A Novel Analytical Wake Model with a Cosine-Shaped Velocity Deficit
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Review of Some Previous Wake Models
1.2. Current Study
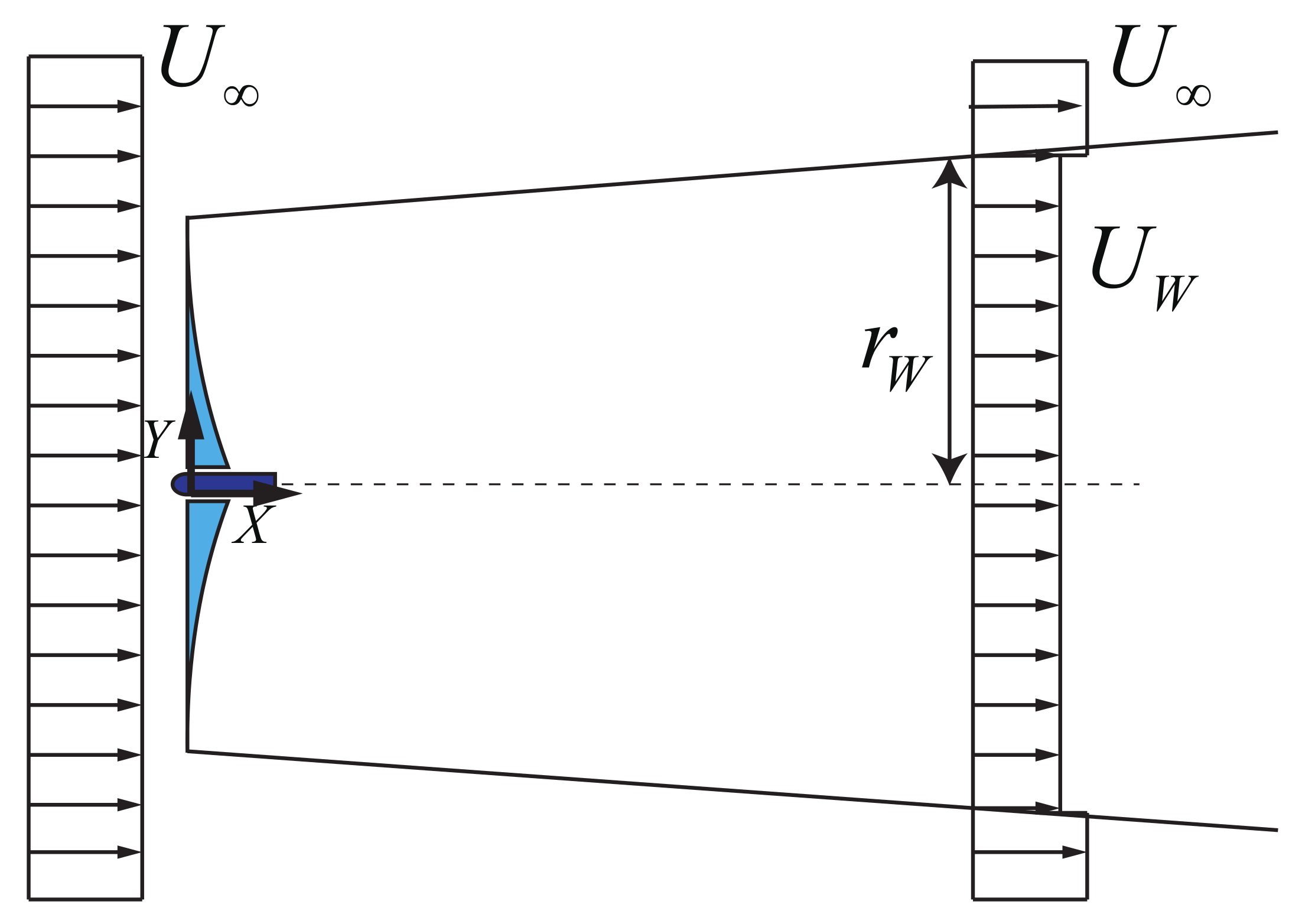
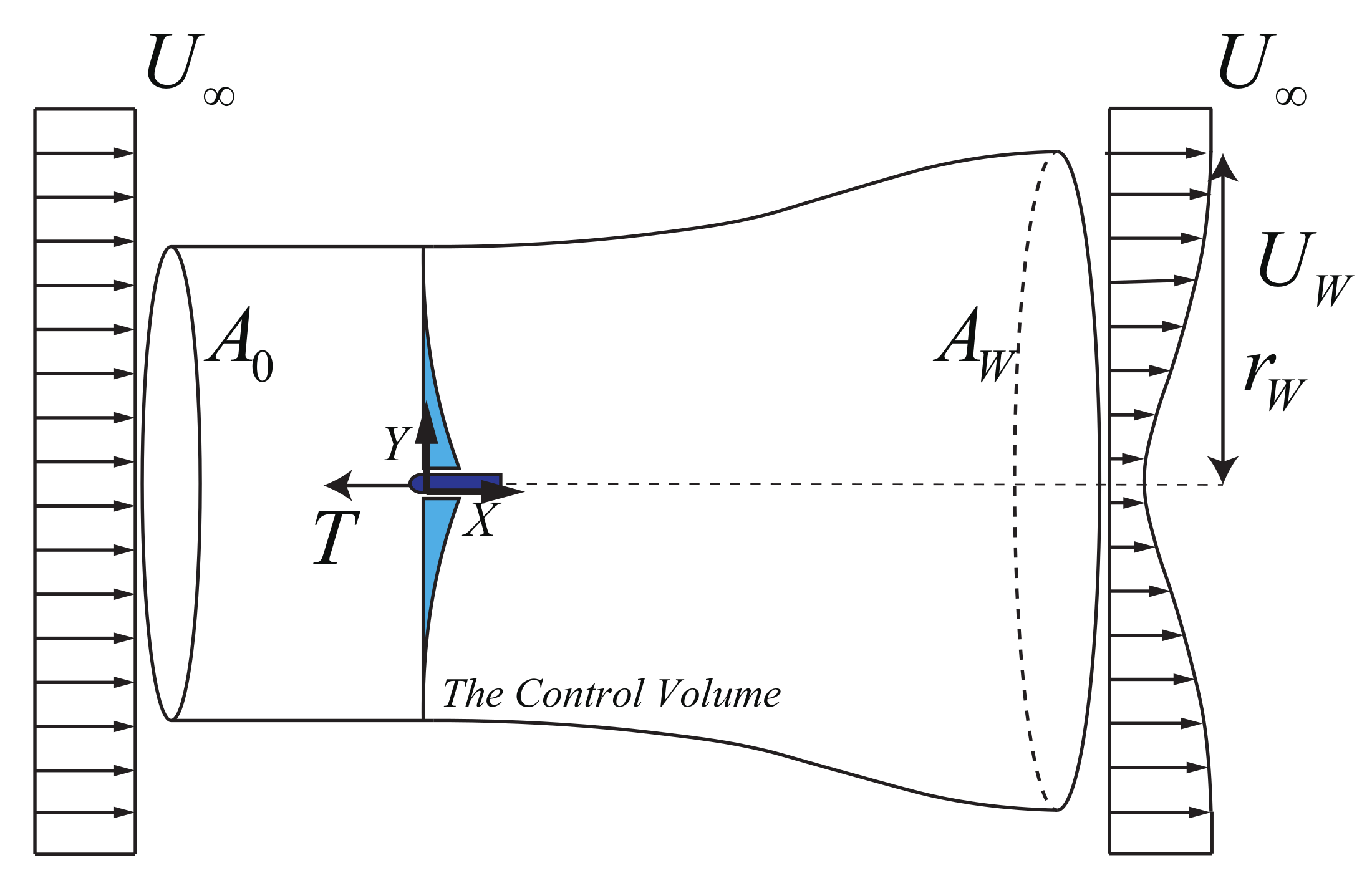
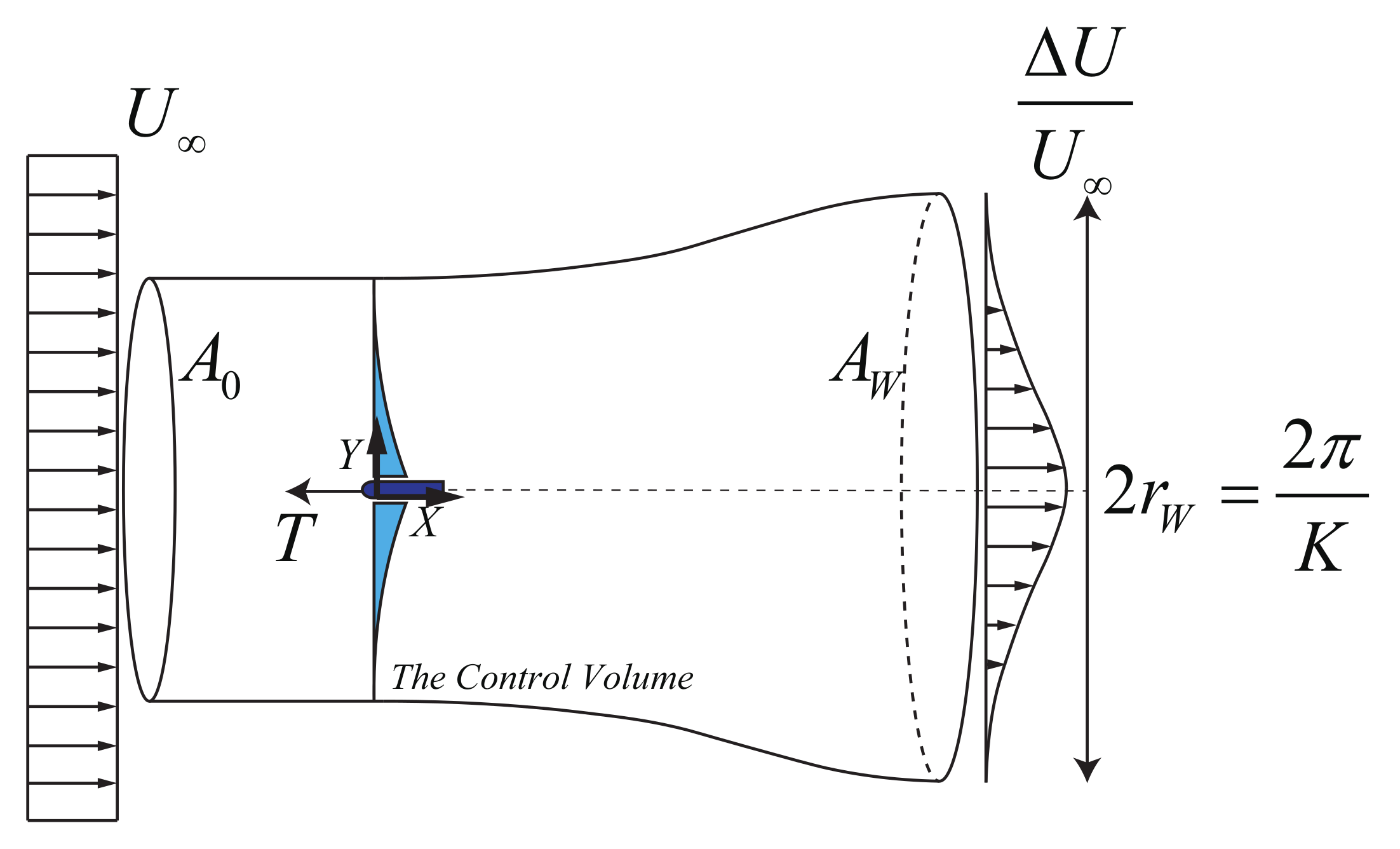
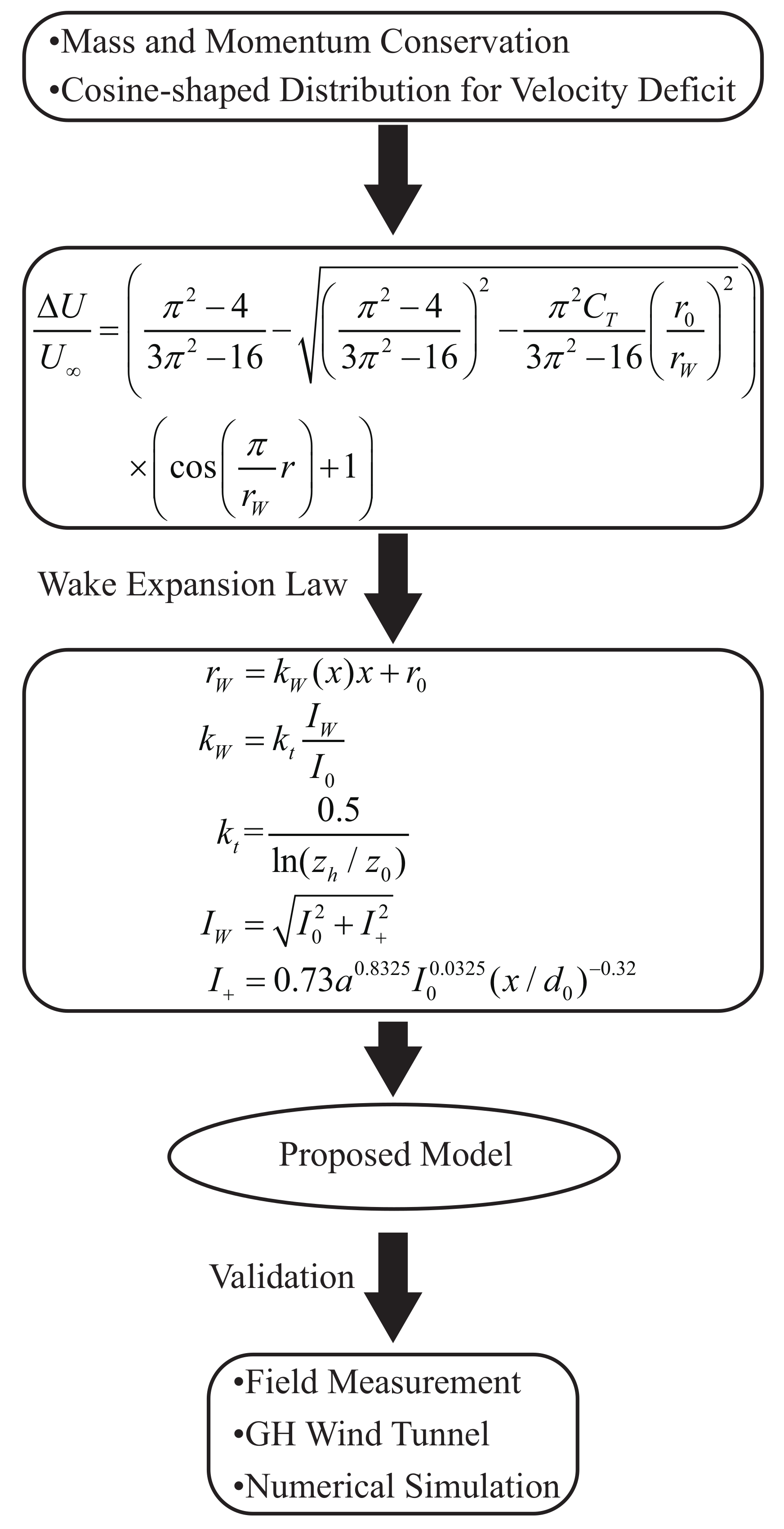
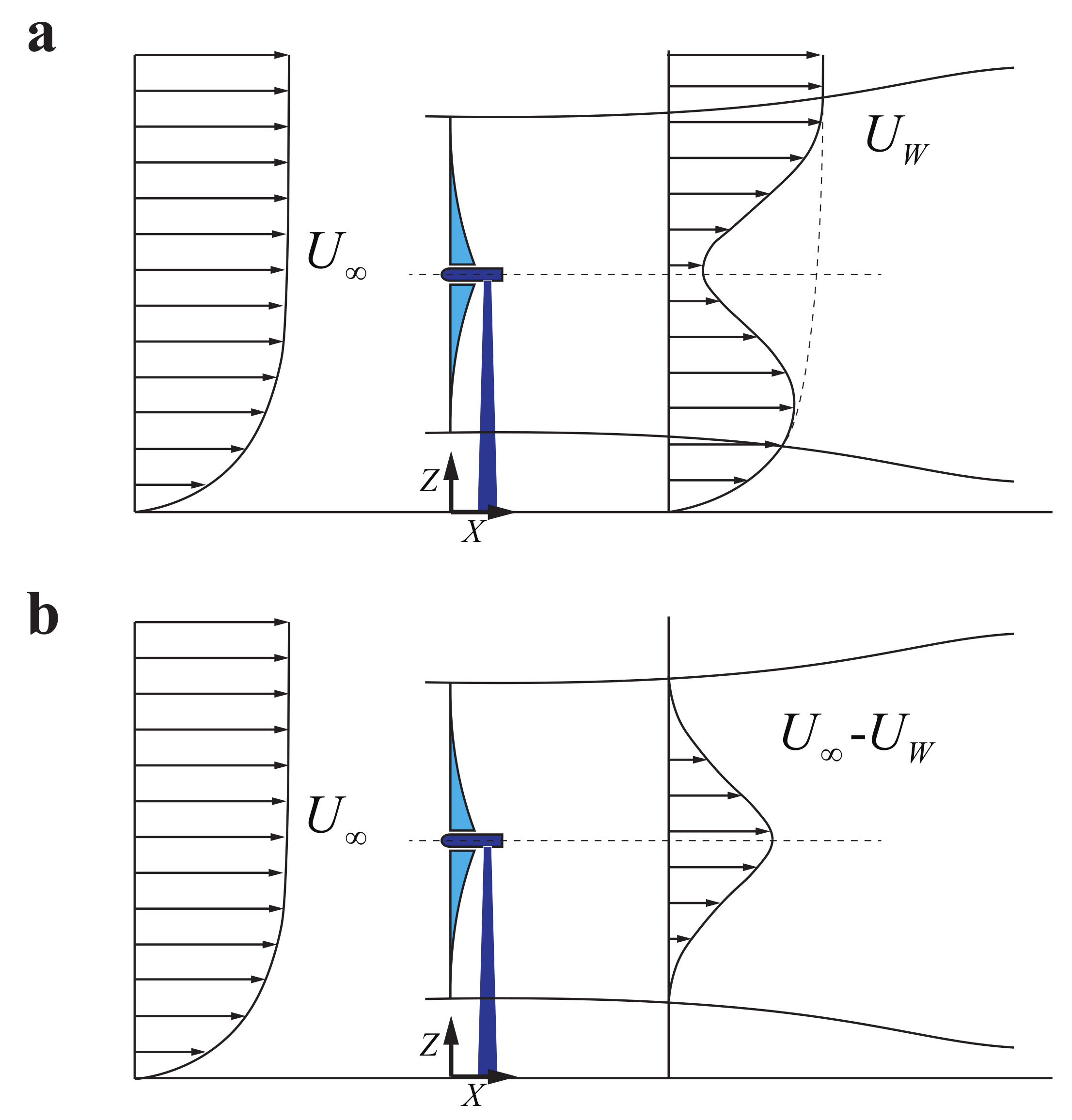
2. Derivation of the Wake Model
3. Validation of the Proposed Model
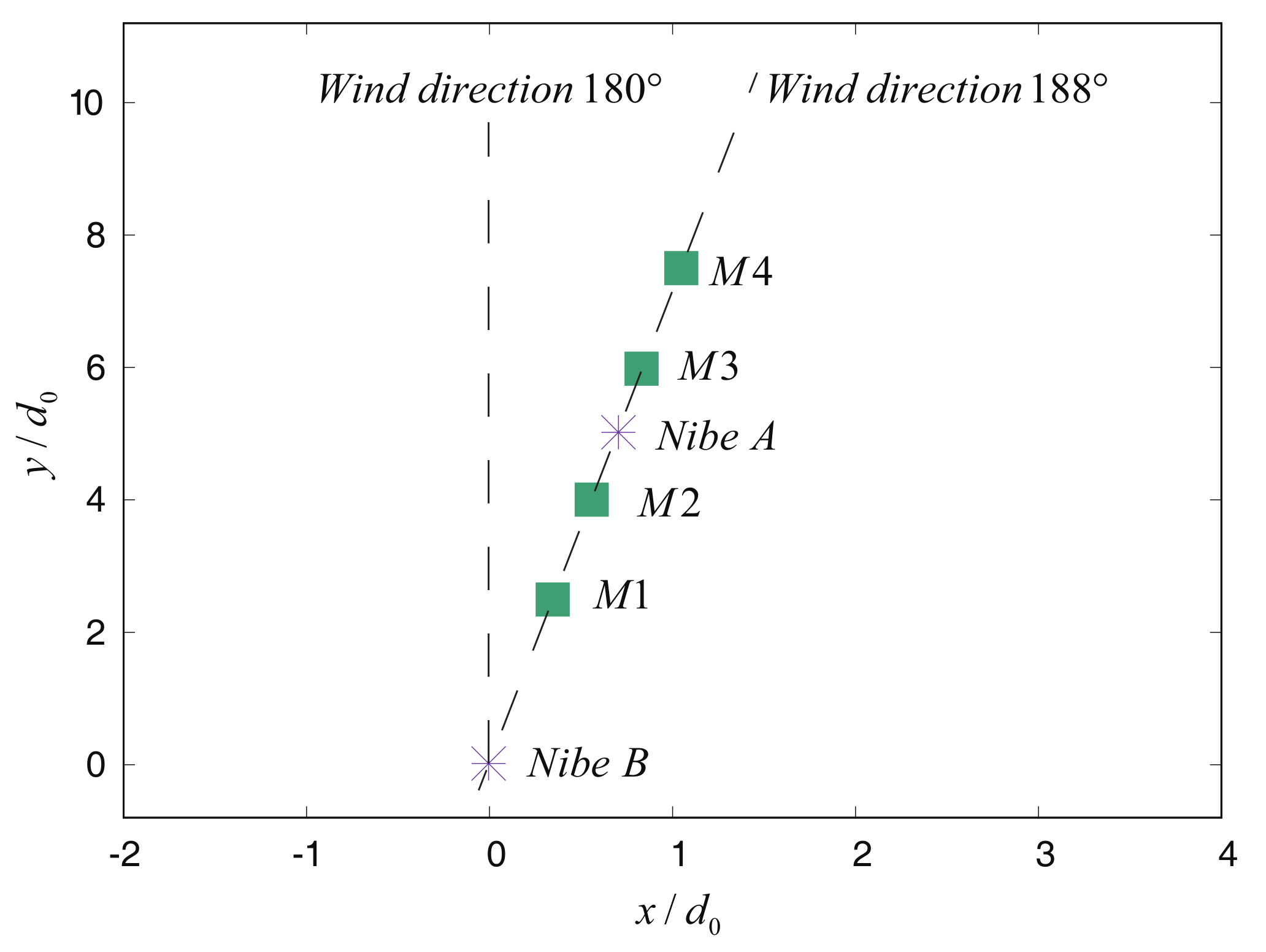
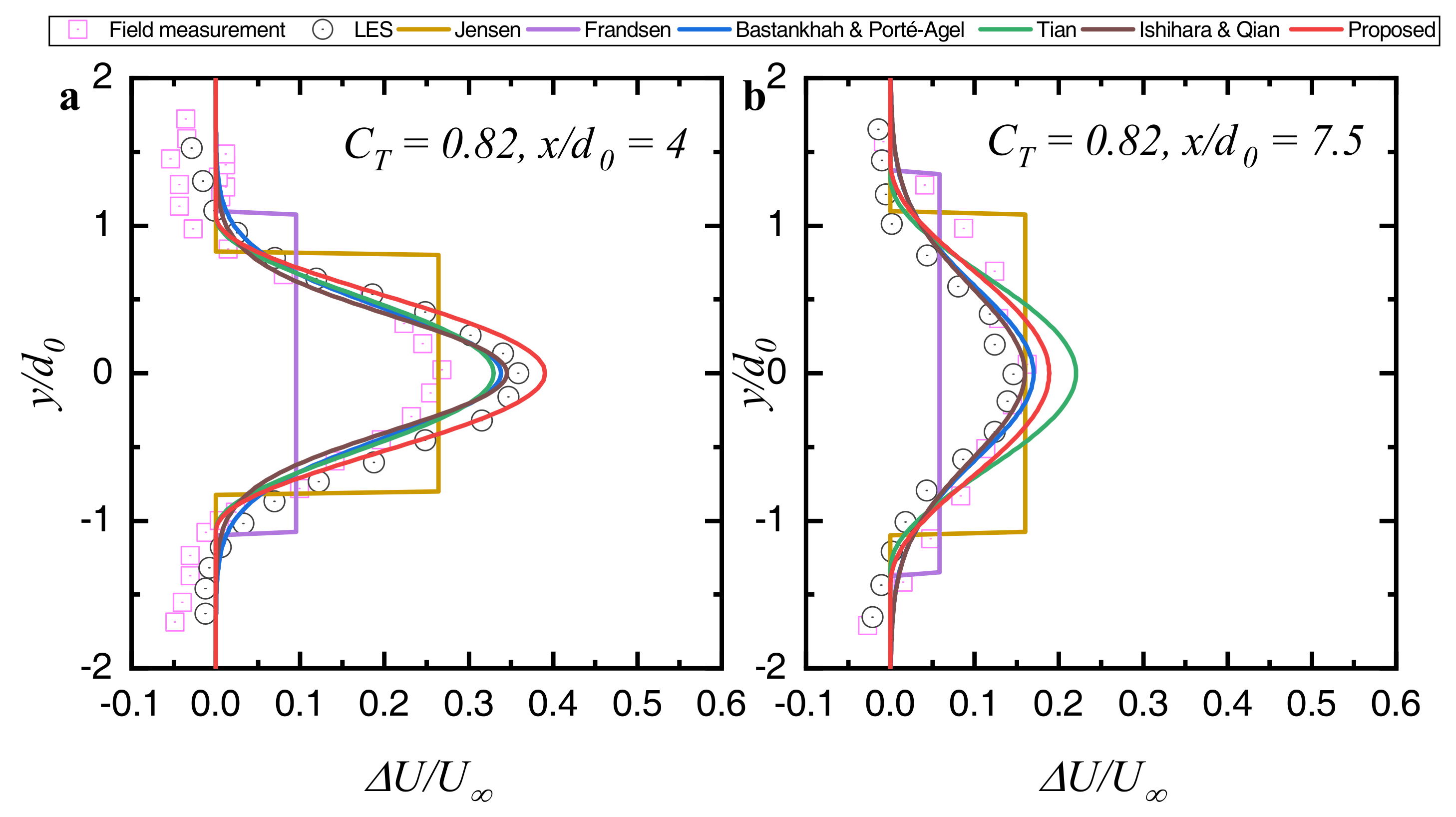
3.1. Field Measurement
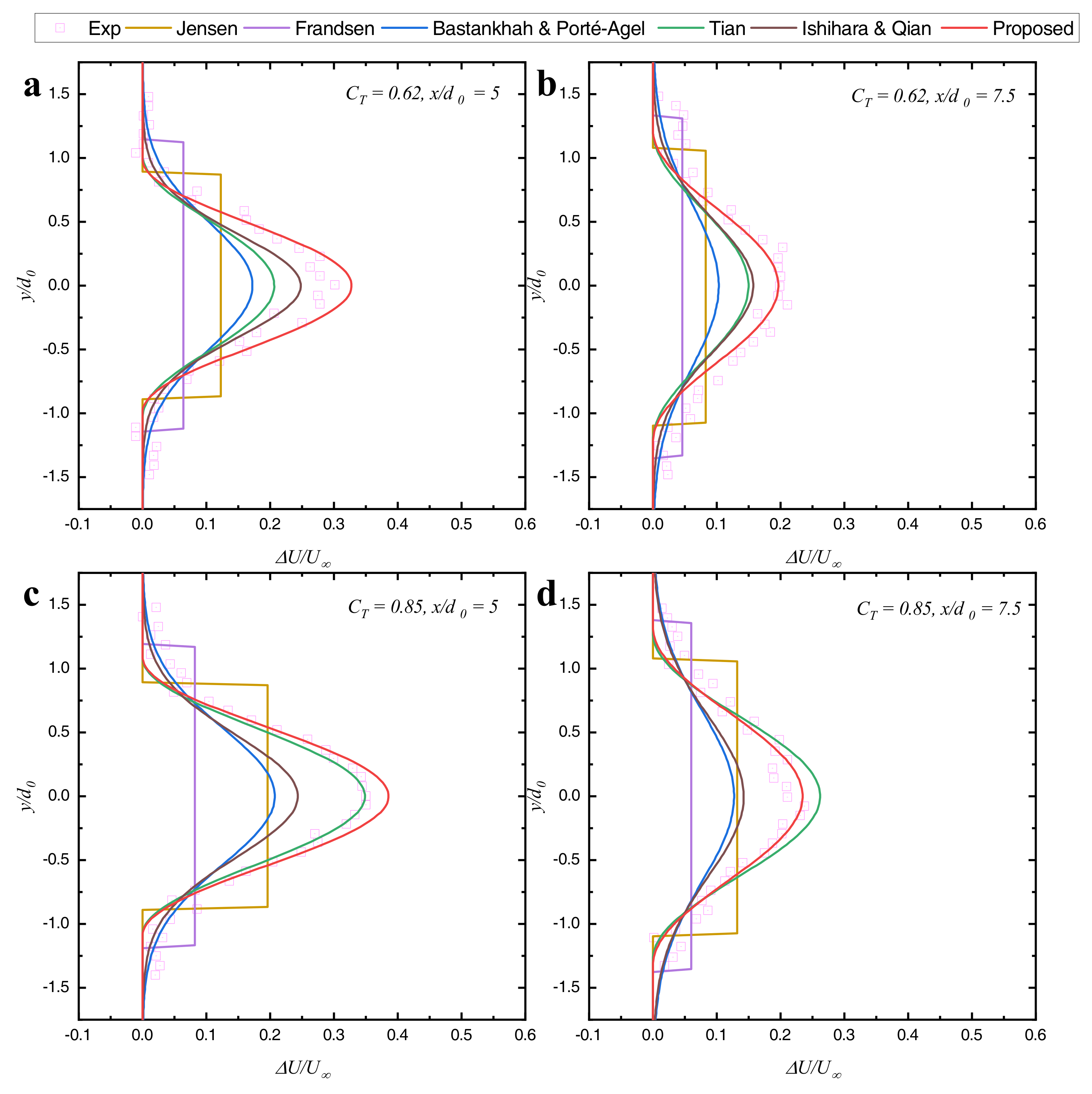
3.2. Wind-Tunnel Measurement
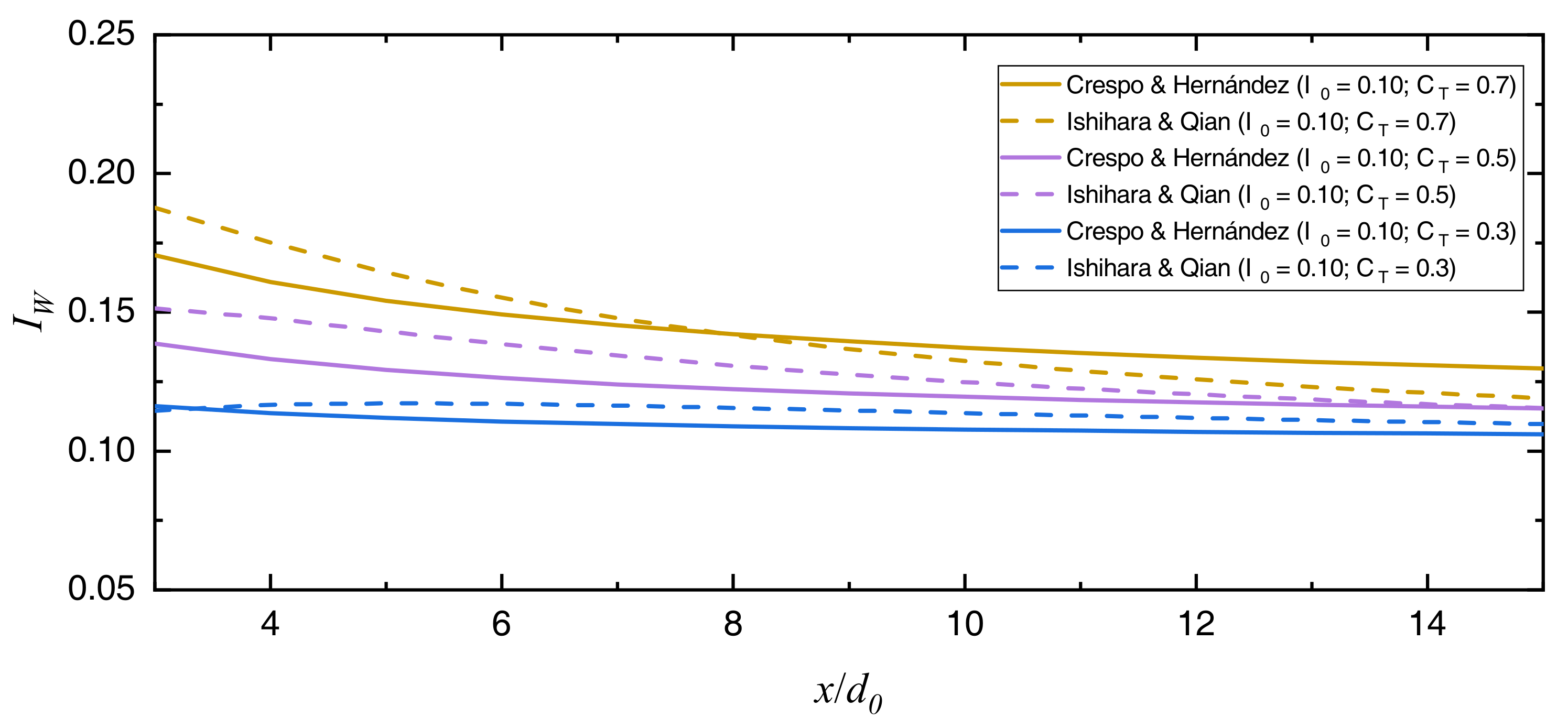
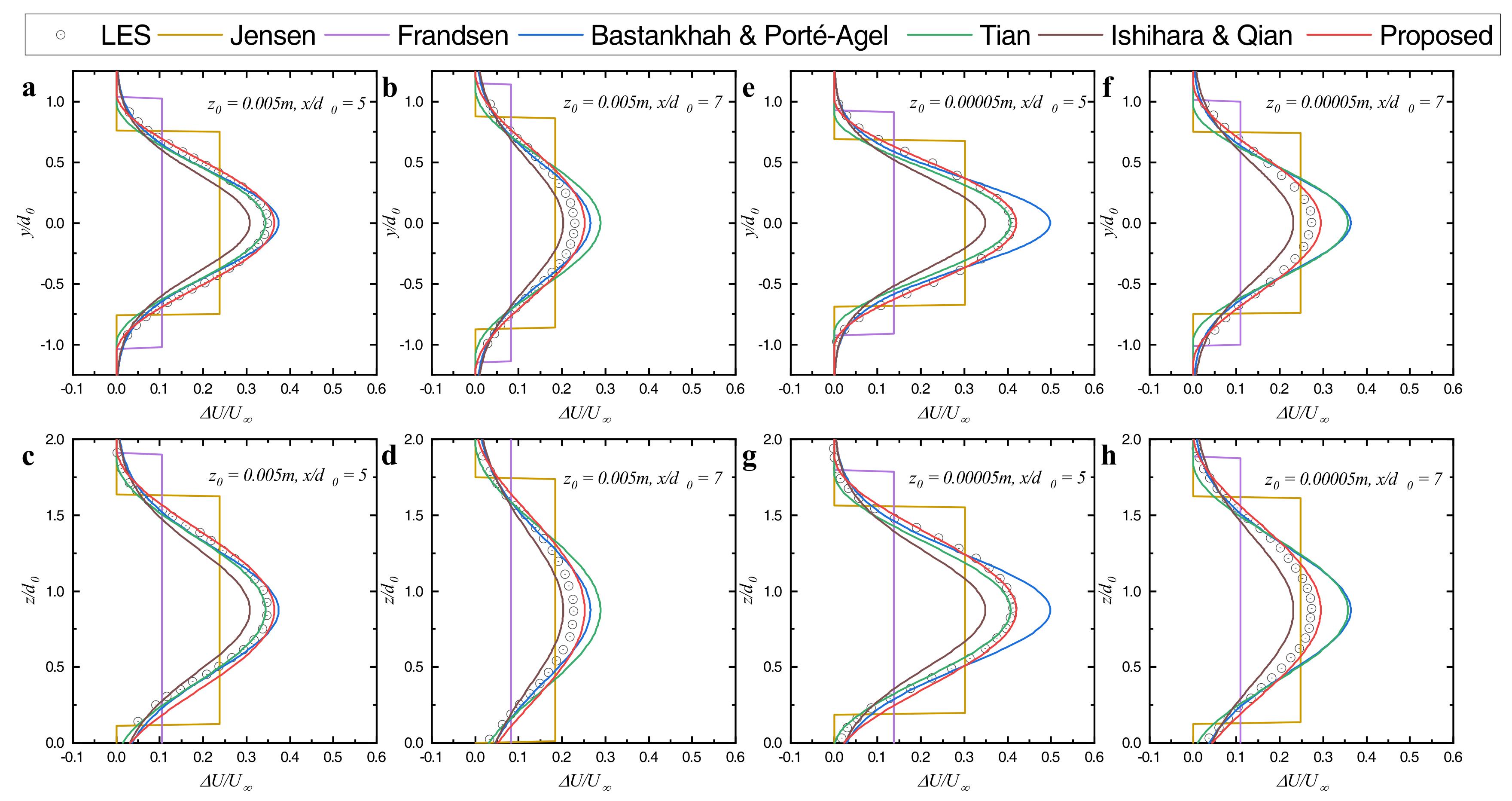
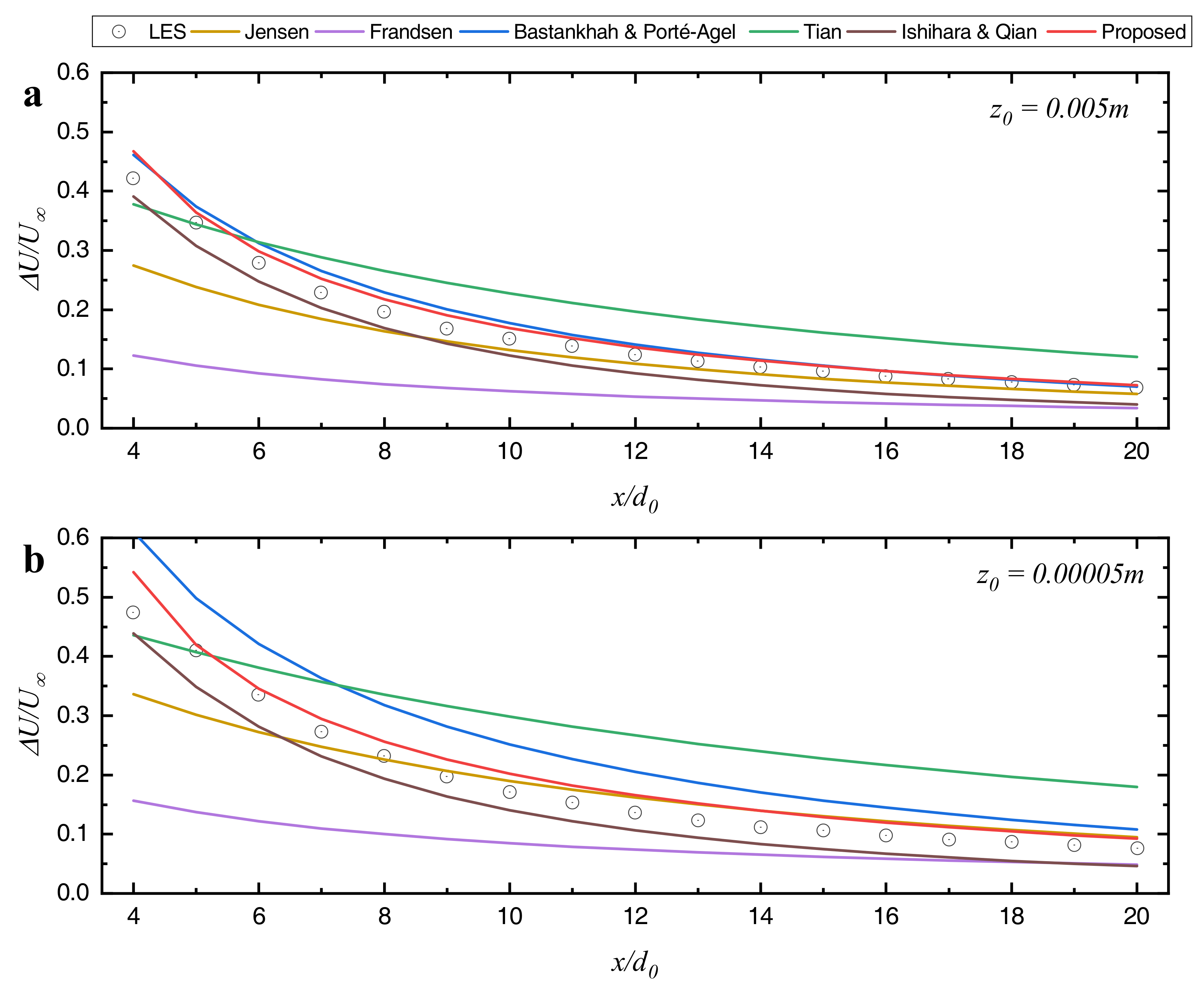
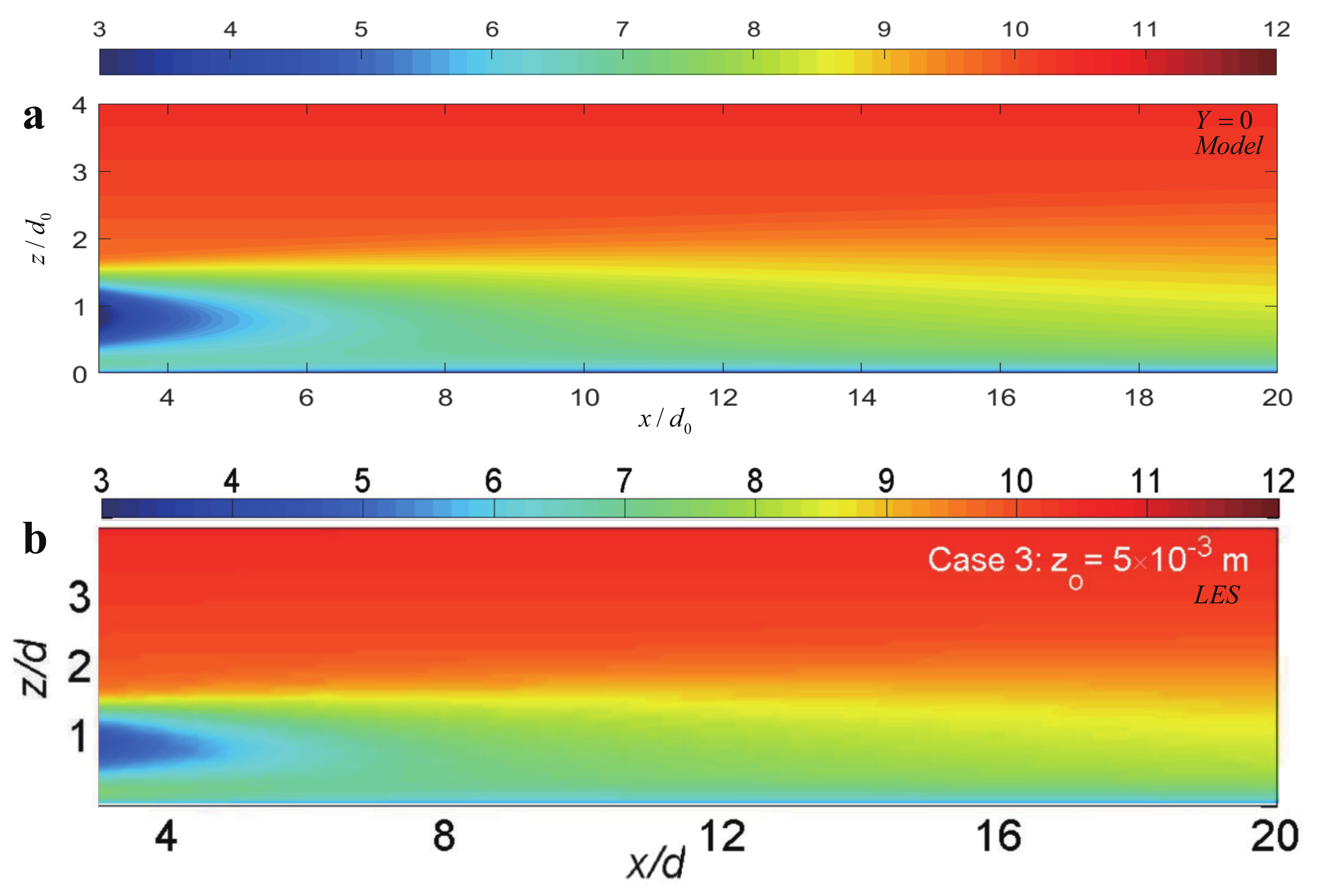
3.3. Numerical Simulation
4. Predictions of the Proposed Model
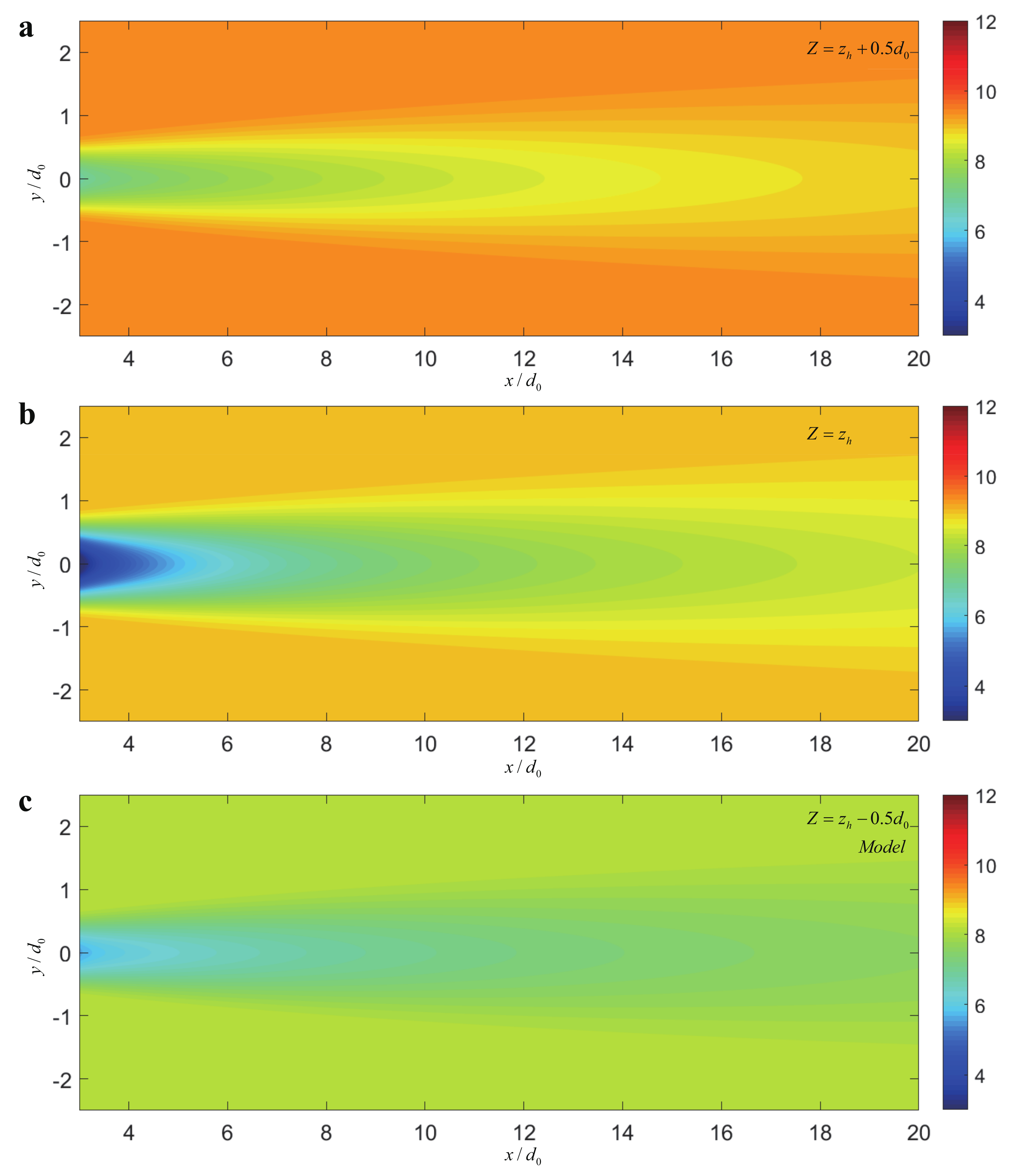
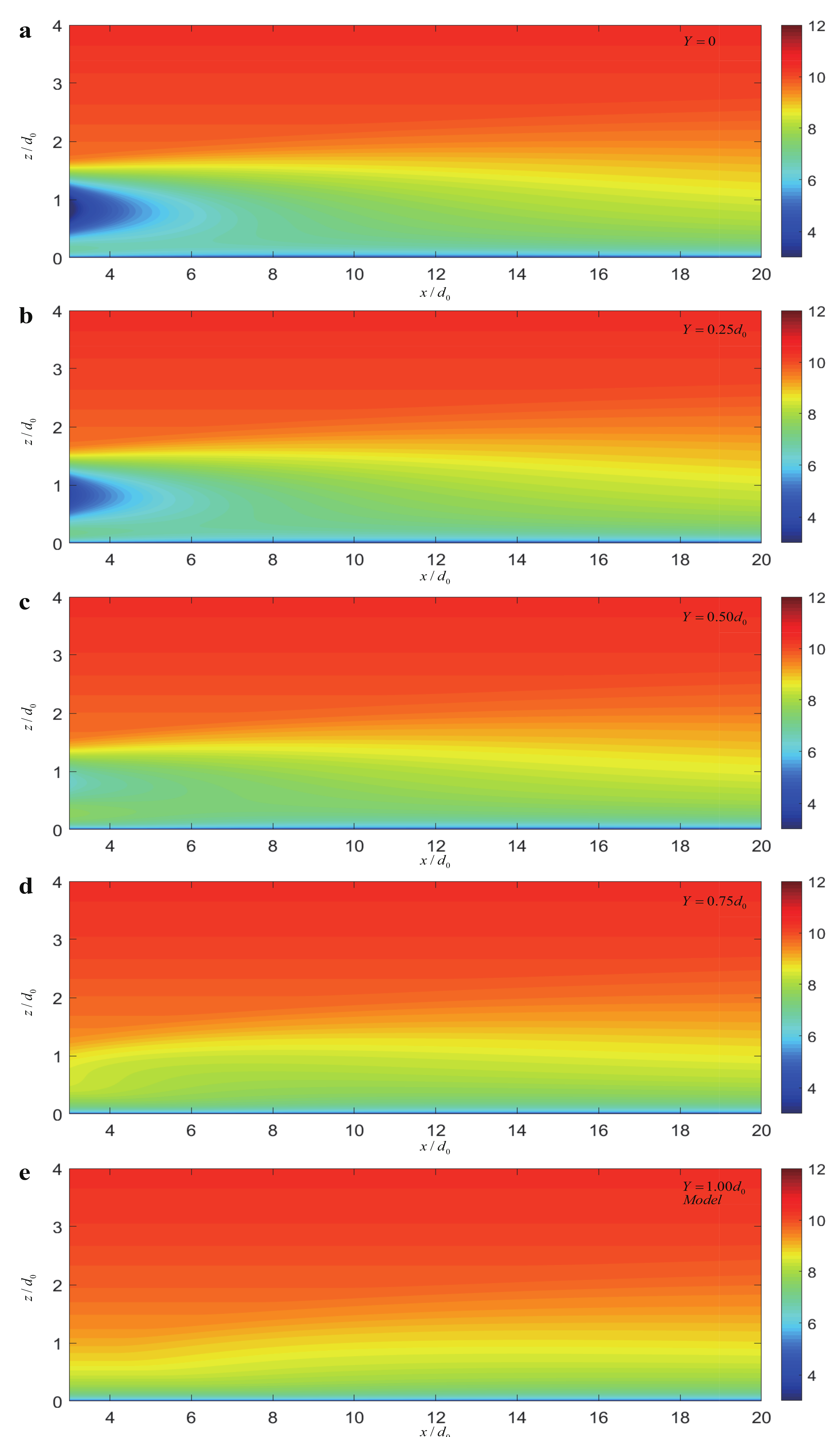
4.1. Wake Profiles from the X – Y View
4.2. Wake Profiles from the X – Z View
4.3. Wake Profiles from the Y – Z View
5. Conclusions and Further Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perveen, R.; Kishor, N.; Mohanty, S.R. Off-shore wind farm development: Present status and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeer, L.J.; Sorensen, J.N.; Crespo, A. Wind turbine wake aerodynamics. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2003, 39, 467–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelmie, R.J.; Hansen, K.; Frandsen, S.T.; Rathmann, O.; Schepers, J.G.; Schlez, W.; Phillips, J.; Rados, K.; Zervos, A.; Politis, E.S.; et al. Modelling and Measuring Flow and Wind Turbine Wakes in Large Wind Farms Offshore. Wind Energy 2009, 12, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, T.; Qian, G.W. A new Gaussian-based analytical wake model for wind turbines considering ambient turbulence intensities and thrust coefficient effects. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2018, 177, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porté-Agel, F.; Bastankhah, M.; Shamsoddin, S. Wind-Turbine and Wind-Farm Flows: A Review. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2019, 174, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthelmie, R.J.; Pryor, S. An overview of data for wake model evaluation in the Virtual Wakes Laboratory. Appl. Energy 2013, 104, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Markfort, C.D.; Porté-Agel, F. Near-wake flow structure downwind of a wind turbine in a turbulent boundary layer. Exp. Fluids 2012, 52, 1219–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howland, M.F.; Bossuyt, J.; Martineztossas, L.A.; Meyers, J.; Meneveau, C. Wake structure in actuator disk models of wind turbines in yaw under uniform inflow conditions. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2016, 8, 043301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastankhah, M.; Porté-Agel, F. Wind tunnel study of the wind turbine interaction with a boundary-layer flow: Upwind region, turbine performance, and wake region. Phys. Fluids 2017, 29, 065105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abkar, M.; Sharifi, A.; Porteagel, F. Wake flow in a wind farm during a diurnal cycle. J. Turbul. 2016, 17, 420–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Ishihara, T. A New Analytical Wake Model for Yawed Wind Turbines. Energies 2018, 11, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, A. Survey of Modelling Methods for Wind Turbine Wakes and Wind Farms. Wind Energy 1999, 2, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocmen, T.; Der Laan, P.V.; Rethore, P.; Diaz, A.P.; Larsen, G.C.; Ott, S. Wind turbine wake models developed at the technical university of Denmark: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 752–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, N.O. A Note on Wind Generator Interaction; Risø National Laboratory: Roskilde, Denmark, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, G.C. A Simple Wake Calculation Procedure; Risø National Laboratory: Roskilde, Denmark, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara, T.; Yamaguchi, A.; Fujino, Y. Development of a new wake model based on a wind tunnel experiment. Glob. Wind Power 2004, 105, 33–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bastankhah, M.; Porté-Agel, F. A New Analytical Model For Wind-Turbine Wakes. Renew. Energy 2014, 70, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhu, W.; Shen, W.; Zhao, N.; Shen, Z. Development and validation of a new two-dimensional wake model for wind turbine wakes. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2015, 137, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yang, H.; Lu, L. Optimization of wind turbine layout position in a wind farm using a newly-developed two-dimensional wake model. Appl. Energy 2016, 174, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yang, H. Study on an innovative three-dimensional wind turbine wake model. Appl. Energy 2018, 226, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yang, H. Study on three wake models’ effect on wind energy estimation in Hong Kong. Energy Procedia 2018, 145, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Han, S.; Liu, Y. Multiple Wind Turbine Wakes Modeling Considering the Faster Wake Recovery in Overlapped Wakes. Energies 2019, 12, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelmie, R.J.; Folkerts, L.; Larsen, G.C.; Rados, K.; Pryor, S.C.; Frandsen, S.T.; Lange, B.; Schepers, G. Comparison of wake model simulations with offshore wind turbine wake profiles measured by sodar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2006, 23, 888–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frandsen, S. On the Wind-Speed Reduction in the Center of Large Clusters of Wind Turbines. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1992, 39, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, G. GH WindFarmer: Theory Manual; Garrad Hassan and Partners Limited: Bristol, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Thørgersen, M.; Sørensen, T.; Nielsen, P.; Grötzner, A.; Chun, S. WindPRO/PARK: Introduction to wind turbine wake modelling and wake generated turbulence. In EMD Modelling and Wake Generated Turbulence; EMD International A/S: Aalborg, Denmark, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Frandsen, S.; Barthelmie, R.; Pryor, S.; Rathmann, O.; Larsen, S.; Højstrup, J.; Thøgersen, M. Analytical modelling of wind speed deficit in large offshore wind farms. Wind Energy Int. J. Prog. Appl. Wind Power Convers. Technol. 2006, 9, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X. A two-dimensional Jensen model with a Gaussian-shaped velocity deficit. Renew. Energy 2019, 141, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, L.P.; Porté-Agel, F. A Wind-Tunnel Investigation of Wind-Turbine Wakes: Boundary-Layer Turbulence Effects. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2009, 132, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.T.; Porté-Agel, F. Atmospheric turbulence effects on wind-turbine wakes: An LES study. Energies 2012, 5, 5340–5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Archer, C.L. A Numerical Study of Wind-Turbine Wakes for Three Atmospheric Stability Conditions. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2017, 165, 87–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, R.J.A.M.; Meneveau, C. Flow Structure and Turbulence in Wind Farms. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2017, 49, 311–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhu, W.J.; Shen, W.Z.; Song, Y.; Zhao, N. Prediction of multi-wake problems using an improved Jensen wake model. Renew. Energy 2017, 102, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niayifar, A.; Porte-Agel, F. Analytical Modeling of Wind Farms: A New Approach for Power Prediction. Energies 2016, 9, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Archer, C. Self-similarity and turbulence characteristics of wind turbine wakes via large-eddy simulation. Wind Energy 2015, 18, 1815–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abkar, M.; Porté-Agel, F. Influence of atmospheric stability on wind-turbine wakes: A large-eddy simulation study. Phys. Fluids 2015, 27, 035104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J. A new analytical model for wind turbine wakes based on Monin-Obukhov similarity theory. Appl. Energy 2019, 239, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q. A two-dimensional model based on the expansion of physical wake boundary for wind-turbine wakes. Appl. Energy 2019, 233, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G. Wake Measurements on the Nibe Wind-Turbines in Denmark; National Power, Technology and Environment Centre: Leatherhead, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Schlez, W.; Tindal, A.; Quarton, D. GH Wind Farmer Validation Report; Garrad Hassan and Partners Ltd: Bristol, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tennekes, H.; Lumley, J.L.; Lumley, J.L. A First Course in Turbulence; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, T.; Jenkins, N.; Sharpe, D.; Bossanyi, E. Wind Energy Handbook; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Yang, H. Numerical investigation of the average wind speed of a single wind turbine and development of a novel three-dimensional multiple wind turbine wake model. Renew. Energy 2020, 147, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarton, D.; Ainslie, J. Turbulence in wind turbine wakes. Wind Eng. 1990, 14, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, U. A Wind Tunnel Investigation of the Wake Structure within Small Wind Turbine Farms; Harwell Laboratory, Energy Technology Support Unit: Harwell, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Crespo, A.; Hernández, J. Turbulence characteristics in wind-turbine wakes. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1996, 61, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troldborg, N.; Sørensen, J.N.; Mikkelsen, R.; Sørensen, N.N. A simple atmospheric boundary layer model applied to large eddy simulations of wind turbine wakes. Wind Energy 2014, 17, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissaman, P.B.S. Energy Effectiveness of Arbitrary Arrays of Wind Turbines. J. Energy 1979, 3, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porté-Agel, F.; Wu, Y.T.; Lu, H.; Conzemius, R.J. Large-eddy simulation of atmospheric boundary layer flow through wind turbines and wind farms. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2011, 99, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Jensen | Frandsen | Bastankhah & Porté-Agel | Tian | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Profile | Top-hat | Top-hat | Gaussian | Cosine | Cosine |
| Principles | MC | MC&MT | MC&MT | MC | MC&MT |
| Wake expansion law | Linear | Nonlinear | Linear | Nonlinear | Nonlinear |
| Expansion coefficient |
| Relative Error (%) | Jensen | Frandsen | Bastankhah & Porté-Agel | Tian | Ishihara & Qian | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | 17.1 | 58.2 | 11.0 | 50.3 | 24.8 | 9.0 |
| m | 18.9 | 49.1 | 41.4 | 81.1 | 24.1 | 16.7 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Huang, P.; Sun, H. A Novel Analytical Wake Model with a Cosine-Shaped Velocity Deficit. Energies 2020, 13, 3353. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13133353
Zhang Z, Huang P, Sun H. A Novel Analytical Wake Model with a Cosine-Shaped Velocity Deficit. Energies. 2020; 13(13):3353. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13133353
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ziyu, Peng Huang, and Haocheng Sun. 2020. "A Novel Analytical Wake Model with a Cosine-Shaped Velocity Deficit" Energies 13, no. 13: 3353. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13133353
APA StyleZhang, Z., Huang, P., & Sun, H. (2020). A Novel Analytical Wake Model with a Cosine-Shaped Velocity Deficit. Energies, 13(13), 3353. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13133353





