Batch and Fed-Batch Ethanol Fermentation of Cheese-Whey Powder with Mixed Cultures of Different Yeasts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganisms and Maintaining
2.2. Culture Medium
2.3. Ethanol Fermentation
2.4. Analytical Methods
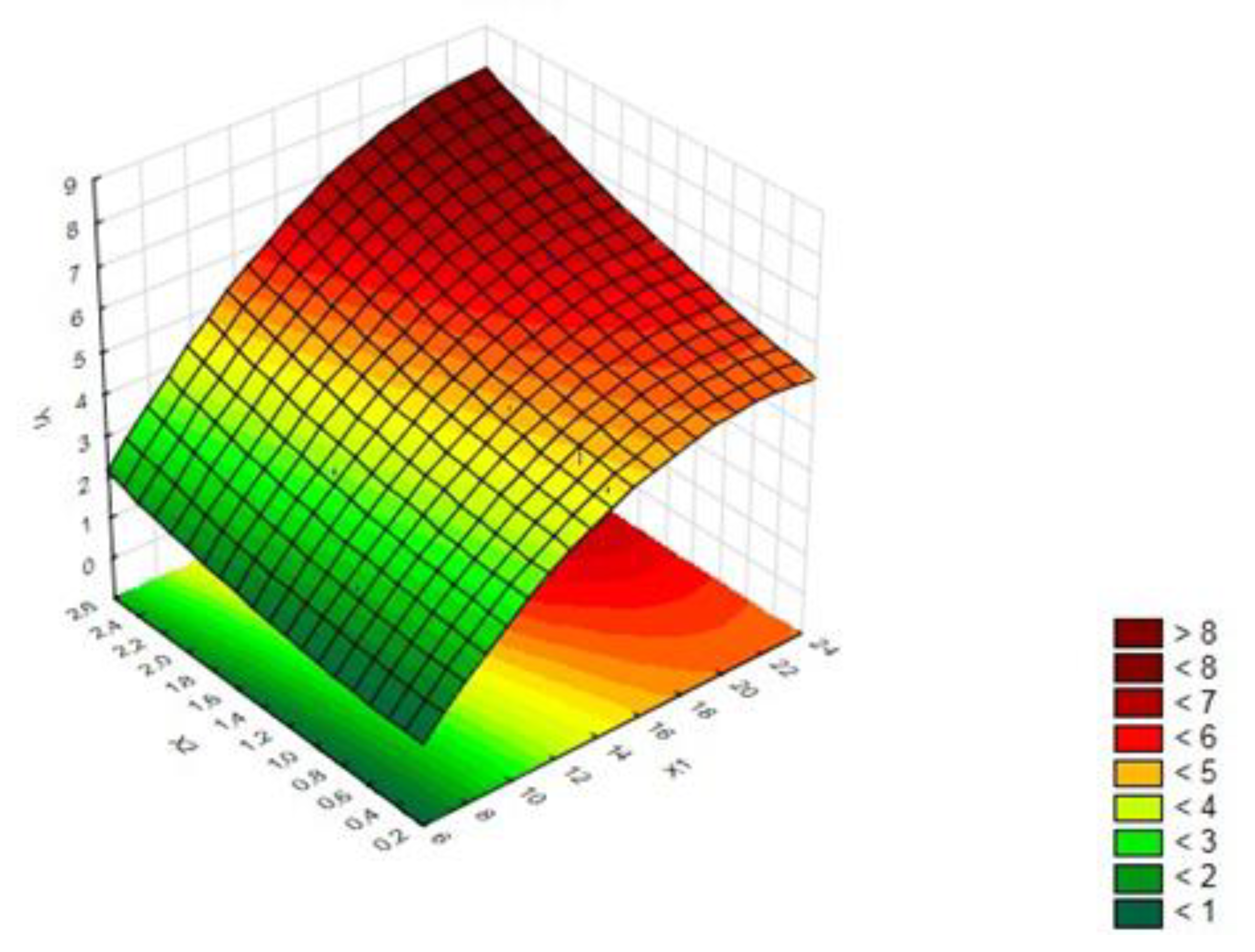
2.5. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection of Lachancea and Kluyveromyces Yeast Strains
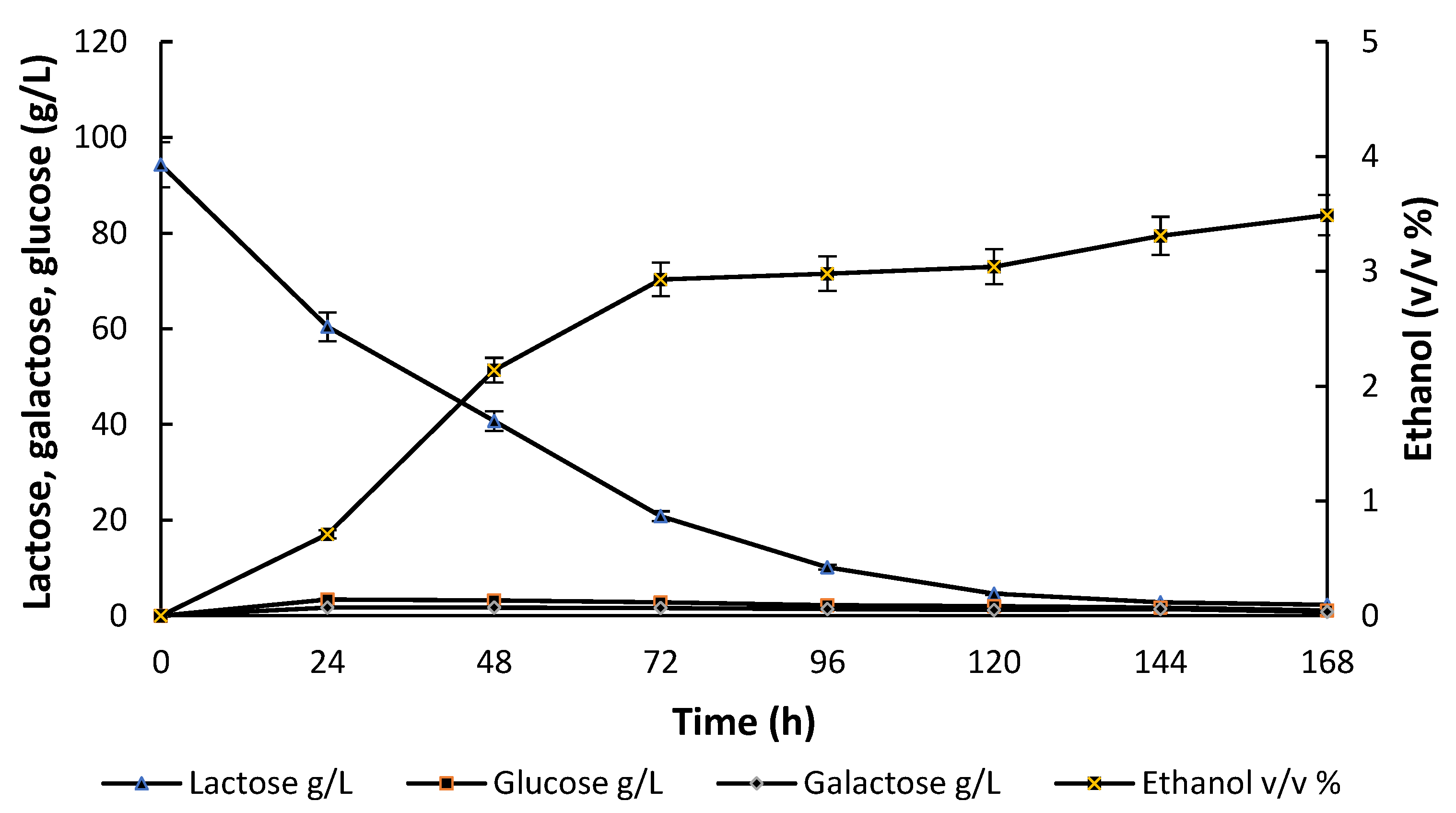
3.2. Batch Fermentation Processes with the Mixed Culture
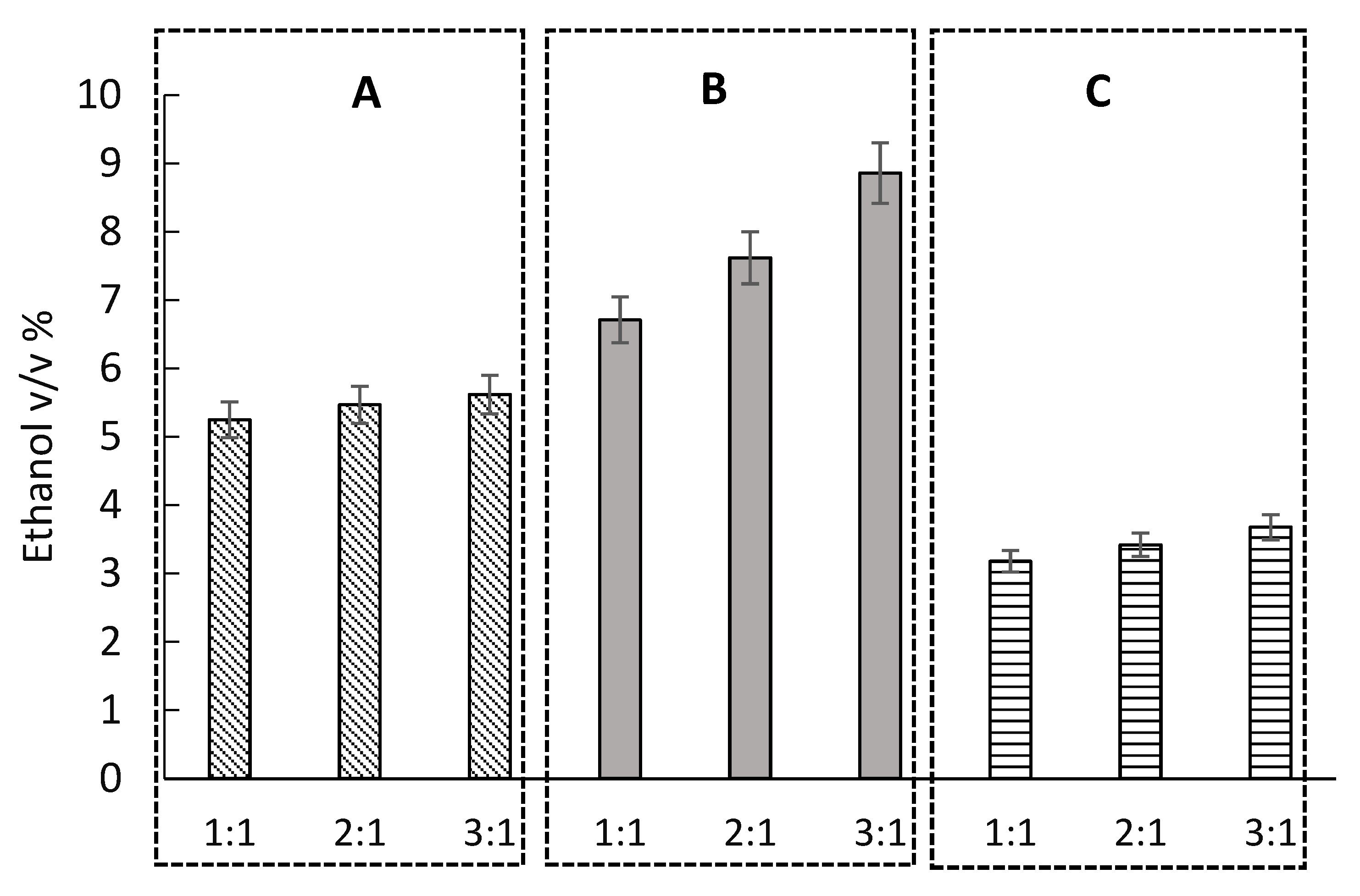
3.3. Effect of Repeated Inoculation Techniques
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jelen, P. Whey processing: Utilization and products. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences; Roginski, H., Fuquay, J.W., Fox, P.F., Eds.; Academic: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 2739–2745. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, S.; Owais, M. Ethanol production from crude whey by Kluyveromyces marxianus. Biochem. Eng. J. 2005, 27, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzipaschali, A.A.; Stamatis, A.G. Biotechnological utilization with a focus on anaerobic treatment of cheese whey: Current status and prospects. Energies 2012, 5, 3492–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithers, G.W. Whey and whey proteins-from ‘gutter-to-gold’. Int. Dairy J. 2008, 18, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, J.; Prazeres, A.R.; Carvalho, F.; Beltrán, F. Treatment of cheese whey wastewater: Combined coagulation, flocculation and aerobic biodegradation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7871–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prazeres, A.R.; Carvalho, F.; Rivas, J. Cheese whey management: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 110, 48–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhawa, S.S.; Kennedy, J.F. Whey—Pollution problem and potential utilization. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1988, 23, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venetsaneas, N.; Antonopoulou, G.; Stamatelatou, K.; Kornaros, M.; Lyberatos, G. Using cheese whey for hydrogen and methane generation in a two-stage continuous process with alternative pH controlling approaches. Biores. Technol. 2009, 100, 3713–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koushki, M.; Jafari, M.; Azizi, M. Comparison of ethanol production from cheese whey permeate by two yeast strains. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, G.; Guillaume, M.; Galzy, P. Alcohol production by yeast in whey ultrafiltrate. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1980, 22, 1277–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourkoutas, Y.; Dimitropoulou, S.; Kanellaki, M.; Marchant, R.; Nigam, P.; Banat, I.M.; Koutinas, A.A. High-temperature alcoholic fermentation of whey using Kluyveromyces marxianus IMB3 yeast immobilized on delignified cellulosic material. Biores. Technol. 2002, 82, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansonetti, S.; Curcio, S.; Calabro, V.; Iorio, G. Bio-ethanol production by fermentation of ricotta cheese whey as an effective alternative non-vegetable source. Biomass Bioenergy 2009, 33, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, W.B.; Mantovani, H.C.; Passos, F.M.L. Ethanol production from cheese whey permeate by Kluyveromyces marxianus UFV-3: A flux analysis of oxido-reductive metabolism as a function of lactose concentration and oxygen levels. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2005, 36, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozmihci, S.; Kargi, F. Kinetics of batch ethanol fermentation of cheese-whey powder (CWP) solution as function of substrate and yeast concentrations. Biores. Technol. 2007, 98, 2978–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, P.R.F.; Santos, S.C.; Silva, E.L. Different ratios of carbon sources in the fermentation of cheese whey and glucose as substrates for hydrogen and ethanol production in continuous reactors. Int. J. Hydr. Energy 2014, 39, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Guo, X.; Shen, T.; Dong, J.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, D. Construction of lactose-consuming Saccharomyces cerevisiae for lactose fermentation into ethanol fuel. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 40, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kargi, F.; Ozmichi, S. Utilization of cheese whey powder (CWP) for ethanol fermentations: Effects of operating parameters. J. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2006, 38, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupte, A.M.; Nair, J.S. β-galactosidase production and ethanol fermentation from whey using Kluyveromyces marxianus NCIM 3551. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2010, 69, 855–859. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, K.C. Whey to Ethanol: A Biofuel Role for Dairy Cooperatives? United States Department of Agriculture, Rural Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; p. 214.
- Ferrari, M.D.; Loperena, L.; Varela, H. Ethanol production from concentrated whey permeate using a fed-batch culture of Kluyveromyces fragilis. Biotechnol. Lett. 1994, 16, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadiyanto, H.; Ariyanti, D.; Aini, A.P.; Pinundi, D.S. Optimization of ethanol production from whey through fed-batch fermentation using Kluyveromyces marxianus. Energy Procedia 2014, 47, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N. A photometric adaptation for the Somogyi method for the determination of glucose. J. Biol. Chem. 1944, 153, 375–380. [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi, M. A new reagent for the determination of sugars. J. Biol. Chem. 1945, 160, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Gabardo, S.; Pereira, G.F.; Klein, M.P.; Rech, R.; Hertz, P.F.; Ayub, M.A.Z. Dynamics of yeast immobilized-cell fluidized-bed bioreactors systems in ethanol fermentation from lactose-hydrolyzed whey and whey permeate. Bioproc. Biosys. Eng. 2016, 39, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dénes, K.; Farkas, C.; Hoschke, Á.; Rezessy-Szabó, J.M.; Nguyen, Q.D. Bioethanol fermentation of Jerusalem artichoke using mixed culture of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Kluyveromyces marxianus. Acta Aliment. 2013, 42, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, B.; Lima-Costa, M.E.; Constantino, A.; Raposo, S.; Felizardo, C.; Gonçalves, D.; Fernandes, T.; Dionísio, L.; Peinado, J.M. Growth kinetics and physiological behaviour of co-cultures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Kluyveromyces lactis, fermenting carob sugars extracted with whey. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2016, 92, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, C.; Kurita, O.; Kubo, T. Improved ethanol tolerance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in mixed cultures with Kluyveromyces lactis on high-sugar fermentation. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez-Antolinez, R.; Hijaso-Valsero, M.; Paniagua, A.I.; Gomez, X. Effect of nutrient supplementation on biobutanol production from cheese whey by ABE (Acetone–Butanol–Ethanol) fermentation. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 49, 217–222. [Google Scholar]
- Dragone, G.; Mussatto, S.I.; Almeida e Silva, J.B.; Teixeira, J.A. Optimal fermentation conditions for maximizing the ethanol production by Kluyveromyces fragilis from cheese whey powder. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 5, 1977–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guimarães, P.M.; Teixeira, J.A.; Domingues, L. Fermentation of lactose to bio-ethanol by yeasts as part of integrated solutions for the valorisation of cheese whey. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawel, J.; Kosikowski, F.V. Improving alcohol fermentation in concentrated ultrafiltration permeates of cottage cheese whey. J. Food Sci. 1978, 43, 1717–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.M.; Kosikowski, F.V. Alcohol and single cell protein production by Kluyveromyces in concentrated whey permeates with reduced ash. J. Dairy Sci. 1982, 65, 2082–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, J.H.; Burris, N.; Woodward, A.; Bailey, R.B. Lipid-enhanced ethanol production by Kluyveromyces fragilis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 45, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ariyanti, D.; Hadiyanto, H. Ethanol production from whey by Kluyveromyces marxianus in batch fermentation system: Kinetics parameters estimation. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal. 2013, 7, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.; Tomaska, M.; Kanuch, J.; Sturdik, E. Improved ethanol production from whey with Saccharomyces cerevisiae using permeabilized cells of Kluyveromyces marxianus. Acta Biotechnol. 1995, 15, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grba, S.; Stehlik-Tomas, V.; Stanzer, D.; Vahcic, N.; Skrlin, A. Selection of yeast strain Kluyveromyces marxianus for alcohol and biomass production on whey. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2002, 16, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaly, A.E.; El-Taweel, A.A. Effect of micro-aeration on the growth of Candida pseudotropicalis and production of ethanol during batch fermentation of cheese whey. Bioresour. Technol. 1995, 52, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczodrak, J.; Szewczuk, D.; Rogalski, J.; Fiedurek, J. Selection of yeast strain and fermentation conditions for high-yield ethanol production from lactose and concentrated whey. Acta Biotechnol. 1997, 17, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhou, J.; Xiao, D. Improved ethanol production by mixed immobilized cells of Kluyveromyces marxianus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae from cheese whey powder solution fermentation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Independent Variable | Symbol | Coded Levels | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| Initial CWP concentration % (w/v) | X1 | 7.5 | 10.0 | 15.0 | 20.0 | 22.5 |
| The ratio of yeast K. marxianus to S. serevisiae * | X2 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 1.7 |
| Strains | CWP % (w/v) | Ethanol % (v/v) | YET % |
|---|---|---|---|
| L. thermotolerans Y00702 | 10 | 2.4 ± 0.11 | 48.15 ± 1.92 |
| L. thermotolerans Y00715 | 10 | 3.0 ± 0.17 | 56.41 ± 2.39 |
| L. thermotolerans Y00775 | 10 | 3.4 ± 0.15 | 61.67 ± 3.61 |
| L. thermotolerans Y00798 | 10 | 2.8 ± 0.11 | 50.98 ± 2.62 |
| L. thermotolerans Y00873 | 10 | 3.3 ± 0.18 | 63.22 ± 3.41 |
| L. thermotolerans Y00959 | 10 | 2.6 ± 0.15 | 49.98 ± 2.15 |
| K. marxianus Y00963 | 10 | 3.5 ± 0.18 | 62.33 ± 2.99 |
| K. waltii Y01184 | 10 | 3.4 ± 0.16 | 62.04 ± 2.44 |
| CWP % (w/v) | Ethanol % (v/v) | YET % | Residual Lactose g/L |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 3.9 ± 0.15 | 69.26 ± 3.43 | 3.03 ± 0.11 |
| 15 | 5.8 ± 0.22 | 82.64 ± 4.25 | 9.71 ± 0.37 |
| 20 | 7.3 ± 0.29 | 70.35 ± 3.22 | 29.19 ± 0.93 |
| 25 | 5.3 ± 0.25 | 32.75 ± 1.27 | 61.86 ± 2.45 |
| 30 | 3.1 ± 0.11 | 11.62 ± 0.42 | 87.32 ± 4.12 |
| Run No. | X1 | X2 * | Y (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 22.0 | 1.0 | 5.8 |
| 2 | 20.0 | 1.5 | 6.5 |
| 3 | 15.0 | 0.5 | 5.1 |
| 4 | 15.0 | 2.4 | 6.2 |
| 5 | 15.0 | 0.3 | 4.4 |
| 6 | 10.0 | 1.5 | 3.5 |
| 7 | 10.0 | 0.5 | 2.8 |
| 8 | 8.0 | 1.0 | 2.3 |
| 9 | 15.0 | 1.0 | 4.9 |
| 10 | 15.0 | 1.0 | 4.6 |
| Factor | Seq SS | DF | Adj M | F | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 10.5615 | 1 | 10.5615 | 95.8273 | 0.0006 |
| X1*X1 | 0.7809 | 1 | 0.7809 | 7.0853 | 0.0562 |
| X2 | 0.6847 | 1 | 0.6847 | 6.2129 | 0.0672 |
| X2*X2 | 0.0399 | 1 | 0.0399 | 0.3619 | 0.5798 |
| X1*X2 | 0.0211 | 1 | 0.0002 | 0.1916 | 0.6841 |
| Error | 0.4408 | 4 | 0.4058 | ||
| Total Seq SS | 17.7290 | 9 |
| Factor | Effect | Standard Error | t-Value | p-Value | Conf. Limit (−95%) | Conf. Limit (+95%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 4.9237 | 0.2022 | 24.3396 | 0.0000 | 4.3620 | 5.4853 |
| X1 (L) | 2.6584 | 0.2715 | 9.7891 | 0.0006 | 1.9044 | 3.4124 |
| X1 (Q) | −0.8684 | 0.3262 | −2.6618 | 0.0562 | −1.7742 | 0.0373 |
| X2 (L) | 0.6866 | 0.2754 | 2.4925 | 0.0672 | −0.0782 | 1.4514 |
| X2 (Q) | 0.0902 | 0.1500 | 0.6016 | 0.5798 | −0.3263 | 0.5069 |
| 1L by 2L | 0.1863 | 0.4255 | 0.4377 | 0.6841 | −0.9953 | 1.3679 |
| Run no. | CWP % (w/v) | Inoculation ratio of K. marxianus to S. cerevisiae | Ethanol % (v/v) | YET % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17.5 | 3:1 | 7.25 ± 0.22 | 72.33 ± 2.85 |
| 2 | 20.0 | 2.5:1 | 6.40 ± 0.18 | 63.48 ± 2.48 |
| 3 | 22.5 | 3:1 | 5.25 ± 0.17 | 55.21 ± 1.64 |
| 4 | 25.0 | 3.5:1 | 4.85 ± 0.17 | 44.07 ± 1.93 |
| Yeast | Fermentation Media | Bioreactor Type | Ethanol Titer (g/L) | Ethanol Yield (%) | Lactose Consumed (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monocultures | ||||||
| K. fragilis | CW permeate (240 g/L lactose) | 3 L static bottles | 80 | 70 | 89 | [31] |
| CW permeate (240 g/L lactose) | 14 L stirred tank | 72 | 91 | 61 | [32] | |
| CWPS (150 g/L lactose) with peptone supplementation | 1 L stirred flasks | 71 | 87 | 100 | [33] | |
| K. marxianus | CW (46 g/L lactose) | 1 L stirred tank | 8.6 | 37 | 93 | [21] |
| CW (48 g/L lactose) with yeast extract supplementation | shake flasks | 7.9 | 32 | - | [34] | |
| CWPS (60 g/L lactose) with yeast extract and salts supplementation | 5 L stirred tank | 26 | 82 | 100 | [35] | |
| CWPS (75 g/L lactose) | shake-flasks | 41 | 100 | 100 | [14] | |
| CW (100 g/L lactose) with yeast extract and salts supplementation | 2 L stirred tank | 43 | >80 | >95 | [36] | |
| CWPS-permeate (170 g/L lactose) | 1 L stirred flasks | 76-80 | >94 | >91 | [13] | |
| CWPS (150 g/L lactose) | shake-flasks | 80 | 100 | 98 | [17] | |
| Candida pseudotropicalis | CW and lactose powder (150 g/L lactose) | 5 L stirred tank | 45 | 98 | 78 | [37] |
| CWP (100 g/L lactose) | 500 mL shake flasks | 30 | 60 | 95 | [38] | |
| CW (100 g/L lactose) | shake-flasks | 41 | 78 | >99 | [38] | |
| Mixed cultures | ||||||
| K. marxianus S. cerevisiae (free cells) | CWP (100 g/L lactose) | 500 mL shake flasks | 36 | 71 | 98 | [39] |
| K. marxianusS. cerevisiae (free cells) | CWP (150 g/L lactose) | 500 mL shake flasks | 80–82 | 86 | 92 | our results |
| K. marxianus S. cerevisiae (immobilized cells) | CWP (100 g/L lactose) | 500 mL shake flasks | 42 | 80 | >99 | [39] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farkas, C.; Rezessy-Szabó, J.M.; Gupta, V.K.; Bujna, E.; Pham, T.M.; Pásztor-Huszár, K.; Friedrich, L.; Bhat, R.; Thakur, V.K.; Nguyen, Q.D. Batch and Fed-Batch Ethanol Fermentation of Cheese-Whey Powder with Mixed Cultures of Different Yeasts. Energies 2019, 12, 4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234495
Farkas C, Rezessy-Szabó JM, Gupta VK, Bujna E, Pham TM, Pásztor-Huszár K, Friedrich L, Bhat R, Thakur VK, Nguyen QD. Batch and Fed-Batch Ethanol Fermentation of Cheese-Whey Powder with Mixed Cultures of Different Yeasts. Energies. 2019; 12(23):4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234495
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarkas, Csilla, Judit M. Rezessy-Szabó, Vijai Kumar Gupta, Erika Bujna, Tuan M. Pham, Klára Pásztor-Huszár, László Friedrich, Rajeev Bhat, Vijay Kumar Thakur, and Quang D. Nguyen. 2019. "Batch and Fed-Batch Ethanol Fermentation of Cheese-Whey Powder with Mixed Cultures of Different Yeasts" Energies 12, no. 23: 4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234495
APA StyleFarkas, C., Rezessy-Szabó, J. M., Gupta, V. K., Bujna, E., Pham, T. M., Pásztor-Huszár, K., Friedrich, L., Bhat, R., Thakur, V. K., & Nguyen, Q. D. (2019). Batch and Fed-Batch Ethanol Fermentation of Cheese-Whey Powder with Mixed Cultures of Different Yeasts. Energies, 12(23), 4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234495









