Energy Management Strategies for Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Review, Classification, Comparison, and Outlook
Abstract
1. Introduction
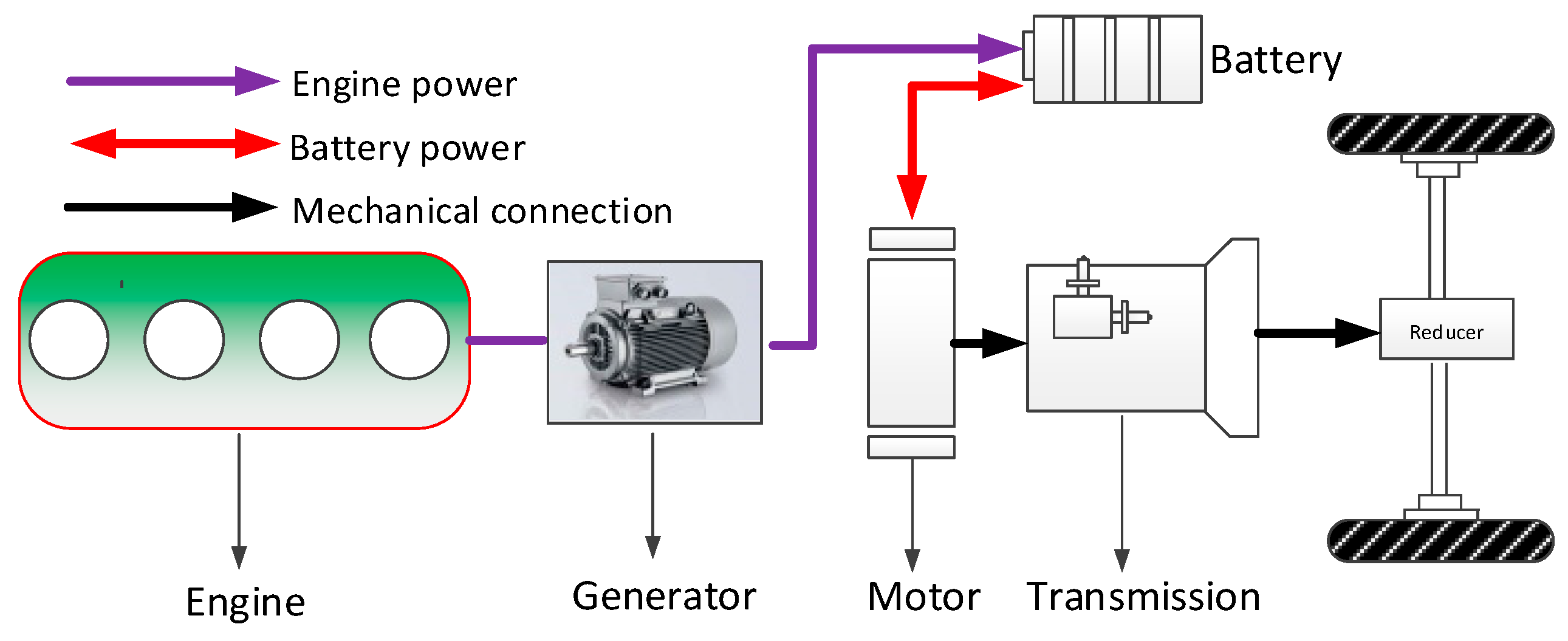
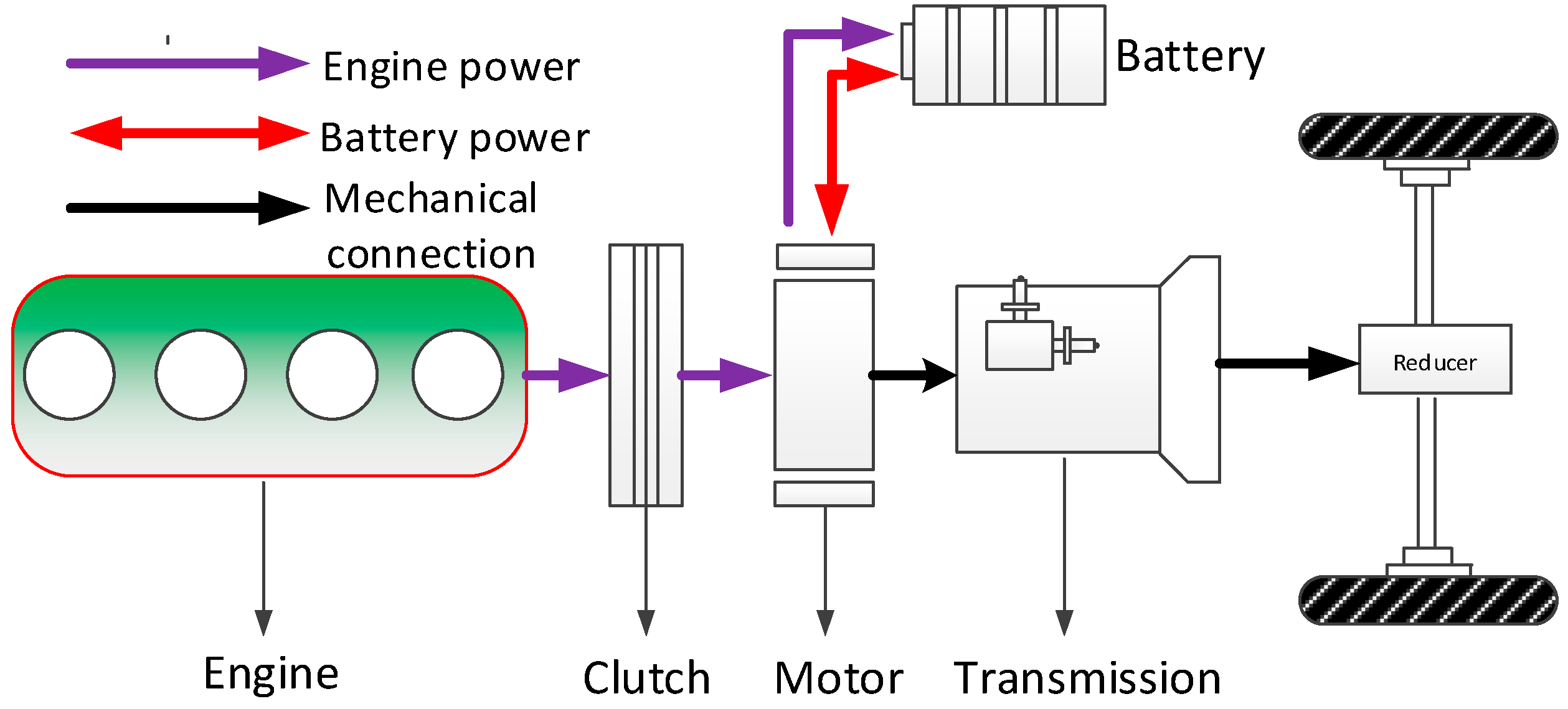
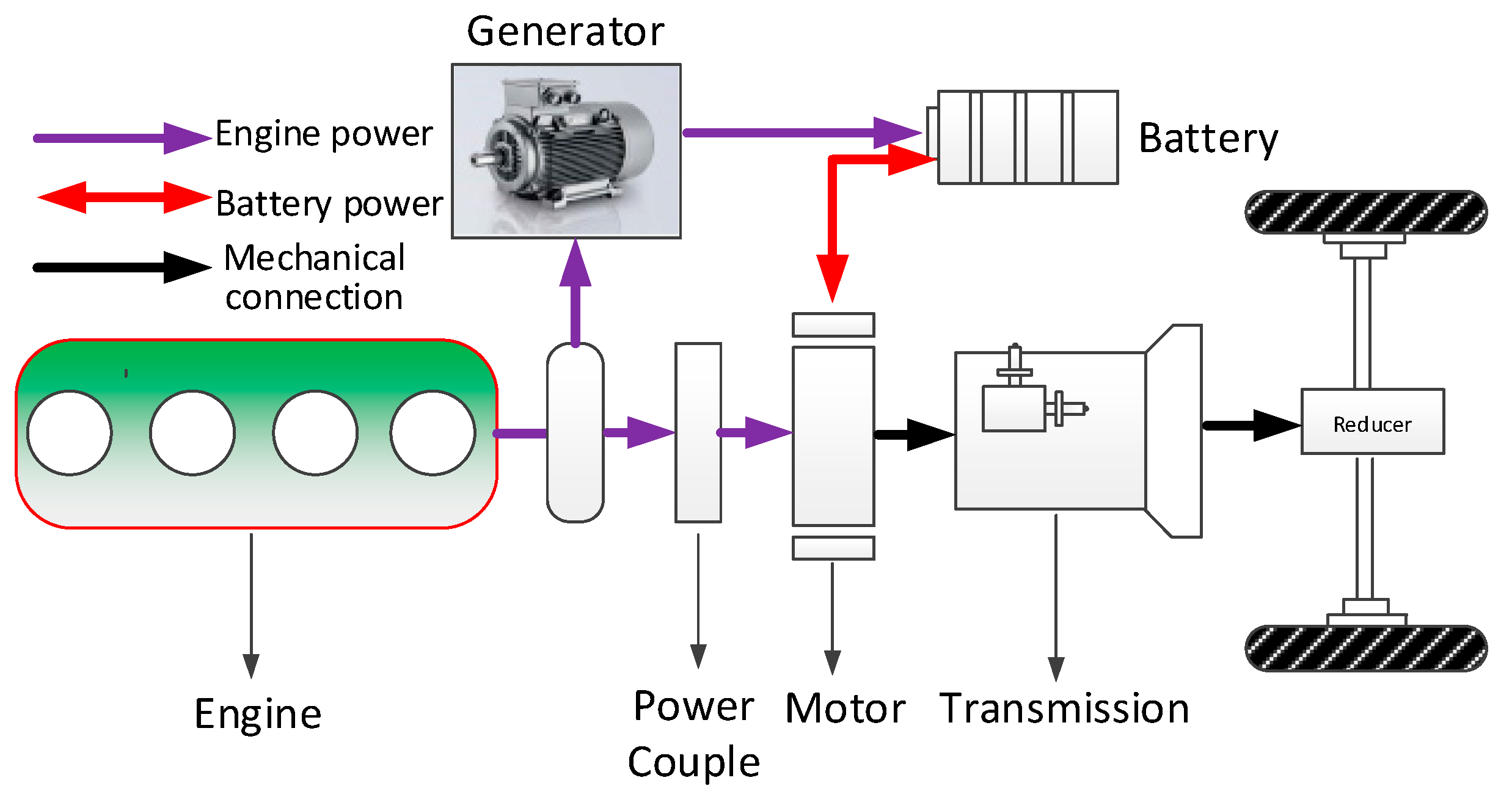
2. The Powertrain Topologies of Hybrid Electric Vehicles
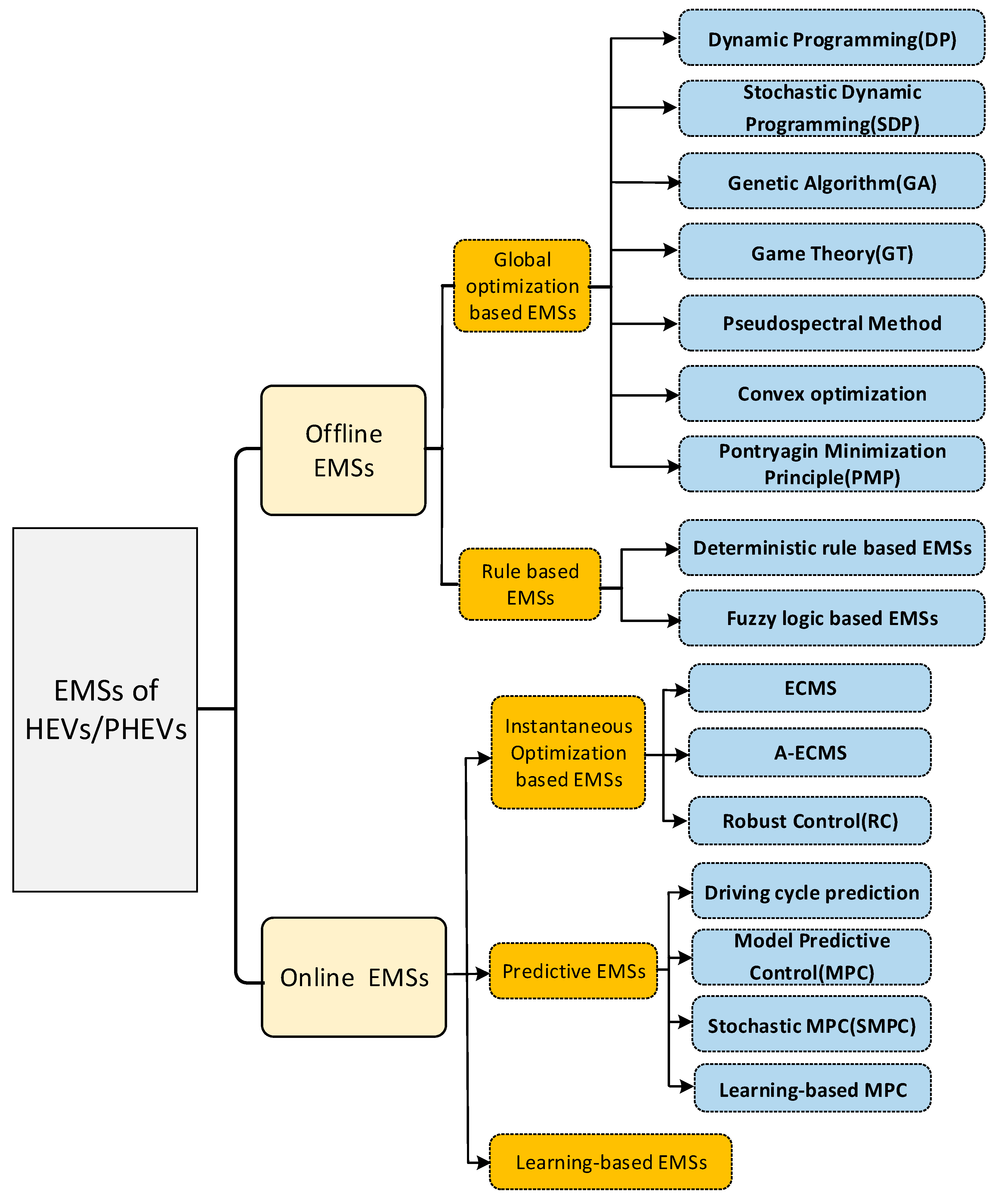
3. The Classification of EMSs
4. Offline EMSs
4.1. Global Optimization-Based EMSs
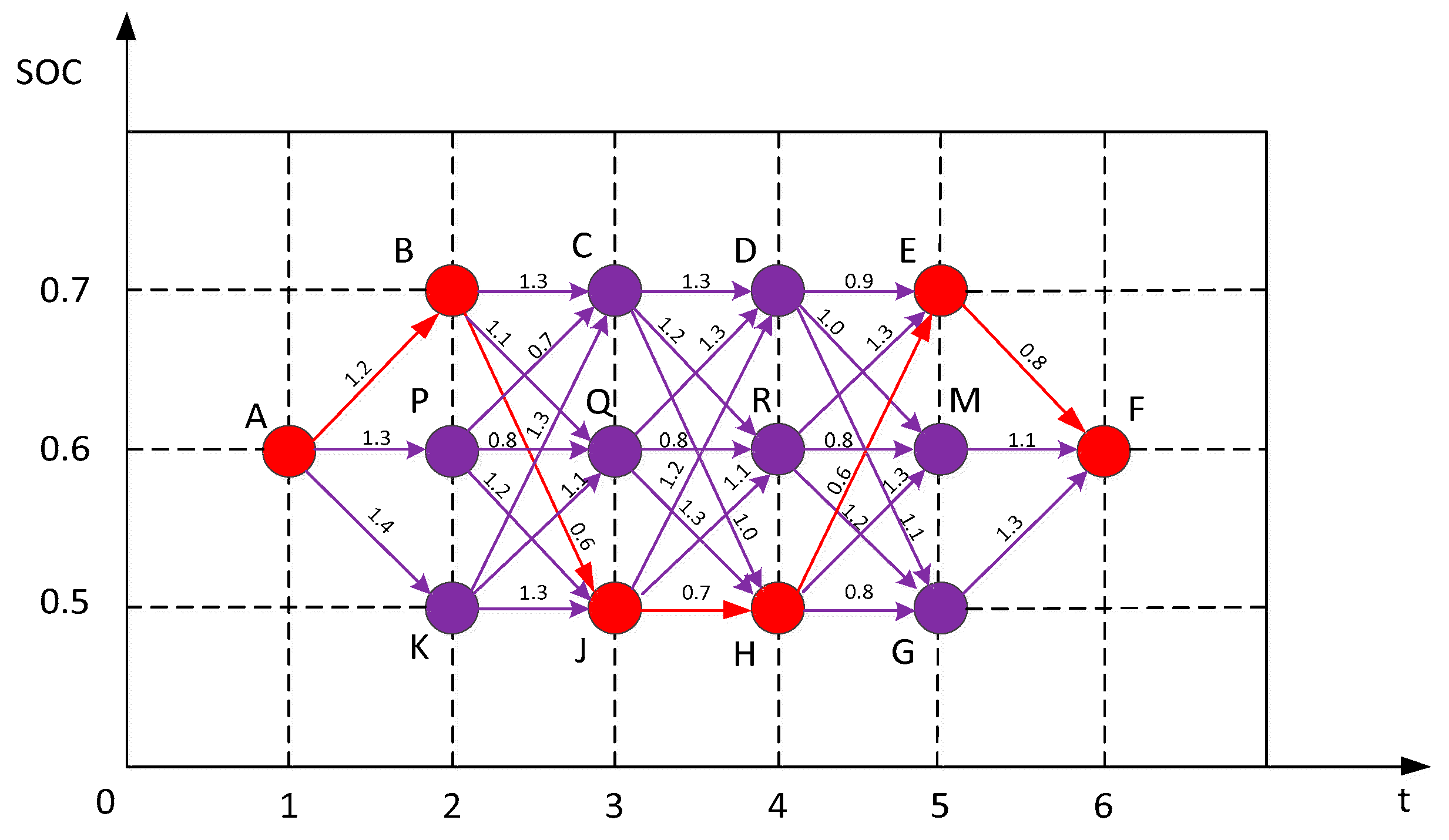
4.1.1. Dynamic Programming (DP)
4.1.2. Stochastic Dynamic Programming (SDP)
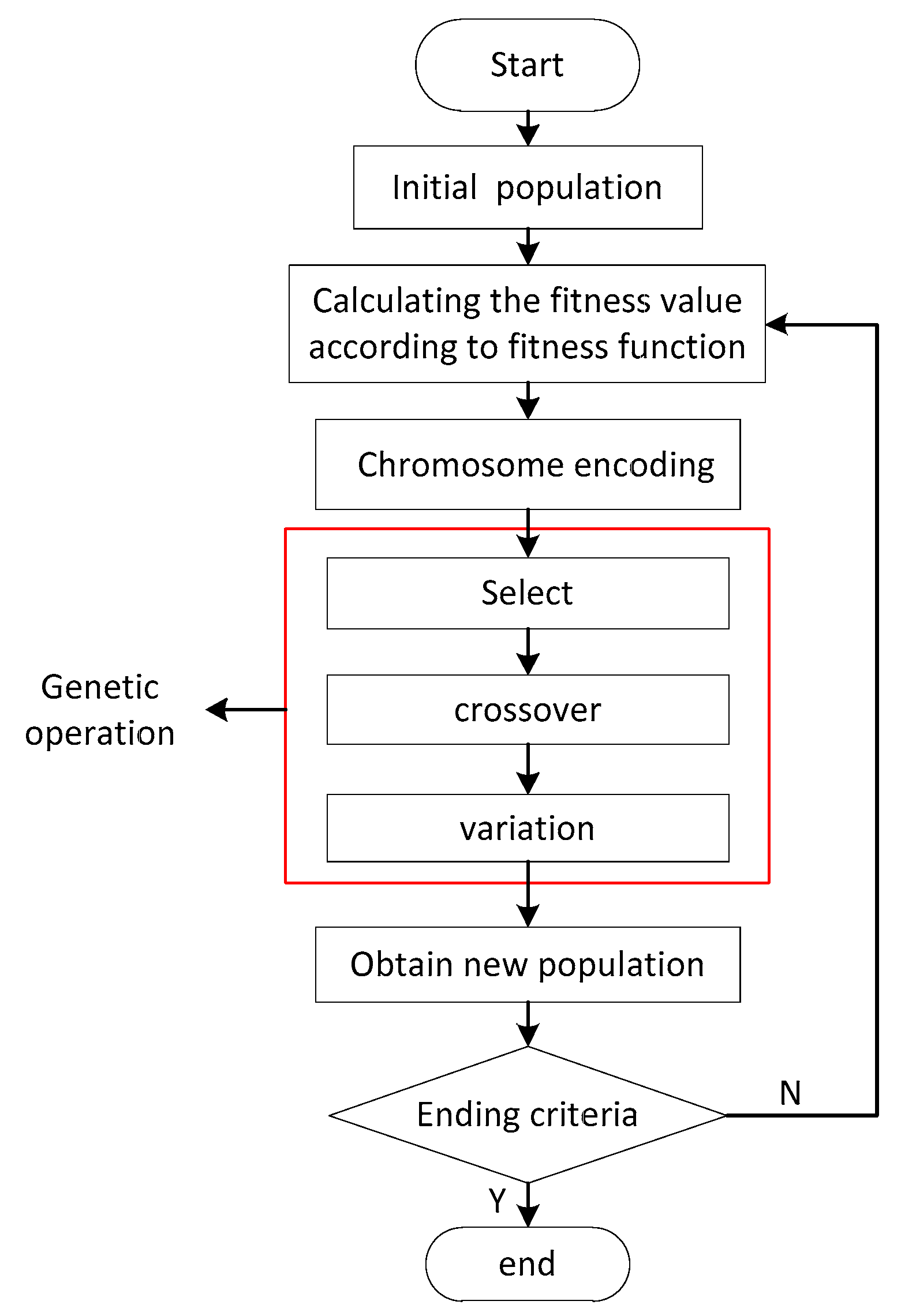
4.1.3. Genetic Algorithm (GA)
- (1)
- Initial population: Select an initial population in a feasible solution domain.
- (2)
- Genetic operation: A new population is generated by the selection, crossover and variation of the initial population to converge to the global optimal solution.
- (3)
- Decide if the population meets the ending criteria, referring to the iterations of the intelligent optimal algorithm.
4.1.4. Game Theory (GT)
4.1.5. Pseudospectral Method
4.1.6. Convex Optimization
4.1.7. Pontryagin’s Minimum Principle (PMP)
4.2. Rule-Based EMSs
4.2.1. Deterministic Rule-Based EMSs
- (1)
- on/off EMSs
- ①
- The engine starts to work at the highest efficiency region or sub-optimal emissions area and supplies constant power when the battery SOC is lower than the preset minimum threshold. A portion of the engine power is provided to the motor to satisfy the power requirement while the rest is used on charging the battery.
- ②
- The engine is shut off when the battery SOC increases to the pre-set maximum threshold and only the battery provides the driving power.
- (2)
- The power follower EMSs
- ①
- If the power demand is less than the maximum engine power at its operating speed, the operation point is adjusted to work at the minimum output power line.
- ②
- If the battery SOC is higher than the preset minimum value and lower than maximum value while driver power demand is less than the battery capacity and greater than the maximum engine power at the operating speed, the engine operates at the maximum output power line and the rest of the power demand is supplied by the battery.
- ③
- If only the battery SOC is higher than the preset maximum value and able to satisfy the power demand, the engine should be shut off.
4.2.2. Fuzzy Logic-Based EMSs
5. Online EMSs
5.1. Instantaneous Optimization-Based EMSs
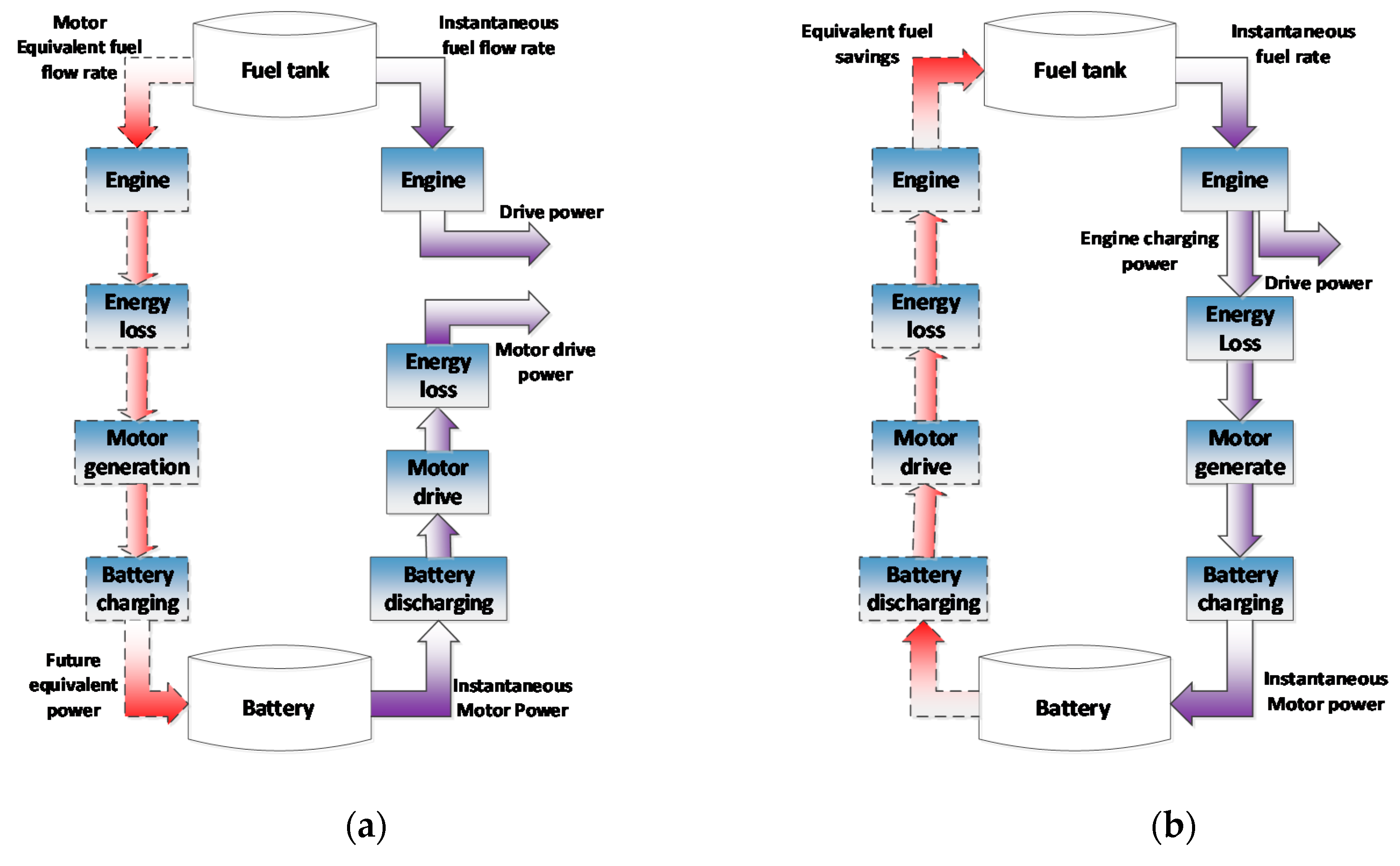
5.1.1. Equivalent Consumption Minimization Strategy (ECMS)
5.1.2. Adaptive Equivalent Consumption Minimization Strategy (A-ECMS)
5.1.3. Robust Control
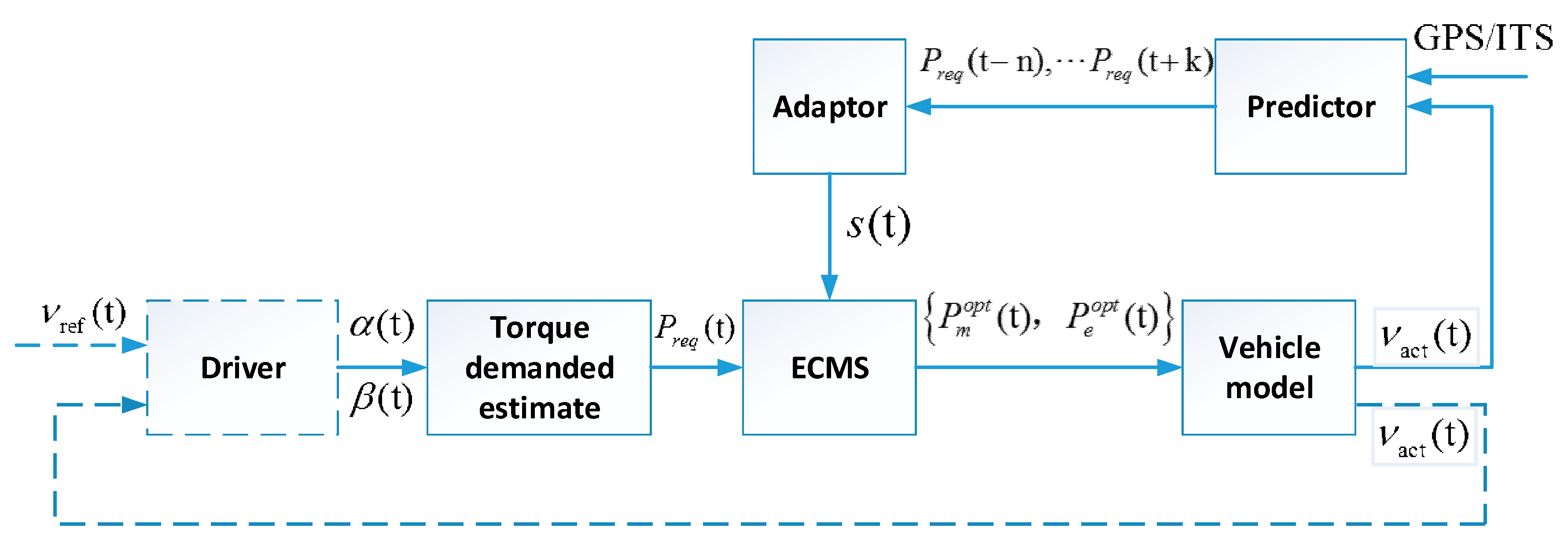
5.2. Predictive EMSs
5.2.1. The Driving Cycle Prediction Approach
5.2.2. Model Predictive Control (MPC)
5.2.3. Stochastic Model Predictive Control (SMPC)
5.2.4. Learning-Based SMPC
5.3. Learning-Based EMSs
6. Conclusion and Future Trends
6.1. The Predictive EMSs Considering Dynamic Traffic Conditions with ITS
6.2. Real-Time EMSs Incorporating Components Response and Accurate Vehicle Models
6.3. Multi-Objectives EMSs Incorporating Battery Aging and Drivability
6.4. Adaptive EMSs Considering Driver Characteristics and More Influential Factors
6.5. Multi-Dimension EMSs Including Route Planning and Velocity Planning
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, F.Q.; Hu, X.S.; Langari, R.; Cao, D.P. Energy management strategies of connected hevs and phevs: Recent progress and outlook. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2019, 73, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onori, S.; Serrao, L.; Rizzoni, G. Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Energy Management Strategies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; You, S.; Li, L.; Yang, C. Survey on energy management strategy for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 53, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirasingha, S.G.; Emadi, A. Classification and review of control strategies for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmasi, F.R. Control strategies for hybrid electric vehicles: Evolution, classification, comparison, and future trends. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2007, 56, 2393–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbaschian, M.; Söffker, D. Review and comparison of power management approaches for hybrid vehicles with focus on hydraulic drives. Energies 2014, 7, 3512–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.-D.; Vafaeipour, M.; Baghdadi, M.E.; Barrero, R.; Hegazy, O. Thorough state-of-the-art analysis of electric and hybrid vehicle powertrains: Topologies and integrated energy management strategies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 119, 109596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M. Propulsion Systems for Hybrid Vehicles; The Institution of Electrical Engineers: London, UK, 2004; Volume 45. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, G. Model predictive control for energy management of a plug-in hybrid electric bus. Energy Procedia 2016, 88, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donitz, C.; Vasile, I.; Onder, C.; Guzzella, L. Dynamic programming for hybrid pneumatic vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2009 American Control Conference, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–12 June 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 3956–3963. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.C.; Peng, H.; Grizzle, J.W.; Kang, J.M. Power management strategy for a parallel hybrid electric truck. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2003, 11, 839–849. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, R.M.; Filipi, Z.; Fathy, H.K. Comparison of supervisory control strategies for series plug-in hybrid electric vehicle powertrains through dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2014, 22, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphey, Y.L.; Park, J.; Kiliaris, L.; Kuang, M.L.; Abul Masrur, M.; Phillips, A.M.; Wang, Q. Intelligent hybrid vehicle power control-part ii: Online intelligent energy management. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2013, 62, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Lin, C.C.; Filipi, Z.; Peng, H.; Assanis, D. Optimal power management for a hydraulic hybrid delivery truck. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2004, 42, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutter, S.; Bäker, B. Predictive online control for hybrids: Resolving the conflict between global optimality, robustness and real-time capability. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Lille, France, 1–3 September 2010; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Fares, D.; Chedid, R.; Panik, F.; Karaki, S.; Jabr, R. Dynamic programming technique for optimizing fuel cell hybrid vehicles. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 7777–7790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; Yin, G.J.A.E. Mode shift map design and integrated energy management control of a multi-mode hybrid electric vehicle. Appl. Energy 2017, 204, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; He, H.; Xiong, R. Rule based energy management strategy for a series–parallel plug-in hybrid electric bus optimized by dynamic programming. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, X.; Pei, H.; Peng, Z. Comparison of power-split and parallel hybrid powertrain architectures with a single electric machine: Dynamic programming approach. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Cheng, S. Hybrid electric vehicle downshifting strategy based on stochastic dynamic programming during regenerative braking process. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 4716–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhan, J.; Shang, F. Heuristic dynamic programming based online energy management strategy for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 4479–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Berkel, K.; de Jager, B.; Hofman, T.; Steinbuch, M. Implementation of dynamic programming for optimal control problems with continuous states. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2015, 23, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, S.J.; Fathy, H.K.; Callaway, D.S.; Stein, J.L. A stochastic optimal control approach for power management in plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2011, 19, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opila, D.F.; Wang, X.Y.; McGee, R.; Gillespie, R.B.; Cook, J.A.; Grizzle, J.W. An energy management controller to optimally trade off fuel economy and drivability for hybrid vehicles. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2012, 20, 1490–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johri, R.; Filipi, Z. Optimal energy management of a series hybrid vehicle with combined fuel economy and low-emission objectives. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2014, 228, 1424–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Kong, Z.; Liu, T.; Liu, D. A real-time markov chain driver model for tracked vehicles and its validation: Its adaptability via stochastic dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 66, 3571–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Jiao, X.; Sasaki, M.; Wang, Y. Energy management optimization in consideration of battery deterioration for commuter plug-in hybrid electric vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2016 55th Annual Conference of the Society of Instrument and Control Engineers of Japan (SICE), Tsukuba, Japan, 20–23 September 2016; pp. 218–222. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, H. Trip-oriented stochastic optimal energy management strategy for plug-in hybrid electric bus. Energy 2016, 115, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, X.; Wu, Y.; Lian, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, P.; Meng, L. Energy management of hybrid electric vehicles: A review of energy optimization of fuel cell hybrid power system based on genetic algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 205, 112474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wen, Z.; Zhi, X.; Jin, J.; Zhou, S. Genetic Algorithm-Based Parameter Optimization of Energy Management Strategy and Its Analysis for Fuel Cell Hybrid Electric Vehicles; 0148-7191; SAE Technical Paper: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Piccolo, A.; Ippolito, L.; Galdi, V.Z.; Vaccaro, A. Optimisation of energy flow management in hybrid electric vehicles via genetic algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics. Proceedings (Cat. No.01TH8556), Como, Italy, 8–12 July 2001; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 434–439. [Google Scholar]
- Xudong, L.; Yanping, W.; Jianmin, D. Optimal sizing of a series hybrid electric vehicle using a hybrid genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Automation and Logistics, Jinan, China, 18–21 August 2007; pp. 1125–1129. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhou, M.; Lu, D. Management strategy based on genetic algorithm optimization for phev. Int. J. Control Autom. 2014, 7, 399–408. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Su, Y.; Peng, L.; Yao, D. A review of game theory applications in transportation analysis. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Computer and Information Application, Tianjin, China, 3–5 December 2010; pp. 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, J.F. Equilibrium points in n-person games. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1950, 36, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J. Non-cooperative games. Ann. Math. 1951, 54, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colman, A.M. Game Theory and Its Applications: In the Social and Biological Sciences; Psychology Press: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gielniak, M.J.; Shen, Z.J. Power management strategy based on game theory for fuel cell hybrid electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE 60th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2004-Fall 2004), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 26–29 September 2004; pp. 4422–4426. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Zhao, C.; Li, M.; Ma, C.; Chow, M.-Y. A game theory approach to energy management of an engine–generator/battery/ultracapacitor hybrid energy system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 4266–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dextreit, C.; Kolmanovsky, I.V. Game theory controller for hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2014, 22, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dextreit, C.; Assadian, F.; Kolmanovsky, I.; Mahtani, J.; Burnham, K. Hybrid Electric Vehicle Energy Management Using Game Theory; 0148-7191; SAE Technical Paper: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Alsabbagh, A.; Yan, D.; Ma, C. Game-theoretic energy management with velocity prediction in hybrid electric vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 28th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12–14 June 2019; pp. 1084–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Kessels, J.; Donkers, M.; Weiland, S. Game-theoretic approach for complete vehicle energy management. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Coimbra, Portugal, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Kessels, J.T.; Weiland, S. Online adaptive approach for a game-theoretic strategy for complete vehicle energy management. In Proceedings of the 2015 European Control Conference (ECC), Linz, Austria, 15–17 July 2015; pp. 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H. Game-Theoretic Solution Concept for Complete Vehicle Energy Management. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Orszag, S.A. Comparison of pseudospectral and spectral approximation. Stud. Appl. Math. 1972, 51, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, S.; Peng, H.; Sun, F. Charging time and loss optimization for linmc and lifepo 4 batteries based on equivalent circuit models. J. Power Sources 2013, 239, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Fathy, H.K. A pseudospectral strategy for optimal power management in series hybrid electric powertrains. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 4813–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Du, G.; Du, G.; Zou, R. A hierarchical energy management for hybrid electric tracked vehicle considering velocity planning with pseudospectral method. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2020, 6, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, C.M.; Hu, X.; Cao, D.; Velenis, E.; Gao, B.; Wellers, M. Energy management in plug-in hybrid electric vehicles: Recent progress and a connected vehicles perspective. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 66, 4534–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgovski, N.; Johannesson, L.; Sjöberg, J.; Egardt, B. Component sizing of a plug-in hybrid electric powertrain via convex optimization. Mechatronics 2012, 22, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafisi, H.; Agah, S.M.M.; Abyaneh, H.A.; Abedi, M. Two-stage optimization method for energy loss minimization in microgrid based on smart power management scheme of phevs. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 7, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.; Boyd, S.P.; Vandenberghe, L. Convex Optimization; Cambridge university press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Nüesch, T.; Elbert, P.; Flankl, M.; Onder, C.; Guzzella, L. Convex optimization for the energy management of hybrid electric vehicles considering engine start and gearshift costs. Energies 2014, 7, 834–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Li, H.; Xin, Z.; Liu, T.; Wei, L. A pontryagin minimum principle-based adaptive equivalent consumption minimum strategy for a plug-in hybrid electric bus on a fixed route. Energies 2017, 10, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Song, C.; Cha, S. A costate estimation for pontryagin’s minimum principle by machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Chicago, IL, USA, 27–30 August 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, C.; Cha, S.W.; Duan, S. Co-state variable determination in pontryagin’s minimum principle for energy management of hybrid vehicles. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2016, 17, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Chen, Z. Adaptive energy management strategy for fuel cell/battery hybrid vehicles using pontryagin’s minimal principle. J. Power Sources 2019, 440, 227105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Song, X. A computationally efficient optimal power management for power split hybrid vehicle based on pontryagin’s minimum principle. In Proceedings of the ASME 2017 Dynamic Systems and Control Conference, Tysons, VA, USA, 11–13 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, B.-H.; German, R.; Trovão, J.P.F.; Bouscayrol, A. Real-time energy management of battery/supercapacitor electric vehicles based on an adaptation of pontryagin’s minimum principle. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 68, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Jeong, J.; Zheng, C. Adaptive energy management strategy for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles with pontryagin’s minimum principle based on daily driving patterns. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Green Technol. 2019, 6, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrao, L.; Onori, S.; Rizzoni, G. A comparative analysis of energy management strategies for hybrid electric vehicles. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2011, 133, 031012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onori, S.; Tribioli, L. Adaptive pontryagin’s minimum principle supervisory controller design for the plug-in hybrid gm chevrolet volt. Appl. Energy 2015, 147, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Rousseau, A.; Lee, D. A jump condition of pmp-based control for phevs. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 10380–10386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Mi, C.C.; Xia, B.; You, C.W. Energy management of power-split plug-in hybrid electric vehicles based on simulated annealing and pontryagin’s minimum principle. J. Power Sources 2014, 272, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Ouyang, M.G.; Xu, L.F.; Wang, H.W. Approximate pontryagin’s minimum principle applied to the energy management of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. Appl. Energy 2014, 115, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wu, X.; Xu, M. Adaptive Energy Management Strategy for Hybrid Vehicles Based on Pontryagin’s Minimum Principle; 0148-7191; SAE Technical Paper: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.; Son, H.; Bae, K.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.; Yun, J.; Kim, H. Optimal control of plug-in hybrid electric vehicle based on pontryagin’s minimum principle considering driver’s characteristic. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems, Porto, Portugal, 22–24 April 2017; pp. 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- Jinming, L.; Huei, P. Modeling and control of a power-split hybrid vehicle. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2008, 16, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsani, M.; Gao, Y.; Longo, S.; Ebrahimi, K. Modern Electric, Hybrid Electric, and Fuel Cell Vehicles: Fundamentals, Theory, and Design; CRC press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W. Introduction to Hybrid Vehicle System Modeling and Control; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mamdani, E.H. Application of fuzzy algorithms for control of simple dynamic plant. Inst. Electr. Eng. 1974, 121, 1585–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, T.; Sugeno, M. Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control. IEEE Trans. Syst. ManCybern. 1985, SMC-15, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, F.U.; Kuang, M.L.; Smith, M.; Okubo, S.; Ying, H. Fuzzy gain-scheduling proportional–integral control for improving engine power and speed behavior in a hybrid electric vehicle. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2008, 58, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, N.; Dubois, M.R.; Desrochers, A. Fuzzy-based blended control for the energy management of a parallel plug-in hybrid electric vehicle. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2014, 9, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawei, M.; Yu, Z.; Meilan, Z.; Risha, N. Intelligent fuzzy energy management research for a uniaxial parallel hybrid electric vehicle. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2017, 58, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.G.; Sharkh, S.; Walsh, F.C.; Zhang, C.-N. Energy and battery management of a plug-in series hybrid electric vehicle using fuzzy logic. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 3571–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Tarsitano, D.; Hu, X.; Cheli, F. Real time energy management strategy for a fast charging electric urban bus powered by hybrid energy storage system. Energy 2016, 112, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Williams, H.; Xu, H. Back-to-back competitive learning mechanism for fuzzy logic based supervisory control system of hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 8900–8909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Yu, H.; Wei, C. Numerical investigation on fuzzy logic control energy management strategy of parallel hybrid electric vehicle. Energy Procedia 2019, 158, 2643–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; He, Y.; Williams, H.; Xu, H. Driver-identified supervisory control system of hybrid electric vehicles based on spectrum-guided fuzzy feature extraction. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.; Schouten, N.J.; Kheir, N.A. Control strategies for parallel hybrid vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2000 American Control Conference. ACC (IEEE Cat. No.00CH36334), Chicago, IL, USA, 28–30 June 2000; Volume 521, pp. 524–528. [Google Scholar]
- Montazeri-Gh, M.; Mahmoodi-k, M. Development a new power management strategy for power split hybrid electric vehicles. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2015, 37, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyeoun-Dong, L.; Seung-Ki, S. Fuzzy-logic-based torque control strategy for parallel-type hybrid electric vehicle. Ieee Trans. Ind. Electron. 1998, 45, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyeoun-Dong, L.; Euh-Suh, K.; Seung-Ki, S.; Joohn-Sheok, K.; Kamiya, M.; Ikeda, H.; Shinohara, S.; Yoshida, H. Torque control strategy for a parallel-hybrid vehicle using fuzzy logic. Ind. Appl. Mag. 2000, 6, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, B.M.; Washington, G.; Glenn, B.C.; Rizzoni, G. Mechatronic design and control of hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2000, 5, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Tian, G. Adaptive fuzzy logic energy management strategy based on reasonable soc reference curve for online control of plug-in hybrid electric city bus. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 19, 1607–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onori, S.; Serrao, L. On adaptive-ecms strategies for hybrid electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference on Hybrid and Electric Vehicles, Malmaison, France, 6–7 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Cai, Y.; Kou, G.; Gao, W.; Qin, D. Energy management for plug-in hybrid electric vehicle based on adaptive simplified-ecms. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, B.; Mills, J.K.; Sun, D. Energy management control of microturbine-powered plug-in hybrid electric vehicles using the telemetry equivalent consumption minimization strategy. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 4238–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Kum, D.; Park, Y. Synthesis of predictive equivalent consumption minimization strategy for hybrid electric vehicles based on closed-form solution of optimal equivalence factor. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 5604–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; He, R.; Sun, X.; Cai, Y.; Xu, Y. An anfis-based ecms for energy optimization of parallel hybrid electric bus. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 69, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Hu, X.; Qi, S.; Lang, K. An artificial neural network-enhanced energy management strategy for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. Energy 2018, 163, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, W.; Zhang, F.; Hu, Y.; Xi, J. Driving-style-oriented adaptive equivalent consumption minimization strategies for hevs. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 9249–9261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganelli, G.; Delprat, S.; Guerra, T.M.; Rimaux, J.; Santin, J.J. Equivalent consumption minimization strategy for parallel hybrid powertrains. In Proceedings of the Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring 2002), Birmingham, AL, USA, 6–9 May 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kleimaier, A.; Schroder, D. An approach for the online optimized control of a hybrid powertrain. In Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Advanced Motion Control. Proceedings (Cat. No.02TH8623), Maribor, Slovenia, 3–5 July 2002; pp. 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Sciarretta, A.; Back, M.; Guzzella, L. Optimal control of parallel hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2004, 12, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodabakhshian, M.; Feng, L.; Wikander, J. Improving fuel economy and robustness of an improved ecms method. In Proceedings of the 2013 10th IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation (ICCA), Hangzhou, China, 12–14 June 2013; pp. 598–603. [Google Scholar]
- Nüesch, T.; Cerofolini, A.; Mancini, G.; Cavina, N.; Onder, C.; Guzzella, L. Equivalent consumption minimization strategy for the control of real driving nox emissions of a diesel hybrid electric vehicle. Energies 2014, 7, 3148–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.P.; Zhu, G.M.G.; Strangas, E.G.; Sun, F.C. Equivalent fuel consumption optimal control of a series hybrid electric vehicle. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2009, 223, 1003–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skugor, B.; Deur, J.; Cipek, M.; Pavkovic, D. Design of a power-split hybrid electric vehicle control system utilizing a rule-based controller and an equivalent consumption minimization strategy. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2014, 228, 631–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torreglosa, J.P.; Jurado, F.; García, P.; Fernández, L.M. Hybrid fuel cell and battery tramway control based on an equivalent consumption minimization strategy. Control Eng. Pract. 2011, 19, 1182–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Park, J.H. Development of equivalent fuel consumption minimization strategy for hybrid electric vehicles. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2012, 13, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; He, H.; Sun, F. The role of velocity forecasting in adaptive-ecms for hybrid electric vehicles. Energy Procedia 2015, 75, 1907–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y.; Xi, J. A supervisory control algorithm of hybrid electric vehicle based on adaptive equivalent consumption minimization strategy with fuzzy pi. Energies 2016, 9, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musardo, C.; Rizzoni, G.; Staccia, B. A-ecms: An adaptive algorithm for hybrid electric vehicle energy management. In Proceedings of the 2005 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and 2005 European Control Conference (CDC-ECC ’05), Seville, Spain, 12–15 December 2005; pp. 1816–1823. [Google Scholar]
- Sezer, V.; Gokasan, M.; Bogosyan, S. A novel ecms and combined cost map approach for high-efficiency series hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 3557–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Vahidi, A. Route preview in energy management of plug-in hybrid vehicles. Control Syst. Technol. IEEE Trans. 2012, 20, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.W.; Lee, D.H.; Zheng, C.; Shin, C.; Seo, H.; Cha, S.W. Realization of pmp-based control for hybrid electric vehicles in a backwards-looking simulation. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2014, 15, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemi, H.; Ghouili, J.; Cheriti, A. A real time energy management for electrical vehicle using combination of rule-based and ecms. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Electrical Power & Energy Conference, Halifax, NS, Canada, 21–23 August 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Serrao, L.; Onori, S.; Rizzoni, G. Ecms as a realization of pontryagin’s minimum principle for hev control. In Proceedings of the 2009 American Control Conference, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–12 June 2009; pp. 3964–3969. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Zulkefli, M.A.; Zheng, J.; Sun, Z.; Liu, H.X. Hybrid powertrain optimization with trajectory prediction based on inter-vehicle-communication and vehicle-infrastructure-integration. Transp. Res. Part C 2014, 45, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xi, J.; Langari, R. Real-time energy management strategy based on velocity forecasts using v2v and v2i communications. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 18, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Sun, F.; He, H. Investigating adaptive-ecms with velocity forecast ability for hybrid electric vehicles. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 1644–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhan, H.; Vahidi, A.; Phillips, A.M.; Kuang, M.L.; Kolmanovsky, I.V.; Di Cairano, S. Mpc-based energy management of a power-split hybrid electric vehicle. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2012, 20, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurkaynak, Y. Neural Adaptive Control Stategy for Hybird Electric Vehciles with Parallel Powertrain; Illinois Institute of Technology: Chicago, IL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, A.; Burl, J.; Solouk, A.; Zhou, B.; Rezaei, M.; Shahbakhti, M. Catch energy saving opportunity (ceso), an instantaneous optimal energy management strategy for series hybrid electric vehicles. Appl. Energy 2017, 208, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Coskun, S.; Zhang, F.; Langari, R.; Xi, J. Energy management of hybrid electric vehicle using vehicle lateral dynamic in velocity prediction. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 3279–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robust Control. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Robust_control (accessed on 30 June 2020).
- Morales-Morales, J.; Cervantes, I.; Cano-Castillo, U. On the design of robust energy management strategies for fchev. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 1716–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motapon, S.N.; Dessaint, L.A.; Al-Haddad, K. A robust h2-consumption-minimization-based energy management strategy for a fuel cell hybrid emergency power system of more electric aircraft. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 6148–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisu, P.; Rizzoni, G. A comparative study of supervisory control strategies for hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2007, 15, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbowski, D.; Kim, N.; Rousseau, A. Route-based online energy management of a phev and sensitivity to trip prediction. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Coimbra, Portugal, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Vadamalu, R.; Beidl, C.; Barth, S.; Rass, F. Multi-objective predictive energy management framework for hybrid electric powertrains: An online optimization approach 27th aachen colloquium. In Proceedings of the 27th Aachen Colloquium Automobile and Engine Technology, Aachen, Germany, 8–10 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Ravey, A.; Péra, M.-C. A survey on driving prediction techniques for predictive energy management of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. J. Power Sources 2019, 412, 480–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langari, R.; Jong-Seob, W. Intelligent energy management agent for a parallel hybrid vehicle-part i: System architecture and design of the driving situation identification process. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2005, 54, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, C.H.; Cui, N.X. Fuzzy energy management strategy for a hybrid electric vehicle based on driving cycle recognition. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2012, 13, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphey, Y.L.; Zhihang, C.; Kiliaris, L.; Jungme, P.; Ming, K.; Masrur, A.; Phillips, A. Neural learning of driving environment prediction for vehicle power management. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Hong Kong, China, 1–8 June 2008; pp. 3755–3761. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.W.; Hui, X.; Yin, Y.; Song, Z.B. The dynamic optimization of control strategy for hybtion city bus based on driving condition self-learing. J. Mech. Eng. 2010, 46, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, F.A.; Kaszynski, M.; Sawodny, O. Drive cycle prediction and energy management optimization for hybrid hydraulic vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2013, 62, 3581–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yaoyu, L.; Qiuming, G.; Zhong-Ren, P. Multi-information integrated trip specific optimal power management for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2009 American Control Conference, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–12 June 2009; pp. 4607–4612. [Google Scholar]
- Qiuming, G.; Yaoyu, L.; Zhong-Ren, P. Trip based optimal power management of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles using gas-kinetic traffic flow model. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 11–13 June 2008; pp. 3225–3230. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y. Vehicle-Infrastructure Integration Enabled Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles for Energy Management; Clemson University: Clemson, SC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Vahidi, A.; Pisu, P.; Li, X.; Tennant, K. Role of terrain preview in energy management of hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2010, 59, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Ozguner, U.; Tulpule, P.; Marano, V. Real-time energy management and sensitivity study for hybrid electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference (ACC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 2113–2118. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Q.; Li, Y.; Peng, Z.R. Optimal power management of plug-in hev with intelligent transportation system. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE/ASME international conference on advanced intelligent mechatronics, Zurich, Switzerland, 4–7 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Q.; Li, Y.; Peng, Z.R. Optimal power management of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles with trip modeling. In Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, IMECE 2007, Seattle, WA, USA, 11–15 November 2007; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 16, pp. 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Qiuming, G.; Yaoyu, L.; Zhong-Ren, P. Trip-based optimal power management of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2008, 57, 3393–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Tang, P.; Zhang, W.J.; Yu, Q. Artificial neural network modelling of driver handling behaviour in a driver-vehicle-environment system. Int. J. Veh. Des. 2005, 37, 24–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.J.; Martins, A.G.; Pires, A.J. Designing the input vector to ann-based models for short-term load forecast in electricity distribution systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2007, 29, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahogianni, E.; Golias, J.C.; Karlaftis, M.G. Short-term traffic forecasting: Overview of objectives and methods. Transp. Rev. 2004, 24, 533–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Hu, X.S.; Moura, S.J.; Sun, F.C. Velocity predictors for predictive energy management in hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2014, 23, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, D.; Waschl, H.; Schmied, R.; Efendic, H.; del Re, L. Short term prediction of a vehicle’s velocity trajectory using its. SAE Int. J. Passeng. Cars Electron. Electr. Syst. 2015, 8, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouvaritakis, B.; Cannon, M. Model Predictive Control; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Khajepour, A.; He, H.; Ji, J. Model predictive control power management strategies for hevs: A review. J. Power Sources 2017, 341, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Goerges, D. Hybrid modeling and predictive control of the power split and gear shift in hybrid electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Belfort, France, 11–14 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Joševski, M.; Abel, D. Distributed predictive control approach for fuel efficient gear shifting in hybrid electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2016 European Control Conference (ECC), Aalborg, Denmark, 29 June–1 July 2016; pp. 2366–2373. [Google Scholar]
- Joševski, M.; Abel, D. Gear shifting and engine on/off optimal control in hybrid electric vehicles using partial outer convexification. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Control Applications (CCA), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 19–22 September 2016; pp. 562–568. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Peng, J.; He, H. Research on model prediction energy management strategy with variable horizon. Energy Procedia 2017, 105, 3565–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Xiao, F.; Chang, C.; Shao, Y.; Song, C. Adaptive model predictive control-based energy management for semi-active hybrid energy storage systems on electric vehicles. Energies 2017, 10, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joševski, M.; Abel, D. Tube-based mpc for the energy management of hybrid electric vehicles with non-parametric driving profile prediction. In Proceedings of the 2016 American Control Conference (ACC), Boston, MA, USA, 6–8 July 2016; pp. 623–630. [Google Scholar]
- Marx, M.; Soffker, D. Optimization of the powerflow control of a hybrid electric powertrain including load profile prediction. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Seoul, Korea, 9–12 October 2012; pp. 395–400. [Google Scholar]
- Stockar, S.; Marano, V.; Canova, M.; Rizzoni, G.; Guzzella, L. Energy-optimal control of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles for real-world driving cycles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 2949–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Shen, T.; Yu, L.; Feng, N.; Song, J. A model-predictive-control-based torque demand control approach for parallel hybrid powertrains. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2013, 62, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xiong, R.; Sun, F. Model predictive control for power management in a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle with a hybrid energy storage system. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Ding, F.; Wang, W.; He, W. Energy management of a dual-mode power-split hybrid electric vehicle based on velocity prediction and nonlinear model predictive control. Appl. Energy 2017, 189, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; You, S.; Yang, C.; Yan, B.; Song, J.; Chen, Z. Driving-behavior-aware stochastic model predictive control for plug-in hybrid electric buses. Appl. Energy 2016, 162, 868–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; He, H.; Peng, J. An energy management strategy based on stochastic model predictive control for plug-in hybrid electric buses. Appl. Energy 2017, 196, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Hu, X.; Xin, Z.; Li, L. Time-efficient stochastic model predictive energy management for a plug-in hybrid electric bus with an adaptive reference state-of-charge advisory. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 5671–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesbah, A.; Kolmanovsky, I.V.; Di Cairano, S. Stochastic model predictive control. In Handbook of Model Predictive Control; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 75–97. [Google Scholar]
- Ripaccioli, G.; Bernardini, D.; Di Cairano, S.; Bemporad, A.; Kolmanovsky, I.V. A stochastic model predictive control approach for series hybrid electric vehicle power management. In Proceedings of the 2010 American Control Conference (ACC), Baltimore, MD, USA, 30 June–2 July 2010; pp. 5844–5849. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Hu, X.; Xin, Z.; Brighton, J. Pontryagin’s minimum principle based model predictive control of energy management for a plug-in hybrid electric bus. Appl. Energy 2019, 236, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Chen, B. Nonlinear model predictive control of a power-split hybrid electric vehicle with consideration of battery aging. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2019, 141, 81008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cairano, S.; Bernardini, D.; Bemporad, A.; Kolmanovsky, I.V. Stochastic mpc with learning for driver-predictive vehicle control and its application to hev energy management. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2014, 22, 1018–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Hu, X.; Li, S.E.; Cao, D. Reinforcement learning optimized look-ahead energy management of a parallel hybrid electric vehicle. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Malmir, F.; Rathod, D.; Filipi, Z. Real-Time Reinforcement Learning Optimized Energy Management for a 48v Mild Hybrid Electric Vehicle; SAE Technical Paper: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, R.; Peng, J.; Wu, Y.; Tan, H.; Zhang, H. Rule-interposing deep reinforcement learning based energy management strategy for power-split hybrid electric vehicle. Energy 2020, 197, 117297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Northrop, W. Reinforcement Learning Based Energy Management of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles for Commuter Route; 0148-7191; SAE Technical Paper: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; He, H.; Wu, J.; Peng, J.; Li, Y. Energy management based on reinforcement learning with double deep q-learning for a hybrid electric tracked vehicle. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 113708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liu, T.; Qi, X.; Barth, M. Reinforcement learning for hybrid and plug-in hybrid electric vehicle energy management: Recent advances and prospects. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2019, 13, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Wu, G.; Boriboonsomsin, K.; Barth, M.J.; Gonder, J. Data-driven reinforcement learning–based real-time energy management system for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. Transp. Res. Rec. 2016, 2572, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Luo, Y.; Wu, G.; Boriboonsomsin, K.; Barth, M.J. Deep reinforcement learning-based vehicle energy efficiency autonomous learning system. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 11–14 June 2017; pp. 1228–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, R.; Cao, J.; Yu, Q. Reinforcement learning-based real-time power management for hybrid energy storage system in the plug-in hybrid electric vehicle. Appl. Energy 2018, 211, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Fu, Z.; Tao, F.; Zhu, L.; Si, P. Data-driven reinforcement-learning-based hierarchical energy management strategy for fuel cell/battery/ultracapacitor hybrid electric vehicles. J. Power Sources 2020, 455, 227964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romijn, T.C.J.; Donkers, M.; Kessels, J.T.; Weiland, S. A distributed optimization approach for complete vehicle energy management. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2018, 27, 964–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Approaches | Main Advantages | Main Disadvantages | Literature |
|---|---|---|---|
| DP |
|
| [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22] |
| SDP |
|
| [23,24,25,26,27,28] |
| GA |
|
| [29,30,31,32,33] |
| GT |
|
| [34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45] |
| Pseudospectral method |
|
| [46,47,48,49] |
| Convex optimization |
|
| [50,51,52,53,54] |
| PMP |
|
| [55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68] |
| Approaches | Main Advantages | Main Disadvantages | Literature |
|---|---|---|---|
| ECMS |
|
| [88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103] |
| A-ECMS |
|
| [104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118] |
| RC |
|
| [119,120,121,122] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, F.; Wang, L.; Coskun, S.; Pang, H.; Cui, Y.; Xi, J. Energy Management Strategies for Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Review, Classification, Comparison, and Outlook. Energies 2020, 13, 3352. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13133352
Zhang F, Wang L, Coskun S, Pang H, Cui Y, Xi J. Energy Management Strategies for Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Review, Classification, Comparison, and Outlook. Energies. 2020; 13(13):3352. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13133352
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Fengqi, Lihua Wang, Serdar Coskun, Hui Pang, Yahui Cui, and Junqiang Xi. 2020. "Energy Management Strategies for Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Review, Classification, Comparison, and Outlook" Energies 13, no. 13: 3352. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13133352
APA StyleZhang, F., Wang, L., Coskun, S., Pang, H., Cui, Y., & Xi, J. (2020). Energy Management Strategies for Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Review, Classification, Comparison, and Outlook. Energies, 13(13), 3352. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13133352







