Microgrid as a Cost-Effective Alternative to Rural Network Underground Cabling for Adequate Reliability
Abstract
1. Introduction
- participation in demand response programs;
- export of on-site generation to the electricity grid;
- reduced costs as a result of added resiliency against outages and lost loads;
- participation in local microgrid energy markets.
2. Distribution Networks, Reliability, and Microgrids—Formation of the Case Studies
2.1. Distribution Network Reliability and Underground Cabling
2.2. Microgrid Case Studies
2.3. Electricity Market Data
3. Electricity Supply Adequacy Assessment in Microgrids during Network Outages
3.1. Microgrid Operation under Normal State
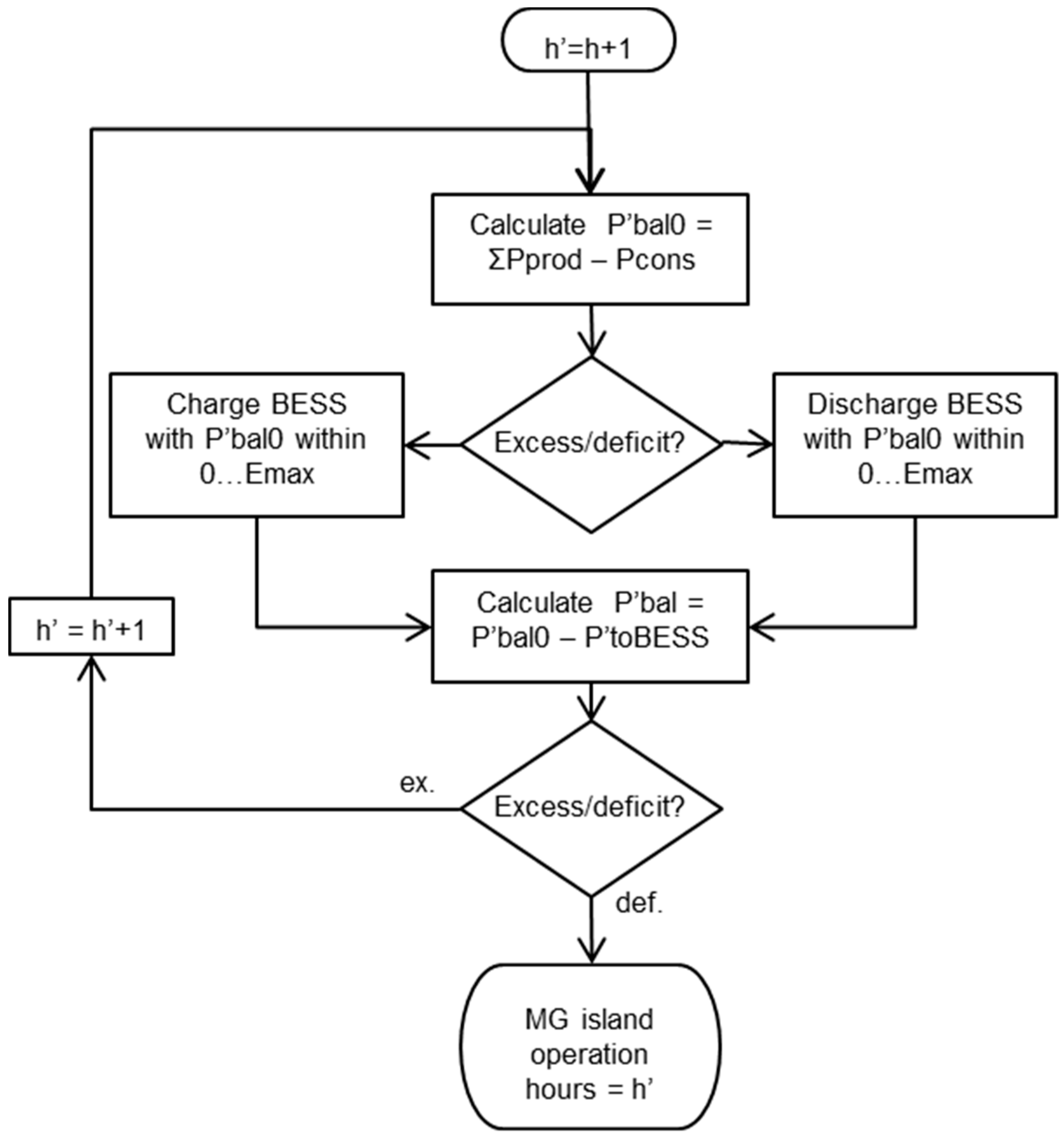
3.2. Microgrid Operation during Network Outage
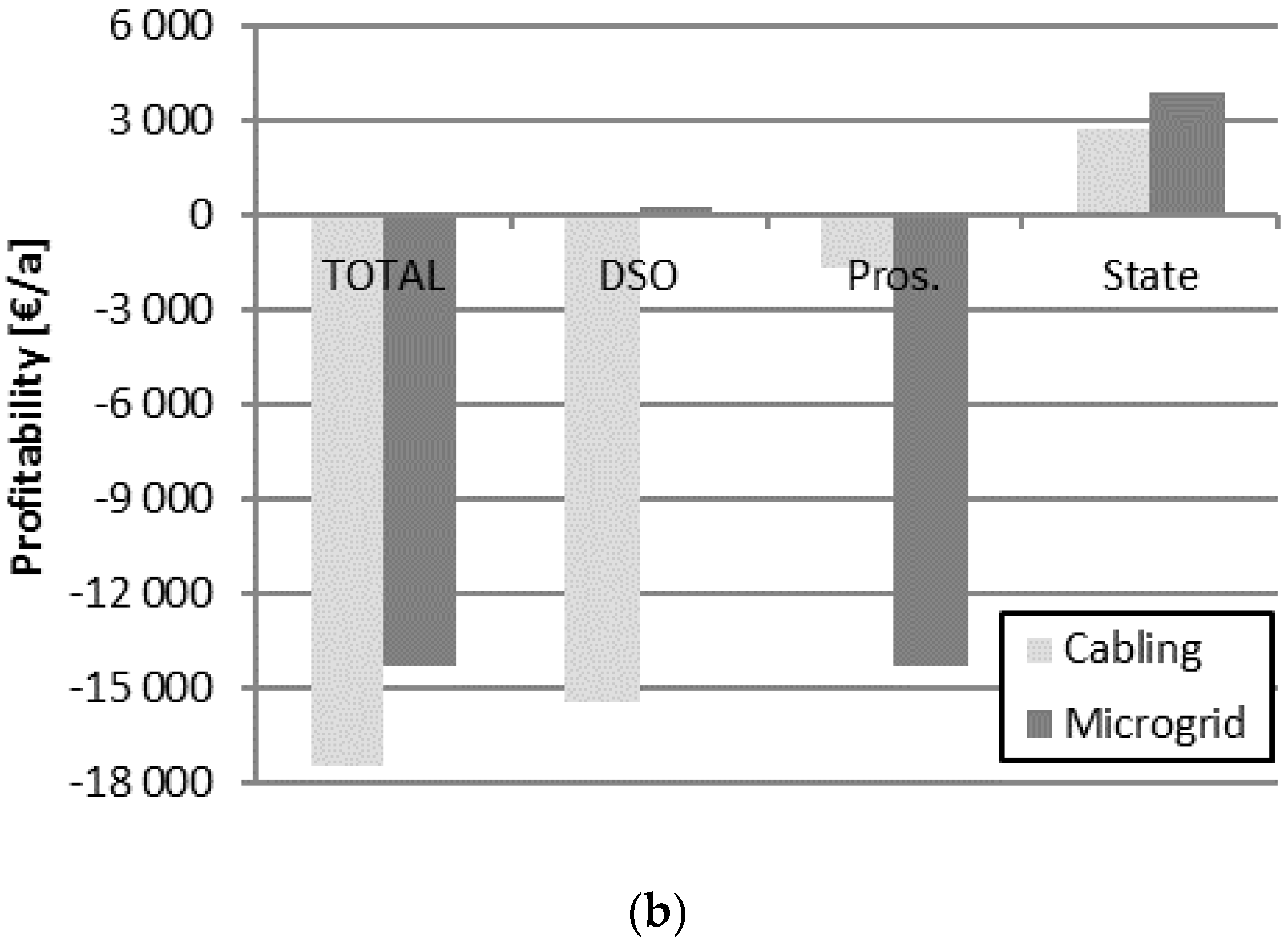
4. Overall Economic Comparison and Economic Influence on Stakeholders
4.1. Calculations for the Overall Economic Comparison
4.1.1. Underground Cabling Option
4.1.2. Microgrid Option
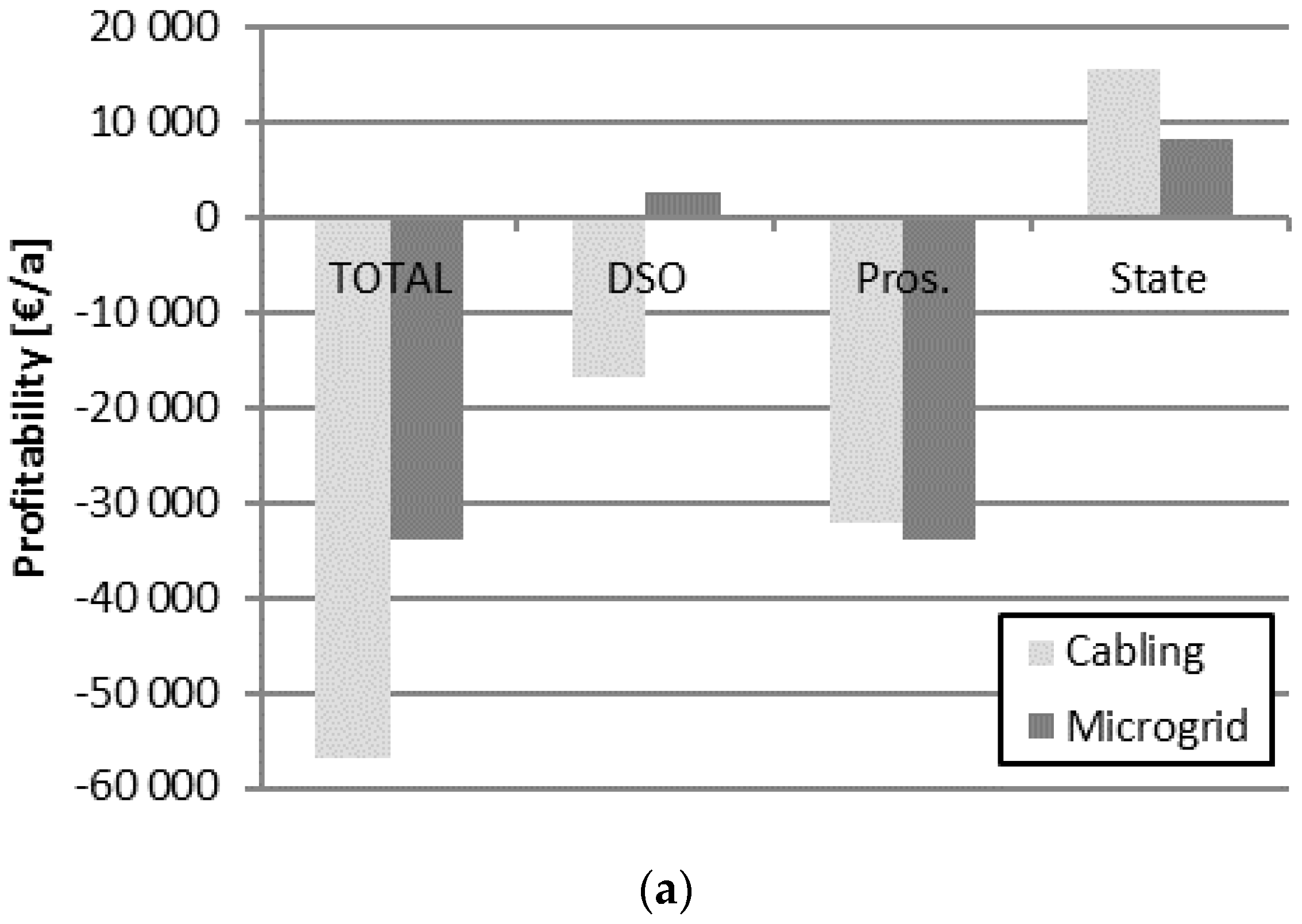
4.2. Economic Influence on the Relevant Stakeholders
4.2.1. Distribution System Operator
4.2.2. Consumers/Prosumers
4.2.3. State
5. Microgrid Data and Specifics for the Case Studies
5.1. Electricity Consumption
5.2. BESS Units
5.3. PV Production
5.4. Micro-CHP Production
6. Case Study Results
6.1. Analysis of Reliability of Power Supply
6.2. Calculations for Economic Comparison
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Mandatory Farm Gen-Set: | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cinv,gs | Investment cost for mandatory gen-set | 4000 € |
| Lgs | Expected lifetime/investment period | 10 a |
| Cable Investment Data: | ||
| Cinv,cab | Investment cost for MV (20 kV) cable 1 | 55,000 €/km |
| Cinv,cab | Investment cost for LV (0.4 kV) cable 1 | 35,000 €/km |
| xcab | Cable length used in the investment | 10 km |
| Lcab | Expected lifetime/investment period | 40 a |
| PV: | ||
|---|---|---|
| PPV,f | Farm PV rated power | 50 kWp |
| PPV,h | Detached-house PV rated power | 5 kWp |
| LPV | Expected lifetime/investment period | 30 a |
| Cinv,PV,f | Investment cost for 50 kWp PV (10–250 kW cost level) | 60,000 € |
| Cinv,PV,h | Investment cost for 5 kWp PV (few kW cost level) | 10,000 € |
| CHP: | ||
| PCHP,el | CHP rated electrical power | 40 kW |
| (PCHP,TOT: 140 kW; PCHP,heat: 100 kW) | ||
| ECHP,ann | Annual electricity produced in the study year | 150 MWh/a |
| CHP power plant investment cost | 400,000 € | |
| Cinv,CHP | Electricity share of CHP plant investment cost | 114,285 € |
| LCHP | Expected lifetime/investment period | 30 a |
| Cfuel | Approximated annual cost for fuel (wood chips) | 2800 € |
| Cmaint | Estimate for other annual maintenance costs | 1000 € |
| BESS: | ||
| Pmax,BESS | Maximum power for charging/discharging | 100 kW |
| Emax, BESS | Maximum/nominal charge | 200 kWh |
| LBESS | Expected lifetime/investment period | 10 a |
| Cinv,BESS | Investment cost for the BES (100 kW; 200 kWh) | 144,000 € |
| FCR-D Reserve Market Data for the Study Cases: | ||
| pFCR-D | FCR-D reserve capacity market price for annual agreements in 2017 | 4.7 €/MW,h |
| PBES,FCR-D | BES capacity available to FCR-D reserve market | 100 kW |
| TBES,FCR-D | Availability of BES for FCR-D reserve market | 7000 h |
| Retail Electricity Costs: | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cel.ret | Retail electricity price for consumer | 0.05 €/kWh |
| Cel.trans | Electricity distribution price for consumer | 0.065 €/kWh |
| Cel.sold | Price paid for sold electricity for prosumer | 0.027 €/kWh |
| Cel.s.tr | Electricity transmission price for prosumer | 0.0007 €/kWh |
| tel | Electricity tax (included in electricity distribution fee) | 0.02253 €/kWh |
| Economics Calculation Parameters: | ||
| r | Interest rate | 2% |
| s | Value-added tax | 24% |
References
- Marnay, C.; Robipalatio, F.J.; Siddiqui, A.S. Shape of the microgrid. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Power Engineering Society Winter Meeting (Conference Proceedings (Cat. No. 01CH37194)), Columbus, OH, USA, 28 January–1 February 2001; Volume 1, pp. 150–153. [Google Scholar]
- Lasseter, B. Microgrids. In Proceedings of the Power Engineering Society Winter Meeting, Columbus, OH, USA, 28 January–1 February 2001; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2001; Volume 1, pp. 146–149. [Google Scholar]
- Dimeas, A.L.; Hatziargyriou, N.D. A Multiagent System for Microgrids. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on, Intelligent Systems Application to Power Systems, Samos, Greece, 5–8 May 2004; Volume 2, pp. 396–401. [Google Scholar]
- Lasseter, R.H.; Paigi, P. Microgrid: A Conceptual Solution. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Aachen, Germany, 20–25 June 2004; pp. 4285–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, M.; Cardoso, G.; Mashayekh, S.; Forget, T.; DeForest, N.; Agarwal, A.; Schönbein, A. Value streams in microgrids: A literature review. Appl. Energy 2016, 162, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanparvar, K.; Al Faruque, M.A. Design Space Exploration for the Profitability of a Rule-Based Aggregator Business Model within a Residential Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, C.; Oudalov, A.; Timbus, A. The Provision of Frequency Control Reserves from Multiple Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avendano-Mora, M.; Camm, E.H. Financial Assessment of Battery Energy Storage Systems for Frequency Regulation Service. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 26–30 July 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haakana, J. Impact of Reliability of Supply on Long-Term Development Approaches to Electricity Distribution Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, Lappeenranta University of Technology, Lappeenranta, Finland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ahokas, J. Maatilojen Energiankäyttö. Enpos-Hankkeen Tulokset (In Finnish, Energy Use on Farms. Results of Enpos Project). 2013. Available online: https://helda.helsinki.fi/bitstream/handle/10138/40241/energian_sst.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 25 July 2018).
- Meta Economics Consulting Group Pty Ltd. Electricity Supply Issues for Farmers; Meta Economics Consulting Group Pty Ltd.: Newcastle, Australia, 2013. Available online: https://energyconsumersaustralia.worldsecuresystems.com/grants/442/AP-442-Meta-Economics-Farmers-electricity-supply-report.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2018).
- Oliveira, D.Q.; Zambroni de Souza, A.C.; Santos, M.V.; Almeida, A.B.; Lopes, B.I.L.; Saavedra, O.R. A fuzzy-based approach for microgrids islanded operation. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 149, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Starke, M.; Xiao, B.; Zhang, X.; Tomsovic, K. Microgrid optimal scheduling with chance-constrained islanding capability. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 145, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, P.P.; López, J.C.; Silva, L.C.P.; Rider, M.J. Security-constrained optimal energy management system for three-phase residential microgrids. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 146, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehir, M.A.; Batman, A.; Sonmez, M.A.; Font, A.; Tsiamitros, D.; Stimoniaris, D.; Kollatou, T.; Bagriyanik, M.; Ozdemir, A.; Dialynas, E. Impacts of microgrids with renewables on secondary distribution networks. Appl. Energy 2017, 201, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hendawi, M.; Gabbar, H.A.; El-Saady, G.; Ibrahim, E.N.A. Control and EMS of a grid-connected microgrid with economical analysis. Energies 2018, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haakana, J.; Lassila, J.; Kaipia, T.; Partanen, J. Comparison of Reliability Indices from the Perspective of Network Automation Devices. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2010, 25, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verho, P.; Mäkinen, A.; Kivikko, K.; Repo, S.; Lassila, J.; Partanen, J.; Pylvänäinen, J. Visionary development of distribution networks. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Electricity Distribution, Vienna, Austria, 21–24 May 2007; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Antikainen, J.; Repo, S.; Järventausta, P.; Verho, P. Interruption Costs Management in Distribution Network by Intentional Islanding Based on Mobile Stand-by Generation Units. In Proceedings of the 8th Nordic Electricity Distribution and Asset Management Conference (NORDAC 2008), Bergen, Norway, 8–9 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Vilppo, O.; Markkula, J.; Järventausta, P.; Repo, S.; Hakala, T. Cost-benefit analysis for using the Li-ion batteries in low-voltage network for decreasing the outage time experienced by customers. In Processed of the CIRED 24st International Conference on Electricity Distribution, Glasgow, Scotland, 12–15 June 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Haakana, J.; Lassila, J.; Kaipia, T.; Partanen, J. Utilisation of energy storages to secure electricity supply in electricity distribution networks. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Electric Distribution, CIRED, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–13 June 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaidan, I.; Alanazi, A.; Gao, W.; Wu, H.; Khodaei, A. State-Of-The-Art in Microgrid-Integrated Distributed Energy Storage Sizing. Energies 2017, 10, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, J. Reliability-based sizing of backup storage. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 1198–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, R.J.; Kazemi, S.; Lehtonen, M.; Saarijärvi, E. Impact of MV Connected Microgrids on MV Distribution Planning. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2012, 3, 2100–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidar, M.; Georgilakis, P.S.; Hatziargyriou, N.D.; Capuder, T.; Škrlec, D. Review of energy storage allocation in power distribution networks: Applications, methods and future research. IET Gener. Trans. Distrib. 2016, 10, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Energiavirasto. Päätös xxx/430/2015, Liite 2: Sähkön Jakeluverkkotoiminta ja Sähkön Suurjännitteinen Jakeluverkkotoiminta—Valvontamenetelmät neljännellä 1.1.2016-31.12.2019 ja Viidennellä 1.1.2020-31.12.2023 Valvontajaksolla; Energiavirasto: Helsinki, Finland, 2015; p. 120. Available online: www.energiavirasto.fi (accessed on 25 July 2018).
- Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO). MERRA-2 tavg1_2d_rad_Nx: 2d,1-Hourly, Time-Averaged, Single-Level, Assimilation, Radiation Diagnostics V5.12.4; Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO). MERRA-2 tavg1_2d_flx_Nx: 2d,1-Hourly, Time-Averaged, Single-Level, Assimilation, Surface Flux Diagnostics V5.12.4; Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Huld, T.; Müller, R.; Gambardella, A. A new solar radition database for estimating PV performance in Europe and Africa. Sol. Energy 2012, 86, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Communities. PVGIS Interactive Application. Available online: http://re.jrc.ec.europa.eu/pvgis/apps4/pvest.php# (accessed on 25 July 2018).

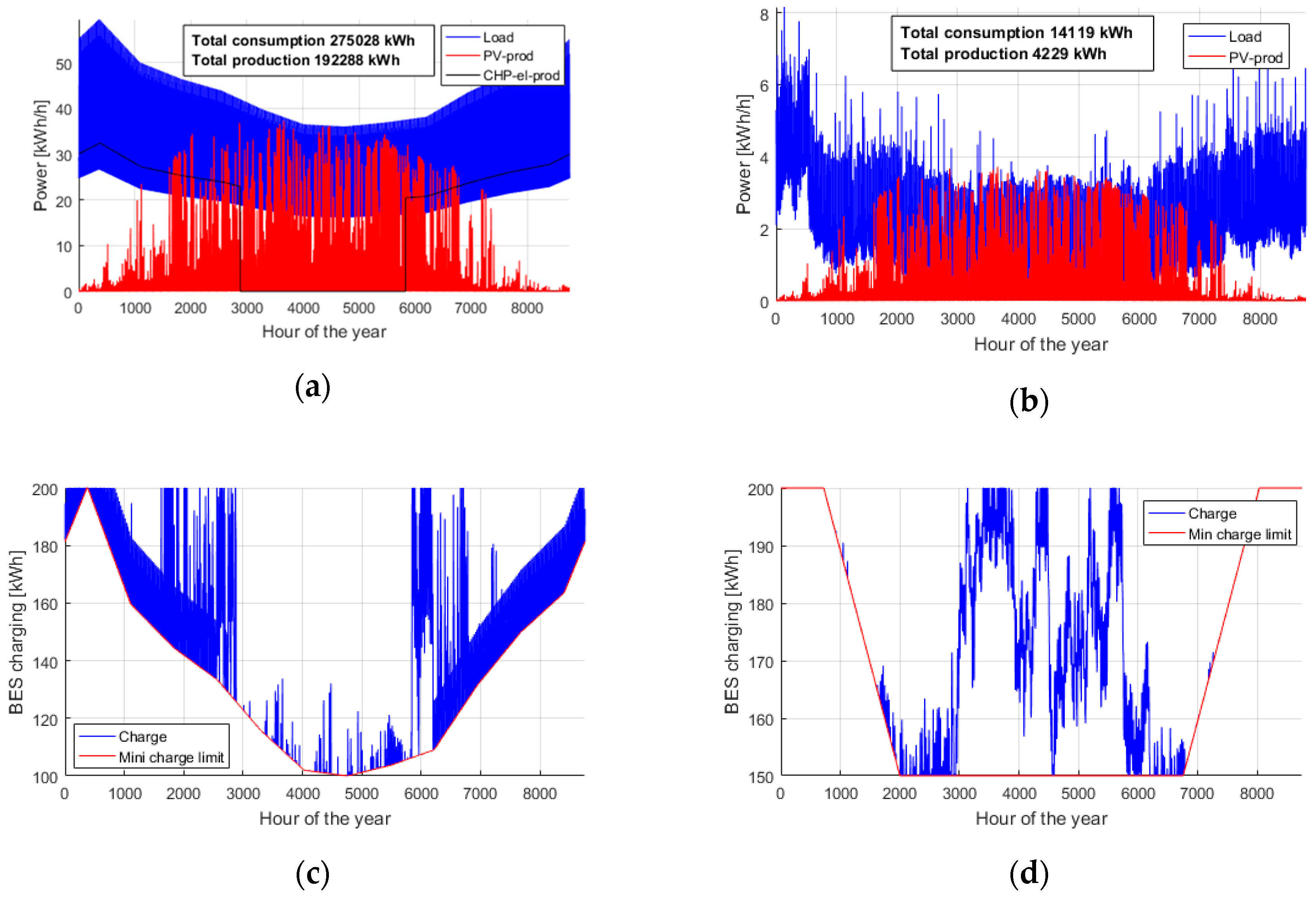
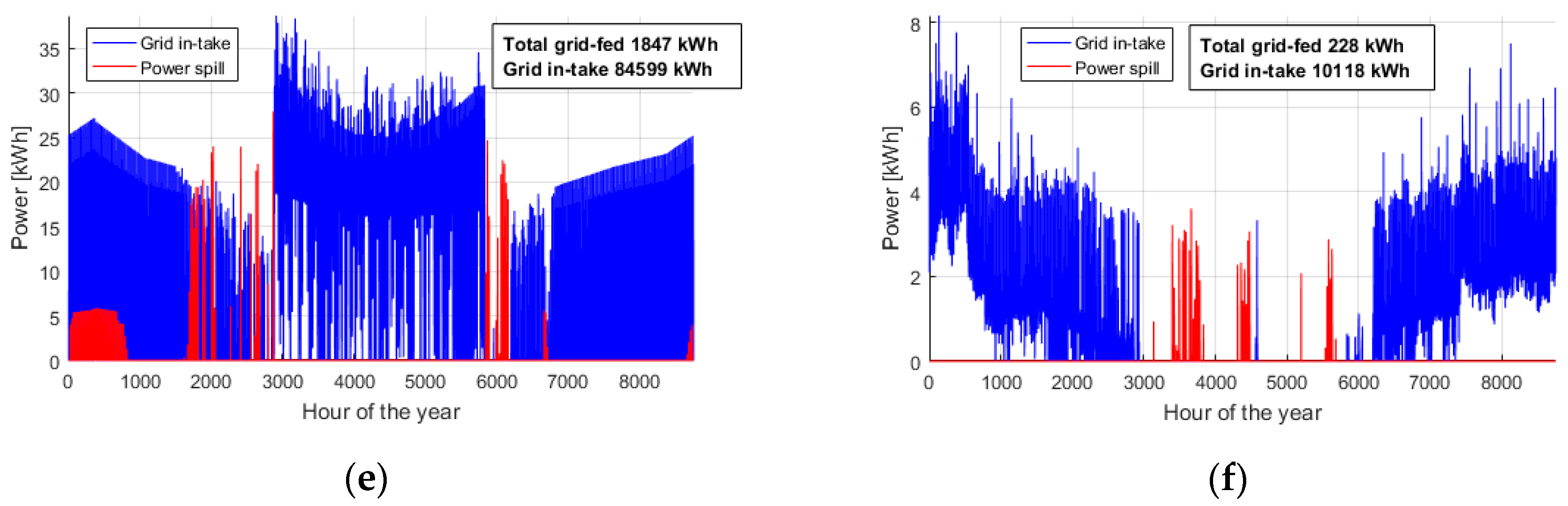
| Case Study | Consumption (kWh/a) | Production (kWh/a) |
|---|---|---|
| Farm | 275,028 | 192,288 |
| Detached house | 14,119 | 4229 |
| Capability Duration | Farm | Detached House | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Occurrences | % of year | Number of Occurrences | % of year | |
| <12 h | 0 | 0.0% | 0 | 0.0% |
| 12 to <24 h | 0 | 0.0% | 0 | 0.0% |
| 24 h to <2 days | 0 | 0.0% | 272 | 3.1% |
| 2 to <3 days | 87 | 1.0% | 593 | 6.8% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uski, S.; Rinne, E.; Sarsama, J. Microgrid as a Cost-Effective Alternative to Rural Network Underground Cabling for Adequate Reliability. Energies 2018, 11, 1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11081978
Uski S, Rinne E, Sarsama J. Microgrid as a Cost-Effective Alternative to Rural Network Underground Cabling for Adequate Reliability. Energies. 2018; 11(8):1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11081978
Chicago/Turabian StyleUski, Sanna, Erkka Rinne, and Janne Sarsama. 2018. "Microgrid as a Cost-Effective Alternative to Rural Network Underground Cabling for Adequate Reliability" Energies 11, no. 8: 1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11081978
APA StyleUski, S., Rinne, E., & Sarsama, J. (2018). Microgrid as a Cost-Effective Alternative to Rural Network Underground Cabling for Adequate Reliability. Energies, 11(8), 1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11081978





