Evaluation of Marine Synechococcus for an Algal Biorefinery in Arid Regions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioprospecting for New Species, Isolation, and Identification
2.2. Culture Growth Media
2.3. Bioreactor Experimental Setup
2.4. Biomass Characterization
2.5. Harvesting
2.6. Cell Disruption
3. Results
3.1. Strain Identification and Growth Characteristics
3.2. Biomass Composition Characterization
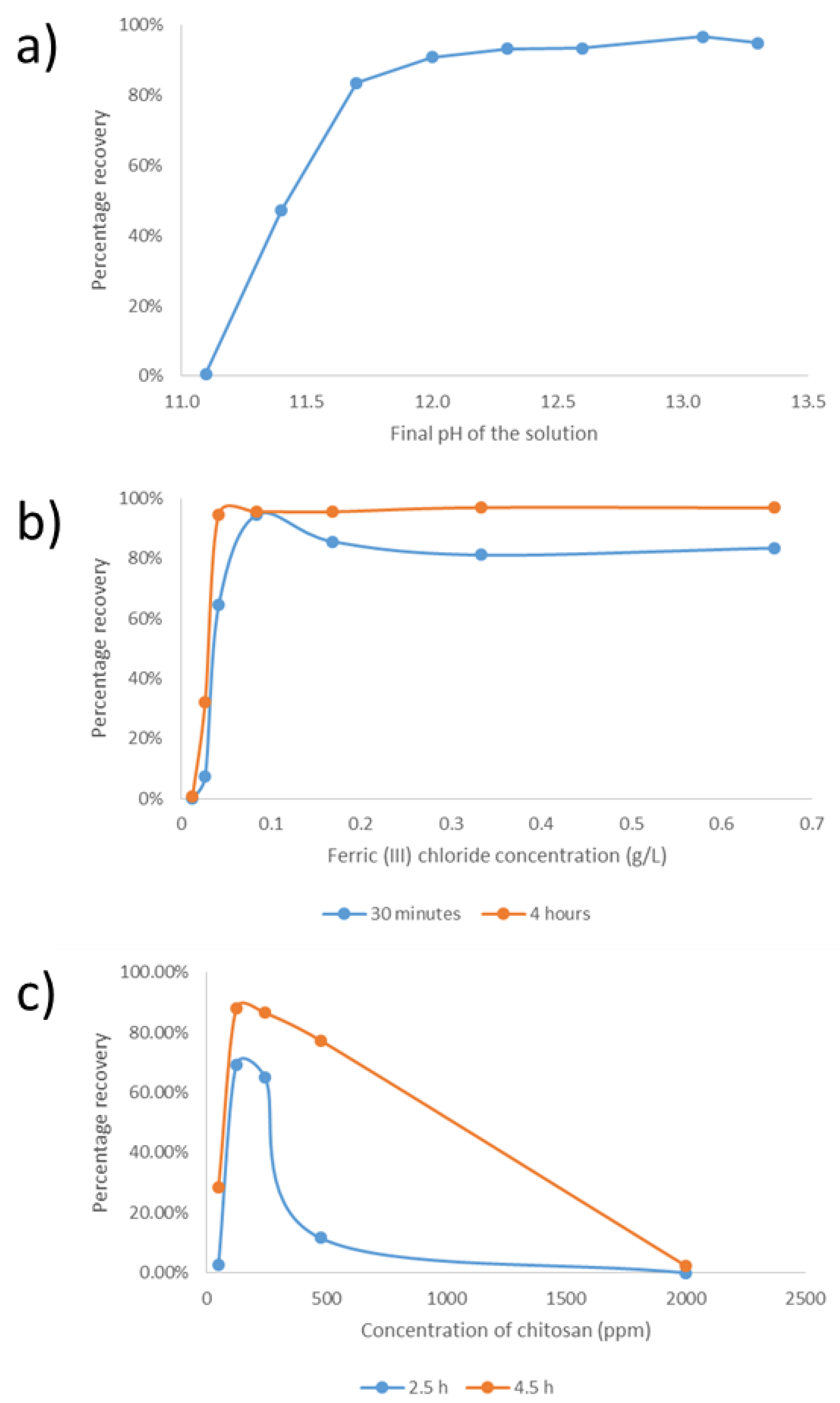
3.3. Harvesting Evaluation
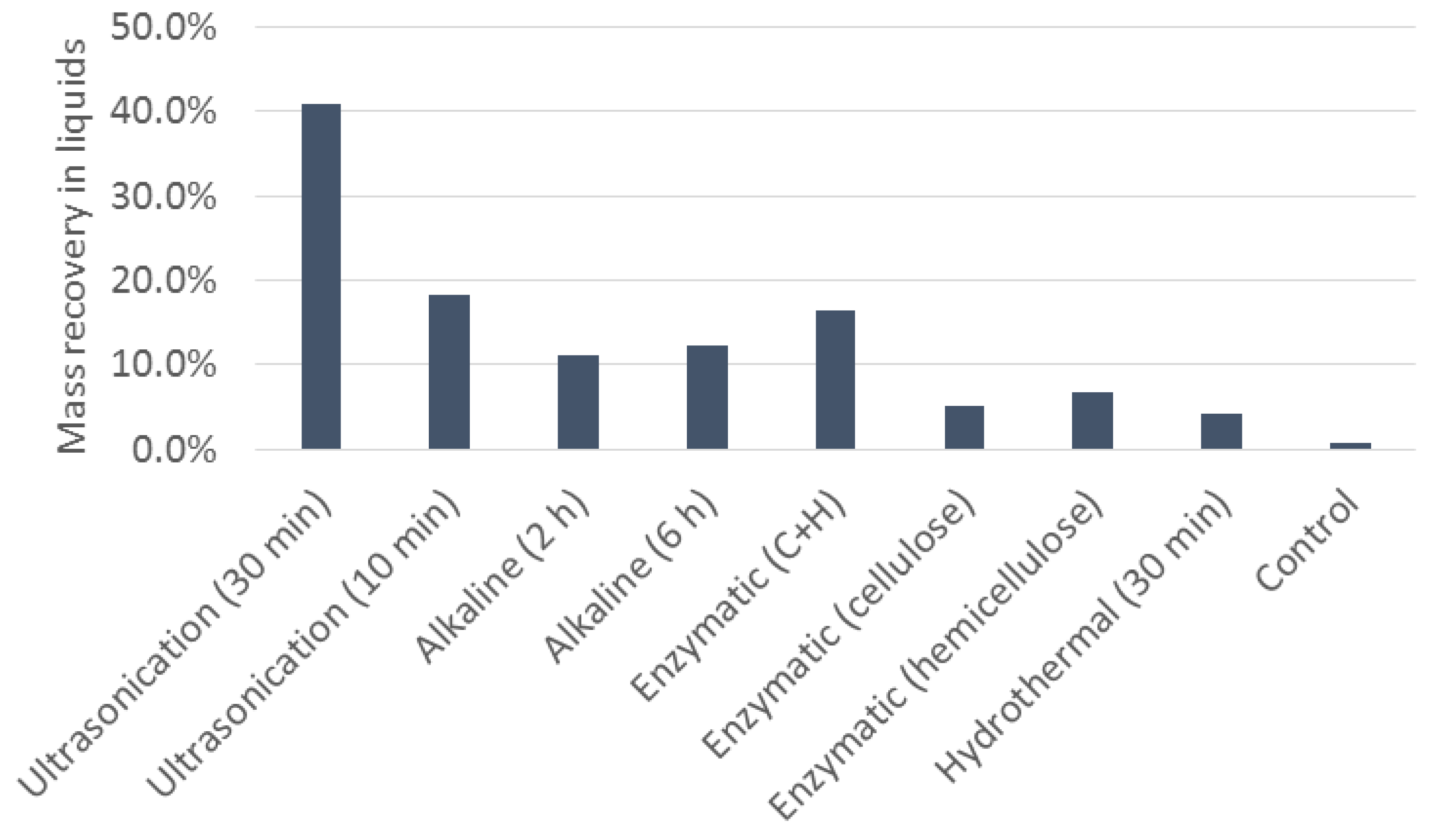
3.4. Cell Disruption and Product Recovery
3.5. Biorefinery Perspective on Product Portfolio
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ang, B.W.; Choong, W.L.; Ng, T.S. Energy security: Definitions, dimensions and indexes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 1077–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marafi, K. Security Concerns in The Middle East For Oil Supply: Problems And Solutions. In Proceedings of the Energy and Environmental Challenges to Security, Budapest, Hungary, 21 November 2007; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 225–235. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, R.A.; Lavoie, J.-M. From first- to third-generation biofuels: Challenges of producing a commodity from a biomass of increasing complexity. Anim. Front. 2013, 3, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Fuel Ethanol Production Continues to Grow in 2017—Today in Energy—U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). Available online: https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=32152 (accessed on 30 April 2019).
- Barros, S. Brazil Biofuels Annual Report 2016; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Mohr, A.; Raman, S. Lessons from first generation biofuels and implications for the sustainability appraisal of second generation biofuels. Energy Policy 2013, 63, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, S.N.; Goud, V.V.; Rout, P.K.; Dalai, A.K. Production of first and second generation biofuels: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 578–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriquiry, M.A.; Du, X.; Timilsina, G.R. Second generation biofuels: Economics and policies. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 4222–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, L.; Owende, P. Biofuels from microalgae—A review of technologies for production, processing, and extractions of biofuels and co-products. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 557–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; You, F. Global optimization for sustainable design and synthesis of algae processing network for CO2 mitigation and biofuel production using life cycle optimization. AIChE J. 2014, 60, 3195–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanthoor-Koopmans, M.; Wijffels, R.H.; Barbosa, M.J.; Eppink, M.H.M. Biorefinery of microalgae for food and fuel. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 135, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ’t Lam, G.P.; Vermuë, M.H.; Eppink, M.H.M.; Wijffels, R.H.; van den Berg, C. Multi-Product Microalgae Biorefineries: From Concept Towards Reality. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, E.W. Micro-algae as a source of protein. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greetham, D.; Zaky, A.; Makanjuola, O.; Du, C. A brief review on bioethanol production using marine biomass, marine microorganism and seawater. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2018, 14, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, R.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Vishal, G.; Lee, H.-S.; Nagra, S. Algal biorefinery: A sustainable approach to valorize algal-based biomass towards multiple product recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 278, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocheński, T.; Torres, A.I.; Ashraf, M.T.; Schmidt, J.E.; Stephanopoulos, G. Evaluation of the production of lipids for fuels and proteins from microalgae by decomposition of the processing network. In Proceedings of the Computer Aided Chemical Engineering, San Diego, CA, USA, 1–5 July 2018; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 38, pp. 1635–1640. [Google Scholar]
- UAE Energy Strategy 2050—The Official Portal of the UAE Government. Available online: https://government.ae/en/about-the-uae/strategies-initiatives-and-awards/federal-governments-strategies-and-plans/uae-energy-strategy-2050 (accessed on 30 April 2019).
- Mokri, A.; Aal Ali, M.; Emziane, M. Solar energy in the United Arab Emirates: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 28, 340–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homepage|World Bank Climate Change Knowledge Portal. Available online: https://climateknowledgeportal.worldbank.org/ (accessed on 30 April 2019).
- Climate: Average Maximum Temperature °C (1977–2009). Available online: https://services.dubaiairports.ae/dubaimet/MET/Climate.aspx (accessed on 30 April 2019).
- Singh, S.P.; Singh, P. Effect of temperature and light on the growth of algae species: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakkak Amir Irrigation Systems in the United Arab Emirates. Available online: https://www.ecomena.org/tag/water-scarcity-in-uae/ (accessed on 30 April 2019).
- Andersen, R.A. Algal Culturing Techniques; Elsevier: Burlington, MA, USA, 2005; ISBN 0080456502. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, J.W.; Johnson, M.D.; Lacey, R.; Oyler, J.; Capareda, S. Harvesting and extraction technology contributions to algae biofuels economic viability. Algal Res. 2014, 5, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milledge, J.J.; Heaven, S. A review of the harvesting of micro-algae for biofuel production. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2013, 12, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theegala, C.S. Algal Cell Disruption and Lipid Extraction: A Review on Current Technologies and Limitations. In Algal Biorefineries; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 419–441. [Google Scholar]
- Eppink, M.H.M.; Olivieri, G.; Reith, H.; van den Berg, C.; Barbosa, M.J.; Wijffels, R.H. From Current Algae Products to Future Biorefinery Practices: A Review; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 99–123. [Google Scholar]
- Mata, T.M.; Martins, A.A.; Caetano, N.S. Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.T. Bacterial cell disruption: A key unit operation in the recovery of intracellular products. Biotechnol. Adv. 1991, 9, 217–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günerken, E.; D’Hondt, E.; Eppink, M.H.M.; Garcia-Gonzalez, L.; Elst, K.; Wijffels, R.H. Cell disruption for microalgae biorefineries. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, M.; King, P.M.; Wu, X.; Joyce, E.M.; Mason, T.J.; Yamamoto, K. Effect of sonication frequency on the disruption of algae. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Mohr, M.; Ma, X.; Cheng, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Chen, P.; Ruan, R. Hydrothermal pretreatment of microalgae for production of pyrolytic bio-oil with a low nitrogen content. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 120, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillard, R.R.L. Culture of Phytoplankton for Feeding Marine Invertebrates. In Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1975; pp. 29–60. [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan, J. Some considerations of the growth of marine algae in artificial media. Can. J. Microbiol. 1964, 10, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanier, R.Y.; Kunisawa, R.; Mandel, M.; Cohen-Bazire, G. Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriol. Rev. 1971, 35, 171–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Axelsson, M.; Gentili, F. A Single-Step Method for Rapid Extraction of Total Lipids from Green Microalgae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurens, L.M.L. Summative Mass Analysis of Algal Biomass—Integration of Analytical Procedures: Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP); National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2013.
- Lourenço, S.O.; Barbarino, E.; Lavín, P.L.; Lanfer Marquez, U.M.; Aidar, E. Distribution of intracellular nitrogen in marine microalgae: Calculation of new nitrogen-to-protein conversion factors. Eur. J. Phycol. 2004, 39, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wychen, S.V.; Laurens, L.M.L. Determination of Total Carbohydrates in Algal Biomass: Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP); National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2016.
- Wychen, S.V.; Laurens, L.M.L. Determination of Total Solids and Ash in Algal Biomass; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2013.
- Whitton, B.A.; Potts, M. The Ecology of Cyanobacteria: Their Diversity in Time and Space; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2007; ISBN 0306468557. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hafedh, Y.S.; Alam, A.; Beltagi, M.S. Food Production and Water Conservation in a Recirculating Aquaponic System in Saudi Arabia at Different Ratios of Fish Feed to Plants. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2008, 39, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Li, Y.; Schenk, P.M. Algal Biorefinery: Sustainable Production of Biofuels and Aquaculture Feed? In The Science of Algal Fuels; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 21–41. [Google Scholar]
- Gunning, D.; Maguire, J.; Burnell, G.; Gunning, D.; Maguire, J.; Burnell, G. The Development of Sustainable Saltwater-Based Food Production Systems: A Review of Established and Novel Concepts. Water 2016, 8, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozzi, V.; Parisi, G.; Di Crescenzo, D.; Giordano, M.; Carnevali, O.; Nozzi, V.; Parisi, G.; Di Crescenzo, D.; Giordano, M.; Carnevali, O. Evaluation of Dicentrarchus labrax Meats and the Vegetable Quality of Beta vulgaris var. cicla Farmed in Freshwater and Saltwater Aquaponic Systems. Water 2016, 8, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafahi, M.; Woolston, D. Aquaponics: A Sustainable Food Production System. In Proceedings of the International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition IMECE2014, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–20 November 2014; ASME: New York, NY, USA; p. V003T03A073. [Google Scholar]
- Bochenski, T.; Chan, W.Y.; Olsen, B.D.; Schmidt, J.E. Techno-economic analysis for the production of novel, bio-derived elastomers with modified algal proteins as a reinforcing agent. Algal Res. 2018, 33, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi Zenooz, A.; Zokaee Ashtiani, F.; Ranjbar, R.; Javadi, N. Synechococcus sp. (PTCC 6021) cultivation under different light irradiances—Modeling of growth rate-light response. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 46, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.C.; Meti, B.S. A Brief Review on Algal Lipid. Int. J. Res. Stud. Biosci. 2014, 2, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Vandamme, D.; Foubert, I.; Fraeye, I.; Meesschaert, B.; Muylaert, K. Flocculation of Chlorella vulgaris induced by high pH: Role of magnesium and calcium and practical implications. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 105, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safi, C.; Ursu, A.V.; Laroche, C.; Zebib, B.; Merah, O.; Pontalier, P.-Y.; Vaca-Garcia, C. Aqueous extraction of proteins from microalgae: Effect of different cell disruption methods. Algal Res. 2014, 3, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Biomass Compositional Analysis | |
|---|---|
| Component | Percentage |
| Proteins | 30 |
| Lipids | 26 |
| Carbohydrates | 34 |
| Ash | 4 |
| Residuals | 6 |
| Type of Media | Weight Percentage of Biomass | |
|---|---|---|
| Proteins | Lipids | |
| F/2 | 28 | 26 |
| ASW/BG | 54 | 3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bochenski, T.; Chaturvedi, T.; Thomsen, M.H.; Schmidt, J.E. Evaluation of Marine Synechococcus for an Algal Biorefinery in Arid Regions. Energies 2019, 12, 2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12122233
Bochenski T, Chaturvedi T, Thomsen MH, Schmidt JE. Evaluation of Marine Synechococcus for an Algal Biorefinery in Arid Regions. Energies. 2019; 12(12):2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12122233
Chicago/Turabian StyleBochenski, Tomasz, Tanmay Chaturvedi, Mette Hedegaard Thomsen, and Jens Ejbye Schmidt. 2019. "Evaluation of Marine Synechococcus for an Algal Biorefinery in Arid Regions" Energies 12, no. 12: 2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12122233
APA StyleBochenski, T., Chaturvedi, T., Thomsen, M. H., & Schmidt, J. E. (2019). Evaluation of Marine Synechococcus for an Algal Biorefinery in Arid Regions. Energies, 12(12), 2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12122233







