The Two-Phase Conical Swirl Atomizers: Spray Characteristics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Flow Characteristics
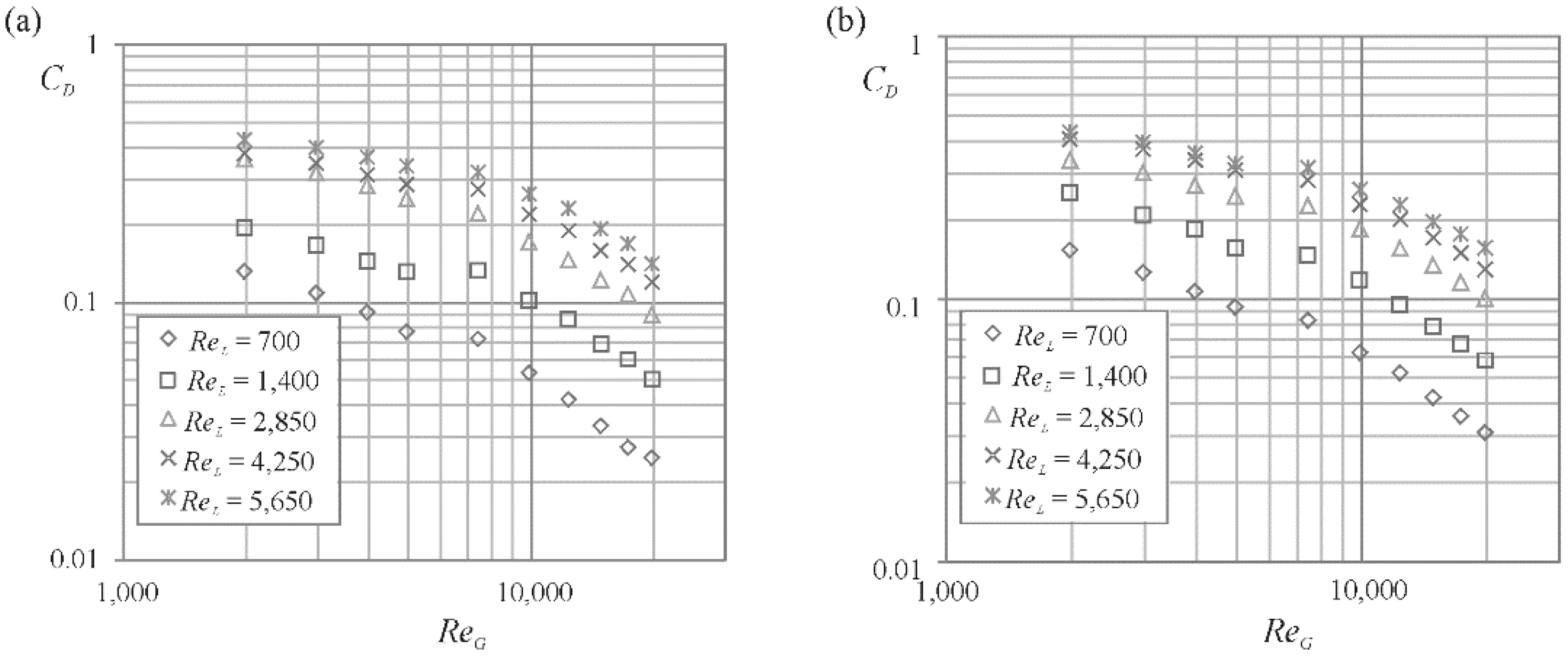
3.2. Discharge Coefficient
3.3. Spray Angle
3.4. Volume Distributions of the Size of Spraydroplets
3.5. Radial Distributions of the Size of Spray Droplets
3.6. Sauter Mean Diameter
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lefebvre, A.H.; Ballal, D.R. Gas Turbine Combustion. Alternative Fuels and Emissions; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Orzechowski, Z.; Prywer, J. Spraying Liquid; WNT: Warsaw, Poland, 1991. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Koch, R.; Noworyta, A. Mechanical Processes in Chemical Engineering; WNT: Warsaw, Poland, 1998. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Bayvel, L.; Orzechowski, Z. Liquid Atomization; Taylor & Francis Inc.: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Jedelsky, J. Some Aspects of Effervescent Atomization: Experimental Study Short Version of Habilitation Thesis. D.Sc. Thesis, Brno University of Technology, Brno, Czech Republic, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. Science and Engineering of Droplets—Fundamentals and Applications; William Andrew Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Orzechowski, Z.; Prywer, J. Production and Use of; WNT: Warsaw, Poland, 2008. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Ochowiak, M.; Krupińska, A.; Włodarczak, S.; Matuszak, M.; Szulc, T. Analysis of spatial distribution of the size of droplets generated by two-phase atomizers with swirl flow. Chem. Eng. Equip. 2018, 57, 34–35. [Google Scholar]
- Grausz, T.W. Chemistry for Farmers BHP. National Labor Inspectorate; Main Labor Inspectorate: Warsaw, Poland, 2015. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Huang, Q.; Liu, B. A pest control model with birth pulse and residual and delay effects of pesticides. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2019, 117, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Song, S.R.; Sun, D.Z.; Xue, X.Y.; Dai, Q.F.; Li, Z. Effects of Liquid Viscosity on Agricultural Nozzle Droplet Parameters. Agric. Sci. 2019, 10, 1217–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, G.M.; Mun, R.; Cooper, G.; Boger, D.V. A note on the effect of polymer rigidity and concentration on spray atomisation. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 1999, 85, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, R. The effects of polymer concetration and molecular weight on the brakup of laminar capillary jets. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 1998, 74, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, A.; Łuczycka, D.; Owsiak, Z.; Cieniawska, B. Effect of droplet size on coverage of sprayed objects. Prog. Plant Prot. 2013, 53, 822–828. [Google Scholar]
- Ramamurthi, K.; Sarkar, U.K.; Raghunandan, B.N. Performance characteristics of effervescent atomizer in different flow regimes. At. Sprays 2009, 19, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, E.; Brenn, G. Viscous flow through the swirl chamber of a pressure-swirl atomizer. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2013, 53, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiou, A.; Hills, N.J.; Long, C.A.; Turner, A.B.; Wong, L.S.; Millward, J.A. Discharge coefficients for flow through holes normal to a rotating shaft. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2000, 21, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, M.; Takamoto, M. Theoretical discharge coefficient of a critical circular-arc nozzle with laminar boundary layer and its verification by measurements using super-accurate nozzles. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2000, 11, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.K.; Lefebvre, A.H. Discharge coefficients for plain-orifice effervescent atomizers. At. Sprays 1994, 4, 275–290. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, A.H. Atomization and Sprays; Hemisphere Publishing Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Jedelsky, J.; Jicha, M. Prediction of discharge coefficient of internally-mixed twin-fluid atomizers. In Proceedings of the 24th European Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems ILASS-Europe, Lisbon/Estoril, Portugal, 5–7 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.J.; Oh, S.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; James, S.C.; Yoon, S.S. Measuring air core characteristics of a pressure-swirl atomizer via a transparent acrylic nozzle at various Reynolds numbers. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2010, 34, 1475–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochowiak, M. The Analysis of Liquid Atomization in Effervescent and Effervescent-Swirl Atomizers. Habilitation Thesis, Rozprawy Nr 519, Wydawnictwo Politechniki Poznańskiej, Poznań, Poland, 2014. (In Polish). [Google Scholar]
- Ochowiak, M.; Broniarz-Press, L.; Różański, J. The discharge coefficient of effervescent atomizers. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2010, 34, 1316–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinn, J.J. The Numeric of the Swirl Atomizer. In Proceedings of the 22th European Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems ILASS-Europe, Como Lake, Italy, 8–10 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Broniarz-Press, L.; Ochowiak, M.; Włodarczak, S.; Matuszak, M.; Maciejewska, A. Analysis of spray angle in pressure-swirl atomizers. Chem. Eng. Equip. 2014, 53, 227–228. [Google Scholar]
- Ochowiak, M.; Broniarz-Press, L.; Różańska, S.; Matuszak, M.; Włodarczak, S. Characteristics of spray angle for effervescent-swirl atomizers. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2015, 98, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavaises, M.; Abo-Serie, E.; Arcoumanis, C. Nozzle hole film formation and its link to spray characteristics in swirl-pressure atomizers for direct injection gasoline engines. Trans. J. Engines 2002, 111, 1942–1954. [Google Scholar]
- Arcoumanis, C.; Gavaises, M. Pressure-swirl atomizers for DISI engines: Further modelling and experiments. Trans. J. Engines 2000, 109, 1225–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Schick, R.J. Spray Technology Reference Guide: Understanding Drop Size; Spraying Systems Co.: Wheaton, IL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pacek, A.W.; Man, C.C.; Nienow, A.W. On the Sauter mean diameter and size distributions in turbulent liquid/liquid dispersions in a stirred vessel. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1998, 53, 2005–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafsari, R.A.; Lee, H.J.; Han, J.; Park, D.C.; Lee, J. Viscosity effect on the pressure swirl atomization of an alternative aviation fuel. Fuel 2019, 240, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasuja, A.K. Atomization of crude and residual fuel oils. ASME J. Eng. Power 1979, 101, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Lefebvre, A.H. Mean drop sizes from pressure-swirl nozzles. AIAA J. Propuls. Power 1987, 3, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, F.; Yang, J.; Mu, Y.; Hu, C.; Xu, G. Experimental investigations of spray generated by a pressure swirl atomizer. J. Energy Inst. 2019, 92, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumouchel, C.; Bloor, M.I.G.; Dombrowski, N.; Ingham, D.B.; Ledoux, M. Viscous flow in a swirl atomizer. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1993, 48, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaeimoghaddam, M.; Moin, H.; Modarres Razavi, M.R.; Pasandideh-Fard, M.; Elahi, R. Optimization of a high pressure swirl injector by using volume-of-fluid (VOF) method. In Proceedings of the ASME 2010 10th Biennial Conference on Engineering Systems Design and Analysis ESDA2010, Istanbul, Turkey, 12–14 July 2010; ESDA2010-24614. pp. 435–445. [Google Scholar]
- Arcoumanis, C.; Gavaises, M.; Argueyrolles, B.; Galzin, F. Modelling of pressure-swirl atomisers for GDI engines. Trans. J. Engines 1999, 108, 516–532. [Google Scholar]
- Le Coz, J.F.; Hermant, L. Visualisation of sprays generated by direct injection gasoline injectors. In Proceedings of the 14th Annual Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems ILASS-Europe, Toulouse, France, 5–7 July 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Gavaises, M.; Arcoumanis, C. Modelling of sprays from high-pressure swirl atomisers. Int. J. Engine Res. 2001, 2, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousin, J.; Ren, W.M.; Nally, S. Transient flows in high pressure swirl injectors. SAE Tech. Pap. 1998, 980499. [Google Scholar]
- Rashad, M.; Yong, H.; Zekun, Z. Effect of geometric parameters on spray characteristics of pressure swirl atomizers. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 15790–15799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Bai, B. Swirl decay in the gas–liquid two-phase swirling flow inside a circular straight pipe. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2015, 68, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochowiak, M. The experimental study on the viscosity effect on the discharge coefficient for effervescent atomizers. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2013, 50, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broniarz-Press, L.; Ochowiak, M.; Włodarczak, S.; Markuszewska, M. Analysis of the liquid outflow coefficient for swirl atomizers with different shapes of the outlet orifice. Chem. Eng. Equip. 2013, 52, 403–404. [Google Scholar]
- Haddadi, H.; Rahimpour, M. A discharge coefficient for a trapezoidal broad-crested side weir in subcritical flow. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2012, 26, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhivyaraja, K.; Gaddes, D.; Freeman, E.; Tadigadapa, S.; Panchagnula, M.V. Dynamical similarity and universality of drop size and velocity spectra in sprays. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 860, 510–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafsari, R.A.; Lee, H.J.; Han, J.; Lee, J. Evaluation of the atomization characteristics of aviation fuels with different viscosities using a pressure swirl atomizer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 145, 118704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkotb, M.M.; Rafat, N.M.; Hanna, M.A. The influence of swirl atomizer geometry on the atomization performance. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 27–31 August 1978; pp. 109–115. [Google Scholar]














| Atomizer | Diameter of Chamber DS [mm] | Height of Chamber HS [mm] |
|---|---|---|
| SA-1 | 20 ± 0.1 | 20 ± 0.1 |
| SA-2 | 20 ± 0.1 | 40 ± 0.1 |
| SA-3 | 20 ± 0.1 | 60 ± 0.1 |
| SA-4 | 20 ± 0.1 | 70 ± 0.1 |
| SA-5 | 20 ± 0.1 | 80 ± 0.1 |
| SA-6 | 40 ± 0.1 | 20 ± 0.1 |
| SA-7 | 40 ± 0.1 | 40 ± 0.1 |
| SA-8 | 40 ± 0.1 | 60 ± 0.1 |
| SA-9 | 40 ± 0.1 | 80 ± 0.1 |
| value | |
| A | 0.050 |
| B | −0.007 |
| C | 0.062 |
| D | 0.110 |
| E | 0.106 |
| value | |
| A | 0.186 |
| B | −1.735 |
| C | 0.020 |
| D | 0.040 |
| E | 0.529 |
| value | |
| A | 0.504 |
| B | 0.083 |
| C | 0.026 |
| D | −0.915 |
| E | 0.038 |
| value | |
| A | 0.246 |
| B | 0.834 |
| C | 0.017 |
| D | −1.011 |
| E | 0.427 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ochowiak, M.; Krupińska, A.; Włodarczak, S.; Matuszak, M.; Markowska, M.; Janczarek, M.; Szulc, T. The Two-Phase Conical Swirl Atomizers: Spray Characteristics. Energies 2020, 13, 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13133416
Ochowiak M, Krupińska A, Włodarczak S, Matuszak M, Markowska M, Janczarek M, Szulc T. The Two-Phase Conical Swirl Atomizers: Spray Characteristics. Energies. 2020; 13(13):3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13133416
Chicago/Turabian StyleOchowiak, Marek, Andżelika Krupińska, Sylwia Włodarczak, Magdalena Matuszak, Małgorzata Markowska, Marcin Janczarek, and Tomasz Szulc. 2020. "The Two-Phase Conical Swirl Atomizers: Spray Characteristics" Energies 13, no. 13: 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13133416
APA StyleOchowiak, M., Krupińska, A., Włodarczak, S., Matuszak, M., Markowska, M., Janczarek, M., & Szulc, T. (2020). The Two-Phase Conical Swirl Atomizers: Spray Characteristics. Energies, 13(13), 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13133416








