Comparison of Shell and Solid Finite Element Models for the Static Certification Tests of a 43 m Wind Turbine Blade
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General
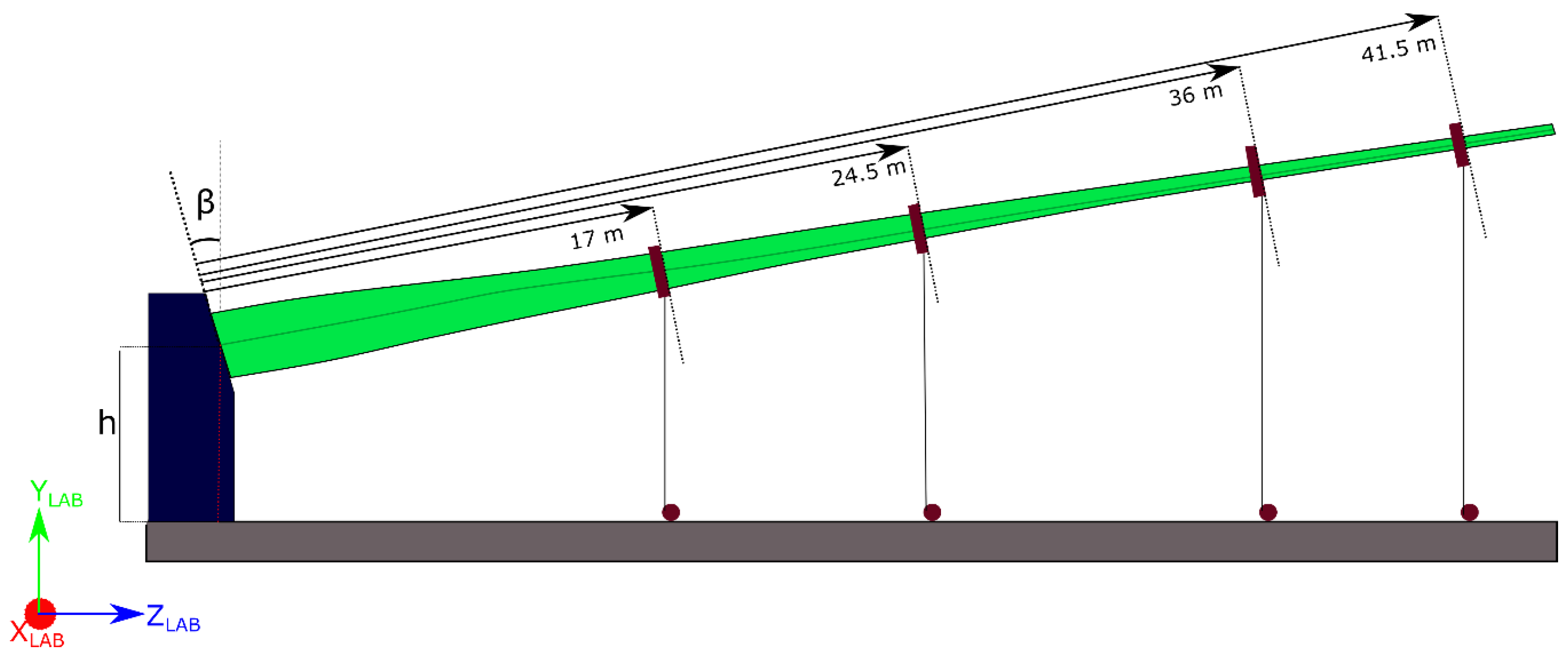
2.2. Static Tests
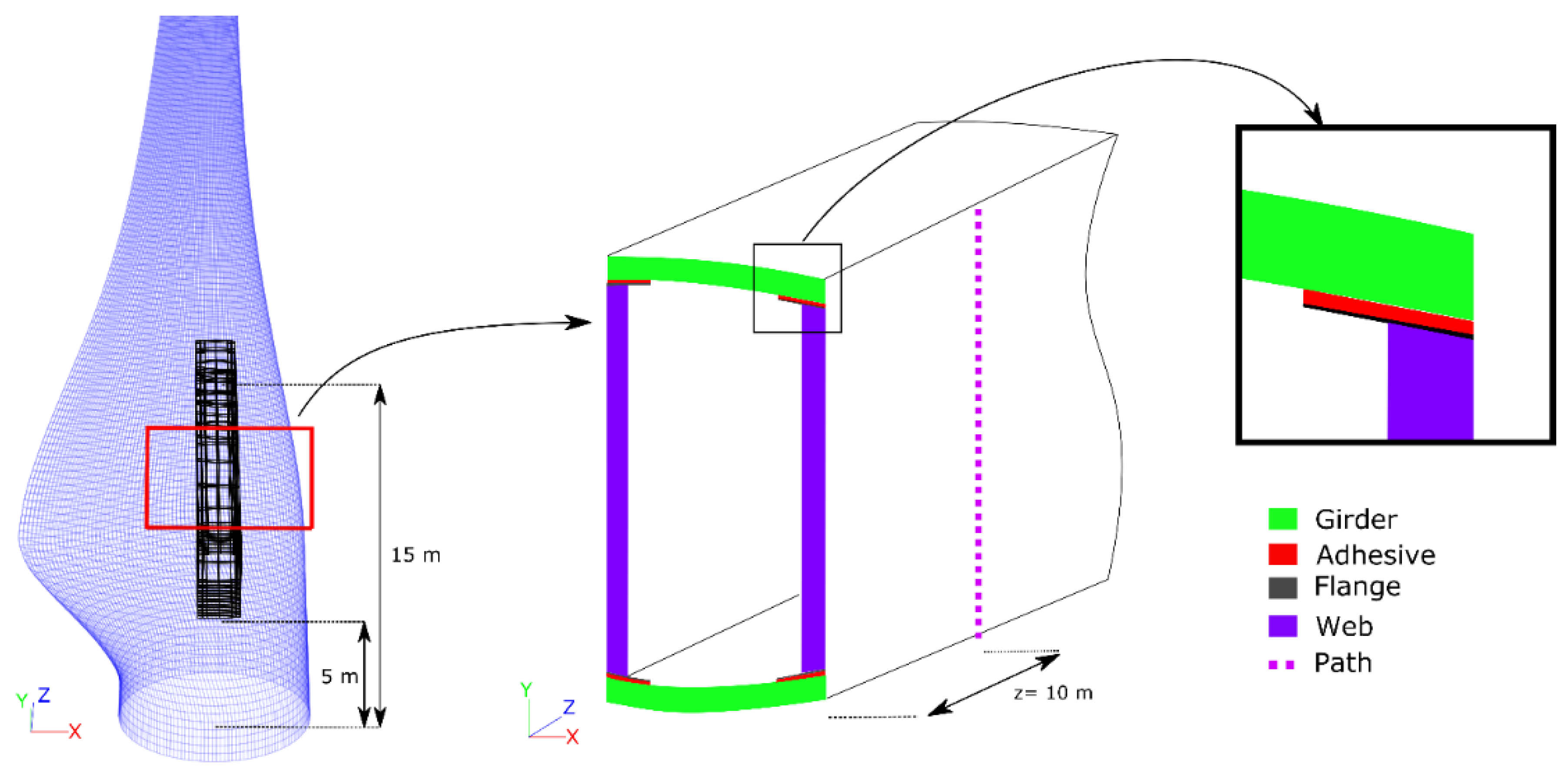
2.3. Spar Segment
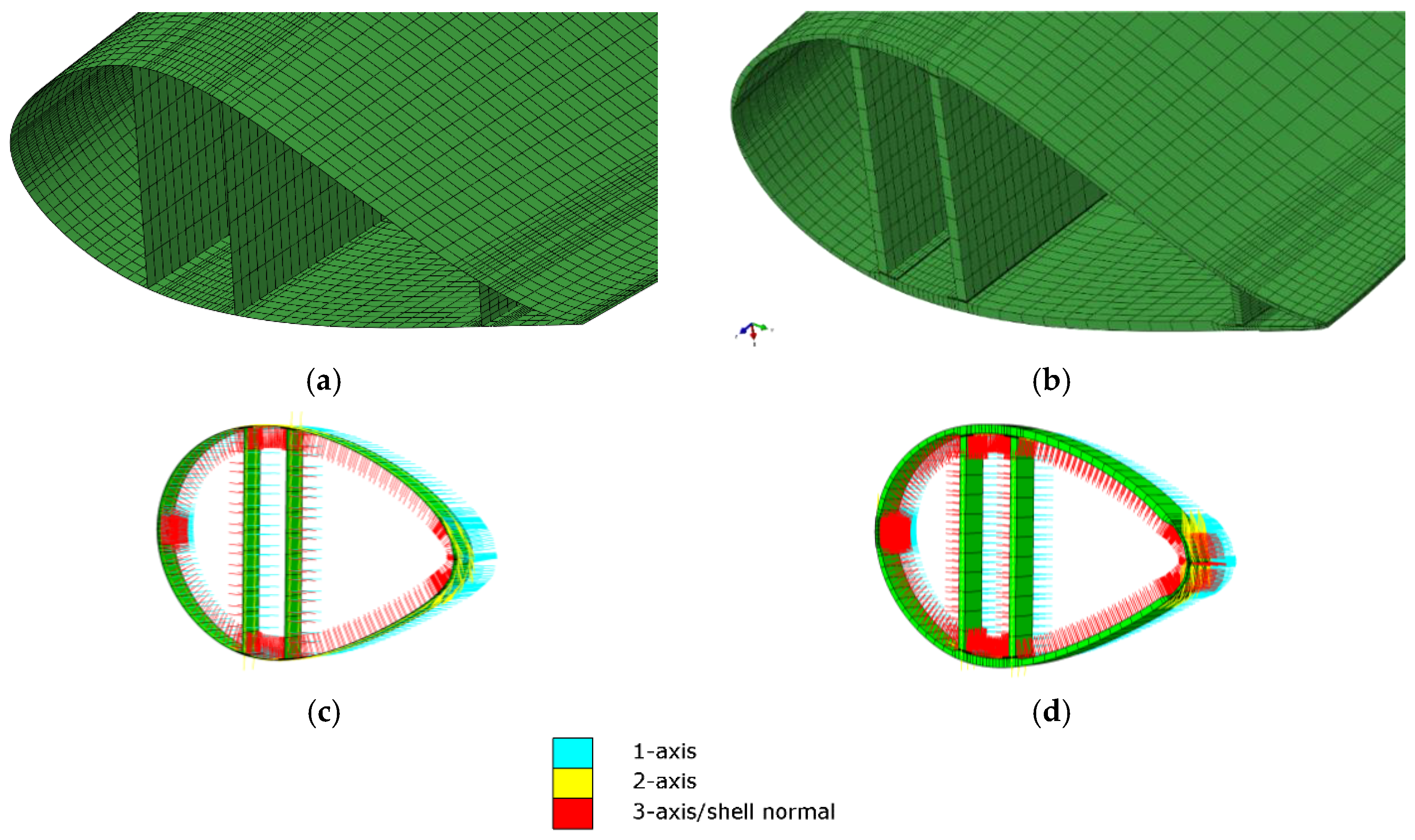
2.4. Full-Scale Blade
3. Results and Discussion
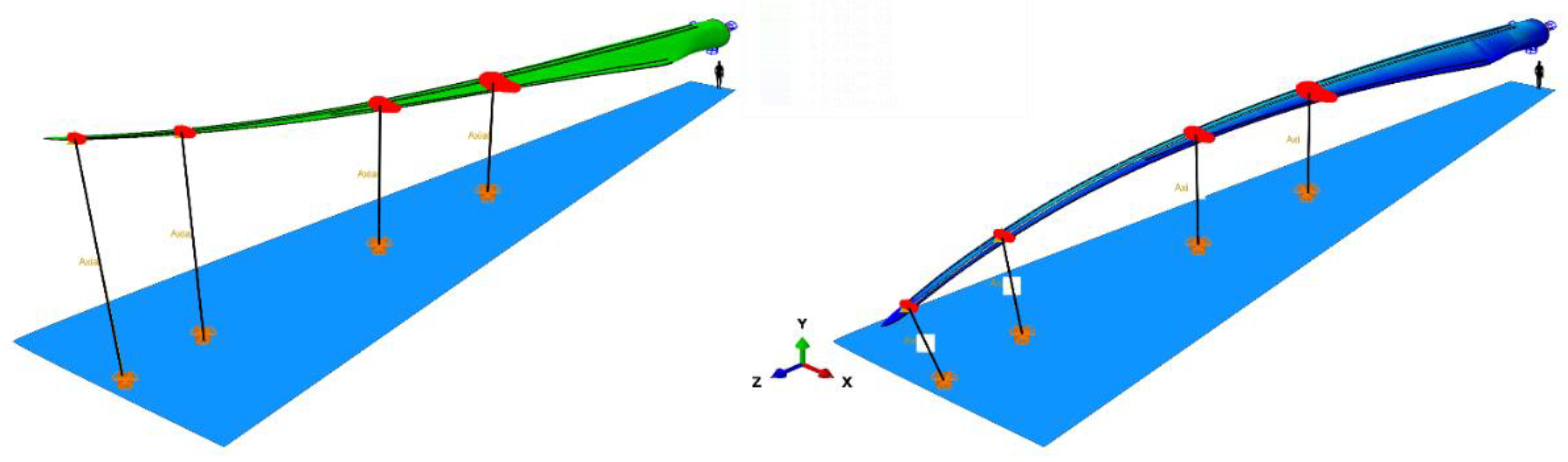
3.1. Importance of Boundary Conditions and Load Introductions
3.1.1. Importance of Geometric Nonlinearity
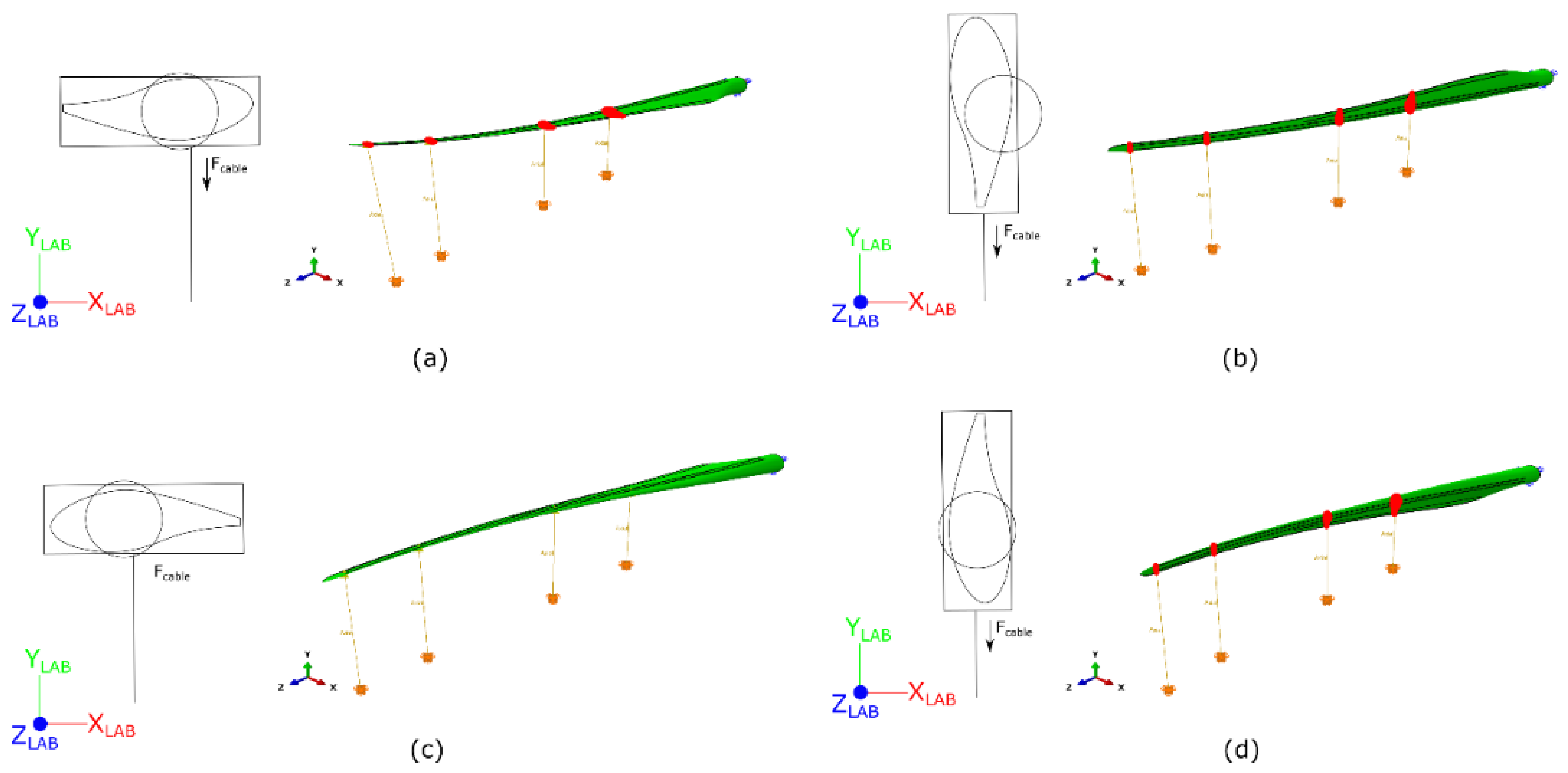
3.1.2. The Influence of the Cables
3.1.3. The Influence of the Coupling
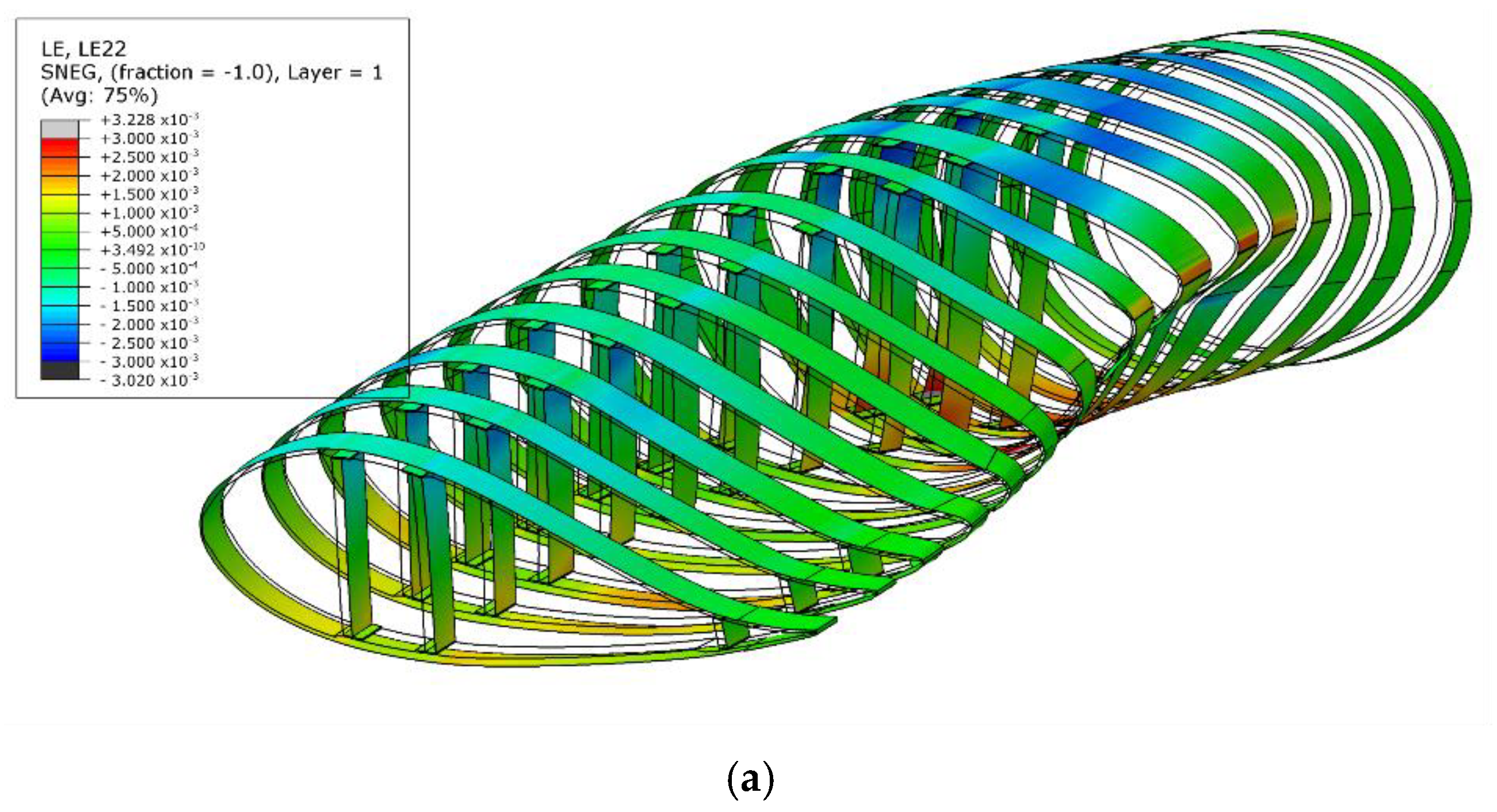
3.2. Comparison of Shell and Solid Models: Spar Segment
3.3. Comparison of Shell and Solid Models: Full-Scale Blade
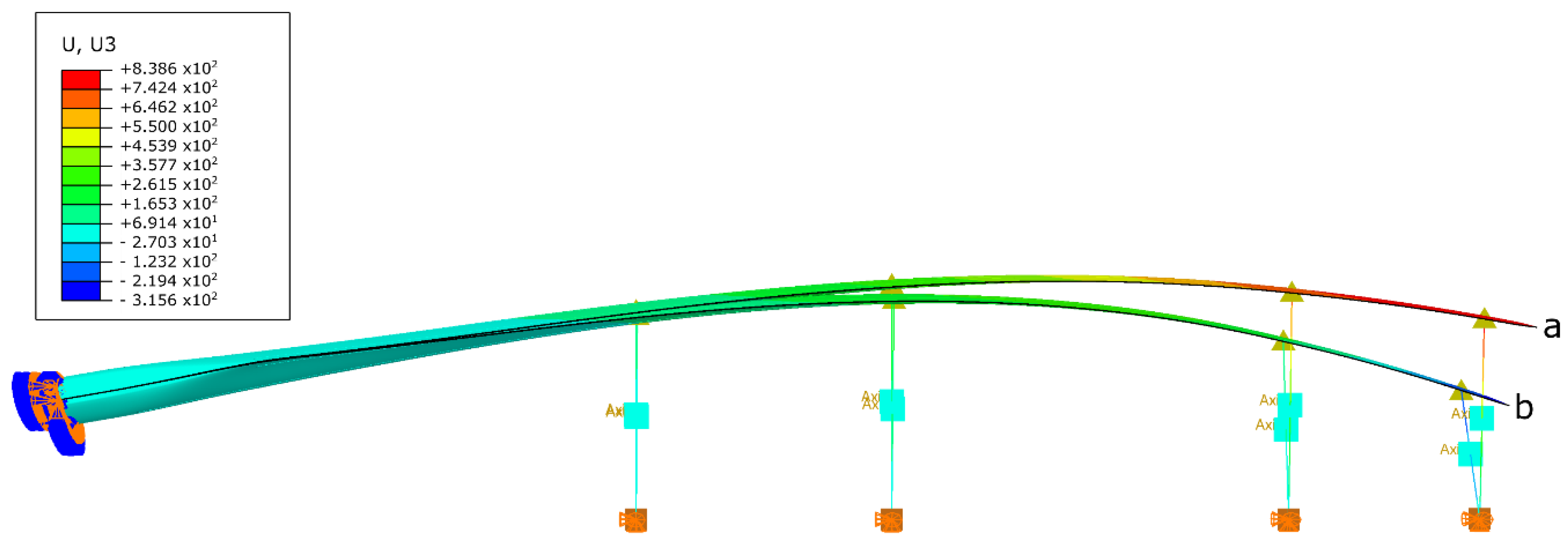
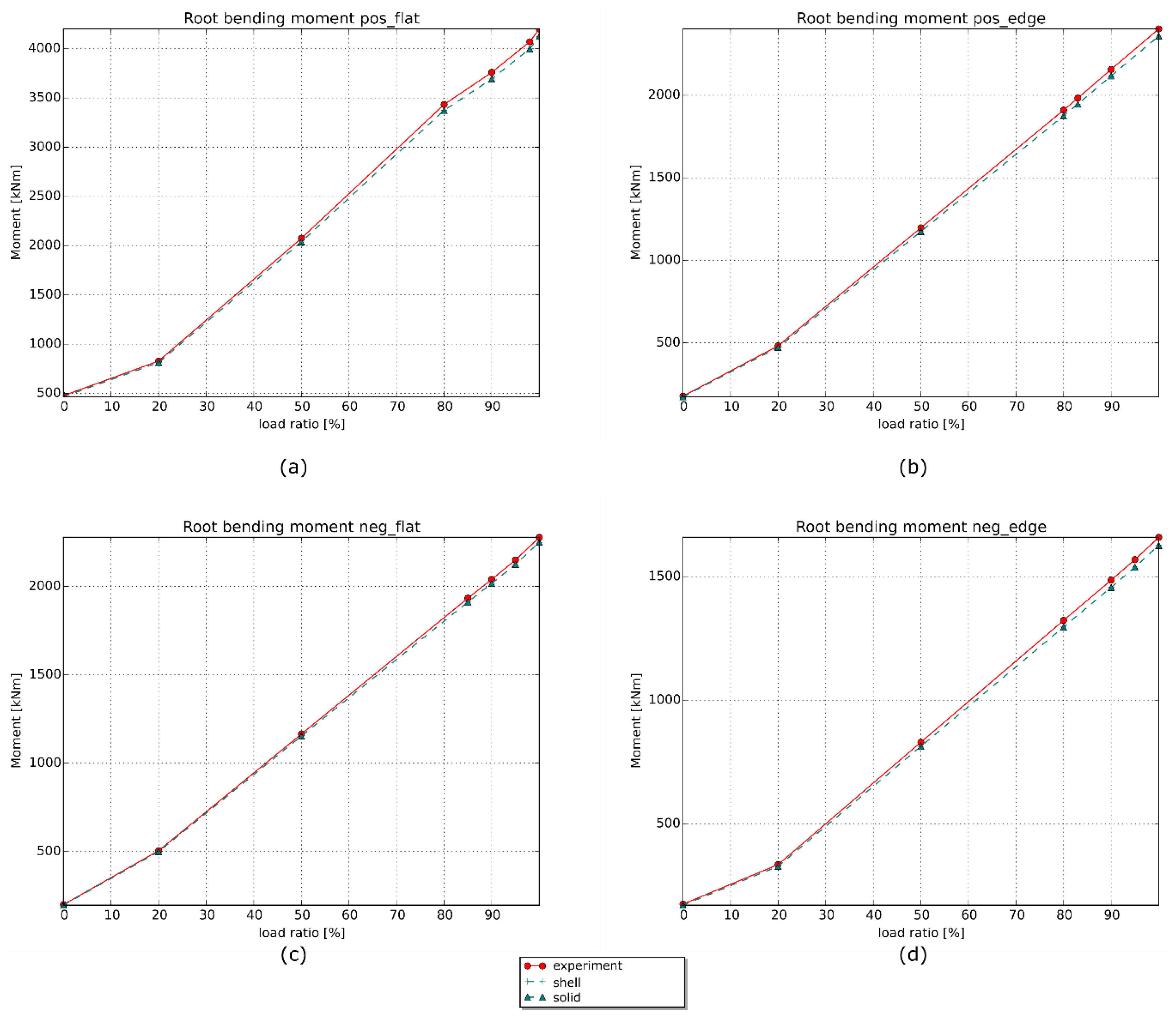
3.3.1. Validation of the Models
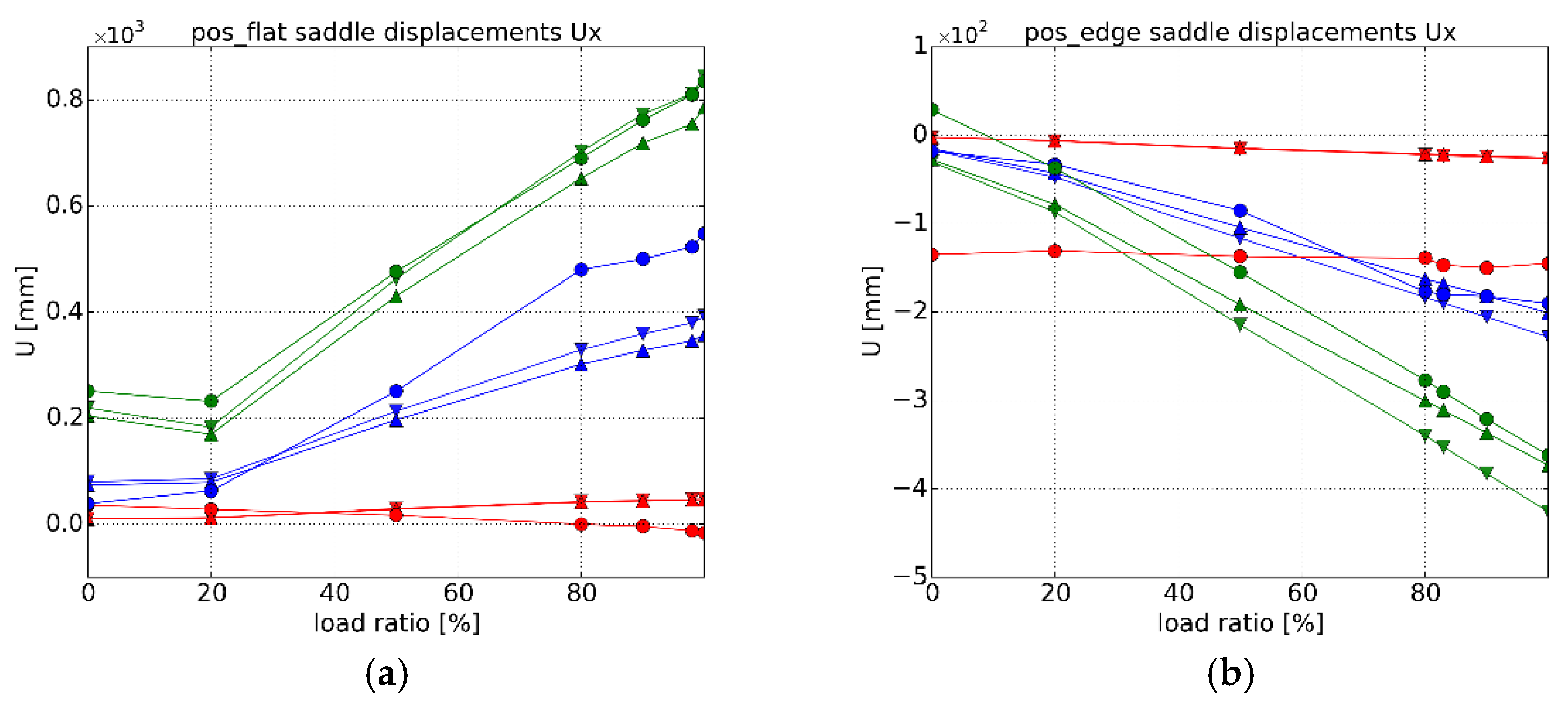
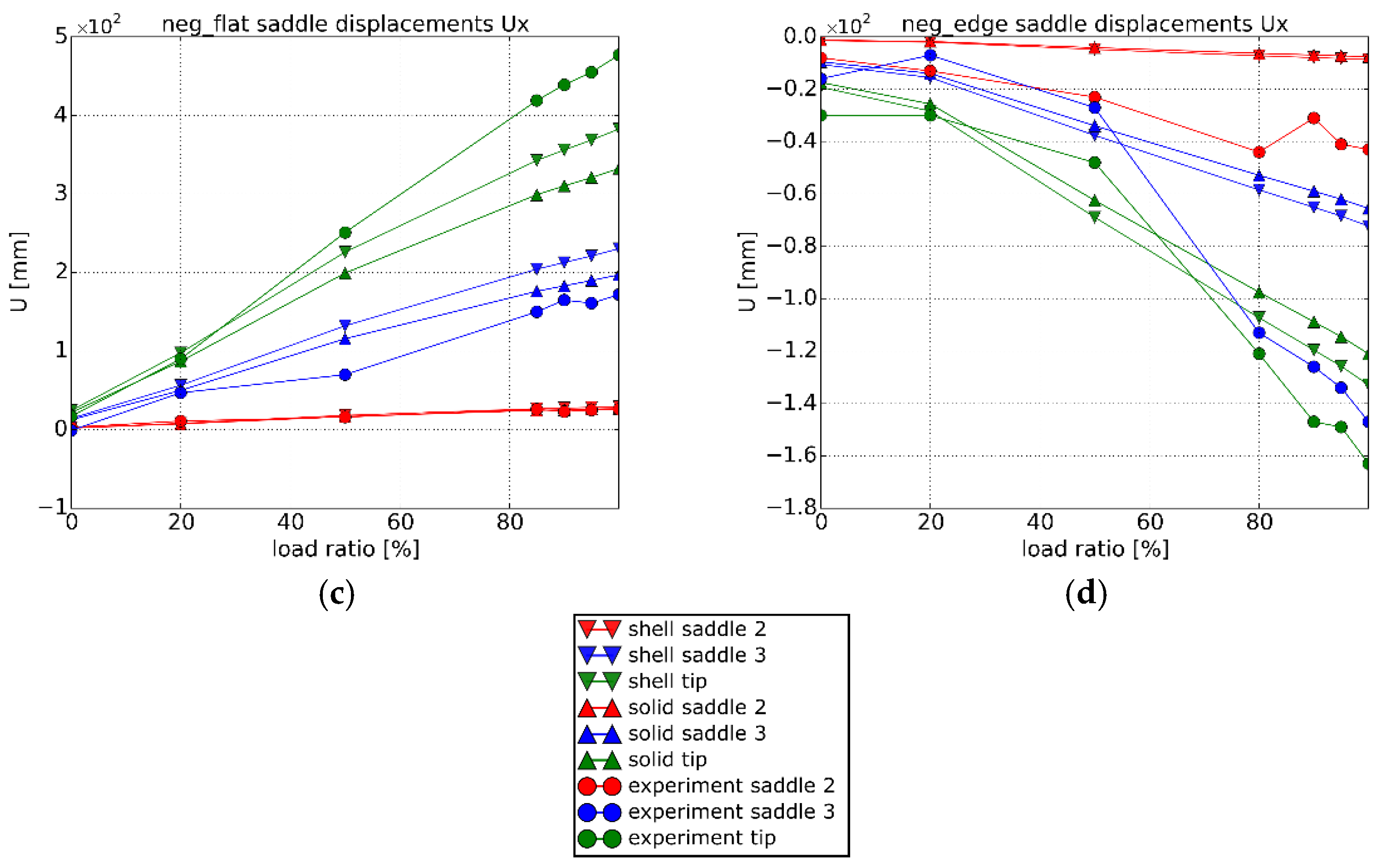
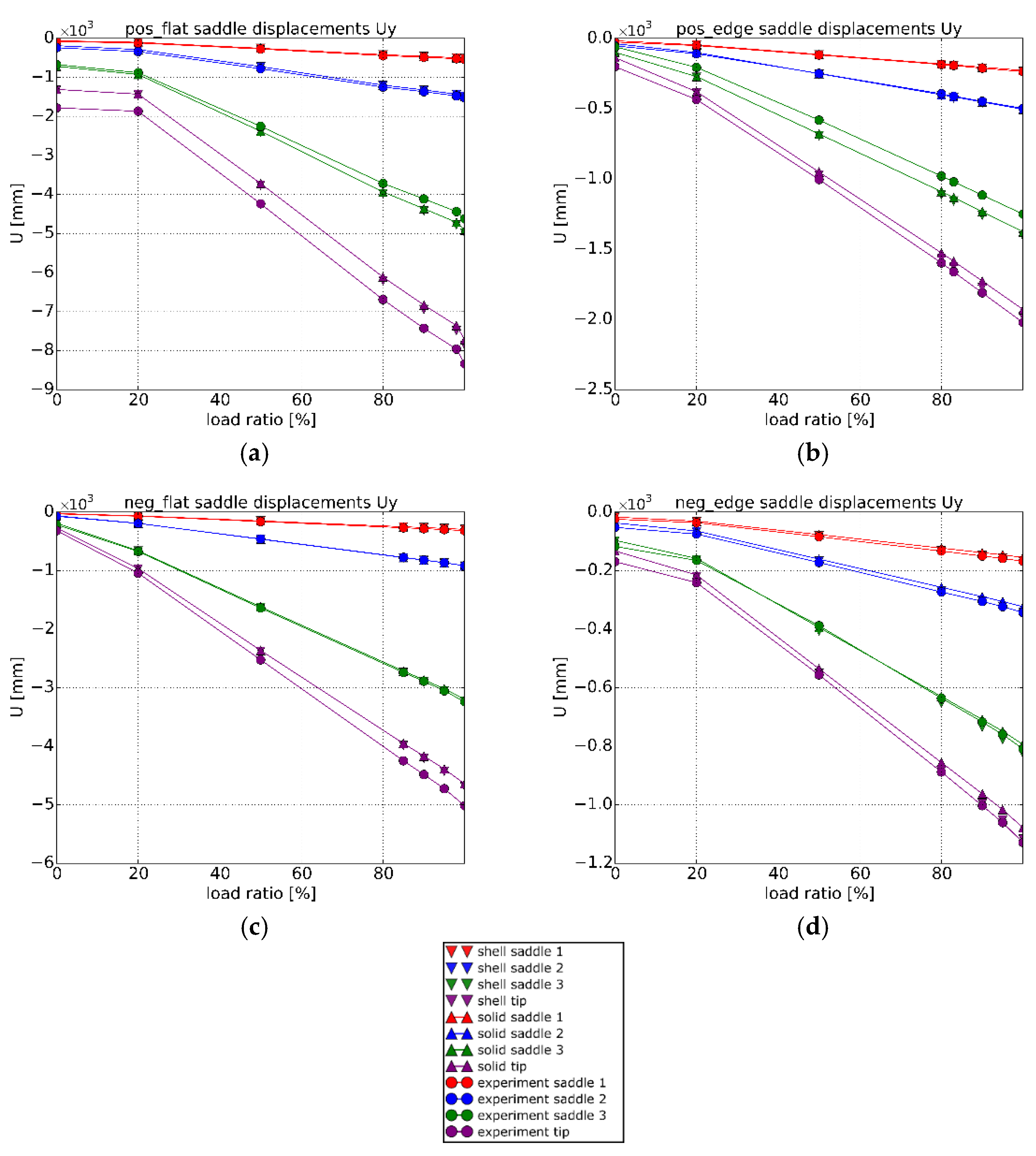
3.3.2. Fixture Displacements
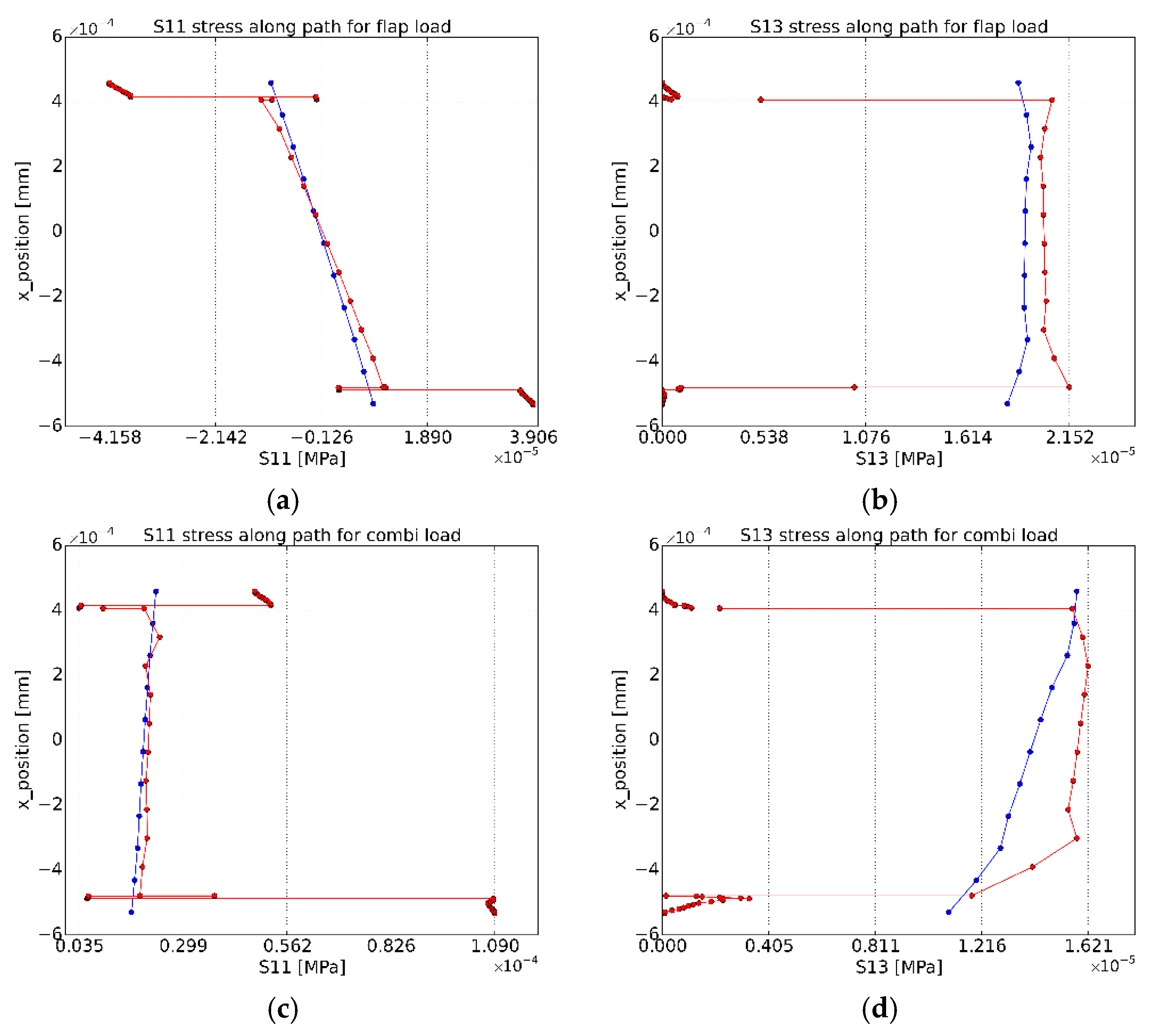
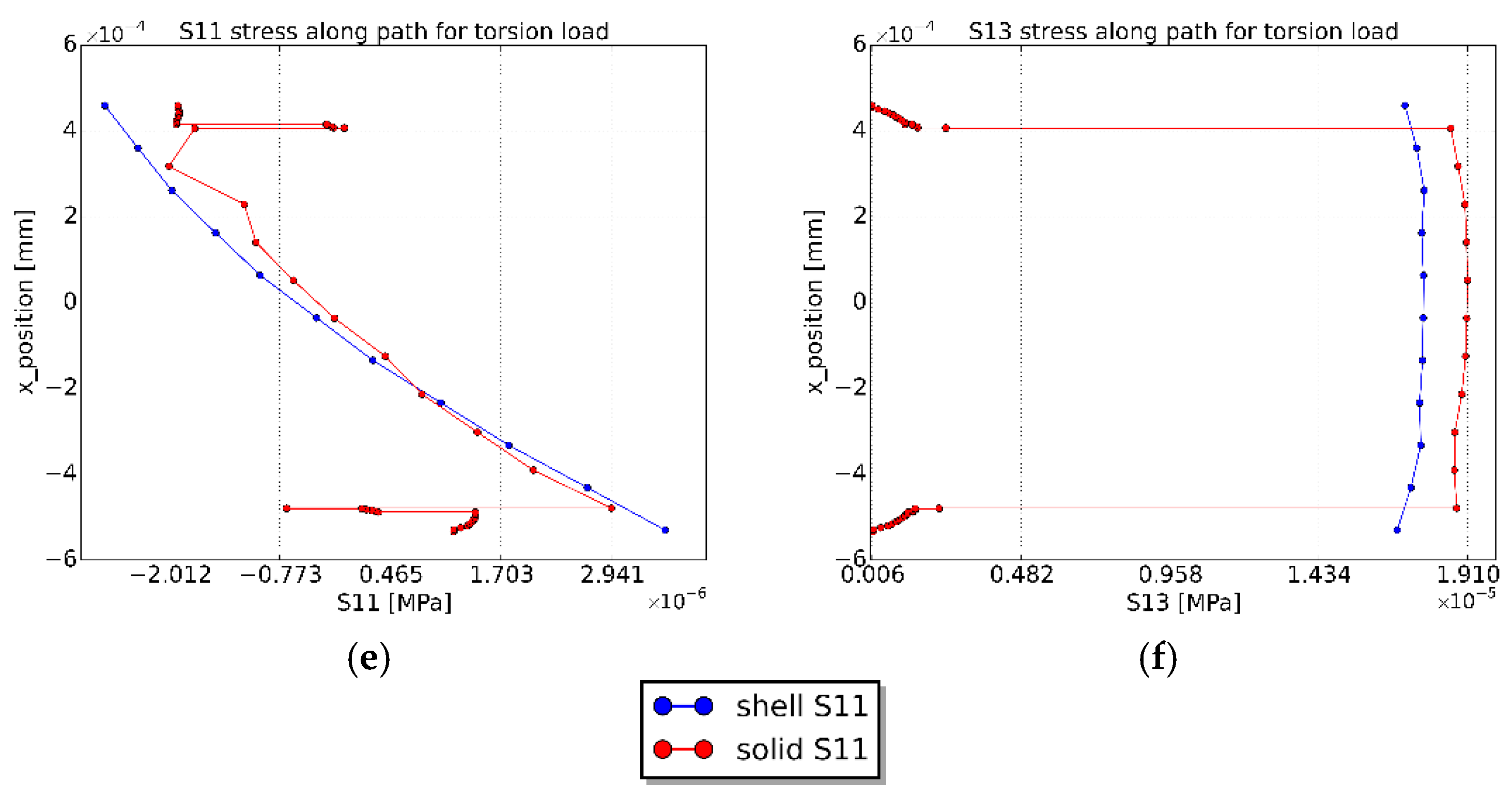
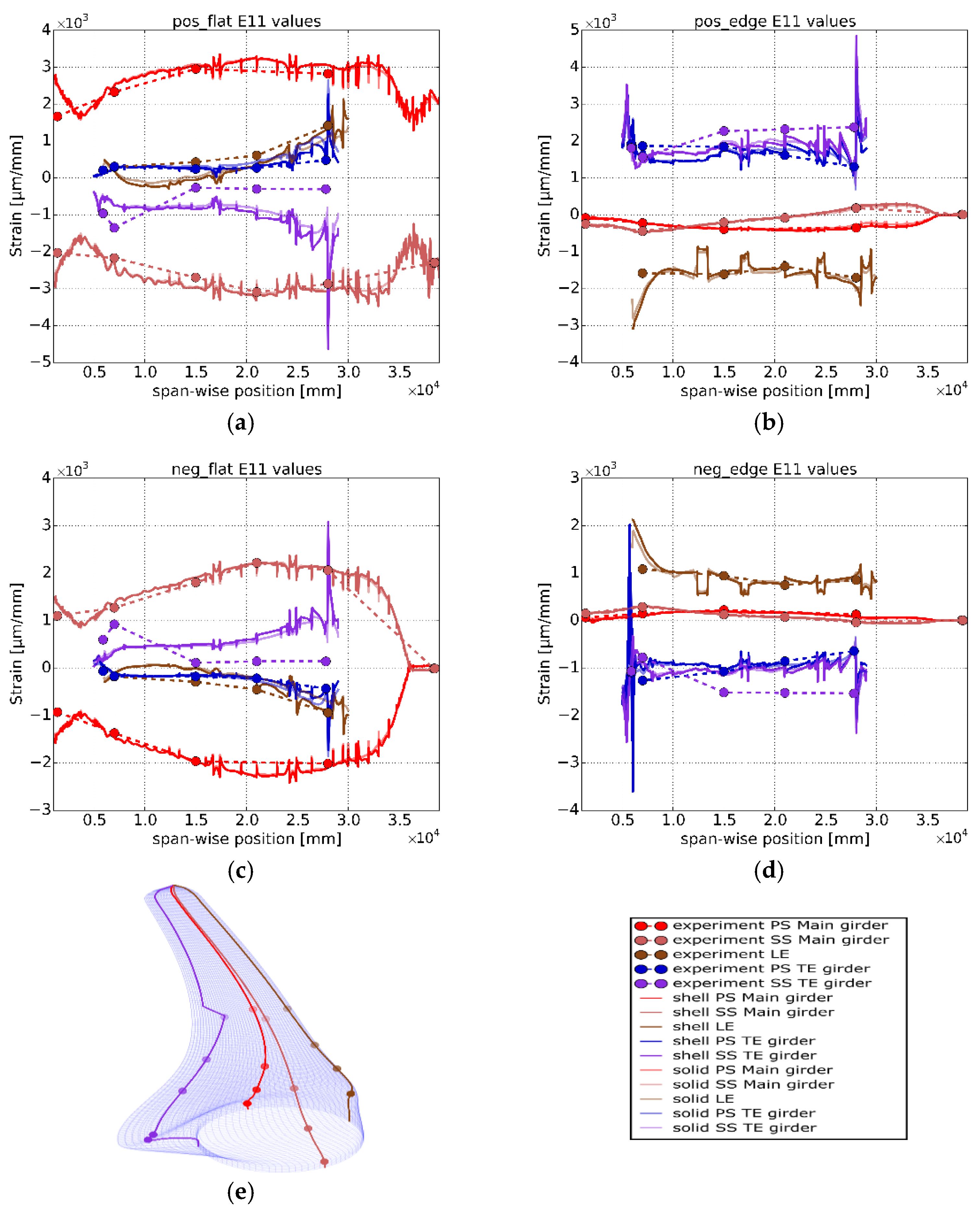
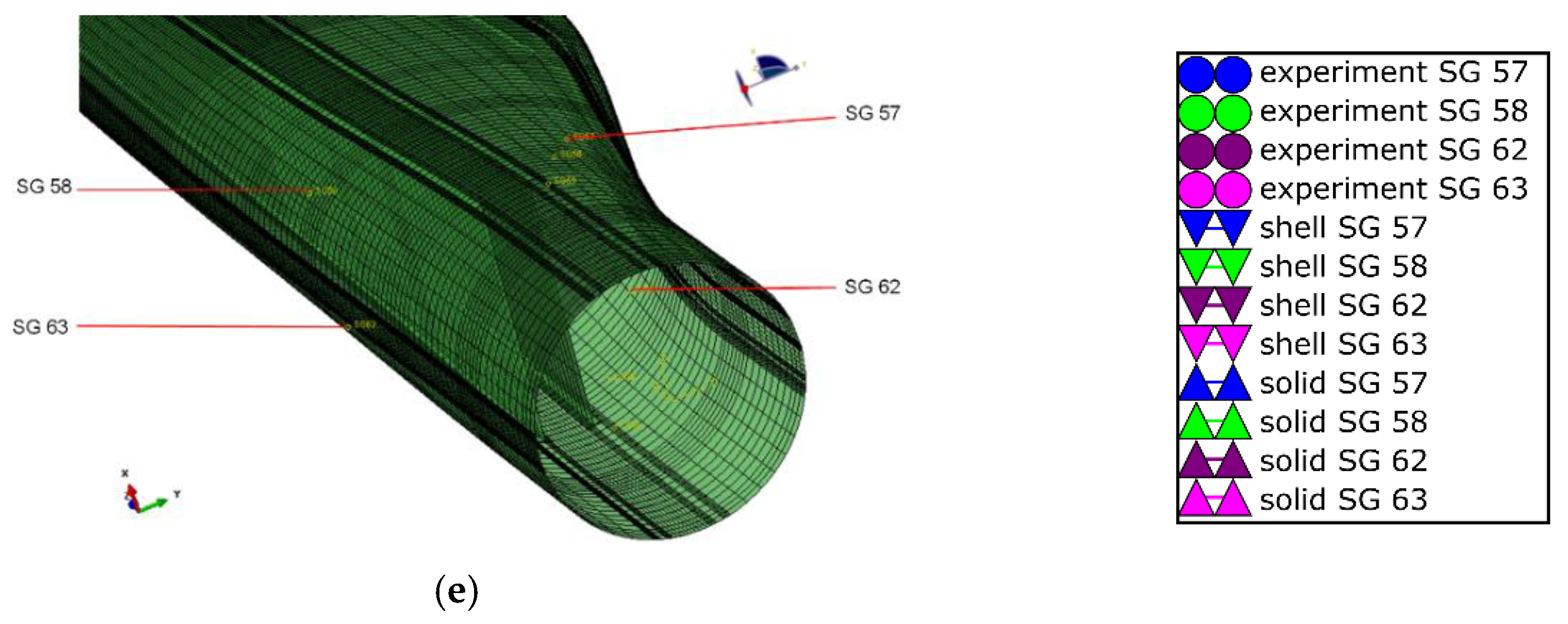
3.3.3. Longitudinal Strain Values
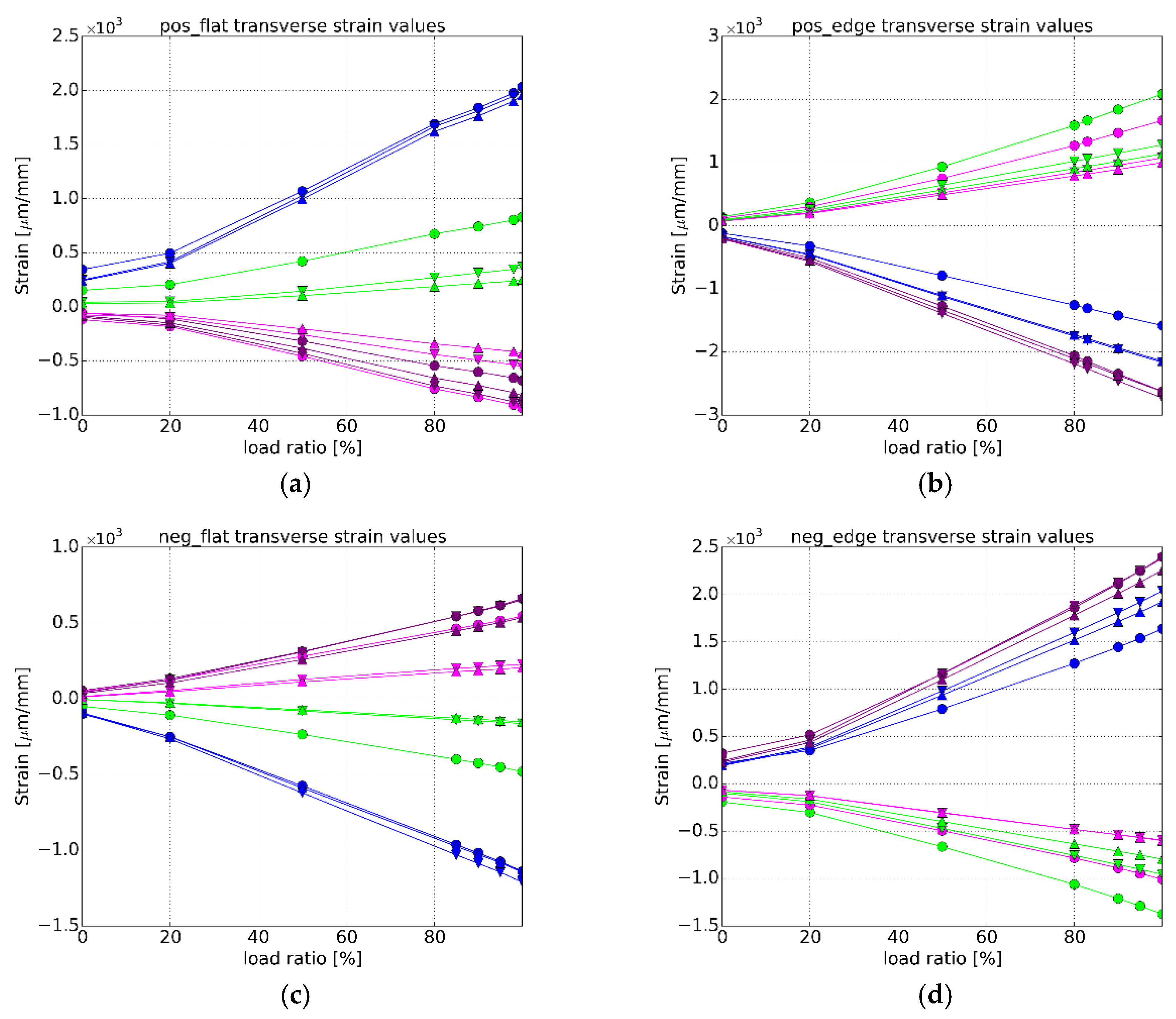
3.3.4. Transverse Strain Values
3.3.5. Strain Differences between the Inner and Outer Surfaces
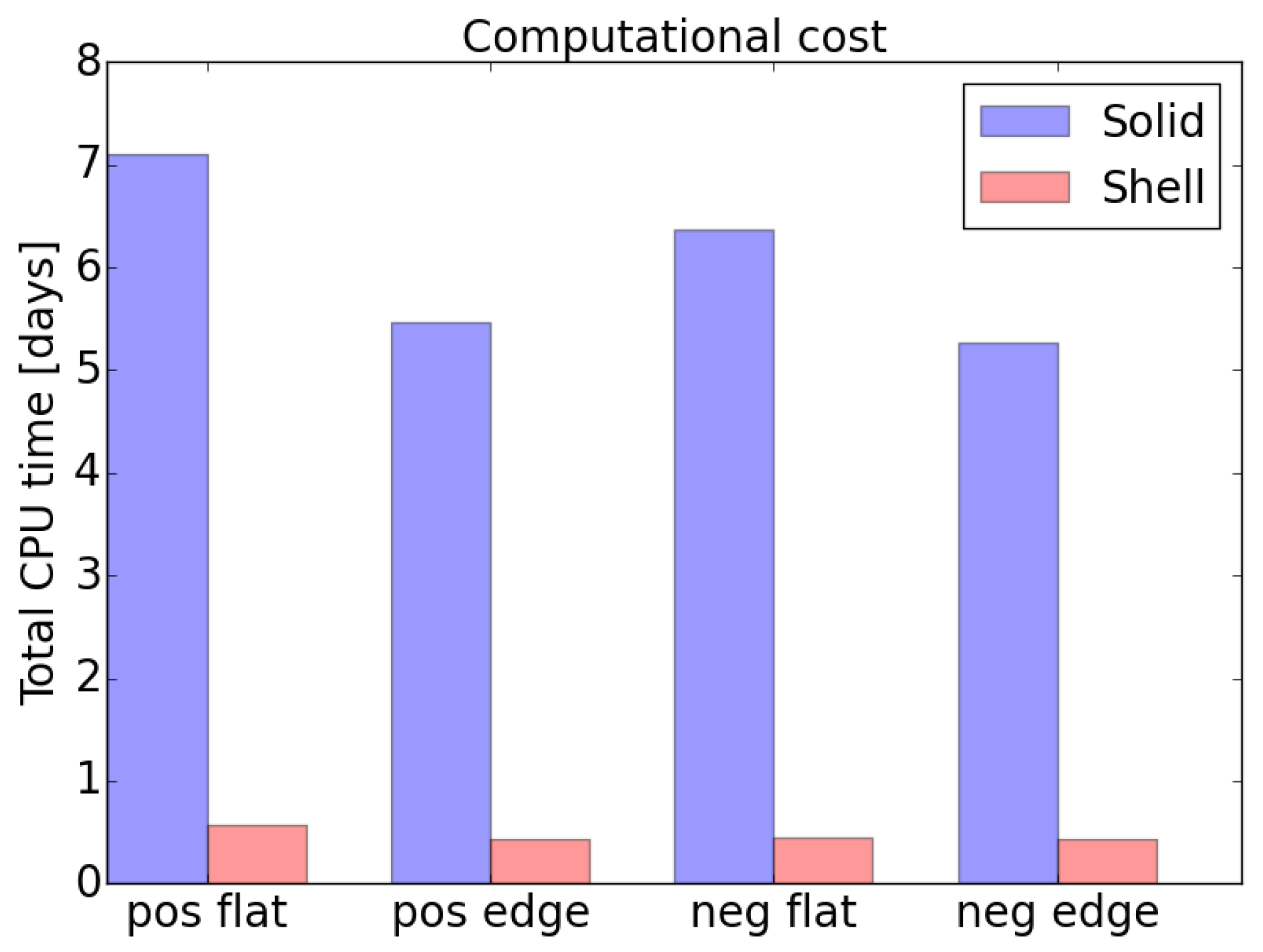
3.3.6. Computational Effort
3.4. Modeling Assumptions and Implications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meet LM 88.4 P—The world’s Longest Wind Turbine Blade. Available online: https://www.lmwindpower.com/en/products-and-services/blade-types/longest-blade-in-the-world (accessed on 6 March 2018).
- Caduff, M.; Huijbregts, M.A.J.; Althaus, H.-J.; Koehler, A.; Hellweg, S. Wind Power Electricity: The Bigger the Turbine, The Greener the Electricity? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4725–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, D.A. WindPACT Turbine Design Scaling Studies Technical Area 1-Composite Blades for 80- to 120-Meter Rotor; National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2001.
- Sieros, G.; Chaviaropoulos, P.; Sørensen, J.D.; Bulder, B.H.; Jamieson, P. Upscaling wind turbines: Theoretical and practical aspects and their impact on the cost of energy. Wind Energy 2012, 15, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquette, J.A. Blade Reliability Collaborative (BRC) Update; Sandia National Laboratories (SNL-NM): Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2011.
- Sheng, S. Report on Wind Turbine Subsystem Reliability—A Survey of Various Databases; National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2013.
- Nielow, D. Prüfstand für die Evaluation der Betriebsfestigkeit von Rotorblattschalensegmenten. Presented at the Rotorblätter von Windenergieanlagen—Wind Turbine Rotor Blades 6th Technical Conference, Essen, Germany, 2–3 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Det Norske Veritas. Design and Manufacture of Wind Turbine Blades, Offshore and Onshore Wind Turbines; Det Norske Veritas: Oslo, Norway, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Germanischer Lloyd. Guideline for the Certification of Wind Turbines, GL-IV-1; Germanischer Lloyd: Hamburg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Peng, C.; Xiao, J.; Zeng, J.; Yuan, Y. Application of videometric technique to deformation measurement for large-scale composite wind turbine blade. Appl. Energy 2012, 98, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, F.M.; Falzon, B.G.; Ankersen, J.; Stang, H. Structural testing and numerical simulation of a 34 m composite wind turbine blade. Compos. Struct. 2006, 76, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosemeier, M.; Berring, P.; Branner, K. Non-linear ultimate strength and stability limit state analysis of a wind turbine blade: Non-linear ultimate strength and stability limit state analysis of a wind turbine blade. Wind Energy 2016, 19, 825–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Bang, H.-J.; Shin, H.-K.; Jang, M.-S. Composite Structural Analysis of Flat-Back Shaped Blade for Multi-MW Class Wind Turbine. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2014, 21, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Peng, C.; Xiao, J.; Zeng, J.; Xing, S.; Jin, J.; Deng, H. Structural investigation of composite wind turbine blade considering structural collapse in full-scale static tests. Compos. Struct. 2013, 97, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, D.; Montoya, F.; Malcolm, D. Finite Element Modeling of Wind Turbine Blades. In Aerospace Sciences Meetings, Proceedings of the 43rd AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reston, VA, USA, 10–13 January 2005; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ashwill, T. Sweep-Twist Adaptive Rotor Blade: Final Project Report; Sandia National Laboratories: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2010.
- Branner, K.; Berring, P.; Berggreen, C.; Knudsen, H.W. Torsional performance of wind turbine blades—Part II: Numerical validation. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Composite Materials, Kyoto, Japan, 8–13 July 2007; ICCM: Kyoto, Japan, 2007; pp. 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Haselbach, P.U. An advanced structural trailing edge modelling method for wind turbine blades. Compos. Struct. 2017, 180, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, K.K. Defect-Tolerant Structural Design of Wind Turbine Blades. In Proceedings of the 50th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials and Co-located Conferences, Palm Springs, CA, USA, 4–7 May 2009; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Overgaard, L.C.T.; Lund, E.; Thomsen, O.T. Structural collapse of a wind turbine blade. Part A: Static test and equivalent single layered models. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overgaard, L.C.T.; Lund, E. Structural collapse of a wind turbine blade. Part B: Progressive interlaminar failure models. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haselbach, P.U.; Bitsche, R.D.; Branner, K. The effect of delaminations on local buckling in wind turbine blades. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, X.; Xu, J. Failure Test and Finite Element Simulation of a Large Wind Turbine Composite Blade under Static Loading. Energies 2014, 7, 2274–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Xu, J. Revisiting the structural collapse of a 52.3 m composite wind turbine blade in a full-scale bending test: Structural collapse of a 52.3 m composite wind turbine blade. Wind Energy 2017, 20, 1111–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, O.R.; Tarfaoui, M. The identification of structurally sensitive zones subject to failure in a wind turbine blade using nodal displacement based finite element sub-modeling. Renew. Energy 2016, 87, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.M.; Han, K.S. Fracture mechanics approach for failure of adhesive joints in wind turbine blades. Renew. Energy 2014, 65, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaqus Unified FEA—SIMULIA™ by Dassault Systèmes®. Available online: https://www.3ds.com/products-services/simulia/products/abaqus/ (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- Jensen, F.M.; Stang, H.; Branner, K. Ultimate Strength of a Large Windturbine Blade; Risø-PhD, no. 34(EN); Risø National Laboratory for Sustainable Energy, Technical University of Denmark: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2009. [Google Scholar]



| Load Case | Tip Side Load | Load Magnitude |
|---|---|---|
| Flapwise | Flap-wise concentrated force Fx | 150 kN |
| Combined | Flap-wise and edge-wise concentrated force Fx, Fy | 150 kN, 50 kN |
| Torsion | Torsional moment Mz | 0.3 kNm |
| Representation | Total Mass (kg) | Spanwise Position COG (m) |
|---|---|---|
| Design excl. T-bolts | 6150 | 13.7 |
| Classic OML shell model | 6240 | 13.5 |
| OML shell model with adhesive | 6120 | 13.6 |
| Solid model | 6180 | 13.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peeters, M.; Santo, G.; Degroote, J.; Van Paepegem, W. Comparison of Shell and Solid Finite Element Models for the Static Certification Tests of a 43 m Wind Turbine Blade. Energies 2018, 11, 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061346
Peeters M, Santo G, Degroote J, Van Paepegem W. Comparison of Shell and Solid Finite Element Models for the Static Certification Tests of a 43 m Wind Turbine Blade. Energies. 2018; 11(6):1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061346
Chicago/Turabian StylePeeters, Mathijs, Gilberto Santo, Joris Degroote, and Wim Van Paepegem. 2018. "Comparison of Shell and Solid Finite Element Models for the Static Certification Tests of a 43 m Wind Turbine Blade" Energies 11, no. 6: 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061346
APA StylePeeters, M., Santo, G., Degroote, J., & Van Paepegem, W. (2018). Comparison of Shell and Solid Finite Element Models for the Static Certification Tests of a 43 m Wind Turbine Blade. Energies, 11(6), 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061346






