Steady-State Modeling of Fuel Cells Based on Atom Search Optimizer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Modeling of PEM Fuel Cell
3. Formulating the Objective Function and Constraints
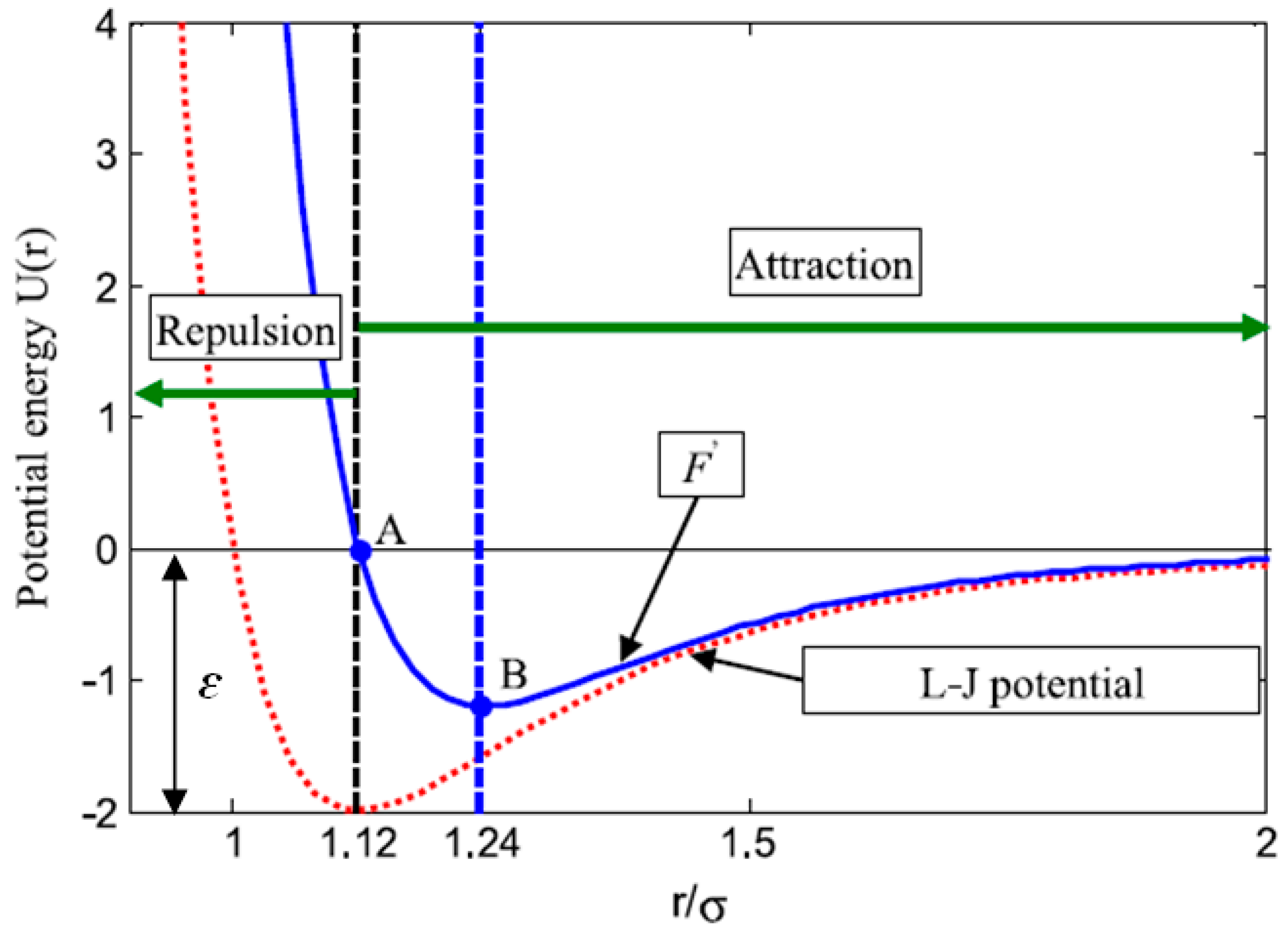
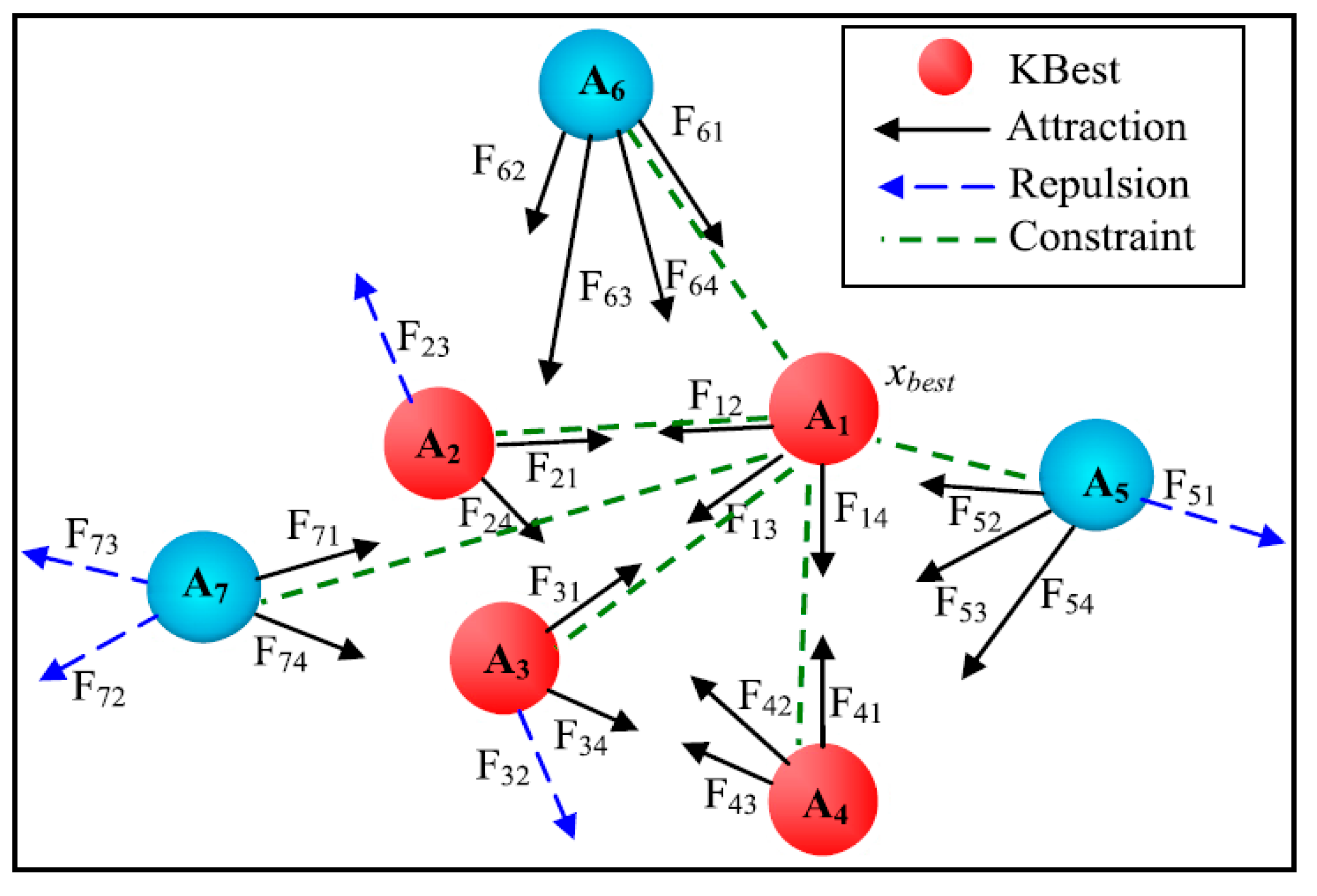
4. Atom Search Optimizer (ASO)
| Step 1: Randomly initialize a set of atoms X (solutions) and their velocity υ, and set = ∞, t = 1, i = 1. Step 2: Increment t = t + 1. Step 3: Increment i = i + 1. Step 4: Calculate the fitness value . Step 5: If ˃ , set = and = . Step 6: Calculate the mass (t) using Equations (30) and (31). Step 7: Determine its K neighbors using Equation (36). Step 8: Calculate the force of interaction Fi and the force of constraint is using Equations (23) and (27), respectively. Step 9: Update the velocity and the position using Equations (34) and (35), respectively. Step 10: If i ≤ go to Step 3. Step 11: If t ≤ T, go to Step 2. Step 12: Find the best solution so far, . Step 13: Stop. |
5. Demonstrated Results, Discussions and Validations
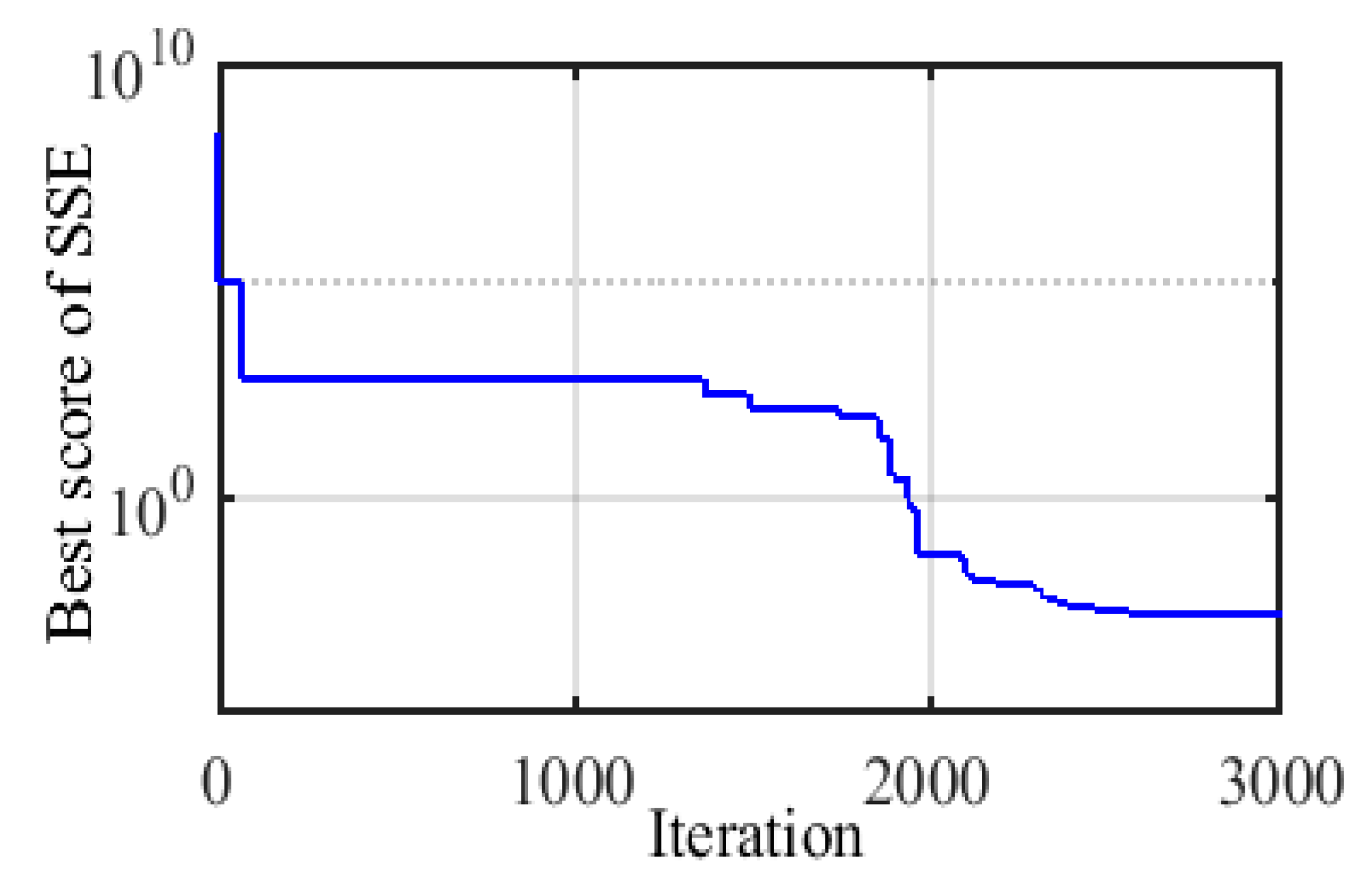
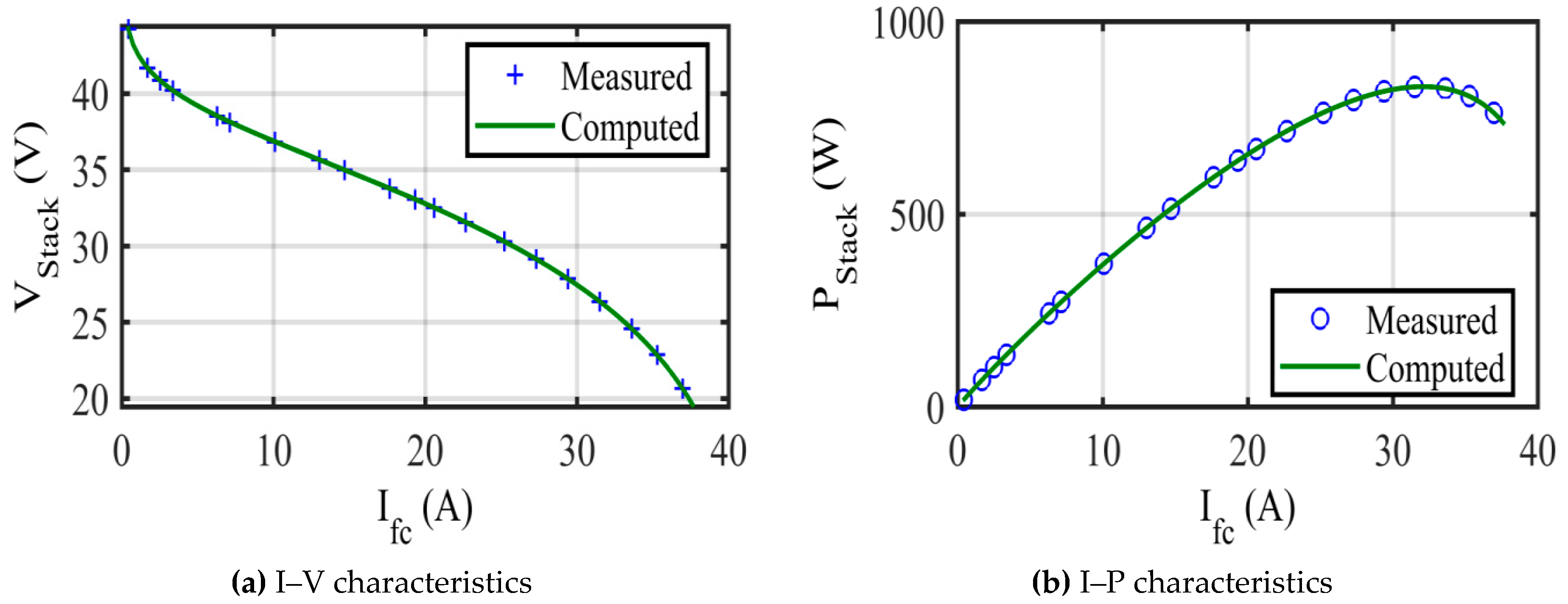
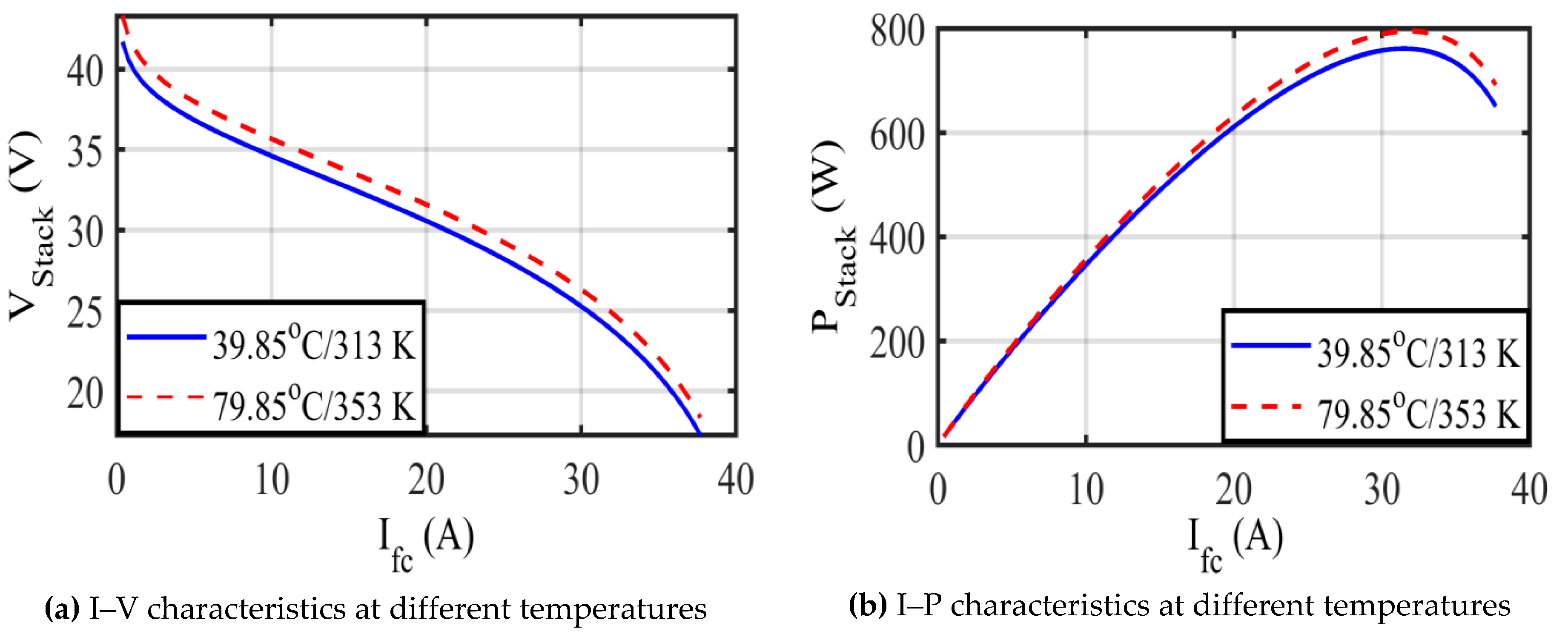
5.1. Test Case 1
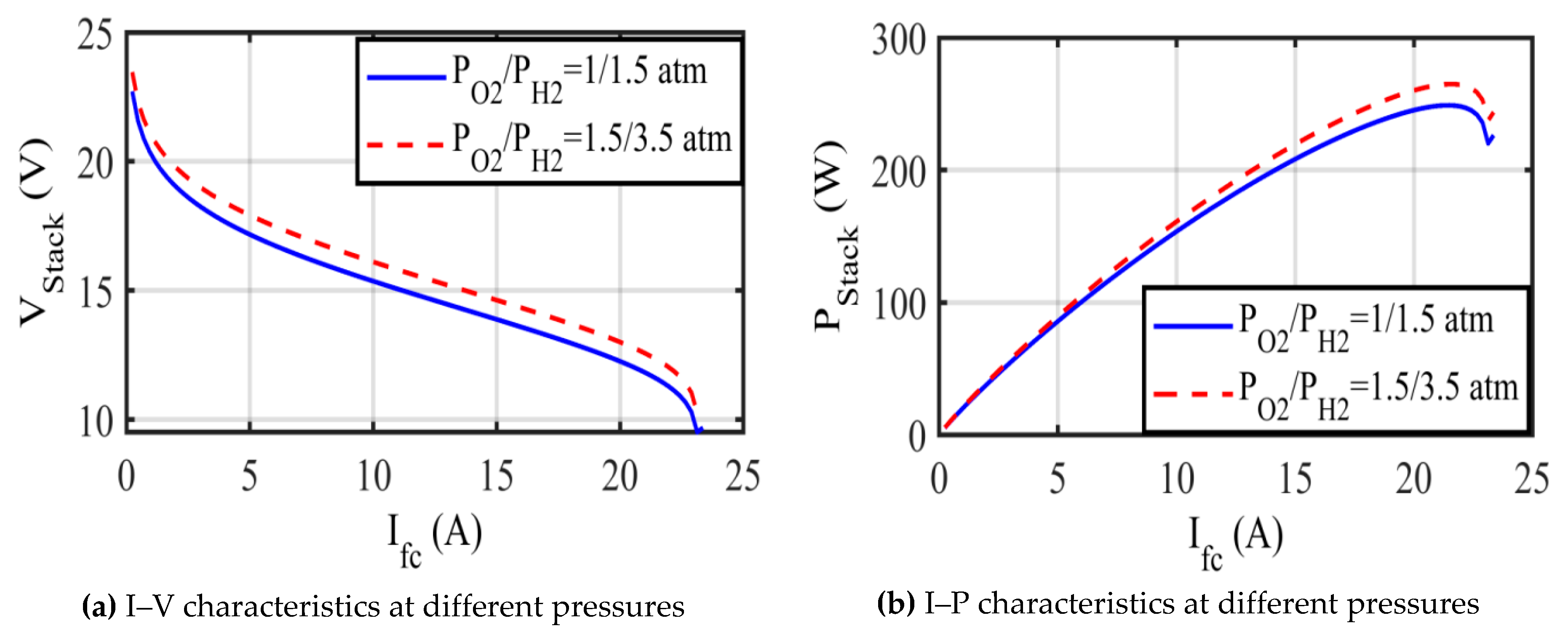
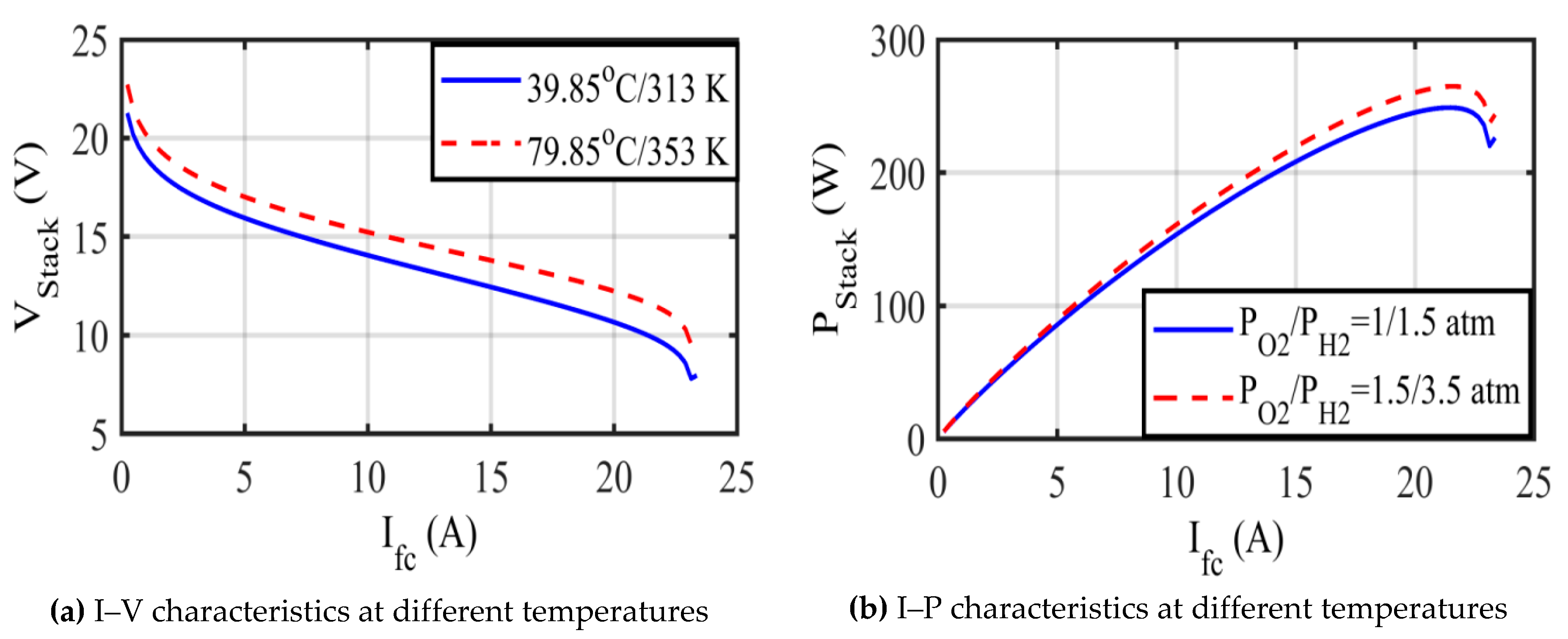
5.2. Test Case 2
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| open circuit potential | |
| activation over-voltage apiece cell | |
| ohmic voltage drop apiece cell | |
| concentration over-voltage apiece cell | |
| temperature of cell | |
| and | partial pressures of and correspondingly |
| saturation pressure of | |
| and | relative humidity of vapor at cathode and anode; correspondingly |
| operating current of the fuel cell | |
| and | inlet pressures at cathode and anode; correspondingly |
| area of membrane | |
| concentration of | |
| experiential parameters | |
| and | resistances of membrane and connections; correspondingly |
| membrane’s thickness | |
| membrane’s resistivity | |
| adjustable coefficient | |
| parametric factor | |
| and | actual and maximum density of current ; respectively |
| M | quantity of point measurements in I–V characteristics |
| k | summation counter |
| ε | potential hollow deepness |
| σ | distance where the potential is zero and considered as the length scale |
| r | spacing among two atoms |
| η(t) | deepness function |
| α | weight of deepness |
| and | upper and lower bounds of h; consecutively |
| vector among the atom i and the atom j | |
| part of a larger group of K atoms | |
| K | the foremost atoms that have the best values of function fitness |
| T | iterations’ maximum number |
| weight randomly exists among 1 and 0 | |
| best atom position at the iteration t | |
| length of fixed bond from the atom i to the best atom | |
| λ(t) | Lagrange multiplier |
| β | weight of multiplier |
| (t) | mass of atom i at the iteration t |
References
- Alshehri, F.; Suarez, V.G.; Torres, J.L.R.; Perilla, A.; Van Der Meijdena, M.A.M.M. Modelling and Evaluation of PEM Hydrogen Technologies for Frequency Ancillary Services in Future Multi-Energy Sustainable Power Systems. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpathy, S.; Padhee, S.; Bhuyan, K.C.; Ingale, G.B. Mathematical modelling and voltage control of fuel cell. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Energy Efficient Technologies for Sustainability (ICEETS), Nagercoil, India, 7–8 April 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, K.; Sathishkumar, K.; Rajasekar, N. A comprehensive review on parameter estimation techniques for Proton Exchange Membrane fuel cell modelling. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 93, 121–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papurello, D.; Silvestri, S.; Tomasi, L.; Belcari, I.; Biasioli, F.; Santarelli, M. Biowaste for SOFCs. Energy Procedia 2016, 101, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarelli, M. Carbon recovery and re-utilization (CRR) from the exhaust of a solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC): Analysis through a proof-of-concept. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 18, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, I.S.; Ursua, A.; Sanchis, P. Modelling of PEM Fuel Cell Performance: Steady-State and Dynamic Experimental Validation. Energies 2014, 7, 670–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Fergany, A.A. Extracting optimal parameters of PEM fuel cells using salp swarm optimizer. Renew. Energy 2018, 119, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wanga, N. An adaptive RNA genetic algorithm for modeling of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafaoli-Masoule, M.; Bahrami, A.; Elsayed, E.M. Optimum design parameters and operating condition for maximum power of a direct methanol fuel cell using analytical model and genetic algorithm. Energy 2014, 70, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, K.; Babu, T.; Balasubramanian, K.; Kumar, K.; Rajaseka, N. A novel approach for fuel cell parameter estimation using simple Genetic Algorithm. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2015, 12, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaseka, N.; Jacob, B.; Balasubramanian, K.; Priya, K.; Sangeetha, K.; Babu, T.S. Comparative study of PEM fuel cell parameter extraction using Genetic Algorithm. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2015, 6, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, R.I.; Noura, H.; Fardoun, A. A Parameter identification approach of a PEM fuel cell stack using particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ASME 2013 11th International. Conference on Fuel Cell Science, Engineering and Technolog, Minneapolis, MA, USA, 14–19 July 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.Y. The optimal design for PEMFC modeling based on Taguchi method and genetic algorithm neural networks. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 13683–13694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarzadeh, A.; Rezazadeh, A. A new heuristic optimization algorithm for modeling of proton exchange membrane fuel cell: Bird mating optimizer. Int. J. Energy Res. 2013, 37, 1196–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Chen, W.; Cheng, Z.; Li, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Jia, J. Seeker optimization algorithm for global optimization: A case study on optimal modelling of proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2011, 33, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnieri, M.; Negro, E.; Noto, V.; Alotto, P. A selective hybrid stochastic strategy for fuel-cell multi-parameter identification. J. Power Sources 2016, 332, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, G. Parameter fitting of PEMFC models based on adaptive differential evolution. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 62, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarzadeh, A.; Rezazadeh, A. An innovative global harmony search algorithm for parameter identification of a PEM fuel cell model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 3473–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, K. A biogeography-based optimization algorithm with mutation strategies for model parameter estimation of solar and fuel cells. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 86, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, K. An improved TLBO with elite strategy for parameters identification of PEM fuel cell and solar cell models. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 3837–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Yan, X.; Xiaobo, L.; Cai, Z. Parameter extraction of different fuel cell models with transferred adaptive differential evolution. Energy 2015, 86, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wang, N.; Bi, Y.; Srinivasan, D. Parameter identification of PEMFC model based on hybrid adaptive differential evolution algorithm. Energy 2015, 90, 1334–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, K.; Jana, A.K. Dynamics and estimator-based nonlinear control of a PEM fuel cell. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2018, 26, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, A.; Rezk, H. Multi-verse optimizer for identifying the optimal parameters of PEMFC model. Energy 2018, 143, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Fergany, A.A. Electrical characterisation of proton exchange membrane fuel cells stack using grasshopper optimiser. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2018, 12, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; El-Hameed, M.A.; Farahat, M.A. Effective parameters’ identification for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell models using grey wolf optimizer. Renew. Energy 2017, 111, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, N. A novel P systems based optimization algorithm for parameter estimation of proton exchange membrane fuel cell model. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 8465–8476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wanga, L.; Zhang, Z. Atom search optimization and its application to solve a hydrogeologic parameter estimation problem. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2019, 163, 283–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wanga, L. A novel atom search optimization for dispersion coefficient estimation in groundwater. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 91, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, H.; Poole, C.P.; Safko, J.L. Classical Mechanics, 3rd ed.; Addison Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]




| ASO Parameters | SR-12 Modular | 250 W Stack |
|---|---|---|
| 25 | 10 | |
| 40 | 50 | |
| 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Parameter | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimized Value | −0.9217 | 0.0033 | 0.0001 | −0.0001 | 13.7608 | 0.0001 | 0.1497 |
| Algorithm | ADE [17] | IGHS [18] | TRADE [21] | ASO |
| MSE | 0.11885 | 0.1039 | 0.247013 | 0.0001015 |
| Algorithm | GOA [25] | GWO [26] | ASO | |
| SSE | 0.0478 | 1.517 | 0.00203 |
| Parameter | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimized Value | −1.1132 | 0.0036 | 0.0001 | −0.0002 | 22.1763 | 0.0001 | 0.0248 |
| Algorithm | ARNA-GA [8] | BBO-M [19] | STLBO [20] | HADE [22] | MVO [24] | BIPOA [27] | ASO |
| SSE | 8.1039 | 7.6165 | 7.6266 | 7.9908 | 3.5846 | 7.9416 | 0.7346 |
| Factor | SR-12 Modular | 250 W Stack |
|---|---|---|
| Best value of SSE | 0.00203 | 0.7346 |
| Worst value of SSE | 0.00304 | 1.0903 |
| Mean value of SSE | 0.00251 | 0.9156 |
| STD value of SSE | 0.0945 | |
| Variance of SSE | 0.0089 | |
| Average processing time per run (s) | 25.50 | 20.10 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agwa, A.M.; El-Fergany, A.A.; Sarhan, G.M. Steady-State Modeling of Fuel Cells Based on Atom Search Optimizer. Energies 2019, 12, 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12101884
Agwa AM, El-Fergany AA, Sarhan GM. Steady-State Modeling of Fuel Cells Based on Atom Search Optimizer. Energies. 2019; 12(10):1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12101884
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgwa, Ahmed M., Attia A. El-Fergany, and Gamal M. Sarhan. 2019. "Steady-State Modeling of Fuel Cells Based on Atom Search Optimizer" Energies 12, no. 10: 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12101884
APA StyleAgwa, A. M., El-Fergany, A. A., & Sarhan, G. M. (2019). Steady-State Modeling of Fuel Cells Based on Atom Search Optimizer. Energies, 12(10), 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12101884






