiport power converter with small capacitance requirement for switched reluctance motor drive. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 3016–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi, M.; Rashidi, A.; Nejad, S.M.S.; Ebrahimi, M. A switched reluctance motor drive based on quasi Z-source converter with voltage regulation and power factor correction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 8330–8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, V.F.; Pires, A.J.; Martins, J.F.; Hao, C. A quasi-Z-source converter to feed a switched reluctance drive with multilevel voltages. In Proceedings of the IECON 2018—44th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Washington, DC, USA, 21–23 October 2018; pp. 3706–3711. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, B.V.R.; Sivakumar, K.; Karunanidhi, S. A new Dual Stator-Dual Rotor Switched Reluctance Motor for Electric vehicle propulsion. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics, Drives and Energy Systems (PEDES), Chennai, India, 18–21 December 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, R.; Jacobina, C.; Lima, A.; Silva, E. A strategy for improving Reliability of Motor Drive Systems Using a Four-Leg Three-Phase Converter. In Proceedings of the APEC 2001 16th Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, Anaheim, CA, USA, 4–8 March 2001; pp. 385–391. [Google Scholar]
- Priya, S.S.; Dhanasekaran, R.; Muthulakshmi, S. Simulation modelling and fault analysis of switched reluctance motor. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Advanced Communication Control and Computing Technologies (ICACCCT), Ramanathapuram, India, 25–27 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, C.M. Fault detection and management systems for fault-tolerant switched reluctance motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1991, 27, 1098–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lequesne, B.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Omekanda, A.M. Classification and remediation of electrical faults in the switched reluctance drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 42, 479–486. [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Delgado, D.U.; Espinoza-Trejo, D.R. An observer-based diagnosis scheme for single and simultaneous open-switch faults in induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Blaabjerg, F. Reliability of capacitors for DC-link applications in power electronic converters—An overview. IEEE Trans. Ind. A 2014, 50, 3569–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azer, P.; Ye, J.; Emadi, A. Advanced fault-tolerant control strategy for switched reluctance motor drives. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cordeiro, A.; Pires, V.F.; Pires, A.J.; Martins, J.F.; Chen, H. Fault-tolerant voltage-source-inverters for switched reluctance motor drives. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 13th International Conference on Compatibility, Power Electronics and Power Engineering (CPE-POWERENG), Sonderborg, Denmark, 23–25 April 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, N.; Gao, Q.; Xu, C.; Makys, P.; Stulrajter, M. Fault diagnosis and tolerant control for power converter in SRM drives. J. Eng. 2018, 2018, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gameiro, N.S.; Marques Cardoso, A.J. Fault tolerant power converter for switched reluctance drives. In Proceedings of the 2008 18th International Conference on Electrical Machines, Vilamoura, Portugal, 6–9 September 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, V.F.; Amaral, T.G.; Cordeiro, A.; Foito, D.; Pires, A.J.; Martins, J.F. Fault-tolerant SRM drive with a diagnosis method based on the entropy feature approach. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wu, J.; Gan, C.; Guo, J. Modular full-bridge converter for three-phase switched reluctance motors with integrated fault-tolerance capability. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 2622–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernão Pires, V.; Cordeiro, A.; Foito, D.; Pires, A.J.; Martins, J.; Chen, H. A multilevel fault-tolerant power converter for a switched reluctance machine drive. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 21917–21931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Gan, C.; Cao, W.; Li, W.; Finney, S.J. Central-tapped node linked modular fault-tolerance topology for SRM applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 1541–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Gan, C.; Cao, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Finney, S.J. Flexible fault-tolerant topology for switched reluctance motor drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 4654–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruba, M.; Oprea, C.; Szabo, L. Comparative study on switched reluctance machine based fault-tolerant electrical drive systems. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference, Miami, FL, USA, 3–6 May 2009; pp. 987–992. [Google Scholar]
- Ruba, M.; Bentia, I.; Szabó, L. Novel modular switched reluctance machine for safety-critical applications. In Proceedings of the XIX International Conference on Electrical Machines—ICEM 2010, Rome, Italy, 6–8 September 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.; Hu, Y.; Wu, L. Investigation and experimental test of fault-tolerant operation of a mutually coupled dual three-phase SRM drive under faulty conditions. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6857–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xu, D.; Xu, L.; Wang, J.; Lin, Z.; Zhu, X. Fault-tolerant operation of a novel dual-channel switched reluctance motor using two 3-phase standard inverters. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2018, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Liu, C.; Wang, K. A novel low-cost and high-performance converter topology for six-phase SRM. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Hangzhou, China, 17–20 October 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]



































| Topology | N° of Switches | Designed for Any Number of Windings | Control Complexity | Fault Tolerance | Machine with Special Design |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Figure 2 [35,36,37,38] | 2/phase | Yes | Low | High | No |
| Figure 3 [29,40,41] | 1/phase | No | Medium | Low | No |
| Figure 4a [42,43] | 1/phase + 1 | Yes | Low | Low | No |
| Figure 4b [42,43] | 1,5/phase | Yes | Low | Low | No |
| Figure 5 [44,45] | 4/phase | Yes | Medium | High | No |
| Figure 6 [33,34] | 2/phase + 2 | No | High | Low | No |
| Figure 7 [46,47,48] | 1/phase + 1 | Yes | Medium | Low | No |
| Figure 8 [29] | 1/phase + 1 | Yes | High | Low | No |
| Figure 9 [49,50,51] | 1/phase | No | Medium | Low | No |
| Figure 10 [52] | 1/phase + 1 | Yes | High | Low | No |
| Figure 11 [51] | 1/phase | Yes | High | High | Yes |
| Figure 12 [52] | 2/phase | Yes | Medium | High | Yes |
| Figure 13 [53,54,55,56] | 1/phase | Yes | Low | High | No |
| Topology | Converter Modularity | Boost Capability | N° of Switches (Machine with 4 Windings) | DC Voltage Sources | Designed for Any Number of Windings | Control Complexity | Machine with Special Design |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Figure 14a [57,58,59] | No | No | 16 | 1 | Yes | Medium | No |
| Figure 14b [59,60] | No | No | 16 | 1 | Yes | Medium | No |
| Figure 14c [59,61,62] | Yes | No | 16 | 5 | Yes | Low | No |
| Figure 14d [59,63] | Yes | No | 18 | 2 | yes | Low | No |
| Figure 15 [64,65] | No | No | 16 | 1 | Yes | Medium | No |
| Figure 16a [66] | No | Yes | 13 | 1 | No | High | No |
| Figure 16b [67] | No | No | 8 | 2 | No | High | Yes |
| Figure 17a [68] | No | Yes | 9 | 1 | Yes | High | No |
| Figure 17b [69] | No | Yes | 8 | 1 | No | High | No |
| Figure 17c [70] | No | Yes | 12 | 1 | Yes | High | No |
| Figure 18a [71] | No | No | 8 | 1 | No | Medium | No |
| Figure 18b [72] | No | No | 6 | 1 | No | Medium | No |
| Topology | N° of Switches | Decouple of Magnetization and Demagnetization Port | Multilevel Operation Capability | Capacitors with Reduced Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Figure 19a [75,76] | 9 | No | No | No |
| Figure 19b [77] | 6 | No | No | No |
| Figure 20 [78] | 8 | Yes | No | Yes |
| Figure 21a [79] | 13 | Yes | Yes | No |
| Figure 21b [79] | 13 | Yes | Yes | No |
| Topology | Full FT Capability | Open- Circuit Faults | Short- Circuit Faults | Multiple Faults | Additional Controlled Power Semicond. Switches (a) | Number of Static Switches | Designed for any Number of Windings | Control Complexity | Machine with Special Design |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Figure 22 [87] | Yes | Yes | No | Yes (c) | 2 | 2/Phase | Yes | Low | No |
| Figure 23a [88] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 2 | 2/Phase | Yes | Low | No |
| Figure 23b [88] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 2 | 4/Phase | Yes | Low | No |
| Figure 24 [89] | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | 4 | 4/Phase | Yes | Low | No |
| Figure 25 [90] | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | 0 | 1/Phase | No | Low | No |
| Figure 26 [91] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 2 | 4/Phase | Yes | Low | No |
| Figure 27 [92] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes (b) | 6 | 4 | Yes | Medium | No |
| Figure 28 [93] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 6/Phase | 0 | Yes | Medium | No |
| Figure 29 [94] | Yes (b) | Yes | Yes | Yes (c) | 2/Phase | 0 | Yes | High | Yes |
| Figure 30 [95] | Yes (c) | Yes | Yes | Yes (d) | 4 | 2/Phase | Yes | Medium | Yes |
| Figure 31 [96] | Yes | Yes | No | Yes (b) | 6/Phase | 0 | Yes | Medium | Yes |
| Figure 32 [98] | Yes (b) | Yes | No | Yes (c) | 0 | 0 | Yes | Low | Yes |
| Figure 33 [99] | Yes | Yes | No | Yes (b) | 2/Phase | 0 | Yes | High | Yes |
| Figure 34 [100] | Yes (c) | Yes | No | Yes (d) | 2 | 0 | No | High | Yes |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pires, V.F.; Pires, A.J.; Cordeiro, A.; Foito, D. A Review of the Power Converter Interfaces for Switched Reluctance Machines. Energies 2020, 13, 3490. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13133490
Pires VF, Pires AJ, Cordeiro A, Foito D. A Review of the Power Converter Interfaces for Switched Reluctance Machines. Energies. 2020; 13(13):3490. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13133490
Chicago/Turabian StylePires, Vitor Fernão, Armando José Pires, Armando Cordeiro, and Daniel Foito. 2020. "A Review of the Power Converter Interfaces for Switched Reluctance Machines" Energies 13, no. 13: 3490. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13133490
APA StylePires, V. F., Pires, A. J., Cordeiro, A., & Foito, D. (2020). A Review of the Power Converter Interfaces for Switched Reluctance Machines. Energies, 13(13), 3490. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13133490






